An Observational Study on Cephalometric Characteristics and Patterns Associated with the Prader–Willi Syndrome: A Structural Equation Modelling and Network Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data—Representative Sample and Measurement Units
2.2. Research Methodology—Models of Analysis
3. Results
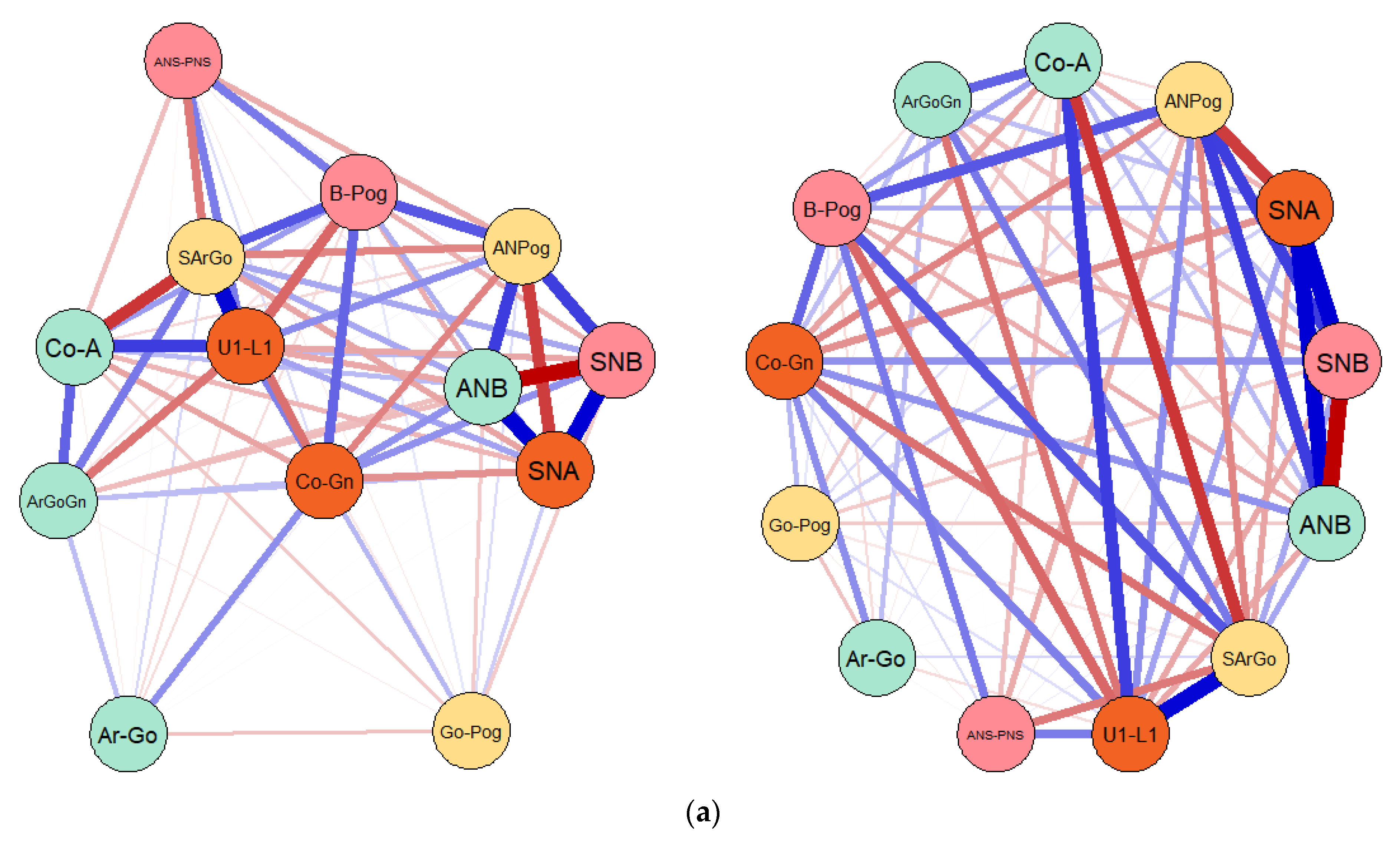
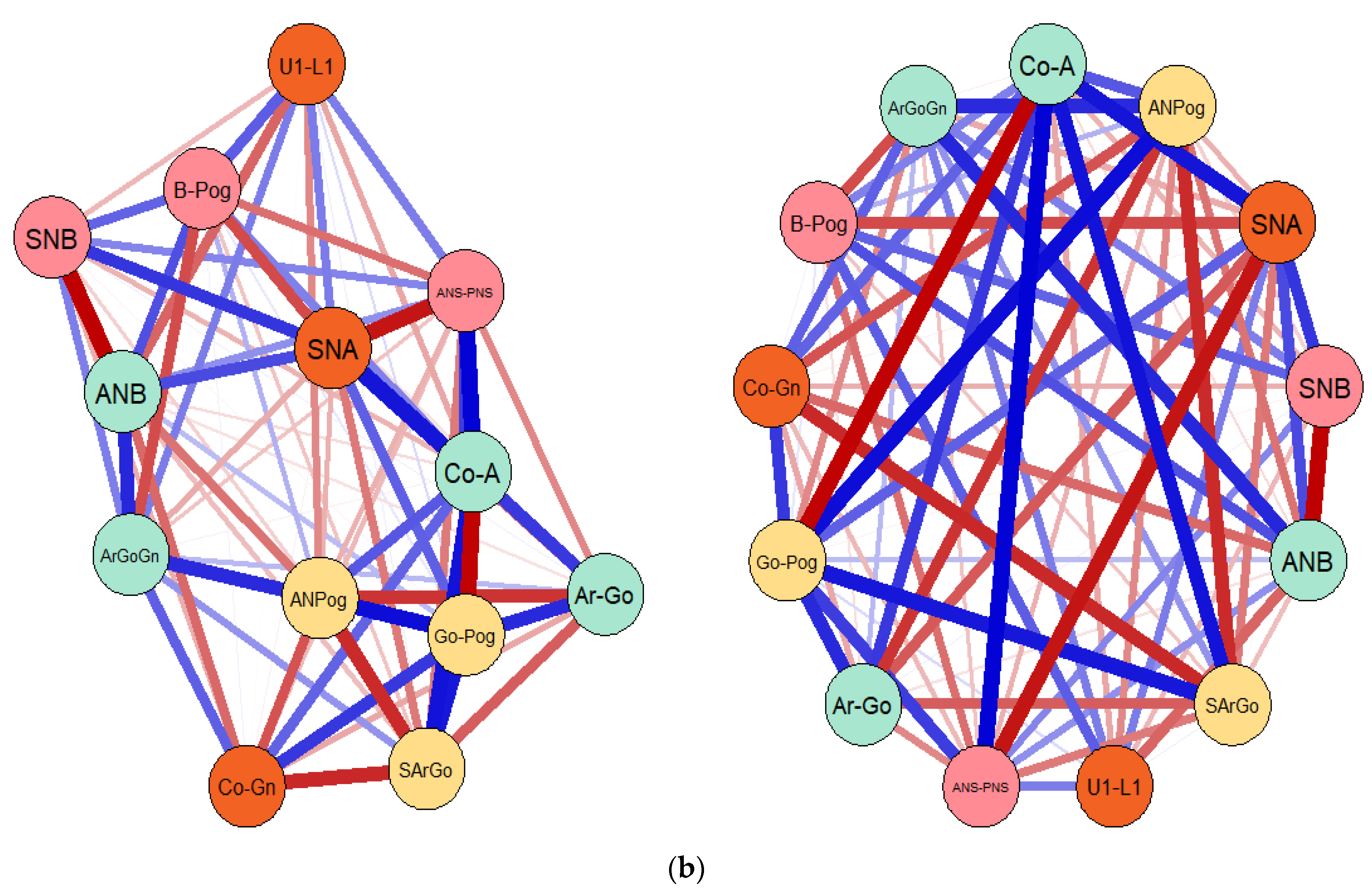
3.1. Results of the Gaussian Graphical Models (GGMs) Entailing the Connections and Correlations between Considered Cephalometric Measures in Both Prader–Willi Syndrome (PWS) Group and Control Sample
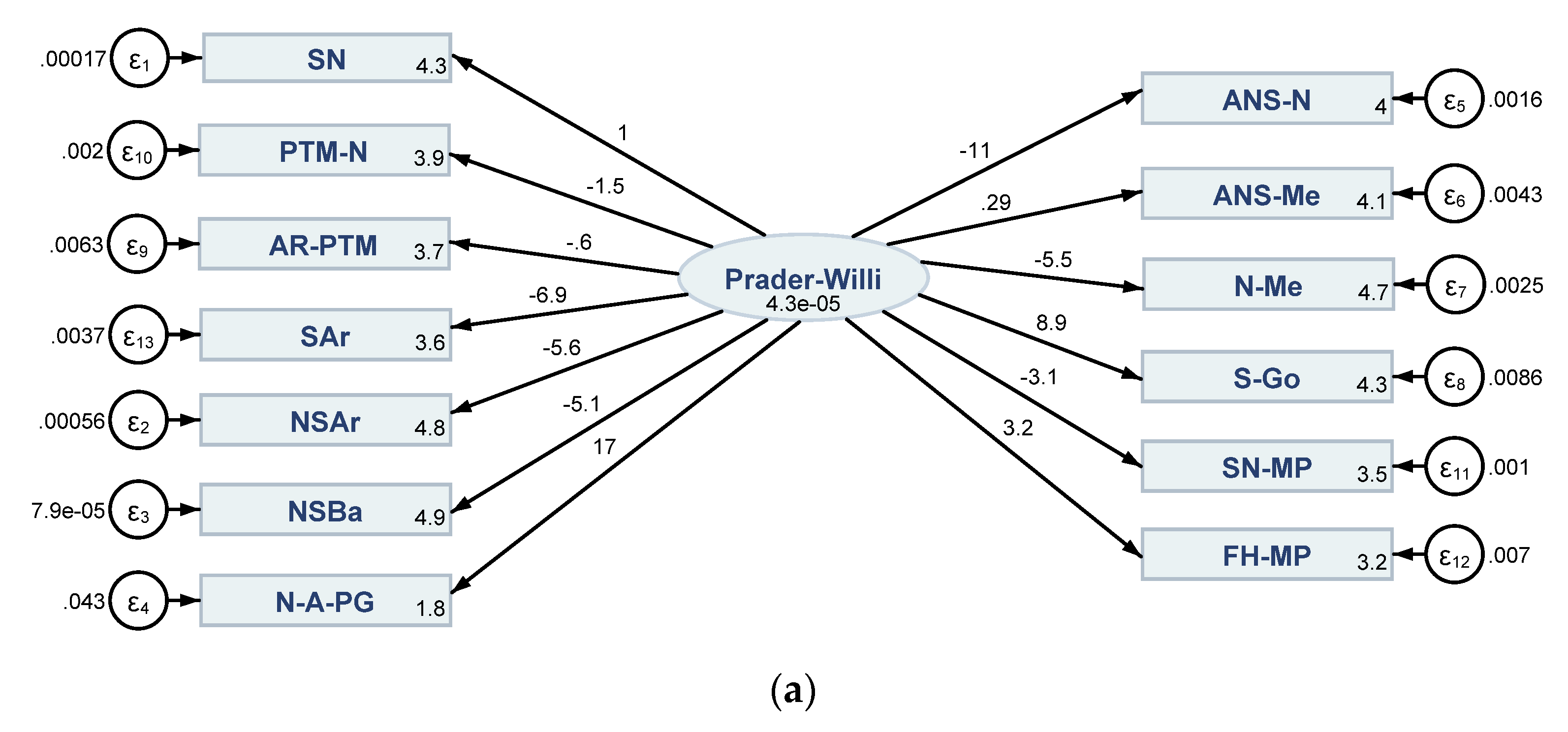
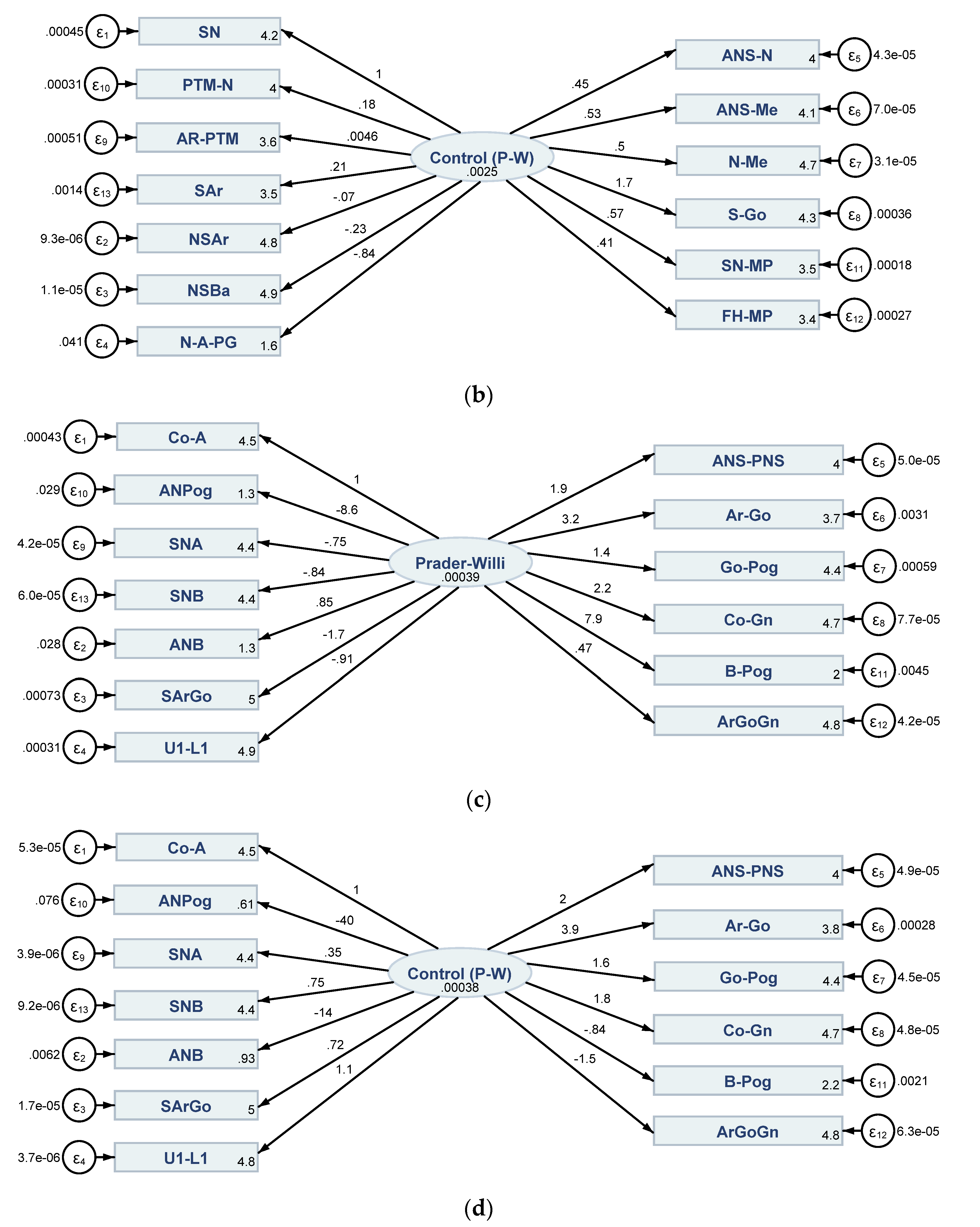
3.2. Results of the Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) Conveying Direct, Indirect and Total Linkages between Cephalometric Characteristics in Both PWS Group and Control Sample
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Acronym | Variable/Measure—Detailed Description |
|---|---|
| SN | SN represents Sella-Nasion line |
| PTM-N | PTM-N represents anterior cranial base length |
| AR-PTM | AR-PTM represents posterior cranial base length |
| SAr | SAr represents posterior cranial base |
| NSAr | NSAr represents saddle angle |
| NSBa | NSBa represents cranial base flexure angle |
| N-A-PG | N-A-PG represents the angle of facial convexity |
| ANS-N | ANS-N (UAFH) represents upper anterior facial height |
| ANS-Me | ANS-Me (LAFH) represents lower anterior facial height |
| N-Me | N-Me represents total anterior facial height |
| S-Go | S-Go represents total posterior facial height |
| SN-MP | SN-MP represents mandibular plane |
| FH-MP | FH-MP represents the inclination of mandibular plane to FH |
| Co-A | Co-A represents maxilla length |
| ANPog | ANPog represents sagittal jaw relationship |
| SNA | SNA represents Sella-Nasion to A Point Angle |
| SNB | SNB represents Sella-Nasion to B Point Angle |
| ANB | ANB represents A point to B Point Angle |
| SArGo | SArGo represents articular angle |
| U1-L1 | U1-L1 represents the interincisal angle |
| ANS-PNS | ANS-PNS represents palatal plane |
| Ar-Go | Ar-Go represents mandibular ramus length |
| Go-Pog | Go-Pog represents mandibular body length |
| Co-Gn | Co-Gn length of mandibular base |
| B-Pog | B-Pog represents chin depth |
| ArGoGn | ArGoGn represents Gonial angle |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Prader-Willi | Control | |
| SN | ||
| Prader–Willi | 1 (.) | 1 (.) |
| _cons | 4.328 *** (0.00348) | 4.250 *** (0.0128) |
| NSAr | ||
| Prader–Willi | −5.631 (2.895) | −0.0695 *** (0.0161) |
| _cons | 4.771 *** (0.0104) | 4.813 *** (0.00109) |
| NSBa | ||
| Prader–Willi | −5.072 * (2.561) | −0.229 *** (0.0278) |
