Featured Application
In this work, we designed a new method of data mining, implemented as a free web application, and a novel protein analysis called chromosome walking, which together enhance the information retrieved from protein databases and ensure better exploitation of the huge amount of data collected in protein and genome databases for new potential translational and clinical applications.
Abstract
Notwithstanding the huge amount of detailed information available in protein databases, it is not possible to automatically download a list of proteins ordered by the position of their codifying gene. This order becomes crucial when analyzing common features of proteins produced by loci or other specific regions of human chromosomes. In this study, we developed a new procedure that interrogates two human databases (genomic and protein) and produces a novel dataset of ordered proteins following the mapping of the corresponding genes. We validated and implemented the procedure to create a user-friendly web application. This novel data mining was used to evaluate the distribution of critical amino acid content in proteins codified by a human chromosome. For this purpose, we designed a new methodological approach called chromosome walking, which scanned the whole chromosome and found the regions producing proteins enriched in a selected amino acid. As an example of biomedical application, we investigated the human chromosome 15, which contains the locus DYX1 linked to developmental dyslexia, and we found three additional putative gene clusters whose expression could be driven by the environmental availability of glutamate. The novel data mining procedure and analysis could be exploited in the study of several human pathologies.
1. Introduction
Genomic databases are widely used not only to extract information about genes, but they also provide the gene position on chromosomes, which is useful when entire regions of chromosomes are analyzed. Neighboring genes can be studied as a whole entity in several circumstances. For example, many gene clusters have been described and their analysis suggests that a set of adjacent genes can be functional. Benefits for gene clustering include co-inheritance, co-transcriptional regulation in the presence of a similar chromatin environment as well as a coordinated handling of post-transcriptional processes such as export for protein synthesis and compartmentalization [1,2,3]. Other examples of analysis that consider large regions of chromosomes are the genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and the linkage disequilibrium studies, which have identified loci related to disorders or pathologies [4,5,6,7].
In all cases, it is important to know the mapping of genes in clusters, loci, or specific regions of the chromosome, in order to analyze their relationships. Unfortunately, the same ordered list of the corresponding codified proteins is not easily retrieved from protein databases. The most used protein database, UniProt Knowledgebase (Uniprot), gives information on human proteins without ordering based on gene position. This lack means that without the ordered list of proteins codified by gene clusters, loci, or other specific regions, it is difficult (and impossible on a large scale) to analyze common features of the products of genes, such as amino acid content. Indeed, we have recently demonstrated that the proteins codified by two gene clusters show a significantly lower ratio glutamate/glutamine compared with the nearby regions of the same chromosome [8].
The aim of this work was to create a new procedure that interrogates two databases (genomic and protein) and matches the results in order to produce a novel dataset in which the human proteins are ordered following the mapping of the corresponding genes on the chromosome, together with their amino acid composition. The novel dataset provides details on the position of the codifying gene and on the amino acid (AA) sequence and length of the translated protein.
Furthermore, we propose a novel analysis of amino acid content of proteins mapped on chromosomes by our new procedure. As an example of application, we investigated the proteins codified by chromosome 15, which contains a locus harboring candidate dyslexia susceptibility genes.
2. Methods
2.1. Building a Novel Dataset: The Ordering Procedure
The procedure proposed in this study matches the results of queries creating a novel dataset in which the human proteins are ordered by the position of the corresponding genes on the chromosome. The manual procedure is described in Supplementary Methods for replicability and details of data, metadata, datasets, methods, and rules to join tables, useful to extract the information for our research.
The two databases searched are UniProt (https://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 16 February 2021)), the central hub for the collection of functional information on proteins (https://www.uniprot.org/help/uniprotkb (accessed on16 February 2021)) [9] and Ensembl (https://www.ensembl.org/index.html (accessed on 16 February 2021)), a genome browser for vertebrate genomes [10]. The queries in UniProt allow the download and analysis of all proteins codified by the same chromosome. Ensembl genomic complex datasets can be retrieved using the Biomart data-mining tool [11] (http://www.ensembl.org/biomart/martview/ff9ecfb63b2cf534ed20a16879eaebb8 (accessed on 16 February 2021)) based on Ensembl Genes 98 (June 2019) and human genes GRCh38.p13.
