Fluid Dynamics in a Continuous Pump-Mixer
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Pump-Mixer Geometry
2.3. Chemical System
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis and Modelling
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Results
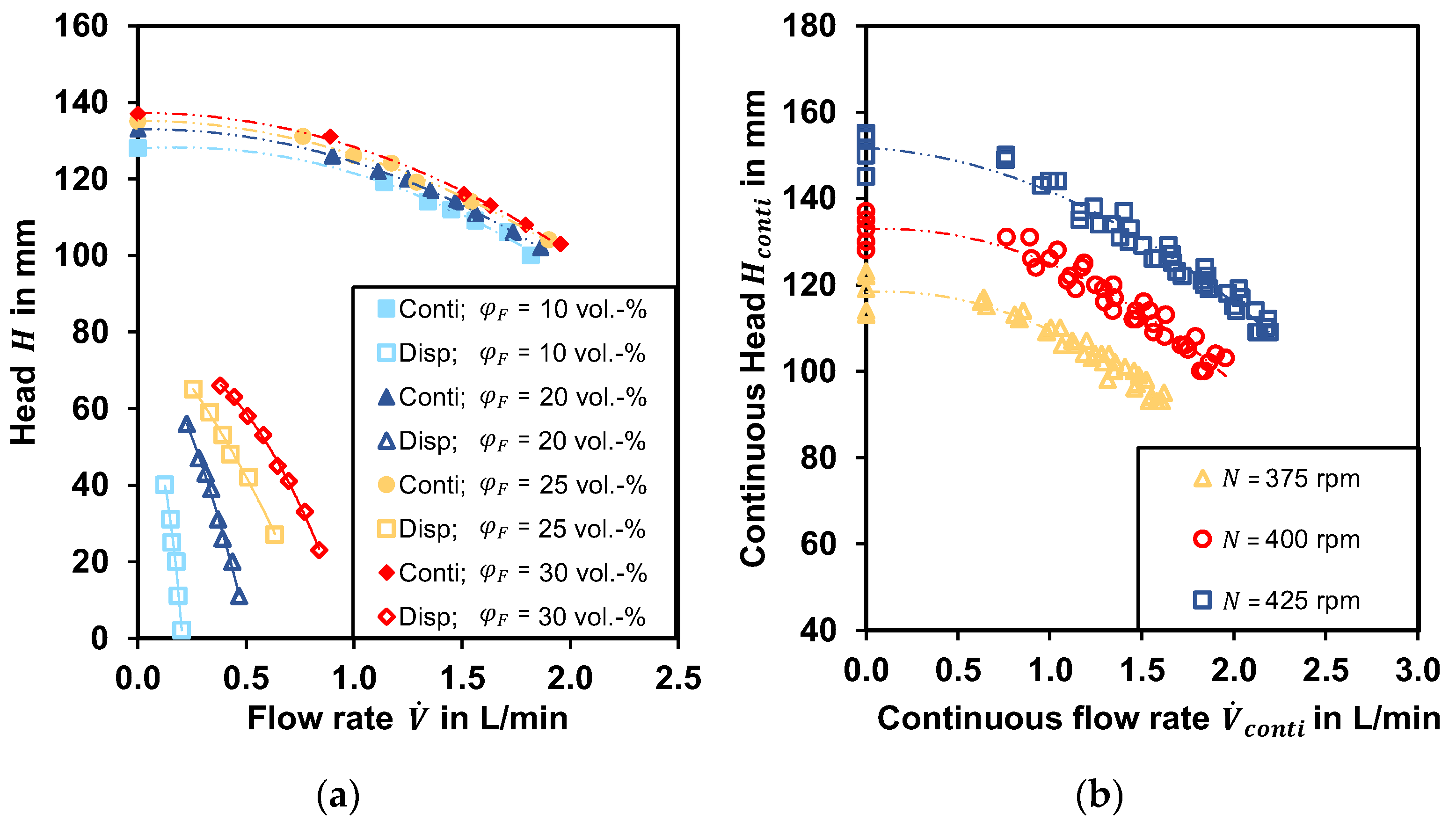
3.1.1. Pumping Behavior
3.1.2. DSD at Different Measurement Positions
3.1.3. Influences on Local Holdup
3.1.4. Effects of the Process Parameters on the DSD
3.2. Modelling
Parameter Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon, J.J.; Zeigler, J.H. Apparatus for Extracting. U.S. Patent Nr. 2,176,899, 24 October 1934. Serial No. 751,843, 7 filed November 1934 and granted 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, J.C. (Ed.) Liquid-Liquid Extraction Equipment; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.K.; Shenoy, K.T.; Mahendra, A.K.; Ghosh, S.K. Artificial neural network based modelling of head and power characteristics of pump-mixer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Mahajani, S.M.; Shenoy, K.T.; Patwardhan, A.W.; Ghosh, S.K. CFD modeling of pilot-scale pump-mixer: Single-phase head and power characteristics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Mahajani, S.M.; Shenoy, K.T.; Ghosh, S.K. CFD modeling of pump-mix action in continuous flow stirred tank. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Mahajani, S.M.; Shenoy, K.T.; Ghosh, S.K. Representative drop sizes and drop size distributions in A/O dispersions in continuous flow stirred tank. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 90, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srilatha, C.; Savant, A.R.; Patwardhan, A.W.; Ghosh, S.K. Head–flow characteristics of pump-mix mixers. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2008, 47, 1678–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srilatha, C.; Morab, V.V.; Mundada, T.P.; Patwardhan, A.W. Relation between hydrodynamics and drop size distributions in pump–mix mixer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 3409–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srilatha, C.; Mundada, T.P.; Patwardhan, A.W. Scale-up of pump-mix mixers using CFD. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2010, 88, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabib, M.; Lane, G.; Yang, W.; Schwarz, M.P. CFD Simulation of a Solvent Extraction Pump Mixer Unit: Evaluating Large Eddy Simulation RANSBased Models. J. Comput. Multiph. Flows 2010, 2, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabib, M.V.; Lane, G.; Yang, W.; Schwarz, M.P. CFD study of single phase and multiphase (liquid–liquid) pump-mixer: Analyzing design parameters, flow structures and turbulence. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 80, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, X.; Jing, S.; Zhou, H.; Lan, W.; Li, S. Measurement of droplet breakage in a pump-mixer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 195, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, J.; Jing, S.; Lan, W.; Zheng, Q.; Li, S. Influence of Dispersed-Phase Viscosity on Droplet Breakup in a Continuous Pump-Mixer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 23458–23467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, B.; Jing, S.; Lan, W.; Li, S. CFD–PBM Simulation of Liquid–Liquid Dispersions in a Pump-Mixer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1926–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ye, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. A study on liquid-liquid dispersions in a continuous mixer via computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation combined with population balance model (PBM). Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 87, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. An experimental study of immiscible liquid–liquid dispersions in a pump–mixer of mixer–settler. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A. The Local Structure of Turbulence in Incompressible Viscous Fluid for Very Large Reynolds’ Numbers. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1941, 30, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Hinze, J.O. Fundamentals of the hydrodynamic mechanism of splitting in dispersion processes. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, C.W.; Hamza, H.A. Predicting the sizes of toluene-diluted heavy oil emulsions in turbulent flow Part 2: Hinze–Kolmogorov based model adapted for increased oil fractions and energy dissipation in a stirred tank. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 7325–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cull, S.G.; Lovick, J.W.; Lye, G.J.; Angeli, P. Scale-down studies on the hydrodynamics of two-liquid phase biocatalytic reactors. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 25, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zerfa, M.; Brooks, B.W. Prediction of vinyl chloride drop sizes in stabilised liquid-liquid agitated dispersion. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 3223–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirz, D.; Friebel, A.; Rave, K.; Hermes, M.; Skoda, R.; Harbou Ev Bart, H.-J. Experimental Investigation and Modelling of the Droplet Size in a DN300 Stirred Vessel at High Disperse Phase Content Using a Telecentric Shadowgraphic Probe. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraume, M. Transportvorgänge in der Verfahrenstechnik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zlokarnik, M. Stirring: Theory and Practice; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany; Chichester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Doulah, M.S. An effect of hold-up on drop sizes in liquid-liquid dispersions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1975, 14, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäbler, A.; Wegener, M.; Paschedag, A.R.; Kraume, M. The effect of pH on experimental and simulation results of transient drop size distributions in stirred liquid–liquid dispersions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 3018–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, J.; Schmitt, P.; Hlawitschka, M.W.; Bart, H.-J. Measuring Particle Size Distributions in Multiphase Flows Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2019, 83, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rave, K.; Lehmenkühler, M.; Wirz, D.; Bart, H.-J.; Skoda, R. 3D flow simulation of a baffled stirred tank for an assessment of geometry simplifications and a scale-adaptive turbulence model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 231, 116262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rave, K.; Hermes, M.; Wirz, D.; Hundshagen, M.; Friebel, A.; Harbou Ev Bart, H.-J.; Skoda, R. Experiments and fully transient coupled CFD-PBM 3D flow simulations of disperse liquid-liquid flow in a baffled stirred tank. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 120, 117518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickler, M.; Bart, H.-J. Optical Multimode Online Probe: Erfassung und Analyse von Partikelkollektiven. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2013, 85, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirz, D.; Bart, H.-J. Advances in particle size analysis with transmitted light techniques. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 52, 554–560. [Google Scholar]
