A Stacking Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Method for the Prediction of Building Construction Project Costs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Ensemble Learning
2.1.1. Bagging
2.1.2. Boosting
2.1.3. Stacking
2.2. Hyperparameter Tuning with Bayesian Optimization
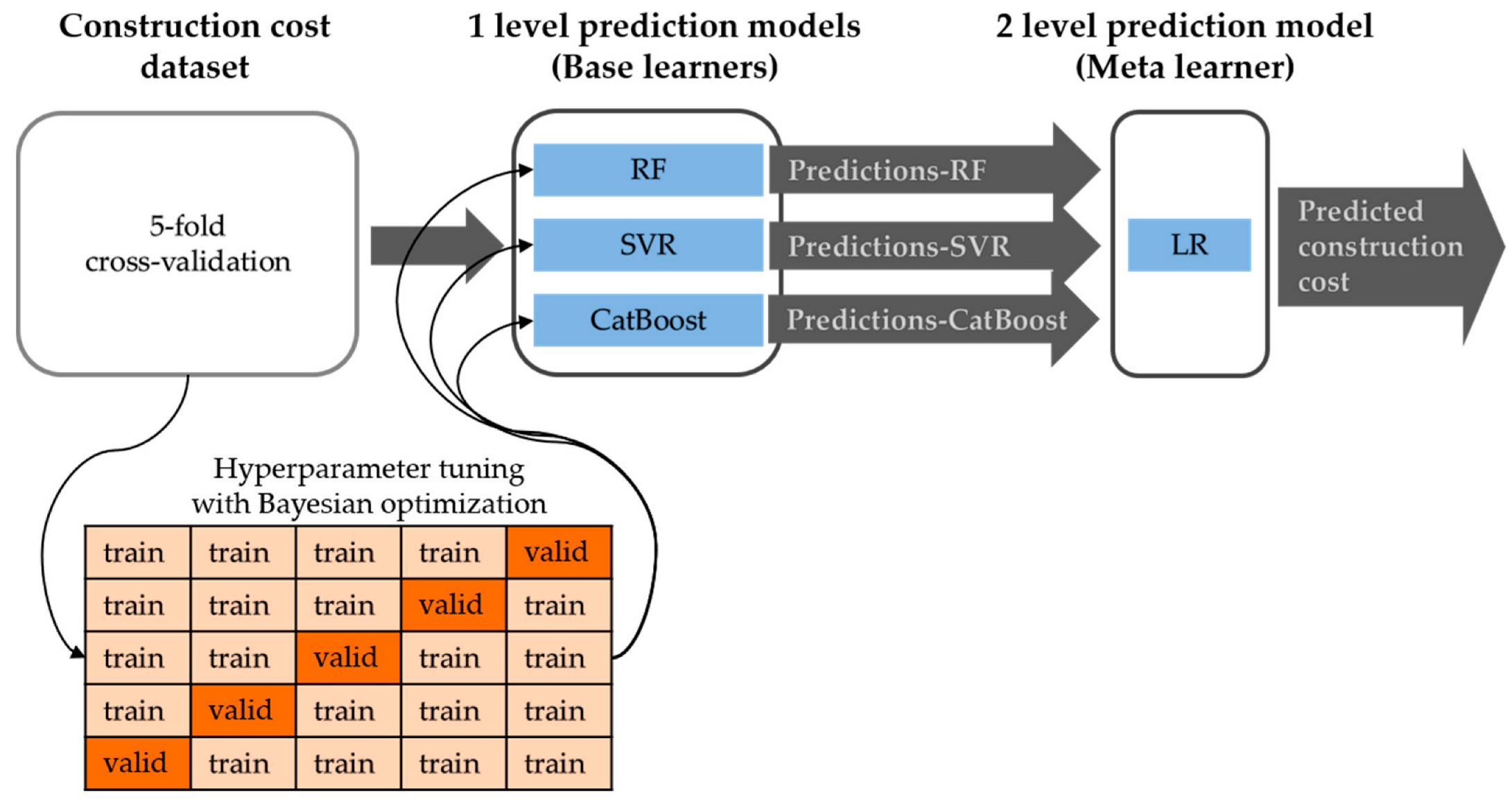
3. Proposed Stacking Ensemble Model
3.1. Stacking-Based Ensemble Learning Modeling
3.2. Model Evalution
- is generally used to measure the performance of regression-based machine learning models. is the proportion of the residual sum of squares with the total sum of squares, which indicates how well the model fits the observed data. The residual is the difference between the observed data and the value predicted by the model. is expressed as:
- RMSE is the square root of the mean squared error, which is expressed as:where is the number of samples to be evaluated in the training, is the model output related to the sample (, is the target output and is the mean of the targets in Equations (1) and (2). For , the larger the value is, the better the model performance is, and it cannot exceed 1. On the other hand, lower values of RMSE are desirable.