| _cons | 4.851 *** (0.00814) | 4.873 *** (0.00282) |
| N_A_PG | ||
| Prader–Willi | 17.00 (11.29) | −0.837 (0.968) |
| _cons | 1.838 *** (0.0556) | 1.628 *** (0.0489) |
| ANS_N | ||
| Prader–Willi | −10.61 * (5.411) | 0.447 *** (0.0549) |
| _cons | 3.968 *** (0.0190) | 3.993 *** (0.00550) |
| ANS_Me | ||
| Prader–Willi | 0.288 (2.466) | 0.528 *** (0.0665) |
| _cons | 4.059 *** (0.0154) | 4.117 *** (0.00654) |
| N_Me | ||
| Prader–Willi | −5.479 (3.241) | 0.505 *** (0.0575) |
| _cons | 4.712 *** (0.0146) | 4.749 *** (0.00610) |
| S_Go | ||
| Prader–Willi | 8.877 (5.565) | 1.651 *** (0.189) |
| _cons | 4.270 *** (0.0259) | 4.295 *** (0.0200) |
| AR-PTM | ||
| Prader–Willi | −0.595 (3.064) | 0.00457 (0.107) |
| _cons | 3.681 *** (0.0188) | 3.616 *** (0.00530) |
| PTM-N | ||
| Prader–Willi | −1.498 (1.856) | 0.177 * (0.0851) |
| _cons | 3.938 *** (0.0108) | 3.953 *** (0.00464) |
| SN-MP | ||
| Prader–Willi | −3.100 (1.917) | 0.572 *** (0.0854) |
| _cons | 3.538 *** (0.00894) | 3.525 *** (0.00744) |
| FH-MP | ||
| Prader–Willi | 3.219 (3.475) | 0.405 *** (0.0874) |
| _cons | 3.237 *** (0.0204) | 3.360 *** (0.00614) |
| SAr | ||
| Prader–Willi | −6.942 (4.059) | 0.206 (0.179) |
| _cons | 3.592 *** (0.0179) | 3.503 *** (0.00918) |
| / | ||
| var(e.SN) | 0.000175 ** (0.0000595) | 0.000452 ** (0.000163) |
| var(e.NSAr) | 0.000557 ** (0.000216) | 0.00000926 ** (0.00000318) |
| var(e.NSBa) | 0.0000789 (0.0000843) | 0.0000107 * (0.00000417) |
| var(e.N-A-PG) | 0.0432 ** (0.0147) | 0.0413 ** (0.0138) |
| var(e.ANS-N) | 0.00160 * (0.000657) | 0.0000430 * (0.0000175) |
| var(e.ANS-Me) | 0.00427 ** (0.00142) | 0.0000703 * (0.0000304) |
| var(e.N-Me) | 0.00254 ** (0.000886) | 0.0000307 (0.0000163) |
| var(e.S-Go) | 0.00863 ** (0.00294) | 0.000357 (0.000191) |
| var(e. AR-PTM) | 0.00635 ** (0.00212) | 0.000506 ** (0.000169) |
| var(e. PTM-N) | 0.00200 ** (0.000670) | 0.000308 ** (0.000103) |
| var(e.SN-MP) | 0.00102 ** (0.000350) | 0.000176 ** (0.0000624) |
| var(e.FH-MP) | 0.00702 ** (0.00235) | 0.000266 ** (0.0000906) |
| var(e.SAr) | 0.00369 ** (0.00128) | 0.00141 ** (0.000470) |
| var(Prader–Willi) | 0.0000433 (0.0000450) | 0.00251 * (0.000977) |
| N | 18 | 18 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Prader–Willi | Control | |
| Co-A | ||
| Prader–Willi | 1 (.) | 1 (.) |
| _cons | 4.493 *** (0.00694) | 4.457 *** (0.00491) |
| ANB | ||
| Prader–Willi | 0.847 (2.110) | −13.56 *** (1.534) |
| _cons | 1.312 *** (0.0410) | 0.933 *** (0.0651) |
| SArGo | ||
| Prader–Willi | −1.750 ** (0.558) | 0.723 *** (0.0808) |
| _cons | 4.985 *** (0.0106) | 4.962 *** (0.00346) |
| ANS-PNS | ||
| Prader–Willi | 1.880 *** (0.496) | 2.012 *** (0.197) |
