Decision Tree Method for Fault Causes Classification Based on RMS-DWT Analysis in 275 kV Transmission Lines Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Parameters Condition
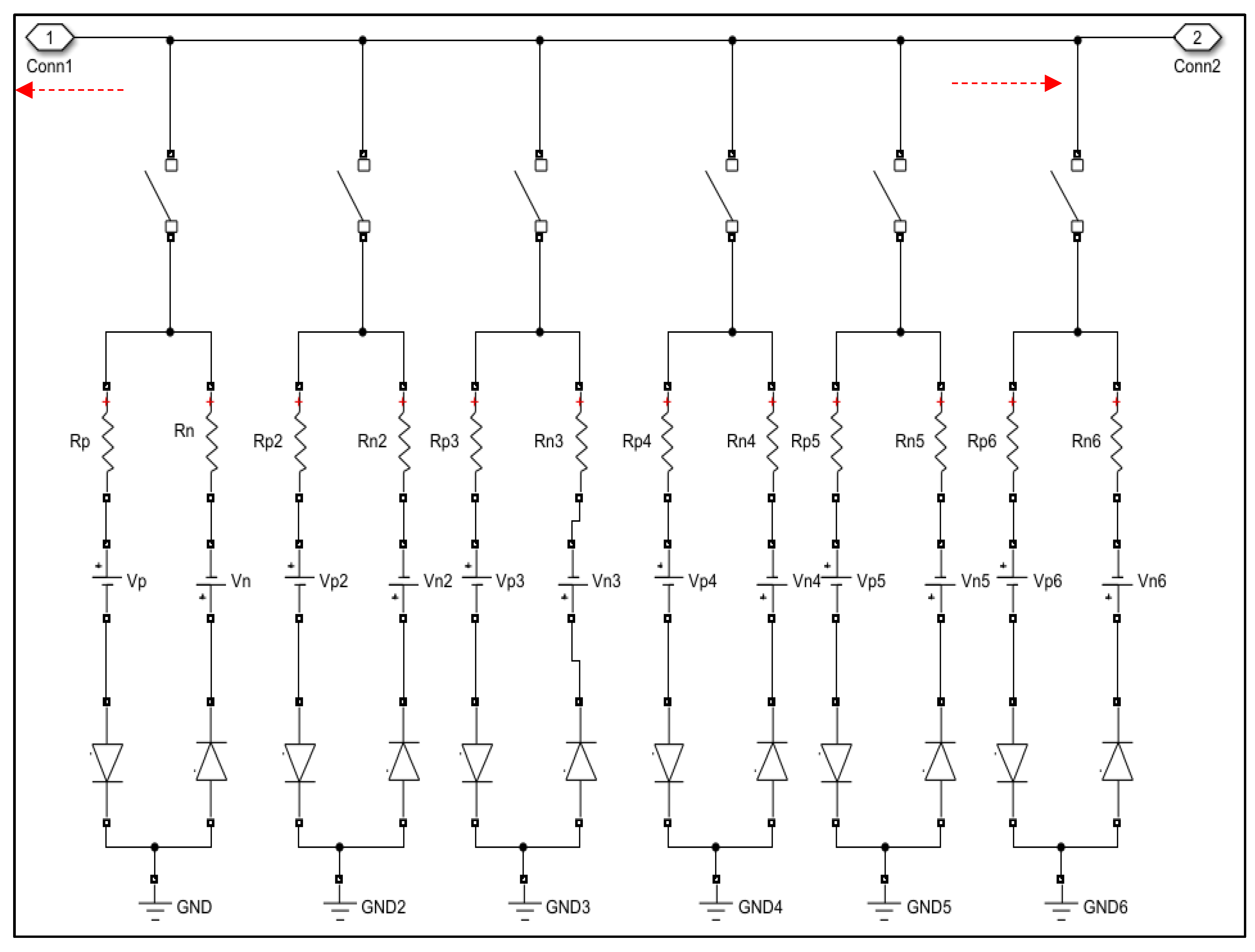
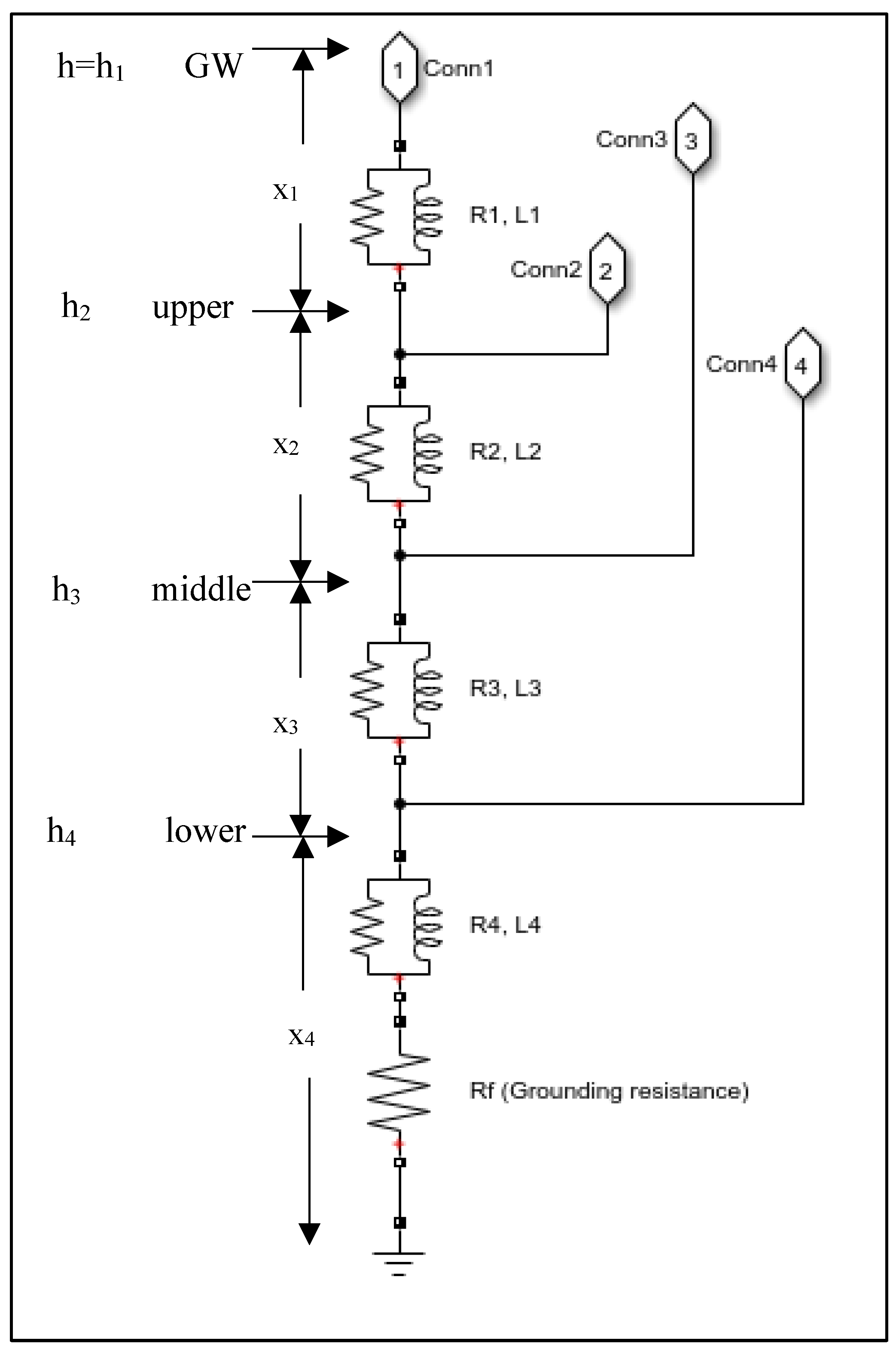
2.2. Fault Model
