A Brief Review of Formaldehyde Removal through Activated Carbon Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Thermodynamics and Kinetics for Adsorption of Formaldehyde on AC
2.1. Thermodynamics and Adsorption Isotherms
2.2. Kinetic Models
3. Physical (Operational) Influence Factors
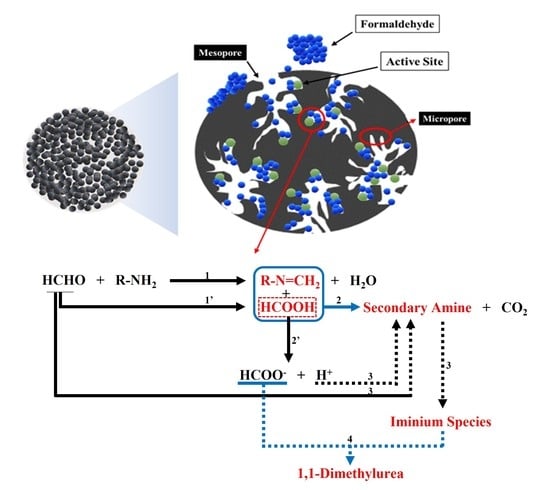
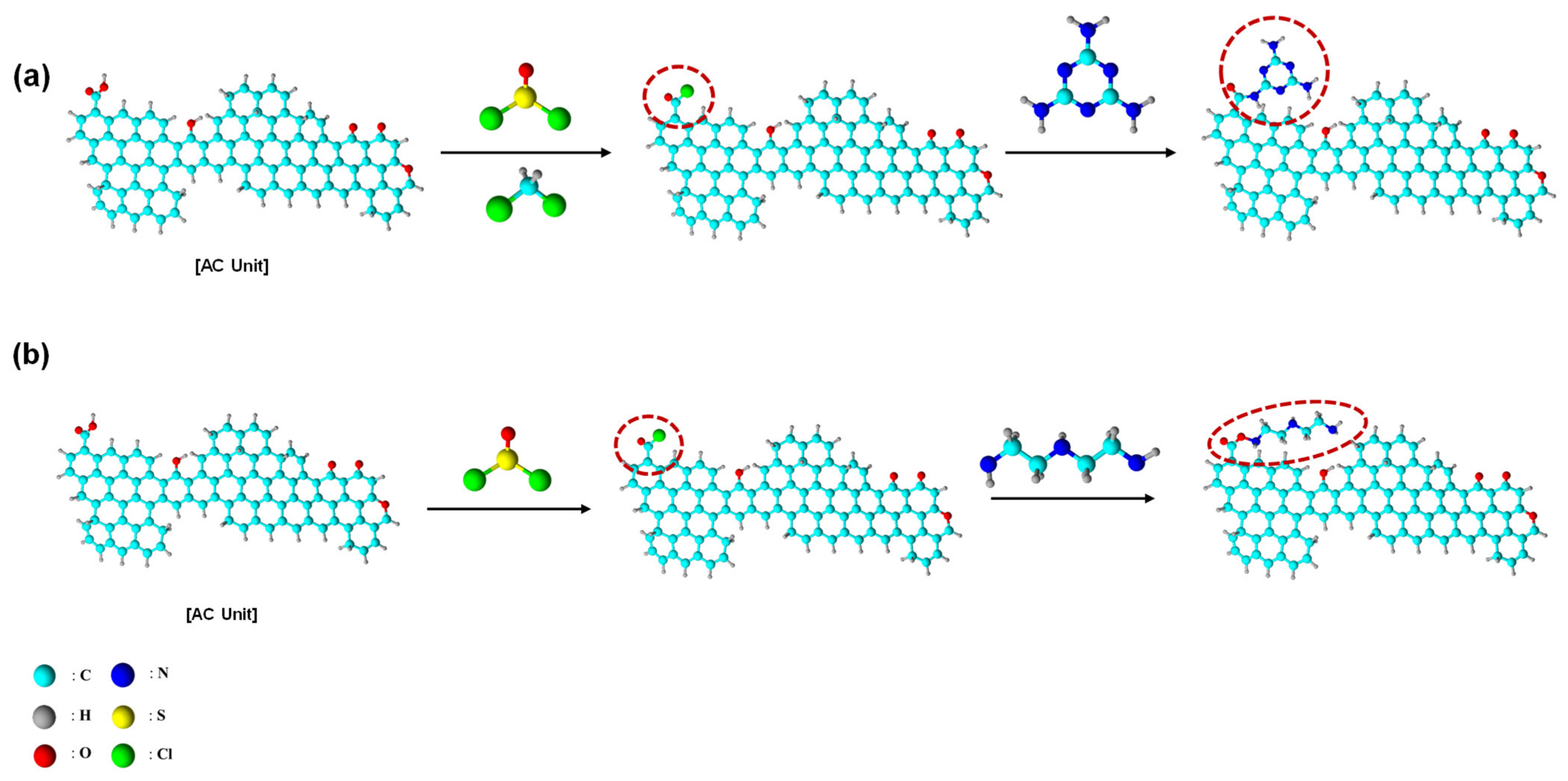
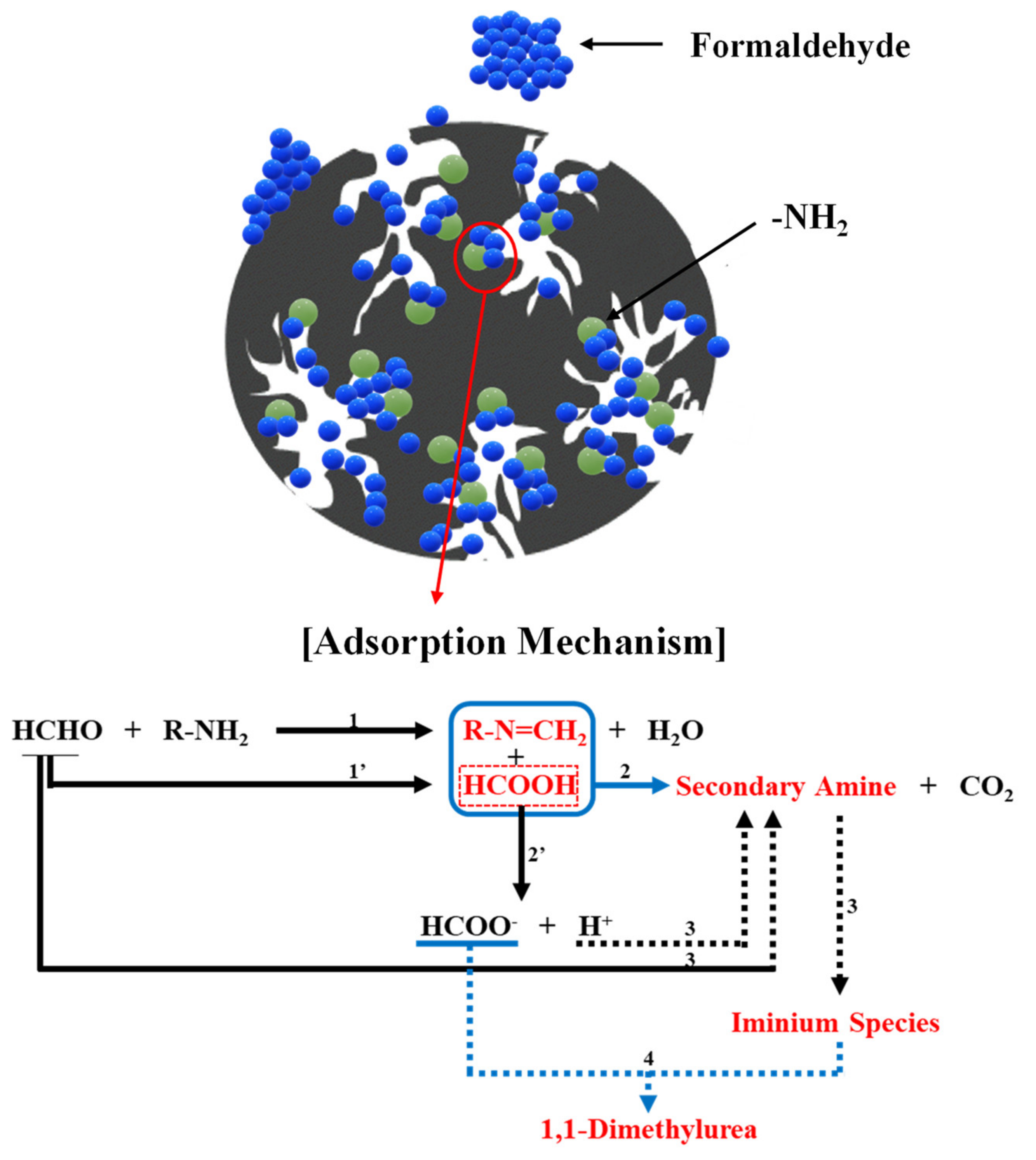
4. Approaches to Chemical Modifications of the AC Surface
| Chemical Structure | Interaction with AC | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
 Polyethyleneimine (PEI) | Physical bonding | Formaldehyde removal | [31] |
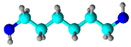 Hexamethylene diamine (HMDA) | Physical bonding and grafting; it was reported that the chemical reaction between HMDA and AC may be dominant | Formaldehyde removal | [57] |
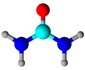 Urea | Physical bonding; formaldehyde and nitric acid were co-impregnated | Formaldehyde removal | [60] |
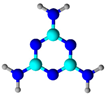 Melamine | Grafting; melamine was used as an intermediate to grow structure with covalent organic polymer | Organic dyes and metals adsorption | [62] |
 Diethylene Triamine (DETA) | Grafting | Phenol removal in aqueous phase | [62] |
| Physical bonding | Formaldehyde removal | [64] | |
 P-aminobenzonic acid (PABA) | Physical bonding (deposition) | Formaldehyde removal | [65] |
 Etilenodiamina (ethylenediamine) | Grafting after nitric acid treatment | Formaldehyde removal | [66] |
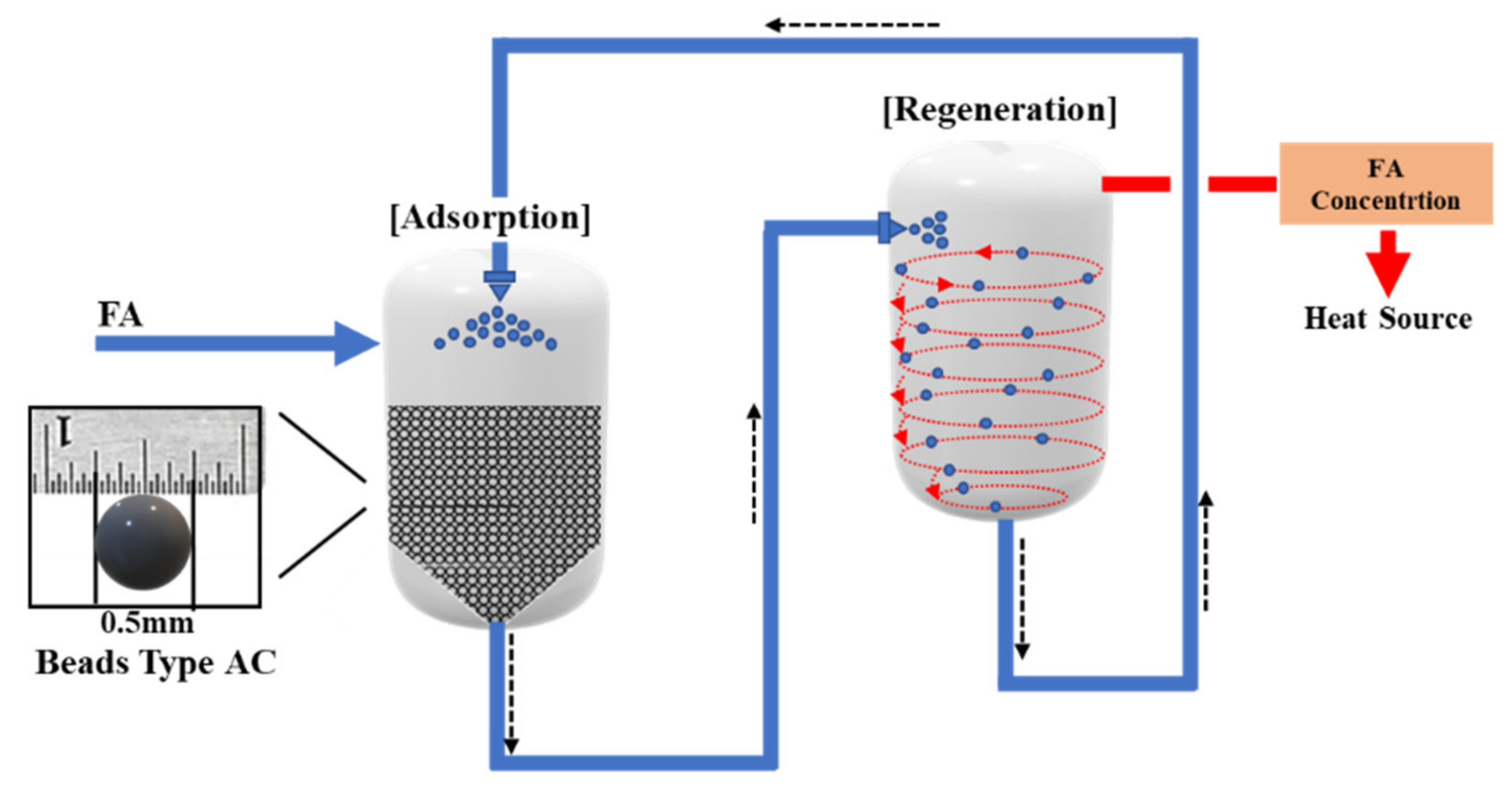
5. Challenge to Industrial Application
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.I.; Park, J.H.; Do Kim, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yim, J.H.; Jeon, J.K.; Park, S.H.; Park, Y.K. Comparison of removal ability of indoor formaldehyde over different materials functionalized with various amine groups. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Nie, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Hao, Z. Characterization and assessment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions from typical industries. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Creamer, A.E.; Cao, C.; Li, Y. Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemon, S.M.; Walker, C.M.; Alter, M.J.; Yi, M. IARAC Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans/world health organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2007, 1, 165–221. [Google Scholar]
