Abstract
Iron-transition metal-based binary and ternary alloys have attracted great attention due to their relevant mechanical, electrical, and magnetic properties. In this paper, we systematically investigate the structural, magnetic, and magnetocaloric behavior of as-milled Fe65T35 (T = Ni and Mn) alloy. The polycrystalline alloys were produced by the planetary ball milling, using a powder-to-ball ratio of 1:3. A structural study reveals that both Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35 compounds have stabilized in α and γ mixed phase within the cubic crystal structure. The alloyed compounds are further characterized by high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscopy (HR-FESEM), which confirms the mixing of both metals in the alloying process. Temperature-dependent magnetic studies do not show any blocking in zero-field-cooled and field-cooled results; however, the field-dependent magnetization study demonstrates the ferromagnetic nature with small hysteresis in both compounds. Both compounds show a significant magnetocaloric effect over a wide temperature range around room temperature. Fe65Ni35 exhibit a slightly higher value in comparison to Fe65Mn35. In both the alloys, magnetic entropy change follows the power law behavior against the external magnetic field, and the value of exponent ‘m’ explains the presence of magnetic correlation. Our investigation in this study communicates that the phase control or coexistence of both phases may be efficacious in obtaining the desirable characteristic of magnetic and magnetocaloric demeanors in such a binary Fe-T alloy.
1. Introduction
The investigation of materials showing an magnetocaloric effect (MCE) has been an important area of research due to its potential application in magnetic refrigeration technology and its fundamental point of view [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Magnetic refrigeration provides highly efficient and environment-friendly cooling compared to conventional gas compression/expansion techniques [1,2,3,4]. Research in this field generally focused on materials with MCE around room temperature and low-temperature regions. The current focus of the researchers is to investigate the various materials that have MCE near room temperature. Moreover, the technological application examination of the magnetocaloric parameters of a magnetic material is interesting from the fundamental point of view as they confer insight into complex magnetic phases present in the system. In the past, researchers have used magnetocaloric parameters to study the nature of magnetic ordering [7,8,9,10,11,12]. In short, a comprehensive investigation of field-dependent MCE can endow helpful insight into the performance of a material in magnetic refrigeration in the actual refrigeration cycle. Instead, such investigations also aim to obtain a deeper understanding of the nature of magnetic-phase transitions and phase coexistence in the material. In practice, the MCE performance is assessed through the change in magnetic entropy in response to an external magnetic field that is significantly controlled by structural changes and equally associated magnetic phase transitions. Intermetallic compounds have been marked by high entropy changes, due to which they secure the highest spot in the quest of finding an excellent MCE material.
Intermetallic alloys offer an ideal playground for maneuvering the MCE and other physical properties in binary, ternary, and quaternary systems [8,9,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21] simply by adjusting the arrangement of constituent metal ions in the crystal structure. In the last few years, various transition metal-based compounds have been explored, which are cost-effective and very good alternatives to rare-earth materials [13,14,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Lately, iron-based alloys have been suggested as economical alternatives in the field of magnetic cooling [19,22,23]. The binary intermetallic compounds Fe100−xMx (M is 3d or 4d metals) provide a good platform to investigate various properties such as magnetic [23,26,27,28,29,30], magnetocaloric [22,23,24,31], electrical [32], magnetoresistance [33,34], and mechanical [35]. Fe100−xMx alloys have a cubic structure with bcc (α-phase) and fcc (γ-phase) crystal structure geometries. In such alloys, most magnetic and related properties are governed by the crystallographic phases. Based on the nature of the structural phase, they showed low and high-temperature magnetic behavior. Various synthesis methods have been reported for preparing such binary alloys [19,22,26,28,29,30,36,37]. Among them, mechanical alloying through the ball-mill technique has been applied extensively, primarily because of its ability to bypass the phase diagram regularities and hence ease the synthesis of metastable structural phases [19,36,38,39]. Moreover, it could cause the impurity phase fractions or lattice disorders to control the magnetocaloric parameter, the broadness of the magnetic transition, and the disordered-derived distributed exchange interactions [19,22,23,38,40]. Fe-M alloys have shown soft ferromagnetic behavior with different stoichiometries. This family has demonstrated a significant magnitude of magnetocaloric parameters with low hysteresis losses and tunable Curie temperatures. Fe-based binary alloys with 3d or 4d substituents have shown mixed structural behavior [30,36], which dictates the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties. Such compounds are crucial for combining two different metals, which can affect their crystallographic phase within the same cubic structure. They can provide a weighty approach for tuning the magnetic and magnetocaloric parameters. For example, pure Fe has a very high magnetic ordering temperature, while FeNi shows magnetic ordering at a relatively lower temperature. Additionally, magnetic ordering in Fe-Ni depends on the crystallographic phase and the presence of different Ni concentrations in Fe-Ni systems [22,23,26]. The γ-phase rich FeNi shows large magnetization along with magnetic ordering slightly above the room temperature [19,22,23,24]. Structural phase-controlled antiferromagnetic behavior is also observed in FeMn [27,41]. Therefore, transition metal-doped Fe-based binary alloys with mixed crystallographic phases may be appropriate for further investigations. Consequently, it may also affect the magnetocaloric performance, which can be highly alluring for technological applications as well as fundamental studies.