2.2.1. Tree Fault Model
2.2.2. Crane Fault Model
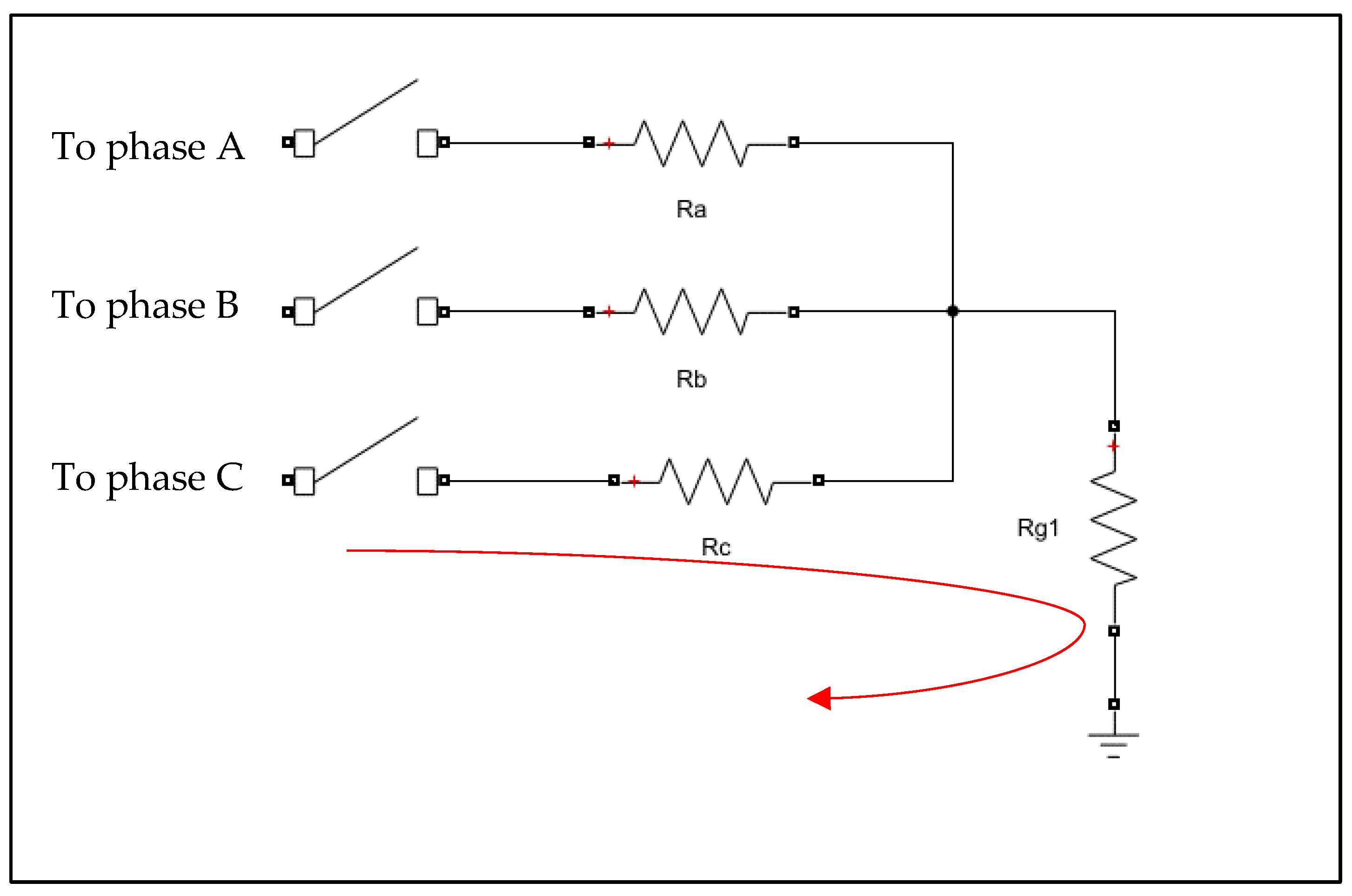
2.2.3. Insulator Fault Model
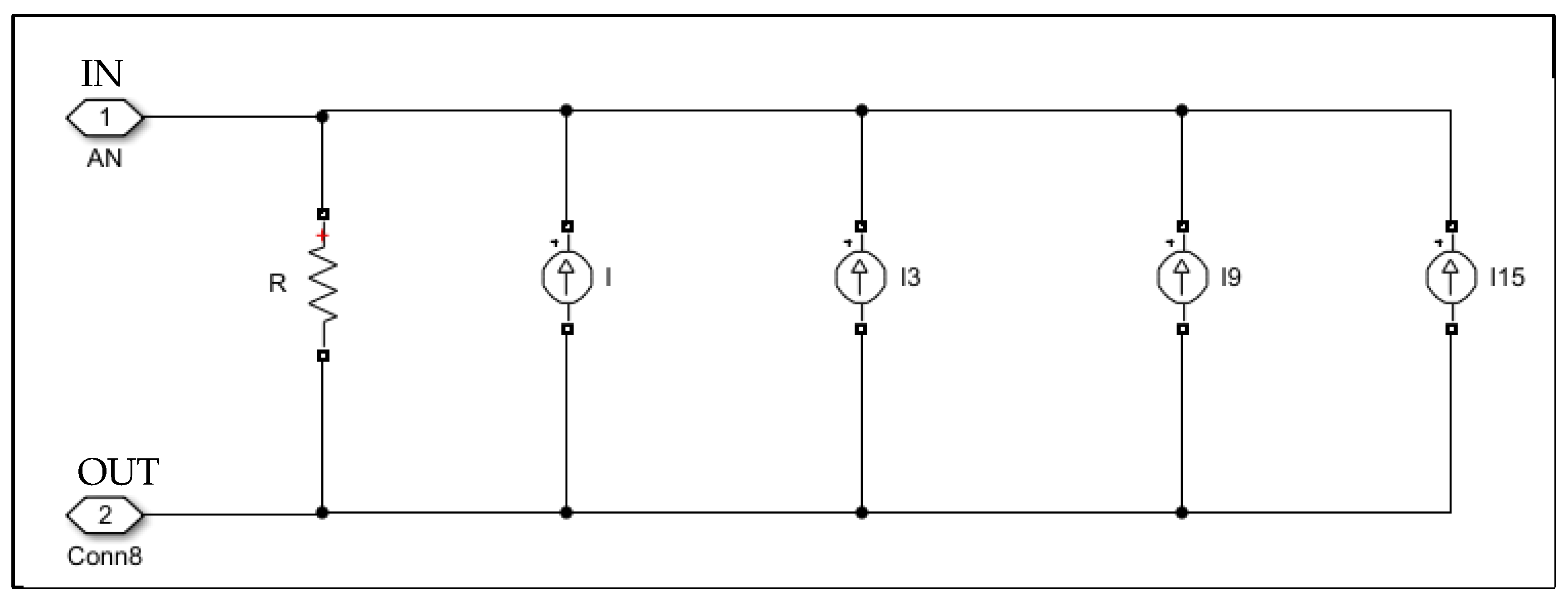
2.2.4. Lightning Fault Model
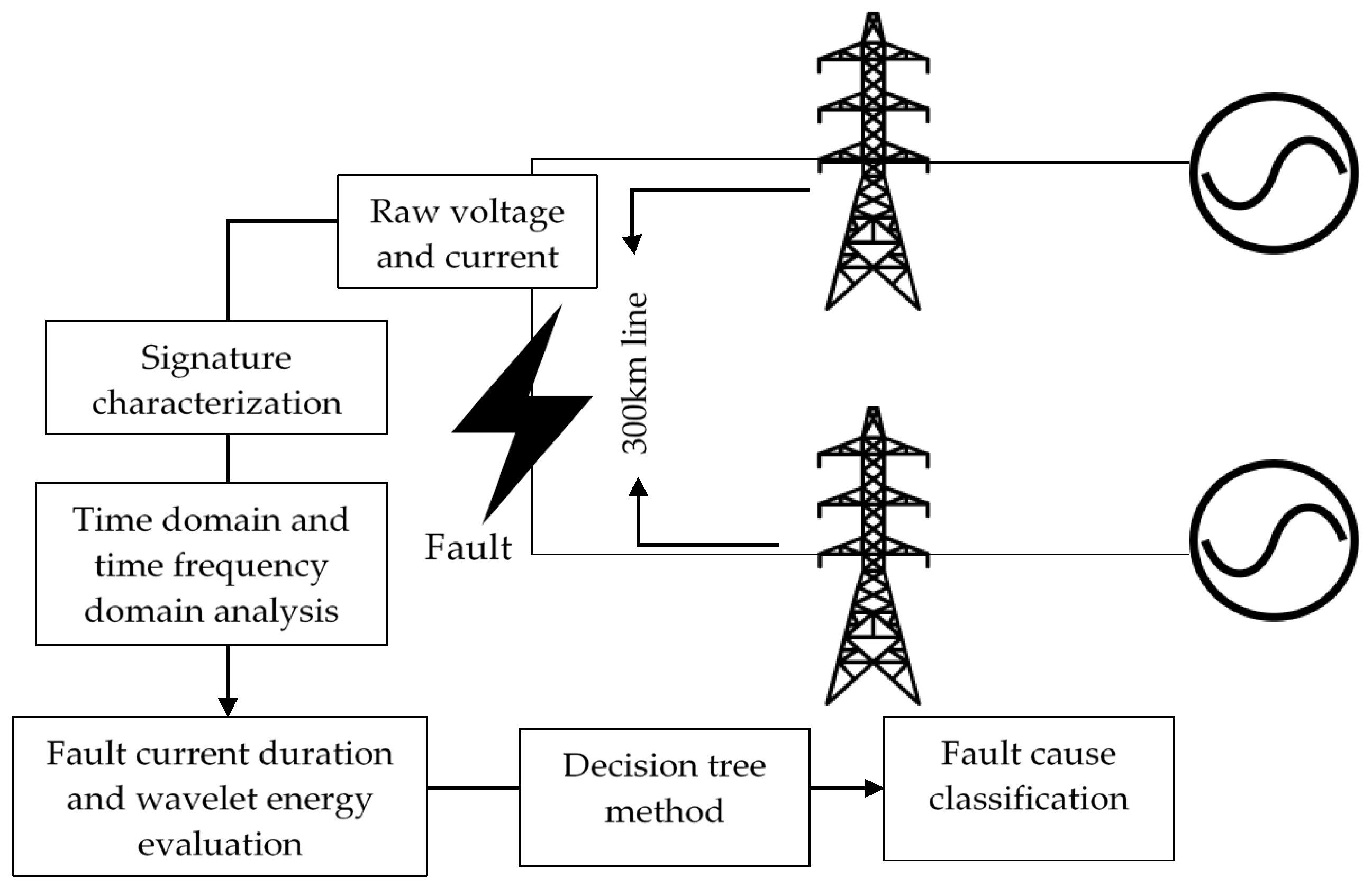
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Characterization of the Root Cause of Fault