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Data
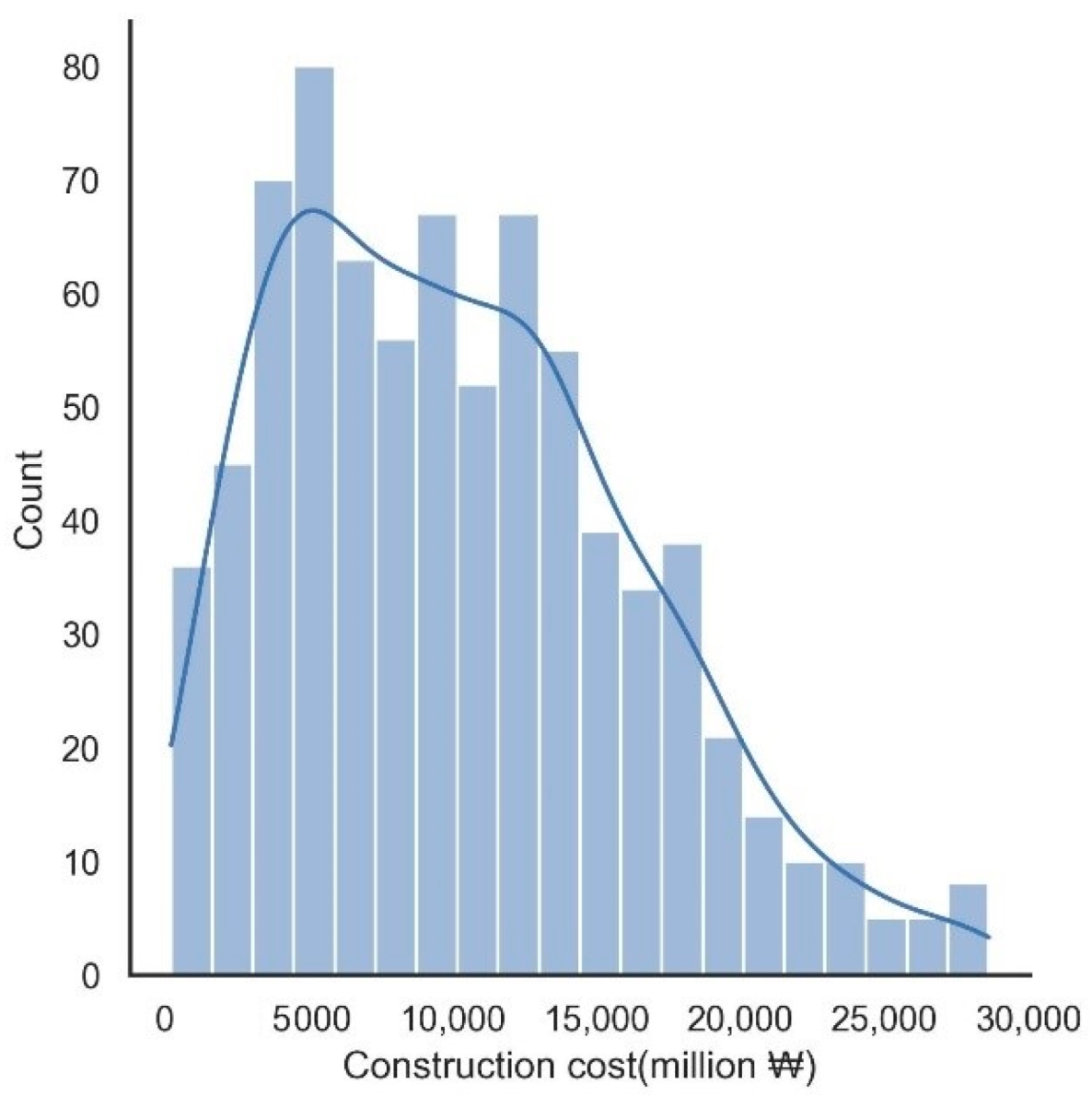
4.1.1. Data Acquisition and Description
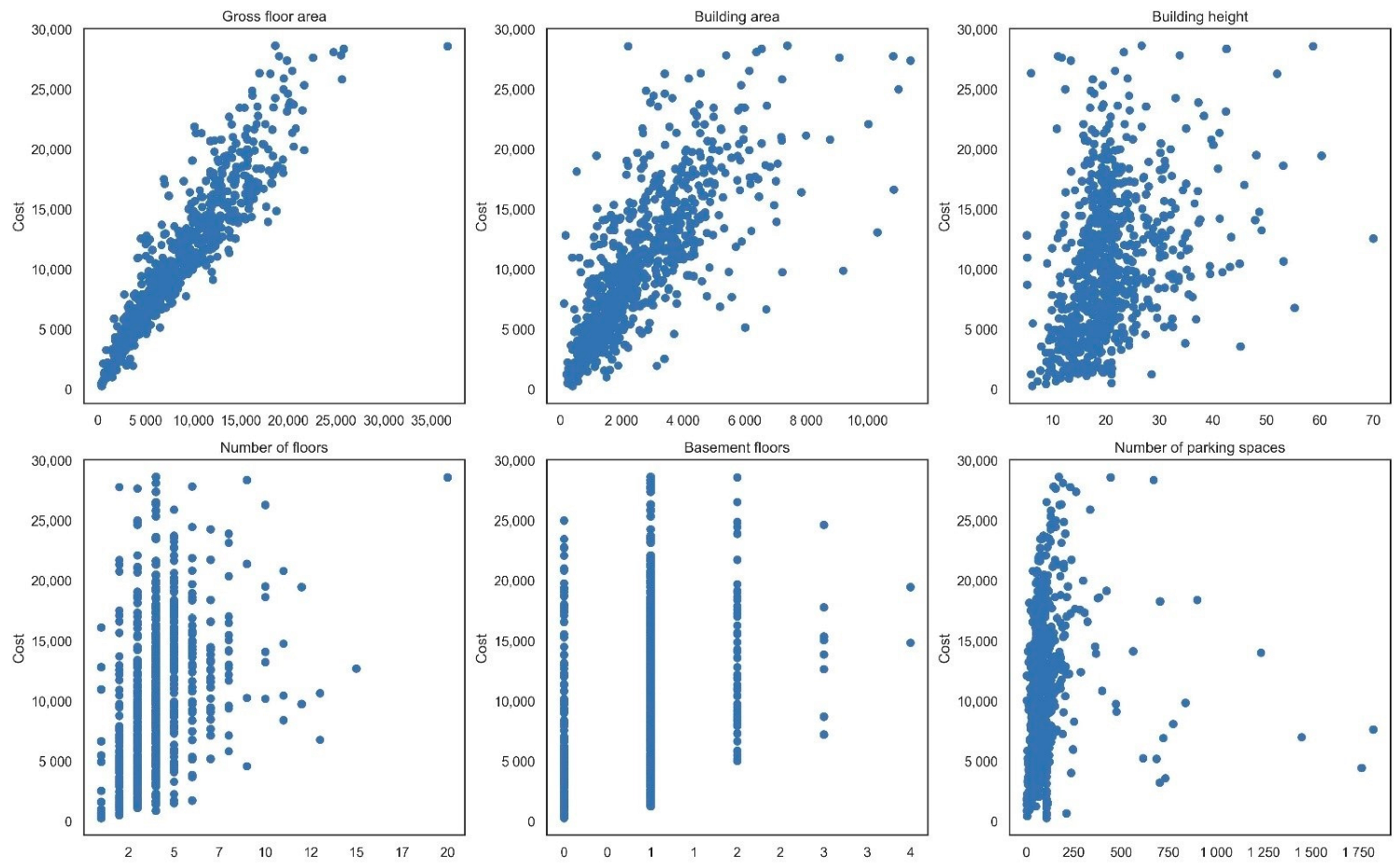
4.1.2. Variables Selection
4.1.3. Data Preprocessing
4.2. Performance of Individual ML Models
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elfaki, A.O.; Alatawi, S.; Abushandi, E. Using Intelligent Techniques in Construction Project Cost Estimation: 10-Year Survey. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2014, 2014, 107926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, T.S.; Ebadati, O.M.; Kaur, H. Cost estimation and prediction in construction projects: A systematic review on machine learning techniques. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagotla, S.K.; Gangashetty, S.V.; Giridhar, K. A novel stacking technique for prediction of diabetes. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Moreira, J.; Soares, C.; Jorge, A.M.; Sousa, J.F.D. Ensemble approaches for regression: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2012, 45, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.; Suganthan, P.N. Ensemble Classification and Regression-Recent Developments, Applications and Future Directions [Review Article]. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2016, 11, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Levinson, D. The ensemble approach to forecasting: A review and synthesis. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 132, 103357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, D.; Cheng, T.C.E.; Wang, Y. Interpretable Multi-modal Stacking-based Ensemble Learning Method for Real Estate Appraisal. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirutchataboon, G.; Prasertthum, S.; Chuangsuwanich, E.; Pratanwanich, P.N.; Ratanamahatana, C. Stacking Ensemble Learning for Housing Price Prediction: A Case Study in Thailand. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Bangsaen, Chonburi, Thailand, 21–24 January 2021; pp. 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Huang, X.; Lin, M.; Jia, J.; Tian, Z. Short-term cooling load prediction for office buildings based on feature selection scheme and stacking ensemble model. Eng. Comput. 