Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Disrupt Established Biofilms of Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Plant Extract
2.3. Synthesis of ZnO-NPs
2.4. Characterization of ZnO-NPs
2.5. Bacteria Used and Their Culture Conditions
2.6. Assays for the Inhibition of Biofilms
2.6.1. Quantitative Inhibition of Biofilms by ZnO-NPs
2.6.2. Inhibition of Biofilms on Solid Surface
Light Microscopic Analysis of Inhibition of Biofilms
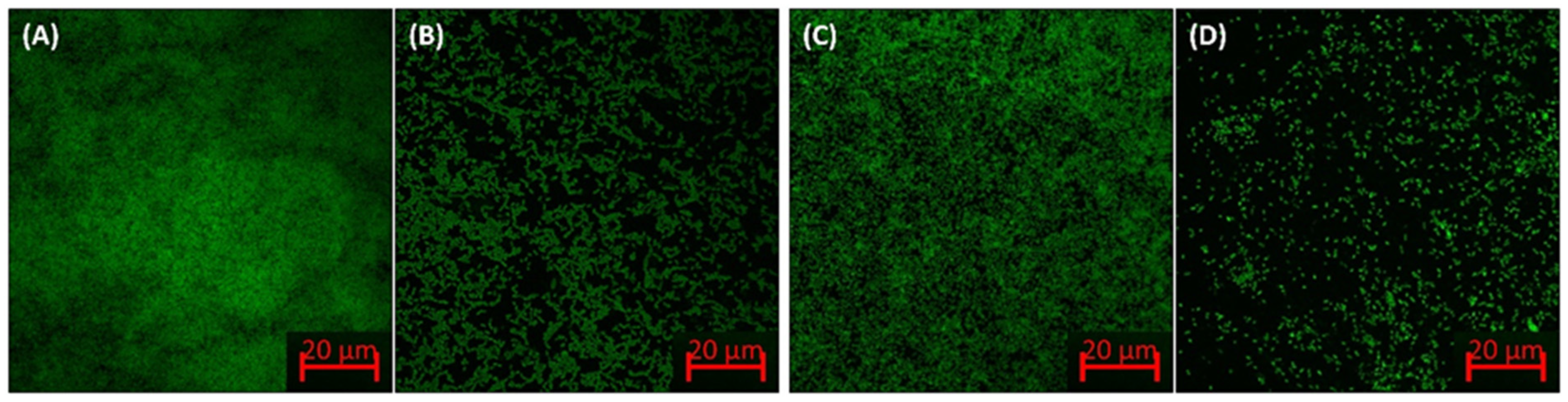
Confocal Microscopic Analysis of Biofilms Inhibition
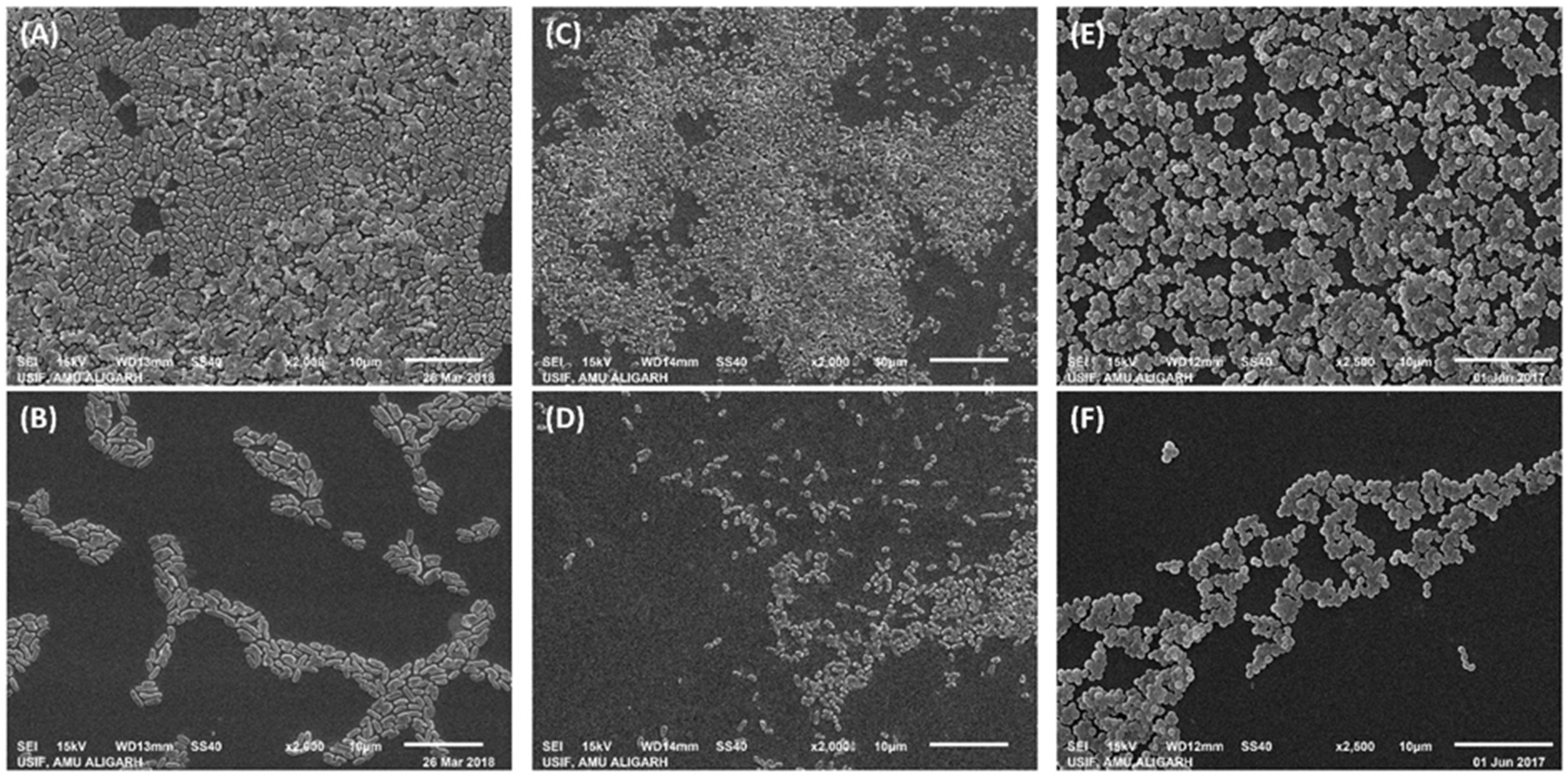
Scanning Electron Microscopic Analysis of Biofilms Inhibition
2.7. Quantification of Exopolysaccharides (EPS) Inhibition by ZnO-NPs
2.8. Eradication of the Established Biofilms by ZnO-NPs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Green Synthesis of ZnO-NPs and Its Characterization
3.2. Inhibition of the Biofilm Development
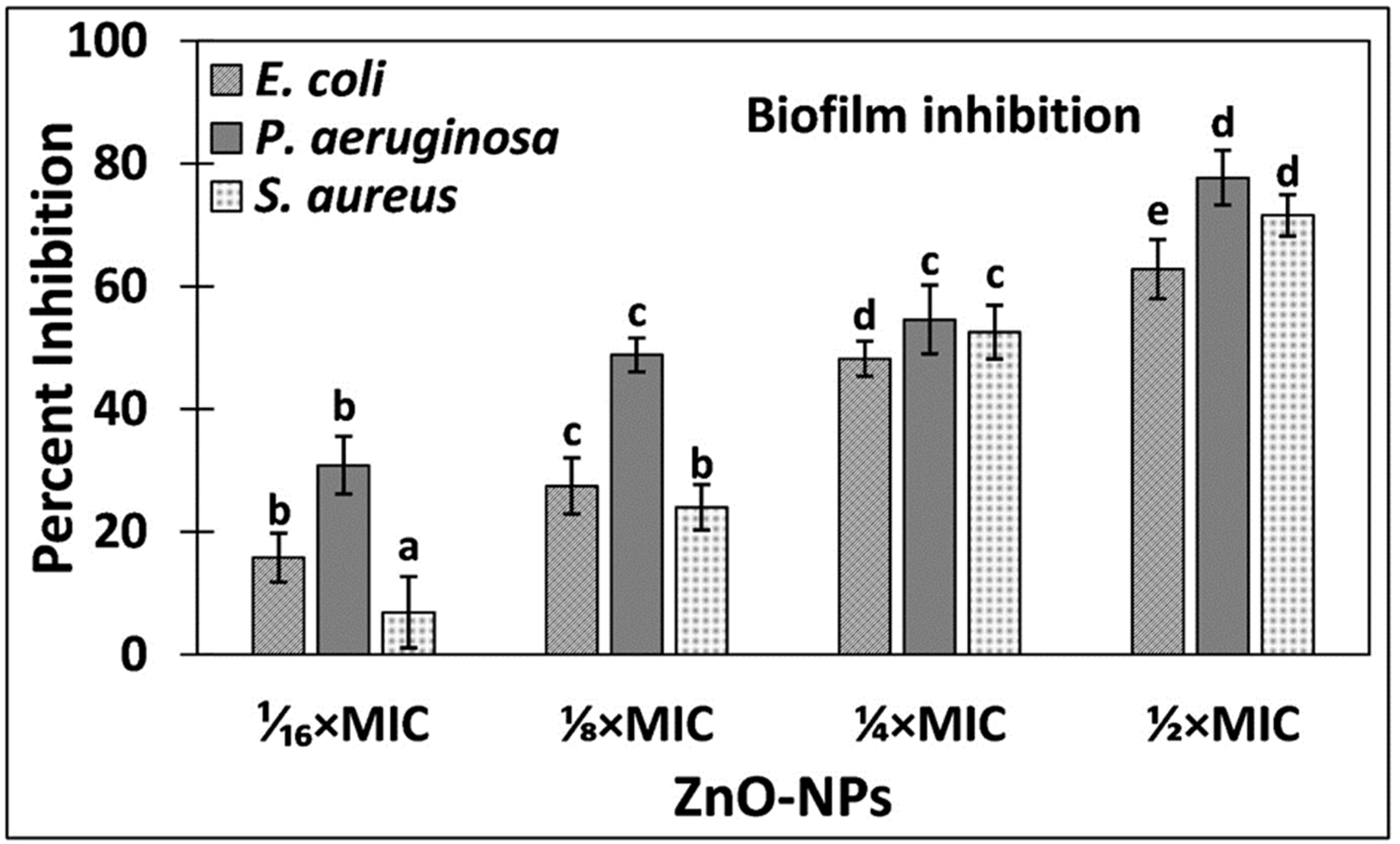
3.2.1. Quantitative Analysis of Biofilms Inhibition
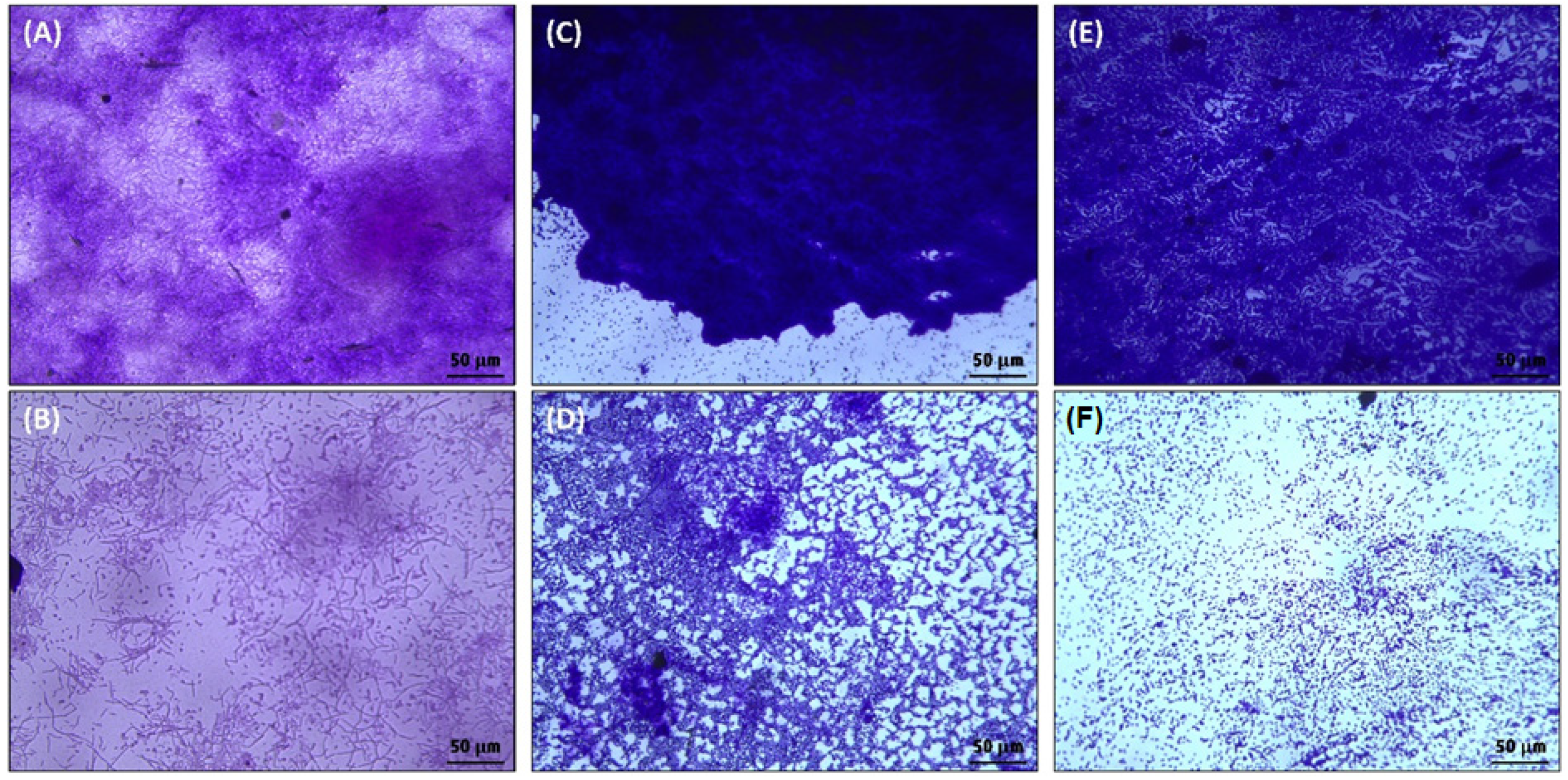
3.2.2. Biofilm Inhibition by ZnO-NPs on the Glass Surface
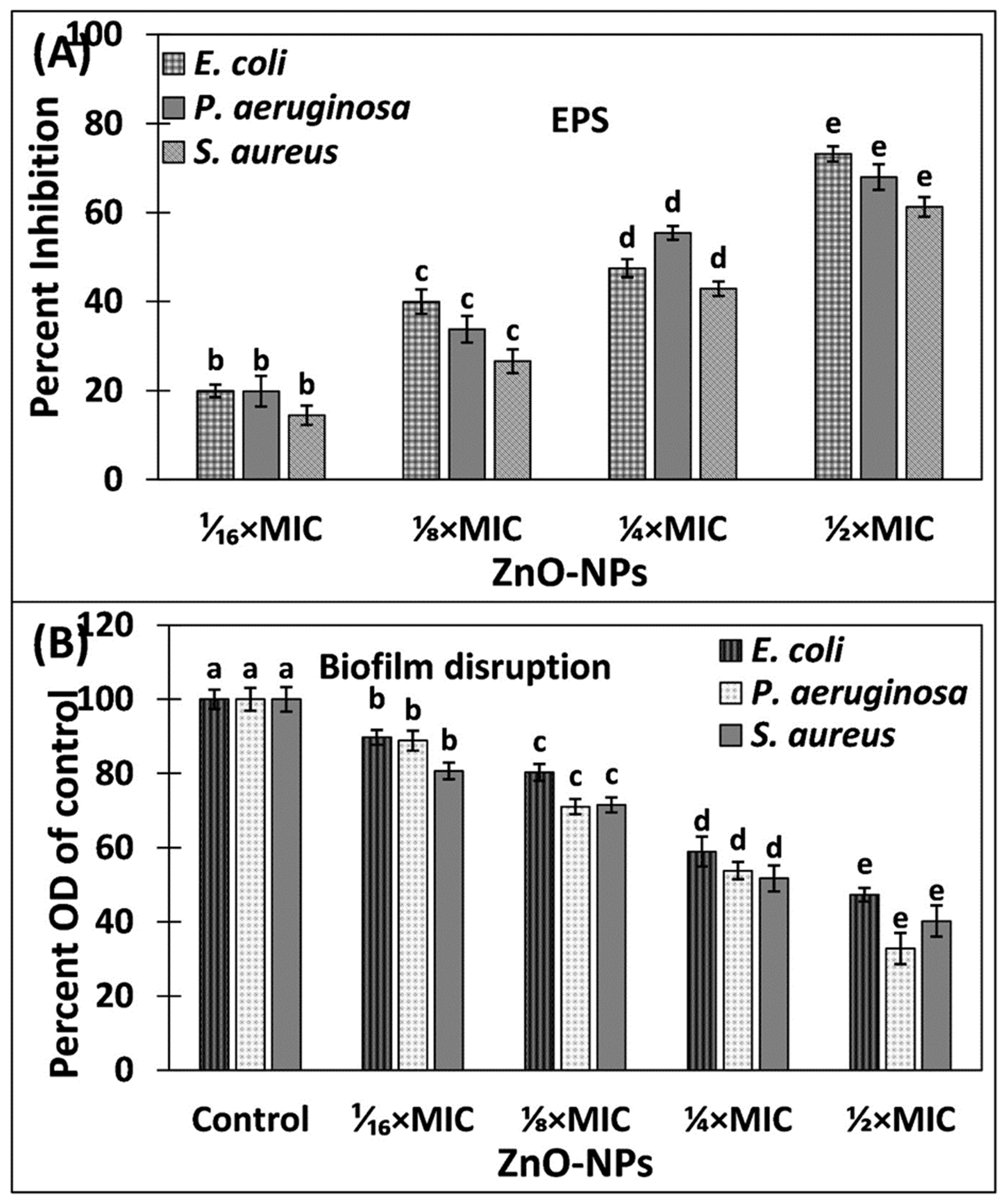
3.3. Inhibition of Exopolysaccharides (EPS) by ZnO-NPs
3.4. Eradication of Established Biofilms of Pathogenic Bacteria by ZnO-NPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistant |
| EPS | Exopolysaccharides |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory concentration |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ZnO-NPs | Zinc oxide nanoparticles |
References