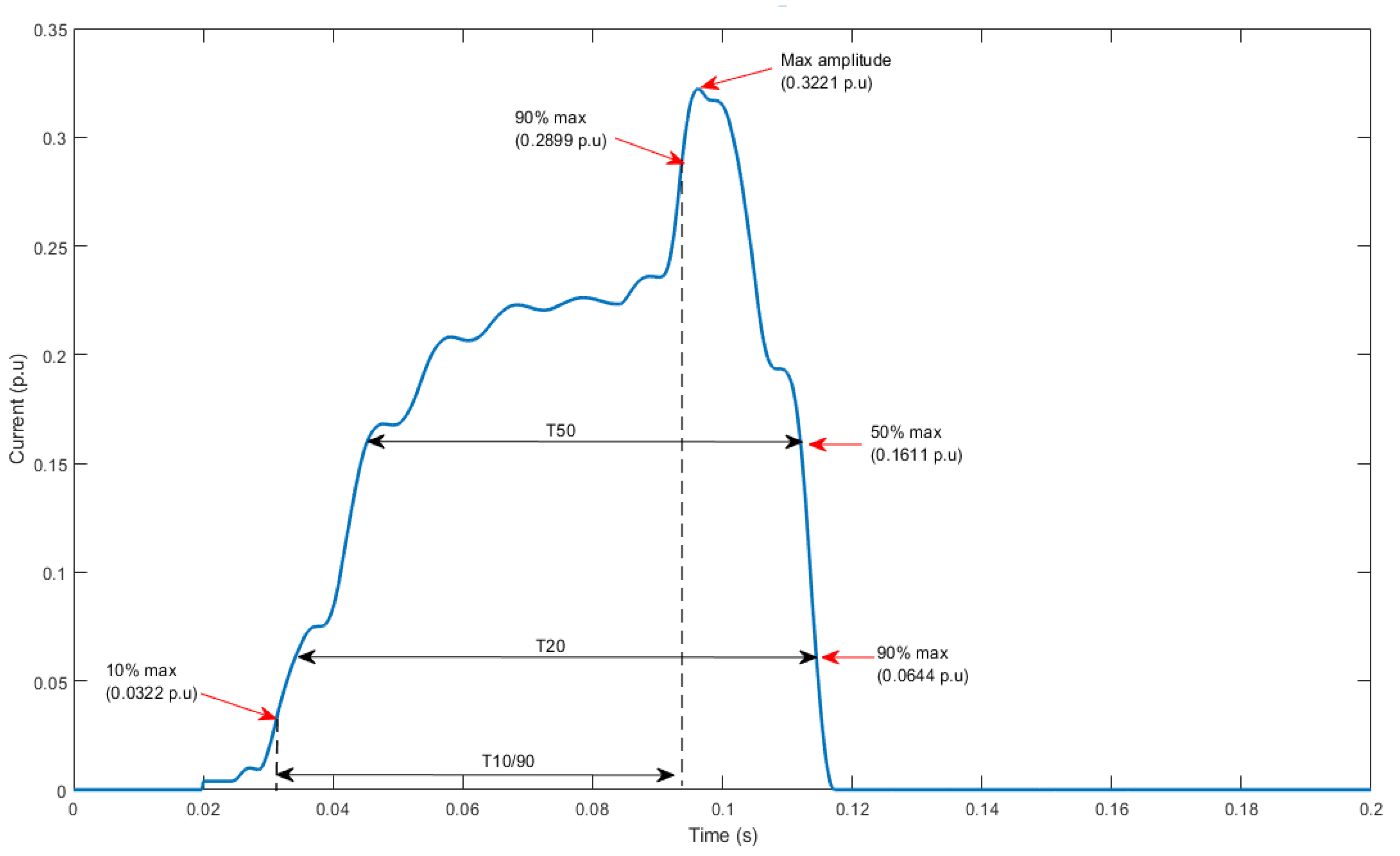
3.1.1. Fault Current Duration
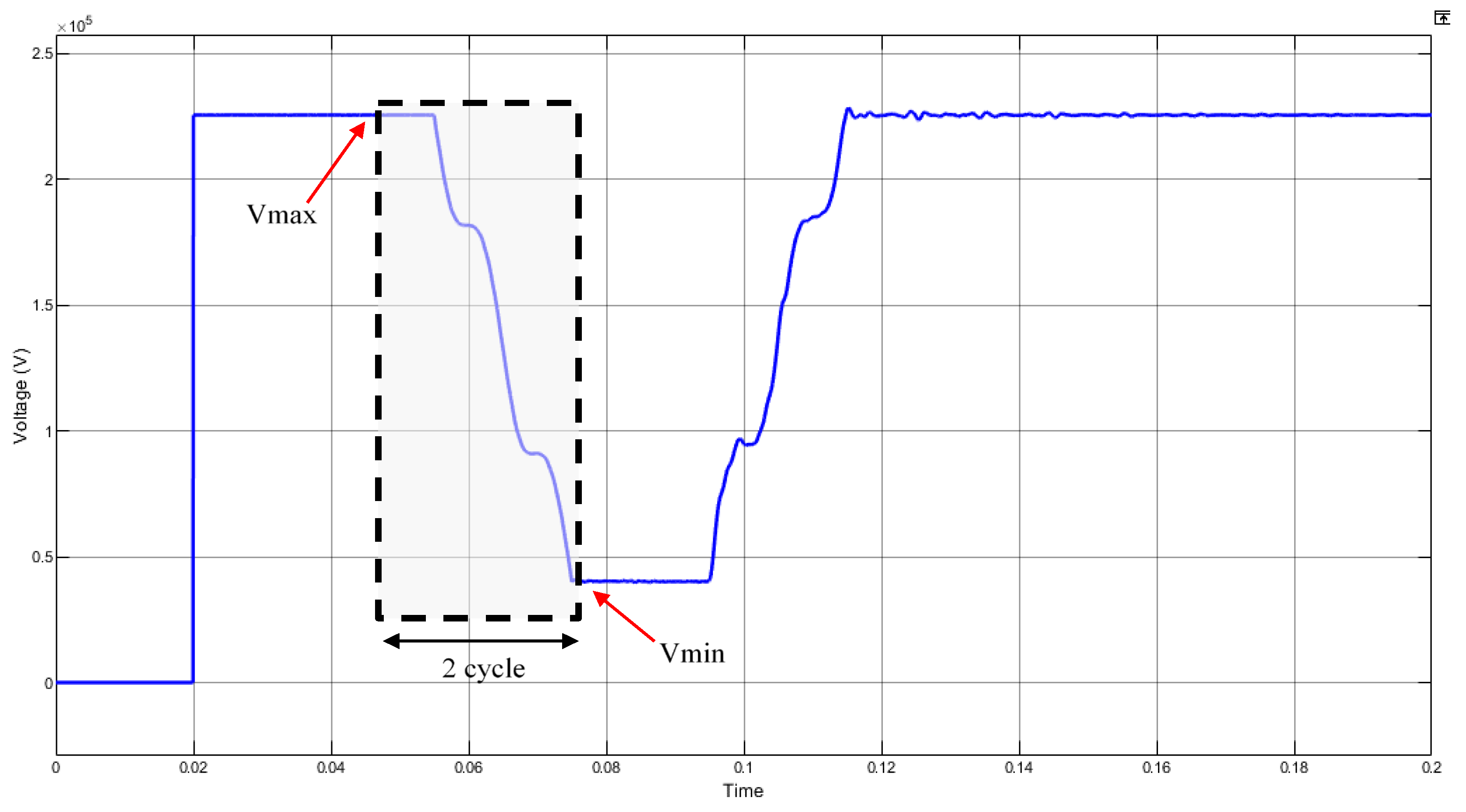
3.1.2. Voltage Dip
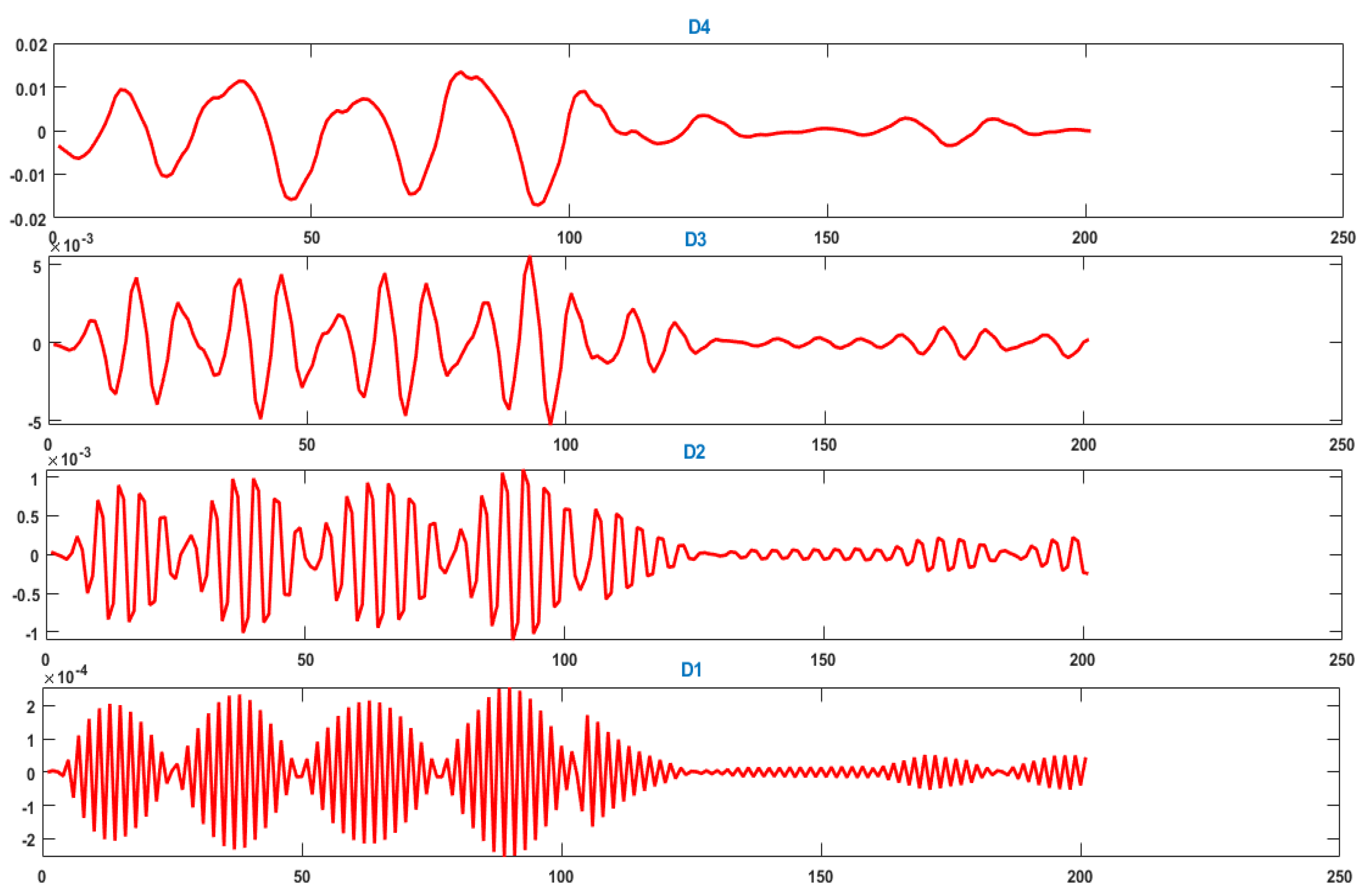
3.1.3. Time-Frequency Domain Analysis Using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT)
