Compressive Properties of Polyurethane Fiber Mattress Filling Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
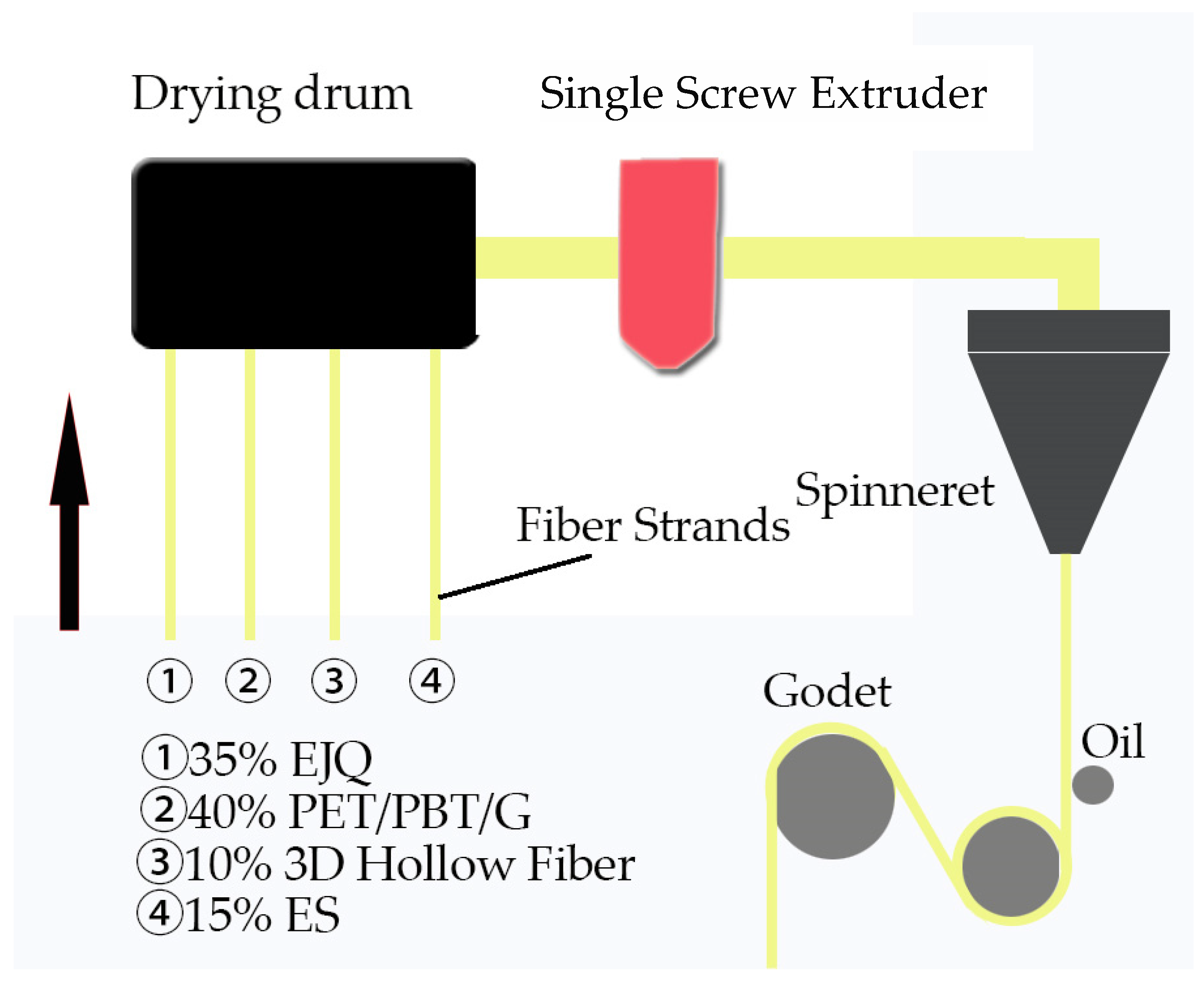
2.2. Methods
3. Results
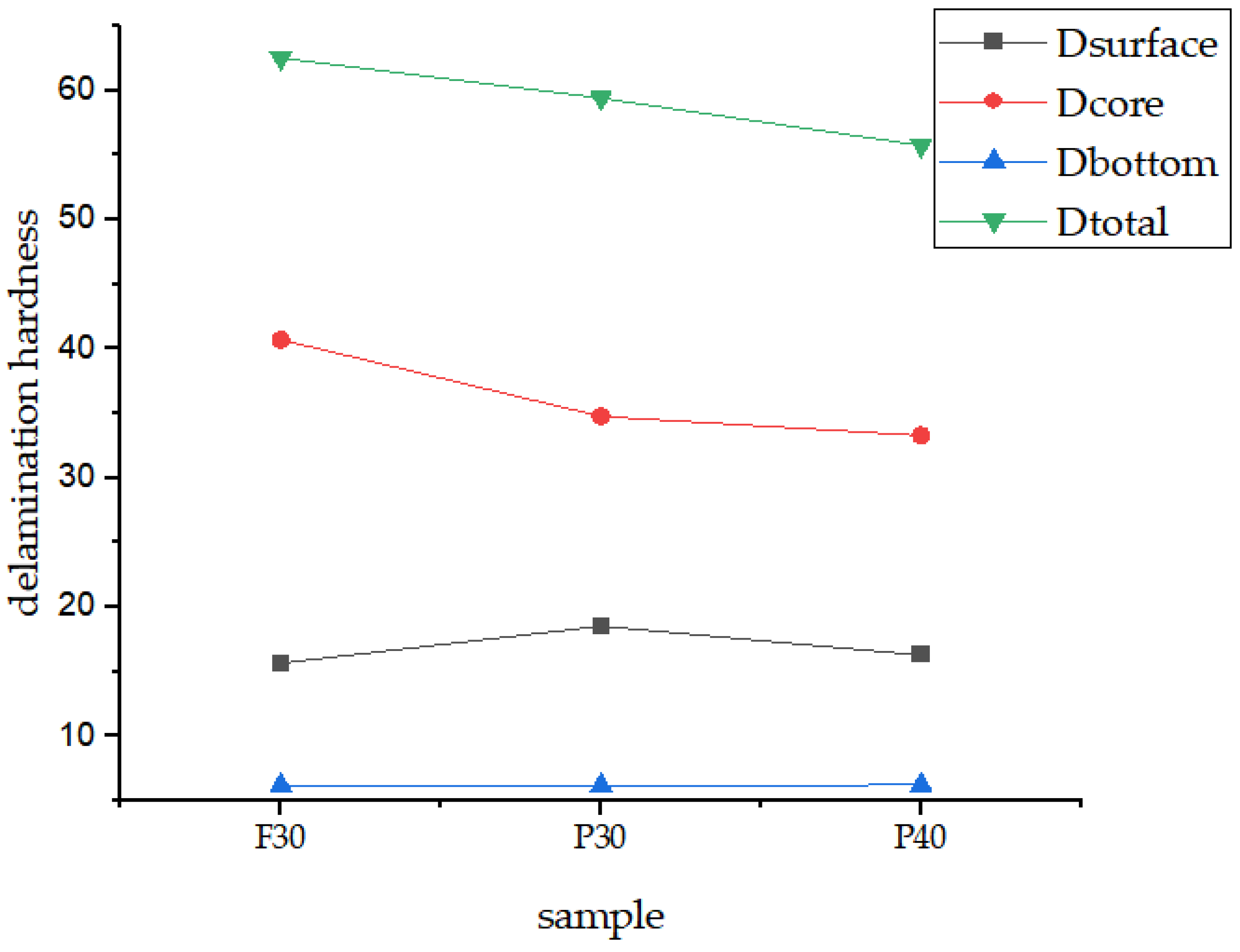
3.1. Delamination Hardness
3.2. Hardness Grade
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.J. Effects of alkali treatment on the structure and properties of jute fibers. Guangdong Build. Mater. 2021, 37, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.D.I.; Qi, Y.F.; Wei, C.Y.; Du, B.; Zheng, L.J.; Zheng, H.D. Research progress on cleaning and modification of jute fiber. Shanghai Text. Technol. 2021, 49, 4–6; 31. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.W. Basic Research and Optimal Design of Palm Fiber Elastic Materials; Jinan University: Guangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Maache, M.; Bezazi, A.; Amroune, S.; Scarpa, F.; Dufresne, A. Characterization of a novel natural cellulosic fiber from Juncus effusus L. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guna, V.; Ilangovan, M.; Adithya, K.; Koushik, C.V.A.; Reddy, N. Biofibers and biocomposites from sabai grassa unique renewable resource. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthamaraikannan, P.; Saravanakumar, S.S.; Arthanarieswaran, V.P.; Sugumaran, P. Physico-chemical properties of new cellulosic fibers from the bark of Acacia planifrons. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2016, 21, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Indran, S.; Raj, R.E.; Sreenivasan, V.S. Characterization of new natural cellulosic fiber from Cissus quadrangularis root. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, R.; Lenin, D.; Singaravelu, A.; Vinod, M.R.; Sanjay, S.; Siengchin, M.; Jawaid, A.; Khan, J.P. Characterization of raw and alkali treated new natural cellulosic fibers from Tridax procumbens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 125, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.S.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, F.L.; Shi, L.L.; Tao, M.X.; Weng, B.B.; Yan, B.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.X. Characterization of potential cellulose fiber from cattail fiber: A study on micro/nano structure and other properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, K.T.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, F.C.