- Khare, S.; Williams, K.; Gokulan, K. Nanotechnology. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 893–900. [Google Scholar]
- Qamar, S.A.; Asgher, M.; Khalid, N.; Sadaf, M. Nanobiotechnology in health sciences: Current applications and future perspectives. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerger, R.; Klaus, T.; Granqvist, C.G. Biologically Produced Silver-Carbon Composite Materials for Optically Functional Thin-Film Coatings. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.P.; Charu, G.; Dhan, P. Methodological advancements in green nanotechnology and their applications in biological synthesis of herbal nanoparticles. Int. J. Bioassays 2012, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ingale, A.G. Biogenic Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Potential Applications: An Eco- Friendly Approach. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Patra, C.R. Biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles: Recent advancement and future perspectives in cancer theranostics. Futur. Sci. OA 2017, 3, FSO203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO The Top 10 Causes of Death; 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Shakoor, S.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Hasan, R. Antibiotic-Resistant Enteric Infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 1105–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andleeb, S.; Majid, M.; Sardar, S. Environmental and public health effects of antibiotics and AMR/ARGs. In Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 269–291. [Google Scholar]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO No Time to Wait: Securing the Future from Drug-Resistant Infections; 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/documents/no-time-to-wait-securing-the-future-from-drug-resistant-infections-en.pdfsfvrsn=5b424d7_6 (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Balcázar, J.L.; Subirats, J.; Borrego, C.M. The role of biofilms as environmental reservoirs of antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilm Formation: A Clinically Relevant Microbiological Process. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schachter, B. Slimy business—The biotechnology of biofilms. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, N.; Qais, F.A.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, J.M.; Shahzad, S.A.; Ahmad, I. Facile Synthesis of Tin Oxide Hollow Nanoflowers Interfering with Quorum Sensing-Regulated Functions and Bacterial Biofilms. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 6845026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Iqbal, A.; Shafi, A.; Qais, F.A.; Ahamad, T.; Srivastava, S. Enhanced Removal of Crystal Violet Dye and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Ti Doped CeO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Phoenix Dactylifera Mediated Green Method. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 32, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Kolter, R. Flagellar and twitching motility are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Altaf, M.; Manoharadas, S.; Al-Rayes, B.F.; Ali Abuhasil, M.S.; Almaroai, Y.A. Biofabricated silver nanoparticles exhibit broad-spectrum antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing activity against Gram-negative bacteria. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13700–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I. Broad-spectrum quorum sensing and biofilm inhibition by green tea against gram-negative pathogenic bacteria: Deciphering the role of phytocompounds through molecular modelling. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, K.; Velmurugan, S. Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (L.). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdagni, P.; Khatri, P.; Rana, J.S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2018, 30, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bala, N.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Maiti, M.; Das, S.; Basu, R.; Nandy, P. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: Effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and anti-diabetic activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajiv, P.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Bio-Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Parthenium hysterophorus L. and its size-dependent antifungal activity against plant fungal pathogens. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 112, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Hassan, I.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Qais, F.A.; Oves, M.; Rahman, M.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, A.; et al. Biofabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle from Ochradenus baccatus Leaves: Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm Activity, Protein Binding Studies, and In Vivo Toxicity and Stress Studies. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 8612158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatami, M.; Alijani, H.Q.; Heli, H.; Sharifi, I. Rectangular shaped zinc oxide nanoparticles: Green synthesis by Stevia and its biomedical efficiency. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 15596–15602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: Structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Geranium Leaf Assisted Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.R.; Khan, M.S.; Zulfequar, M.; Shahid Khan, M. Optical and Structural Properties of ZnO Thin Films Fabricated by Sol-Gel Method. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, K.; Nomura, N.; Suzuki, S. Biofilms: Hot spots of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) in aquatic environments, with a focus on a new HGT mechanism. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; Wahab, R.; Khan, F.; Mishra, Y.K.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A. Reactive oxygen species mediated bacterial biofilm inhibition via zinc oxide nanoparticles and their statistical determination. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peulen, T.O.; Wilkinson, K.J. Diffusion of nanoparticles in a biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Khan, A.A.; Cameotra, S.S.; Saquib, Q.; Musarrat, J. Gum arabic capped-silver