UHT Milk Characterization by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
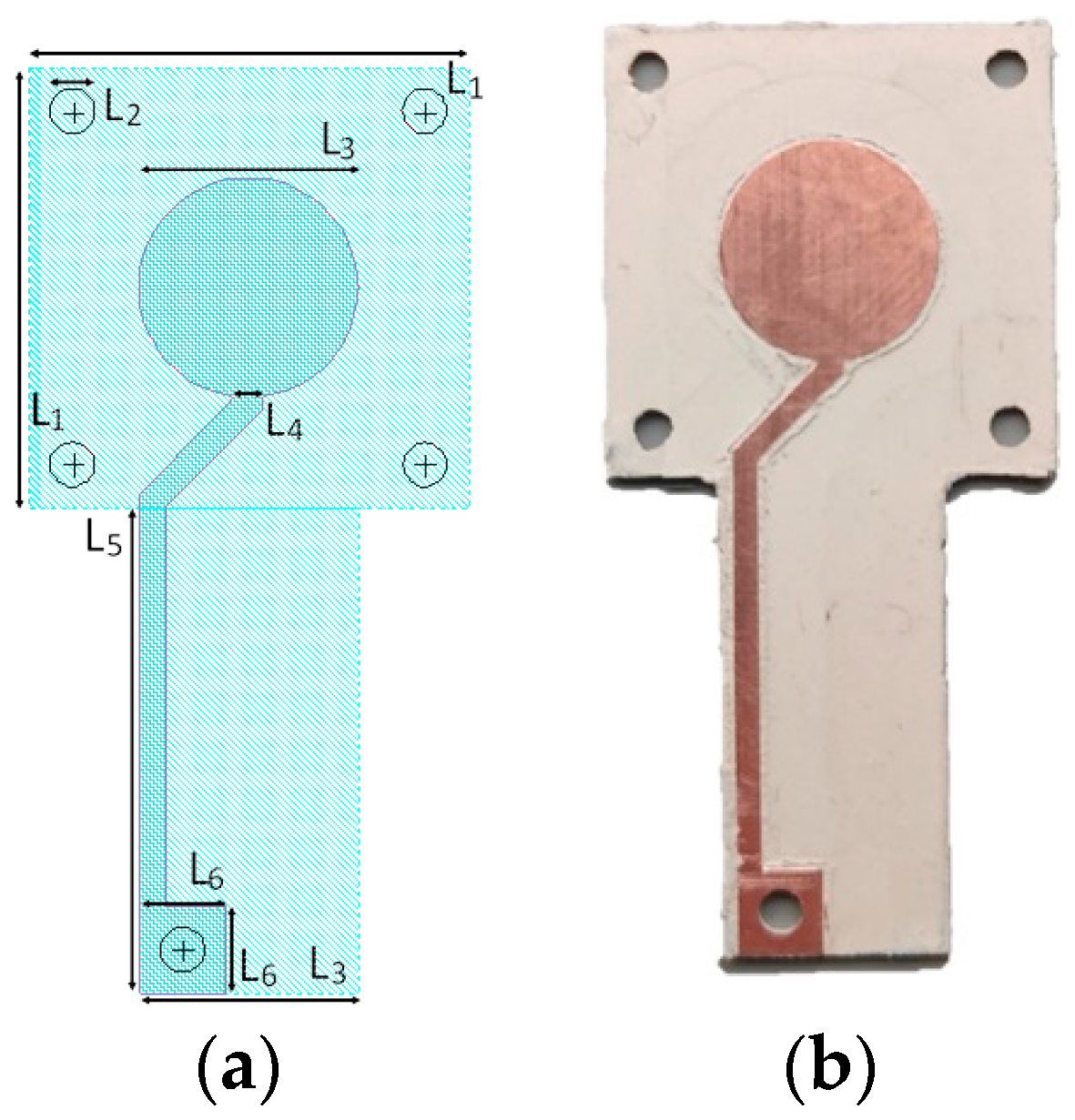
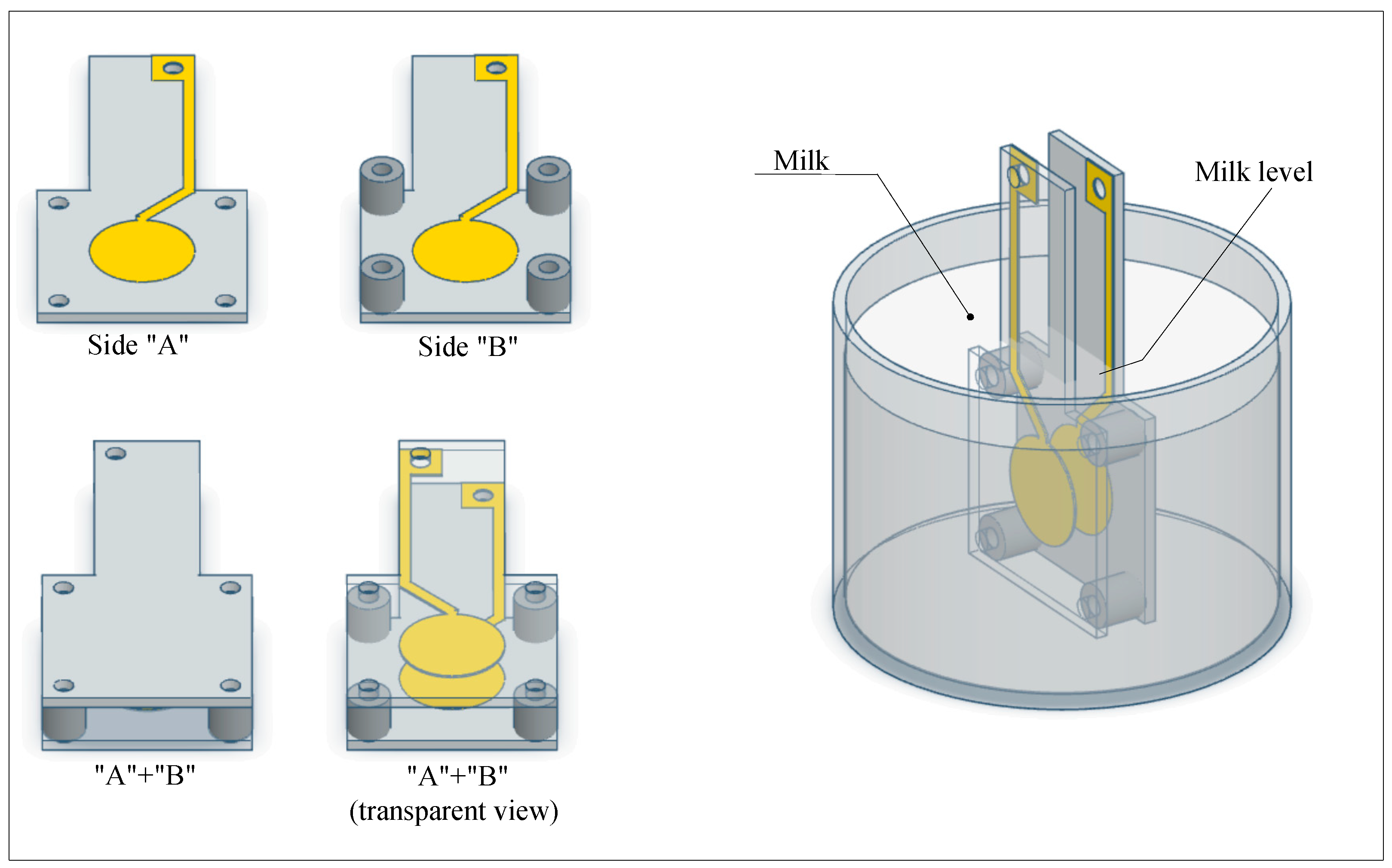
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
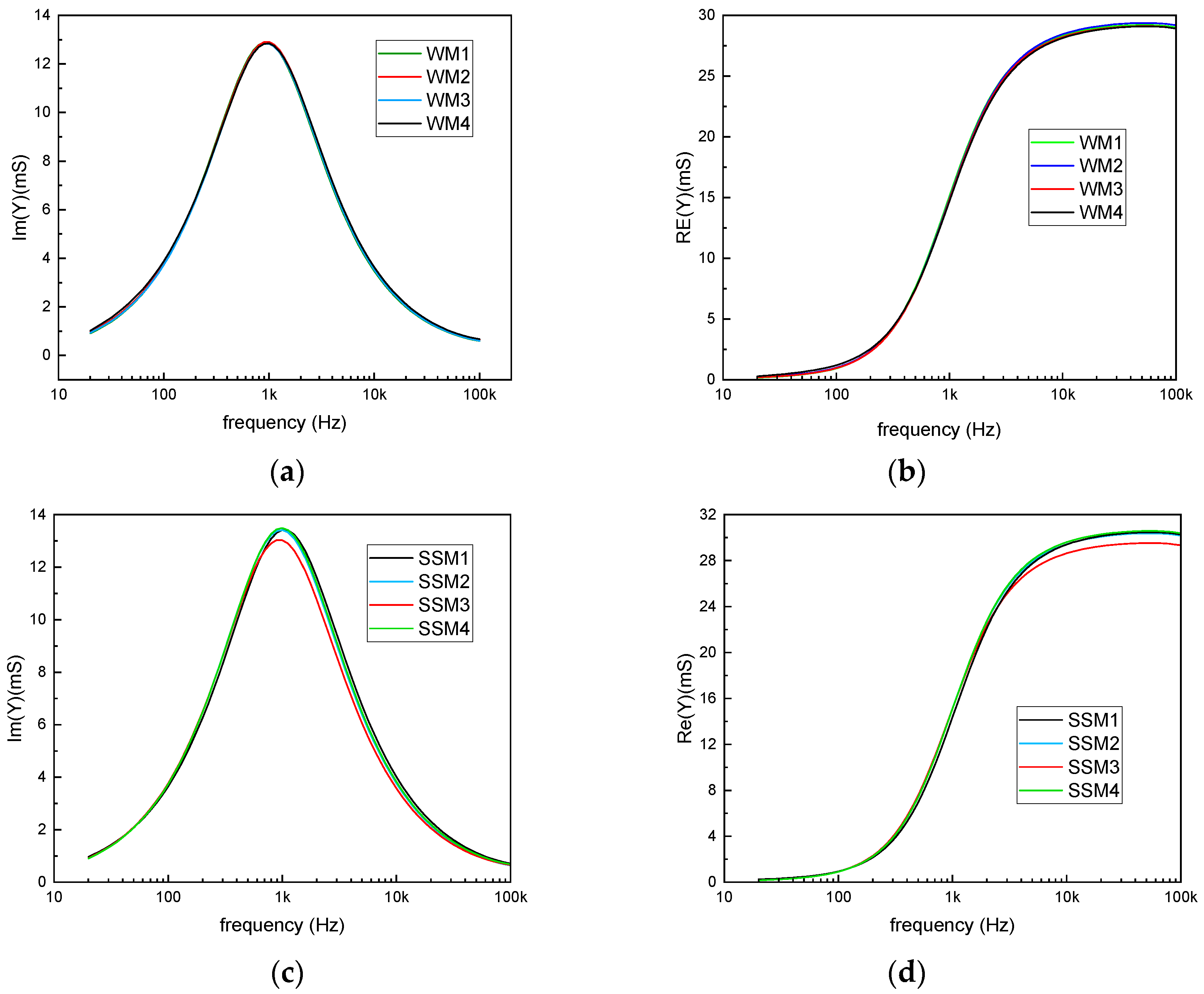
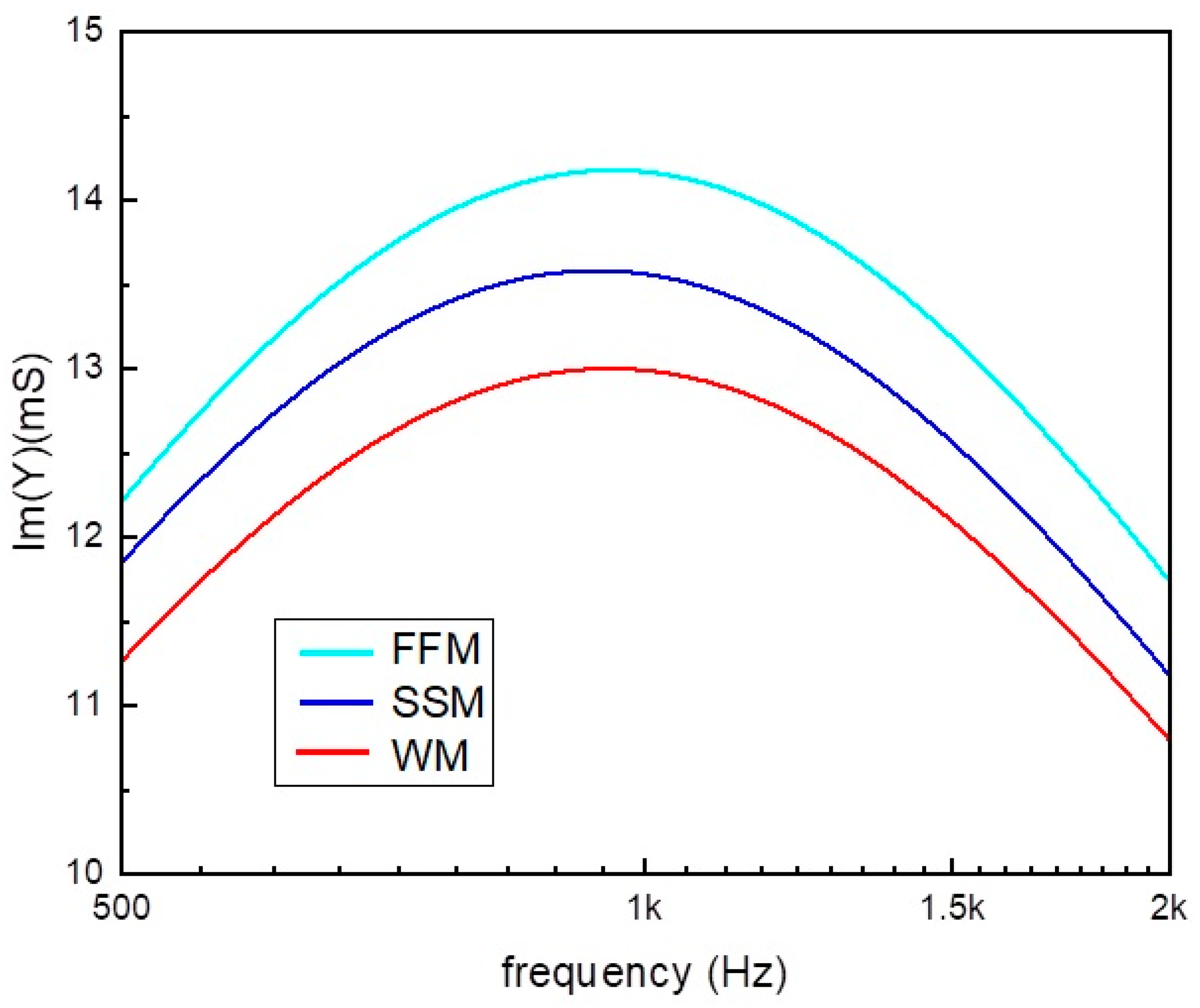
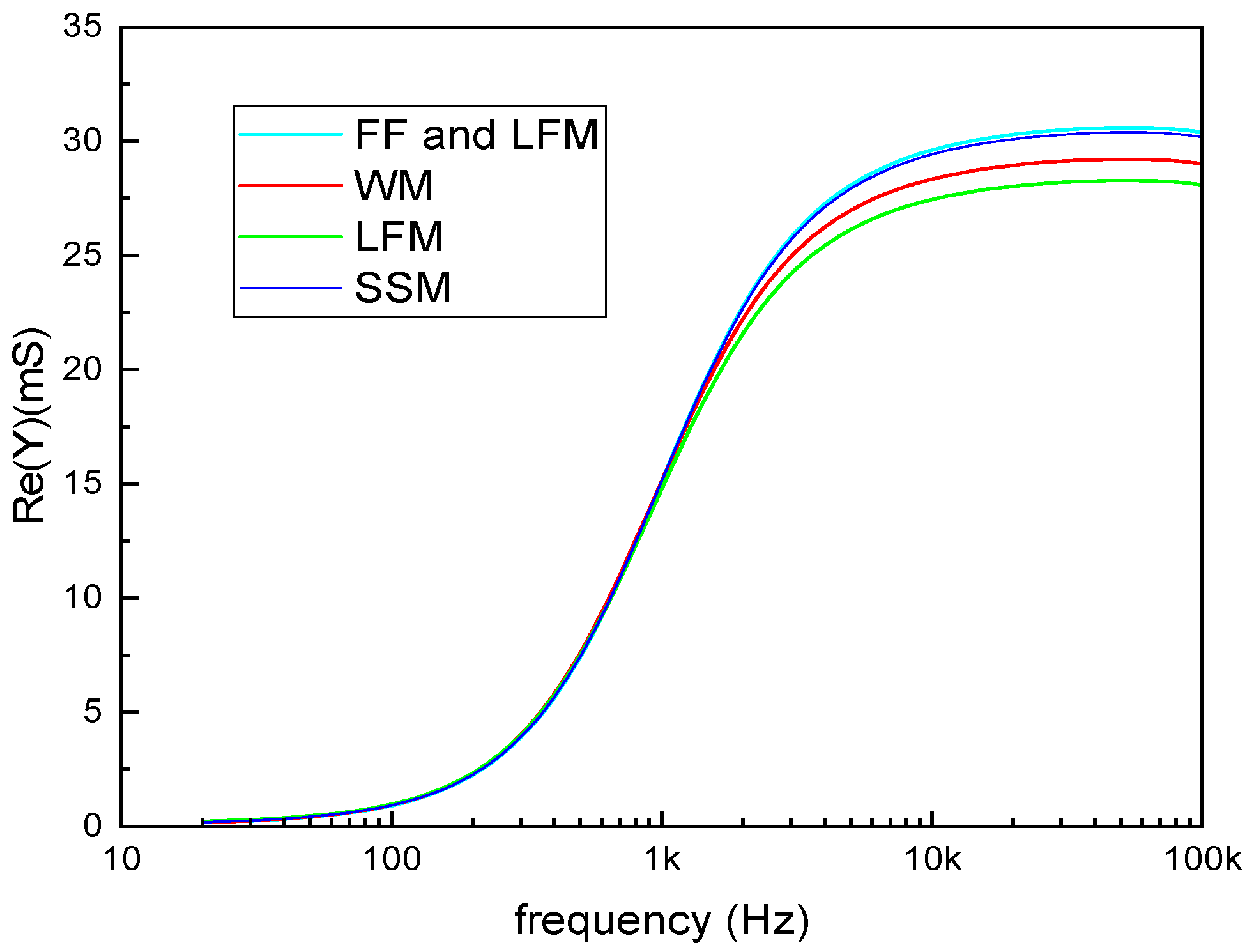
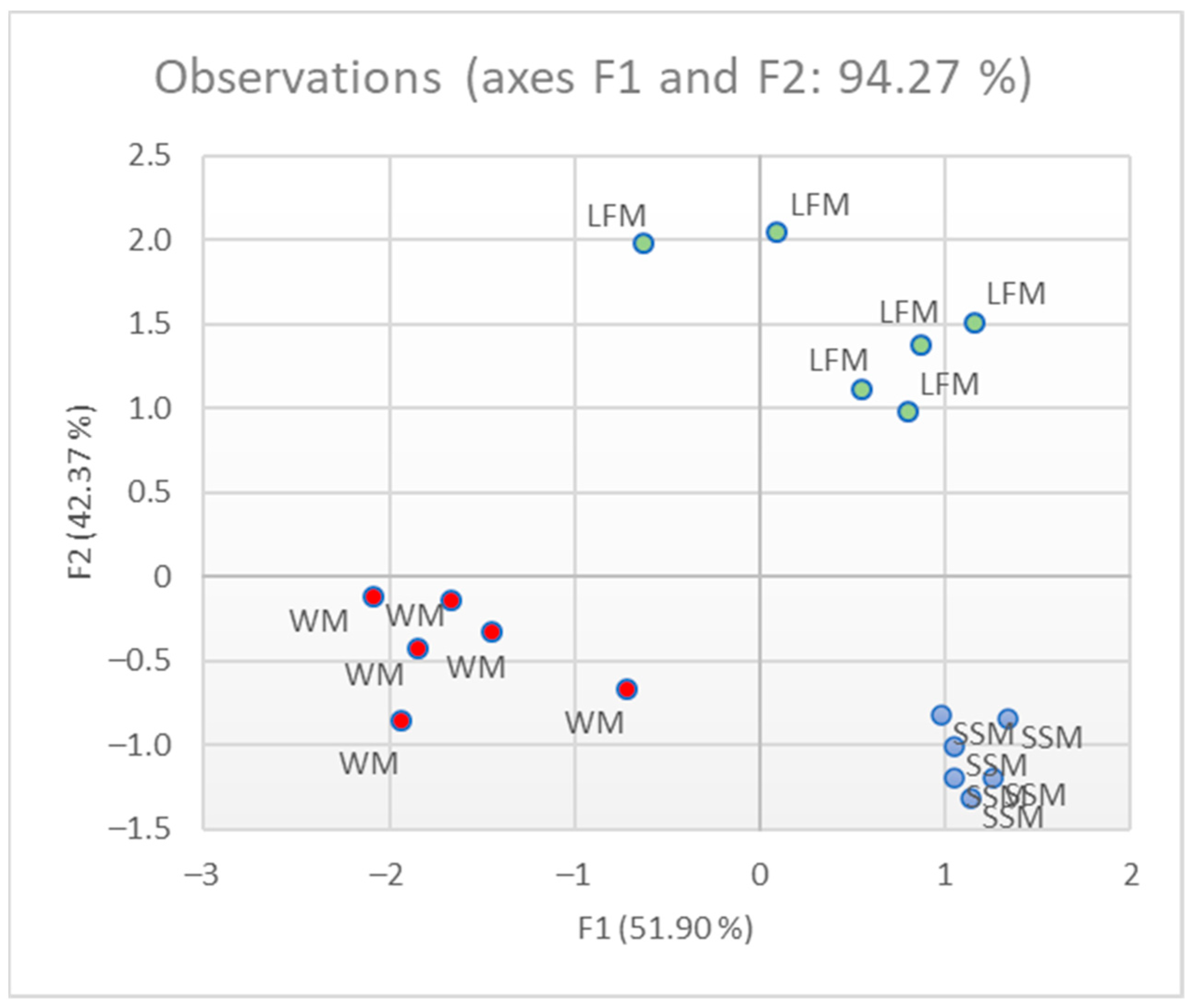
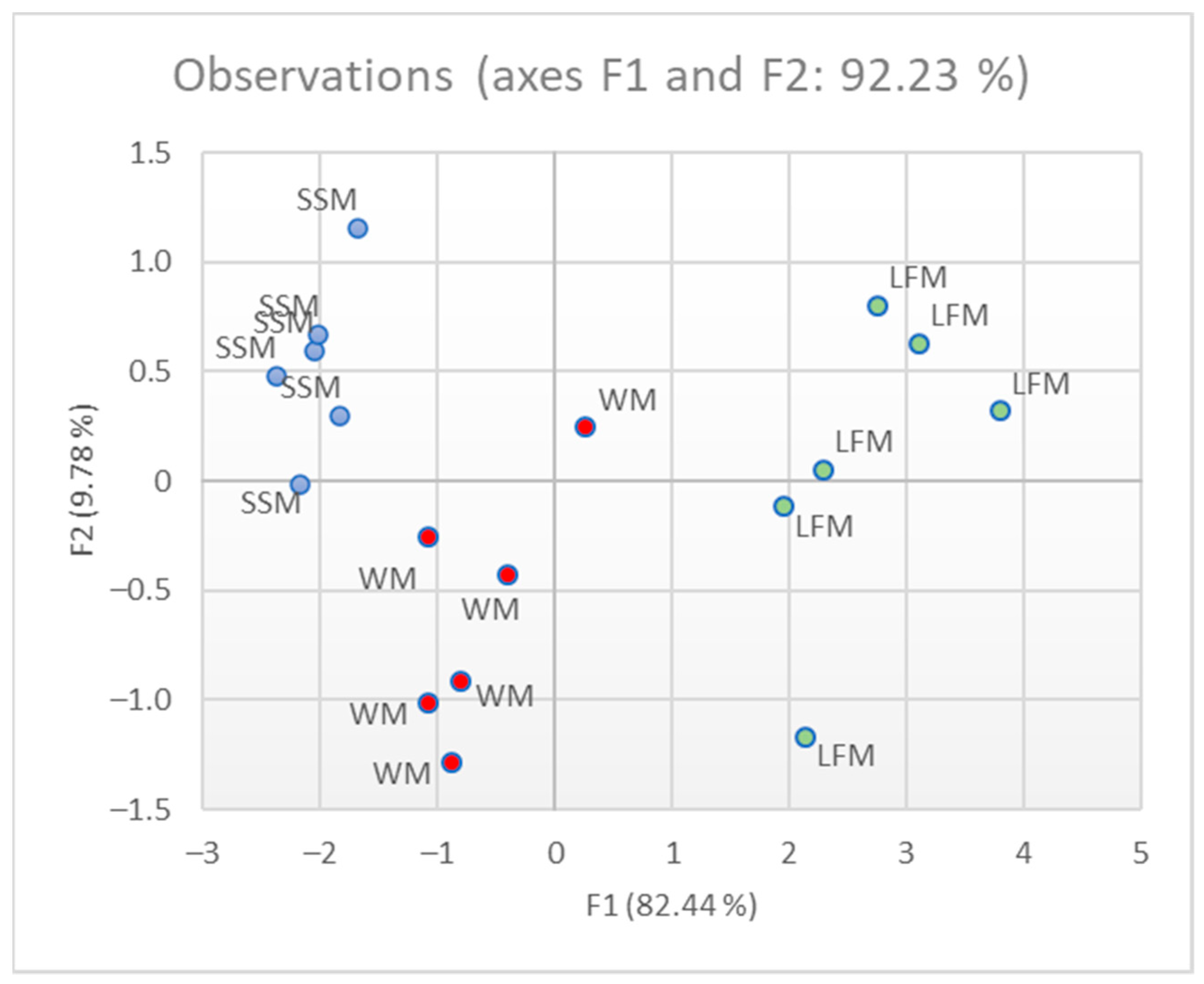
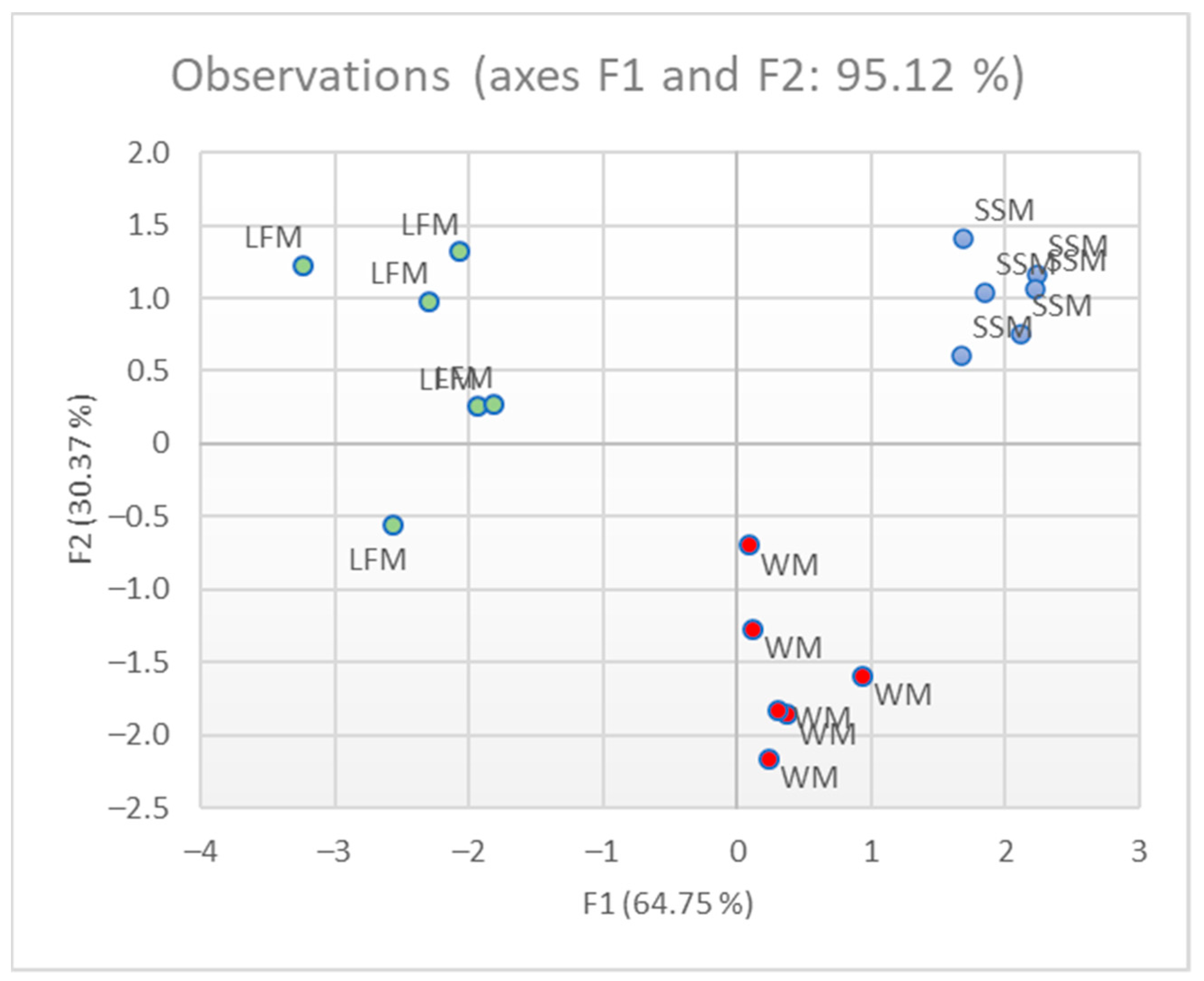
3.1. Qualitative Analysis and Milk Classification
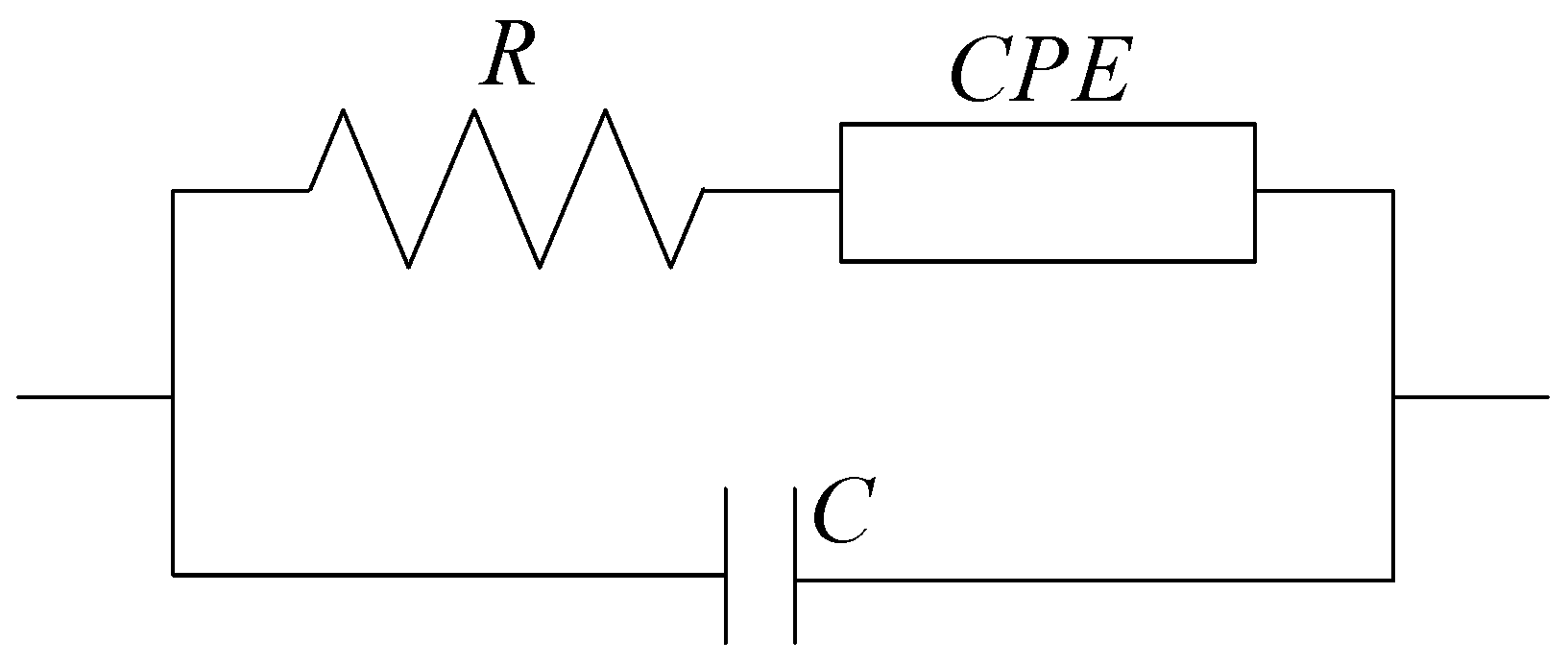
3.2. Quantitative Analysis: Milk Identification
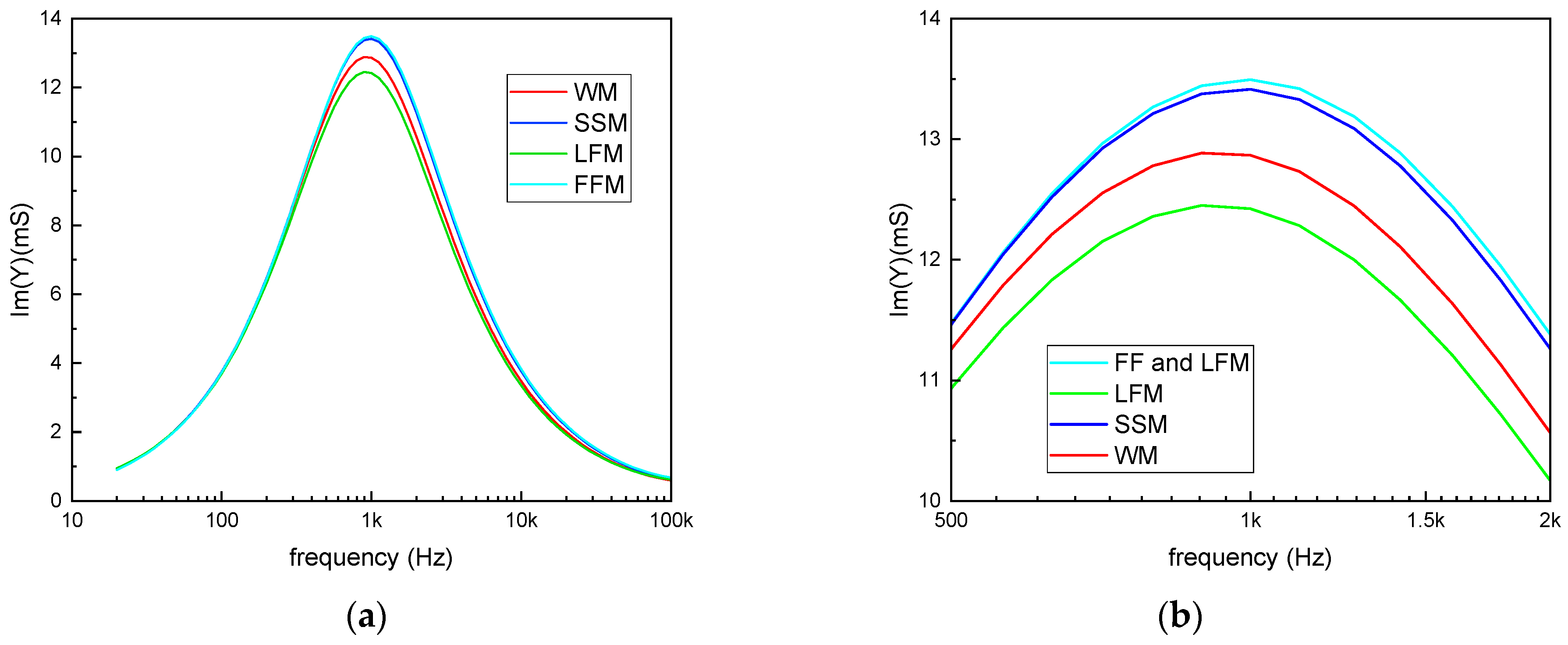
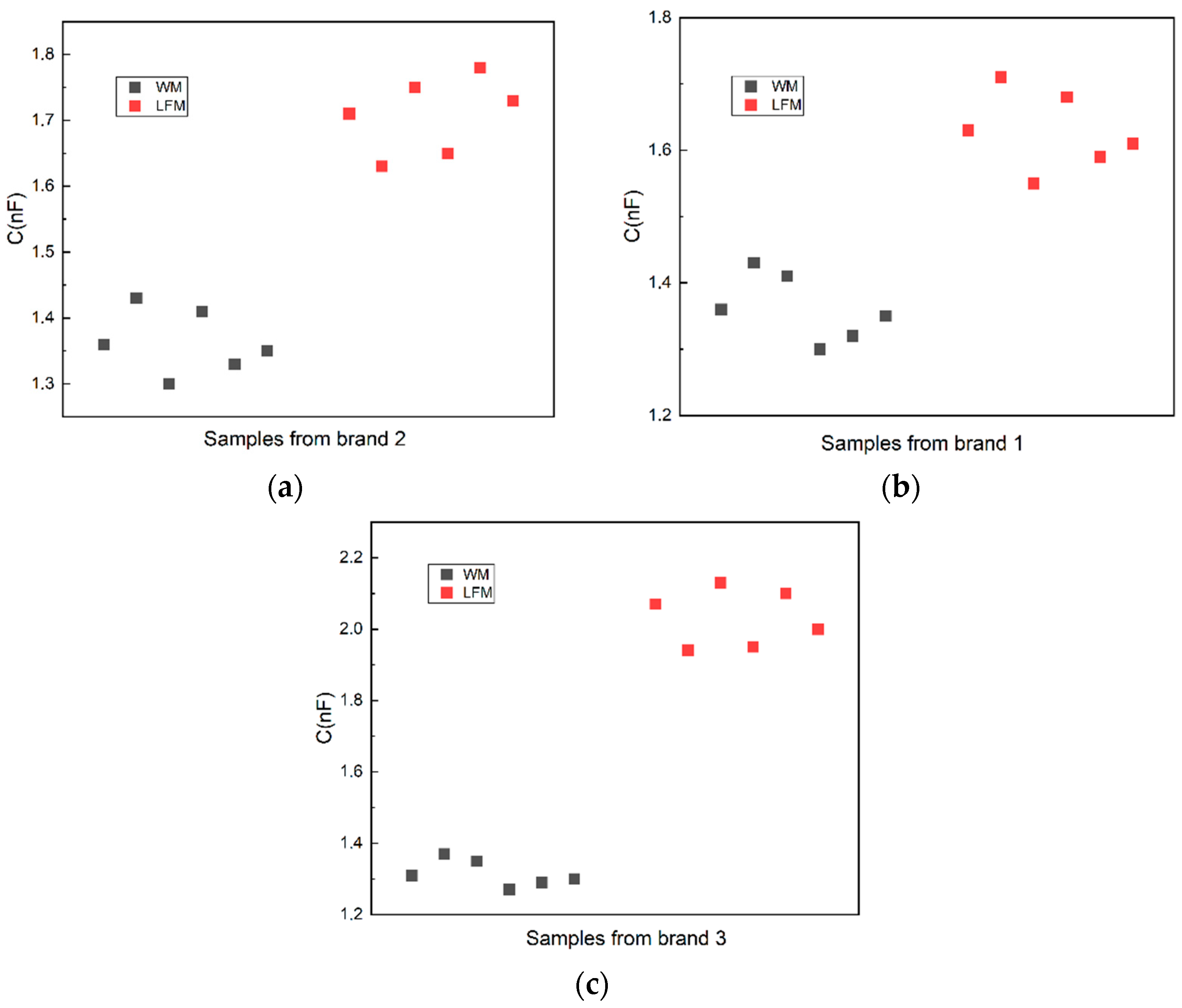
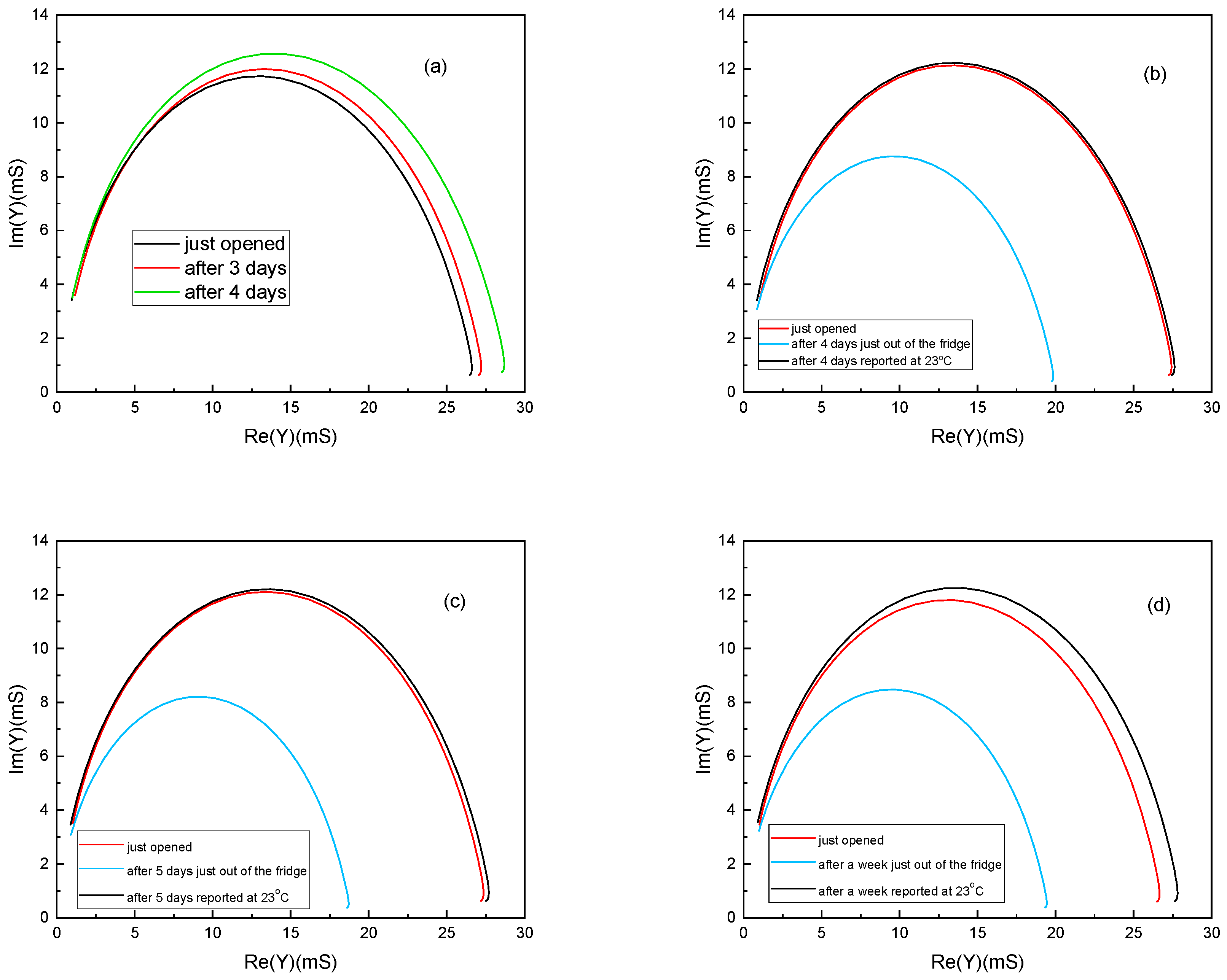
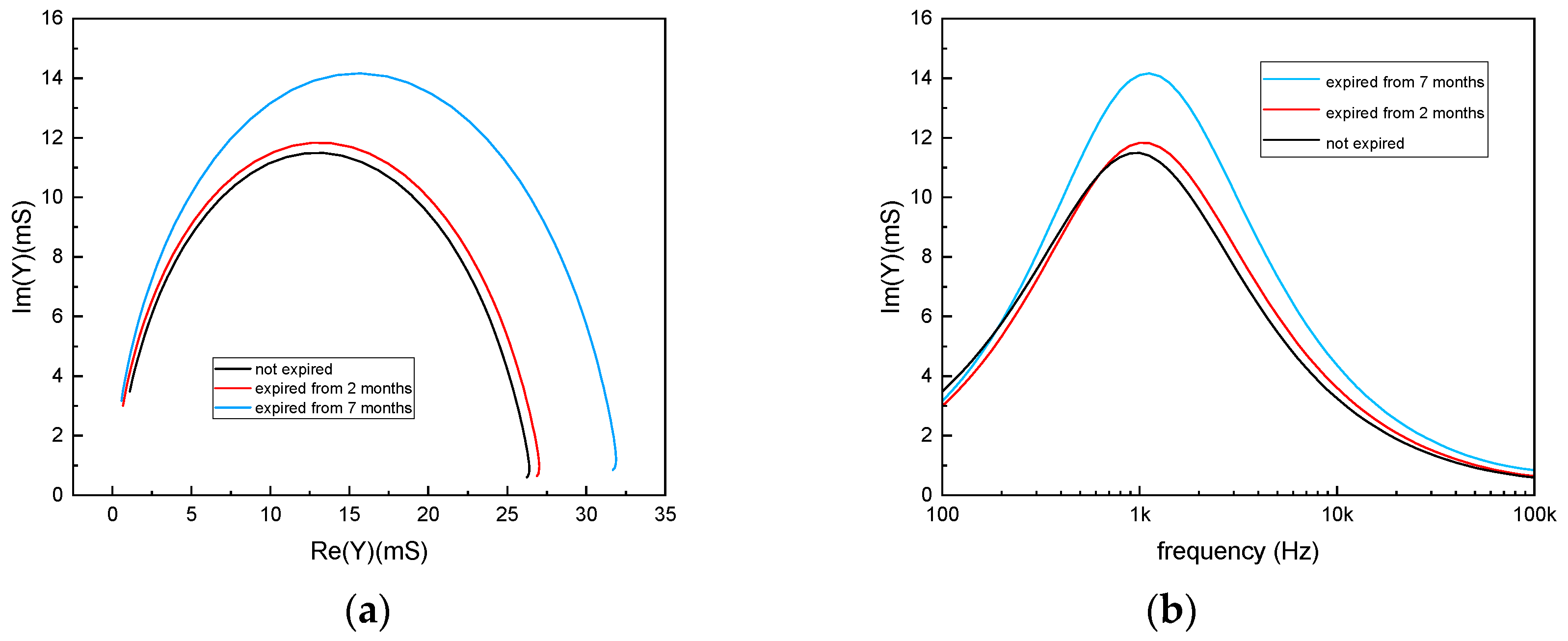
3.3. Analysis of Milk: Storage Method Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, N.W.; Fletcher, A.J.; Hill, J.P.; McNabb, W.C. Modeling the Contribution of Milk to Global Nutrition. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 716100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, Á.; Ortega, R.M. Introduction and executive summary of the supplement, role of milk and dairy products in health and prevention of noncommunicable chronic diseases: A series of systematic reviews. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S67–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Du, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y. Milk consumption and multiple health outcomes: Umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in humans. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysstad, G.; Kolstad, J. Extended shelf life milk—Advances in technology. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2006, 59, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.S.; Chavan, S.R.; Khedkar, C.D.; Jana, A.H. UHT Milk Processing and Effect of Plasmin Activity on Shelf Life: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, N.; Behzad, M.; Homay Razavi, S.; Jannat, B.; Oveisi, M.; Hajimahmoodi, M. Measurement of Zinc, Copper, Lead, and Cadmium in the Variety of Packaging Milk and Raw Milk in Tehran Markets by Anodic Striping Voltammetry. J. Chem. Health Risks 2020, 10, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavelli, L.U.R.; Galuch, M.B.; Senes, C.E.R.; Maia, L.C.; Lopes, T.A.M.; Rufato, K.B.; Santos, O.O.; Visentainer, J.V. Validation of UHPLC-MS/MS Method and Measurement Uncertainty Evaluation for Lactose Quantification in Lactose-Free and Regular UHT Milk. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 1418–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandurra, G.; Tripodi, G.; Verzera, A. Impedance spectroscopy for rapid determination of honey floral origin. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, D.; Ossart, F.; Ghommidh, C. Development of a non-destructive salt and moisture measurement method in salmon (Salmo salar) fillets using impedance technology. Food Control 2006, 17, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhuang, H.; Yoon, S.-C.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, W. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy for Quality Assessment of Meat and Fish: A Review on Basic Principles, Measurement Methods, and Recent Advances. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 6370739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Mao, H.; Wu, Y. Diagnosis and detection of phosphorus nutrition level for Solanum lycopersicum based on electrical impedance spectroscopy. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 143, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuson, P.; Terdwongworakul, A. Minimally-destructive evaluation of durian maturity based on electrical impedance measurement. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Bera, T.K.; Ghoshal, D.; Chakraborty, B. Studying the electrical impedance variations in banana ripening using electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd International Conference on Computer, Communication, Control and Information Technology, Hooghly, India, 7–8 February 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Vázquez-Gutiérrez, J.L.; Pérez-Gago, M.B.; Vonasek, E.; Nitin, N.; Barrett, D.M. Application of nondestructive impedance spectroscopy to determination of the effect of temperature on potato microstructure and texture. J. Food Eng. 2014, 133, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Ando, Y.; Orikasa, T.; Shiina, T.; Kohyama, K. Effect of short time heating on the mechanical fracture and electrical impedance properties of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). J. Food Eng. 2017, 194, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, G.M.; Sinha, A.; Ali, A.E.; Jeoti, V.; Radoičić, M.B.; Marković, D.D.; Radetić, M.M. Impedance analysis of milk quality using functionalized polyamide textile-based sensor. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 191, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrook, M.F.; Petty, M.C. Application of electrical admittance measurements to the quality control of milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 84, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.M.; Machado, J.A.T.; Ramalho, E.; Silva, V. Milk Characterization Using Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy and Fractional Models. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.F.; Hojjatoleslamy, M.; Kiani, H.; Molavi, H. Monitoring of Aflatoxin M1 in milk using a novel electrochemical aptasensor based on reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Catanante, G.; Huang, X.; Marty, J.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Screen-printed electrochemical immunosensor based on a novel nanobody for analyzing aflatoxin M1 in milk. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Popolin-Neto, M.; Paulovich, F.V.; Oliveira, O.N.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk samples using impedance spectroscopy and data processing with information visualization techniques and multidimensional calibration space. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, R.W.; Ayres, L.C.; Neuenfeld, R.H.; Carvalho, C.W.; Geller, A.M.; Oliveira, W.C. Electrical Bioimpedance Scanning in Bacterial Diagnosis and Mastitis Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, E.A.; Bertemes-Filho, P. Bioelectrical impedance analysis of bovine milk fat. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 407, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Biswas, K. Hardware Platform to Detect Fat Percent in Milk Using a Lipase Immobilized PMMA-Coated Sensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 4526–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Q.; Guo, W. Dielectric properties of raw milk as influenced by frequency, salts, and salt contents. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, 12885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X. Effect of lactose content on dielectric properties of whole milk and skim milk. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciosek, P.; Brudzewski, K.; Wroblewski, W. Milk classification by means of an electronic tongue and Support Vector Machine neural network. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, B.A.; Pethig, R. Determining the fat content of milk and cream using AC conductivity measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1993, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrook, M.F.; Petty, M.C. Effect of composition on the electrical conductance of milk. J. Food Eng. 2003, 60, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashoorirad, M.; Baghbani, R.; Ghalamboran, M.R. Bioimpedance sensor to detect water content in milk based on van Der Pauw method. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 15, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minetto, T.A.; França, B.D.; Dariz, G.D.S.; Veiga, E.A.; Galvão, A.C.; Robazza, W.D.S. Identifying adulteration of raw bovine milk with urea through electrochemical impedance spectroscopy coupled with chemometric techniques. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Bertotti, M. Fabrication of disposable voltammetric electronic tongues by using Prussian Blue films electrodeposited onto CD-R gold surfaces and recognition of milk adulteration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottram, T.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Legin, A.; Fitzpatrick, J.L.; Eckersall, P.D. Evaluation of a novel chemical sensor system to detect clinical mastitis in bovine milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2689–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vique, F.; Marichal, H.; Steinfeld, L. Inline mastitis detection system measuring the electrical conductivity of quarter milk. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimie, E.; Ebrahimi, F.; Ebrahimi, M.; Tomlinson, S.; Petrovski, K.R. Hierarchical pattern recognition in milking parameters predicts mastitis prevalence. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.J.; Valledor, M.; Campo, J.C. Screening method for early detection of mastitis in cows. Measurement 2014, 47, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggadike, H.J.; Ohnstad, I.; Laven, R.A.; Hillerton, J.E. Evaluation of measurements of the conductivity of quarter milk samples for the early diagnosis of mastitis. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norberg, E.; Hogeveen, H.; Korsgaard, I.R.; Friggens, N.C.; Sloth, K.H.M.N.; Løvendahl, P. Electrical conductivity of milk: Ability to predict mastitis status. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lien, C.-C.; Wan, Y.-N.; Ting, C.-H. Online detection of dairy cow subclinical mastitis using electrical conductivity indices of milk. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2016, 9, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RO3000 Series High Frequency Laminates, Rogers Corporation. Available online: https://rogerscorp.com/advanced-electronics-solutions/ro3000-series-laminates/ro3010-laminates (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Shoar Abouzari, M.R.; Berkemeier, F.; Schmitz, G.; Wilmer, D. On the physical interpretation of constant phase elements. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K.; Kaatze, U. Dielectric spectra of mono- and disaccharide aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucchetti, G.; Gatti, M.; Neviani, E. Electrical Conductivity Changes in Milk Caused by Acidification: Determining Factors. Int. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MILK SAMPLE | Fat | Saturated | Carbohydrates | Proteins | Salt | Calcium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM1 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 3.2 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| WM2 | 3.6 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 3.2 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| WM3 | 3.6 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 3.3 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| WM4 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 3.2 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| SSM1 | 1.6 | 1 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| SSM2 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 5.0 | 3.2 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| SSM3 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 5.0 | 3.3 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| SSM4 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| LFFM1 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| FFM2 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 5.0 | 3.2 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| LFM1 | 1 | 0.7 | 4.9 | 3.2 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| LFM2 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 5 | 3.3 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| LFM3 | 1 | 0.8 | 4.9 | 3.1 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| Parameter | Value (mm) |
|---|---|
| L1 | 20 |
| L2 | 2 |
| L3 | 10 |
| L4 | 1.27 |
| L5 | 22 |
| L6 | 4 |
| MILK SAMPLE | C (nF) | R (Ω) | Q (×10−5) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM1 | 1.41 | 37.73 | 7.98 | 0.848 |
| WM2 | 1.36 | 37.57 | 8.12 | 0.838 |
| WM3 | 1.31 | 39.11 | 7.96 | 0.843 |
| WM4 | 1.22 | 37.88 | 8.42 | 0.843 |
| SSM1 | 1.36 | 36.26 | 7.99 | 0.847 |
| SSM2 | 1.51 | 36.16 | 8.09 | 0.838 |
| SSM3 | 1.72 | 37.28 | 8.23 | 0.843 |
| SSM4 | 1.43 | 36.43 | 8.16 | 0.843 |
| LFFM1 | 1.78 | 36.06 | 7.94 | 0.848 |
| FFM2 | 1.84 | 35.83 | 8.01 | 0.838 |
| LFM1 | 1.63 | 39.01 | 8.08 | 0.846 |
| LFM2 | 1.71 | 38.37 | 8.13 | 0.838 |
| LFM3 | 2.03 | 40.53 | 8.15 | 0.843 |
| C | R | Q | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Fitting Error | 10% | 0.1% | 1% | 0.1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scandurra, G.; Cardillo, E.; Ciofi, C.; Ferro, L. UHT Milk Characterization by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157559
Scandurra G, Cardillo E, Ciofi C, Ferro L. UHT Milk Characterization by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157559
Chicago/Turabian StyleScandurra, Graziella, Emanuele Cardillo, Carmine Ciofi, and Luigi Ferro. 2022. "UHT Milk Characterization by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157559
APA StyleScandurra, G., Cardillo, E., Ciofi, C., & Ferro, L. (2022). UHT Milk Characterization by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157559









