The Relationship between Personality and Postural Control in Young Adults—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Nonlinear Parameters Calculation
2.2.1. Sample Entropy (SampEn)
- (1)
- From a vector , two sequences of m consecutive points— and —were selected to compute the maximum distance and compared to tolerance, r, for repeated sequence counting, according to:where the tolerance r is equal to 0.1∼0.2 × SD and SD is the standard deviation of XN [36].
- (2)
- is the average amount of for and is the average of m + 1 consecutive points; thus, sample entropy can be computed as follows:
2.2.2. Fractal Dimension (FD)
- (1)
- For one dimensional time series: , a new k time series can be formed as follows:where k and m are integers, is the integral part of , k indicates the discrete time interval between points, whereas m = 1, 2, …, k.
- (2)
- The length of each new time series can be defined as follows:where N is length of the original time series X.
- (3)
- The length of the curve for the time interval k is defined as the average of the k values L(m, k), for m = 1, 2, …, k:
2.2.3. The Lyapunov Exponent (LyE)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Big-Five Personality Group Characteristics
3.2. Effects of Personality and Trial on Nonlinear Parameter Results
3.3. Correlations of Nonlinear within Trials Coefficients with Personality Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35, ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazkiewicz, M.; Kedziorek, J.; Hadamus, A. The Impact of Visual Input and Support Area Manipulation on Postural Control in Subjects after Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture. Entropy 2021, 23, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedziorek, J.; Blazkiewicz, M. Nonlinear Measures to Evaluate Upright Postural Stability: A Systematic Review. Entropy 2020, 22, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiszomirska, I.; Kaczmarczyk, K.; Blazkiewicz, M.; Wit, A. The Impact of a Vestibular-Stimulating Exercise Regime on Postural Stability in People with Visual Impairment. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 136969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kędziorek, J.; Błażkiewicz, M. Effect of voluntary muscle contraction on postural stability in healthy adults. Adv. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobera, M.; Siedlecka, B.; Syczewska, M. Posture control development in children aged 2–7 years old, based on the changes of repeatability of the stability indices. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 491, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Barbosa, R.; Vieira, M.F. Postural Control of Elderly Adults on Inclined Surfaces. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadamus, A.; Bialoszewski, D.; Blazkiewicz, M.; Kowalska, A.J.; Urbaniak, E.; Wydra, K.T.; Wiaderna, K.; Boratynski, R.; Kobza, A.; Marczynski, W. Assessment of the Effectiveness of Rehabilitation after Total Knee Replacement Surgery Using Sample Entropy and Classical Measures of Body Balance. Entropy 2021, 23, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażkiewicz, M. Nonlinear measures in posturography compared to linear measures based on yoga poses performance. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2020, 22, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briñol, P.; Petty, R.E.; Wagner, B. Body posture effects on self-evaluation: A self-validation approach. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 39, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dael, N.; Mortillaro, M.; Scherer, K.R. Emotion expression in body action and posture. Emotion 2012, 12, 1085–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaback, M.; Cleworth, T.W.; Carpenter, M.G.; Adkin, A.L. Personality traits and individual differences predict threat-induced changes in postural control. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 40, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochat, S.; Büla, C.J.; Martin, E.; Seematter-Bagnoud, L.; Karmaniola, A.; Aminian, K.; Piot-Ziegler, C.; Santos-Eggimann, B. What is the relationship between fear of falling and gait in well-functioning older persons aged 65 to 70 years? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R.; Campbell, A.D.; Adkin, A.L.; Carpenter, M.G. The relationship between fear of falling and human postural control. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, L.J.; Carpenter, M.G.; Frank, J.S. Task-specific measures of balance efficacy, anxiety, and stability and their relationship to clinical balance performance. Gait Posture 2008, 27, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolmont, B.; Gangloff, P.; Vouriot, A.; Perrin, P.P. Mood states and anxiety influence abilities to maintain balance control in healthy human subjects. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 329, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.A.; Polych, M.A.; Doan, J.B. The effect of anxiety on the regulation of upright standing among younger and older adults. Gait Posture 2006, 24, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, N.L.; Luberto, C.M.; Avallone, K.; Kraemer, K.; McLeish, A.; Riley, M.A. Characteristics of postural control among young adults with asthma. J. Asthma 2015, 52, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerdink, M.; Hlavackova, P.; Vuillerme, N. Center-of-pressure regularity as a marker for attentional investment in postural control: A comparison between sitting and standing postures. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2011, 30, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.H.; Buffett-Jerrott, S.E.; Kokaram, R. Heartbeat awareness and heart rate reactivity in anxiety sensitivity: A further investigation. J. Anxiety Disord. 2001, 15, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, T.M.; Volchan, E.; Imbiriba, L.A.; Rodrigues, E.C.; Oliveira, J.M.; Oliveira, L.F.; Lutterbach, L.G.; Vargas, C.D. A freezing-like posture to pictures of mutilation. Psychophysiology 2005, 42, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinetti, L.D.; Imbiriba, L.A.; Azevedo, T.M.; Vargas, C.D.; Volchan, E. Postural modulation induced by pictures depicting prosocial or dangerous contexts. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 410, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Attilio, M.; Rodolfino, D.; Abate, M.; Festa, F.; Merla, A. Effects of Affective Picture Viewing on Postural Control in Healthy Male Subjects. CRANIO 2013, 31, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strus, W.; Cieciuch, J.; Rowiński, T. Polska adaptacja kwestionariusza IPIP-BFM-50 do pomiaru pięciu cech osobowości w ujęciu leksykalnym. Ann. Psychol. 2014, 17, 327–346. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, C.; Jackson, J. Five-Factor Model of Personality. J. Res. Personal. 2013, 42, 1285–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Shariati, M.; Bakhtiari, S. Comparison of Personality Characteristics Athlete and Non-Athlete Student, Islamic Azad University of Ahvaz. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 30, 2312–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McKelvie, S.; Lemieux, P.; Stout, D. Extraversion and Neuroticism in Contact Athletes, No Contact Athletes and Non-athletes: A Research Note. Athl. Insight 2003, 5, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Eagleton, J.R.; McKelvie, S.J.; de Man, A. Extraversion and neuroticism in team sport participants, individual sport participants, and nonparticipants. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2007, 105, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimond, S.; Massrieh, W. Intricate Correlation between Body Posture, Personality Trait and Incidence of Body Pain: A Cross-Referential Study Report. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska-Maszkowska, B.; Borzucka, D.; Rogowska, A. Impact of personality on postural control in football players-a pilot study. Probl. Hig. Epidem. 2018, 99, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Rusnakova, K.G.; Gerych, D.; Stehlik, M. Relationship between Personality Traits and Postural Stability among Czech Military Combat Troops. Int. J. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 2021, 15, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Higginson, C.I.; Valenti, M.; Ibrahim, K.; Knarr, B.A.; Ryan, R.; Higginson, J.S. Neuroticism and Extraversion Are Related to Changes in Postural Stability During Anatomically-Related Cognitive Tasks. J. Mot. Behav. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghofrani, M.; Olyaei, G.; Talebian, S.; Bagheri, H.; Malmir, K. Test-retest reliability of linear and nonlinear measures of postural stability during visual deprivation in healthy subjects. J. Phys. Sci. 2017, 29, 1766–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Promsri, A.; Haid, T.; Federolf, P. How does lower limb dominance influence postural control movements during single leg stance? Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, L.R. The development of markers for the Big-Five factor structure. Psychol. Assess. 