nanoparticles inhibit biofilm formation by multi-drug resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, F.M.; Hasan, I.; Qais, F.A.; Khan, R.A.; Alam, P.; Alsalme, A. Fabrication of Zinc Oxide-Xanthan Gum Nanocomposite via Green Route: Attenuation of Quorum Sensing Regulated Virulence Functions and Mitigation of Biofilm in Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. Coatings 2020, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chinese Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Visnapuu, M.; Vija, H.; Kisand, V.; Kasemets, K.; Kahru, A.; Ivask, A. Selective antibiofilm properties and biocompatibility of nano-ZnO and nano-ZnO/Ag coated surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishwarya, R.; Vaseeharan, B.; Kalyani, S.; Banumathi, B.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Al-anbr, M.N.; Khaled, J.M.; Benelli, G. Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ulva lactuca seaweed extract and evaluation of their photocatalytic, antibiofilm and insecticidal activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 178, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Camper, A.K. Characterization of Phenotypic Changes inPseudomonas putida in Response to Surface-Associated Growth. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6579–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maunders, E.; Welch, M. Matrix exopolysaccharides; the sticky side of biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yildiz, F.H.; Schoolnik, G.K. Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor: Identification of a gene cluster required for the rugose colony type, exopolysaccharide production, chlorine resistance, and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4028–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czaczyk, K.; Myszka, K. Biosynthesis of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) and Its Role in Microbial Biofilm Formation. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 799–806. [Google Scholar]
- Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Johansen, H.K.; Song, Z.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T. The clinical impact of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 3, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, S.; Vishakha, K.; Das, S.; Dutta, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Mondal, J.; Mondal, S.; Ganguli, A. Antibacterial, anti-biofilm activity and mechanism of action of pancreatin doped zinc oxide nanoparticles against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qais, F.A.; Samreen; Ahmad, I. Broad-spectrum inhibitory effect of green synthesised silver nanoparticles from Withania somnifera (L.) on microbial growth, biofilm and respiration: A putative mechanistic approach. IET Nanobiotechnology 2018, 12, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
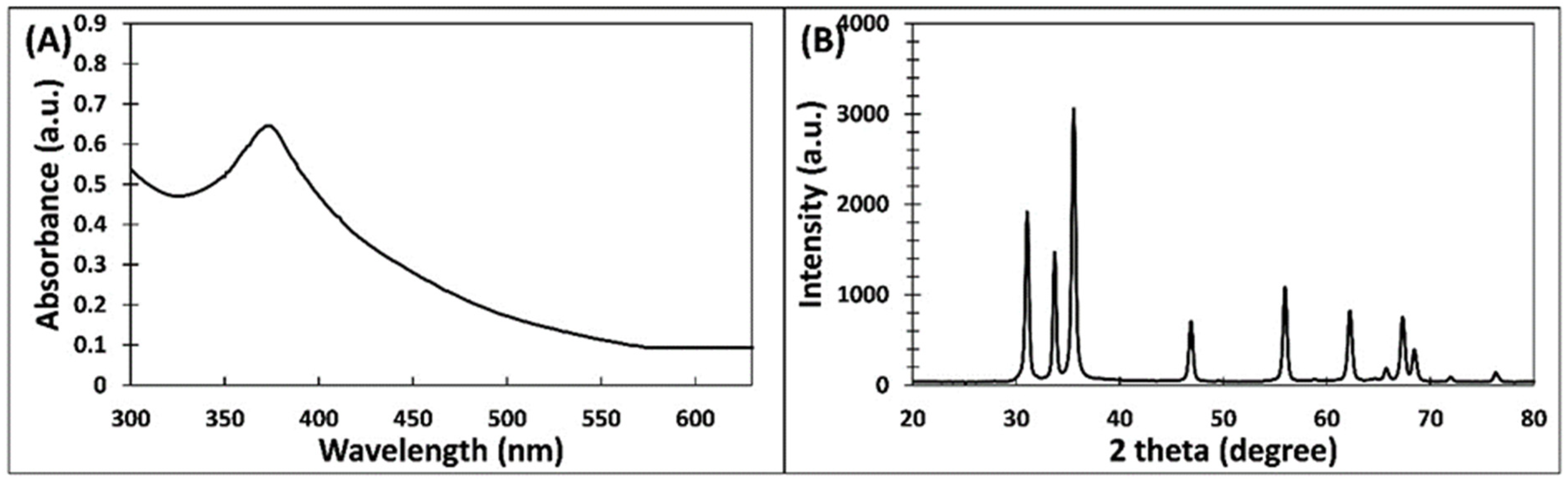
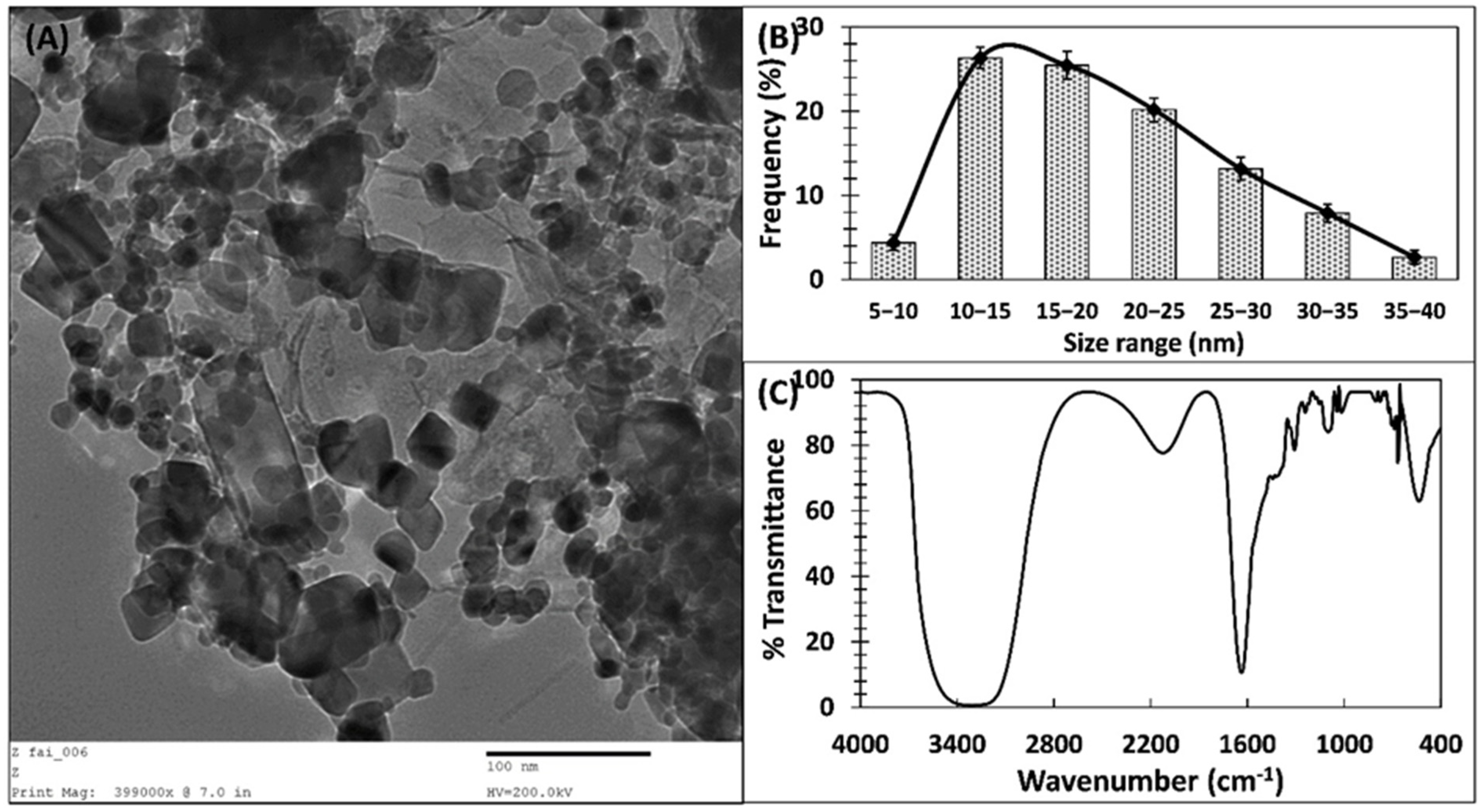
| S. No. | 2θ (degree) | Height (a.u.) | Area | FWHM | Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31.090 | 2283.5 | 35,996.0 | 0.3219 | 25.61 |
| 2 | 33.719 | 1854.0 | 24,809.3 | 0.2789 | 29.76 |
