Thymoquinone, but Not Metformin, Protects against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Renal Dysfunction in Rats
Abstract
1. Background
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Groups
2.3. Renal Function
2.4. Oxidative Status Analysis
3. Histopathological Evaluation of the Kidneys
Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Biochemical Changes in the Different Groups
Nephrotoxic Effects and Oxidative Stress of GM in Treated Rats
4.2. Renoprotective Effects of TQ on GM-Treated Rats
4.3. Renoprotective Effects of MF on GM-Treated Rats
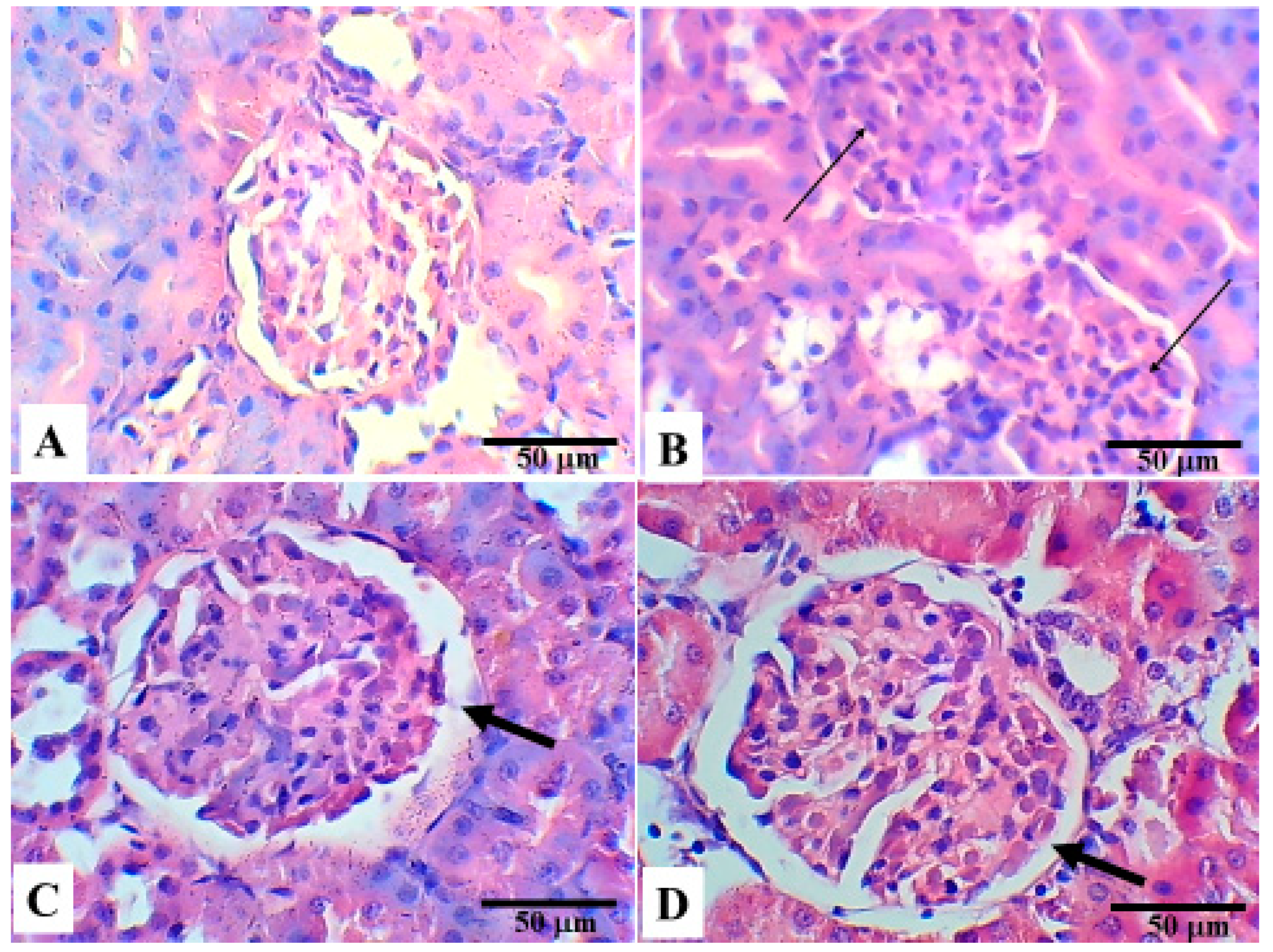
5. Histopathological Changes in the Different Groups
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval
References
- Gad, G.F.; Mohamed, H.A.; Ashour, H.M. Aminoglycoside Resistance Rates, Phenotypes, and Mechanisms of Gram-Negative Bacteria from Infected Patients in Upper Egypt. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbarth, S.; Rohner, P.; Safran, E.; Garbino, J.; Auckenthaler, R.; Pittet, D. Resistance to amikacin and gentamicin among Gram-negative bloodstream isolates in a university hospital between 1989 and 1994. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1998, 4, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Suleimani, Y.M.; Abdelrahman, A.M.; Karaca, T.; Manoj, P.; Ashique, M.; Nemmar, A.; Ali, B.H. The effect of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin on gentamicin nephrotoxicity in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiros, Y.; Vicente-Vicente, L.; Morales, A.I.; López-Novoa, J.M.; López-Hernández, F.J. An Integrative Overview on the Mechanisms Underlying the Renal Tubular Cytotoxicity of Gentamicin. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 119, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J.P.; Viotte, G.; Vandewalle, A.; Van Hoof, F.; Tulkens, P.; Fillastre, J.P. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: A cell biology approach. Kidney Int. 1980, 18, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Jin, W.W.; Huang, M.; Ji, H.; Capen, D.E.; Xia, Y.; Yuan, J.; Păunescu, T.G.; Lu, H.A.J. Gentamicin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in an Animal Model Involves Programmed Necrosis of the Collecting Duct. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2097–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, P.; Rohilla, A.; Thangathirupathi, A. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: Do we have a promising therapeutic approach to blunt it? Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, A.; Yildirim, A.; Simsek, N.; Kalkan, Y.; Celebi, F. Spirulina platensisprotects against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1506–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitha, B.; Janardhanan, K. Aqueous-ethanolic extract of morel mushroom mycelium Morchella esculenta, protects cisplatin and gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, I.; Balikci, E. Protective effects of nigella sativa against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 62, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, P.; Chakkarwar, V.A.; Kumar, V.; Jain, A.; Reddy, J.; Singh, M. Experimental models for nephropathy. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2008, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Quiros, Y.; Vicente, L.; Morales, A.I.; Lopez-Hernandez, F.J. New insights into the mechanism of aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity: An integrative point of view. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Salgado, C.; Eleno, N.; Morales, A.I.; Pérez-Barriocanal, F.; Arévalo, M.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M. Gentamicin treatment induces simultaneous mesangial proliferation and apoptosis in rats. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarifi, S.; Al-Doaiss, A.; Alkahtani, S.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; Al-Eissa, M.S.; Al-Dahmash, B.; Al-Yahya, H.; Mubarak, M. Blood chemical changes and renal histological alterations induced by gentamicin in rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, C.; Pari, L. Thymoquinone ameliorates chemical induced oxidative stress and β-cell damage in experimental hyperglycemic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2011, 190, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, M.S. The anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity of Nigella sativa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 76, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, M.; Demir, H.; Karakaya, C.; Ozbek, H. Gastroprotective activity ofNigella sativaL oil and its constituent, thymoquinone against acute alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 6662–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Padhye, S.; Priyadarsini, K.I.; Newton, C. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of curcumin semicarbazone. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2738–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Bhattacharyya, M. Effect of metformin on oxidative stress, nitrosative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Od, N.; Oer, O. Guide Laboratory Animals for The Care and Use of Eighth Edition Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals Institute for Laboratory Animal Research Division on Earth and Life Studies; 2011; ISBN 9780309154000. Available online: http://www.nap.edu (accessed on 3 January 2019).
