Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion: Formulation Design, Evaluation and Antihyperalgesic Activity in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of Ternary Phase Diagrams
2.2. Preparation of Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
2.3. Characterization of Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
2.3.1. Macroscopic Appearance
2.3.2. Determination of Chrysin Content and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.3.3. Physicochemical Parameters
2.3.4. Polarized Light Microscopy
2.3.5. Droplet Size, Zeta Potential and Polydispersity Index
2.3.6. Thermodynamic Stability
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release from Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
Kinetic Modeling of Drug Release from Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
2.5. Anti-Hyperalgesic Activity of Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
2.5.1. Animals
2.5.2. Carrageenan-Induced Inflammation
Carrageenan-Induced Mechanical Hyperalgesia
Cytokines Assays
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ternary Phase Diagram and Preparation of Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
3.2. Characterization of Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
3.2.1. Macroscopic Appearance, Chrysin Content, and Microemulsion Encapsulation Efficiency
3.2.2. Physicochemical Parameters and Polarized Light Microscopy
3.2.3. Droplet Size and Zeta Potential
3.2.4. Thermodynamic Stability
3.3. Kinetics of In Vitro Drug Release from Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
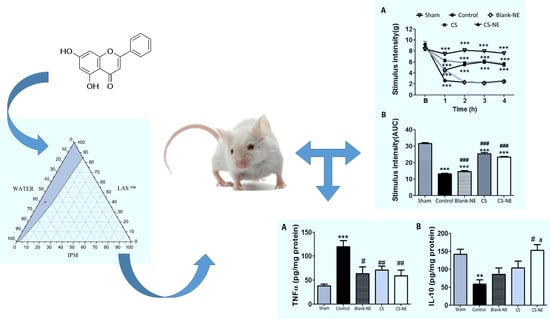
3.4. Antinociceptive Activity of Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tartaro, G.; Mateos, H.; Schirone, D.; Angelico, R.; Palazzo, G. Microemulsion microstructure(s): A tutorial review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakshit, A.K.; Naskar, B.; Moulik, S.P. Commemorating 75 years of microemulsion. Curr. Sci. 2019, 116, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Rathod, H. Microemulsions: A Potential Novel Drug Delivery System. Acta Sci. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 1, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, G.; Mehta, S.K. Developments of Polysorbate (Tween) based microemulsions: Preclinical drug delivery, toxicity and antimicrobial applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 134–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouri, A.; Legrand, P.; El Ghzaoui, A.; Dorandeu, C.; Maurel, J.C.; Devoisselle, J.M. Formulation, physicochemical characterization and stability study of lithium-loaded microemulsion system. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouri, A.; Diat, O.; Lerner, D.A.; El Ghzaoui, A.; Ajovalasit, A.; Dorandeu, C.; Maurel, J.C.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Legrand, P. Water solubilization capacity of pharmaceutical microemulsions based on Peceol®, lecithin and ethanol. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzecki, M.S.; Araujo, S.M.; Bortolotto, V.C.; de Paula, M.T.; Jesse, C.R.; Prigol, M. Hypolipidemic action of chrysin on Triton WR-1339-induced hyperlipidemia in female C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol. Reports 2014, 1, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pushpavalli, G.; Kalaiarasi, P.; Veeramani, C.; Pugalendi, K.V. Effect of chrysin on hepatoprotective and antioxidant status in d-galactosamine-induced hepatitis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 631, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, T.C.; Silva, J.C.; De Lima-Saraiva, S.R.G.; Ribeiro, F.P.R.D.A.; Pacheco, A.G.M.; De Freitas, R.M.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Quintans, J.D.S.S.; Mendes, R.L.; Almeida, J.R.G.D.S. The role of flavonoids on oxidative stress in epilepsy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 171756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H. Chrysin suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: Involvement of calcium, caspase-1 and nuclear factor-κB. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 254, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T.; Otake, Y.; Brubaker, J.A.; Walle, U.K.; Halushka, P.V. Disposition and metabolism of the flavonoid chrysin in normal volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 51, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timcheh-Hariri, A.; Balali-Mood, M.; Aryan, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Riahi-Zanjani, B. Toxic hepatitis in a group of 20 male body-builders taking dietary supplements. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3826–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viuda-Martos, M.; Ruiz-Navajas, Y.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A. Functional properties of honey, propolis, and royal jelly. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Sammarrae, K.W.A.; Ad’hiah, A.H.; Zucchetti, M.; Frapolli, R.; Bello, E.; Erba, E.; D’Incalci, M.; Bagnati, R. Chemical characterization of iraqi propolis samples and assessing their antioxidant potentials. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2415–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.Q.; Peng, S.M.; Hu, C.P.; Tan, L.F.; Yuan, Q.; Deng, H.W.; Li, Y.J. Synthesis, characterization and vasculoprotective effects of nitric oxide-donating derivatives of chrysin. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3020–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichichero, E.; Cicconi, R.; Mattei, M.; Canini, A. Chrysin-induced apoptosis is mediated through p38 and Bax activation in B16-F1 and A375 melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villar, I.C.; Jiménez, R.; Galisteo, M.; Garcia-Saura, M.F.; Zarzuelo, A.; Duarte, J. Effects of chronic chrysin treatment in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Khan, R.; Raza, M.; Khan, H.; Pervez, S.; De Feo, V.; Maione, F.; Mascolo, N. Suppression of inflammatory response by chrysin, a flavone isolated from Potentilla evestita Th. Wolf. in silico predictive study on its mechanistic effect. Fitoterapia 2015, 103, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.C.; Zhou, C.; Sherman, M.; Laughton, C.A.; Chen, S. Molecular basis of the inhibition of human aromatase (estrogen synthetase) by flavone and isoflavone phytoestrogens: A site-directed mutagenesis study. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambelunghe, C.; Rossi, R.; Sommavilla, M.; Ferranti, C.; Rossi, R.; Ciculi, C.; Gizzi, S.; Micheletti, A.; Rufini, S. Effects of Chrysin on Urinary Testosterone Levels in Human Males. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T. Absorption and metabolism of flavonoids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T. Methylation of dietary flavones increases their metabolic stability and chemopreventive effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5002–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.B.; Martins, A.O.B.P.B.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Cesário, F.R.A.S.; e Castro, F.F.; de Albuquerque, T.R.; Fernandes, M.N.M.; da Silva, B.A.F.; Quintans Júnior, L.J.; de Sousa Araújo, A.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of the essential oil obtained from Ocimum basilicum complexed with β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, W.A.; Cunha, T.M.; Parada, C.A.; Poole, S.; Cunha, F.Q.; Ferreira, S.H. Hypernociceptive role of cytokines and chemokines: Targets for analgesic drug development? Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 116–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, T.M.; Verri, W.A.; Silva, J.S.; Poole, S.; Cunha, F.Q.; Ferreira, S.H. A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabelo, T.K.; Guimarães, A.G.; Oliveira, M.A.; Gasparotto, J.; Serafini, M.R.; de Souza Araújo, A.A.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Gelain, D.P. Shikimic acid inhibits LPS-induced cellular pro-inflammatory cytokines and attenuates mechanical hyperalgesia in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintans, J.S.S.; Antoniolli, Â.R.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Santana-Filho, V.J.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. Natural products evaluated in neuropathic pain models—A systematic review. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wu, H.; Niu, F.; Yan, C.; Yang, X.; Jia, Y. Design of fenofibrate microemulsion for improved bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogerio, A.P.; Dora, C.L.; Andrade, E.L.; Chaves, J.S.; Silva, L.F.C.; Lemos-Senna, E.; Calixto, J.B. Anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin-loaded microemulsion in the airways allergic inflammatory model in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhai, W.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, R.; Liu, L.; Dai, J.; Gong, W.; Du, S.; Wu, Q. Curcumin-piperine mixtures in self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for ulcerative colitis therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathne, E.P.N.; Karunaratne, D.N.; Perera, A.D.L.C. Controlled release of diclofenac sodium in glycolipid incorporated micro emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik-Pastuszka, D.; Krzak, J.; Macikowski, B.; Berkowski, R.; Osiński, B.; Musiał, W. Evaluation of the release kinetics of a pharmacologically active substance from model intra-articular implants replacing the cruciate ligaments of the knee. Materials 2019, 12, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcanti, A.L.M.; Reis, M.Y.F.A.; Silva, G.C.L.; Ramalho, Í.M.M.; Guimarães, G.P.; Silva, J.A.; Saraiva, K.L.A.; Damasceno, B.P.G.L. Microemulsion for topical application of pentoxifylline: In vitro release and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoui, W.; Bolzinger, M.A.; Fenet, B.; Pelletier, J.; Valour, J.P.; Kalfat, R.; Chevalier, Y. Microemulsion microstructure influences the skin delivery of an hydrophilic drug. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Yadav, P.; Verma, A.; Pandit, J.K. Ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of microemulsion based transdermal delivery of E. coli specific T4 bacteriophage: A rationale approach to treat bacterial infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Wanderley Neto, A.; Moura, E.F.; Júnior, H.S.; Dantas, T.N.d.C.; Neto, A.A.D.; Gurgel, A. Preparation and application of self-assembled systems containing dodecylammonium bromide and chloride as corrosion inhibitors of carbon-steel. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 398, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.J.; Huang, Y.B.; Fang, J.W.; Fu, Y.S.; Wu, P.C. Preparation and evaluation of submicron-carriers for naringenin topical application. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 481, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, J.M.; Burgess, D.J. In vitro release testing methods for vitamin e nanoemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panapisal, V.; Charoensri, S.; Tantituvanont, A. Formulation of microemulsion systems for dermal delivery of silymarin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cojocaru, V.; Ranetti, A.E.; Hinescu, L.G.; Ionescu, M.; Cosmescu, C.; Poștoarcă, A.G.; Cinteză, L.O. Formulation and evaluation of in vitro release kinetics of Na3CaDTPA decorporation agent embedded in microemulsion-based gel formulation for topical delivery. Farmacia 2015, 63, 656–664. [Google Scholar]