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Weng, B.B.; Dai, L.H.; Wu, S.S.; Su, N. Compression Properties of Two Novel Natural Luffa Mattress Filling Materials. J. Nat. Fibers 2019, 18, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, N.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Effect of fiber surface treatment on structure, moisture absorption and mechanical properties of luffa FPF fiber bundles. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 123, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Weng, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, S.; Wang, C.; Xu, R.; Guo, J.; Lv, Y.; Shi, L.; Guo, Y. Characterization of potential cellulose fiber from Luffa vine: A study on physicochemical and structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, A.; Ya, D.; Dan, Y.; Wei, W.; Yang, W.Z.; Sun, B.; Zhu, M.F. Synthesis, characterization of a DOPO-based polymeric flame retardant and its application in polyethylene terephthalate. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.W.; Pan, F.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhong, Y.; Mao, Z.P. The flame-retardancy and anti-dripping properties of novel poly(ethylene terephalate)/cyclotriphosphazene/silicone composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 110, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Gu, Y.T.; Xu, W.; Lu, T.; Li, W.J.; Fan, H.B. Compressive Properties of Green Velvet Material Used in Mattress Bedding. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; He, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, X. Modeling and optimizing the specific cutting energy of medium density fiberboard during the helical up-milling process. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yao, Q.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Study of Cutting Power and Power Efficiency during Straight-Tooth Cylindrical Milling Process of Particle Boards. Materials 2022, 15, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Buck, D.; Guo, X.; Xiong, X.; Xu, W.; Cao, P. Energy Efficiency Optimization for Machining of Wood Plastic. Compos. Mach. 2022, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Hong, L.; Guo, J. Analysis of upper-limb muscle fatigue in the process of rotary handling. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2021, 83, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.S.; Shen, L.M.; Zhao, H. Effects of mattress padding material and structure on its comprehensive stiffness. Furniture 2019, 40, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, N.; Yu, C.; Li, M. Effects of mattress firmness on infant body pressure distribution. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2021, 83, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | G9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | F30+ Spring | P30+ Spring | P40+ Spring | F30+ Coir | P30+ Coir | P40+ Coir | F30+ P50 | P30+ P50 | P40+ P50 | |
| Fabric layer | First layer | 5 mm Anti-mite FPF, density 18 kg/m3 | ||||||||
| Second layer | 10 mm FPF, density 18 kg/m3 | |||||||||
| Third layer | non-woven fabric, density 6 kg/m3 | |||||||||
| Cushion layer | Fourth layer | 2 cm FPF, 30 kg/m3 | 2 cm PLON, 30 kg/m3 | 2 cm PLON, 40 kg/m3 | 2 cm PLON, 30 kg/m3 | 2 cm PLON, 30 kg/m3 | 2 cm PLON, 40 kg/m3 | 2 cm FPF, 30 kg/m3 | 2 cm PLON, kg/m3 | 2 cm PLON, 40 kg/m3 |
| Supporting layer | Fifth layer | spring | spring | spring | coir | coir | coir | P50 | P50 | P50 |
| Fabric layer | First layer | nonwoven fabric, density 6 kg/m3 | ||||||||
| Second layer | 10 mm FPF, density 18 kg/m3 | |||||||||
| Third layer | 5 mm Anti-mite FPF, density 18 kg/m3 | |||||||||
| Source | Dsurface | Dcore | Dbottom | Dtotal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Value | p Value | F Value | p Value | F Value | p Value | F Value | p Value | |
| Cushion layer material | 170.30 | <0.0001 | 394.14 | <0.0001 | 0.27 | 0.7693 | 125.03 | <0.0001 |
| Supporting layer material | 371.72 | <0.0001 | 8562.48 | <0.0001 | 5634.12 | <0.0001 | 6649.70 | <0.0001 |
| Cushion layer material × Supporting layer material | 27.10 | <0.0001 | 22.89 | <0.0001 | 11.69 | <0.0001 | 13.87 | <0.0001 |
| Dsurface | Dcore | Dbottom | Dtotal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F30 + spring | 19.14 (2) B | 58.93 (3) A | 11.2 (3) A | 89.28 (3) A |
| P30 + spring | 19.79 (1) A | 54.68 (1) B | 10.63 (2) B | 85.1 (1) B |
| P40 + spring | 18.78 (1) B | 53.09 (1) C | 10.59 (1) B | 82.46 (5) C |
| F30 + coir | 13.29 (4) F | 25.61 (2) G | 2.54 (2) E | 41.44 (1) F |
| P30 + coir | 16.67 (5) C | 15.99 (2) H | 2.49 (2) E | 35.15 (5) G |
| P40 + coir | 14.56 (2) E | 15.98 (2) H | 2.73 (3) E | 33.28 (1) H |
| F30 + P50 | 14.51 (2) E | 37.57 (1) D | 4.7 (2) D | 56.87 (1) D |
| P30 + P50 | 19.09 (1) B | 33.63 (1) E | 5.32 (3) C | 58.03 (1) D |
