Effects of Glucose Addition on Dynamics of Organic Carbon Fractions and cbbL-Containing Bacteria in Wetlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
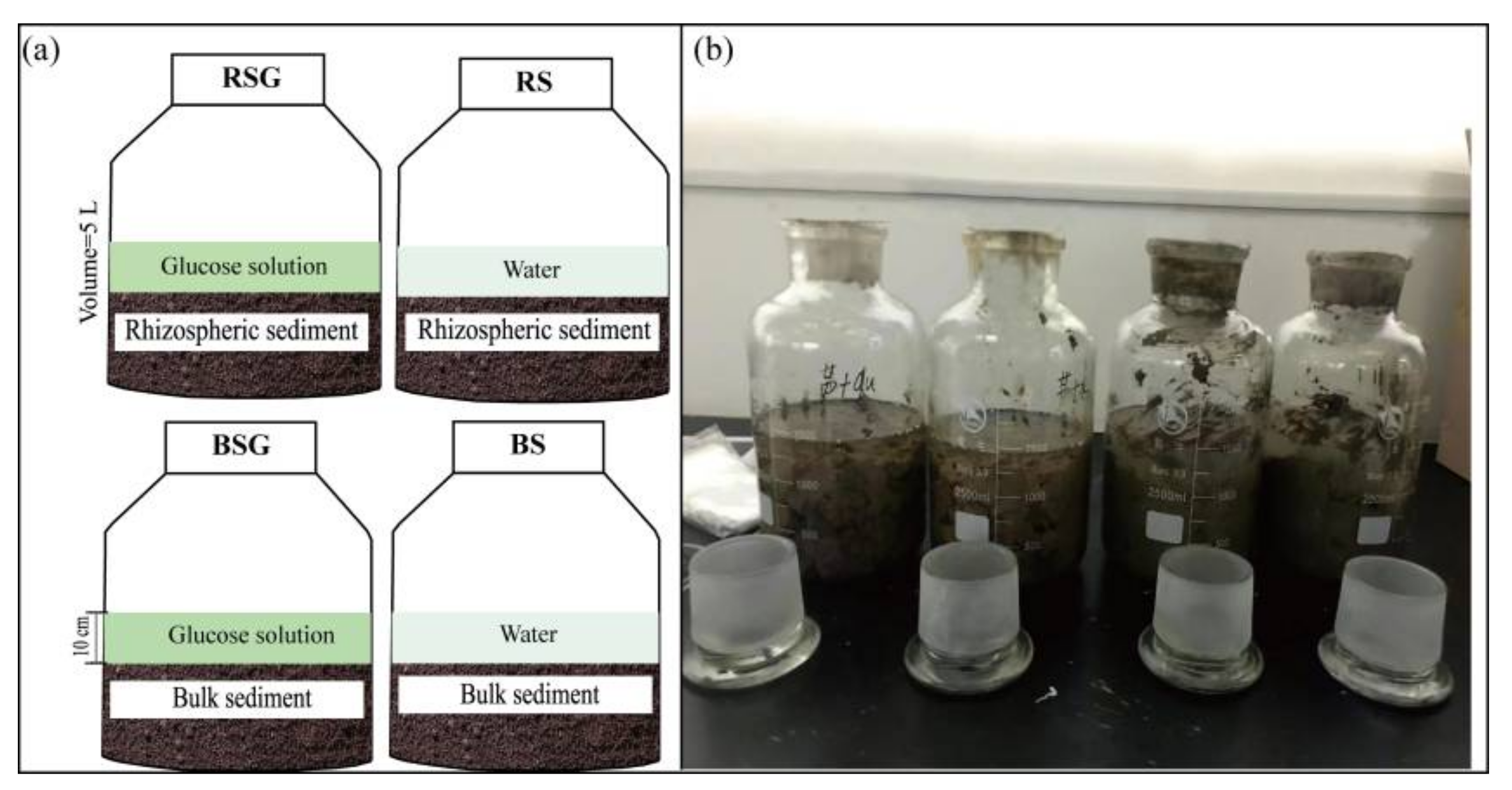
2.1. Field Sampling and Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Analysis
2.2.1. Analysis of LFOM and HFOM
2.2.2. RubisCO Activity Analysis
2.2.3. DNA Extraction, Illumina MiSeq Sequencing, and Real-Time PCR of cbbL Gene
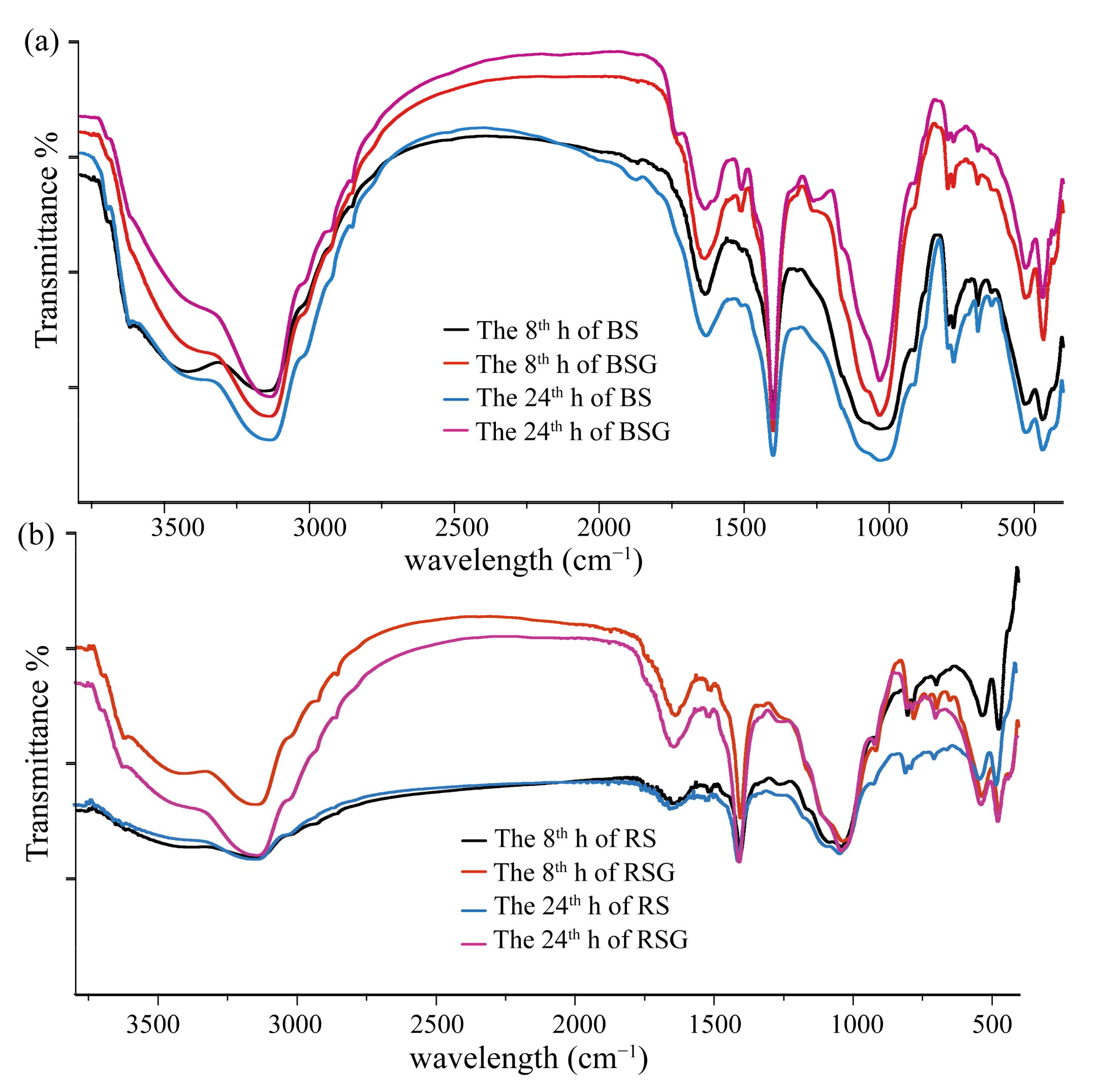
2.2.4. Spectroscopy Measurement of LFOM
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
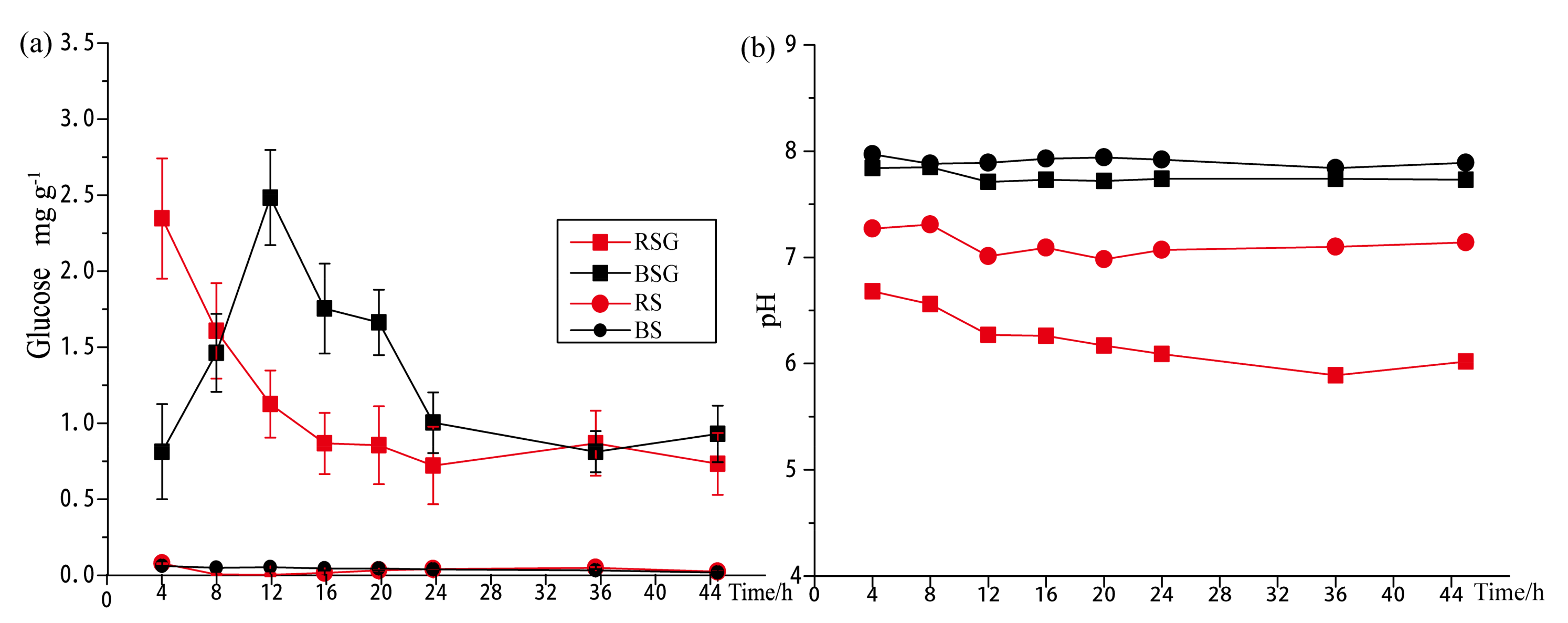
3.1. Glucose Degradation
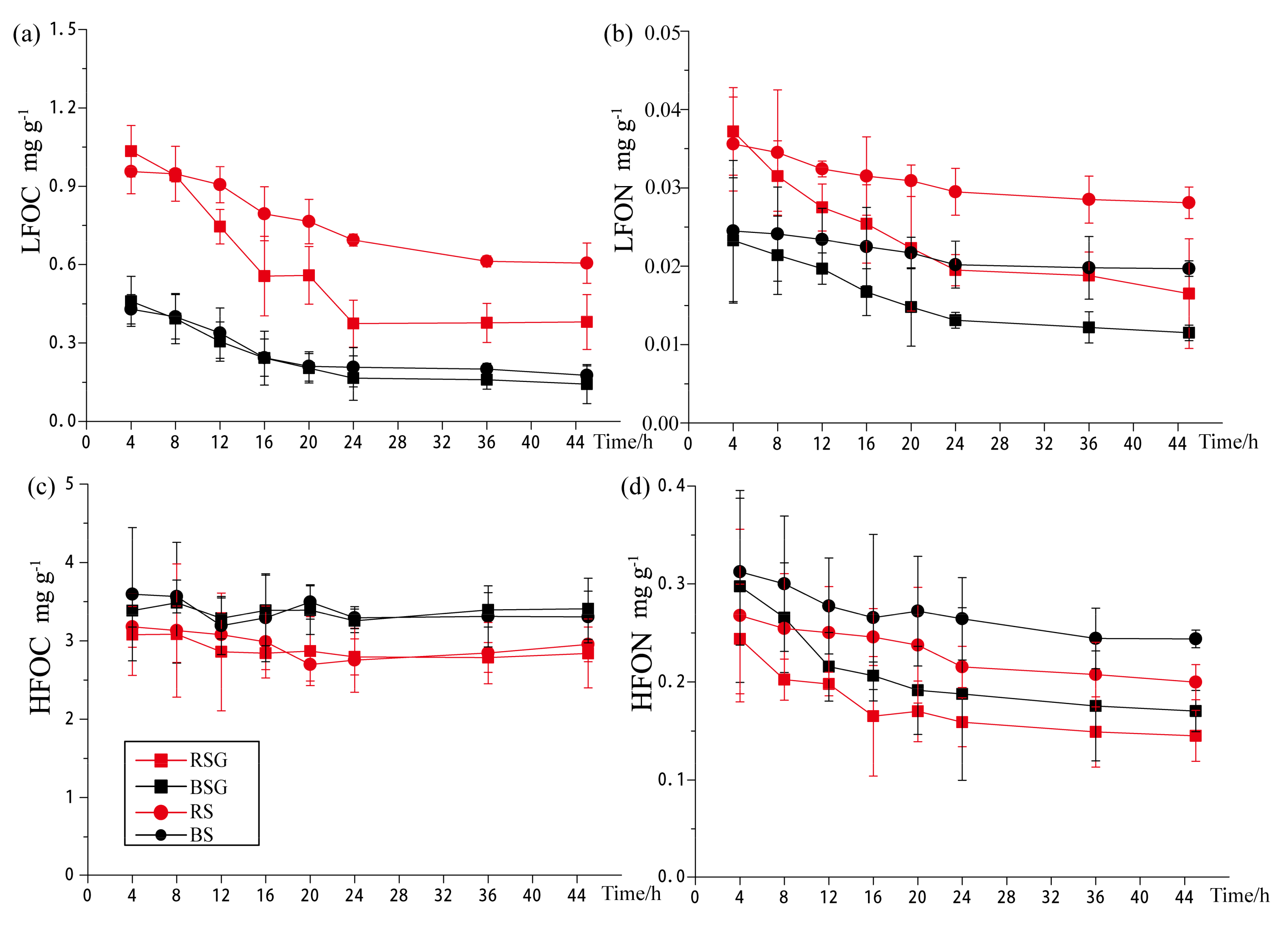
3.2. Changes of LFOM and HFOM
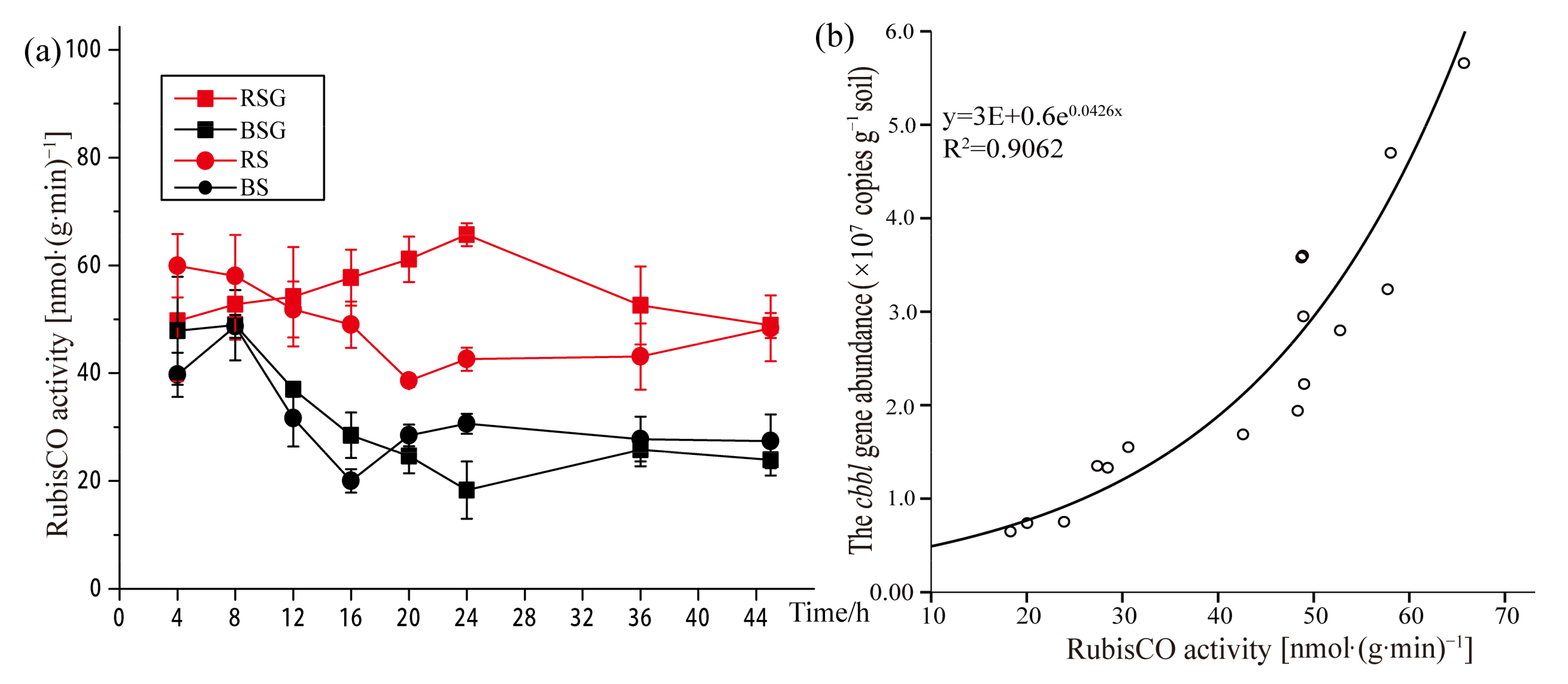
3.3. RubisCO Activity and Abundances Changes of cbbL Gene
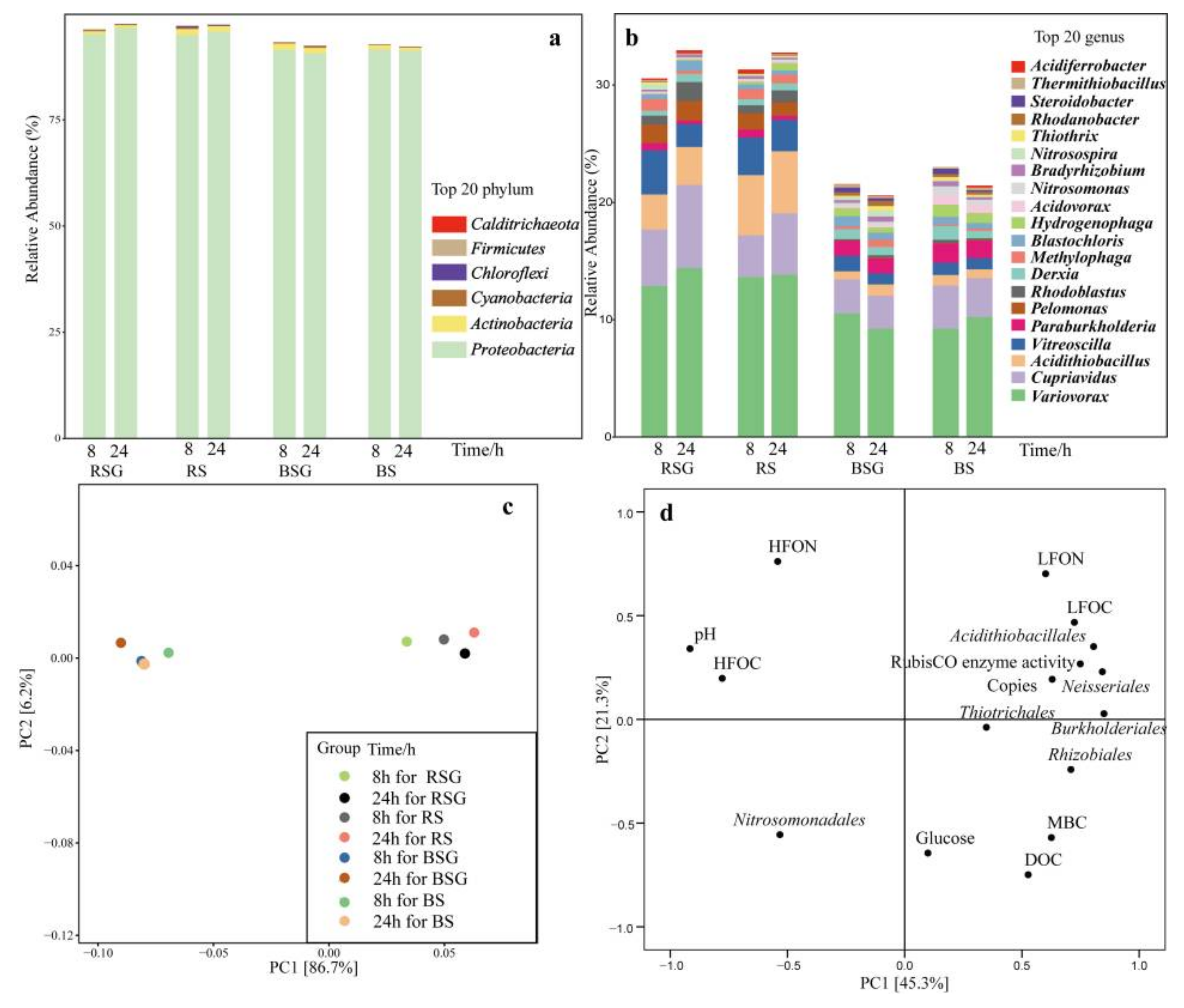
3.4. Composition and Changes of cbbL-Containing Bacteria
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Glucose Addition on OM Fractions
4.2. Effects of Glucose Addition on RubisCO Activity and cbbL-Containing Bacteria
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.W.; Bai, Y.Z.; Wang, X.Q.; Xia, P.; Yang, G.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhang, H. Sources and features of particulate organic matter in tropical small mountainous rivers (SW China) under the effects of anthropogenic activities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochera, C.; Picazo, A.; Murueta, N.; Camacho, A. In situ bioremediation techniques to reduce total organic matter oversaturation of fluvial sediments: An experimental study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguinaga, O.E.; White, K.N.; Dean, A.P.; Pittman, J.K. Addition of organic acids to acid mine drainage polluted wetland sediment leads to microbial community structure and functional changes and improved water quality. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.I.; Shao, W.; Hui-Li, Y.U.; Qiao, X.S.; Yang, X.J.; Gao, D.T.; Wang, Z.Q. Response of microbial communities and enzyme activities to soil amendment with low-molecular-weight organic substances. Soil Fertilizer Sci. China 2019, 2, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jiapeng, W.U.; Guan, F.; Xiang, H.E.; Jiao, L.; Hong, Y. Controls of organic matters on denitrification and anammox in sediments of pearl river estuary by mesocosm experiments. Ecol. Sci. 2018, 37, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sakagami, N.; Shiotsu, F.; Asagi, N.; Nitta, M.K.; Suprapta, D.N. The carbon degradation of paddy soil under organic and conventional farming in bali, indonesia as measured by sequential loss on ignition. Trop. Agric. Dev. 2019, 63, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Chang, J.; Scott, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y. Plant species diversity impacts nitrogen removal and nitrous oxide emissions as much as carbon addition in constructed wetland microcosms. Ecol. Eng. J. Ecotechnol. 2016, 93, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.B.; Gabor, R.S.; Schooler, S.; McKnight, D.M.; Nemergut, D.R.; Knelman, J.E. Oligotrophic wetland sediments susceptible to shifts in microbiomes and mercury cycling with dissolved organic matter addition. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Si, G.; Xu, R.; Zhou, J.; Xi, C.; Hu, A.; Zhang, G. Excessive nitrogen addition accelerates N assimilation and P utilization by enhancing organic carbon decomposition in a Tibetan alpine steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Evans, S.E.; Friesen, M.L.; Tiemann, L.K. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the abundance of nitrogen cycling genes in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis of field studies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, G.; Limpert, K.E.; Brodersen, K.E.; Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Carnell, P.E.; Mareadie, P.I. The combined effect of short-term hydrological and N-fertilization manipulation of wetlands on CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Metagenomics reveals divergent functional profiles of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling under long-term addition of chemical and organic fertilizers in the black soil region. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.X.; Li, Z.P.; Che, Y.P. Effects of glucose addition on nitrogen transformation in black soils different in organic carbon content. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2011, 48, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Yin, P.; Nong, X.; Liao, J.H. Effect of exogenous carbon addition and the freeze-thaw cycle on soil microbes and mineral nitrogen pools1. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 108, 032046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, H.; Meier, S.; Bunge, M.; Widmer, F.; Zeyer, J. Effect of model root exudates on structure and activity of a soil diazotroph community. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Sun, X.; Ding, J.; Jiang, Z.W.; Xu, J.Z. Effects of biochar addition on the NEE and soil organic carbon content of paddy fields under water-saving irrigation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2019, 26, 8303–8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieger, A.; Kaiser, K.; Guayasamín, P.R.; Kaupenjohann, M. Massive carbon addition to an organic-rich andosol increased the subsoil but not the topsoil carbon stock. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2743–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, Z.Q.; Zhong, M.C. Soil moisture alters the response of soil organic carbon mineralization to litter addition. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, N.S.; Butterly, C.R.; Sale, P.W.G.; Tang, C. Residue addition and liming history interactively enhance mineralization of native organic carbon in acid soils. Biol. Fert. Soils 2017, 53, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, X.; Zhuang, G. Cryosphere microbiome biobanks for mountain glaciers in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Han, Y. Promotion of carbon dioxide biofixation through metabolic and enzyme engineering. Catalysts 2022, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusian, B.; Bowien, B. Operator binding of the CbbR protein, which activates the duplicate cbb CO2 assimilation operons of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6568–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yuan, H.Z.; Ge, T.D.; Zou, S.Y.