- (a)
- Discrete Wavelet Transform Algorithm
- (b)
- Decomposition
- (c)
- Sub-Band Filters
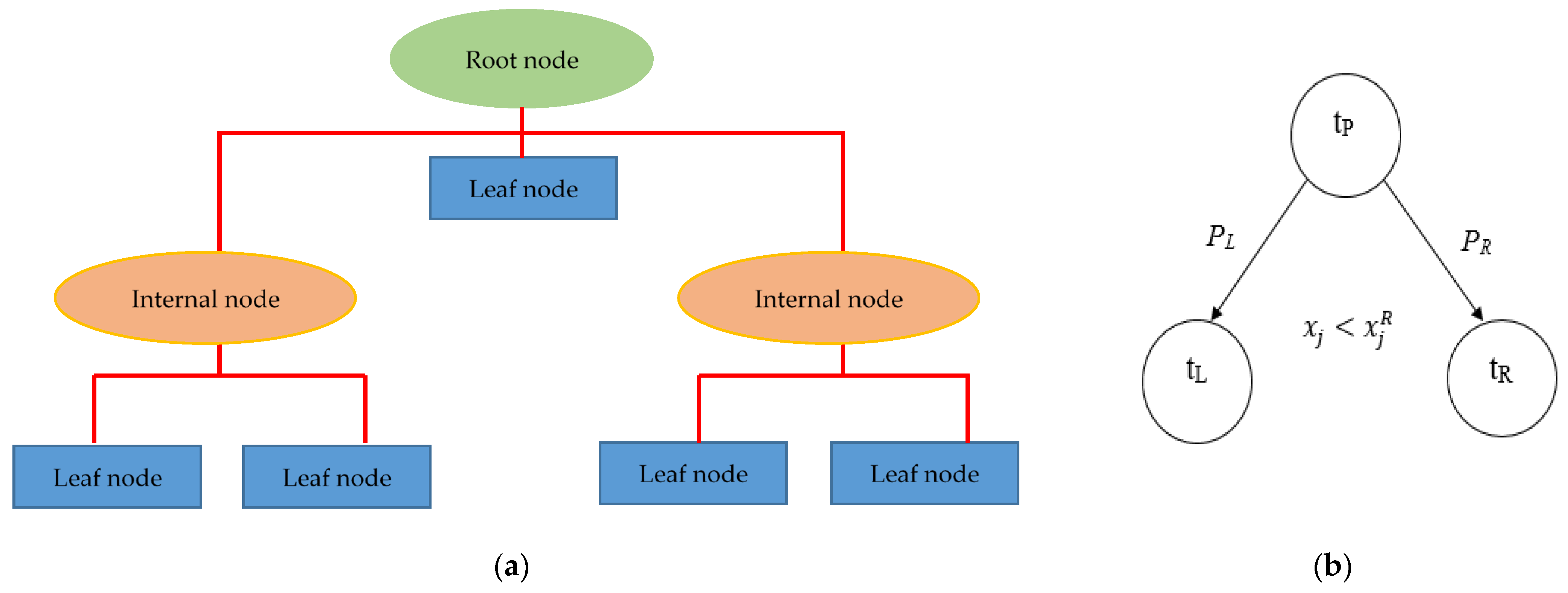
3.2. Decision Tree Algorithm
3.3. Confusion Matrix Algorithm
- True Positive (TP) is the cases that we predicted yes and they do have the cases.