In this paper, we addressed the structural phase controlled magnetic and magnetocaloric properties through X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, magnetization, and magnetocaloric studies on Fe65T35 (M = Ni and Mn). We carried out all the investigations on as-milled compounds. Our results reveal that both alloys are found in the mixed (α + γ) crystallographic phase, which may be established due to the diffusion of both metal cations during the mixing/milling. The ferromagnetic nature with small hysteresis is confirmed in the magnetization study. Interestingly, both compounds show that the MCE is approximately at room temperature. We also investigate the magnetic nature by the field-dependent magnetic entropy change, followed by a power law behavior (ΔSM~Hm). The exponent (m) value indicates the presence of ferromagnetic correlation in Fe65Ni35 compounds; however, antiferromagnetic correlation within ferromagnetic correlation occurred in the Fe65Mn35 compound.
2. Materials and Methods
The highly pure Fe, Ni, and Mn powders (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA; purity ≥ 99.6%), as raw materials, were used for the synthesis of polycrystalline Fe65T35 (T = Ni and Mn) alloy. Both of these alloys were synthesized by the planetary ball milling technique. In this process, the stoichiometric ratio of all raw materials was mixed and ground in 250 mL ball mill container under Toluene medium for 24 h. Milling speed was 600 rpm, and the powder-to-ball (diameter 5 mm) ratio of 3:1 was maintained for each composition. As-milled powder has been used for the further investigation. The structural characterization and phase analysis of the alloys were carried out through X-ray diffraction (XRD); they were recorded with a PANalytical (Malvern, UK) X-pert Pro-diffractometer containing a Cu-Kα X-ray radiation (λ = 1.54 °A) source. The microstructure and elemental composition of the samples were acquired from the high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscope provided by Jeol (HR-FE-SEM; JSM-7900F/15 kV). The magnetic properties of the as-milled samples were carried out from the vibrating sample magnetometer option of the cryogen free versa lab physical properties measurement system (PPMS) (Quantum Design, San Diego, CA, USA). The magnetocaloric properties in terms of isothermal magnetic entropy change are derived from the isothermal magnetization data, calculation, and protocol adopted from [11,42].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Morphological Properties of Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35 Alloys
The room temperature XRD patterns for Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35 are displayed in Figure 1a,b, respectively. Five Braggs peaks (111), (110), (200), (200), and (220) are observed in the diffraction pattern. Among the above peaks, two are corresponding to the α-phase and three denote the γ-phase of large crystals of Fe-Ni and Fe-Mn alloys, as confirmed by the literature report [26,39] and JCPDS data (as describes in Figure 1). It can be inferred that both alloys crystallize in the cubic structure with two different space groups: Fm-3m (γ-phase, fcc structure) and Im-3m (α-phase, bcc structure). In both compounds, two structural phases coexist, which are confirmed by the presence of different diffraction planes (as identified in Figure 1). The formation of the γ-phase in both compounds is promoted by the diffusion of Ni/Mn into the Fe site during the ball milling. The diffraction peak (110) has a higher intensity than the (111) peak, which means the α-phase is dominated as compared to the γ-phase; such behavior commonly occurs in as-prepared Fe-based alloys [26,36,40]. From the phase diagram study, generally Fe-Ni based systems have contained an α-phase up to 30% Ni composition and from the α + γ, mixed phase to the γ phase as the Ni composition increased [39,43,44,45,46]. Similar behavior also occurred in the Fe-Mn compound.