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, S.L.; Zhou, P. Effect of land use on the abundance and diversity of autotrophic bacteria as measured by ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) large subunit gene abundance in soils. Biol. Fert. Soils 2013, 49, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.B.; Lin, D.; Cai, L.; Jiang, Y.M.; Zhu, D. Effects of different vegetation communities on soil carbon fraction, rubisco activity and cbbl genes in Nanjishan wetland of poyang lake. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.H.; Ge, T.D.; Yuan, H.Z.; Li, B.Z.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhou, P. Changes in bacterial CO2 fixation with depth in agricultural soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2014, 98, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.C.; Murphy, D.V.; Wang, X.L.; Hoyle, F.C. Microbial respiration, but not biomass, responded linearly to increasing light fraction organic matter input: Consequences for carbon sequestration. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 35496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.D.; Fan, Y.; Bing, J.; Li, D.C.; Zhao, Y.G.; Yang, J.L.; Zhang, G.L. The influence of the conversion of grassland to cropland on changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Catena 2018, 171, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Lal, R.; Owens, L.; Izaurralde, R.C. Distribution of light and heavy fractions of soil organic carbon as related to land use and tillage practice. Soil Till. Res. 2007, 92, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Dong, J.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, T.; He, H.; Liu, J. Response of microbial community composition and function to emergent plant rhizosphere of a constructed wetland in northern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 385, 114884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Guo, Z.L.; Cai, C.F.; Wang, J.G.; Deng, J. Effect of water content, bulk density, and aggregate size on mechanical characteristics of Aquults soil blocks and aggregates from subtropical China. J. Soil Sediment. 