- True Negative (TN) is the cases that we predicted no and they do not have the cases.
- False Positive (FP) is the cases that we predicted yes but they do not have the cases.
- False Negative (FN) is the cases that we predicted not but they do have the cases.
4. Result and Discussion
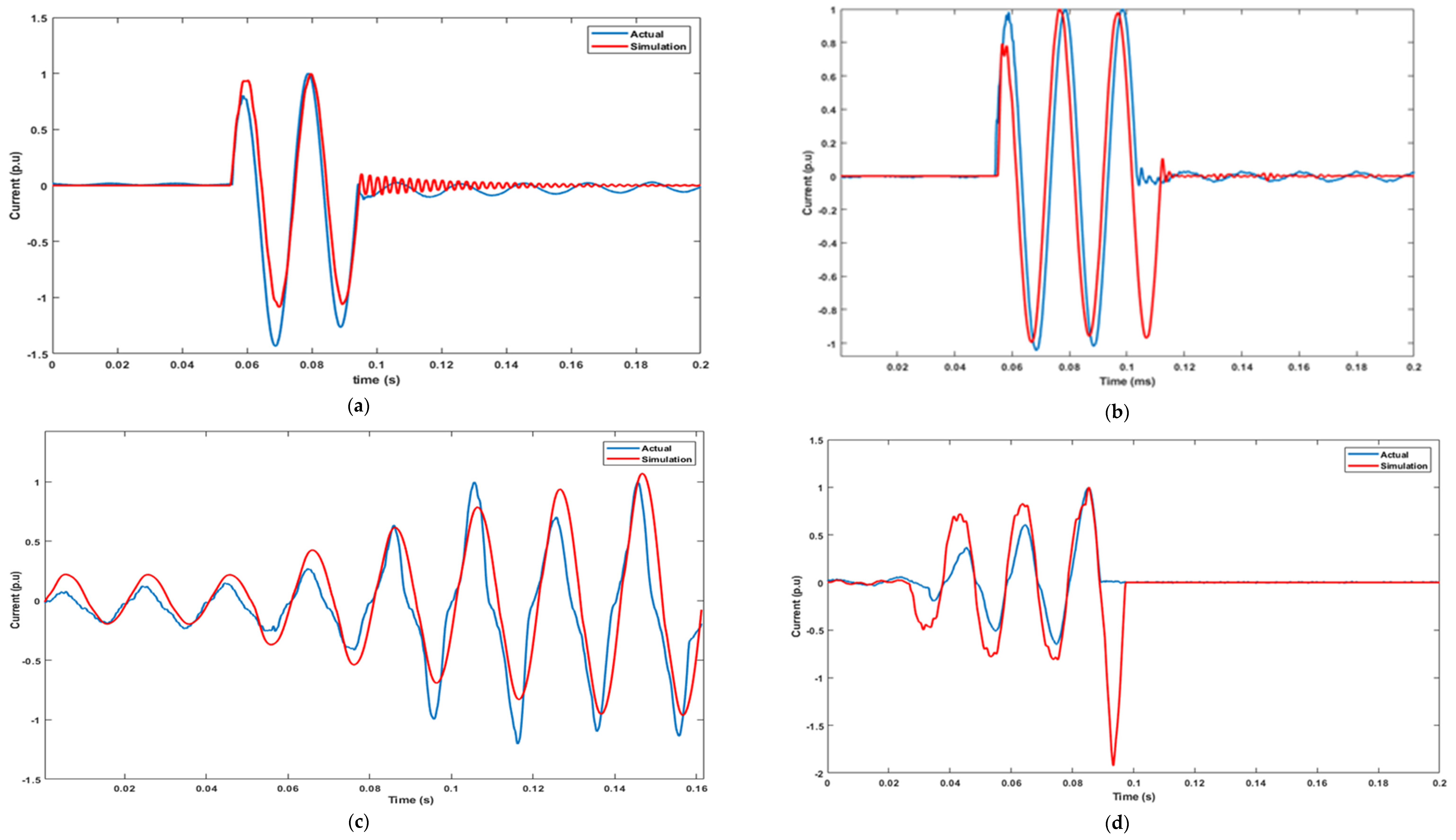
4.1. Fault Model Validation Result
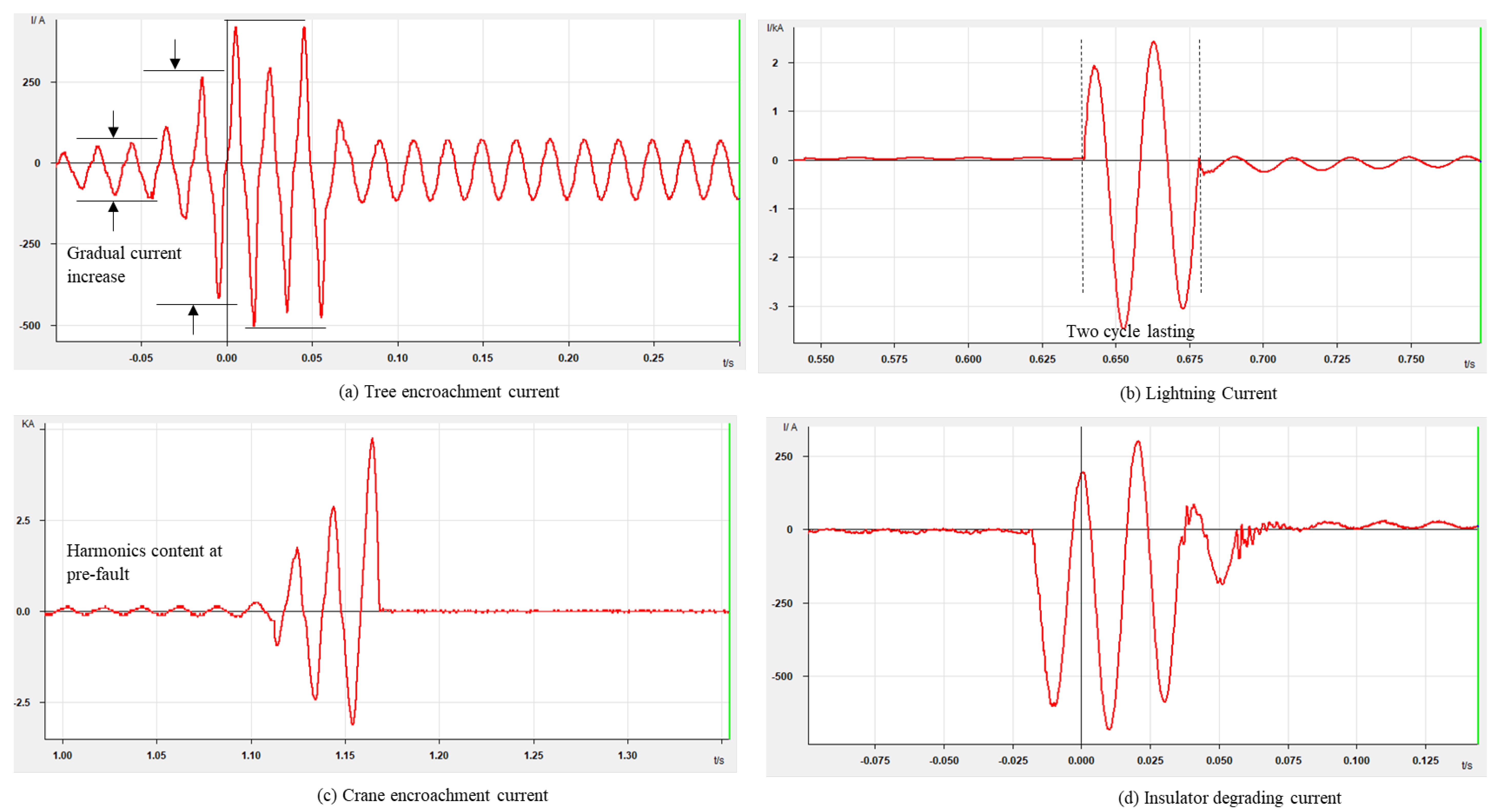
4.2. Fault Signature Characterization
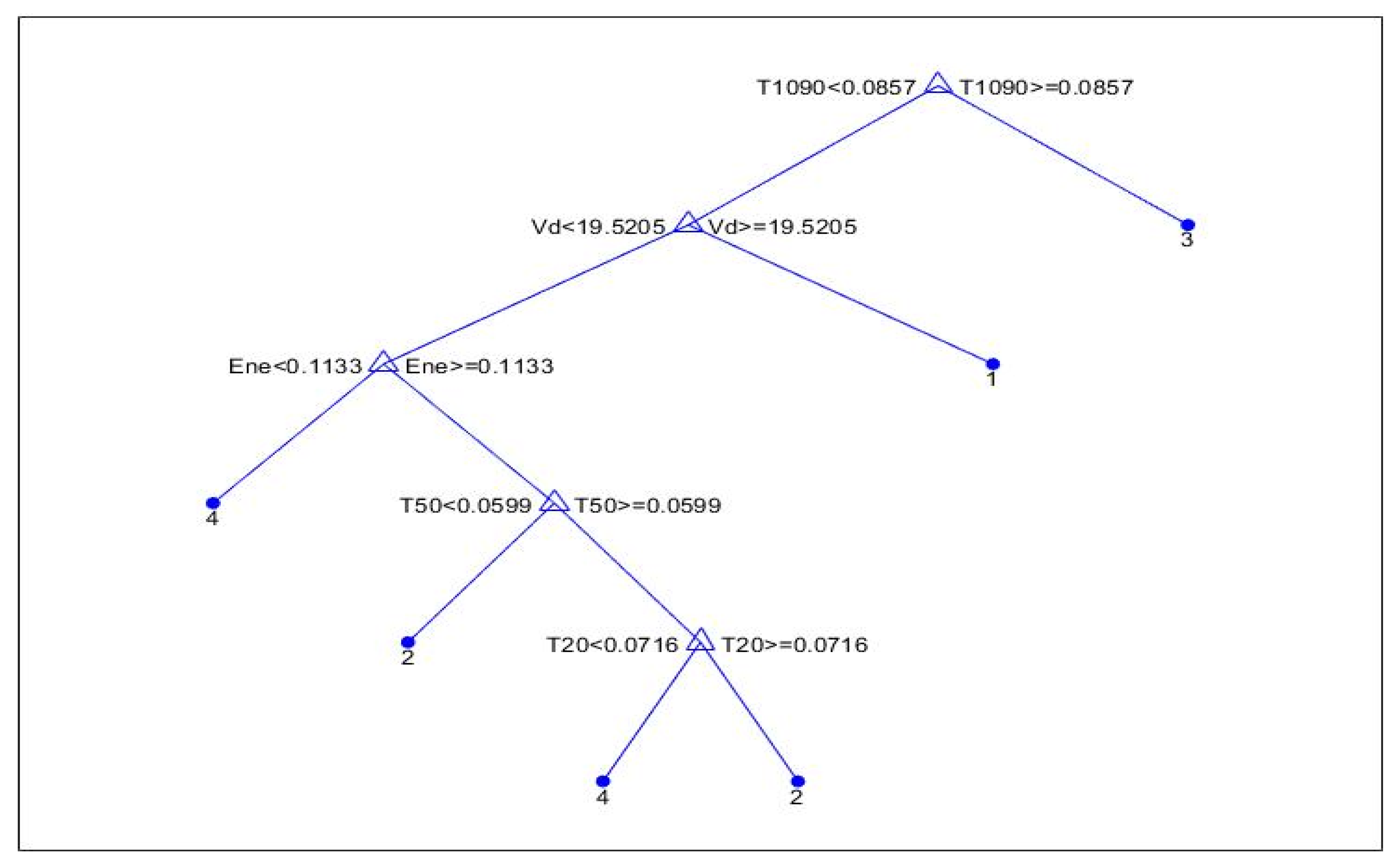
4.3. Decision Tree Method Sample Selection
4.4. Decision Tree Classification Performance of Fault Causes Based on Different Predictor Selection
4.5. Computational Time
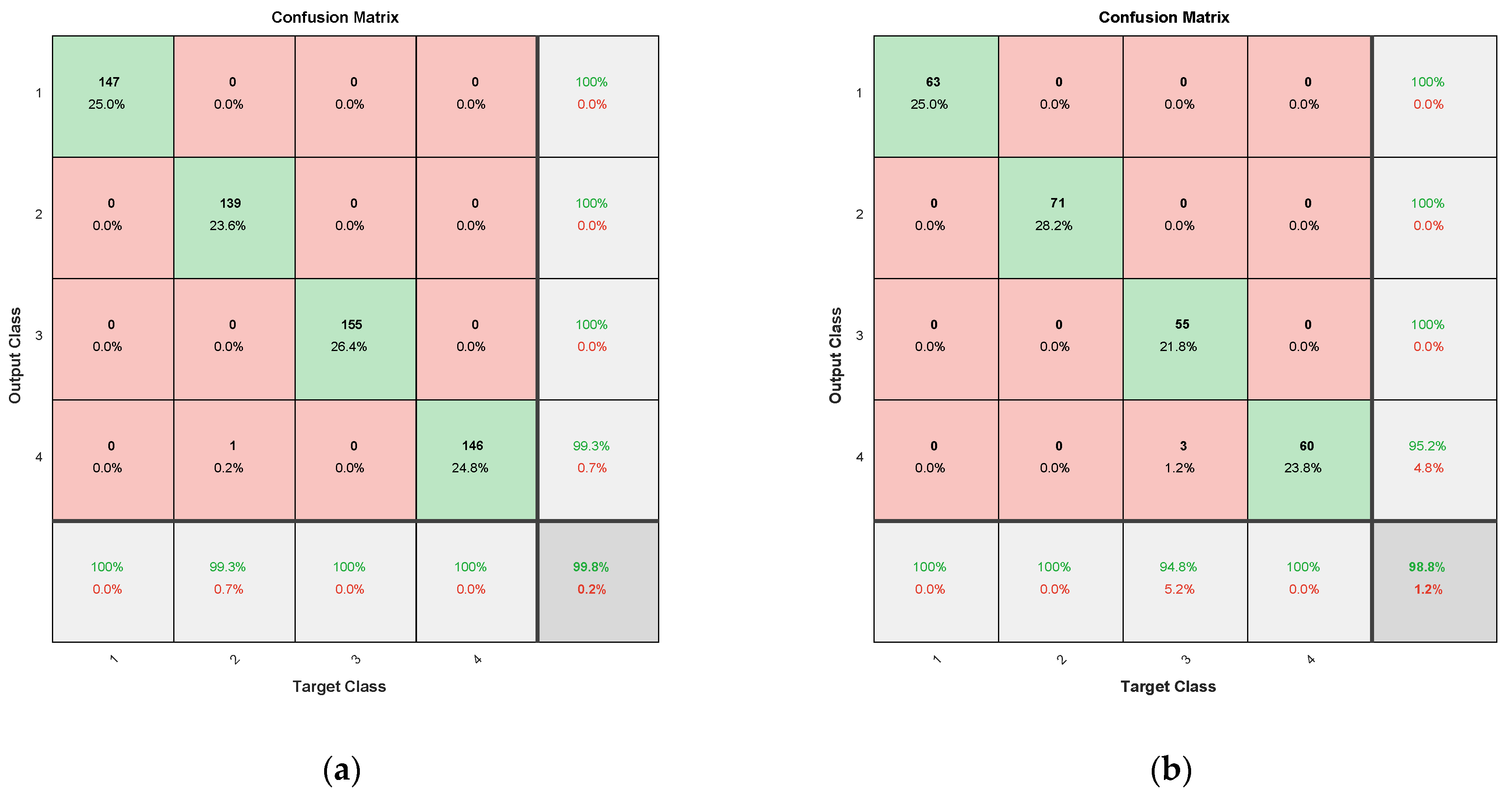
4.6. Confusion Matrix Performance for Decision Tree on Different Predictor Selection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlsson, F.; Kataria, M.; Lampi, E.; Martinsson, P. Past and present outage costs—A follow-up study of households’ willingness to pay to avoid power outages. Resour. Energy Econ. 2021, 64, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, N.; Ramachandran, K.I. Incipient gear box fault diagnosis using discrete wavelet transform (DWT) for feature extraction and classification using artificial neural network (ANN). Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4168–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.P.; Souza, J.C.S.; Schilling, M.T.; Filho, M.B.D.C. Fault diagnosis in electrical power systems using artificial neural networks. Int. Conf. Electr. Power Eng. Power Tech. Bp. 1999, 2, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Asman, S.H.; Ab Aziz, N.F.; Abd Kadir, M.Z.A.; Amirulddin, U.A.U. Fault signature analysis based on digital fault recorder in malaysia overhead line system. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon), Penang, Malaysia, 7–8 December 2020; pp. 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Kadir, M.Z.A.A.; Cooper, M.A.; Gomes, C. An overview of the global statistics on lightning fatalities. In Proceedings of the 30th InternationalInternational Conference on Lightning Protection-ICLP 2010, Cagliari, Italy, 13–17 September 2010; Volume 2010, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Asman, S.H.; Ab Aziz, N.F.; Abd Kadir, M.Z.A.; Amirulddin, U.A.U. Fault signature analysis for medium voltage overhead line based on new characteristic indices. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon), Penang, Malaysia, 7–8 December 2020; pp. 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Emperuman, M.; Chandrasekaran, S. Hybrid Continuous Density Hmm-Based Ensemble Neural Networks for Sensor Fault Detection and Sensor Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Yang, T.; Gao, W.; Zhang, C. A Novel Fault Diagnosis Method for Rotating Machinary Based on a Convoluttional Neural Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhimish, M.; Holmes, V.; Mehrdadi, B.; Dales, M. Comparing Mamdani Sugeno fuzzy logic and RBF ANN network for PV fault detection. Renew. Energy 2018, 117, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; EI-Khattam, W.; Galal, Y. A novel fuzzy cause-and-effect-networks based methodology for a distribution system’ s fault diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2013 3rd International Conference on Electric Power and Energy Conversion Systems, Istanbul, Turkey, 2–4 October 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.L.; Ma, H.Y.; Yang, Y. Study on the Test Data Fault Mining Technology Based on Decision Tree. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 154, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, N.; Ramachandran, K.I. Fault diagnosis of spur bevel gear box using discrete wavelet features and Decision Tree classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 9564–9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upendar, J.; Gupta, C.P.; Singh, G.K. Statistical decision-tree based fault classification scheme for protection of power transmission lines. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkercha, R.; Moulahoum, S. Fault detection and diagnosis based on C4.5 decision tree algorithm for grid connected PV system. Sol. Energy 2018, 173, 610–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, M.; Hoad, R.R.; Bruton, T.D.; Das, R.; Kunsman, S.A.; Peterson, J.M. Staged-fault testing for high impedance fault data collection. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers, College Station, TX, USA, 5–7 April 2005; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- AsghariGovar, S.; Pourghasem, P.; Seyedi, H. High impedance fault protection scheme for smart grids based on WPT and ELM considering evolving and cross-country faults. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 107, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavi, M.; Mishra, Y.; Vilathgamuwa, M.D. High-impedance fault detection and classification in power system distribution networks using morphological fault detector algorithm. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12, 3699–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Brahma, S.M. Detection of high impedance fault in power distribution systems using mathematical morphology. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheili, A.; Sadeh, J.; Bakhshi, R. Modified FFT based high impedance fault detection technique considering distribution non-linear loads: Simulation and experimental data analysis. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 94, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, C.G. High impedance fault detection on distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 1998 Rural Electric Power Conference Presented at 42nd Annual Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 26–28 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.; Costa, P.; Gouvea, M.; Lacerda, A.; Alves, F.; Leite, D. High impedance fault detection in power distribution systems using wavelet transform and evolving neural network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 154, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.R.N.; Carvalho, A.P.A.; Vieira, P.; Costa, C.T. Characterization of failures in insulators to maintenance in transmission lines. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering, Oshawa, ON, Canada, 14–17 August 2017; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Waluyo; Pakpahan, P.M. Suwarno Study on the electrical equivalent circuit models of polluted outdoor insulators. IEEE 2006, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Redfern, M.A.; Bo, Z.Q.; Montjean, D. Detection of broken conductors using the positional protection technique. Proc. IEEE Power Eng. Soc. Transm. Distrib. Conf. 2001, 2, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Mariut, L.; Helerea, E. Electromagnetic Analysis—Application to Lightning Surge Phenomena on Power Lines. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, Bucharest, Romania, 28–29 November 2014; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- CIGRE, W. Guideline for Numerical Electromagnetic Analysis Method and Its Application to Surge Phenomena. 2013. Available online: https://e-cigre.org/publication/543-guideline-for-numerical-electromagnetic-analysis-method-and-its-application-to-surge-phenomena (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Ijaz, M.; Shafiullah, M.; Abido, M.A. Classification of power quality disturbances using Wavelet Transform and Optimized ANN. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Intelligent System Application to Power Systems (ISAP), Porto, Portugal, 11–16 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, N.; Ali, S.; Kapoor, G. Detection of fault in series capacitor compensated double circuit transmission line using wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON) Greater, Noida, India, 28–29 September 2019; pp. 760–764. [Google Scholar]
- Kaitwanidvilai, S.; Pothisarn, C.; Jettanasen, C.; Chiradeja, P.; Ngaopitakkul, A. Discrete wavelet transform and back-propagation neural networks algorithm for fault classification in underground cable. In Proceedings of the IMECS 2011 International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2011, Hong Kong, China, 16–18 March 2011; Volume 2, pp. 996–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Asman, S.H.; Aziz, N.F.A.; Kadir, M.Z.A.A.; Amirulddin, U.A.U.; Izadi, M. Determination of Different Fault Features in Power Distribution System Based on Wavelet Transform. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 6256–6261. [Google Scholar]