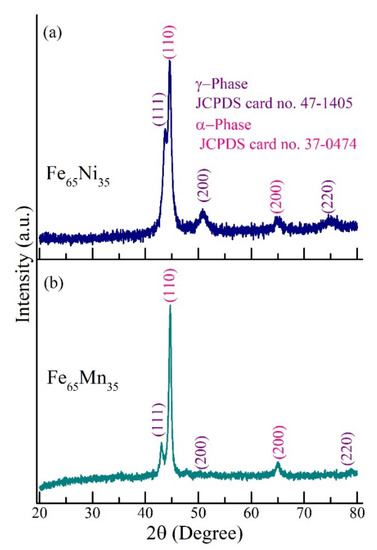
Figure 1.
Room temperature X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD): (a) XRD results for Fe65Ni35; (b) XRD results for Fe65Mn35.
The powder morphology of the Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35 alloys are studied by HR-FE-SEM. Figure 2a,b displays the morphological micrograph of both the studied alloys. The as-milled alloy evidently shows the irregular distribution of the bulk alloys, which may arise due to the presence of two crystallographic phases and/or the presence of different Fe-Ni and Fe-Mn clusters. These results are analogous to the XRD results where two crystallographic phases coexist.
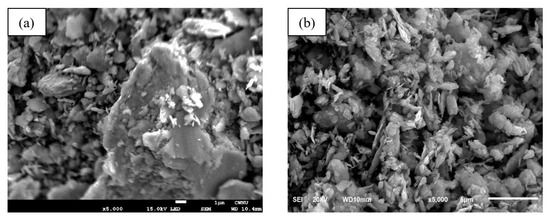
Figure 2.
SEM micrograph: (a) SEM image for Fe65Ni35; (b) SEM image of Fe65Mn35.
3.2. Magnetic Properties of Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35 Alloys
Temperature-dependent DC magnetization curves, obtained under zero-field-cooled (ZFC) and field-cooled (FC) conditions at H = 1 kOe for Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35, are shown in Figure 3a,b, respectively. In this study, we have recorded the temperature-dependent magnetization data in the temperature range of 50 K to 400 K. In the case of the Fe65Ni35 alloy, as displayed in Figure 3a, it is noticed that as the temperature decreases, bifurcation among the ZFC and FC curves increases up to the lowest measured temperature. However, the ZFC and FC curves have not merged up to the highest measured temperature, i.e., 400 K. This substantiates that Fe65Ni35 has a magnetic ordering at a higher temperature, as reported in the literature [22,23,24]. Additionally, determining the blocking temperature, in this case, is very difficult because of the absence of any clear/sharp peak in the ZFC magnetization plot. This behavior may arise from the presence of different Fe-Ni magnetic clusters of the α and γ phases, either ferromagnetic or super-paramagnetic [26]. Interestingly, arc-like behavior has appeared in ZFC magnetization, followed by an abrupt change in the slope just above 250 K, perhaps due to competition between two different structural/magnetic clusters, and the abrupt change in the slope occurred due to the dominance of the concerned phase in that particular temperature region. In order to check the presence of any magnetic ordering within this measured temperature range, we further analyze the derivative curve of the magnetization data (not shown), confirming a broad minimum of around 260 K. For the case of Fe65Mn35, ZFC and FC magnetization do not merge in common with Fe65Ni35 in the measured temperature range (as shown in Figure 3b). However, the nature of the magnetization curves changes as the temperature increases. The ZFC and FC plot depicts a small peak around 320 K. The reason behind this peak and curve modification is the coexistence of two magnetic correlations, i.e., ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic. Such antiferromagnetic correlations in these alloys are not unusual. They also sometimes depend on the presence of two crystallographic phases. This statement consent with the literature reports, which communicate that FeMn compounds have crystallographic phase-controlled magnetic properties, i.e., γ-FeMn has antiferromagnetic behavior [41].