2017, 17, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Y.; Quan, Q.; Zhao, D.; Li, C.C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Fang, J.F.; Wang, L.F.; Liu, J. A combined method for the source apportionment of sediment organic carbon in rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.Z.; Ge, T.D.; Wu, X.L.; Liu, S.L.; Tong, C.L.; Qin, H.L.; Wu, M.N.; Wei, W.X.; Wu, J.S. Long-term field fertilization alters the diversity of autotrophic bacteria based on the ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) large-subunit genes in paddy soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2012, 95, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Walker, R. Trust between primary health care organizations. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2001, 11, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Xu, L.; Gao, M.; Jiao, Y.; Wei, X.; Jin, L.; Cheng, S.; Li, X.; Feng, S. Optical Properties Research of Bacillus Subtilis Spores by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2012, 32, 3193–3196. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.H.; Sun, Z.G.; Wang, L.L.; Sun, W.L.; Sun, W.G.; Song, H.L. A preliminary study on methane production potential of soil in tidal wetlands of the yellow river estuary and its responses to organic matter and nitrogen import. Wetland Sci. 2012, 10, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Xiao, H. Effects of exogenous carbon input on soil organic carbon mineralization and temperature sensitivity of cropland and wetland in the North China Plain. Chinese J. Eco-Agri. 2019, 27, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Chuks, C.A.; Solomon, B.A.; Olisa, O. Response of Sarotherodon Melanotheron Rüppell (1852) in the Niger Delta wetland, Nigeria to changes in pH. Rev. Científica UDO Agrícola 2008, 8, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Lee, S.Y. Contribution of microplastics to carbon storage in coastal wetland sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Soil microorganisms have a threshold concentration of glucose to in-crease the ratio of respiration to assimilation. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 54, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Singh, B.; Dijkstra, F.A. Microbial carbon use efficiency of glucose varies with soil clay content: A meta-analysis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apek, P.; Choma, M.; Tahovská, K.; Kaňa, J.; Antrková, H. Coupling the resource stoichiometry and microbial biomass turnover to predict nutrient mineralization and immobilization in soil. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114884. [Google Scholar]
- Chuckran, P.F.; Fofanov, V.; Hungate, B.A.; Morrissey, E.M.; Schwartz, E.; Walkup, J.; Dijkstra, P. Rapid response of nitrogen cycling gene transcription to labile carbon amendments in a soil microbial community. mSystems 2021, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Wang, N.; Yu, M.K.; Yu, J.G.; Xue, L.H. Rhizosphere and straw return interactively shape rhizosphere bacterial community composition and nitrogen cycling in paddy soil. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 945927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Bimueller, C.; Porras, R.; Curtis, B.; Chafe, O.; Abramoff, R.; Bill, M.; Torn, M. Soil Mesocosm CO2 Emissions after 13C-Glucose Addition, Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics, and Microbial Biomass, Barrow, Alaska, 2014–2016; Next Generation Ecosystem Experiments Arctic Data Collection, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, R.; Zhang, X.; Song, C. Effects of nitrogen addition on plant functional traits in freshwater wetland of sanjiang plain, northeast china. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumböck, M.; Conrad, R. Metabolism of position-labelled glucose in anoxic methanogenic paddy soil and lake sediment. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol. 1991, 85, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham-Cheatham, S.M.; Zhao, Q.; Obrist, D.; Yang, Y. Unexpected mechanism for glucose-primed soil organic carbon mineralization under an anaerobic–aerobic transition. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudicianni, P.; Cardone, G.; Ragucci, R. Cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin slow steam pyrolysis: Thermal decomposition of biomass components mixtures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2013, 100, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, P.K.; Entry, J.A.; Crawford, D.L.; Cromack, K.J. Cellulose and lignin degradation in forest soils: Response to moisture, temperature, and acidity. Microb. Ecol. 1990, 20, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.B.; Wang, S.M.; Zhou, Y.K. Dynamic of organic matter in the heavy fraction after abandonment of cultivated wetlands. Biol. Fert. Soils 2008, 44, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Z.A.; Chao, G.B.; Wz, B.; Hao, Z.B.; Jing, Z.C.; Cs, B. Labile carbon addition alters soil organic carbon mineralization but not its temperature sensitivity in a freshwater marsh of Northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 160, 103844. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.W.; He, Z.Q.; Zhou, J.M. Characterization of soil humic substances using mid-infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy. In Functions of Natural Organic Matter in Changing Environment; Zhejiang University Press: Zhejiang, China; Springer Science Business Media Dordrecht: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fultz, L.M.; Jennifer, M.K.; Francisco, C.; Veronica, A.M. Using fourier-transform mid-Infrared spectroscopy to distinguish soil organic matter composition dynamics in aggregate fractions of two agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Du, C.W.; Ma, F.; Shen, Y.Z.; Wu, K.; Liang, D.; Zhou, J.M. Detection of soil organic matter from laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and mid-infrared spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR) coupled