1992, 4, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Approach to an irregular time series on the basis of the fractal theory. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1988, 31, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.L.A.; Dugan, E.L.; Humphries, B.; Newton, R.U. Discriminating between elderly and young using a fractal dimension analysis of centre of pressure. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2004, 1, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Physica 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, W. Wolf Lyapunov Exponent Estimation from a Time Series. MATLAB Central File Exchange. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/48084-wolf-lyapunov-exponent-estimation-from-a-time-series2022 (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Bernards, J.R.; Sato, K.; Haff, G.G.; Bazyler, C.D. Current research and statistical practices in sport science and a need for change. Sports 2017, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adkin, A.L.; Carpenter, M.G. New Insights on Emotional Contributions to Human Postural Control. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainaut, J.P.; Caillet, G.; Lestienne, F.G.; Bolmont, B. The role of trait anxiety on static balance performance in control and anxiogenic situations. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, D. Scalar Equivalence of OPQ32:Big Five Profiles of 31 Countries. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 2013, 44, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omid Khayat, M.S. Complex Feature Analysis of Center of Pressure Signal for Age-Related Subject Classification. Ann. Mil. Health Sci. Res. 2014, 12, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Redfern, M.S.; Furman, J.M.; Jacob, R.G. Visually induced postural sway in anxiety disorders. J. Anxiety Disord. 2007, 21, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumas, M.; Smolders, C.; Brunfaut, E.; Bouckaert, F.; Krampe, R.T. Dual task performance of working memory and postural control in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychology 2012, 26, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleworth, T.W.; Horslen, B.C.; Carpenter, M.G. Influence of real and virtual heights on standing balance. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horslen, B.C.; Carpenter, M.G. Arousal, valence and their relative effects on postural control. Exp. Brain Res. 2011, 215, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumas, M.; Morsanyi, K.; Young, W.R. Cognitively and socially induced stress affects postural control. Exp. Brain Res. 2018, 236, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geh, C.L.; Beauchamp, M.R.; Crocker, P.R.; Carpenter, M.G. Assessed and distressed: White-coat effects on clinical balance performance. J. Psychosom. Res. 2011, 70, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffalt, P.C.; Spedden, M.E.; Geertsen, S.S. Dynamics of postural control during bilateral stance—Effect of support area, visual input and age. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2019, 67, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