| _cons | 4.017 *** (0.00917) | 4.010 *** (0.00940) |
| Ar-Go | ||
| Prader–Willi | 3.209 ** (1.080) | 3.873 *** (0.397) |
| _cons | 3.659 *** (0.0205) | 3.785 *** (0.0182) |
| Go-Pog | ||
| Prader–Willi | 1.448 ** (0.487) | 1.632 *** (0.165) |
| _cons | 4.394 *** (0.00911) | 4.409 *** (0.00767) |
| Co-Gn | ||
| Prader–Willi | 2.158 *** (0.571) | 1.770 *** (0.177) |
| _cons | 4.713 *** (0.0106) | 4.724 *** (0.00830) |
| SNA | ||
| Prader–Willi | −0.752 *** (0.209) | 0.353 *** (0.0393) |
| _cons | 4.432 *** (0.00393) | 4.405 *** (0.00169) |
| ANPog | ||
| Prader–Willi | −8.604 ** (3.067) | −40.00 *** (4.861) |
| _cons | 1.324 *** (0.0583) | 0.609 ** (0.195) |
| B-Pog | ||
| Prader–Willi | 7.940 *** (2.212) | −0.836 (0.559) |
| _cons | 1.984 *** (0.0413) | 2.158 *** (0.0115) |
| ArGoGn | ||
| Prader–Willi | 0.467 ** (0.144) | −1.541 *** (0.167) |
| _cons | 4.822 *** (0.00274) | 4.845 *** (0.00733) |
| SNB | ||
| Prader–Willi | −0.839 *** (0.237) | 0.753 *** (0.0760) |
| _cons | 4.387 *** (0.00444) | 4.371 *** (0.00354) |
| U1–L1 | ||
| Prader–Willi | −0.906 ** (0.317) | 1.139 *** (0.103) |
| _cons | 4.938 *** (0.00609) | 4.839 *** (0.00526) |
| / | ||
| var(e.Co-A) | 0.000430 ** (0.000151) | 0.0000532 ** (0.0000185) |
| var(e.ANB) | 0.0282 ** (0.00969) | 0.00624 ** (0.00217) |
| var(e.SArGo) | 0.000734 ** (0.000259) | 0.0000168 ** (0.00000586) |
| var(e.U1-L1) | 0.000310 ** (0.000110) | 0.00000370 (0.00000225) |
| var(e.ANS-PNS) | 0.0000504 (0.0000315) | 0.0000495 ** (0.0000191) |
| var(e.Ar-Go) | 0.00314 ** (0.00110) | 0.000281 ** (0.000102) |
| var(e.Go-Pog) | 0.000592 ** (0.000211) | 0.0000448 ** (0.0000162) |
| var(e.Co-Gn) | 0.0000772 (0.0000443) | 0.0000478 ** (0.0000174) |
| var(e.SNA) | 0.0000418 * (0.0000171) | 0.00000390 ** (0.00000136) |
| var(e.ANPog) | 0.0288 ** (0.0100) | 0.0759 ** (0.0261) |
| var(e.B_Pog) | 0.00445 ** (0.00168) | 0.00210 ** (0.000701) |
| var(e.ArGoGn) | 0.0000422 ** (0.0000156) | 0.0000629 ** (0.0000221) |
| var(e.SNB) | 0.0000605 ** (0.0000224) | 0.00000918 ** (0.00000334) |
| var(Prader–Willi) | 0.000390 (0.000242) | 0.000381 ** (0.000144) |
| N | 18 | 18 |
| SEM 1 (Figure 6a) | SEM 2 (Figure 6b) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Obs | Sign | Item-Test Correlation | Alpha | Sign | Item-Test Correlation | Alpha |
| SN | 18 | − | 0.4909 | 0.8009 | + | 0.8890 | 0.9198 |
| NSAr | 18 | + | 0.7462 | 0.7754 | − | 0.7974 | 0.9237 |
| NSBa | 18 | + | 0.8229 | 0.7668 | − | 0.9180 | 0.9186 |
| N-A-PG | 18 | − | 0.5083 | 0.7993 | − | 0.3205 | 0.9412 |
| ANS-N | 18 | + | 0.9083 | 0.7567 | + | 0.8920 | 0.9197 |
| ANS-Me | 18 | + | 0.2839 | 0.8188 | + | 0.9209 | 0.184 |
