ACA-Net: An Adaptive Convolution and Anchor Network for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Detection Approaches
2.2. Deep-Learning-Based Detection Approaches
2.3. Feature Fusion
2.4. Convolutional Neural Networks
2.5. Anchor Boxes
3. Materials and Methods
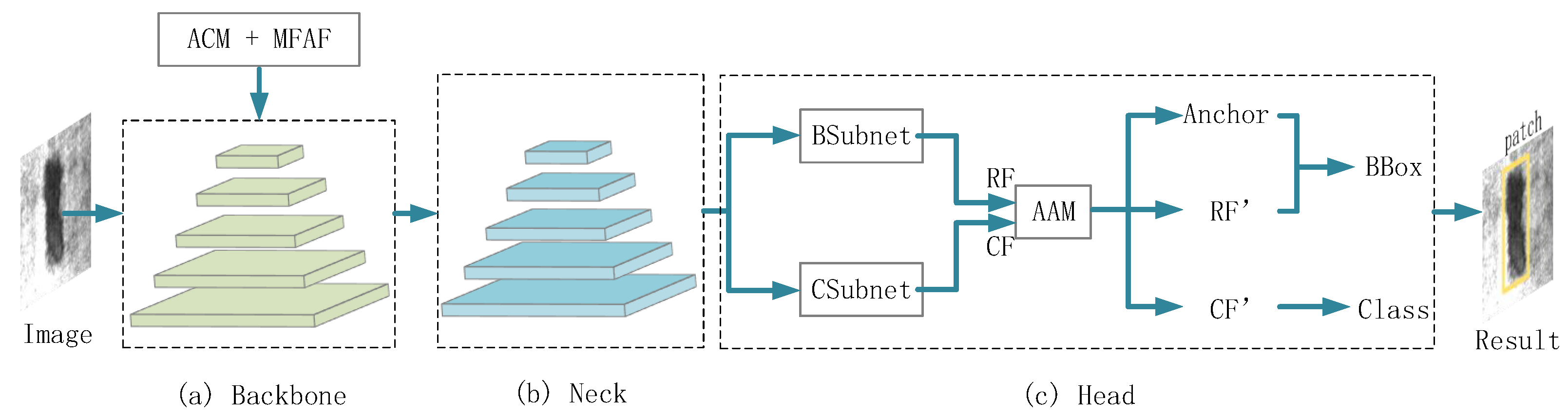
3.1. Overall Network Architecture
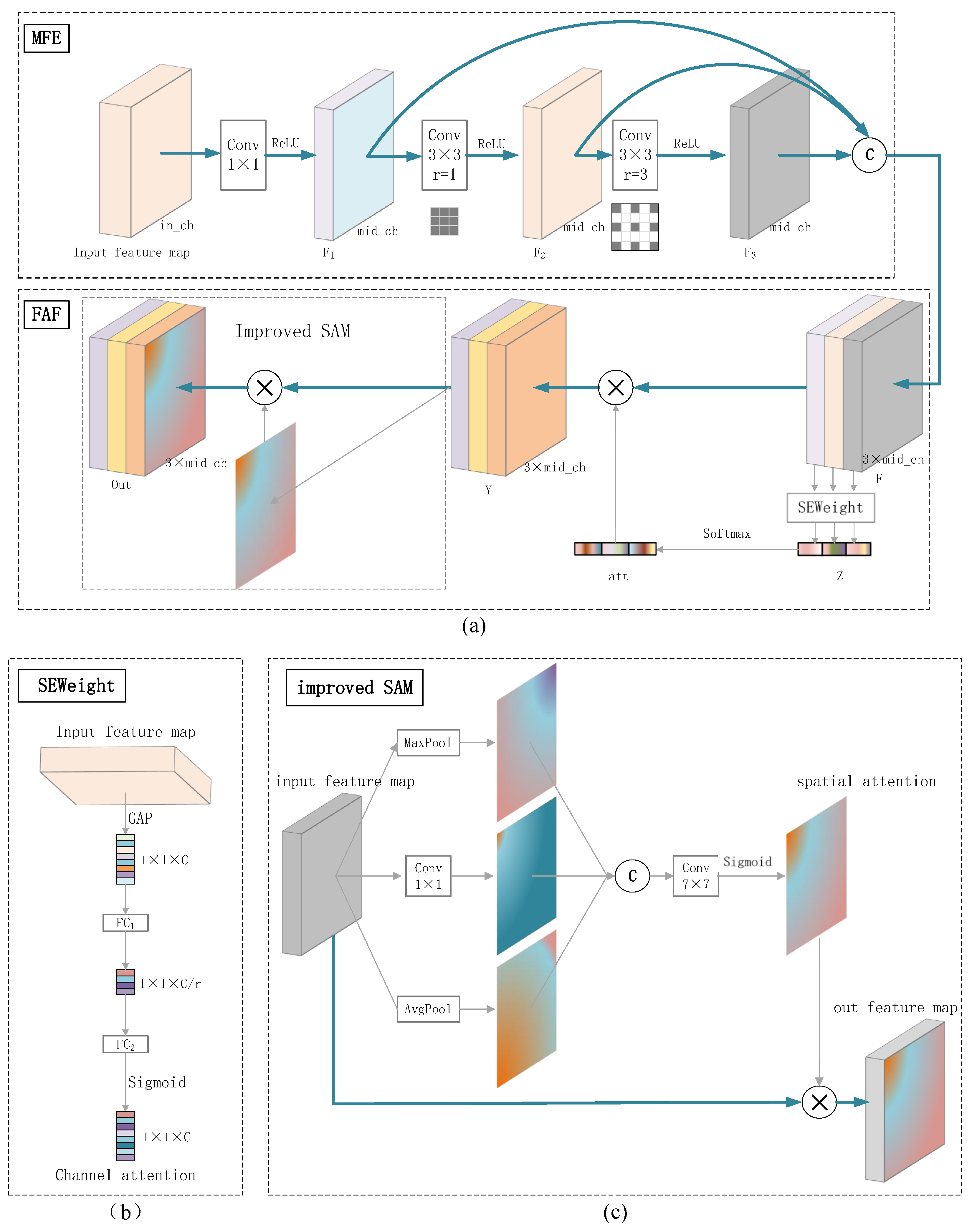
3.2. Multi-Scale Feature Adaptive Fusion
3.3. Adaptive Convolution Module
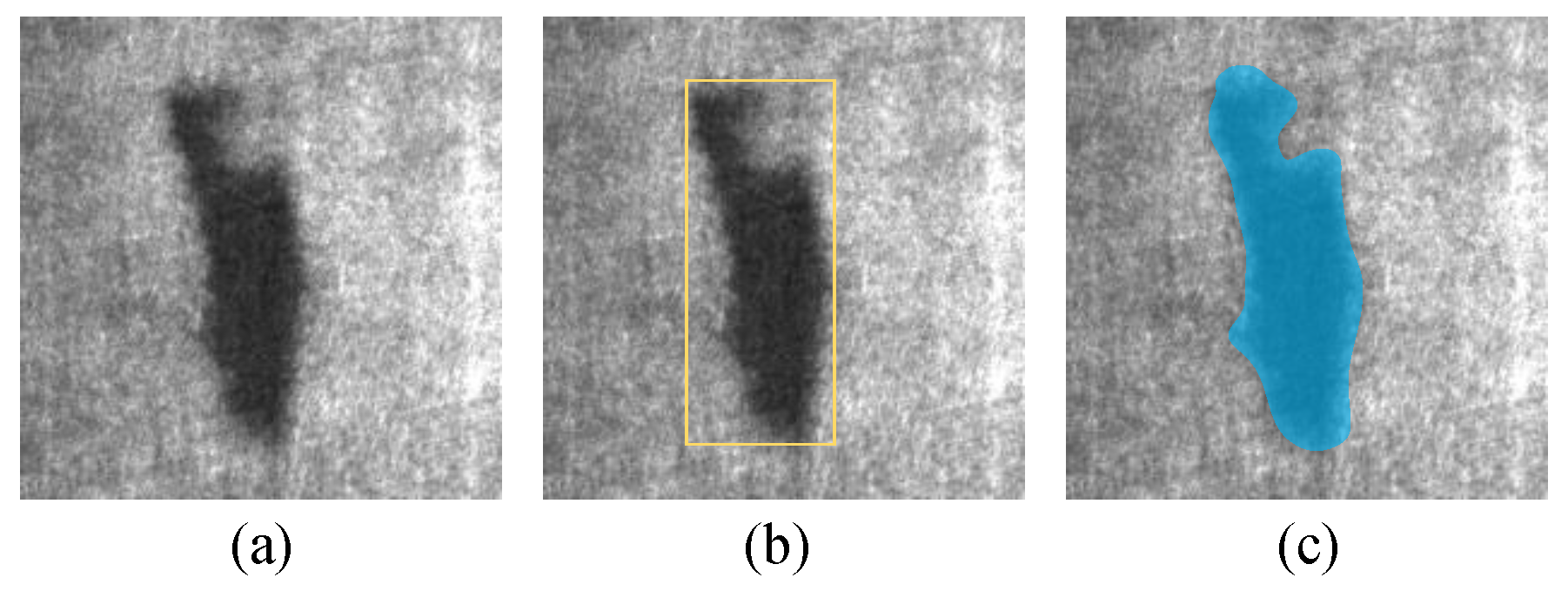
3.4. Adaptive Anchor Module
3.5. Dataset
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Ablation Studies
4.3. Comparsion
4.4. Additional Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | convolutional neural networks |
| ACA-Net | adaptive convolution and anchor network |
| ACA | adaptive convolution and anchor |
| ACM | adaptive convolution module |
| MFAF | multi-scale feature adaptive fusion |
| AAM | adaptive anchor module |
| NEU-DET | Northeastern University Detection |
| AP | Average Precision |
| DC | Deformable convolutional |
| DCN | Deformable convolutional networks |
| SOTA | state-of-the-art |
| GA | Guided Anchoring |
| SIFT | scale-invariant feature transform |
| HOG | histogram of oriented gradient |
| SVM | support vector machines |
| LBP | local binary pattern |
| FPN | feature pyramid network |
| YOLO | you only look once |
| SSD | Single Shot MultiBox Detector |
| SPP | Spatial pyramid pooling |
| RFB | Receptive Fields Block |
| PHA | Hybrid Pooling-Atrous |
| PSA | Pyramid Split Attention |
| VGG | Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition |
| ResNet | Residual Network |
| CF | classification features |
| RF | regression features |
| BBox | bounding boxes |
| MFE | multi-scale feature extract |
| FAF | feature adaptive fusion |
| SGD | Stochastic gradient descent |
| COCO | Microsoft coco |
References
- Marr, D. Vision: A Computational Investigation into the Human Representation and Processing of Visual Information; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Song, K.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Yan, Y.; Meng, Q. PGA-Net: Pyramid feature fusion and global context attention network for automated surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 7448–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ye, H.; Zhan, B.; Huang, X. An efficient network for surface defect detection. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zheng, H.; Guo, Z.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Z. SDD-CNN: Small data-driven convolution neural networks for subtle roller defect inspection. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhou, B.; Li, C.; Tian, L. Research progress of automated visual surface defect detection for industrial metal planar materials. Sensors 2020, 20, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Sahoo, D.; Hoi, S.C. Recent advances in deep learning for object detection. Neurocomputing 2020, 396, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, Y.; Santhi, N.; Ramasamy, N.; Ramar, K. Localization and segmentation of metal cracks using deep learning. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutschl, E.; Gasser, C.; Niel, A.; Werschonig, J. Defect detection on rail surfaces by a vision based system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Parma, Italy, 14–17 June 2004; pp. 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Ngan, H.Y.; Pang, G.K.; Yung, S.P.; Ng, M.K. Wavelet based methods on patterned fabric defect detection. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Liu, G.; Fan, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z. YOT-Net: YOLOv3 Combined Triplet Loss Network for Copper Elbow Surface Defect Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yu, J. RetinaNet with difference channel attention and adaptively spatial feature fusion for steel surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, F. Study on Surface Defect Detection of Metal Sheet and Strip using Faster R-CNN with Multilevel Feature. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2021, 2, 262–269. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, T.; Huang, N.; Zhang, D.; Han, J. Revisiting feature fusion for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 1804–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zu, K.; Lu, J.; Zou, Y.; Meng, D. EPSANet: An Efficient Pyramid Squeeze Attention Block on Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.14447. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Yang, S.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D. Region proposal by guided anchoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2965–2974. [Google Scholar]
- Paz, D.; Zhang, H.; Christensen, H.I. Tridentnet: A conditional generative model for dynamic trajectory generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems, Singapore, 22–25 June 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 403–416. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Jia, L.; Li, Y. Railway track fastener defect detection based on image processing and deep learning techniques: A comparative study. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 80, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resendiz, E.; Hart, J.M.; Ahuja, N. Automated visual inspection of railroad tracks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 14, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Gangadaran, M.; Dutta, P.K. Automatic defect detection on hot-rolled flat steel products. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 62, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Yan, Y. A noise robust method based on completed local binary patterns for hot-rolled steel strip surface defects. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 285, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Gong, R.; Gao, S.; Zhao, J. Steel surface defects recognition based on multi-type statistical features and enhanced twin support vector machine. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 171, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Yuan, X.; Li, L.; Sun, B. Distributed defect recognition on steel surfaces using an improved random forest algorithm with optimal multi-feature-set fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 16741–16770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (NIPS 2015), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognitio, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE international Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Xie, Q.; Yao, L.; Chen, Q. Research on a surface defect detection algorithm based on MobileNet-SSD. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhang, D.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, D. Automatic metallic surface defect detection and recognition with convolutional neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wei, D.; Suo, D.; Jia, L.; Li, Y. Multi-target defect identification for railway track line based on image processing and improved YOLOv3 model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 61973–61988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 60, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Li, G.; Jiang, M. An end-to-end steel strip surface defects recognition system based on convolutional neural networks. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1600068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J. MMDetection: Open mmlab detection toolbox and benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Sun, J. You only look one-level feature. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13039–13048. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- AI Studio. Available online: https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/index (accessed on 2 August 2022).