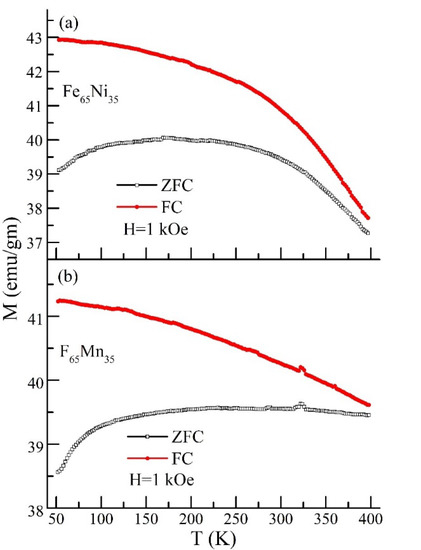
Figure 3.
Temperature response of DC magnetization results measured at 1 kOe under zero field cooled (ZFC) and field cooled (FC) conditions: (a) ZFC and FC magnetization curve for Fe65Ni35; (b) ZFC and FC magnetization curve for Fe65Mn35.
In order to obtain better insight into the magnetic nature of the compound, investigating the isothermal magnetization as a function of the applied magnetic field is necessary, along with conducting a temperature-dependent magnetization study. Isothermal magnetization (M) behavior as a function of the applied magnetic field (H) was obtained up to ±30 kOe in the temperature range 50 K to 400 K. Representative curves at different temperatures (50 K and 300 K) for Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35 are shown in Figure 4a,b, respectively. Both compounds have shown a small magnetic hysteresis below 4 kOe, and magnetization follows a saturation. This type of behavior supports the existence of the ferromagnetic state. For the Fe65Ni35 case, at 50 K, the magnetization shows complete saturation around 20 kOe, with a considerable saturation magnetization value (M = 111 emu/gm). This sample also shows weak magnetic hysteresis (Inset Figure 4a). The saturation tendency of the M-H curve, along with small hysteresis, is usually noted in the soft ferromagnetic compounds [26,29,39], while in the case of Fe65Mn35, at 50 K, the shape of the characteristic curve is modified, and a non-saturating behavior is also noted up to 26 kOe and has a slightly lower saturation magnetization value (M = 108 emu/gm). Both of these characteristics indicate the magnetic states modification in the Fe65Mn35. The literature report also confirmed the presence of the antiferromagnetic nature of γ-FeMn [27,41]. In this case, we can say that the crystallographic arrangement or phase may govern the magnetic properties of these compounds.
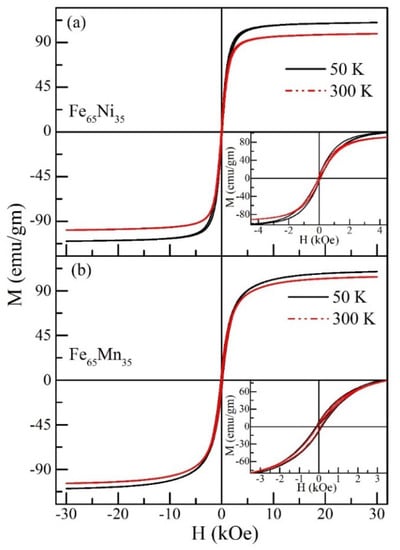
Figure 4.
Applied field response of isothermal magnetization curves at 50 K and 300 K: (a) M−H isotherms for Fe65Ni35; inset: M(H) curves expanded in the low-field region; (b) M−H isotherms for Fe65Mn35; inset: M(H) curves expanded in the low-field region.
Hence, temperature and applied magnetic field-dependent magnetization studies confirm the ferromagnetic nature of the compounds. This magnetic state may modify by the presence of different dopants or the coexistence of the various crystallographic phases.