| N-Me | 18 | + | 0.7710 | 0.7727 | + | 0.9171 | 0.9186 |
| S-Go | 18 | − | 0.5724 | 0.7932 | + | 0.9399 | 0.9176 |
| AR-PTM | 18 | − | 0.2849 | 0.8187 | + | 0.2284 | 0.9442 |
| PTM-N | 18 | + | 0.2532 | 0.8212 | + | 0.6200 | 0.9307 |
| SN-MP | 18 | + | 0.4036 | 0.8087 | + | 0.8800 | 0.9202 |
| FH-MP | 18 | − | 0.4201 | 0.8073 | + | 0.8199 | 0.9227 |
| SAr | 18 | + | 0.6876 | 0.7817 | + | 0.4809 | 0.9357 |
| Total scale | 0.8081 | 0.9313 | |||||
| SEM 3 (Figure 6c) | SEM 4 (Figure 6d) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Obs | Sign | Item-Test Correlation | Alpha | Sign | Item-Test Correlation | Alpha |
| Co-A | 18 | + | 0.7352 | 0.9114 | + | 0.9438 | 0.9846 |
| ANB | 18 | − | 0.1889 | 0.9335 | − | 0.9510 | 0.9844 |
| SArGo | 18 | − | 0.8377 | 0.9068 | + | 0.9667 | 0.9841 |
| U1-L1 | 18 | − | 0.7984 | 0.9087 | + | 0.9897 | 0.9836 |
| ANS-PNS | 18 | + | 0.8582 | 0.9057 | + | 0.9819 | 0.9838 |
| Ar-Go | 18 | + | 0.7641 | 0.9102 | + | 0.9740 | 0.9840 |
| Go-Pog | 18 | + | 0.4413 | 0.9235 | + | 0.9730 | 0.8840 |
| Co-Gn | 18 | + | 0.8389 | 0.9066 | + | 0.9799 | 0.9838 |
| SNA | 18 | − | 0.8441 | 0.9063 | + | 0.9687 | 0.9841 |
| ANPog | 18 | − | 0.7266 | 0.9087 | − | 0.9572 | 0.9843 |
| B-Pog | 18 | + | 0.6388 | 0.9150 | − | 0.4166 | 0.9945 |
| ArGoGn | 18 | + | 0.7140 | 0.9121 | − | 0.9584 | 0.9843 |
| SNB | 18 | − | 0.7913 | 0.9090 | + | 0.9744 | 0.9840 |
| Total scale | 0.9187 | 0.9861 | |||||
| SEM 1 (Figure 6a) | SEM 2 (Figure 6b) | SEM 3 (Figure 6c) | SEM 4 (Figure 6d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Likelihood ratio | ||||
| “Model vs. saturated chi2_ms (65)” | 312.611 | 143.313 | 306.380 | 165.709 |
| p > chi2 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| “Baseline vs. saturated chi2_bs (78)” | 390.637 | 408.698 | 535.035 | 706.875 |
| p > chi2 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Information criteria | ||||
| “AIC (Akaike’s information criterion)” | −642.733 | −1175.074 | −887.142 | −1295.027 |
| “BIC (Bayesian information criterion)” | −608.009 | −1140.350 | −854.646 | −1260.303 |
| Baseline comparison | ||||
| “CFI (Comparative fit index)” | 0.208 | 0.769 | 0.472 | 0.840 |
| “TLI (Tucker–Lewis index)” | 0.050 | 0.723 | 0.366 | 0.808 |
| Size of residuals | ||||
| “CD (Coefficient of determination)” | 0.957 | 0.989 | 0.987 | 0.997 |
References