with multivariate techniques. Geoderma 2019, 35, 113905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Liu, S.G.; Wang, Q.K.; Sun, T.; Blagodatskaya, E. Organic N deposition favours soil C sequestration by decreasing priming effect. Plant Soil 2019, 445, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. The progresses of studies on rubisco activase. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2000, 17, 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V. Microbial response time to sugar and amino acid additions to soil. Soil Bio. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2178–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Farrell, M.; Bolan, N. Priming of soil organic carbon by malic acid addition is differentially affected by nutrient availability. Soil Bio. Biochem. 2014, 77, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesak, I.; Lesak, H. The activity of RubisCO and energy demands for its biosynthesis. Comparative studies with CO2-reductases. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 257, 153337. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Q.; Wu, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, B.; Xiao, H. Effects of Glucose Addition on Dynamics of Organic Carbon Fractions and cbbL-Containing Bacteria in Wetlands. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010239
Cao Q, Wu J, Ma W, Liu B, Xiao H. Effects of Glucose Addition on Dynamics of Organic Carbon Fractions and cbbL-Containing Bacteria in Wetlands. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010239
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Qingqing, Jinhang Wu, Wen Ma, Bing Liu, and Huabin Xiao. 2022. "Effects of Glucose Addition on Dynamics of Organic Carbon Fractions and cbbL-Containing Bacteria in Wetlands" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010239
APA StyleCao, Q., Wu, J., Ma, W., Liu, B., & Xiao, H. (2022). Effects of Glucose Addition on Dynamics of Organic Carbon Fractions and cbbL-Containing Bacteria in Wetlands. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010239