| 3 | 35.566 | 3608.0 | 60,054.7 | 0.3421 | 24.38 |
| 4 | 46.880 | 833.0 | 14,037.3 | 0.3468 | 24.96 |
| 5 | 55.963 | 1288.7 | 23,612.0 | 0.3690 | 24.37 |
| 6 | 62.197 | 931.4 | 19,461.3 | 0.4272 | 21.71 |
| 7 | 67.340 | 852.0 | 18,560.0 | 0.4420 | 21.59 |
| Average | 24.62 ± 2.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Husain, F.M.; Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Hakeem, M.J.; Baig, M.H.; Masood Khan, J.; Al-Shabib, N.A. Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Disrupt Established Biofilms of Pathogenic Bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020710
Husain FM, Qais FA, Ahmad I, Hakeem MJ, Baig MH, Masood Khan J, Al-Shabib NA. Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Disrupt Established Biofilms of Pathogenic Bacteria. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(2):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020710
Chicago/Turabian StyleHusain, Fohad Mabood, Faizan Abul Qais, Iqbal Ahmad, Mohammed Jamal Hakeem, Mohammad Hassan Baig, Javed Masood Khan, and Nasser A. Al-Shabib. 2022. "Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Disrupt Established Biofilms of Pathogenic Bacteria" Applied Sciences 12, no. 2: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020710
APA StyleHusain, F. M., Qais, F. A., Ahmad, I., Hakeem, M. J., Baig, M. H., Masood Khan, J., & Al-Shabib, N. A. (2022). Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Disrupt Established Biofilms of Pathogenic Bacteria. Applied Sciences, 12(2), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020710