3.3. Magnetocaloric Properties of Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35
To determine the magnetocaloric effect in these particular Fe65T35 (T = Ni and Mn) alloys, the magnetocaloric effect is derived from the virgin magnetic isotherms (M-H) in the range of 200 K to 400 K. From this procedure, the magnetocaloric effect is usually measured in terms of the change in isothermal magnetic entropy (ΔSM), produced by the change in the applied magnetic field. In the present study, we have taken each isotherm after cooling the respective compound from the maximum operating temperature (400 K) to the measured temperature. The isothermal magnetic entropy change has been computed by using the following expression [11,47]: ∆SM = Σ [(Mn − Mn+1)/(Tn+1 − Tn)] ∆Hn, where Mn and Mn+1 are the magnetization values measured at field Hn and Hn+1 at temperature Tn and Tn+1, respectively. Figure 5a,b display the temperature-dependent ∆SM curve for different applied magnetic fields (5 kOe to 30 kOe) of Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35, respectively. For Fe65Ni35, it is observed from the results that ∆SM showed a broad peak and gained the maximum value of ~−0.35 J/kg-K near 262 K for a 30 kOe applied magnetic field. However, in the case of Fe65Mn35, the value of ∆SM reduces to −0.27 J/kg-K for the same applied magnetic field near 318 K. Here, we noticed that for both the compounds, the peak temperature of ∆SM matches well with the magnetic transition temperature, as observed in temperature-dependent magnetization results. From the viewpoint of ∆SM value, we get a slightly lower value than those reported literature report [20,22,23,24]; such a lower value may arise due to the competitive nature of the magnetic state, which actually originates from the mixed crystallographic phase in these compounds. Though such a mixed phase affects the magnetocaloric parameters, it may broaden the magnetic entropy change. Therefore, such investigations could provide better insights into the fundamental magnetism of such systems.
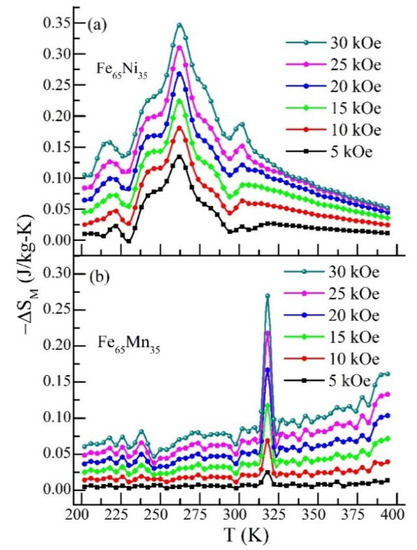
Figure 5.
Temperature response of isothermal magnetic entropy change (ΔSM) at different applied field: (a) ΔSM vs. T curve for Fe65Ni35; (b) ΔSM vs. T curve for Fe65Mn35.
Interestingly, it is noticed from the ΔSM curve’s nature that both the compounds exhibit different characteristics of the curves; such behavior is analogous to the temperature and magnetic field-dependent magnetization results, where both curves change their nature as Ni replaces the Mn in Fe65T35 alloy. Hence, it can be concluded that, in these alloys, the observed MCE is owing to the magnetic entropy variation arising from iron transition metal sub-lattice interactions along with the competition between the α and γ phase. Additionally, the ΔSM peak’s broadness indicates the magnetic transition’s second-order nature; the nature of magnetic transition investigation by ΔSM data has already been reported in the literature [7,8]. These alloys have significant MCE in a broad temperature range near room temperature. In the case of Fe65Ni35, it exhibits greater magnetization change; consequently, it has more MCE than Fe65Mn35. Additionally, this could be another possible reason that the modification of Fe-Ni exchange interactions provides more MCE value. The small magnetic hysteresis and second-order nature of such alloys have suitable properties of a magnetic refrigerant, which are helpful for practical application.
The small magnetic hysteresis and second-order nature of such alloys have suitable properties for a magnetic refrigerant which are helpful for practical application.
