MCF-Net: Fusion Network of Facial and Scene Features for Expression Recognition in the Wild
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A novel deep learning model with a two-stream structure, named MCF-Net, is proposed for facial expression recognition.
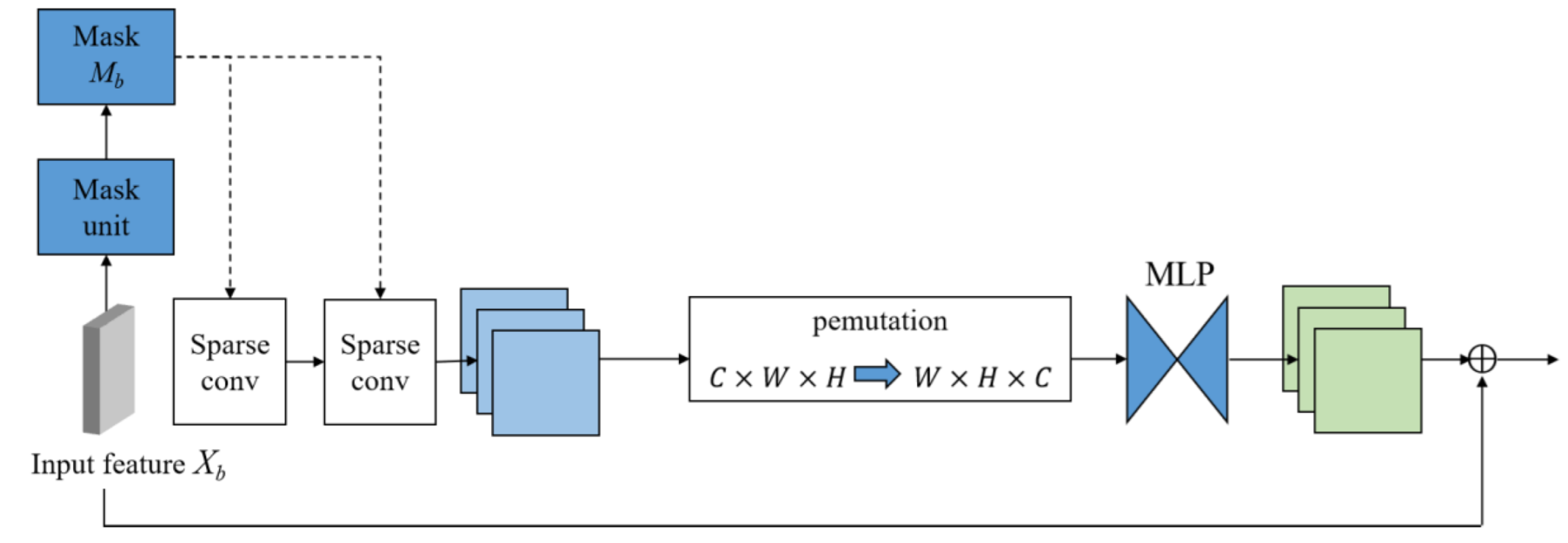
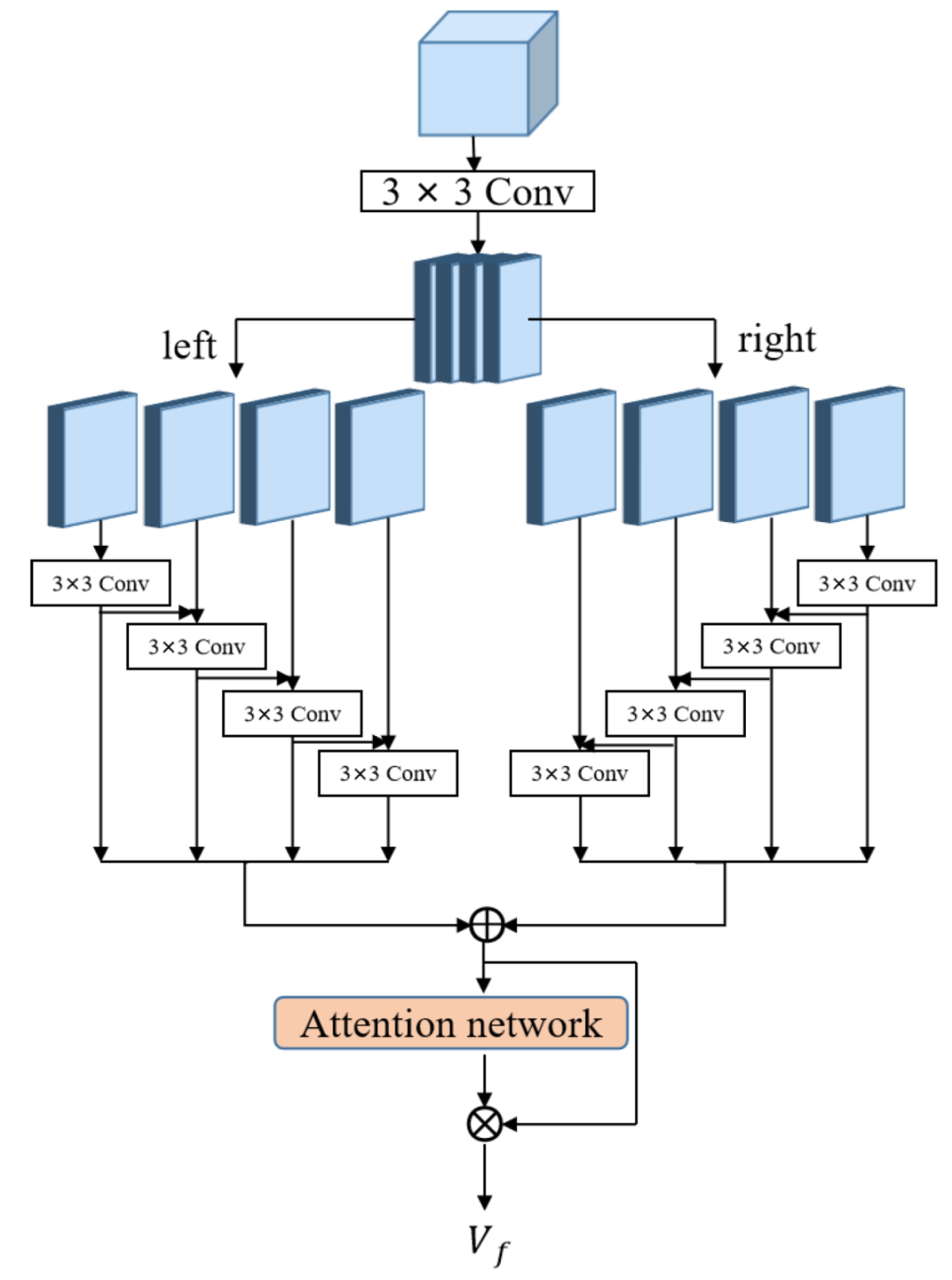
- In the face coding stream, the Sparse Mask Attention Learning module can adaptively generate the key sparse mask, which avoids manual and mechanical segmentation to extract facial features. Furthermore, the Multi-scale Attention module is employed to extract multi-scale global features at a fine-grained level and richer channel information.
- In the scene coding stream, the Relational Attention module captures more important contextual information about non-facial regions and establishes the connection between the facial and contextual features, so as to guide the network to focus on more meaningful regions in the real-world scene.
- A large number of experiments are carried out on two standard FER datasets to evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of our proposed model. By comparing the performance of our MCF-Net with some existing FER methods, the advantage of the proposed method can be demonstrated.
2. Related Work
2.1. FER Methods in the Controlled Environment
2.2. FER Methods in the Wild
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sparse Mask Attention Learning
3.2. Multi-Scale Attention
3.3. Relational Attention
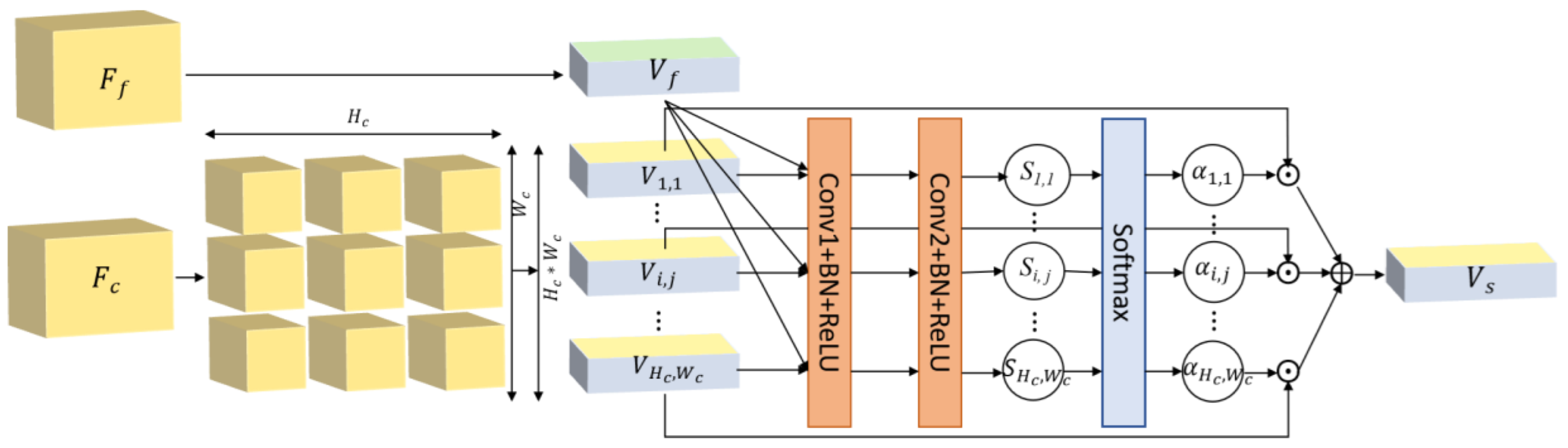
3.4. Adaptive Fusion Module
4. Results
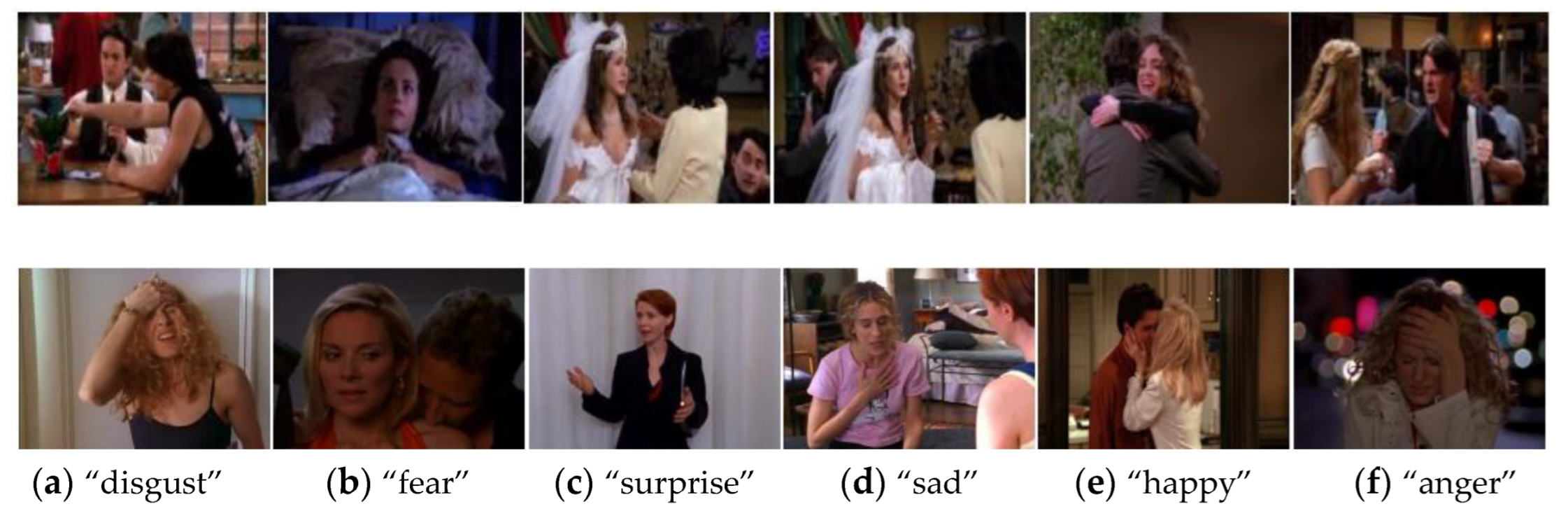
4.1. Experimental Dataset
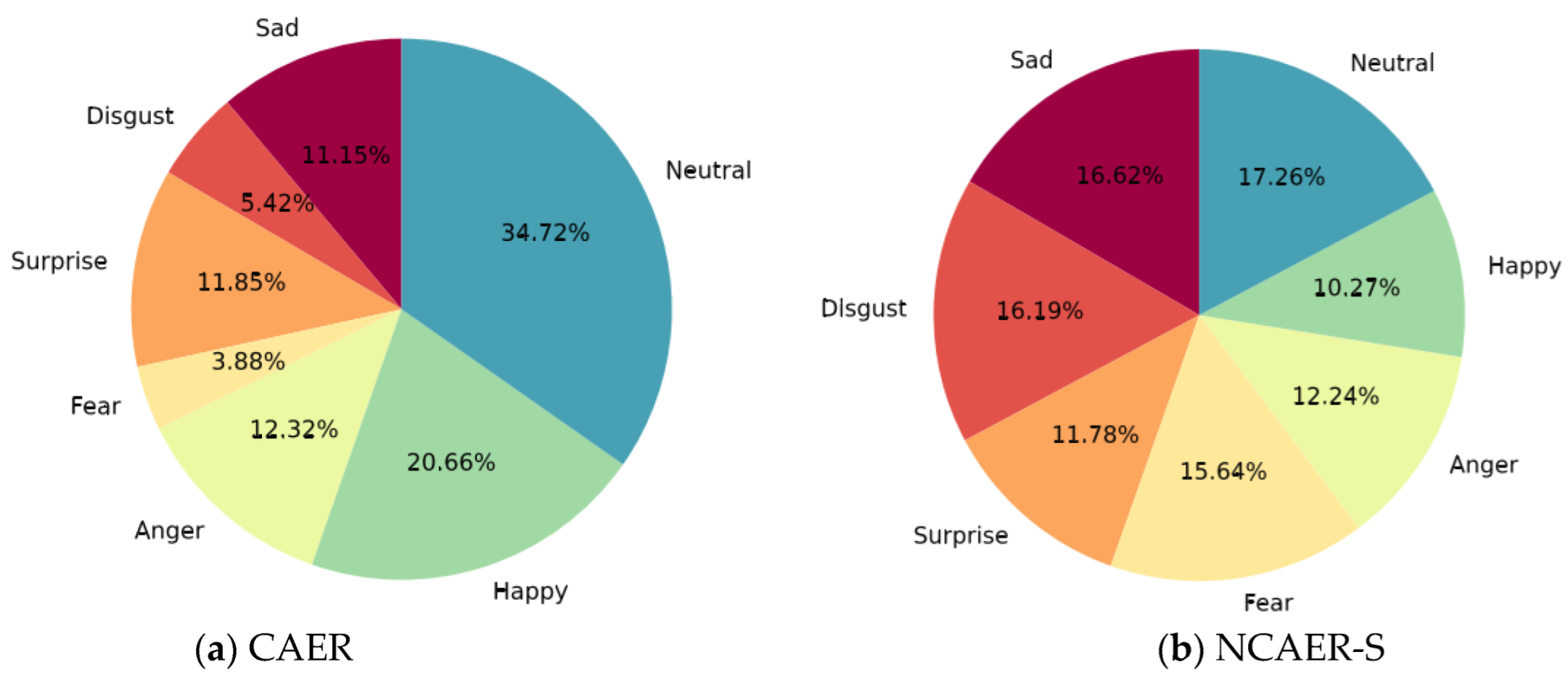
4.1.1. CAER-S Dataset
4.1.2. NCAER-S Dataset