- McGwin, J.G.; Lienert, J.; Kennedy, J.I. Formaldehyde exposure and asthma in children: A systemic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salthammer, T.; Sibel, M.; Rainer, M. Formaldehyde in the Indoor Environment. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2536–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ji, J.; Huang, H.; He, M. Efficient activation of Pd/CeO2 catalyst by non-thermal plasma for complete oxidation of indoor formaldehyde at room temperature. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; Nallathambi, G. Indoor formaldehyde removal by catalytic oxidation, adsorption and nanofibrous membranes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2551–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guieysse, B.; Hort, C.; Platel, V.; Munoz, R.; Ondarts, M.; Revah, S. Biological treatment of indoor air for VOC removal: Potential and challenges. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J.; Jiang, C. Few-layered graphene-like boron nitride: A highly efficient adsorbent for indoor formaldehyde removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Zhang, J.S. On the performance and mechanisms of formaldehyde removal by chemi-sorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Miyawaki, J.; Shiratori, N.; Yoon, S.H.; Jang, J. Toward an effective adsorbent for polar pollutants: Formaldehyde adsorption by activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Hayashi, A.; Eguchi, T.; Nakamura, N.; Tsuhako, M. Adsorption of formaldehyde by polyamine-intercalated α-zirconium phosphate. Solid State Sci. 2002, 4, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Yan, H. Novel silicone-based polymer containing active methylene designed for the removal of indoor formaldehyde. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qiao, W.; Yoon, S.H.; Mochida, I.; Guo, A.; Liu, L. Removal of formaldehyde at low concentration using various activated carbon fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuda, S.; Virote, B. Adsorption of formaldehyde vapor by amine-functionalized mesoporous silica materials. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Meng, T.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. CNT-enhanced amino-functionalized graphene aerogel adsorbent for highly efficient removal of formaldehyde. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xue, F.; Sun, Q.; Yue, R.; Lin, D. Adsorption of volatile organic compounds by metal-organic frameworks MOF-177. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Chen, Q.; Sui, Z.Y.; Pan, L.; Yu, J.; Han, B.H. Preparation and adsorption performance of cross-linked porous polycarbazoles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16181–16189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokry, H.; Elkady, M.; Hamad, H. Nano activated carbon from industrial mine coal as adsorbents for removal of dye from simulated textile wastewater: Operational parameters and mechanism study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4477–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wara, D.P.R.; Wahyuni, S.; Feinnudin, A. Thermodynamics of Formaldehyde Removal by Adsorption onto Nanosilver Loaded Bamboo-Based Activated Carbon. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 890, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Khaleghi, H.; Esmaeili, H.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Ramavandi, B. Date seed activated carbon decorated with CaO and Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a reusable sorbent for removal of formaldehyde. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, E.M.; Katz, L.E.; Speitel, G.E., Jr.; Ramirez, D. Gas-phase formaldehyde adsorption isotherm studies on activated carbon: Correlations of adsorption capacity to surface functional group density. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6498–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhou, J. MnO2-loaded activated carbon and its adsorption of formaldehyde. BioResources 2019, 14, 7193–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, X.Z.; Shiue, A.; Huang, P.H.; Zhou, B. Characterization and adsorption capacity of potassium permanganate used to modify activated carbon filter media for indoor formaldehyde removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28525–28545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, F.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, K. Amino-Decorated Activated Carbon Fibers with Efficient Static Adsorptivity for Low-Concentration Formaldehyde Gas in a Confined Space. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengga, W.D.P.; Suibandriyo, M.; Nasikin, M. Adsorptive removal of formaldehyde by chemically bamboo activated carbon with addition of Ag nanoparticle: Equilibrium and kinetic. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 59, 04004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiue, A.; Hu, S.C.; Tseng, C.H.; Chuang, C.M.; Leggett, G. Assessment of adsorptive filter for removal of formaldehyde from indoor air. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 3147–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.M.; Hu, S.C.; Shiue, A.; Lee, P.Y.; Leggett, G. Adsorption of silver nano-particles modified activated carbon filter media for indoor formaldehyde removal. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 757, 137864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengga, W.D.P.; Sudibandriyo, M.; Nasikin, M. Adsorption of low-concentration formaldehyde from air by silver and copper nano-particles attached on bamboo-based activated carbon. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2013, 4, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Ding, F.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Cui, L. Efficient removal of formaldehyde by polyethyleneimine modified activated carbon in a fixed bed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18109–18116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratuito, M.K.B.; Panyathanmaporn, T.; Chumnanklang, R.A.; Sirinuntawittaya, N.B.; Dutta, A. Production of activated carbon from coconut shell: Optimization using response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4887–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budianto, A.; Kusdarini, E.; Effendi, S.S.W.; Aziz, M. The production of activated carbon from Indonesian mangrove charcoal. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 462, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Zhang, J.S. Critical review of catalytic oxidization and chemisorption methods for indoor formaldehyde removal. Hvac&R Res. 2011, 17, 476–503. [Google Scholar]
- de Falco, G.; Li, W.; Cimino, S.; Bandosz, T.J. Role of sulfur and and nitrogen surface groups in adsorption of formaldehyde on nanoporous carbons. Carbon 2018, 138, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.J.; Yoo, M.J.; Tsang, D.C.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.H. High-performance materials for effective sorptive removal of formaldehyde in air. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
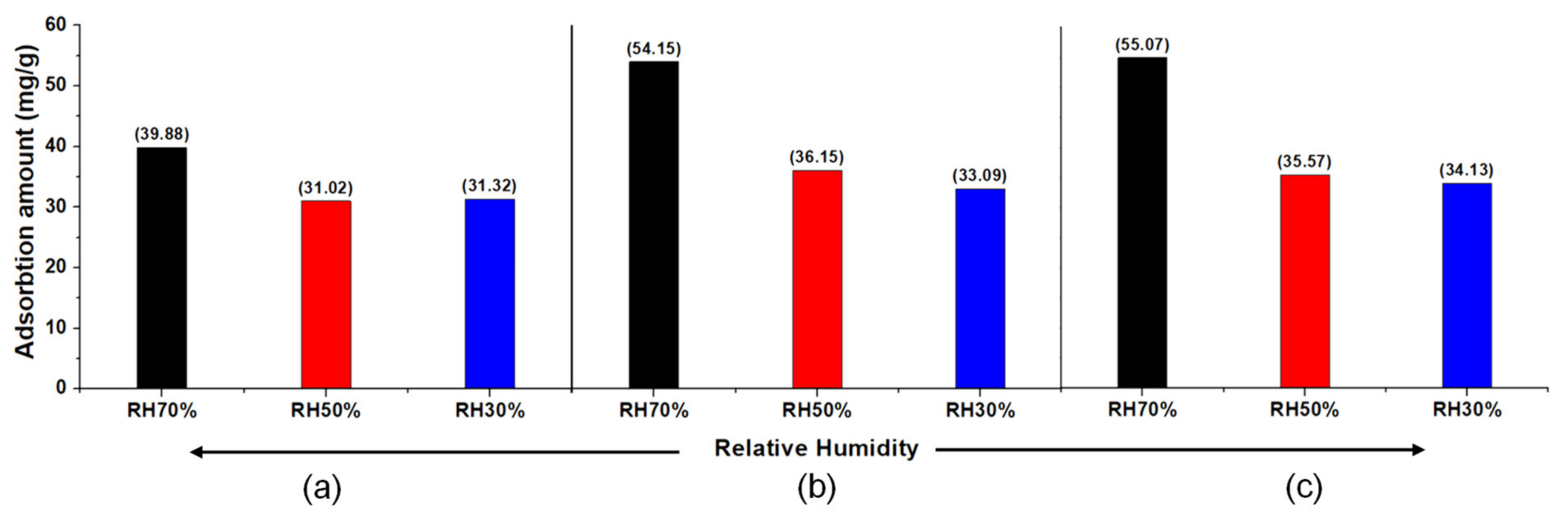
- Jing, L.I.; Zhong, L.I.; Bing, L.I.U.; Qibin, X.I.A.; Hongxia, X.I. Effect of relative humidity on adsorption of formaldehyde on modified activated carbons. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 16, 871–875. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, W.K.; Yang, C.H. Granular-activated carbon adsorption followed by annular-type photocatalytic system for control of indoor aromatic compounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Marin, F.; Fairen-Jimenez, D.; Moreno-Castilla, C. Carbon aerogels from gallic acid–resorcinol mixtures as adsorbents of benzene, toluene and xylenes from dry and wet air under dynamic conditions. Carbon 2009, 47, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L. Adsorption effect of nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus surface functional group on formaldehyde at ambient temperature: Experiments associated with calculations. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Shiratori, N.; Lee, G.H.; Miyawaki, J.; Mochida, I.; Yoon, S.H.; Jang, J. Activated carbon nanofiber produced from electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber as a highly efficient formaldehyde adsorbent. Carbon 2010, 48, 4248–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Falco, G.; Barczak, M.; Montagnaro, F.; Bandosz, T.J. A New generation of surface active carbon textiles as reactive adsorbents of indoor formaldehyde. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8066–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz Torres, J.; Royer, S.; Bellat, J.P.; Giraudon, J.M.; Lamonier, J.F. Formaldehyde: Catalytic oxidation as a promising soft way of elimination. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, Y. Removal of formaldehyde from the indoor environment using porous carbons and silicas. Recent Innov. Chem. Eng. 2020, 13, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, M.; Chen, L. Coal-based granular activated carbon loaded with MnO2 as an efficient adsorbent for removing formaldehyde from aqueous solution. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahed, M.; Jafari, D.; Esfandyari, M. Adsorption of formaldehyde from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Garcia, M.; Fernandez-Morales, I.; Lopez-Garzon, F.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Perez-Mendoza, M. On the Adsorption of Formaldehyde at High Temperatures and Zero Surface Coverage. Langmuir 1999, 15, 3226–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarawal, M.; Manan, D.; Upadhayaya, S. Adsorption of formaldehyde on treated activated carbon and activated alumina. Curr. World Environ. 2011, 6, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, H.; Qu, Z.; He, M.; Tang, Z.; Lai, S.; Wang, Z. The effect of oxygen-containing functional groups on formaldehyde adsorption in solution on carbon surface: A density functional theory study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanada, S.; Kawasaki, N.; Nakamura, T.; Araki, M.; Isomura, M. Removal of formaldehyde by activated carbons containing amino groups. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 214, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Arafat, H.A.; Pinto, N.G. Effect of chemical surface heterogeneity on theadsorption mechanism of dissolved aromatics on activated carbon. Carbon 2000, 38, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, H.; Ang, H.M.; Tade, M.O. Adsorptive remediation of environmental pollutants using novel graphene-based nanomaterials. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrasheed, A.A.