In the research area of magnetocaloric material, it is necessary to draw a comparison regarding the experimental results for various compounds since all magnetocaloric parameters exhibit an applied magnetic field-dependent behavior; also, these parameters vary from material to material. Therefore, the magnetic field-dependent investigation of the isothermal magnetic entropy change is necessary for the preferable comprehension of the intrinsic nature of the magnetocaloric effect [10,11,12,48,49]. The applied magnetic field response of isothermal magnetic entropy change (ΔSM) is characterized by power law behavior, i.e., (ΔSM~Hm), where m is the exponent. This exponent explains the nature of the magnetic state of the material. Here, we fit the magnetic field response of ΔSM near the maximum entropy change temperature for both compounds. Figure 6a,b represent the resulting curves of field-dependent ΔSM at peak temperature for Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35, respectively. For Fe65Ni35, it is explored that the ΔSM obeys a power law, and the obtained value of m is 0.57. Similarly, in Fe65Mn35, ΔSM furthermore observes the power law, whereas the value of m is 1.2 more elevated than those obtained in Fe65Ni35. For the antiferromagnetic correlation, the value of the exponent found was 2 [10,11], while in the case of ferromagnetic correlation it was 0.6 [49,50]. Therefore, in our case study, Fe65Ni35 compounds exhibit ferromagnetic correlations; however, Fe65Mn35 display the higher value of the exponent, confirming the antiferromagnetic correlation within the ferromagnetic correlations. Such a kind of antiferromagnetic correlation is also found in FeMn systems (earlier reported magnetization studies) [41]; additionally, the change in nature of the magnetization and ΔSM curves also support that.
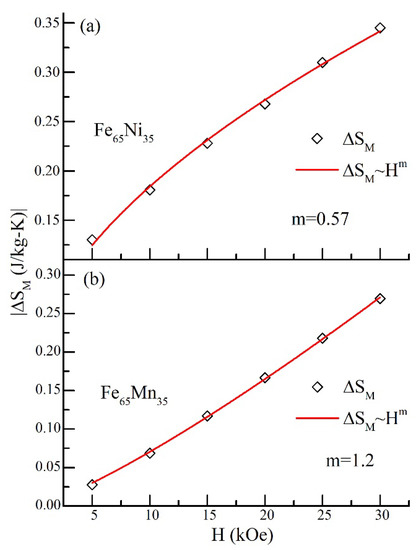
Figure 6.
Field response of isothermal magnetic entropy change (ΔSM) at maximum entropy temperature: (a) ΔSM vs. H curve for Fe65Ni35; (b) ΔSM vs. H curve for Fe65Mn35. The plot through the points is fit to the power law behavior (ΔSM~Hm).
4. Conclusions
In summary, we present a systematical investigation of the structural, magnetic, and magnetocaloric studies of ball milled as-prepared Fe65Ni35 and Fe65Mn35 alloys. Our structural investigations reveal that both alloys contain two distinct crystallographic phases: α and γ. The magnetization results confirmed the long-range ferromagnetic ordering for the Fe65Ni35 compound, in contrast to the antiferromagnetic correlations within the ferromagnetic one observed for Fe65Mn35. A broad range and large value of the magnetocaloric figures in the Fe65Ni35 compound advocate its suitability for near-room-temperature refrigeration over the Fe65Mn35 compound. The field-dependent magnetocaloric effect and power law investigations again confirmed the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic correlations. Thus, based on the above investigations, it can be said that the crystallographic phases control the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of such alloys, which are helpful from fundamental and technological points of view.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: B.-H.K. and M.K.S.; Methodology: M.K.S., A.K. and B.-H.K.; Software: M.K.S. and A.K.; Validation: B.-H.K.; Formal analysis: K.K. and M.K.S.; Investigation: M.K.S.; Resources: B.-H.K.; Data curation: S.-j.P. and N.Y.; Writing: M.K.S.; Writing—review and editing: M.K.S., A.K., K.K. and B.-H.K.; Visualization: B.-H.K. and S.-H.H.; Supervision: B.-H.K.; Project administration: B.-H.K.; Funding acquisition: B.-H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research support by National Research Foundation of Korea: (Grant Number 2021R1I1A3049533) and convergence research financial program for instructors, graduate students, and professors in 2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the experimental facilities of central lab Changwon National University Changwon Republic of Korea. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2021R1I1A3049533). This research was funded by the convergence research financial program for instructors, graduate students, and professors in 2022. M.K.S. acknowledges Mechatronics Research Institute Changwon National University, Changwon Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Tishin, A.M.; Spichkin, Y.I. The Magnetocaloric Effect and its Applications; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Magnetocaloric effect and magnetic refrigeration. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, E. Developments in magnetocaloric refrigeration. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, R381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneider, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Tsokol., A.O. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479. [Google Scholar]