- Chiradeja, P.; Pothisarn, C. Identification of the fault location for three-terminal transmission lines using discrete wavelet transforms. In Proceedings of the 2009 Transmission & Distribution Conference & Exposition: Asia and Pacific, Seoul, Korea, 26–30 October 2009; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Habsah Asman, S.; Farid Abidin, A. Comparative Study of Extension Mode Method in Reducing Border Distortion Effect for Transient Voltage Disturbance. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 6, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanfretti, L.; Arava, V.S.N. Decision tree-based classification of multiple operating conditions for power system voltage stability assessment. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 123, 106251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Stone, C.J.; Olshen, R.A. Classification and Regression Trees; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984; ISBN 0412048418. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, W.-Y. Regression tress with unbiased variable selection and interaction detection. Stat. Sin. 2002, 361–386. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, W.-Y.; Shih, Y.-S. Split selection methods for classification trees. Stat. Sin. 1997, 815–840. [Google Scholar]




| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency (Hz) | 50 |
| Sample per cycle | 100 |
| Sampling time (s) | 2 × 10−4 |
| Run time (s) | 0.2 |
| Variable Parameters | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Fault distance (km) | 10 to 100 (step size 10 km) |
| Phase angle (°) | 0, 30, 45, 60, 90, 180, 270 |
| Load (MW) | 200, 300, 330 |
| Tower Height/Geometry (m) | Surge Impedance (Ω) | Footing Resistance (Ω) | Lightning Speed | Attenuation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h1 | h2 | h3 | h4 | Zt1 | Zt4 | Rf | m/μs | a1 | |
| 31.76 | 2.70 | 5.55 | 5.55 | 17.96 | 220 | 150 | 5 | 300 | 0.89 |
| Symbol | Matrix | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| ACC | Accuracy | |
| SNS | Sensitivity | |
| SPC | Specificity | |
| PRC | Precision | |
| F1 | F1 Score |
| Sample | Input | Categorical Variable/Output | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Var 1 | Var 2 | Var 3 | Var 4 | Var 5 | ||
| 1 | 0.0142 | 0.0720 | 0.0596 | 7.7798 | 0.1695 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.0136 | 0.0826 | 0.0768 | 39.3691 | 0.9252 | 1 |
| 3 | 0.0150 | 0.0708 | 0.0580 | 9.1606 | 0.2659 | 2 |
| 4 | 0.0138 | 0.0712 | 0.0584 | 6.7943 | 0.1474 | 2 |
| 5 | 0.1208 | 0.1462 | 0.0368 | 2.2889 | 0.0054 | 3 |
| 6 | 0.1072 | 0.1228 | 0.0799 | 0.5959 | 0.0014 | 3 |
| 7 | 0.0142 | 0.0724 | 0.0632 | 10.8221 | 0.1757 | 2 |
| 8 | 0.0142 | 0.0816 | 0.0680 | 28.7403 | 0.7757 | 1 |
| 8 | 0.0688 | 0.0878 | 0.0764 | 0.3635 | 0.0003 | 4 |
| 10 | 0.0278 | 0.0224 | 0.0000 | 0.7551 | 0.0022 | 4 |
| 11 | 0.0184 | 0.0698 | 0.0572 | 13.6512 | 0.5133 | 2 |
| 12 | 0.0184 | 0.0814 | 0.0660 | 40.7826 | 1.0624 | 1 |
| 13 | 0.1200 | 0.1588 | 0.0487 | 0.6651 | 0.0010 | 3 |
| 14 | 0.1192 | 0.2138 | 0.0387 | 3.5494 | 0.0069 | 3 |
| 15 | 0.1158 | 0.2780 | 0.0392 | 0.8545 | 0.0024 | 3 |
| Label | Description | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Var 1 | Fault duration from 10% to 90% increase (T10/90) | s |
| Var2 | Fault duration from at 20% increase (T20) | s | |
| Var 3 | Fault duration from at 20% increase (T50) | s | |
| Var 4 | Voltage drop (Vd) | % | |
| Var 5 | Wavelet energy (Ener) | - | |
| Categorical variable / Output | 1 | Lightning | - |
| 2 | Insulator degrading | - | |
| 3 | Tree encroachment | - | |
| 4 | Crane encroachment | - |
| Iteration (ith) | Percentage Accuracy (%) | Maximum Number of Split |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 52.0408 | 1 |
| 2 | 76.5306 | 2 |
| 3 | 99.8299 | 3 |
| 4 | 99.8299 | 4 |
| 5 | 99.4898 | 5 |
| 6 | 99.4898 | 6 |
| 7 | 99.3197 | 7 |
| 8 | 99.8299 | 8 |
| 9 | 99.8299 | 9 |
| 10 | 99.6599 | 10 |