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Gambo, Y.; Ibrahim, M. Surface modification of activated carbon for adsorption of SO2 and NOx: A review of existing and emerging technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 1067–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ma, X.; Zha, Q.; Kim, K.; Chen, Y.; Song, C. Maximizing the number of oxygen-containing functional groups on activated carbon by using ammonium persulfate and improving the temperature-programmed desorption characterization of carbon surface chemistry. Carbon 2011, 49, 5002–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, F.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, B. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photong, S.; Boonamnuayvitaya, V. Enhancement of formaldehyde degradation by amine functionalized silica/titania films. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, T. Removal of low-concentration formaldehyde in air by adsorption on activated carbon modified by hexamethylene diamine. Carbon 2011, 49, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar]
- Shalbafan, A.; Hassannejad, H.; Rahmaninia, M. Formaldehyde adsorption capacity of chitosan derivatives as bio-adsorbents for wood-based panels. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 102, 102669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, B.; Ferrer, N.; Sempere, J.; Gonzalez-Olmos, R. A key parameter on the adsorption of diluted aniline solutions with activated carbons: The surface oxygen content. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, D.-Y.; Shimohara, T.; Nakabayashi, K.; Miyawaki, J.; Park, J.-I.; Yoon, S.-H. Urea/nitric acid co-impregnated pitch-based activated carbon fiber for the effective removal of formaldehyde. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 80, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mines, P.D.; Thirion, D.; Uthuppu, B.; Hwang, Y.; Jakobsen, M.H.; Andersen, H.R.; Yavuz, C.T. Covalent organic polymer functionalization of activated carbon surfaces through acyl chloride for environmental clean-up. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleh, T.A.; Adio, S.O.; Asif, M.; Dafalla, H. Response surface optimization and statistical analysis of phenols adsorption on diethylenetriamine-modified activated carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.-Y.; Nakabayashi, K.; Shimohara, T.; Morio, U.; Mochida, I.; Miyawaki, J.; Jeon, Y.; Park, J.-I.; Yoon, S.-H. Behaviors of cellulose-bsed activated carbon fiber for acetaldehyde adsorption at low concentration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baur, G.B.; Spring, J.