Suspension Control and Characterization of a Variable Damping Magneto-Rheological Mount for a Micro Autonomous Railway Inspection Car
Abstract
:1. Introduction
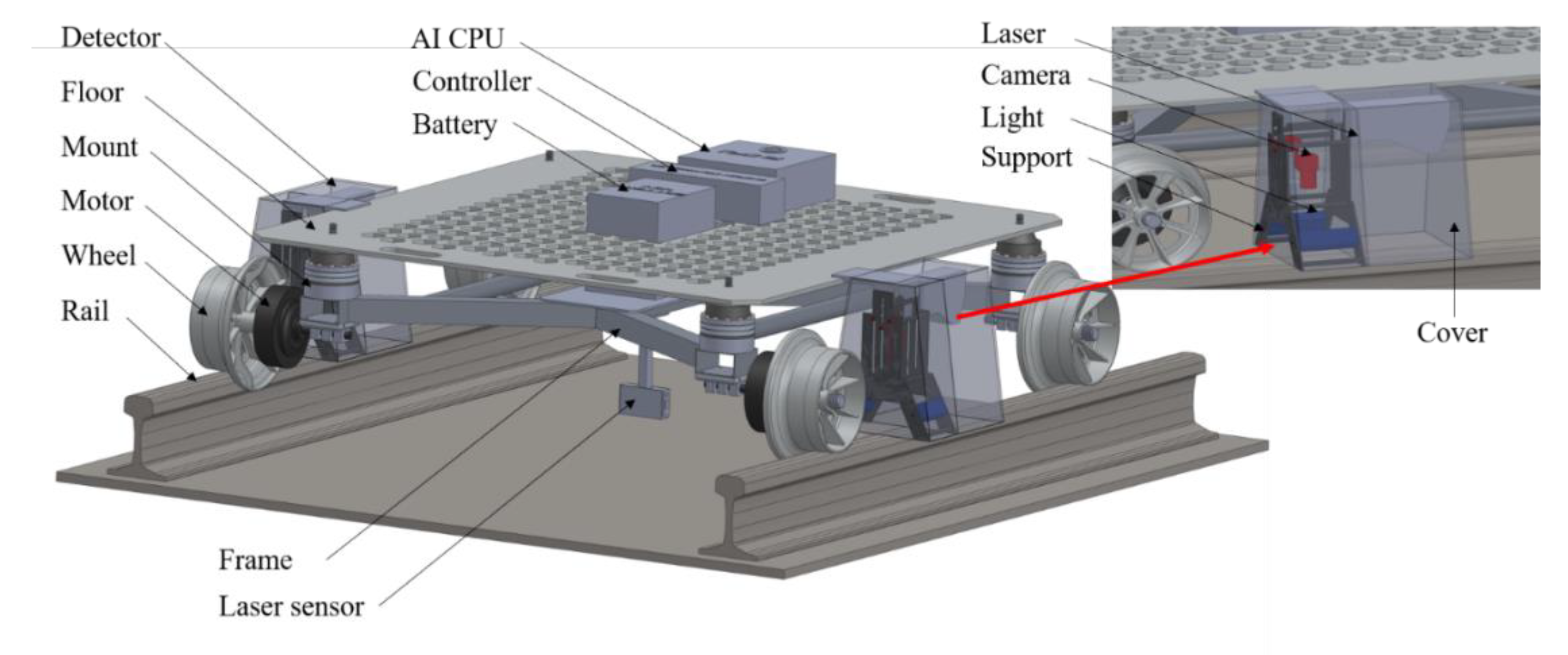
2. Concepts for the RSD Inspection Car
3. The Proposed MR Mount
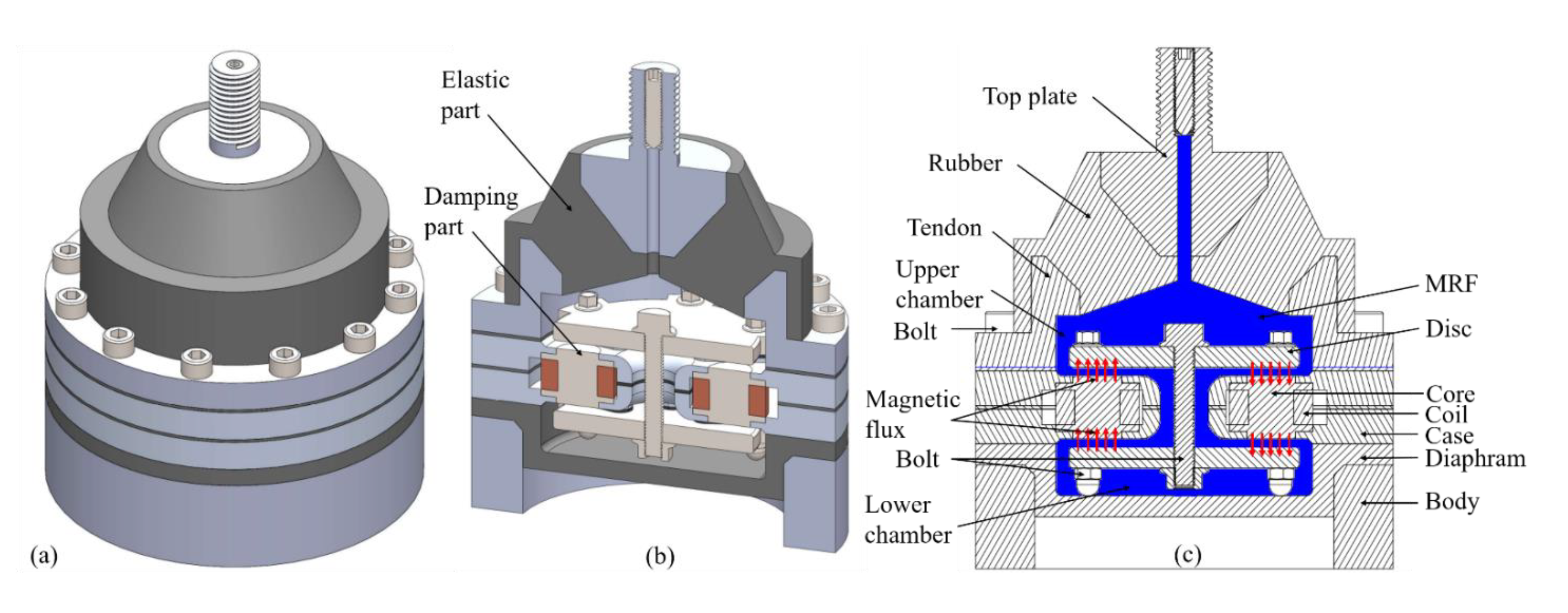
3.1. Conceptual Design of Mount
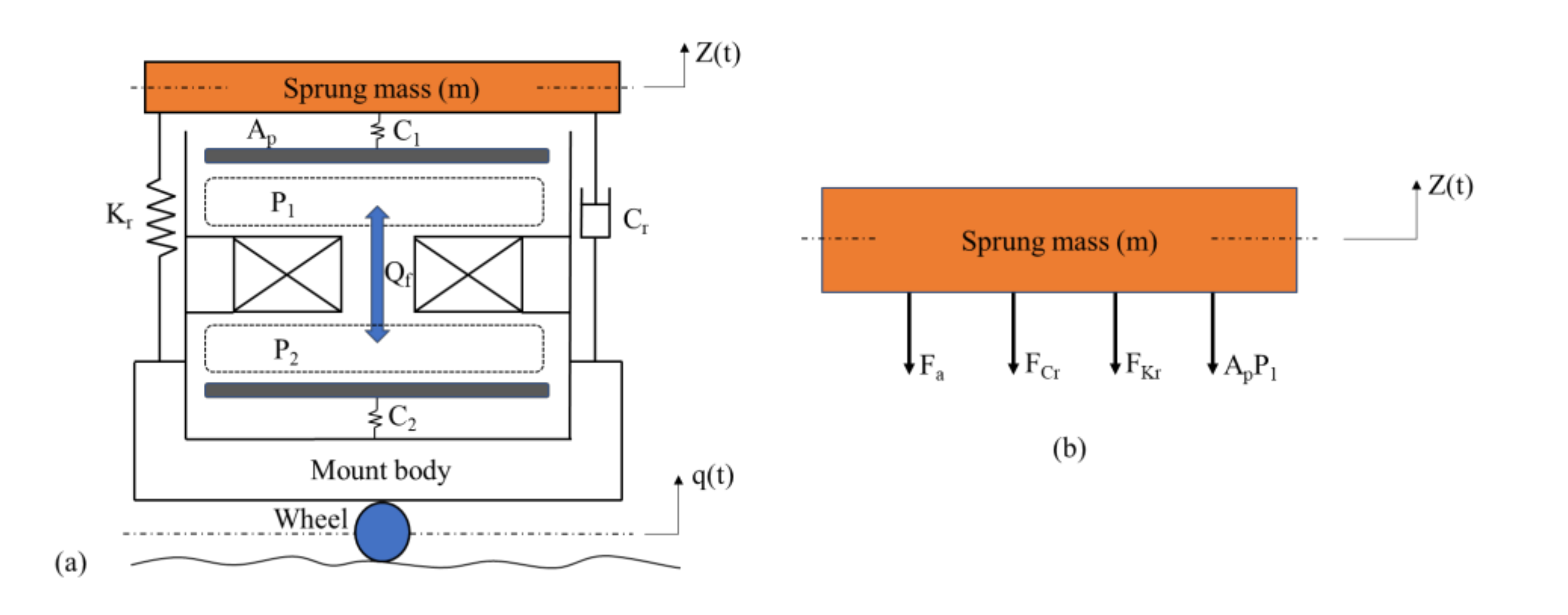
3.2. Mathematical Model of the Mount
3.2.1. A Damping Force Model
3.2.2. Mount Dynamic Model
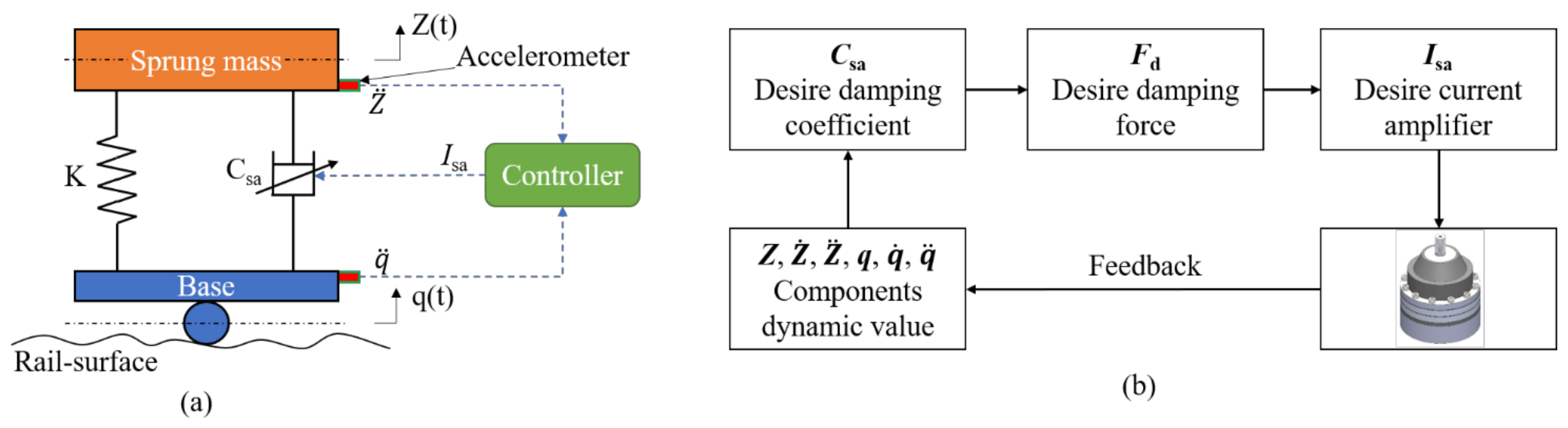
4. Controller for the MR Mount
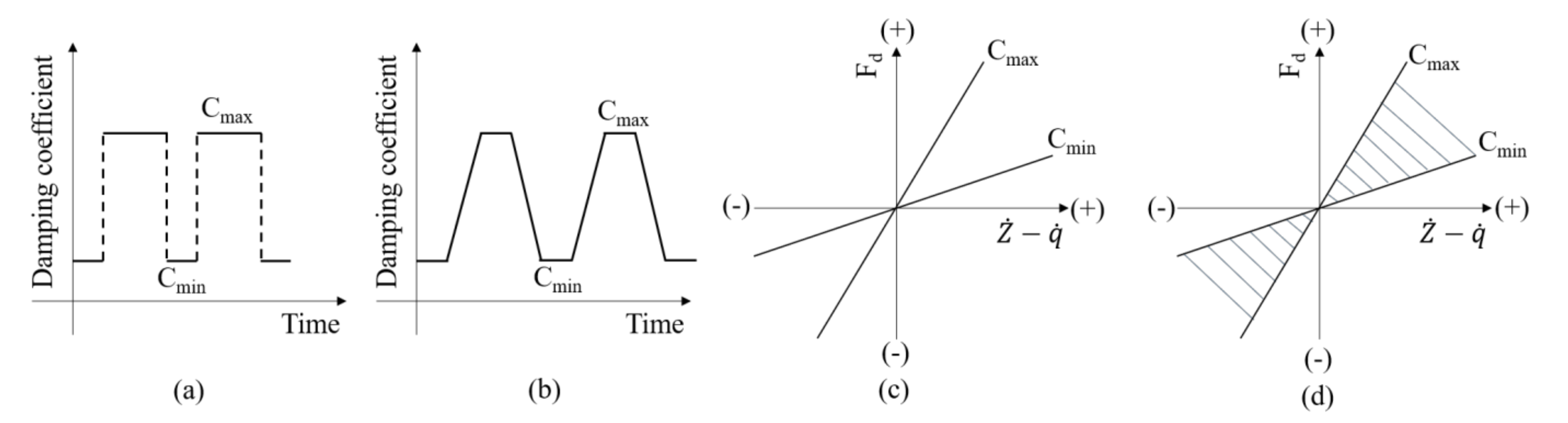
4.1. Analysis of a Skyhook Control Strategy
4.2. Diagram for Semi-Active Controller
5. Results and Discussion
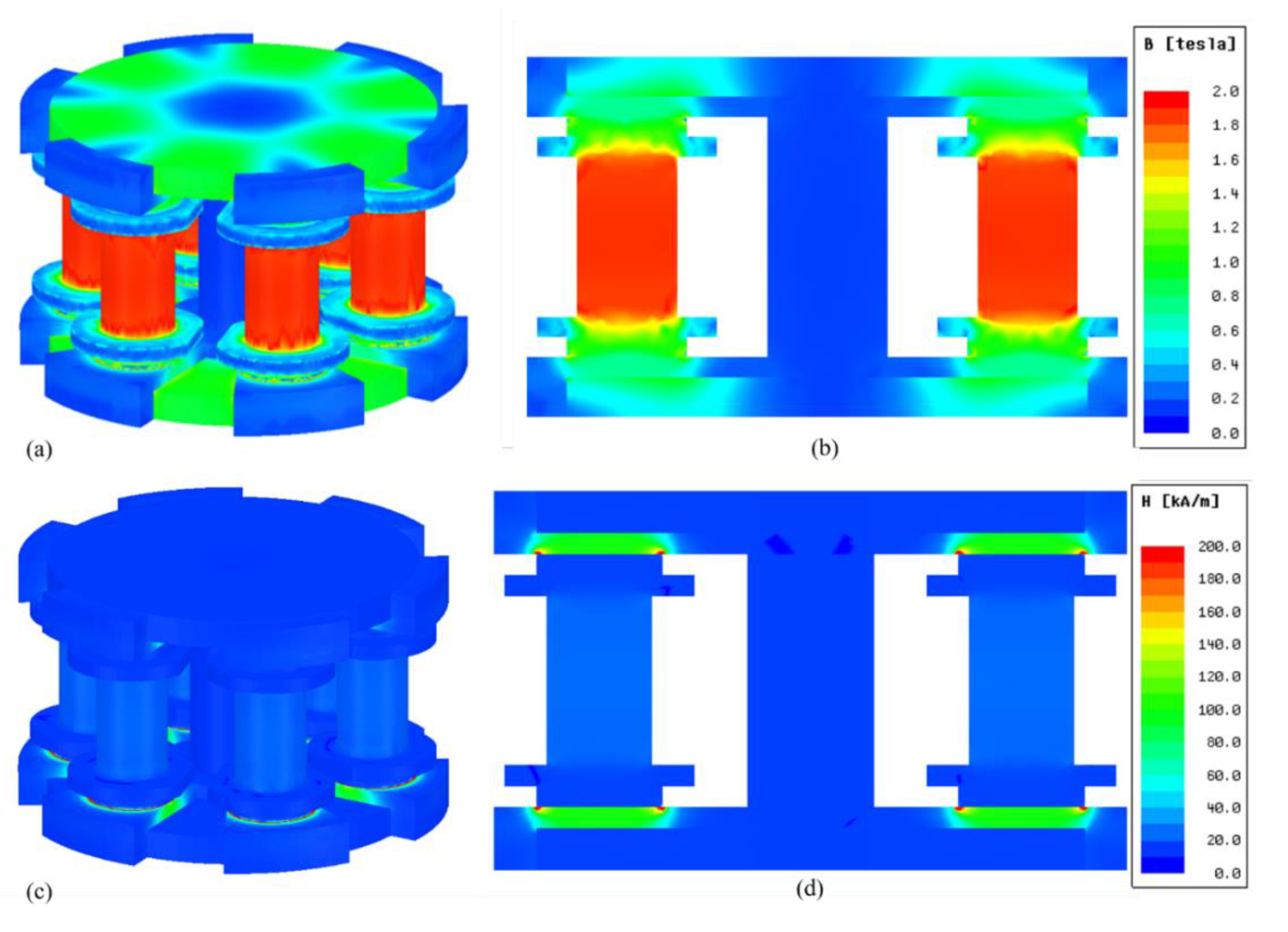
5.1. Results of Magnetic Simulation
5.2. Results of the Control Simulation
5.2.1. Response of the Frequency Domain
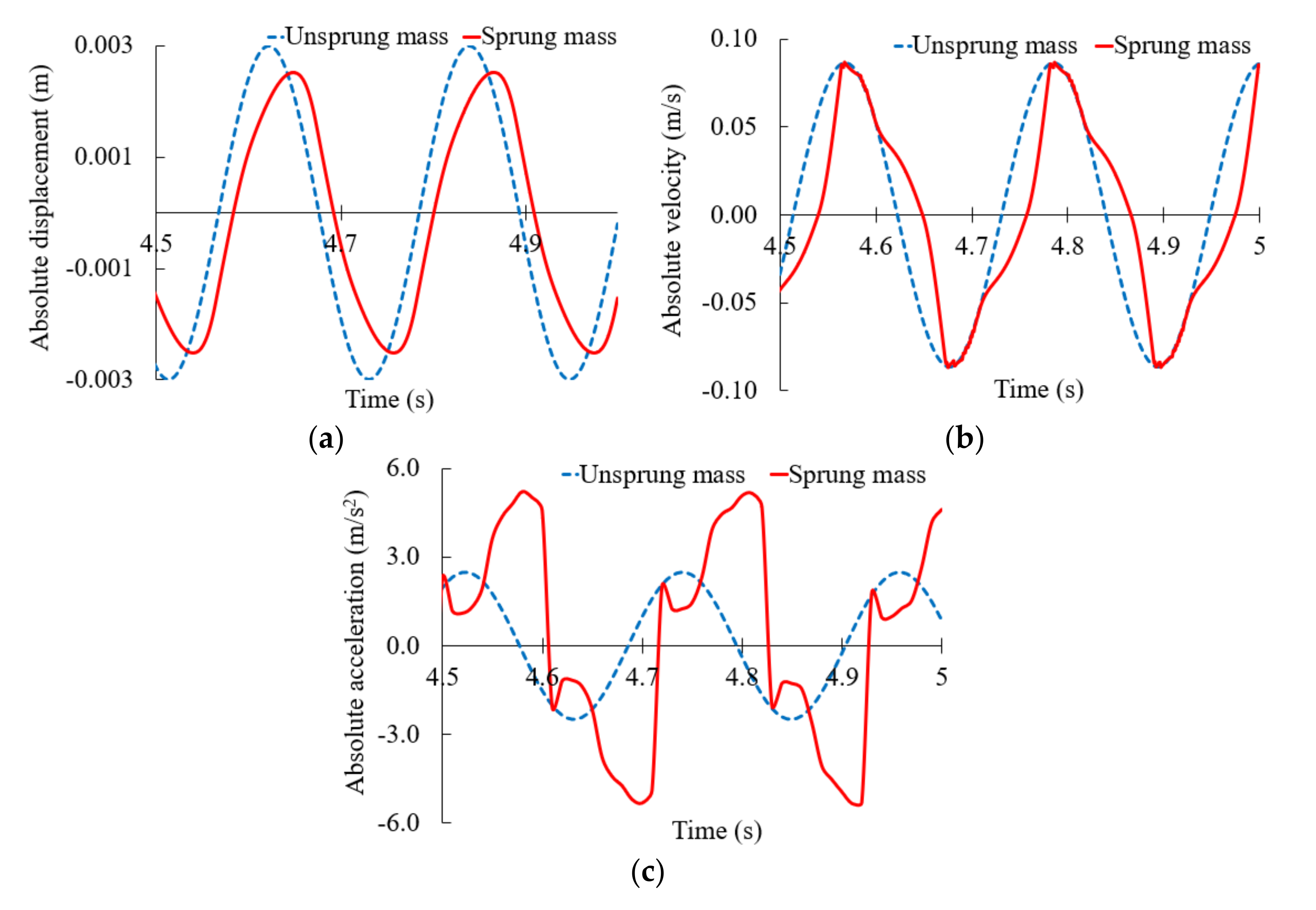
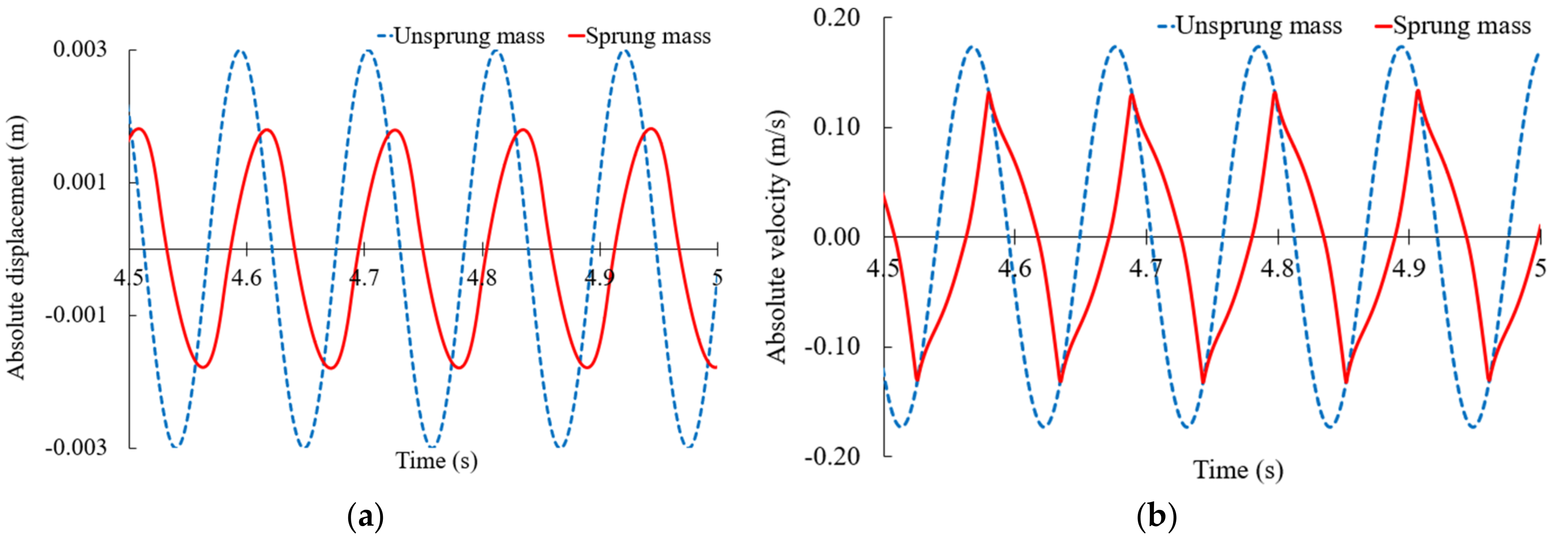
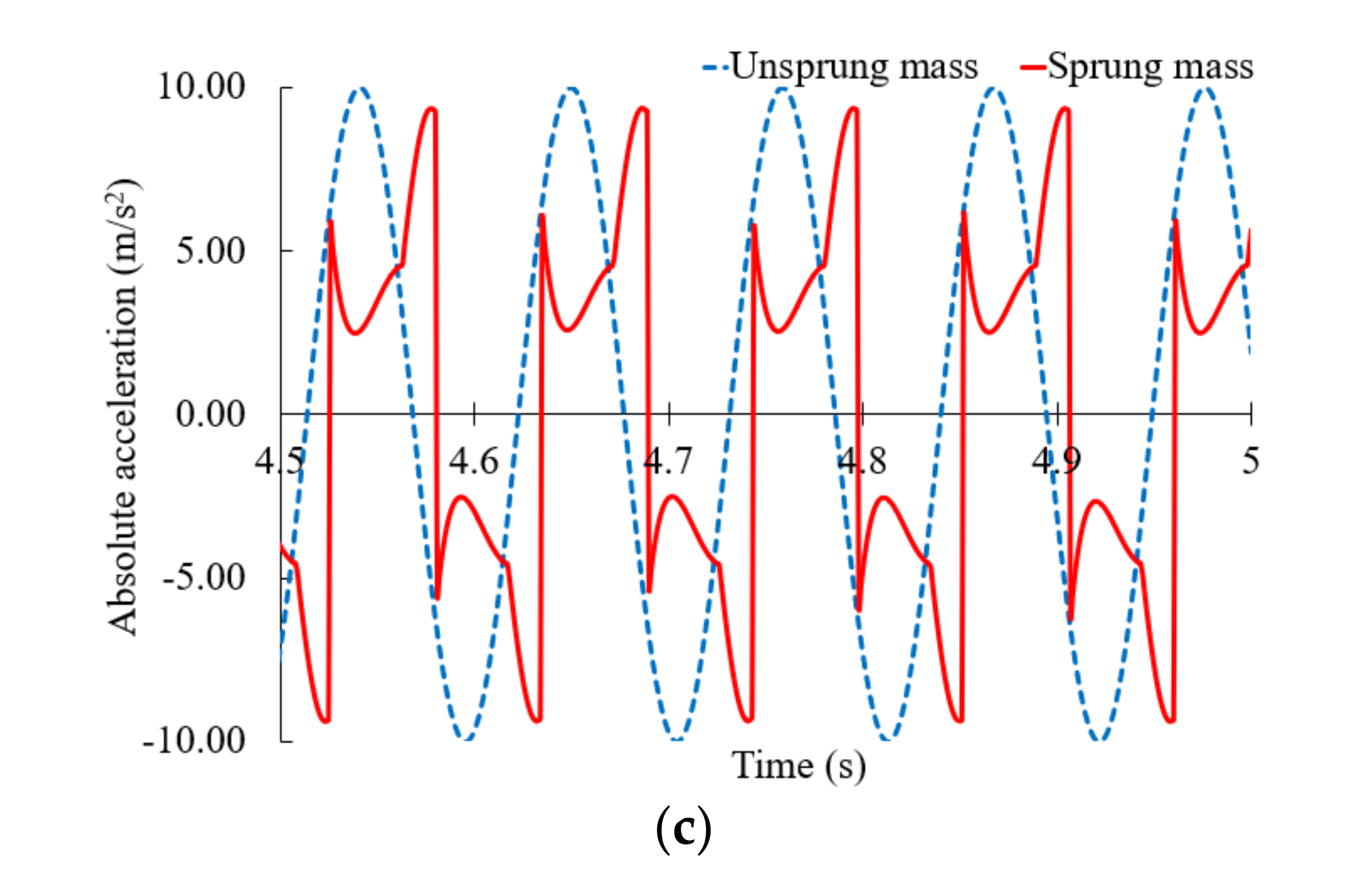
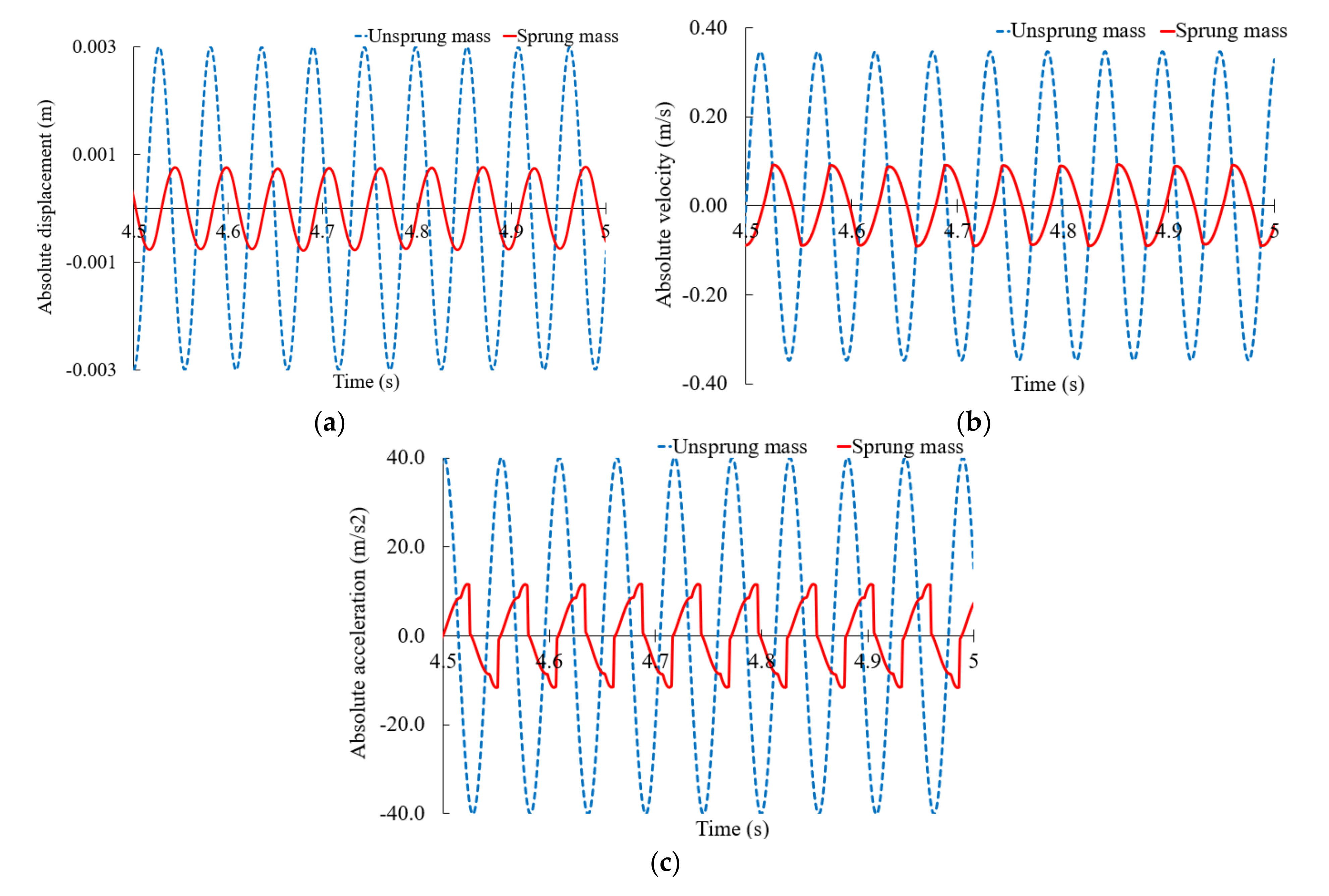
5.2.2. Response of the Time Domain with a Semi-Active Mount