Briefly, the UniProt Table gives all the information about proteins, including length and amino acid composition, but without reference to the position of the coding gene on the chromosome. The construction of the chromosome table using Biomart requires first the selection of some attributes and the creation of a new dataset called Biomart Table. Then, the columns of the Ensembl table were manipulated to obtain a new table comparable with the UniProt table, called Biomart Elab Table. Finally, we matched the information from UniProt and Ensembl, building a new table called the Canonical Table, which gives a list of proteins ordered by gene position and supplies their amino acid content.
Figure 1 outlines the whole procedure.
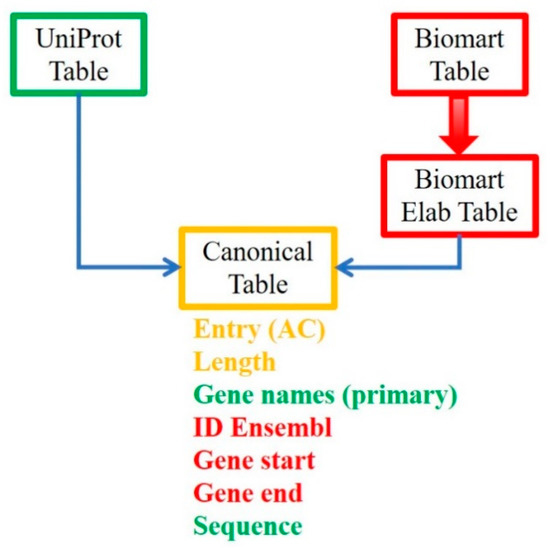
Figure 1.
Workflow for building a dataset in which the proteins are ordered by their position on the chromosome. Protein data extracted from the UniProt database are matched with genetic data extracted from the Ensembl database and retrieved by Biomart. In green are the data collected from UniProt, in red the data obtained from Biomart search, and in yellow the data identical in both collections and used to merge the tables.
2.2. Implementation: A Web Application
Based on the procedure described, we implemented a web application, written in python, available at https://gplab.diff.org, which in the section “Chromosomes”, allows downloading the canonical file for each chromosome. The web application accesses UniProt and Ensembl databases programmatically, using python interfaces in order to obtain data always updated. By this automated procedure, the amino acid content inserted in the canonical data table is always computed starting from the latest data available online from the two databases. Moreover, the web interface was designed to easily download data for each chromosome.
In order to download Uniprot canonical proteins data, we used Bioservices at
(https://bioservices.readthedocs.io/en/master/index.html (accessed on 16 February 2021)) and in particular (https://bioservices.readthedocs.io/en/master/references.html#bioservices.uniprot.UniProt (accessed on 16 February 2021)) with the Uniprot class.
To query Biomart databases we used pybiomart, a biomart interface for python (https://pypi.org/project/pybiomart/ (accessed on 16 February 2021)) to retrieve and query datasets.
Ensembl protein columns table were manipulated based on Step 2.3 “Ensembl protein columns table manipulation” of the Methods section, using the python data analysis toolkit pandas (https://pandas.pydata.org/ (accessed on 16 February 2021)).
The Uniprot Table and the Ensembl final table were merged based on Uniprot/Swissprot id accession number (AC), length, and sequence. In order to count the amino acids listed in the protein sequence we used the Bio.SeqUtils.ProtParam module (https://biopython.org/docs/1.75/api/Bio.SeqUtils.ProtParam.html (accessed on 16 February 2021)). Finally, the table was ordered by the column Gene start (bp).
2.3. Validation
We applied the procedure described above to four human chromosomes of different sizes: chromosome 1, chromosome 14, chromosome 15, and chromosome 21 with the aim of checking the rate of protein loss in our final canonical table compared to the complete UniProt protein table.