- Samarghandian, S.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Mehrad-Majd, H.; Mirhafez, S.R. Thymoquinone Ameliorates Acute Renal Failure in Gentamicin-Treated Adult Male Rats. Pharmacology 2015, 96, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fararh, K.M.; Shimizu, Y.; Shiina, T.; Nikami, H.; Ghanem, M.M.; Takewaki, T. Thymoquinone reduces hepatic glucose production in diabetic hamsters. Res. Vet. Sci. 2005, 79, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sena, C.M.; Matafome, P.; Louro, T.; Nunes, E.; Fernandes, R.; Seiça, R.M. Metformin restores endothelial function in aorta of diabetic rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiny, D.L.; Ertingshausen, G. Automated Reaction-Rate Method for Determination of Serum Creatinine with the CentrifiChem. Clin. Chem. 1971, 17, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacco, A.; Meiattini, F.; Moda, E.; Tarli, P. Simplified enzymic/colorimetric serum urea nitrogen determination. Clin. Chem. 1979, 25, 336–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestry, S.N.; Gawali, N.B.; Pai, S.A.; Gursahani, M.S.; Dhodi, J.B.; Munshi, R.; Juvekar, A.R. Punica granatum improves renal function in gentamicin-induced nephropathy in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2020, 11, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farombi, E.O.; Ekor, M. Curcumin attenuates gentamicin-induced renal oxidative damage in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Aleisa, A.M.; Al-Yahya, A.A.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Bakheet, S.A.; Fatani, A.G.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.M. Increased urinary losses of carnitine and decreased intramitochondrial coenzyme A in gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Ahmed, O.M.; Galaly, S.R. Thymoquinone and curcumin attenuate gentamicin-induced renal oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kalayarasan, S.; Prabhu, P.N.; Sriram, N.; Manikandan, R.; Arumugam, M.; Sudhandiran, G. Diallyl sulfide enhances antioxidants and inhibits inflammation through the activation of Nrf2 against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 606, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, A.; Parlakpinar, H.; Tasdemir, S.; Colak, C.; Vardi, N.; Ucar, M.; Emre, M.H.; Acet, A. Protective role of aminoguanidine on gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Acta Histochem. 2006, 108, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.H.; Al Za’Abi, M.; Blunden, G.; Nemmar, A. Experimental Gentamicin Nephrotoxicity and Agents that Modify it: A Mini-Review of Recent Research. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.I.; Detaille, D.; Prieto, M.; Puente, A.; Briones, E.; Arévalo, M.; Leverve, X.; López-Novoa, J.M.; El-Mir, M.-Y. Metformin prevents experimental gentamicin-induced nephropathy by a mitochondria-dependent pathway. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CL (n = 5) | GM (n = 5) | TQ (n = 5) | MF (n = 5) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renal function | |||||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.65 ± 0.05 | 2.25 ± 0.46 | 0.70 ± 0.14 | 1.58 ± 0.55 | CL vs. GM < 0.001 * GM vs. TQ < 0.001 * GM vs. MF = 0.073 TQ vs. MF = 0.010 * |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 73 ± 1.3 | 148.31 ± 21.16 | 74.37 ± 4.14 | 126.86 ± 25.16 | CL vs. GM < 0.001 * GM vs. TQ < 0.001 * GM vs. MF = 0.183 TQ vs. MF = 0.002 * |
| Oxidative Stress status | |||||
| Glutathione peroxidase-1 (GLPX1) (pg/mL) | 106.51 ± 5.07 | 76.79 ± 14.22 | 111.88 ± 8.97 | 104.80 ± 5.01 | CL vs. GM = 0.002 * GM vs. TQ = 0.002 * GM vs. MF = 0.003 * TQ vs. MF = 0.162 |
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD) (ng/mL) | 2.76 ± 0.17 | 1.25 ± 0.54 | 2.61 ± 0.17 | 2.61 ± 0.13 | CL vs. GM < 0.001 * GM vs. TQ = 0.001 * GM vs. MF = 0.001 * TQ vs. MF = 0.969 |
| Malondialdehyde (MDA) (ng/mL) | 325.93 ± 8.83 | 356.32 ± 12.5 | 319.41 ± 8.21 | 327.82 ±15.04 | CL vs. GM = 0.002 * GM vs. TQ = 0.001 * GM vs. MF = 0.012 * TQ vs. MF = 0.305 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsharidah, M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.H.; Alsharidah, A.S.; Mobark, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H.; Shata, A.; Abdellatif, A.A.H.; El-Readi, M.Z.; Mohany, K.M.; Al Rugaie, O. Thymoquinone, but Not Metformin, Protects against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Renal Dysfunction in Rats. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093981
Alsharidah M, Abdel-Moneim A-MH, Alsharidah AS, Mobark MA, Rahmani AH, Shata A, Abdellatif AAH, El-Readi MZ, Mohany KM, Al Rugaie O. Thymoquinone, but Not Metformin, Protects against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Renal Dysfunction in Rats. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093981
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsharidah, Mansour, Abdel-Moneim Hafez Abdel-Moneim, Ashwag Saleh Alsharidah, Mugahid A. Mobark, Arshad Husain Rahmani, Ahmed Shata, Ahmed A. H. Abdellatif, Mahmoud Zaki El-Readi, Khalid M. Mohany, and Osamah Al Rugaie. 2021. "Thymoquinone, but Not Metformin, Protects against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Renal Dysfunction in Rats" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093981
APA StyleAlsharidah, M., Abdel-Moneim, A.-M. H., Alsharidah, A. S., Mobark, M. A., Rahmani, A. H., Shata, A., Abdellatif, A. A. H., El-Readi, M. Z., Mohany, K. M., & Al Rugaie, O. (2021). Thymoquinone, but Not Metformin, Protects against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Renal Dysfunction in Rats. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 3981. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093981