| Train/Test | Lightning | Insulator | Tree | Crane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning | 100% (63/63) | - | - | - |
| Insulator | - | 100% (71/71) | - | - |
| Tree | - | - | 100% (55/55) | - |
| Crane | - | - | - | 100% (63/63) |
| Train/Test | Lightning | Insulator | Tree | Crane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning | 100% (63/63) | - | - | - |
| Insulator | - | 100% (71/71) | - | - |
| Tree | - | - | 100% (55/55) | - |
| Crane | - | - | 3 | 85.71% (60/63) |
| Train/Test | Lightning | Insulator | Tree | Crane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning | 98.4% (62/63) | 1 | - | - |
| Insulator | - | 100% (71/71) | - | - |
| Tree | - | - | 100% (55/55) | - |
| Crane | - | - | - | 100% (63/63) |
| Train/Test | Lightning | Insulator | Tree | Crane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning | 100% (38/38) | - | - | - |
| Insulator | - | 100% (44/44) | - | - |
| Tree | - | - | 100% (48/48) | - |
| Crane | - | - | 1 | 97.4% (37/38) |
| Train/Test | Lightning | Insulator | Tree | Crane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning | 100% (42/42) | - | - | - |
| Insulator | - | 100% (50/50) | - | - |
| Tree | - | - | 100% (35/35) | - |
| Crane | - | - | - | 100% (41/41) |
| Train/Test | Lightning | Insulator | Tree | Crane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning | 100% (55/55) | - | - | - |
| Insulator | - | 100% (37/37) | - | - |
| Tree | - | - | 100% (32/32) | - |
| Crane | - | - | 3 | 93.2% (41/44) |
| Sample Ratio | Computation Time (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| All Splits | Curvature | Interaction-Curvature | |
| 70/30 | 11.622430 | 12.270969 | 11.688976 |
| 80/20 | 12.392414 | 12.783483 | 11.775463 |
| Fault Causes | Sample Size | Predictor Selection | ACC | SNS | SPC | PRC | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | |||||||
| Lightning | 30% test | All splits | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 98.90 | 100 | 94.50 | 94.80 | 97.30 | ||
| 20% test | All splits | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Insulator degrading | 30% test | All splits | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 99.60 | 100 | 99.40 | 98.60 | 99.30 | ||
| 20% test | All splits | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Tree encroachment | 30% test | All splits | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Curvature | 98.80 | 100 | 98.50 | 94.80 | 97.30 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 20% test | All splits | 99.40 | 100 | 99.20 | 98.00 | 99.00 | |
| Curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 98.20 | 100 | 97.80 | 91.40 | 95.50 | ||
| Crane encroachment | 30% test | All splits | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Curvature | 98.80 | 95.20 | 100 | 100 | 97.50 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 20% test | All splits | 99.40 | 97.40 | 100 | 100 | 98.70 | |
| Curvature | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Interaction- curvature | 98.20 | 93.20 | 100 | 100 | 96.50 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asman, S.H.; Ab Aziz, N.F.; Ungku Amirulddin, U.A.; Ab Kadir, M.Z.A. Decision Tree Method for Fault Causes Classification Based on RMS-DWT Analysis in 275 kV Transmission Lines Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094031
Asman SH, Ab Aziz NF, Ungku Amirulddin UA, Ab Kadir MZA. Decision Tree Method for Fault Causes Classification Based on RMS-DWT Analysis in 275 kV Transmission Lines Network. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094031
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsman, Saidatul Habsah, Nur Fadilah Ab Aziz, Ungku Anisa Ungku Amirulddin, and Mohd Zainal Abidin Ab Kadir. 2021. "Decision Tree Method for Fault Causes Classification Based on RMS-DWT Analysis in 275 kV Transmission Lines Network" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094031
APA StyleAsman, S. H., Ab Aziz, N. F., Ungku Amirulddin, U. A., & Ab Kadir, M. Z. A. (2021). Decision Tree Method for Fault Causes Classification Based on RMS-DWT Analysis in 275 kV Transmission Lines Network. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094031