- Kim, Y.; Wang, S.E.; Jiang, Y.H. Epigenetic therapy of PraderWilli syndrome. Transl. Res. 2019, 208, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Bittel, D.C.; Kibiryeva, N.; Talebizadeh, Z.; Thompson, T. Behavioral differences among subjects with Prader-Willi syndrome and type I or type II deletion and maternal disomy. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G. Management of obesity in Prader-Willi syndrome. Nat. Clin Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 2, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledbetter, D.H.; Mascarello, J.T.; Riccardi, V.M.; Harper, V.D.; Airhart, S.D.; Strobel, R.J. Chromosome 15 abnormalities and the Prader-Willi syndrome: A follow-up report of 40 cases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1982, 34, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buiting, K.; Cassidy, S.B.; Driscoll, D.J. Clinical utility gene card for: Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsai, T.F.; Bressler, J.; Beaudet, A.L. Imprinting in Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimonis, V.E.; Tamura, R.; Gold, J.A.; Patel, N.; Surampalli, A.; Manazir, J.; Miller, J.L.; Roof, E.; Dykens, E.; Butler, M.G.; et al. Early diagnosis in Prader-Willi syndrome reduces obesity and associated co-morbidities. Genes 2019, 10, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Sturich, J.; Lee, J.; Myers, S.E.; Whitman, B.Y.; Gold, J.A.; Kimonis, V.; Scheimann, A.; Terrazas, N.; Driscoll, D.J. Growth standards of infants with Prader-Willi syndrome. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, S.B.; Schwartz, S.; Miller, J.L.; Driscoll, D.J. Prader-Willi syndrome. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, M.A.; Butler, M.G.; Cataletto, M.E. Prader-Willi syndrome: A review of clinical, genetic, and endocrine findings. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crino, A.; Fintini, D.; Bocchini, S.; Grugni, G. Obesity management in Prader–willi syndrome: Current perspectives. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heksch, R.; Kamboj, M.; Anglin, K.; Obrynba, K. Review of Prader-Willi syndrome: The endocrine approach. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 4, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionti, T.; Reid, S.M.; White, S.M.; Rowell, M.M. A population-based profile of 160 Australians with Prader-Willi syndrome: Trends in diagnosis, birth prevalence and birth characteristics. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 2, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaedel, R.; Poole, A.E.; Cassidy, S.B. Cephalometric Analysis of the Prader-Willi Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1990, 36, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G.; Meaney, F.J. An anthropometric study of 38 individuals with Prader-Labhart-Willi syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1987, 26, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuca, M.R.; Inglese, R.; Caruso, S.; Gatto, R.; Marz, O.G.; Pasini, M. Craniofacial morphology in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome: A retrospective study. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2016, 19, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenbuchinger, M.; Weihs, A.; Quackenbush, J.; Grabe, H.J.; Zacharias, H. Gaussian and Mixed Graphical Models as (multi-)omics data analysis tools. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo Lee, J.; Moen, E.; Punshon, T.; Hoen, A.; Stewart, D.; Li, H.; Karagas, M.; Gui, J. An Integrated Gaussian Graphical Model to evaluate the impact of expires on metabolic networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 114, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujarati, D.N. Basic Econometrics, 4th ed.; McGraw Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Beran, T.; Violato, C. Structural equation modeling in medical research. BMC Res. Note 2010, 3, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, A. Sella-Nasion line revisited. J. Oral Rehabil. 1995, 22, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andria, L.M.; Leite, L.P.; Prevatte, T.M.; King, L.B. Correlation of the cranial base angle and its components with other dental/skeletal variables and treatment time. Angle Orthod. 2004, 74, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fields, H.W.; Proffit, W.R.; Nixon, W.L.; Phillips, C.; Stanek, E. Facial pattern differences in long-faced children and adults. Am. J. Orthod. 1984, 85, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeves, R.; Asten, P.; Storhaug, K.; Bagesund, M. Orofacial dysfunction in individuals with Prader–Willi syndrome assessed with NOT-S. Acta Odontol. Scand 2011, 69, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, K.D.; Steinbach, H.L.; Bier, D.M. Roentgenographic manifestations of the Prader–Willi syndrome. Radiology 1971, 100, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.D.; Smith, D.W. Prader–Willi syndrome. A resume of 32 cases including an instance of affected first cousins, one of whom is of normal stature and intelligence. J. Pediatr. 1972, 81, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belengeanu, D.; Bratu, C.; Stoian, M.; Motoc, A.; Ormerod, E.; Podariu, A.C.; Farcas, S.; Andreescu, N. The heterogeneity of craniofacial morphology in Prader–Willi patients. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2012, 53, 527–532. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, M.; Hamilton, J.; Narang, I. Clinically important age-related differences in sleep related disordered breathing in infants and children with Prader–Willi Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidopoulou, S.; Chatzigianni, A. Craniofacial morphology and dental maturity in children with reduced somatic growth of different aetiology and the effect of growth hormone treatment. Prog. Orthod. 