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Amine functionalized activated carbon fibers as effective structured adsorbents for formaldehyde removal. Adsorption 2018, 24, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Pan, D.; Zheng, J. Formaldehyde removal by Rayon-based activated carbon fibers modified by p-aminobenzoic acid. Cellulose 2010, 17, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Huang, X.; Xiang, L. Removal of formaldehyde using the aminated activated carbon by etilenodiamina. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 311, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.T.; Gillespie, H.B.; Weisshaus, S.Z. The action of formaldehyde on amines and amino acids1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 4571–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, C. Modification of the wood-plastic composite for enhancement of formaldehyde clearance and the 3D printing application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, R.; Xie, D.; Xie, Y.; Wu, H.; Mei, Y. Amine-Containing Resin for Coating with Excellent Formaldehyde Removal Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 10674–10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangwanwatana, W.; Saiwan, C.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P. Study of CO2 adsorption using adsorbent modified with piperazine. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 35, 403–408. [Google Scholar]

| Methods | Technology | Concentration | Operating Temp. | Operating Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery | Adsorption | Low, High | Ambient | Acceptable |
| Membrane | High | Ambient | High cost of material | |
| Condensation | High | Ambient and cryogenic | High cost of energy | |
| Destruction | Thermal Oxidation | High | ~815 °C | High cost of Energy |
| Catalysis | Low, High | Ambient, 200~500 °C | Acceptable | |
| Photo catalysis | Low, High | Ambient | Costly dopants required | |
| Non-thermal plasma w/wo catalyst | Low | Ambient | High cost of system assembly | |
| Biological/Botanical filtration | Low | - | - |
| Modification AC | Operating Conditions: T (°C)/Humidity (%)/pH | Ce, Feed Concentration (ppm) of FA Up to | Qe (mg/g) | Ce vs. Qe, Linear/Nonlinear (Isotherm Model) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag-AC | 25, 35, 45, 60/-/- | 1000 | <120 | Nonlinear (Langmuir) | [21] |
| CaO-AC Fe3O4-AC | 25/-/2–10 | 10 | <20 | Nonlinear (Freundlich) | [22] |
| Granular AC and ACF | 26/-/- | 35 | <450 | Nonlinear (Qi-LeVan) | [23] |
| MnO2-AC | 25/-/- | 0.2 | <0.1 | Nonlinear (Langmuir) | [24] |
| Potassium-AC | 28 ± 2/40 ± 2/- | 0.9 | <0.4 | Nonlinear (Freundlich and Langmuir) | [25] |