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Tan, Y.; Gan, J.; Wang, J.; Geng, Y.-a.; Jia, L. A Coarse-to-Fine Model for Rail Surface Defect Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Akilan, T.; Wu, Q.M.J. Multi-Model Rail Surface Defect Inspection System Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentoumi, M.; Aknin, P.; Bloch, G. On-line rail defect diagnosis with differential eddy current probes and specific detection processing. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 23, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masmoudi, M.; Yaacoubi, S.; Koabaz, M.; Akrout, M.; Skaiky, A. On the use of ultrasonic guided waves for the health monitoring of rails. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2022, 236, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, N.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y. Acoustic emission detection of rail defect based on wavelet transform and Shannon entropy. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 339, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.W.; Lee, C.W. Dynamic analysis and control of an active engine mount system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2002, 216, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausberg, F.; Scheiblegger, C.; Pfeffer, P.; Plöchl, M.; Hecker, S.; Rupp, M. Experimental and analytical study of secondary path variations in active engine mounts. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 340, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, M. Dynamic characterization of controlled multi-channel semi-active magneto-rheological fluid mount. Mech. Sci. 2021, 12, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Bai, G.-D.; Liu, Z.-H.; Bai, X.-X.F.; Du, H.; Chen, P.; Qian, L.-J. Magneto-rheological semi-active mount system for engines: Prototyping and testing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2020, 234, 3081–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X. Low-Frequency Performance Analysis of Semi-Active Cab’s Hydraulic Mounts of an Off-Road Vibratory Roller. Shock. Vib. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Han, C.; Shin, C.; Choi, S.