Flexible Sample Environments for the Investigation of Soft Matter at the European Spallation Source: Part I—The In Situ SANS/DLS Setup
Abstract
1. Introduction
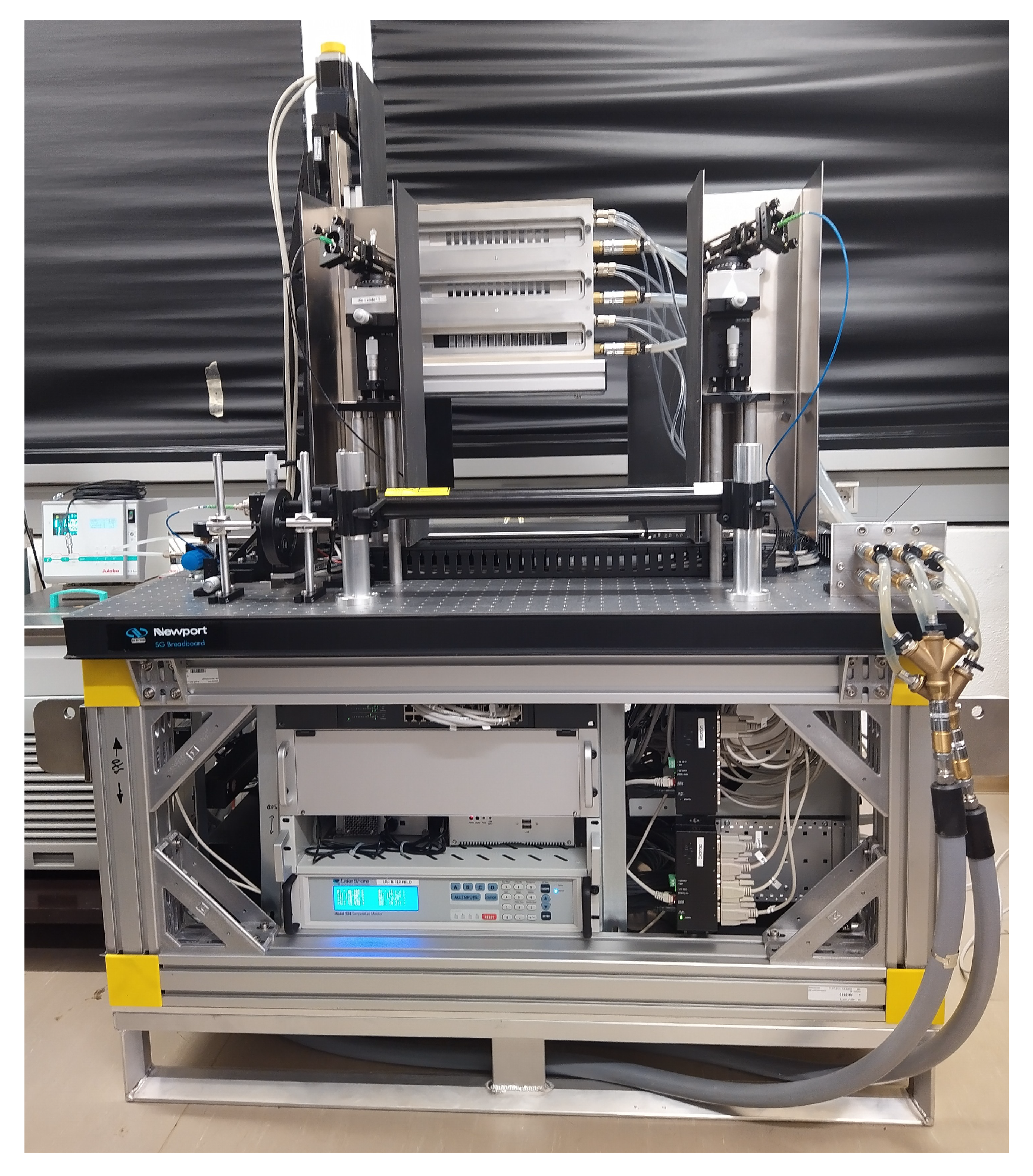
2. Sample Environment Components
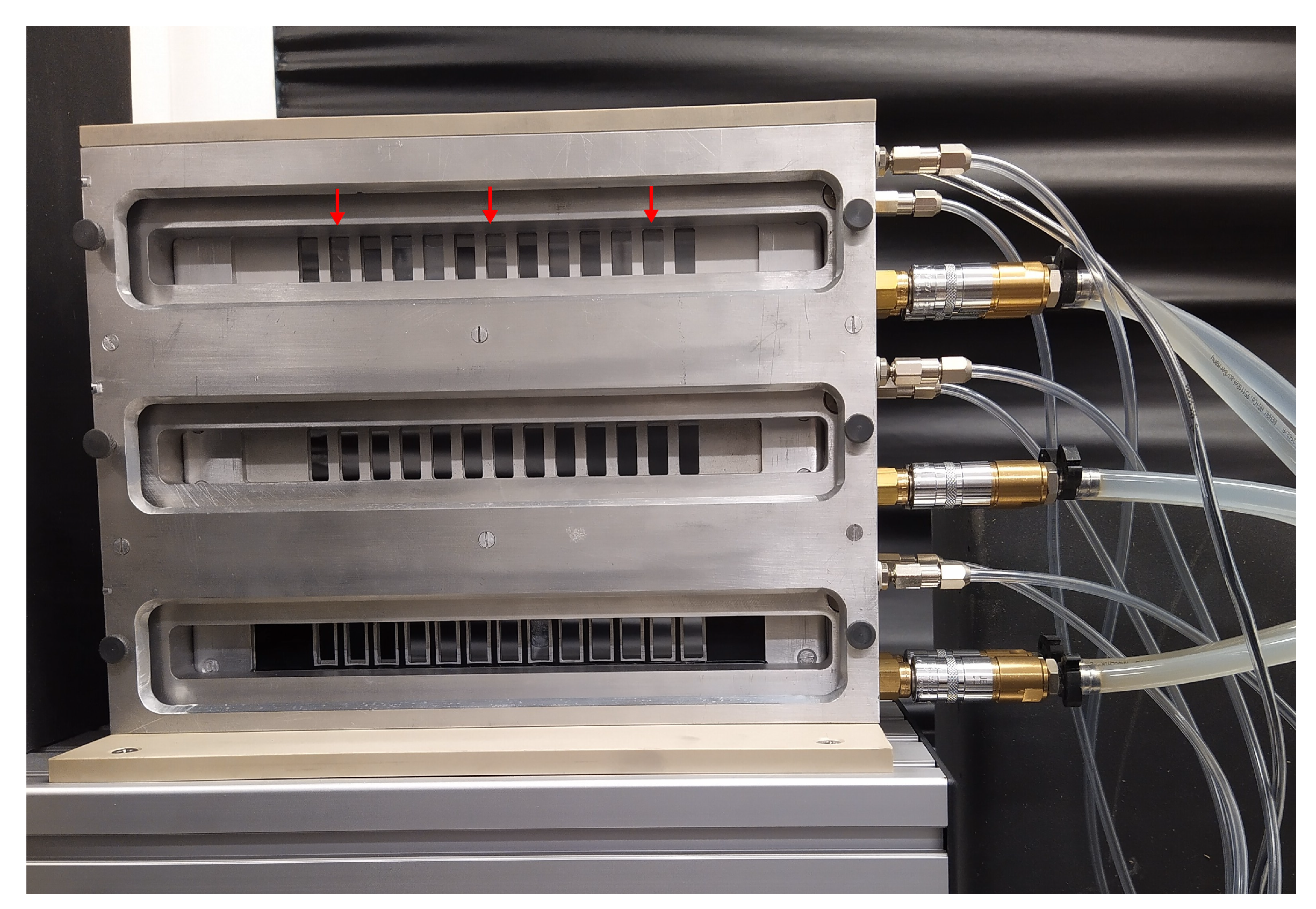
2.1. Sample Rack/Sample Magazines
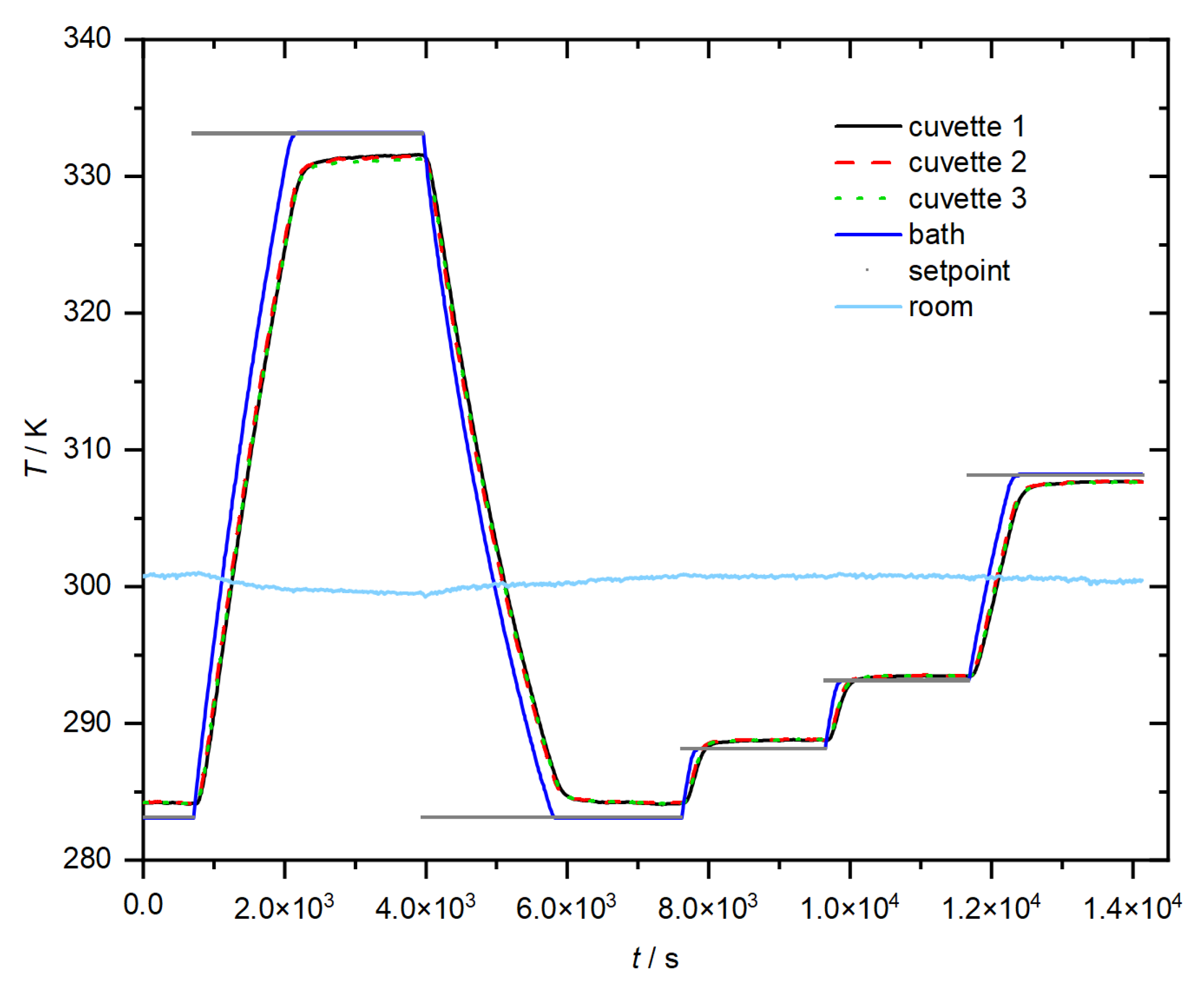
Temperature Control
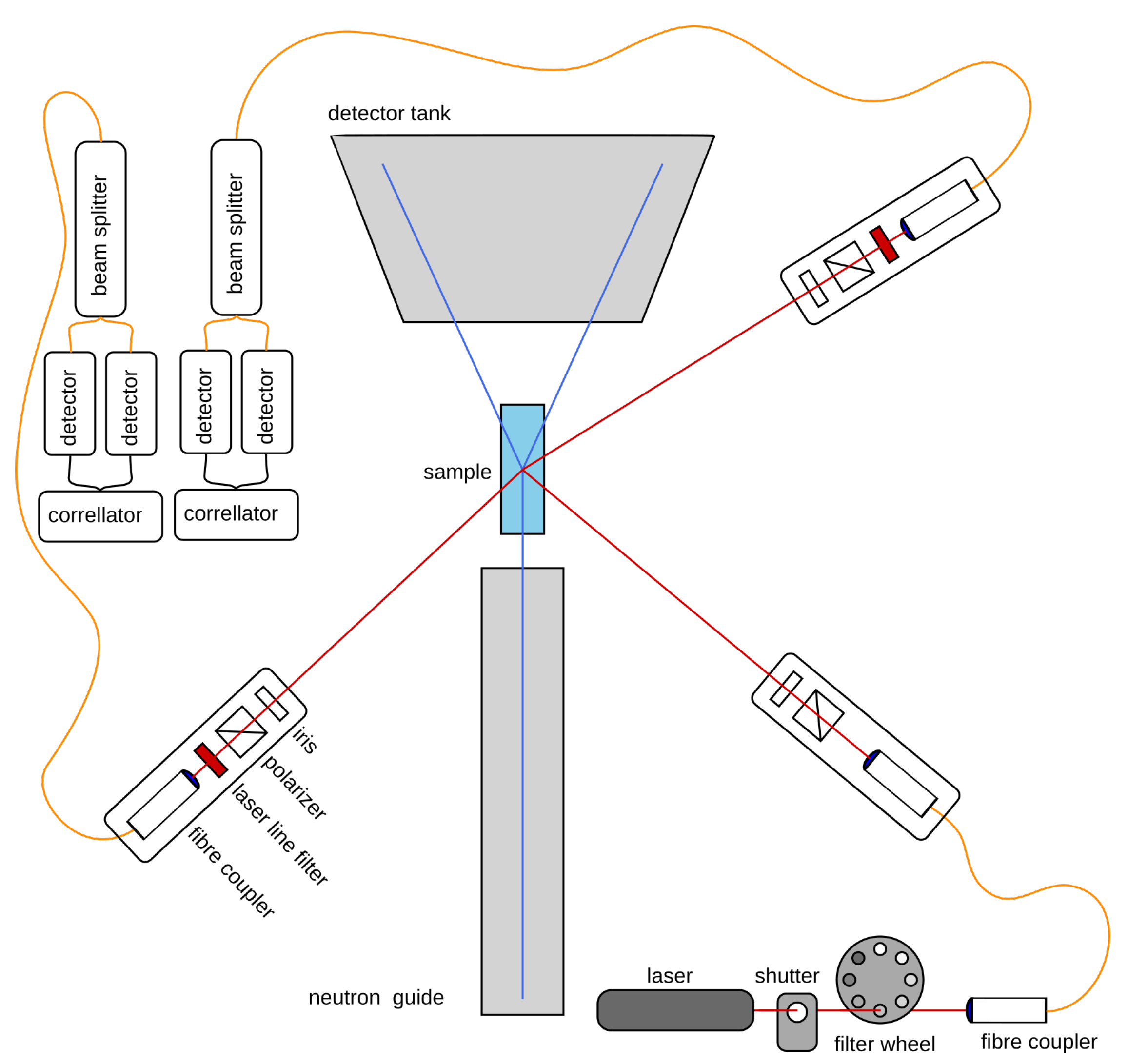
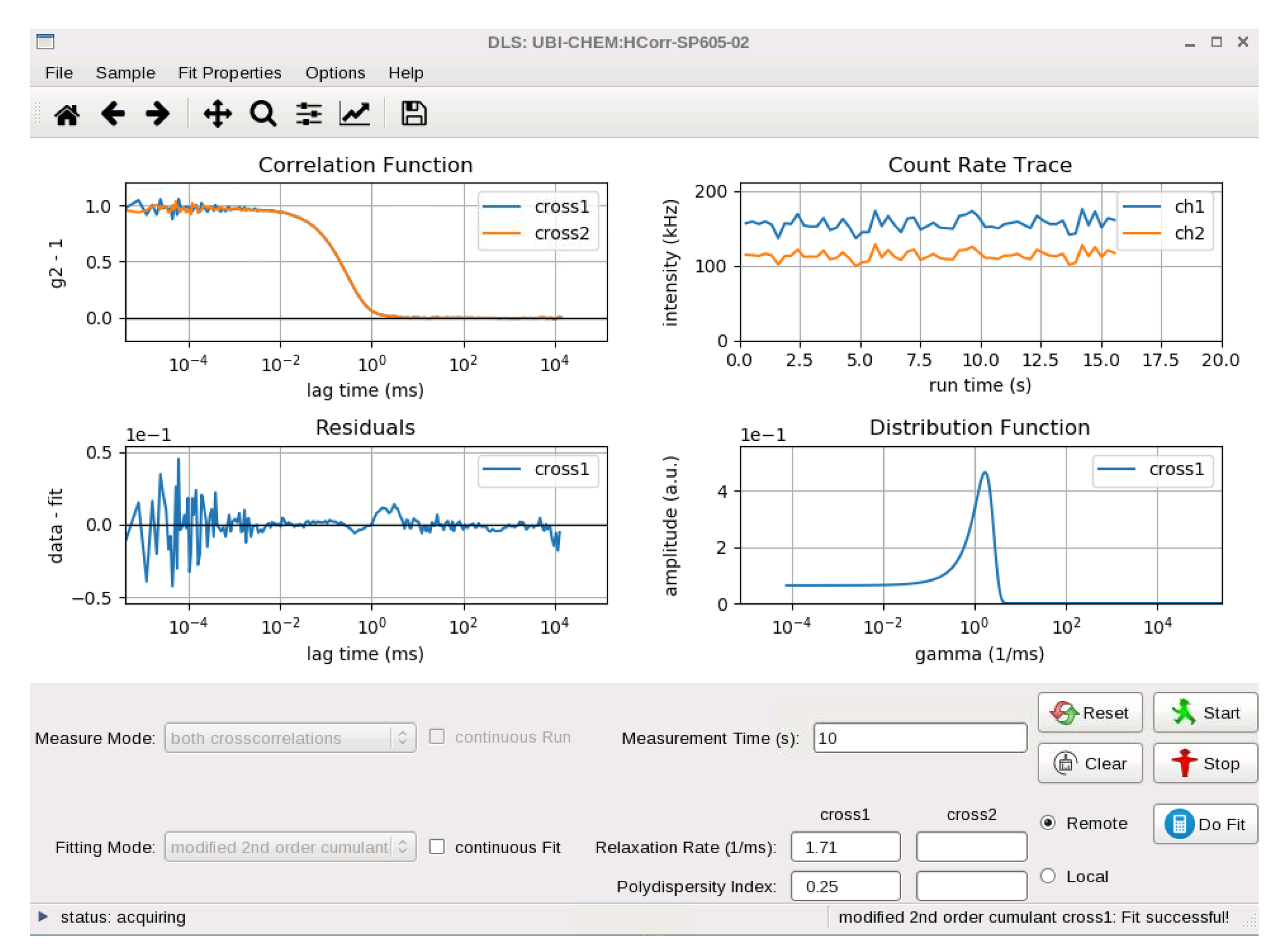
2.2. Light Scattering
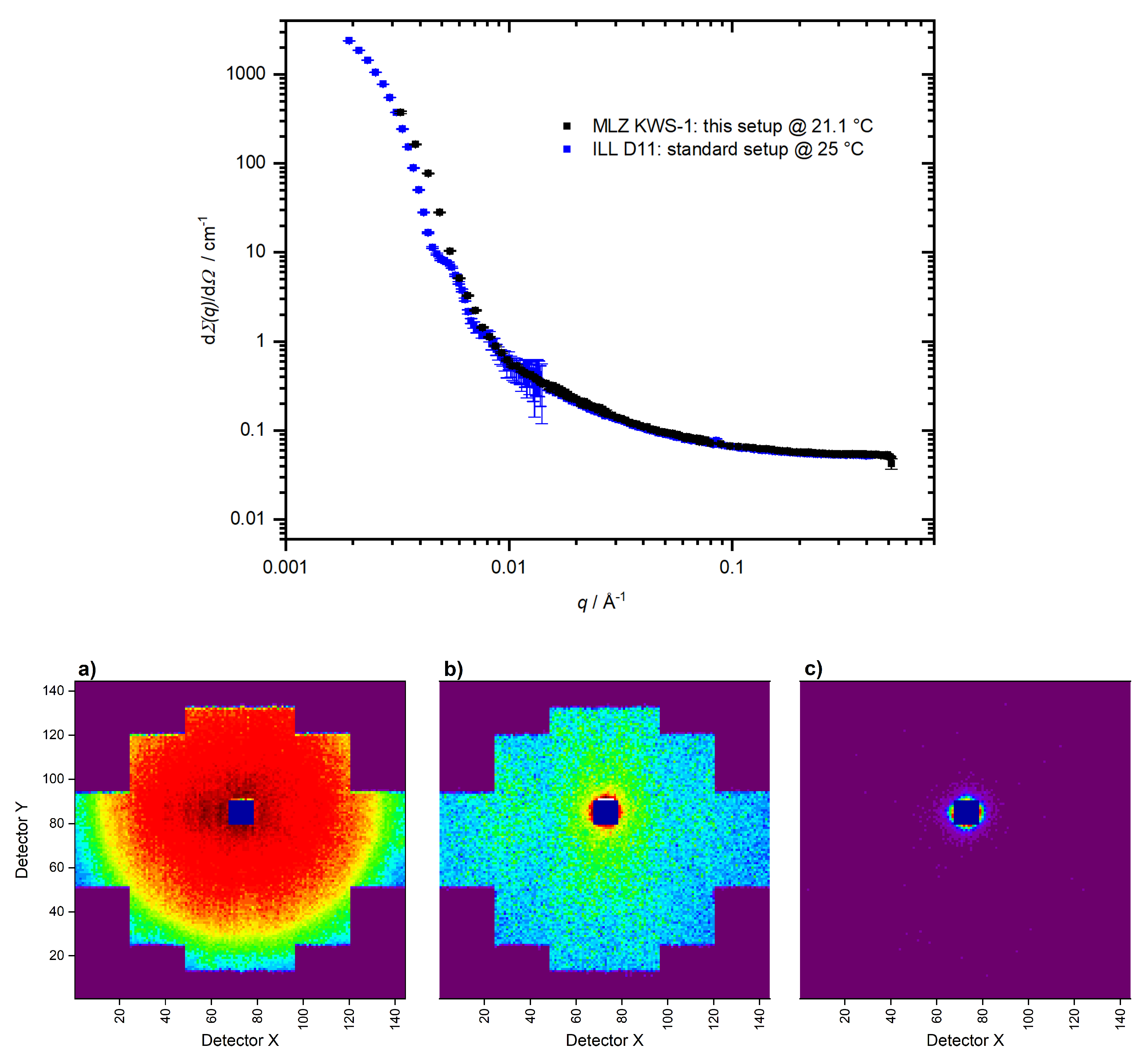
2.3. SANS Measurements
3. The Fully Assembled Sample Environment
3.1. General Remarks
3.1.1. Safety Precautions
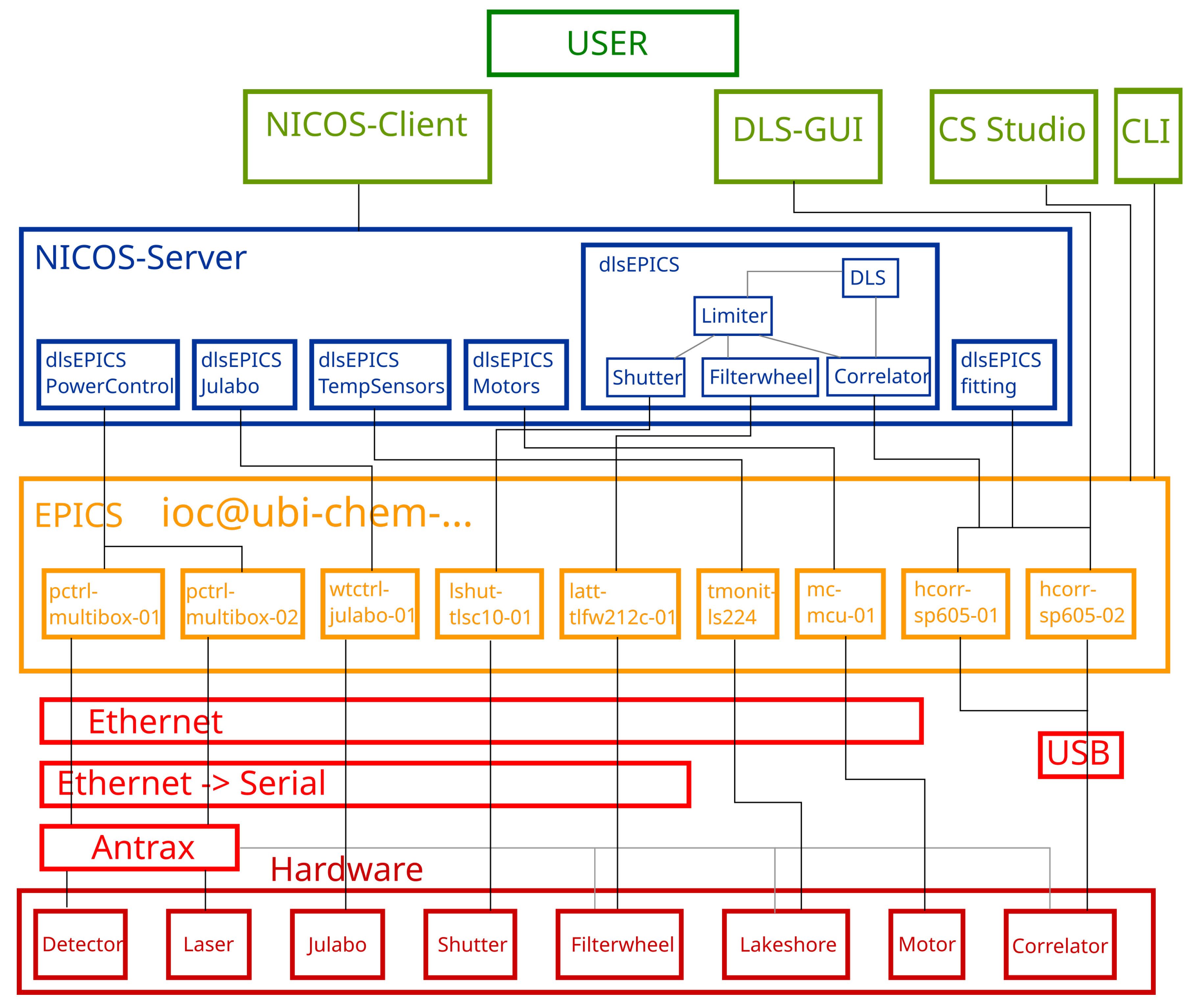
3.1.2. Automated Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garoby, R.; Vergara, A.; Danared, H.; Alonso, I.; Bargallo, E.; Cheymol, B.; Darve, C.; Eshraqi, M.; Hassanzadegan, H.; Jansson, A.; et al. The European Spallation Source Design. Phys. Scr. 2017, 93, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.; Argyriou, D.; Jackson, A.; Houston, J.; Henry, P.; Deen, P.; Toft-Petersen, R.; Beran, P.; Strobl, M.; Arnold, T.; et al. The instrument suite of the European Spallation Source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2020, 957, 163402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frielinghaus, P.H. ESS Instrument Construction Proposal SKADI; ESS: Lund, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.J.; Kanaki, K. ESS Construction Proposal LoKI—A Broad-Band SANS Instrument; ESS: Lund, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Widmann, T.; Kreuzer, L.P.; Kühnhammer, M.; Löhmann, O.; Schmid, A.J.; Wiehemeier, L.; Jaksch, S.; Frielinghaus, H.; Schneider, H.; Hiess, A.; et al. Flexible sample environment for the investigation of soft matter at the European Spallation Source: Part II-The GISANS setup. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnhammer, M.; Widmann, T.; Kreuzer, L.; Schmid, A.J.; Wiehemeier, L.; Frielinghaus, H.; Jaksch, S.; Bögershausen, T.; Barron, P.; Schneider, H.; et al. Flexible sample environments for the investigation of soft matter at the European Spallation Source: Part III–The macroscopic foam cell. Appl. Sci. 2021. to be submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Feoktystov, A.V.; Frielinghaus, H.; Di, Z.; Jaksch, S.; Pipich, V.; Appavou, M.S.; Babcock, E.; Hanslik, R.; Engels, R.; Kemmerling, G.; et al. KWS-1 high-resolution small-angle neutron scattering instrument at JCNS: Current state. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, J.F.; Haese, M. REFSANS: Reflectometer and evanescent wave small angle neutron spectrometer. J. Large-Scale Res. Facil. JLSRF 2015, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.; Pich, A.; Hellweg, T.; Hoare, T.; Lyon, L.A.; Crassous, J.J.; Suzuki, D.; Gumerov, R.A.; Schneider, S.; Potemkin, I.I.; et al. Nanogels and microgels: From model colloids to applications, recent developments, and future trends. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6231–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, A.; Denton, A.R.; Brugnoni, M.; Houston, J.E.; Schweins, R.; Potemkin, I.I.; Richtering, W. Deswelling of microgels in crowded suspensions depends on cross-link density and architecture. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3995–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Nöjd, S.; van Gruijthuijsen, K.; Crassous, J.J.; Obiols-Rabasa, M.; Schweins, R.; Stradner, A.; Schurtenberger, P. Interpenetration of polymeric microgels at ultrahigh