- Pundir, S.; Badola, A.; Sharma, D. Sustained Release Matrix Technology and Recent Advance in Matrix Drug Delivery System: A Review. Int. J. Drug Res. Technol. 2013, 3, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- García, M.D.; Fernández, M.A.; Alvarez, A.; Saenz, M.T. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effect of the aqueous extract from leaves of Pimenta racemosa var. ozua (Mirtaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 91, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, R.C.; Simão Da Silva, K.A.B.; Bento, A.F.; Marcon, R.; Paszcuk, A.F.; Meotti, F.C.; Pianowski, L.F.; Calixto, J.B. Euphol, a tetracyclic triterpene produces antinociceptive effects in inflammatory and neuropathic pain: The involvement of cannabinoid system. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of extract and two isolated flavonoids of Carthamus tinctorius L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Waheed, I. Evaluation of anti-nociceptive, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activities of Artemisia scoparia hydromethanolic extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Inoue, H.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, T.K. Chrysin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression through the inhibition of nuclear factor for IL-6 (NF-IL6) DNA-binding activity. Fed. Eur. Biochem. Soc. 2005, 579, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Bi, M.G.; Du, G.H. Chrysin improves cognitive deficits and brain damage induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 680, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, F.L.; Zhao, G.B.; Li, J. Chrysin Suppressed Inflammatory Responses and the Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Pathway after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12270–12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, J.; Noboru, N.; Young, A.; Thomas, D. Pro and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10) in rat model of neuroma. Pathophysiology 2017, 24, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhitpanichkul, M.; Torre, O.M.; Gruen, J.; Walter, B.A.; Hecht, A.C.; Iatridis, J.C. Do mechanical strain and TNF-α interact to amplify pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human annulus fibrosus cells? J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ujhelyi, Z.; Kalantari, A.; Vecsernyés, M.; Róka, E.; Fenyvesi, F.; Póka, R.; Kozma, B.; Bácskay, I. The enhanced inhibitory effect of different antitumor agents in self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems on human cervical cancer HeLa cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 13226–13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M.; DePalo, V.A. Anti-inflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 117, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramalho, Í.M.d.M.; Bezerra, G.S.; Ostrosky, E.A.; Ferrari, M.; Oliveira, V.d.S.; Wanderley Neto, A.d.O.; Quintans, J.d.S.S.; Passos, F.R.S.; Heimfarth, L.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; et al. Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion: Formulation Design, Evaluation and Antihyperalgesic Activity in Mice. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010477
Ramalho ÍMdM, Bezerra GS, Ostrosky EA, Ferrari M, Oliveira VdS, Wanderley Neto AdO, Quintans JdSS, Passos FRS, Heimfarth L, Quintans-Júnior LJ, et al. Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion: Formulation Design, Evaluation and Antihyperalgesic Activity in Mice. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(1):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010477
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamalho, Ízola Morais de Medeiros, Gabriela Suassuna Bezerra, Elissa Arantes Ostrosky, Márcio Ferrari, Verônica da Silva Oliveira, Alcides de Oliveira Wanderley Neto, Jullyana de Souza Siqueira Quintans, Fabiolla Rocha Santos Passos, Luana Heimfarth, Lucindo José Quintans-Júnior, and et al. 2022. "Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion: Formulation Design, Evaluation and Antihyperalgesic Activity in Mice" Applied Sciences 12, no. 1: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010477
APA StyleRamalho, Í. M. d. M., Bezerra, G. S., Ostrosky, E. A., Ferrari, M., Oliveira, V. d. S., Wanderley Neto, A. d. O., Quintans, J. d. S. S., Passos, F. R. S., Heimfarth, L., Quintans-Júnior, L. J., Damasceno, B. P. G. d. L., Converti, A., & de Lima, Á. A. N. (2022). Chrysin-Loaded Microemulsion: Formulation Design, Evaluation and Antihyperalgesic Activity in Mice. Applied Sciences, 12(1), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010477