The error rate was calculated as follows: (the number of UniProt sequences subtracted by the number of sequences in Canonical table) divided by the number of UniProt sequences.
The outcomes are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Rate of protein loss in each chromosome.
We conclude that the protein loss from the Uniprot table to the final Canonical table is limited even in the largest chromosomes, thus demonstrating the accuracy of our procedure that obtains a list of proteins roughly corresponding to the list of proteins given by the Uniprot database, but ordered by their position on chromosomes.
3. Results
3.1. One Application of the Novel Dataset Obtained in Canonical Table: The Walking Procedure
One aspect of the proteome not yet investigated is the importance of AA composition in terms of the relative abundance of single amino acids in human proteins. Proteins sharing similar percentages of critical AA could be translated in the same conditions or even simultaneously because of the availability of the AA. We set out to verify whether the content in amino acids of the proteins codified by a certain chromosome shows a non-random distribution. In fact, some regions of a chromosome could codify for proteins enriched in few AA; we could define these spots as environment-driven gene clusters, because their translation would be dependent on and synchronized by AA availability.
Because the Canonical table provides information about the gene/protein position in each chromosome as well as AA composition, we can investigate the content of single amino acids of proteins translated along the whole chromosome, and we devised a new procedure defining the distribution of a chosen amino acid, called walking procedure. We used the columns of the canonical table to extract useful additional information, and we created new supplemental columns which were used as input for the walking procedure. The steps to construct the new table are listed below.
The column “sequence”, containing the canonical UniProt protein sequence, and the column “length”, containing the length of the protein sequence, were used to calculate the absolute content and relative frequencies (% of the total) of the AAs of each protein, generating one new column for each AA.
The walking procedure was applied to the columns of amino acids absolute content. We carried out a frameshift, counting in each frame the number of proteins enriched in a selected AA. In short, we moved alongside the chromosome, and we checked whether the content of a chosen AA was changing among the proteins of that segment.
The first block analyzed went from the first element (relative to the first protein codified by the chromosome), which we called SBe (Start Block element), to the twenty-fifth element in the column AA absolute content, which we called FBe (Final Block element). The length of the block LB was twenty-five.
The software counts how many proteins have an absolute value of a certain amino acid greater than a fixed threshold T. The resulting number is written in a new column named Surfing E at position FP (First Position). Next, we shift the block position by position. The software writes the resulting values in the column Walking at positions following FP. The procedure stops when FBe reaches the last protein codified by the chromosome. All values generated this way are written in a new table that contains all columns from canonical table plus the new generated columns. This table is named CHR + chromosome number (two digits) canonical_WALKING.xls; for example, CHR01_canonical_WALKING.xls.
3.2. The Surfing Analysis
The table created in the previous step provides new columns with the walking values data, which can be plotted on a graph. The threshold T and the length LB of the blocks vary depending on the analyzed amino acids.
The surfing analysis works on the graphical representation of the data calculated by the walking procedure. The combination of the position of the gene/protein (x-axis) with the walking data (y-axis) provides information about segments of the chromosome in which the values increase until reaching a peak. When we plot the walking data along the frame shifts, we design a wave that reaches its peaks when the proteins of that segment have the highest content of that AA. The analysis (called surfing analysis) spots the fragments of the chromosome that codify for proteins enriched in one or more AAs; a schematic view of chromosome walking procedure and surfing analysis is shown in Figure 2.
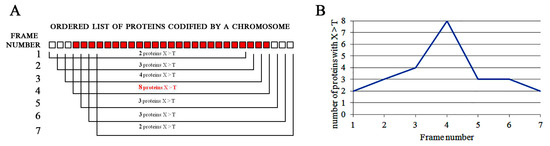
Figure 2.
Outline of the walking procedure and surfing analysis. (A) The frameshift throughout the ordered list of proteins (represented by squares) is carried out, and in each frame, the number of proteins having the amount of a selected AA (X) higher than the threshold (T) is counted. The frame most enriched in X is shown in red. (B) These numbers are plotted on graph, obtaining a peak that highlights the region of the chromosome codifying for proteins enriched in the chosen AA.