densities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, L.A.; Meng, Z.; Singh, N.; Sorrell, C.D.; John, A.S. Thermoresponsive microgel-based materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, D.; Pitsch, F.; Wong, J.E.; Pich, A.; Wessling, M. Temperature-modulated water filtration using microgel-functionalized hollow-fiber membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5706–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlig, K.; Wegener, T.; He, J.; Zeiser, M.; Bookhold, J.; Dewald, I.; Godino, N.; Jaeger, M.; Hellweg, T.; Fery, A.; et al. Patterned thermoresponsive microgel coatings for noninvasive processing of adherent cells. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bookhold, J.; Dirksen, M.; Wiehemeier, L.; Knust, S.; Anselmetti, D.; Paneff, F.; Zhang, X.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Kottke, T.; Hellweg, T. Smart membranes by electron beam cross-linking of copolymer microgels. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergström, M.; Pedersen, J.S.; Schurtenberger, P.; Egelhaaf, S.U. Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) study of vesicles and lamellar sheets formed from mixtures of an anionic and a cationic surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 9888–9897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargel, C.; Geisler, R.; Hannappel, Y.; Kemker, I.; Sewald, N.; Hellweg, T. Self-assembly of the bio-surfactant aescin in solution: A small-angle x-ray scattering and fluorescence study. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.; Pesce, J.J.; Picot, C. Chain conformation in sheared polymer melts as revealed by SANS. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 4356–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, B. SANS from homogeneous polymer mixtures: A unified overview. In Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 87–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennenbaum, M.; Anderson, C.; Hyatt, J.S.; Do, C.; Fernandez-Nieves, A. Internal structure of ultralow-crosslinked microgels: From uniform deswelling to phase separation. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 103, 022614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, T.; Kreuzer, L.P.; Hohn, N.; Bießmann, L.; Wang, K.; Rinner, S.; Moulin, J.F.; Schmid, A.J.; Hannappel, Y.; Wrede, O.; et al. Hydration and Solvent Exchange Induced Swelling and Deswelling of Homogeneous Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Microgel Thin Films. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16341–16352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, O.L.J.; Kather, M.; Meyer-Kirschner, J.; Melle, A.; Radulescu, A.; Viell, J.; Mitsos, A.; Pich, A.; Richtering, W. Direct monitoring of microgel formation during precipitation polymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide using in situ SANS. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3690–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cors, M.; Wiehemeier, L.; Hertle, Y.; Feoktystov, A.; Cousin, F.; Hellweg, T.; Oberdisse, J. Determination of internal density profiles of smart acrylamide-based microgels by small-angle neutron scattering: A multishell reverse Monte Carlo approach. Langmuir 2018, 34, 15403–15415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieger, M.; Pedersen, J.S.; Lindner, P.; Richtering, W. Are thermoresponsive microgels model systems for concentrated colloidal suspensions? A rheology and small-angle neutron scattering study. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7283–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, H.M.; Saunders, B.R.; Mears, S.J.; Cosgrove, T.; Vincent, B.; King, S.M.; Yu, G.E. Poly(NIPAM) microgel particle de-swelling: A light scattering and small-angle neutron scattering study. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 152, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, B.; Zeiser, M.; Hellweg, T. Non NIPAM based smart microgels: Systematic variation of the volume phase transition temperature by copolymerization. Z. Phys. Chem. 2012, 226, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehemeier, L.; Cors, M.; Wrede, O.; Oberdisse, J.; Hellweg, T.; Kottke, T. Swelling behaviour of core–shell microgels in H2O, analysed by temperature-dependent FTIR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochor, B.; Düdükcü, Ö.; Lübtow, M.M.; Schummer, B.; Jaksch, S.; Luxenhofer, R. Probing the complex loading-dependent structural changes in ultrahigh drug-loaded polymer micelles by small-angle neutron scattering. Langmuir 2020, 36, 3494–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayter, J.B. Neutron scattering from concentrated micellar solutions. Berichte Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svergun, D.I.; Richard, S.; Koch, M.H.J.; Sayers, Z.; Kuprin, S.; Zaccai, G. Protein hydration in solution: Experimental observation by x-ray and neutron scattering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2267–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, F.; Gummel, J.; Ung, D.; Boué, F. Polyelectrolyte-protein complexes: Structure and conformation of each specie revealed by SANS. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9675–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreij, R.; Dargel, C.; Geisler, P.; Hertle, Y.; Radulescu, A.; Pasini, S.; Perez, J.; Moleiro, L.H.; Hellweg, T. DMPC vesicle structure and dynamics in the presence of low amounts of the saponin aescin. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 9070–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, V.; Angelini, R.; King, S.; Franco, S.; Buratti, E.; Bomboi, F.; Mahmoudi, N.; Corvasce, F.; Scaccia, R.; Church, A.; et al. Apparatus for simultaneous dynamic light scattering–small angle neutron scattering investigations of dynamics and structure in soft matter. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 023907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawroth, T.; Buch, P.; Buch, K.; Langguth, P.; Schweins, R. Liposome formation from bile salt–lipid micelles in the digestion and drug delivery model FaSSIFmod estimated by combined time-resolved neutron and dynamic light scattering. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 2162–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balacescu, L.; Vögl, F.; Staringer, S.; Ossovyi, V.; Brandl, G.; Lumma, N.; Feilbach, H.; Holderer, O.; Pasini, S.; Stadler, A.; et al. In situ dynamic light scattering complementing neutron spin-echo measurements on protein samples. J. Surf. Investig. X-Ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2020, 14, S185–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlbrecher, J.; Bollhalder, A.; Vavrin, R.; Meier, G. A high pressure cell for small angle neutron scattering up to 500 MPa in combination with light scattering to investigate liquid samples. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 125101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavrin, R.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Wilk, A.; Ratajczyk, M.; Lettinga, M.P.; Buitenhuis, J.; Meier, G. Structure and phase diagram of an adhesive colloidal dispersion under high pressure: A small angle neutron scattering, diffusing wave spectroscopy, and light scattering study. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 154903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berne, B.J.; Pecora, R. Dynamic Light Scattering: With Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics; Dover Publications Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0486442276. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinin, S.; Kühnemuth, R.; Vardanyan, H.; Seidel, C.A.M. Note: A 4 ns hardware photon correlator based on a general-purpose field-programmable gate array development board implemented in a compact setup for fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 096105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Urquidi, J.; Singh, S.; Robinson, G.W. Thermal offset viscosities of liquid H2O, D2O, and T2O. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 1991–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, J.; Blochowicz, T.; Stühn, B. Compressed exponential decays in correlation experiments: The influence of temperature gradients and convection. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, G.; Felder, C.; Pedersen, B.; Faulhaber, E.; Lenz, A.; Krüger, J. NICOS–The Instrument Control solution at the MLZ. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Personal Computers and Particle Accelerator Controls, Karlsruhe, Germany, 14–17 October 2014. Number IMPULSE-2014-00016. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://nicos-controls.org/ (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Dalesio, L.R.; Kozubal, A.J.; Kraimer, M.R. EPICS Architecture; Los Alamos National Lab.: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1991.