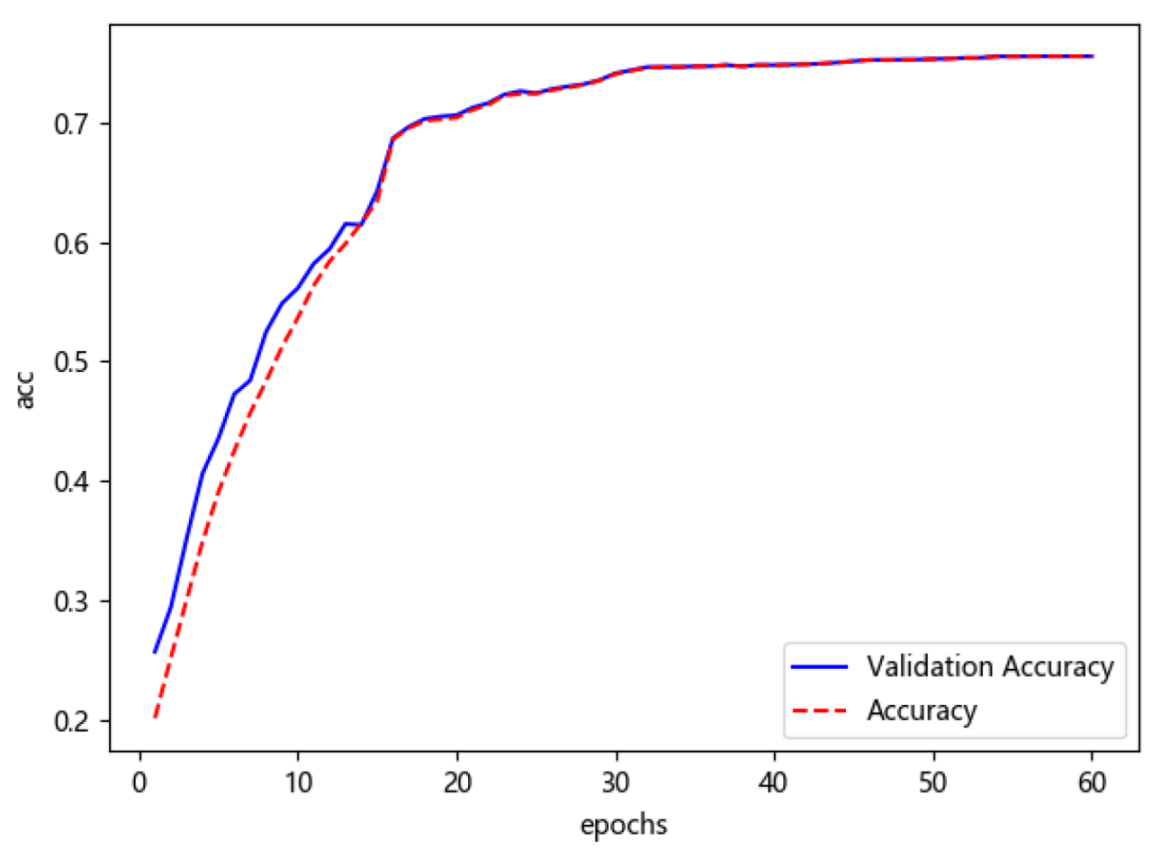
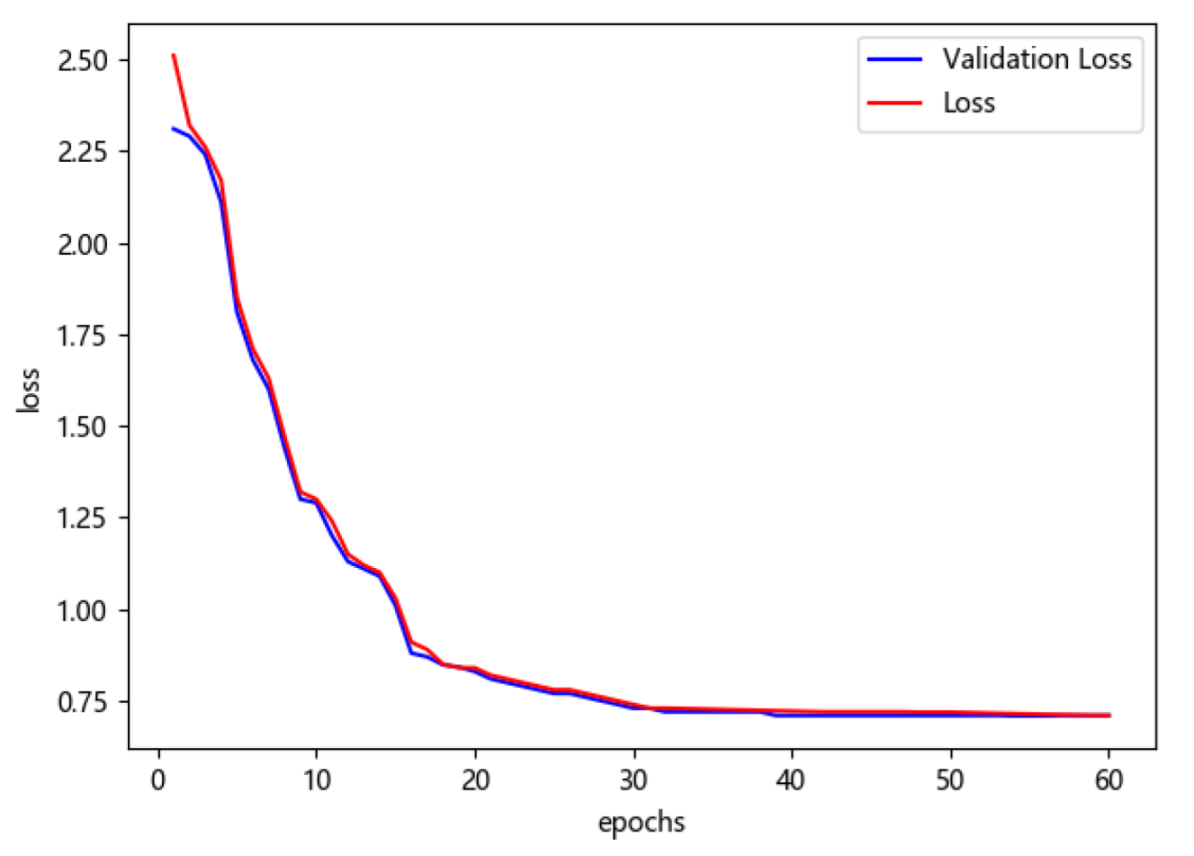
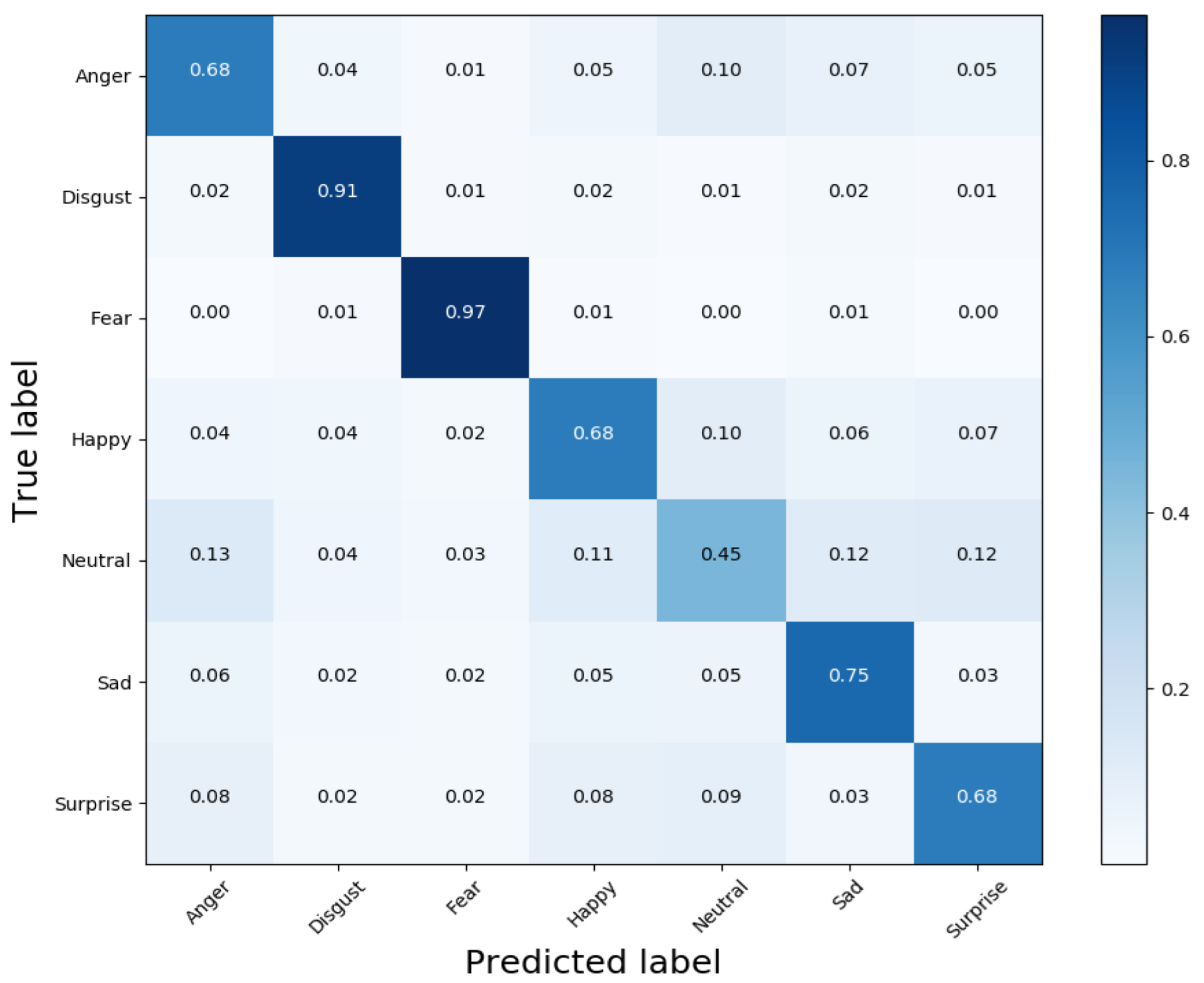
4.2. Experiments and Result Analysis
4.2.1. Experiments and Result Analysis of MCF-Net on CAER-S Dataset
4.2.2. Ablation Experiment and Result Analysis of MCF-Net on CAER-S Dataset
4.2.3. Multi-Cue Feature Weights of Adaptive Fusion Network
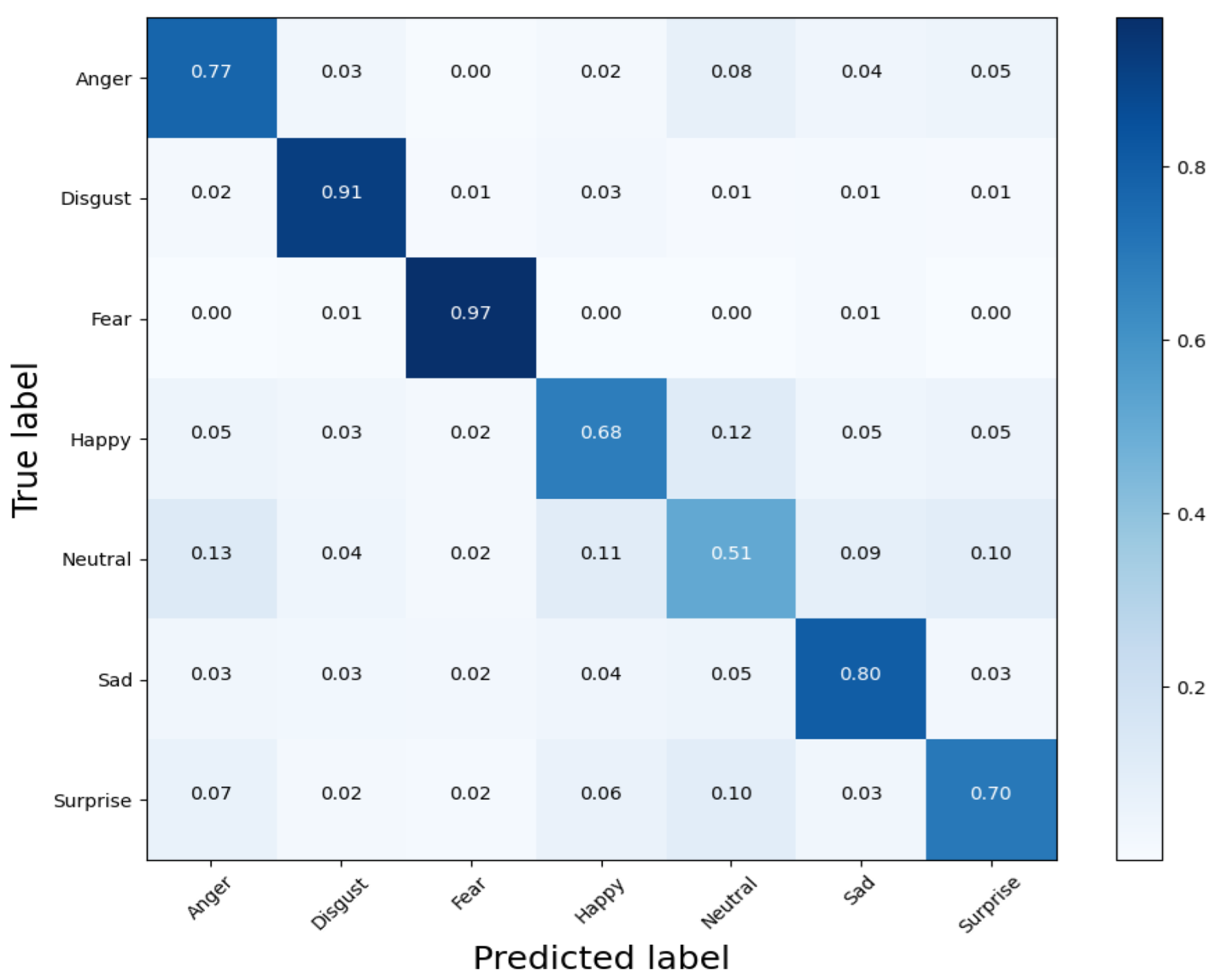
4.2.4. Experiments and Result Analysis of MCF-Net on NCAERS Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehrabian, A. Communication without Words. Psychol. Today 1968, 2, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.I.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F. Recognizing action units for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 23, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, C.; Gong, S.; McOwan, P.W. Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns: A comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhi, R.; Flierl, M.; Ruan, Q.; Kleijn, W.B. Graph-preserving sparse nonnegative matrix factorization with application to facial ex-pression recognition. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2010, 41, 38–52. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, M.H.; Ali, R.; Sattar, A.; Khan, A.M.; Lee, S. Depth Camera-Based Facial Expression Recognition System Using Multilayer Scheme. IETE Technol. Rev. 2014, 31, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happy, S.L.; Routray, A. Automatic facial expression recognition using features of salient facial patches. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, S. An Effificient Expression Recognition Method using Contourlet Transform. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Perception and Machine Intelligence, Bengal, India, 26–27 February 2015; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Cossetin, M.J.; Nievola, J.C.; Koerich, A.L. Facial expression recognition using a pairwise feature selection and classifification approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 5149–5155. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, G.P.; Seetha, M.; Hegde, N. Kernel locality preserving symmetrical weighted fifisher discriminant analysis based subspace approach for expression recognition. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Rameshan, B.K.S. Dictionary Based Approach for Facial Expression Recognition from Static Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, Warsaw, Poland, 19–21 September 2016; pp. 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Nigam, S.; Singh, R.; Misra, A.K. Efficient facial expression recognition using histogram of oriented gradients in wavelet domain. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 28725–28747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 60, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Comput. Sci. 2014, 73, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, T.A. Convolutional Neural Networks based Method for Improving Facial Expression Recognition. In The International Symposium on Intelligent Systems Technologies and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, K.; Guo, J.; You, W.; Lu, D.; Bie, R. Automatic facial expression recognition based on a deep convolution-al-neural-network structure. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th International Conference on Software Engineering Research, Management and Applications, London, UK, 7–9 June 2017; pp. 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Liu, P.; Cai, J.; Han, S.; Tong, Y. Identity-aware convolutional neural network for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 29 June 2017; pp. 558–565. [Google Scholar]