3.3. A Case Study on Chromosome 15
The walking procedure and the surfing analysis were applied to chromosome 15, which contains the locus DYX1 on 15q21, one of the nine loci (DYX1-9) identified from Online Mendelian inheritance in man (OMIM, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim (accessed on 16 February 2021)) for Developmental Dyslexia (DD). Because it has been reported that there is a link between the levels of some AA in brain and the reading abilities [11], and some proteins appear critical in the onset of the disorder (some proteins located within the loci and other proteins defined markers of dyslexia), we decided to verify whether in the proteins codified by the dyslexia locus there was a different distribution of AA. If so, we expected to find the proteins enriched in a selected AA in one of the peaks identified by our surfing analysis. Dyslexia is caused by multiple genetic and environmental risk factors [12,13]. Based on the literature, we identified the following gene markers for dyslexia: CYP19A1, DCDC2, DYX1C1, CFAP36, S100B, MRPL19, GCFC2, FOXP2, ZNF280D, SLITRK2. For each gene/locus we annotated the cytogenetic position in order to identify them on chromosomes. The cytogenetic position was then converted to the molecular position using data from the University of California Santa Cruz (https://genome.ucsc.edu/index.html) (accessed on 16 February 2021), freely available online at http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg38/database/ (accessed on 16 February 2021) for (GRCh38/hg38). We used the cytogenetic location, (column Cyto in Table 2) to identify the molecular position on Chromosome 15, using the transcoding file cytoBand.txt.

Table 2.
Median values of selected amino acids calculated in protein markers of dyslexia as absolute content or relative frequencies (% of the total). Cytogenetic location of markers is indicated (Cyto).
We first applied the ordering procedure (step 2.1) to create the canonical table with genes and proteins of chromosome 15. Next, we selected the amino acid whose content could be possibly critical in dyslexia; based on literature search, our choice fell on glutamate (glu) and glutamine (gln) because high values of glutamate and low levels of glutamine have a positive correlation with reading ability [11] and because the availability of these AA could depend on local conditions, for example in hypoxia glutamate can be converted to glutamine [8]. We calculated the absolute content of glutamate and glutamine for each protein of chromosome 15, and we defined the threshold T and the length LB of the blocks necessary to carry out the Walking procedure. LB was established equal to 25 because it gave a reasonably deep frameshift (it allowed to obtain N = 533 values of walking steps) and a good compromise between precision and predictability of the model.
In order to select one AA and to define the threshold needed in the walking procedure, we calculated the median value of glutamate (E) and glutamine (Q) of the proteins considered markers of dyslexia. The values are reported in Table 2.
Of note, three markers were located in chromosome 15. We compared the median values of markers with the median values of the whole chromosome 15, as shown in Figure 3. We decided to consider only the relative frequencies and not the absolute content of Glu and Gln in each protein in order to ignore the differences in protein size, which would render the values extremely variable and barely comparable.
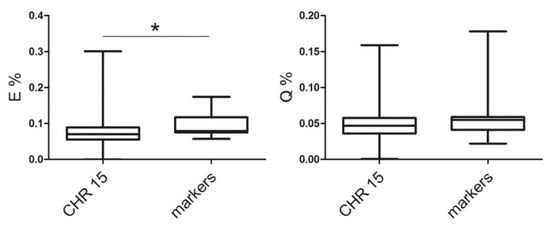
Figure 3.
The content of glutamate and glutamine of protein codified by chromosome 15 and markers of dyslexia. Box plots of values for proteins of each group. Bottoms and tops of the boxes are the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively; the lines across the boxes are the median values, the ends of the whiskers represent minimum and maximum values. * p < 0.05.
We found that only the medians calculated for E were significantly different. Because the median of chromosome 15 was lower than the markers, we assumed that many proteins in that chromosome had a content of glutamate lower than the markers, and we wanted to verify where they are located. In other words, only for E could we expect variability among proteins throughout the chromosome. On the other hand, the medians for Q were similar, therefore, the majority of proteins in chromosome 15 would have values similar to the markers.