- Wirz, D.; Hofmann, M.; Lorenz, H.; Bart, H.-J.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A.; Temmel, E. A Novel Shadowgraphic Inline Measurement Technique for Image-Based Crystal Size Distribution Analysis. Crystals 2020, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichti, M.; Bart, H.-J. Bubble size distributions with a shadowgraphic optical probe. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2018, 60, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villwock, J.; Gebauer, F.; Kamp, J.; Bart, H.-J.; Kraume, M. Systematic Analysis of Single Droplet Coalescence. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, F. Fundamentals of Binary Droplet Coalescence in Liquid-Liquid Systems, Dissertation. Technical University of Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Montante, G.; Brucato, A.; Lee, K.C.; Yianneskis, M. An experimental study of double-to-single-loop transition in stirred vessels. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1999, 77, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montante, G.; Lee, K.C.; Brucato, A.; Yianneskis, M. Numerical simulations of the dependency of flow pattern on impeller clearance in stirred vessels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 3751–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Measurement Position | Measurement Height | in mm | Measurement Radius | in mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 195.0 | 75.0 | |||
| 332.5 | 290.0 | |||
| 59.0 | 115.0 | |||
| 240.0 | 75.0 |
| Substance | in kg/m3 | in mm2/s | Interfacial Surface Tension |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wer + Na2SO4 (50 mmol/L) | 1000 | 1.0 | - |
| Paraffin oil FC 2006 | 825 | 13.1 | 37 |
| Impeller Speed in rpm | Constants | Confidence Intervals (95 %) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in s·m−3 | in s·m−3 | in s·m−3 | in s·m−3 | |||||
| 375 | 0.072 | 1434 | 2.4 | –10,390 | 0.04048 to 0.1044 | 199.3 to 2668 | 0.436 to 4.369 | –81,550 to 60,770 |
| 400 | 0.089 | 1202 | 1.9 | –8408 | 0.07799 to 0.09957 | 844.4 to 1559 | 1.369 to 2.424 | –24,660 to 7848 |
| 425 | 0.069 | 1256 | 5.0 | –48,970 | 0.05464 to 0.08277 | 870.7 to 1641 | 3.916 to 6.157 | –76,170 to –21,770 |
| Mean value | in s·m−3 | in s·m−3 | ||||||
| 0.077 | 1297 | 3.1 | –22,589 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wirz, D.; Gründken, S.; Friebel, A.; Rave, K.; Hermes, M.; Skoda, R.; von Harbou, E.; Bart, H.-J. Fluid Dynamics in a Continuous Pump-Mixer. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8195. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168195
Wirz D, Gründken S, Friebel A, Rave K, Hermes M, Skoda R, von Harbou E, Bart H-J. Fluid Dynamics in a Continuous Pump-Mixer. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(16):8195. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168195
Chicago/Turabian StyleWirz, Dominic, Simon Gründken, Anne Friebel, Kevin Rave, Mario Hermes, Romuald Skoda, Erik von Harbou, and Hans-Jörg Bart. 2022. "Fluid Dynamics in a Continuous Pump-Mixer" Applied Sciences 12, no. 16: 8195. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168195
APA StyleWirz, D., Gründken, S., Friebel, A., Rave, K., Hermes, M., Skoda, R., von Harbou, E., & Bart, H.-J. (2022). Fluid Dynamics in a Continuous Pump-Mixer. Applied Sciences, 12(16), 8195. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168195