- Provencher, S.W. CONTIN: A general purpose constrained regularization program for inverting noisy linear algebraic and integral equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, D.E. Analysis of macromolecular polydispersity in intensity correlation spectroscopy: The method of cumulants. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 57, 4814–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisken, B.J. Revisiting the method of cumulants for the analysis of dynamic light-scattering data. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, P.; Kulshreshtha, S. Modification to the cumulant analysis of polydispersity in quasielastic light scattering data. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


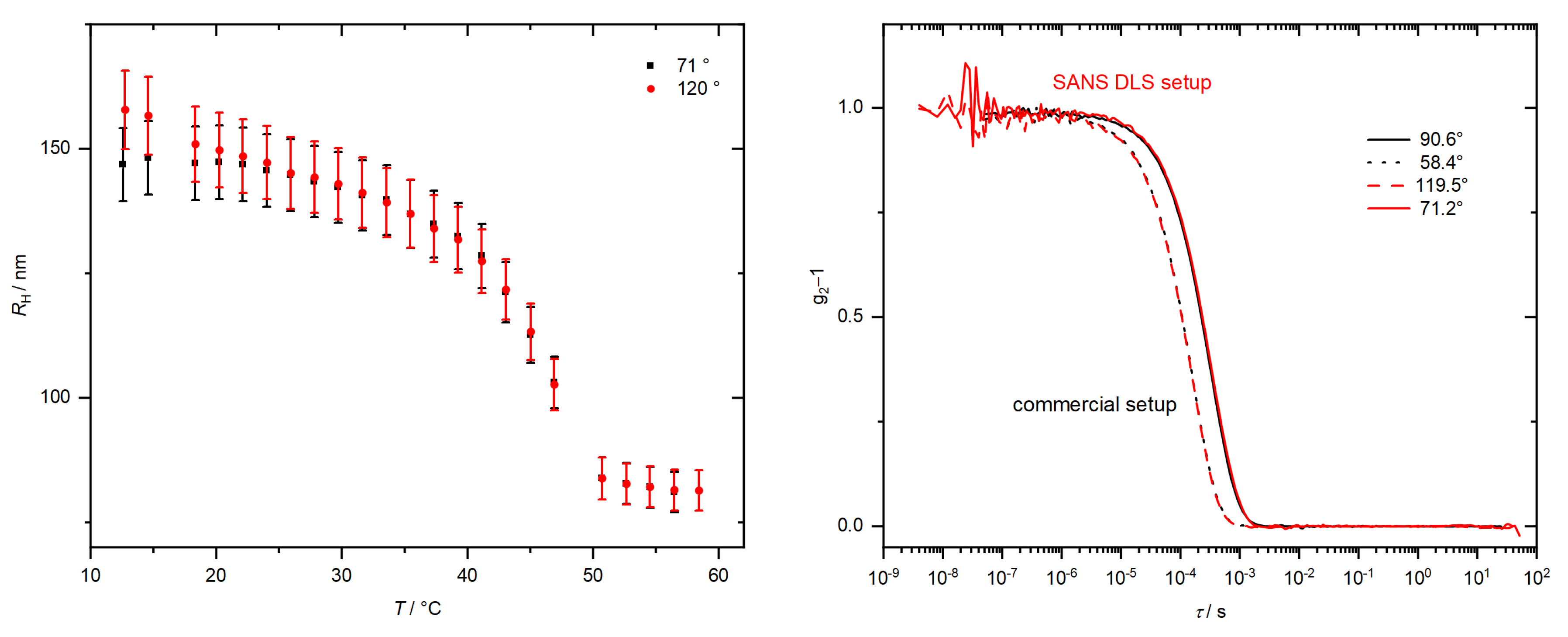
| 25 nm | 200 nm | |
|---|---|---|
| 71 | 29.9 ± 0.1 nm | 209 ± 6 nm |
| 120 | 28.5 ± 0.2 nm | 215 ± 3 nm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmid, A.J.; Wiehemeier, L.; Jaksch, S.; Schneider, H.; Hiess, A.; Bögershausen, T.; Widmann, T.; Reitenbach, J.; Kreuzer, L.P.; Kühnhammer, M.; et al. Flexible Sample Environments for the Investigation of Soft Matter at the European Spallation Source: Part I—The In Situ SANS/DLS Setup. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094089
Schmid AJ, Wiehemeier L, Jaksch S, Schneider H, Hiess A, Bögershausen T, Widmann T, Reitenbach J, Kreuzer LP, Kühnhammer M, et al. Flexible Sample Environments for the Investigation of Soft Matter at the European Spallation Source: Part I—The In Situ SANS/DLS Setup. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094089
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmid, Andreas Josef, Lars Wiehemeier, Sebastian Jaksch, Harald Schneider, Arno Hiess, Torsten Bögershausen, Tobias Widmann, Julija Reitenbach, Lucas P. Kreuzer, Matthias Kühnhammer, and et al. 2021. "Flexible Sample Environments for the Investigation of Soft Matter at the European Spallation Source: Part I—The In Situ SANS/DLS Setup" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094089
APA StyleSchmid, A. J., Wiehemeier, L., Jaksch, S., Schneider, H., Hiess, A., Bögershausen, T., Widmann, T., Reitenbach, J., Kreuzer, L. P., Kühnhammer, M., Löhmann, O., Brandl, G., Frielinghaus, H., Müller-Buschbaum, P., von Klitzing, R., & Hellweg, T. (2021). Flexible Sample Environments for the Investigation of Soft Matter at the European Spallation Source: Part I—The In Situ SANS/DLS Setup. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094089