2022, 39, 2003–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.; Praça, I.; Vale, Z.; Silva, J. Ensemble learning for electricity consumption forecasting in office buildings. Neurocomputing 2021, 423, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.; Akashdeep, S.; Harshvardhan, R.; Sowmya, S.K. Stacking Deep learning and Machine learning models for short-term energy consumption forecasting. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 52, 101542. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Asteris, P.G.; Koopialipoor, M.; Alexakis, D.E.; Lemonis, M.E.; Armaghani, D.J. Stacking Ensemble Tree Models to Predict Energy Performance in Residential Buildings. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Pham, A. Enhanced artificial intelligence for ensemble approach to predicting high performance concrete compressive strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H. Stacked generalization. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džeroski, S.; Ženko, B. Is Combining Classifiers with Stacking Better than Selecting the Best One? Mach. Learn. 2004, 54, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syarif, I.; Zaluska, E.; Prugel-Bennett, A.; Wills, G. Application of bagging, boosting and stacking to intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition, Berlin, Germany, 13–20 July 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 593–602. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, D.; Elhegazy, H.; Elzarka, H.; Gutierrez, L. A novel construction cost prediction model using hybrid natural and light gradient boosting. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 46, 101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meharie, M.; Mengesha, W.; Gariy, Z.; Mutuku, R. Application of stacking ensemble machine learning algorithm in predicting the cost of highway construction projects. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2021, 29, 2836–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. Experiments with a new boosting algorithm. icml 1996, 96, 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhosseini, M.; Hu, G.; Pham, H. Optimizing ensemble weights and hyperparameters of machine learning models for regression problems. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2022, 7, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, P.; Freund, Y.; Lee, W.S.; Schapire, R.E. Boosting the margin: A new explanation for the effectiveness of voting methods. Ann. Stat. 1998, 26, 1651–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Unbiased boosting with categorical features. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Liang, K.; Guo, W.; Zhou, L. A Novel Stacking Heterogeneous Ensemble Model with Hybrid Wrapper-Based Feature Selection for Reservoir Productivity Predictions. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6675638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yin, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. A stacking-based ensemble learning method for earthquake casualty prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 101, 107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.H.D.M.; dos Santos Coelho, L. Ensemble approach based on bagging, boosting and stacking for short-term prediction in agribusiness time series. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 86, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.H.D.M.; da Silva, R.G.; Moreno, S.R.; Mariani, V.C.; dos Santos Coelho, L. Efficient bootstrap stacking ensemble learning model applied to wind power generation forecasting. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 136, 107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek, J.; Larochelle, H.; Adams, R.P. Practical bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter Type | Parameter | Average | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input variables | Gross floor area (m2) | 8135.8 | 5342.9 | 325 | 36,699.0 |
| Building area (m2) | 2628.3 | 1791.7 | 122.8 | 11,392.40 | |
| Building height (m) | 20.5 | 7.9 | 5.2 | 70 | |
| Number of floors | 4.1 | 1.9 | 1 | 20 | |
| Number of basement floors | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0 | 4 | |
| Number of parking spaces | 94.8 | 147.2 | 3 | 1830 | |
| Target variables | Construction cost (million ₩) | 10,260.3 | 6113.2 | 251.0 | 28,622.0 |
| ML Models | Hyperparameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| ANN | activation batch_size epochs initializer optimizer | relu 16 100 normal adam |
| SVM | Regularization parameter (C) epsilon Kernel type RBF gamma | 400 0.005 RBF 0.010 |
| RF | n_estimators max_depth min_samples_leaf | 715 5 4 |
| DT | min_samples_split max_depth min_samples_leaf max_leaf_nodes | 25 6 10 30 |