For these reasons, we used E values for chromosome walking, with the threshold greater than the median of markers (49). The results of chromosome walking and surfing analysis are shown in Figure 4. The analysis of the peaks shows the regions where the proteins have the highest amount of E. The median value for walking content was 9; from Figure 4 it is evident that the regions were the walking content is higher than 9, for example in 10, fell within 4 peaks.
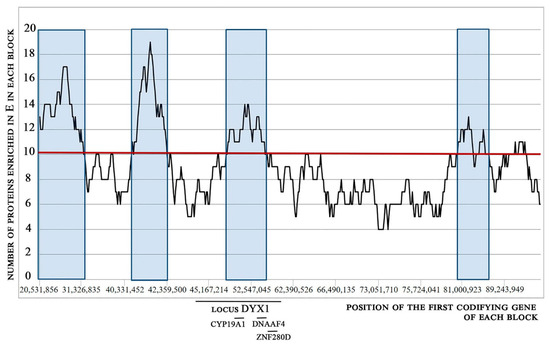
Figure 4.
Chromosome walking and surfing analysis of chromosome 15. A block of 25 proteins was shifted along the whole chromosome. At each position of the block, the number of proteins having more than 49 E was calculated and reported on the ordinates. On the x-axis, the graph shows the position of the first codifying gene of each block (only a few values are displayed). The position of the locus and gene markers of dyslexia is indicated. The regions of chromosome codifying for many proteins with high content of E are highlighted.
Interestingly, the Locus DYX1 (genetic position 44,800,000–59,100,000) and the markers of dyslexia codified by the locus fall in the third peak found by chromosome walking. This finding validates the utility of scanning the content of AA in proteins following their translation order throughout the chromosomes. Moreover, the presence of peaks in some not yet explored regions of chromosome 15 suggests further investigation about dyslexia markers.
4. Discussion
This work stemmed from the necessity of working on a sequential list of proteins, ordered as the codifying genes, together with their amino acid composition, in all studies striving for finding similarities among proteins produced by neighboring genes. To the best of our knowledge, at the moment, no database was able to provide such an ordered list, therefore, we created a procedure matching the information supplied by UniProt Knowledgebase and by Ensembl databases.
The aim of this work was to describe a novel procedure of data mining and validate its output. Given the complexity of the novel multi-step procedure, we verified that the loss of proteins extracted from the UniProt database was very limited. Confident of its validation and reproducibility, with this study, we propose a new useful method by which the human proteins are ordered following the mapping of the corresponding genes on the chromosome. Data, method, and procedure were described and made available under the FAIR data principles in order to enhance reusability [22].
FAIR data from Uniprot [23] were combined with Ensembl FAIR data [24] in order to obtain the new datasets used in this study, which were uploaded and univocally identified on Zenodo, the open globally scoped repository (https://about.zenodo.org/principles/ (accessed on 16 February 2021)) under FAIR principle [22]. We described metadata identifying the digital object and the process used to integrate data. However, the data and the procedure described in this work were only a starting point for further development. In fact, our effort was focused on automating this multi-step procedure and to deposit a user-friendly open tool, which is available to the whole scientific community under FAIR Principle at https://gplab.diff.org/home (accessed on 16 February 2021). In the section “Chromosomes”, the procedure described in Methods has been implemented in order to create datasets always updated to the latest release, and easy to retrieve; indeed, the tool has been specially designed for researchers with a little bioinformatics training and with the necessity of downloading protein information from a list of proteins ordered by their gene position. A future development of the tool could include linking proteins to other useful databases such as the KEEG PATHWAY and Reactome Pathway database. We believe that this tool can retrieve precious information not delivered by databases, thus representing a step forward in the utilization of science data.