- Clawson, K.; Delicato, L.S.; Bowerman, C. Human Centric Facial Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the 32nd International BCS Human Computer Interaction Conference (HCI), Belfast, UK, 4–6 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Peng, X.; Yang, J.; Meng, D.; Qiao, Y. Region attention networks for pose and occlusion robust facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4057–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gera, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Landmark guidance independent spatio-channel attention and complementary context information based facial expression recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 145, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Sohn, K. Context-aware emotion recognition networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 10143–10152. [Google Scholar]
- Verelst, T.; Tuytelaars, T. Dynamic convolutions: Exploiting spatial sparsity for faster inference. In Proceedings of the Ieee/cvf conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2320–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S. Learning deep global multi-scale and local attention features for facial expression recognition in the wild. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 6544–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Hoffmann, N. Global Attention Mechanism: Retain Information to Enhance Channel-Spatial Interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05561. [Google Scholar]
- Le, N.; Nguyen, K.; Le, B. Global-local attention for emotion recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Minaei, M.; Abdolrashidi, A. Deep-Emotion: Facial Expression Recognition Using Attentional Convolutional Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero Fernandez, P.D.; Guerrero Pena, F.A.; Ren, T.; Cunha, A. Feratt: Facial expression recognition with attention net. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Peng, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Qiao, Y. Suppressing uncertainties for large-scale facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, P.; Chellappa, R. Occlusion-Adaptive Deep Network for Robust Facial Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Houston, TX, USA, 28 September–1 October 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, J.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Occlusion Aware Facial Expression Recognition Using CNN With Attention Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Zhu, Z.; Dai, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, X. Facial expression recognition based on deep learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L. Multiple Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 7383–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Arunachalam, S.; Balakrishnan, R. Deep self-attention network for facial emotion recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 171, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Deng, W. Deep facial expression recognition: A survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 13, 1195–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, S.K.; Chellappa, R. FaceNet2ExpNet: Regularizing a Deep Face Recognition Net for Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Ma, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xing, T.; Xu, P.; Hu, R.; Chai, H.; Keutzer, K. An End-to-End Visual-Audio Attention Network for Emotion Recognition in User-Generated Videos. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, T.; Guhan, P.; Bhattacharya, U.; Chandra, R.; Bera, A.; Manocha, D. Emoticon: Context-aware multimodal emotion recognition using frege’s principle. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 14234–14243. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Sricharan, K.; Chellappa, R. ExprGAN: Facial Expression Editing With Controllable Expression Intensity. In Proceedings of the ExprGAN: Facial Expression Editing With Controllable Expression Intensity, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tian, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, N.; Xie, L. A novel feature separation model exchange-gan for facial expression recog-nition. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2020, 204, 106217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Lee, H.; Roh, J.; Lee, S.Y. Hierarchical Committee of Deep CNNs with Exponentially-Weighted Decision Fusion for Static Facial Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Seattle, WA, USA, 9–13 November 2015; pp. 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shan, S. Meta Auxiliary Learning for Facial Action Unit Detection. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2021, 19, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, F. Robust Lightweight Facial Expression Recognition Network with Label Distribution Training. Proc Conf AAAI Artif Intell 2021, 35, 3510–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Mendieta, M.; Chen, C. POSTER: A Pyramid Cross-Fusion Transformer Network for Facial Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Xu, H. Co-attentive multi-task convolutional neural network for facial expression recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 123, 108401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.P.; Mahoor, M.H. Ad-Corre: Adaptive Correlation-Based Loss for Facial Expression Recognition in the Wild. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 26756–26768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, V.; Sullivan, J. One millisecond face alignment with an ensemble of regression trees. In Proceedings of the IEEE con-ference on computer vision and pattern recognition Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1867–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, E.; Gu, S.; Poole, B. Categorical reparameterization with gumbel-softmax. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01144. [Google Scholar]
- Kosti, R.; Alvarez, J.; Recasens, A.; Lapedriza, A. Context Based Emotion Recognition using EMOTIC Dataset. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Zeng, H.; Li, G. Graph reasoning-based emotion recognition network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 6488–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Li, G.; Tong, T.; Gao, Q. A Graph Convolutional Network for Emotion Recognition in Context. In Proceedings of the 2020 Cross Strait Radio Science & Wireless Technology Conference (CSRSWTC), Fuzhou, China, 13–16 December 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Methods | Params (M) | MAC (M/G) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ImageNet-AlexNet [13] | ~89.92 | 102G | 47.36 |
| ImageNet-VGGNet [14] | ~102.34 | 198G | 49.89 |