| Alias | IoU | Area | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.50–0.95 | all | at IoU thresholds from 0.50 to 0.95 | |
| 0.50 | all | at 0.50 IoU threshold | |
| 0.75 | all | at 0.75 IoU threshold | |
| 0.50–0.95 | small | for small objects: | |
| 0.50–0.95 | medium | for medium objects: | |
| 0.50–0.95 | large | for large objects: |
| ACM | MFAF | AAM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.355 | 0.728 | 0.290 | 0.231 | 0.283 | 0.437 | |||
| ✓ | 0.361 | 0.736 | 0.311 | 0.272 | 0.293 | 0.431 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.366 | 0.732 | 0.324 | 0.291 | 0.295 | 0.452 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.373 | 0.746 | 0.332 | 0.306 | 0.302 | 0.440 |
| Method | Backbone | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| one- stage | YOLOv3 [42] | Darknet-53 | 0.284 | 0.661 | 0.209 | 0.337 | 0.238 | 0.270 | 18.8 |
| YOLOF [49] | ResNet-50 | 0.330 | 0.675 | 0.265 | 0.303 | 0.277 | 0.372 | 18.6 | |
| YOLOX-l [50] | CSPDarknet | 0.373 | 0.726 | 0.326 | 0.330 | 0.309 | 0.456 | 16.6 | |
| SSD [37] | VGG-16 | 0.319 | 0.692 | 0.237 | 0.200 | 0.266 | 0.395 | 18.1 | |
| GA-RetinaNet [25] | ResNet-50 | 0.355 | 0.728 | 0.290 | 0.231 | 0.283 | 0.437 | 8.6 | |
| ACA-Net (ours) | ResNet-50 | 0.373 | 0.746 | 0.332 | 0.306 | 0.302 | 0.440 | 7.6 | |
| two- stage | TridentNet [26] | ResNet-50 | 0.401 | 0.753 | 0.390 | 0.371 | 0.337 | 0.474 | 4.9 |
| Faster R-CNN [35] | ResNet-50 | 0.383 | 0.731 | 0.370 | 0.289 | 0.320 | 0.459 | 10.6 | |
| GA-Faster R-CNN [25] | ResNet-50 | 0.391 | 0.756 | 0.370 | 0.343 | 0.325 | 0.465 | 7.5 | |
| ACA-Faster R-CNN (ours) | ResNet-50 | 0.403 | 0.764 | 0.380 | 0.440 | 0.336 | 0.461 | 6.0 |
| Method | Backbone | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-RetinaNet [25] | ResNet-50 | 0.281 | 0.589 | 0.257 | 0.050 | 0.172 | 0.267 | 6.1 |
| ACA-Net (ours) | ResNet-50 | 0.293 | 0.605 | 0.268 | 0.100 | 0.190 | 0.272 | 5.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, F.; Deng, M.; Gao, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D. ACA-Net: An Adaptive Convolution and Anchor Network for Metallic Surface Defect Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8070. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168070
Chen F, Deng M, Gao H, Yang X, Zhang D. ACA-Net: An Adaptive Convolution and Anchor Network for Metallic Surface Defect Detection. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(16):8070. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168070
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Faquan, Miaolei Deng, Hui Gao, Xiaoya Yang, and Dexian Zhang. 2022. "ACA-Net: An Adaptive Convolution and Anchor Network for Metallic Surface Defect Detection" Applied Sciences 12, no. 16: 8070. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168070
APA StyleChen, F., Deng, M., Gao, H., Yang, X., & Zhang, D. (2022). ACA-Net: An Adaptive Convolution and Anchor Network for Metallic Surface Defect Detection. Applied Sciences, 12(16), 8070. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168070