2017, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewyllie, A.; Roosenboom, J.; Indencleef, K.; Claes, P.; Swillen, A.; Devriendt, K.; Carels, C.; Cadenas De Llano-Pérula, M.; Willems, G.; Hens, G.; et al. A Comprehensive Craniofacial Study of 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 12, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjan, I.; Balaton, G.; Balaton, P.; Vajo, Z. The role of dental evaluation and cephalometric analysis in the diagnosis of Williams-Beuren syndrome. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2005, 5–6, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
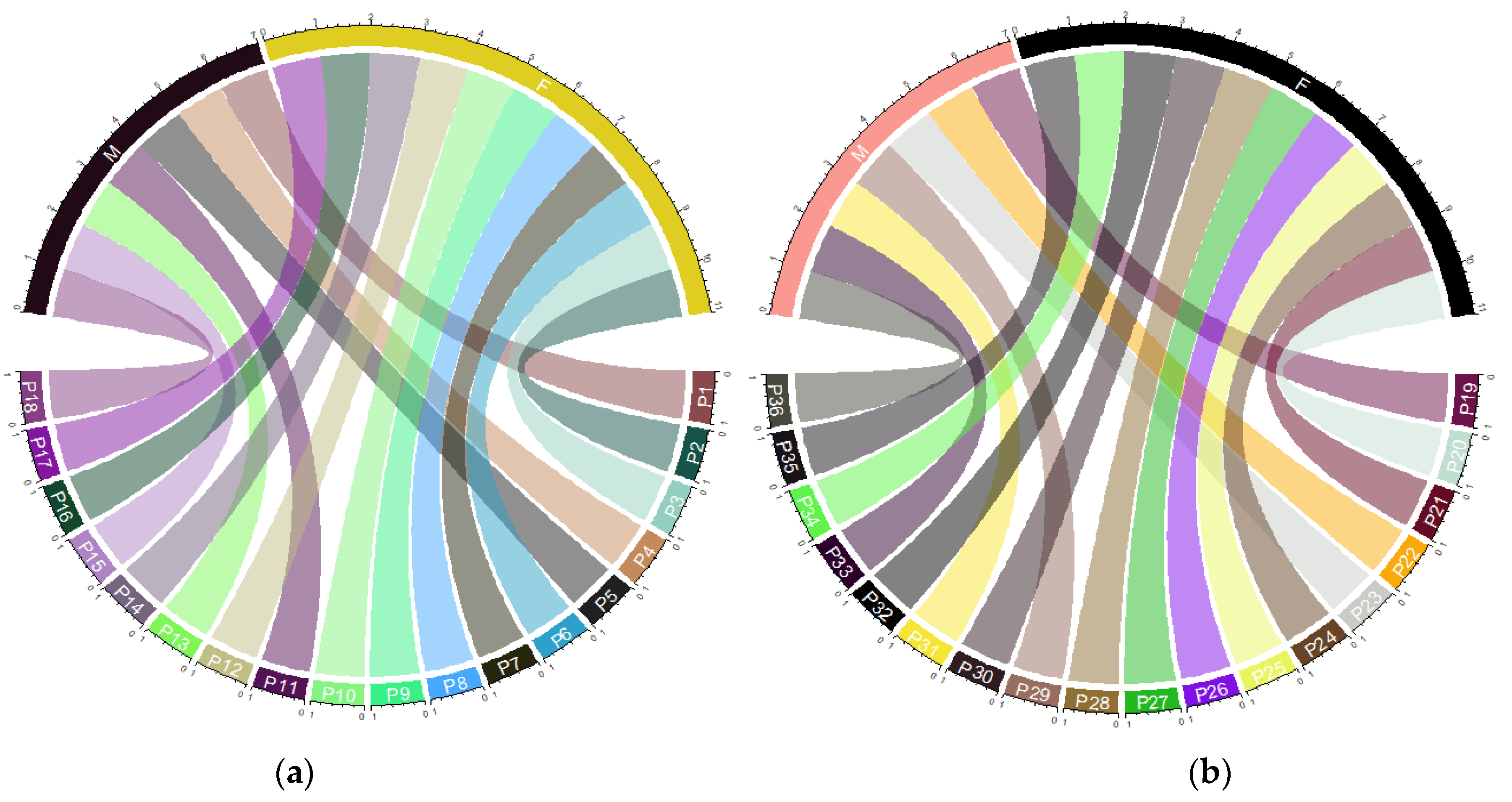
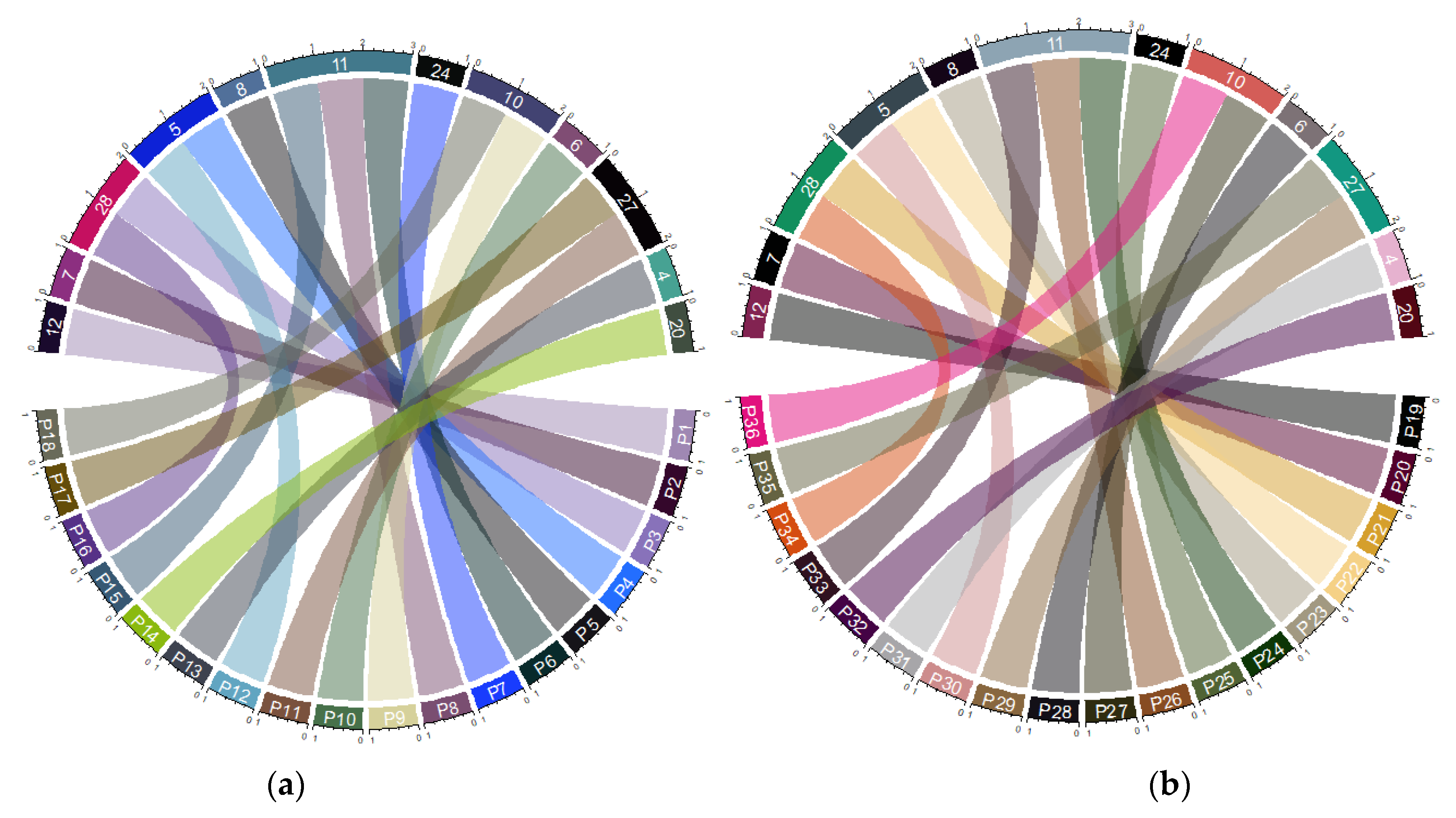

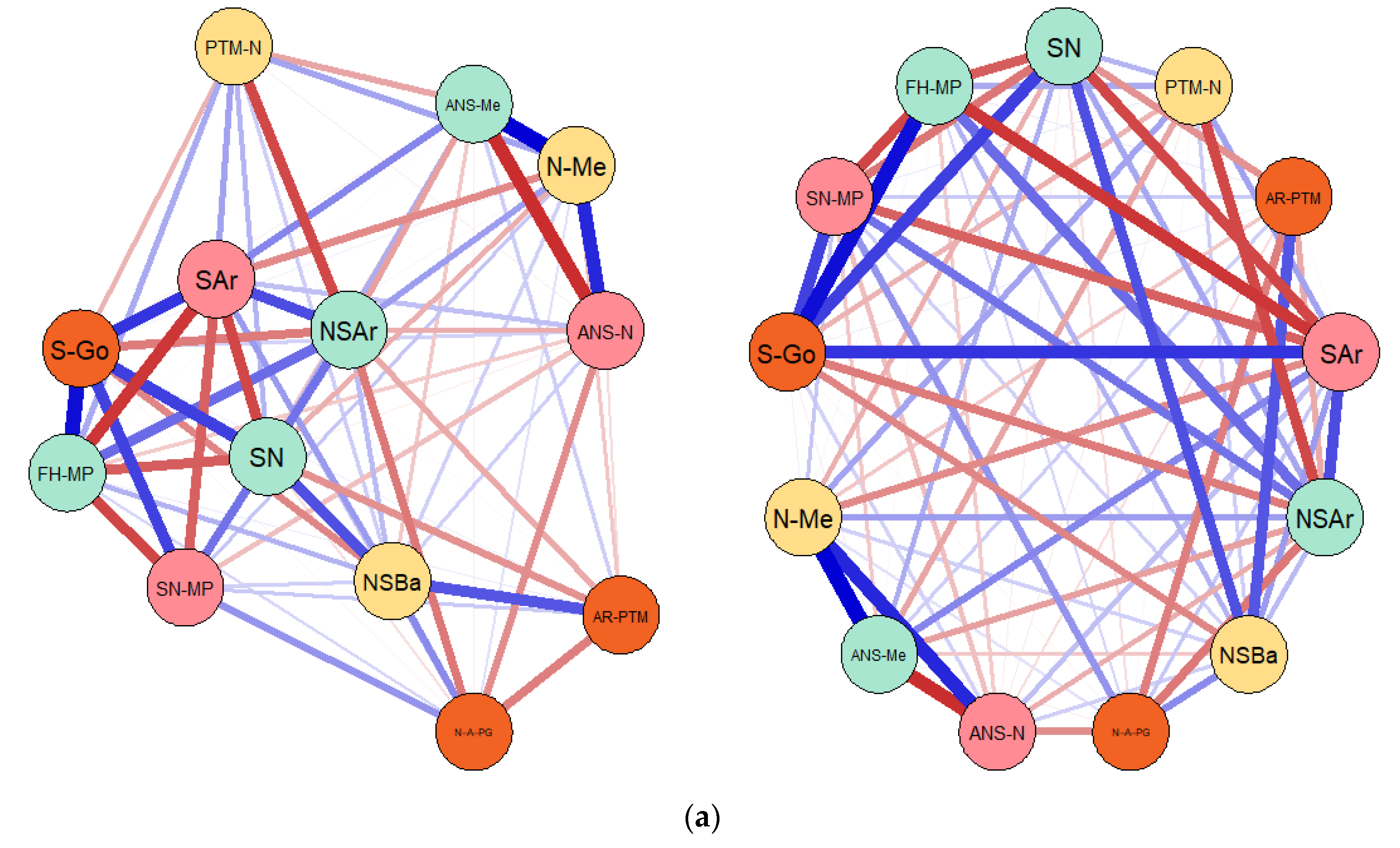
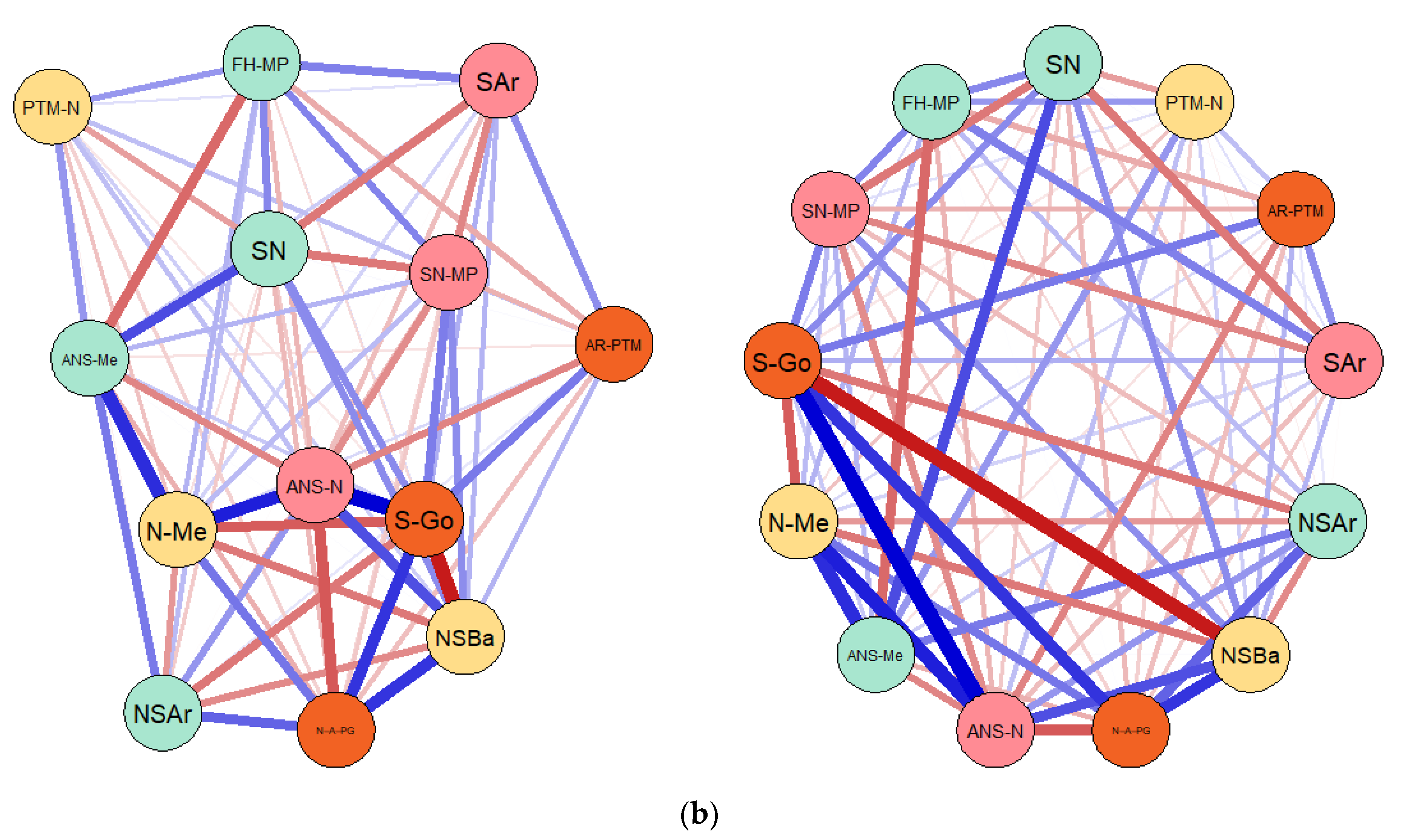
| (a) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean | Sd | Min | Max | |
| SN | 18 | 75.83333 | 1.158697 | 73.84 | 78.22 |
| PTM-N | 18 | 51.36722 | 2.375254 | 47.15 | 53.94 |
| AR-PTM | 18 | 39.80333 | 3.095097 | 31.77 | 43.31 |
| SAr | 18 | 36.40722 | 2.750743 | 30.76 | 39.71 |
| NSAr | 18 | 118.1539 | 5.262845 | 109.65 | 126.52 |
| NSBa | 18 | 127.9272 | 4.531925 | 120.73 | 133.84 |
| N-A-PG | 18 | 6.463333 | 1.5576 | 4.43 | 9.22 |
| ANS-N | 18 | 53.02833 | 4.486369 | 48.92 | 60.81 |
| ANS-Me | 18 | 58.04833 | 4.10118 | 55.18 | 68.02 |
| N-Me | 18 | 111.4622 | 7.348106 | 105.02 | 128.83 |
| S-Go | 18 | 71.94833 | 8.449223 | 65.23 | 85.98 |
| SN-MP | 18 | 34.42056 | 1.398527 | 33.12 | 39.15 |
| FH-MP | 18 | 25.56389 | 2.428631 | 23.28 | 31.54 |
| Co-A | 18 | 89.36333 | 2.57655 | 85.26 | 92.47 |
| ANPog | 18 | 3.172778 | 3.092271 | −8.65 | 5.72 |
| SNA | 18 | 83.85167 | 1.831523 | 78.95 | 86.52 |
| SNB | 18 | 80.11778 | 1.816926 | 75.79 | 82.42 |
| ANB | 18 | 3.730556 | 0.7057868 | 2.89 | 5.74 |
| SArGo | 18 | 146.2617 | 6.500576 | 137.51 | 159.19 |
| U1-L1 | 18 | 138.9233 | 4.288158 | 129.27 | 147.82 |
| ANS-PNS | 18 | 55.48167 | 2.146248 | 53.52 | 58.91 |
| Ar-Go | 18 | 39.53444 | 4.258378 | 35.89 | 49.15 |
| Go-Pog | 18 | 80.60833 | 3.458699 | 74.18 | 87.52 |
| Co-Gn | 18 | 111.2456 | 5.011898 | 106.14 | 118.97 |
| B-Pog | 18 | 7.232778 | 1.473267 | 4.67 | 9.75 |
| ArGoGn | 18 | 124.6311 | 2.364735 | 121.95 | 132.26 |
| N | 18 | ||||
| (b) | |||||
| N | Mean | Sd | Min | Max | |
| SN | 18 | 70.19833 | 3.893115 | 63.23 | 77.32 |
| PTM-N | 18 | 52.11556 | 1.050738 | 50.28 | 53.46 |
| AR-PTM | 18 | 37.20333 | 0.8617149 | 35.9 | 38.45 |
| SAr | 18 | 33.22944 | 1.340042 | 31.25 | 36.04 |
| NSAr | 18 | 123.0789 | 0.5853593 | 122.25 | 123.93 |