| * EDA-AC | 25/-/- | 2.45 | <2.5 | Nonlinear (Langmuir) | [26] |
| Ag-AC | 25/-/- | 14 | <7 | Linear (Langmuir and Freundlich) | [27] |
| AC adsorptive filter media | 28 ± 2/40 ± 2/- | 0.8 | <0.75 | Nonlinear (Langmuir) | [28] |
| Ag-AC | Room/-/- | 0.9 | <35 | Linear (Langmuir) | [29] |
| Ag-AC, Cu-AC | 25/-/- | 20 | <0.6 | Linear (Langmuir and Freundlich) | [30] |
| Modification AC | Adapted Model | Concentration (ppm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaO-AC Fe3O4-AC | Pseudo-second-order | 5–50 | [22] |
| Potassium-AC | Pseudo-second-order | 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.9 | [25] |
| EDA-AC | Pseudo-first-order | 2.45, 8.15 | [26] |
| Bangham | |||
| Ag-AC | Pseudo-second-order | 0~14 | [27] |
| AC adsorptive filter media | Pseudo-second-order | 0.25, 0.56, 0.79 | [28] |
| * PEI-AC | Pseudo-second-order | 50 | [31] |
| Chemicals | Toxic/Non-Toxic | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethyleneimine | Toxic | [31] |
| Dicyandiamide | Toxic | [42] |
| Thiourea | Toxic | [42] |
| Penicillin G | Toxic | [42] |
| Nitric Acid/Sulfuric Acid | Toxic | [50] |
| Hexamethylene Diamine | Toxic | [57] |
| Urea | Non-toxic | [60] |
| Melamine | Non-toxic | [62] |
| Diethylene triamine | Toxic | [64] |
| P-aminobenzoic acid | Toxic | [65] |
| Etilenodiamina | Toxic | [66] |
| Hexamethylenetetramine | Toxic | [67] |
| 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane | Toxic | [68] |
| Diallylamine | Toxic | [69] |
| Piperazine | Non-toxic | [70] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Y.-J.; Jo, H.-K.; Jang, M.-H.; Ma, X.; Jeon, Y.; Oh, K.; Park, J.-I. A Brief Review of Formaldehyde Removal through Activated Carbon Adsorption. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105025
Kang Y-J, Jo H-K, Jang M-H, Ma X, Jeon Y, Oh K, Park J-I. A Brief Review of Formaldehyde Removal through Activated Carbon Adsorption. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(10):5025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105025
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Yu-Jin, Hyung-Kun Jo, Min-Hyeok Jang, Xiaoliang Ma, Yukwon Jeon, Kyeongseok Oh, and Joo-Il Park. 2022. "A Brief Review of Formaldehyde Removal through Activated Carbon Adsorption" Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 5025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105025
APA StyleKang, Y.-J., Jo, H.-K., Jang, M.-H., Ma, X., Jeon, Y., Oh, K., & Park, J.-I. (2022). A Brief Review of Formaldehyde Removal through Activated Carbon Adsorption. Applied Sciences, 12(10), 5025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105025