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, I. Dynamic characteristics of passive and semi-active cabin mounts for vibration control of a wheel loader. Int. J. Heavy Veh. Syst. 2019, 26, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-R.; Choi, S.-B.; Han, M.-S. Vibration control of a frame structure using electro-rheological fluid mounts. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2002, 44, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yao, G.-f.; Zhao, J.-z.; Qin, M. A novel design of semi-active hydraulic mount with wide-band tunable notch frequency. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 2196–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.Q.; Ahn, K.K. A new type of semi-active hydraulic engine mount using controllable area of inertia track. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Bai, X.-X.; Qian, L.-J.; Choi, S.-B. A magneto-rheological fluid mount featuring squeeze mode: Analysis and testing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-B.; Hong, S.-R.; Sung, K.-G.; Sohn, J.-W. Optimal control of structural vibrations using a mixed-mode magneto-rheological fluid mount. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2008, 50, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Choi, S.B.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, M.S. Optimal design of high damping force engine mount featuring MR valve structure with both annular and radial flow paths. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 115024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, D.X.; Choi, S.B.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, M.S. Design of a new engine mount for vertical and horizontal vibration control using magneto-rheological fluid. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, D.; Wang, X.; Gordaninejad, F. A New Magnetorheological Mount for Vibration Control. J. Vib. Acoust. 2011, 133, 031003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnopp, D.; Crosby, M.J.; Harwood, R.A. Vibration Control Using Semi-Active Force Generators. J. Eng. Ind. 1974, 96, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.Y.; Gao, X.; Xia, C.G.; Cai, H. Research on Fuzzy PID Control for Power-Train MR Mount System. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 397–400, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bai, J.; Lai, J.; Li, P.; Yu, M.; Lam, H.-K. Adaptive fuzzy control of a magneto-rheological elastomer vibration isolation system with time-varying sinusoidal excitations. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 456, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data, L.T. MRF-140CG Magneto-Rheological Fluid. 2008. Available online: https://lordfulfillment.com/pdf/44/DS7012_MRF-140CGMRFluid.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Nguyen, Q.-H.; Han, Y.-M.; Choi, S.-B.; Wereley, N.M. Geometry optimization of MR valves constrained in a specific volume using the finite element method. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Ai, H.X.; Liao, W.H. A magneto-rheological valve with both annular and radial fluid flow resistance gaps. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopherson, J.; Jazar, G.N. Dynamic behavior comparison of passive hydraulic engine mounts. Part 2: Finite element analysis. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 290, 1071–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Semi-Active Damping Control for Vibration Isolation of Base Disturbances. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, England, 2004. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Stiffness of the rubber, Ks (kN/m) | 50 |
| Damping coefficient of the rubber, Cs (N·m/s) | 50 |
| Compliance of the upper chamber, C1 (m5/N) | 2 × 10−10 |
| Compliance of the lower chamber, C2 (m5/N) | 2 × 10−8 |
| Effective area of the upper chamber cross-section, Ap (m2) | 7.065 × 10−4 |
| Gap of MRF, g (m) | 0.002 |
| Outer radius of the magnetic part Rmp (m) | 0.03 |
| Equivalent viscous coefficient caused by MRF, Rμ (Ns/m5) | 9.91 × 107 |
| Ratio of the effective area caused by the magnetic field, kt | 0.58 |
| Weight of the sprung mass per each mount, m (kg) | 15 |
| Density of MRF 140-CG (kg/m−3) | 3540 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiao, Y.; Huynh, T.-L. Suspension Control and Characterization of a Variable Damping Magneto-Rheological Mount for a Micro Autonomous Railway Inspection Car. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147336
Shiao Y, Huynh T-L. Suspension Control and Characterization of a Variable Damping Magneto-Rheological Mount for a Micro Autonomous Railway Inspection Car. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(14):7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147336
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiao, Yaojung, and Tan-Linh Huynh. 2022. "Suspension Control and Characterization of a Variable Damping Magneto-Rheological Mount for a Micro Autonomous Railway Inspection Car" Applied Sciences 12, no. 14: 7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147336
APA StyleShiao, Y., & Huynh, T.-L. (2022). Suspension Control and Characterization of a Variable Damping Magneto-Rheological Mount for a Micro Autonomous Railway Inspection Car. Applied Sciences, 12(14), 7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147336