| NSBa | 18 | 130.6839 | 1.605671 | 128.12 | 133.56 |
| N-A-PG | 18 | 5.203333 | 1.134165 | 3.53 | 7.23 |
| ANS-N | 18 | 54.25111 | 1.308829 | 52.54 | 56.35 |
| ANS-Me | 18 | 61.36778 | 1.744421 | 58.01 | 64.21 |
| N-Me | 18 | 115.5078 | 3.07832 | 110.86 | 120.56 |
| S-Go | 18 | 73.60722 | 6.495733 | 65.02 | 83.98 |
| SN-MP | 18 | 33.96944 | 1.104602 | 32.12 | 35.67 |
| FH-MP | 18 | 28.79222 | 0.7744261 | 27.45 | 30.56 |
| Co-A | 18 | 86.21722 | 1.84672 | 83.52 | 88.9 |
| ANPog | 18 | 2.386667 | 1.388444 | .34 | 4.24 |
| SNA | 18 | 81.83611 | 0.6042703 | 81.12 | 82.85 |
| SNB | 18 | 79.16556 | 1.225226 | 77.23 | 81.09 |
| ANB | 18 | 2.637222 | 0.7130614 | 1.56 | 3.89 |
| SArGo | 18 | 142.9033 | 2.160136 | 139.41 | 145.89 |
| U1-L1 | 18 | 126.3667 | 2.913298 | 122.85 | 130.56 |
| ANS-PNS | 18 | 55.21111 | 2.278048 | 52.24 | 59.11 |
| Ar-Go | 18 | 44.18667 | 3.546436 | 39.56 | 49.96 |
| Go-Pog | 18 | 82.20111 | 2.778252 | 79.12 | 87.23 |
| Co-Gn | 18 | 112.6739 | 4.123416 | 107.36 | 119.56 |
| B-Pog | 18 | 8.666111 | 0.4311973 | 7.93 | 9.35 |
| ArGoGn | 18 | 127.1172 | 4.059518 | 121.36 | 132.87 |
| N | 18 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Istodor, A.V.; Rusu, L.-C.; Noja, G.G.; Roi, A.; Roi, C.; Bratu, E.; Moise, G.; Puiu, M.; Farcas, S.S.; Andreescu, N.I. An Observational Study on Cephalometric Characteristics and Patterns Associated with the Prader–Willi Syndrome: A Structural Equation Modelling and Network Approach. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073177
Istodor AV, Rusu L-C, Noja GG, Roi A, Roi C, Bratu E, Moise G, Puiu M, Farcas SS, Andreescu NI. An Observational Study on Cephalometric Characteristics and Patterns Associated with the Prader–Willi Syndrome: A Structural Equation Modelling and Network Approach. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073177
Chicago/Turabian StyleIstodor, Alin Viorel, Laura-Cristina Rusu, Gratiela Georgiana Noja, Alexandra Roi, Ciprian Roi, Emanuel Bratu, Georgiana Moise, Maria Puiu, Simona Sorina Farcas, and Nicoleta Ioana Andreescu. 2021. "An Observational Study on Cephalometric Characteristics and Patterns Associated with the Prader–Willi Syndrome: A Structural Equation Modelling and Network Approach" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073177
APA StyleIstodor, A. V., Rusu, L.-C., Noja, G. G., Roi, A., Roi, C., Bratu, E., Moise, G., Puiu, M., Farcas, S. S., & Andreescu, N. I. (2021). An Observational Study on Cephalometric Characteristics and Patterns Associated with the Prader–Willi Syndrome: A Structural Equation Modelling and Network Approach. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073177