In this work, to demonstrate the utility of the procedure, we applied it to investigate a biological issue. In our previous study, we demonstrated that the amino acid composition of proteins reflects the availability of amino acid imposed by the cellular context [8] and, we showed that when the tissue has a local utilization of AA, the ratio Glu/Gln is proportional to oxygenation. In fact, because glutamate decreases in hypoxia due to interconversion to glutamine, we concluded that the oxygenated environment would advantage the biosynthesis of proteins enriched in glutamate, while the hypoxic condition would increase the availability of glutamine and thus favor the translation of glutamine-rich proteins. Based on these tenets and on the experimental work reporting a link between the cerebral levels of glutamate and reading abilities, we wondered whether the proteins described as markers of dyslexia could be proteins enriched in glutamate and thus particularly dependent on oxygenation for their expression. In particular, the investigation of several cerebral areas has demonstrated that high values of glutamate have a positive correlation with reading ability in 6 to 10-year-old children, while glutamine has a negative correlation with language skills [11]. Indeed, the median value of Glu in proteins markers of dyslexia is higher than the value calculated for all proteins codified by the human genome: 49 vs. 27 respectively, as absolute content, and 0.08 vs. 0.06, as relative frequencies (% of the total).
In our previous work, we also found some evidence suggesting that gene clustering may represent an adaptation for responding to amino acid availability [8]. Again, we hypothesized that dyslexia loci could be regions of chromosome codifying for proteins enriched in glutamate, therefore, sensitive to oxygenation for their translation.
To test our hypothesis, we performed a proof of concept investigation; we used our novel procedure to analyze the content of Glu of proteins codified by chromosome 15, which encompasses a locus for dyslexia. We obtained a list of proteins ordered by their translation position on the chromosome, and by chromosome walking and surfing analysis, we were able to find the regions of the chromosome codifying for proteins most enriched in Glu. By this analysis, we found the confirmation that the dyslexia locus DYX1 overlaps with a length of DNA producing proteins with more glutamate than what codified by the neighboring genes. We concluded that the DYX1 is a gene cluster whose expression could be limited by environmental conditions and AA availability. For example, it is reasonable to expect that the proteins of the locus will be scarcely expressed in a hypoxic environment, thus revealing an interesting link between hypoxia and dyslexia. Most intriguing, our analysis discovered other three regions whose proteins are enriched in Glu; these regions could be potential loci of dyslexia, yet to be explored. We believe that this novel method of matching databases and analyzing AA content could be applied to many other disorders linked to hypoxia and to many AA other than Glu.
The linkage to a region of chromosome 15 has also been demonstrated for autism (reviewed in [25]). Interestingly, several studies assessing the levels of amino acids in the brain and serum of patients with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have reported increased levels of glutamine, or the sum of glutamate and glutamine, in specific brain regions of ASD patients, in association with lower intelligence quotient and greater impairments in social cognition, compared to typically developing individuals [26,27]. Moreover, recent studies have described a reduction of essential amino acid levels and sex-specific alterations in serum amino acid concentration profiles in children with autism spectrum disorder, and an increasing number of studies indicate that patients with ASD may have unique metabolic patterns with a variety of amino acid metabolism dysregulations [28,29]. Based on these observations, the analysis of chromosomes, focusing particularly on chromosome 15, could exploit the chromosome walking approach to discover differences in the amino acid composition of proteins codified by the reported ASD loci [30,31,32] and could reveal further critical regions. Although there are many influencing factors, the base composition is considered as the driving force in amino acid usage. In fact, the variability of the amino acidic composition of human proteins has been found strongly correlated with the GC content of first and second codon positions and the GC level of the corresponding flanking regions. Therefore, it is believed that the main force shaping amino acid usage among human proteins is the compositional constraints determined by the isochore in which each gene is embedded [33]. This is a mechanism possibly driving amino acid usage, however, the aim of this work was to describe regions codifying for proteins enriched in specific amino acid, based on the information available on databases, independently from the evolutionary mechanisms selecting the composition of such proteins. It will be interesting, in further investigation, to use the dataset created by the proposed approach with the aim of checking the influence of isochores on amino acid composition.