| Adaboost | n_estimators learning_rate | 114 0.089 |
| XGBoost | max_depth max_depth learning_rate | 200 3 0.023 |
| LightGBM | n_estimators max_depth learning_rate | 100 4 0.056 |
| CatBoost | iterations learning_rate depth l2_leaf_reg | 250 0.050 2 0.2 |
| Models | Training Dataset | Testing Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | |
| ANN | 1973.05 | 0.90 | 2012.30 | 0.89 |
| LR | 1991.61 | 0.89 | 2026.00 | 0.89 |
| SVR | 2006.20 | 0.89 | 2041.48 | 0.89 |
| BDT | 937.08 | 0.98 | 2115.27 | 0.88 |
| RF | 1632.91 | 0.93 | 2018.72 | 0.89 |
| Adaboost | 1700.85 | 0.92 | 2086.06 | 0.88 |
| XGboost | 1557.83 | 0.93 | 1974.73 | 0.89 |
| LightGBM | 1509.55 | 0.94 | 1977.16 | 0.89 |
| CatBoost | 1712.98 | 0.92 | 2003.19 | 0.89 |
| Cross-Validation | Training Dataset | Testing Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | |
| 1 | 1775.01 | 0.92 | 1644.83 | 0.91 |
| 2 | 1706.94 | 0.92 | 1933.24 | 0.90 |
| 3 | 1776.34 | 0.92 | 1649.95 | 0.92 |
| 4 | 1729.90 | 0.92 | 1821.91 | 0.91 |
| 5 | 1695.12 | 0.92 | 1951.54 | 0.91 |
| Average | 1736.66 | 0.92 | 1800.29 | 0.91 |
| Stdv 1 | 37.75 | 0.002 | 148.15 | 0.007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, U.; Kang, Y.; Lee, H.; Yun, S. A Stacking Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Method for the Prediction of Building Construction Project Costs. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199729
Park U, Kang Y, Lee H, Yun S. A Stacking Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Method for the Prediction of Building Construction Project Costs. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):9729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199729
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Uyeol, Yunho Kang, Haneul Lee, and Seokheon Yun. 2022. "A Stacking Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Method for the Prediction of Building Construction Project Costs" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 9729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199729
APA StylePark, U., Kang, Y., Lee, H., & Yun, S. (2022). A Stacking Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Method for the Prediction of Building Construction Project Costs. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 9729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199729