- Moya, X.; Kar-Narayan, V.; Mathur, N.D. Caloric materials near ferroic phase transitions. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-W. Review of magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in the intermetallic compounds of rare earth with low boiling point metals. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 037502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubina, J. Magnetocaloric materials for energy efficient cooling. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Mukherjee, K. Evidence of large magnetic cooling power and double glass transition in Tb5Pd2. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 466, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Yadav, K.; Mukherjee, K. Complex magnetic behaviour and evidence of superspin glass state in the binary intermetallic compound Er5Pd2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2018, 30, 215803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Chandra, S.; Samanta, T.; Phan, M.H.; Das, I.; Srikanth, H. The universal behavior of inverse magnetocaloric effect in antiferromagnetic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17A902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Mukherjee, K. Magnetic and universal magnetocaloric behavior of rare-earth substituted DyFe0.5Cr0.5O3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 444, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Kaur, G.; Mukherjee, K. Nature of glassy magnetic state in magnetocaloric materials Dy5Pd2-xNix (x = 0 and 1) and universal scaling analysis of R5Pd2 (R = Tb, Dy and Er). J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xuexi Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, M.; Geng, L. Enhanced magnetocaloric efect in Ni-Mn-Sn-Co alloys with two successive magnetostructural transformations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Sarita; Babu, P.; Biswas, A.; Siruguri, V.; Krishnan, M. Giant magnetocaloric effect from reverse martensitic transformation in Ni-Mn-Ga-Cu ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 670, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.Q.; Zhuang, Y.H.; Li, J.Q.; Zhou, K.W. Magnetic phase transition and magnetocaloric effect in (Gd1−xTbx)5Si1.72Ge2.28 compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 428, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quetz, A.; Koshkid’Ko, Y.S.; Titov, I.; Rodionov, I.; Pandey, S.; Aryal, A.; Ibarra-Gaytan, P.J.; Prudnikov, V.; Granovsky, A.; Dubenko, I.; et al. Giant reversible inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni50Mn35In15 Heusler alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 683, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, N.H.; Duc, N.H.; Yen, N.H.; Thanh, P.T.; Bau, L.V.; An, N.M.; Anh, D.T.K.; Bang, N.A.; Mai, N.T.; Anh, P.K.; et al. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in Ni-Mn-Sn alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, R.Y.; Kusakari, Y.; Kanomata, T.; Suga, K.; Sawai, Y.; Kindo, K.; Oikawa, K.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Metamagnetic behaviour under high magnetic fields in Ni50Mn50−xInx (x=14.0 and 15.6) shape memory alloys. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 075003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Chen, X.; Ramanujan, R.V. Iron and manganese based magnetocaloric materials for near room temperature thermal management. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 100, 64–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Ramanujan, R.V. Magnetic and structural properties of high relative cooling power (Fe70Ni30)92Mn8 magnetocaloric nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 305003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Ramanujan, R.V. High Relative Cooling Power in a Multiphase Magnetocaloric FeNiB Alloy. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2015, 6, 6700104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, H.; Craven, M.; Laughlin, D.E.; McHenry, M.E. Effect of Mo addition on structure and magnetocaloric effect in γ-FeNi nanocrystals. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, H.; Ipus, J.J.; Laughlin, D.E.; McHenry, M.E. Tuning the Curie temperature in gamma-FeNi nanoparticles for magnetocaloric applications by controlling the oxidation kinetics. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17A918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Ramanujan, R.V. Magnetocaloric Properties of Fe-Ni-Cr Nanoparticles for Active Cooling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlar, K.; Tekgul, A.; Küçük, N.; Etemoğlu, A.B. Structural and magnetocaloric properties of FeNi high entropy alloys. Phys. Scr. 2021, 96, 125847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Bhagat, S.M.; Bagazeev, A.V.; Medvedev, A.I.; Ballesteros, A.; Beketov, I.V.; Safronov, A.P. Structure, magnetic and microwave properties of FeNi invar nanoparticles obtained by electrical explosion of wire in different preparation conditions. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2016, 98, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduani, C.; Krause, J.C. Local magnetic properties of γ-Fe-Mn alloys. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Kumar, A.; Shin, M.; Kumar, S.; Huh, S.H.; Koo, B.H. Investigating the magnetocrystalline anisotropy and the exchange bias through interface efects of nanocrystalline FeCo. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2021, 79, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Kumar, A.; Koo., B.H. Investigating the origin of exchange bias efect in ferromagnetic FeNi nanoparticles prepared via controlled synthesis. Appl. Nanosci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisari, K.; Oh, J.T.; Javapour, S. The effect of heat treatment on the structure and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed Fe—45%Ni nanostructured powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.Q.; Chan, K.C.; Xia, L.; Yu, P. Magneto-caloric effect of FexZryB100−x−y metallic ribbons for room temperature magnetic refrigeration. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 423, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, F.; Lucassont, A.; Lucasson, P.; Loreaux, Y.; Moserg, P. Interstitial mobility in FeNi, FeCo, and FeMn dilute alloys. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1986, 16, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vas’kovskiy, V.O.; Lepalovskij, V.N.; Gor’kovenko, A.N.; Kulesh, N.A.; Savin, P.A.; Svalov, A.V.; Stepanova, E.A.; Shchegoleva, N.N.; Yuvchenko, A.A. Fe20Ni80/Fe50Mn50 Film Magnetoresistive Medium. Tech. Phys. 2015, 60, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gor’kovenko, A.N.; Lepalovskij, V.N.; Savin, P.A.; Vas’kovskiy, V.O. Effect of Technological Conditions on the Magnetic and Magnetoresistive Properties of Fe20Ni80/Fe50Mn50 Films. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2014, 78, 925–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, F.; Han, W.; Du, Y.; Hua, K.; Wang, H. Effect of Al addition on the microstructure, mechanical and wear properties of TiZrNbHf refractory high entropy alloys. Tribol. Int. 2021, 160, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.B.; Fultz, B. Two-phase coexistence in Fe–Ni alloys synthesized by ball milling. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 3946–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Repaka, D.V.M.; Chaudhary, V.; Ramanujan, R.V. Enhanced magnetocaloric properties and critical behavior of (Fe0.72Cr0.28)3 Al alloys for near room temperature cooling. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 145001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bla´zquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Moreno-Ramirez, L.M.; Alvarez-Gomez, J.M.; Sanchez-Jimenez, D.; Lozano-Perez, S.; Franco, V.; Conde, A. Ball milling as a way to produce magnetic and magnetocaloric materials: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11834–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhrt, C.; Schultz, L. Phase formation and martensitic transformation in mechanically alloyed nanocrystalline Fe-Ni. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Bassett, W.A.; Weathers, M.S. Phase Diagram and Elastic Properties of Fe 30% Ni alloy by synchrotron radiation. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 4497–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, Y.; Ishikawa, Y. Antiferromagnetism of γ iron manganese alloy. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1971, 30, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumari, K.; Sharma, M.K.; Vij, A.; Kumar, S.; Huh, S.H.; Koo, B.H. Chemically inducing room temperature spin-crossover in double layered magnetic refrigerants Pr1.4+xSr1.6-xMn2O7 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5). J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzendruber, L.J.; Itkin, V.P.; Alcock, C.B. The Fe-Ni (Iron-Nickel) system. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 1991, 12, 288–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, J.; Lilova, K.; Vassilev, G. Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-B-X Systems. Part 3: Fe-B-Mn. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, J.; Lilova, K.; Vassilev, G. Thermodynamic description of ternary Fe-B-X systems. Part 2: Fe-B-Ni. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witusiewicz, V.T.; Sommer, F.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Reevaluation of the Fe-Mn Phase Diagram. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2004, 25, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Földeàki, M.; Chahine, R.; Bose, T.K. Magnetic measurements: A powerful tool in magnetic refrigerator design. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Singh, K.; Mukherjee, K. Exchange bias in a mixed metal oxide based magnetocaloric compound YFe0.5Cr0.5O3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 414, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’NASSRI, R. Magnetocaloric effect and its implementation in critical behaviour study of La0.67Ca0.33Mn0.9Fe0.1O3. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Blazquez, J.S.; Conde, A. Field dependence of the magnetocaloric effect in materials with a second order phase transition: A master curve for the magnetic entropy change. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 222512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).