| P40 + P50 | 15.43 (5) D | 30.81 (1) F | 5.29 (3) C | 51.53 (2) E |
| LSD values | 0.5965 | 1.0172 | 0.2885 | 1.5595 |
| Source | K | S | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Value | p Value | F Value | p Value | |
| Cushion layer material | 1.46 | 0.2576 | 3.34 | 0.0585 |
| Supporting layer material | 314.46 | <0.0001 | 642.44 | <0.0001 |
| Cushion layer material × Supporting layer material | 0.37 | 0.8249 | 0.87 | 0.4991 |
| Source | K | S |
|---|---|---|
| F30 + spring | 2208.30 (6) A | 6.97 (4) A |
| P30 + spring | 2290.16 (11) A | 7.13 (7) A |
| P40 + spring | 2240.70 (18) A | 6.98 (12) C |
| F30 + coir | 332.48 (3) C | 0.89 (4) C |
| P30 + coir | 414.66 (1) BC | 1.17 (17) C |
| P40 + coir | 310.2 (7) C | 0.82 (82) C |
| F30 + P50 | 533.50 (1) BC | 1.6 (60) B |
| P30 + P50 | 641.27 (2) B | 2 (2.00) B |
| P40 + P50 | 371.09 (53) BC | 1.06 (1.06) C |
| LSD values | 304.60 | 0.68 |
| Cushion Layer Material | K | S |
|---|---|---|
| F30 | 1024.76 (1.01) A | 4.15 (1.06) A |
| P30 | 1115.36 (0.92) B | 3.43 (0.94) C |
| P40 | 974.00 (1.13) B | 2.95 (1.18) B |
| LSD values | 175.86 | 0.3922 |
| Supporting Layer Material | K | S |
|---|---|---|
| spring | 2246.38 (1.84) A | 7.03 (1.20) AB |
| coir | 352.45 (16.61) A | 0.96 (19.14) A |
| P50 | 515.29 (26.39) A | 1.55 (30.38) C |
| LSD values | 175.86 | 0.3922 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Gu, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, T.; Li, W.; Fan, H. Compressive Properties of Polyurethane Fiber Mattress Filling Material. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126139
Liu Q, Gu Y, Xu W, Lu T, Li W, Fan H. Compressive Properties of Polyurethane Fiber Mattress Filling Material. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):6139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126139
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qingqing, Yanting Gu, Wei Xu, Tao Lu, Wenjun Li, and Haibin Fan. 2022. "Compressive Properties of Polyurethane Fiber Mattress Filling Material" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 6139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126139
APA StyleLiu, Q., Gu, Y., Xu, W., Lu, T., Li, W., & Fan, H. (2022). Compressive Properties of Polyurethane Fiber Mattress Filling Material. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 6139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126139