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we designed a new method of data mining, able to retrieve information about human proteins, such as amino acid composition, sorted by the position of the corresponding codifying gene. Working on the new datasets, we propose a novel approach able to spot the regions of a chromosome producing proteins similar in amino acid content. The chromosome walking and surfing analysis can identify clusters of genes whose translation is dependent of AA availability, which could be relevant in many human pathologies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supplementary methods are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app11083511/s1, S1: Building a novel dataset: the ordering procedure, S2: Nomenclature.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.V., G.P. and F.S.; methodology, A.V. and F.S.; software, A.V.; validation, C.R.; formal analysis, A.V. and F.S.; investigation, F.S.; resources, A.V.; data curation, C.R.; writing—original draft preparation, A.V. and F.S.; writing—review and editing, A.V., C.R., G.P. and F.S.; visualization, F.S.; supervision, G.P.; project administration, A.V.; funding acquisition, F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in Zenodo at [10.5281/zenodo.3642653] [34]. The tool in Perl language used in this work was deposited in Zenodo [34]. Moreover, also the files created by the novel procedure and used for analysis can be found in Zenodo [34] and they were named as explained in Section S2 of Supplementary Material. The automated procedure is available at the following URL: https://gplab.diff.org/home (accessed on 16 February 2021) under the section: chromosomes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Osbourn, A. Secondary Metabolic Gene Clusters: Evolutionary Toolkits for Chemical Innovation. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbourn, A.E.; Field, B. Operons. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3755–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, L.D.; Pál, C.; Lercher, M.J. The Evolutionary Dynamics of Eukaryotic Gene Order. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, B.A.; Shriner, D.; Rotimi, C.N. Accounting for Linkage Disequilibrium in Association Analysis of Diverse Populations. Genet. Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, Y.; Soucy, P.; Adoue, V.; Michailidou, K.; Canisius, S.; Lemaçon, A.; Droit, A.; Andrulis, I.L.; Anton-Culver, H.; Arndt, V.; et al. Association of Breast Cancer Risk with Genetic Variants Showing Differential Allelic Expression: Identification of a Novel Breast Cancer Susceptibility Locus at 4q21. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 80140–80163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, J.D.; Powers, N.R.; Miller, L.L.; Mueller, K.L.; Mascheretti, S.; Marino, C.; Willcutt, E.G.; DeFries, J.C.; Olson, R.K.; Smith, S.D.; et al. Characterization of the DYX2 Locus on Chromosome 6p22 with Reading Disability, Language Impairment, and IQ. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffenbacher, K.E.; Kenyon, J.B.; Hoover, D.M.; Olson, R.K.; Pennington, B.F.; DeFries, J.C.; Smith, S.D. Refinement of the 6p21.3 Quantitative Trait Locus Influencing Dyslexia: Linkage and Association Analyses. Hum. Genet. 2004, 115, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernone, A.; Ricca, C.; Merlo, D.; Pescarmona, G.; Silvagno, F. The Analysis of Glutamate and Glutamine Frequencies in Human Proteins as Marker of Tissue Oxygenation. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D158–D169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Boddu, S.; et al. Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D745–D751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, C.; MacMaster, F.P.; Dewey, D. Brain Metabolite Levels and Language Abilities in Preschool Children. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e00547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, N.; Vasconcelos, M.; Oliveira, V.; Santos, F.C.D.; Bizarro, L.; Almeida, R.M.M.D.; Salles, J.F.D.; Carvalho, M.R.S. Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors for Developmental Dyslexia in Children: Systematic Review of the Last Decade. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2017, 42, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.L.; Pennington, B.F. Developmental Dyslexia. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2015, 11, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Benítez-Burraco, A. Toward the Language Oscillogenome. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthoni, H.; Sucheston, L.E.; Lewis, B.A.; Tapia-Páez, I.; Fan, X.; Zucchelli, M.; Taipale, M.; Stein, C.M.; Hokkanen, M.-E.; Castrén, E.; et al. The Aromatase Gene CYP19A1: Several Genetic and Functional Lines of Evidence Supporting a Role in Reading, Speech and Language. Behav. Genet. 2012, 42, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsson, H.; Huss, M.; Persson, H.; Einarsdottir, E.; Tiraboschi, E.; Nopola-Hemmi, J.; Schumacher, J.; Neuhoff, N.; Warnke, A.; Lyytinen, H.; et al. Polymorphisms in DCDC2 and S100B Associate with Developmental Dyslexia. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascheretti, S.; Facoetti, A.; Giorda, R.; Beri, S.; Riva, V.; Trezzi, V.; Cellino, M.R.; Marino, C. GRIN2B Mediates Susceptibility to Intelligence Quotient and Cognitive Impairments in Developmental Dyslexia. Psychiatr. Genet. 2015, 25, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascheretti, S.; De Luca, A.; Trezzi, V.; Peruzzo, D.; Nordio, A.; Marino, C.; Arrigoni, F. Neurogenetics of Developmental Dyslexia: From Genes to Behavior through Brain Neuroimaging and Cognitive and Sensorial Mechanisms. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerheim, T.; Raeymaekers, P.; Tønnessen, F.E.; Pedersen, M.; Tranebjaerg, L.; Lubs, H.A. A New Gene (DYX3) for Dyslexia Is Located on Chromosome 2. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 664–669. [Google Scholar]
- Buonincontri, R.; Bache, I.; Silahtaroglu, A.; Elbro, C.; Nielsen, A.-M.V.; Ullmann, R.; Arkesteijn, G.; Tommerup, N. A Cohort of Balanced Reciprocal Translocations Associated with Dyslexia: Identification of Two Putative Candidate Genes at DYX1. Behav. Genet. 2011, 41, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannula-Jouppi, K.; Kaminen-Ahola, N.; Taipale, M.; Eklund, R.; Nopola-Hemmi, J.; Kääriäinen, H.; Kere, J. The Axon Guidance Receptor Gene ROBO1 Is a Candidate Gene for Developmental Dyslexia. PLoS Genet. 2005, 1, e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for Scientific Data Management and Stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, L.; Bolleman, J.; Gehant, S.; Redaschi, N.; Martin, M.; UniProt Consortium. FAIR Adoption, Assessment and Challenges at UniProt. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Cummins, C.; Gall, A.; Girón, C.G.; et al. Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D754–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhle, R.; Trentacoste, S.V.; Rapin, I. The Genetics of Autism. Pediatrics 2004, 113, e472–e486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, J.; Bansal, R.; Goh, S.; Rodie, M.; Sawardekar, S.; Peterson, B.S. Parsing the Heterogeneity of Brain Metabolic Disturbances in Autistic Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, D.M.; Sikoglu, E.M.; Hodge, S.M.; Edden, R.A.E.; Foley, A.; Kennedy, D.N.; Moore, C.M.; Frazier, J.A. Relationship among Glutamine, γ-Aminobutyric Acid, and Social Cognition in Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluegge, K. Impaired Amino Acid Metabolism in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Qian-Qian, L.; Cong, Y.; Xiao-Bing, Z.; Hong-Zhu, D. Reduction of Essential Amino Acid Levels and Sex-Specific Alterations in Serum Amino Acid Concentration Profiles in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 297, 113675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.; Scherer, S.W. Identification of Candidate Intergenic Risk Loci in Autism Spectrum Disorder. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, P.; Paterson, A.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Roberts, W.; Brian, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Vincent, J.; Skaug, J.; Thompson, A.; Senman, L.; et al. Mapping Autism Risk Loci Using Genetic Linkage and Chromosomal Rearrangements. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yao, X.; March, M.E.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Sleiman, P.M.A.; Hakonarson, H.; Xia, Q.; Li, J. Target Genes of Autism Risk Loci in Brain Frontal Cortex. Front. Genet. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbía, V.; Piovani, R.; Naya, H.; Rodríguez-Maseda, H.; Romero, H.; Musto, H. Trends of Amino Acid Usage in the Proteins from the Human Genome. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2007, 25, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernone, A.; Silvagno, F. Chromosome Walking. Zenodo 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).