| ImageNet-ResNet [15] | ~132.54 | 247G | 57.33 |
| Fine-tuned AlexNet [13] | ~89.92 | 102G | 61.73 |
| Fine-tuned VGGNet [14] | ~102.34 | 198G | 64.85 |
| Fine-tuned ResNet [15] | ~132.54 | 247G | 68.46 |
| CAER-Net-S [24] | ~2.39 | 385M | 73.51 |
| Kosti et al. [51] | ~27.86 | 78G | 74.48 |
| Gao et al. [52] | -- | -- | 81.31 |
| Zeng et al. [53] | ~68.24 | 115G | 81.31 |
| Zhao et al. [45] | -- | -- | 81.48 |
| MCF-Net | ~4.25 | 369M | 75.68 |
| MCF-Net(ResNet18) | ~14.2 | 756M | 81.82 |
| Methods | Params (M) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | ~2.39 | 73.51 |
| Baseline+SML | ~2.44 | 73.97 |
| Baseline+SMAL | ~2.45 | 74.21 |
| Baseline+SMAL+MS | ~3.92 | 74.72 |
| Baseline+SMAL+MSA | ~3.96 | 74.81 |
| Baseline+SMAL+MS+RA | ~4.22 | 75.21 |
| Baseline+SMAL+MSA+RA | ~4.25 | 75.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Kong, J.; Kong, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J. MCF-Net: Fusion Network of Facial and Scene Features for Expression Recognition in the Wild. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010251
Xu H, Kong J, Kong X, Li J, Wang J. MCF-Net: Fusion Network of Facial and Scene Features for Expression Recognition in the Wild. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010251
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hui, Jun Kong, Xiangqin Kong, Juan Li, and Jianzhong Wang. 2022. "MCF-Net: Fusion Network of Facial and Scene Features for Expression Recognition in the Wild" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010251
APA StyleXu, H., Kong, J., Kong, X., Li, J., & Wang, J. (2022). MCF-Net: Fusion Network of Facial and Scene Features for Expression Recognition in the Wild. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010251