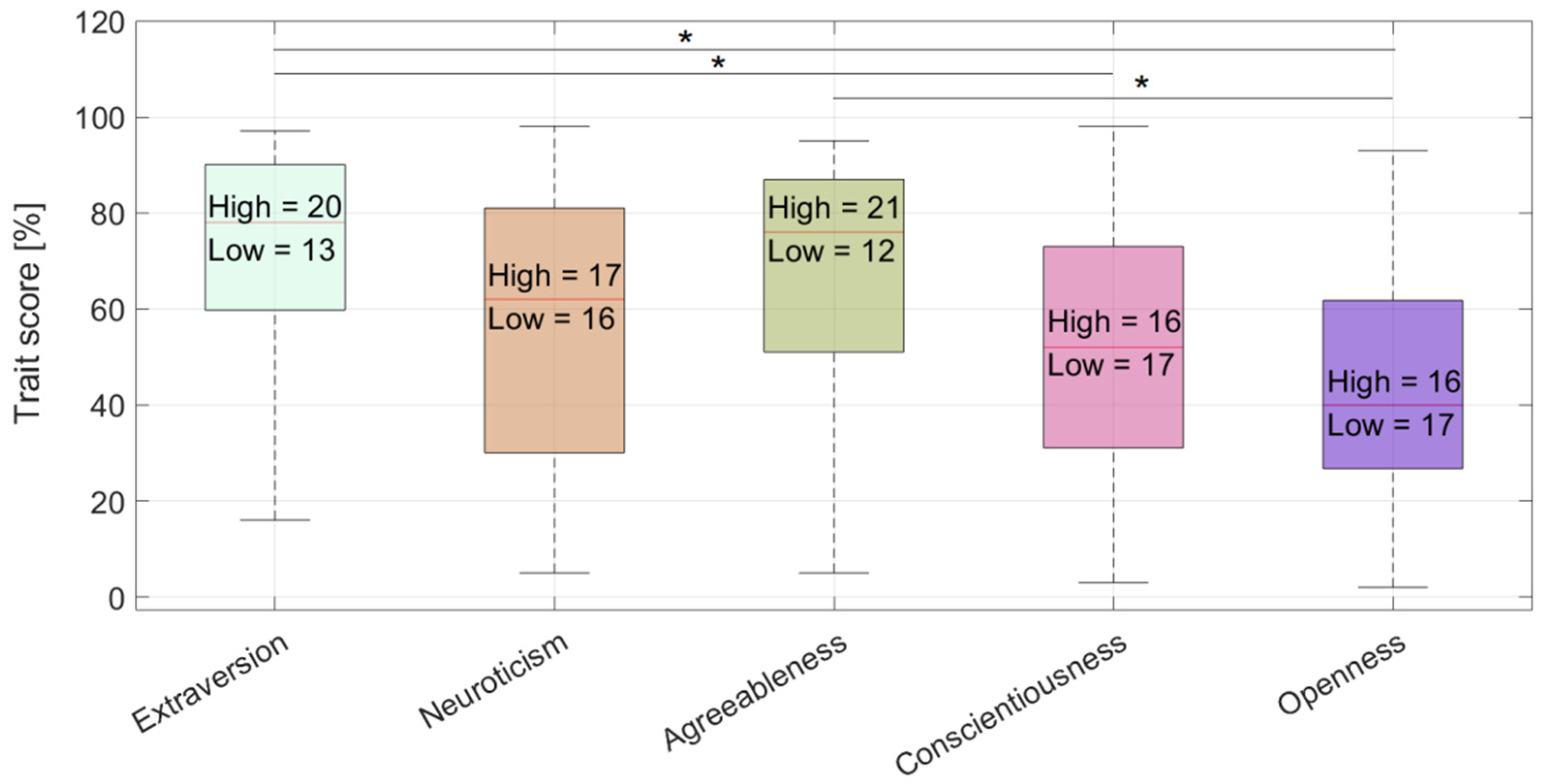
| Factor Label | Descriptions | High Score | Low Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factor I— Extraversion | Trait that describes a person’s assertiveness, emotional expression, and comfort levels in social situations. |
|
|
| Factor II— Neuroticism (Emotional Stability) | Refers to a person’s ability to remain stable and balanced. |
|
|
| Factor III— Agreeableness | Trait that describes a person’s overall kindness, affection levels, trust, and sense of altruism. |
|
|
| Factor IV— Conscientiousness | Trait that describes a person’s ability to self-discipline and self-control. |
|
|
| Factor V— Openness (Intellect/ Imagination) | Trait that describes a person’s preference for imagination, artistic, and intellectual activities. |
|
|
| Size of Correlation (Range) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| (0.90, 1.00); (−0.90, −1.00) | Very high positive (negative correlation) |
| (0.70, 0.90); (−0.70, −0.90) | High positive (negative) correlation |
| (0.50, 0.70); (−0.50, −0.70) | Moderate positive (negative) correlation |
| (0.30, 0.50); (−0.30, −0.50) | Low positive (negative) correlation |
| (0, 0.30); (0, −0.30) | Negligible correlation |
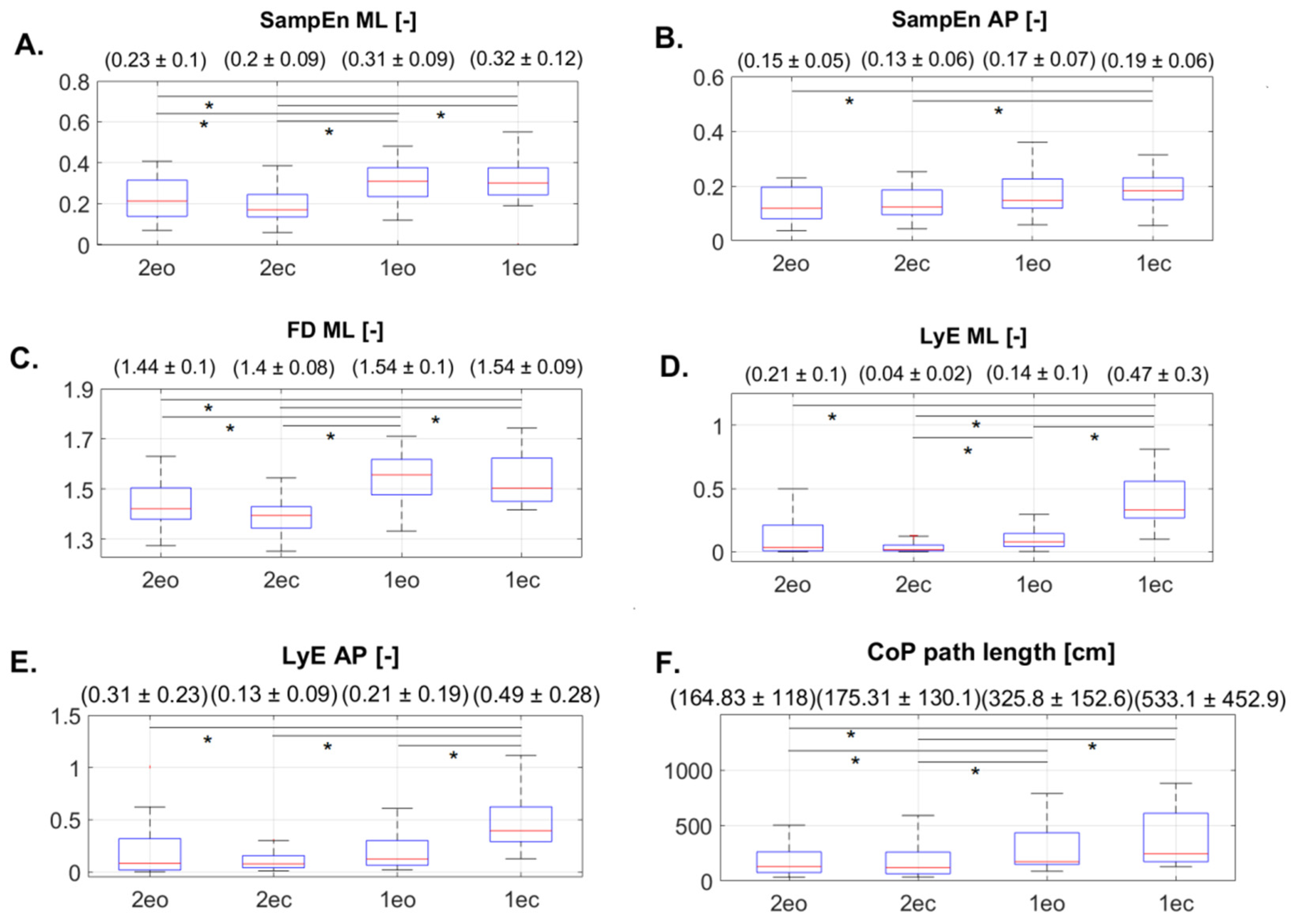
| Trial | Correlations | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 2eo | Agreeableness and SampEn_ML (r = −0.37) | Low negative association |
| Openness and SampEn_AP (r = −0.44) | Low negative association | |
| 2ec | Neuroticism and FD_ML (r = 0.47) | Low positive association |
| Conscientiousness and FD_ML (r = −0.34) | Low negative association | |
| Agreeableness and LyE_ML (r = −0.41) | Low negative association | |
| 1eo | Neuroticism and FD_ML (r = −0.50) | Moderate negative association |
| Openness and LyE_AP (r = 0.53) | Moderate positive association | |
| Openness and LyE_ML (r = 0.59) | Moderate positive association | |
| 1ec | Openness and LyE_AP (r = 0.37) | Low positive association |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Błażkiewicz, M.; Kędziorek, J.; Wit, A. The Relationship between Personality and Postural Control in Young Adults—A Pilot Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104978
Błażkiewicz M, Kędziorek J, Wit A. The Relationship between Personality and Postural Control in Young Adults—A Pilot Study. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(10):4978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104978
Chicago/Turabian StyleBłażkiewicz, Michalina, Justyna Kędziorek, and Andrzej Wit. 2022. "The Relationship between Personality and Postural Control in Young Adults—A Pilot Study" Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 4978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104978
APA StyleBłażkiewicz, M., Kędziorek, J., & Wit, A. (2022). The Relationship between Personality and Postural Control in Young Adults—A Pilot Study. Applied Sciences, 12(10), 4978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104978








