A Systematic Mapping with Bibliometric Analysis on Information Systems Using Ontology and Fuzzy Logic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Questions
- RQ-1: When is ontology- and fuzzy-based IS research published?
- RQ-2: Which ontology- and fuzzy-based IS development topics are covered?
- RQ-3: What are the main future directions found in the analyzed topic?
- RQ-4: What are the visible trends for the countries that participate in the study of ontology- and fuzzy-based IS?
2.2. Conducting the Search
2.3. Study Selection and Quality Assessment
- IC1: Include papers that are works on ontology- and fuzzy-based IS.
- EC1: Exclude papers that contain relevant research keywords, but the ontology- and fuzzy-based IS topic is not discussed in the abstract.
- EC2: Exclude duplicate papers that repeat ideas described in earlier works, and their abstracts are similar, i.e., if one paper is an extension of another, the less extended (i.e., containing fewer pages) paper is excluded [51].
- EC3: Exclude papers that analyze generic topics, such as fuzzy mathematical operations, ontological approximation, etc., without concrete application in IS.
2.4. Used Tools
2.5. Data Extraction
- Merge different spellings of the same word, such as “fuzzy cognitive maps” and “fuzzy cognitive map,” “modelling,” “modeling,” etc.;
- Merge abbreviated keywords with full keywords, such as “ontology web language” and “OWL”;
- Merge synonyms, such as “fuzzy theory” and “fuzzy set theory”;
- Exclude general keywords, such as paper, study, goal, etc., since they provide very little information, and the usefulness of a map tends to increase when they are excluded.
2.6. Method Used for the Results Analysis
- Keywords chronological occurrence analysis, based on analyzing the keywords occurrences per year (RQ-1, RQ-3).
- Keywords occurrence analysis, based on the Pareto distribution (80-20) [58] (RQ-2).
- Keywords co-occurrence analysis, based on the analysis of the relationships among keywords (RQ-2).
- Keywords clustering analysis, based on the analysis of the keywords clustering in VOSviewer [59] (RQ-2).
- Countries occurrence and co-occurrence analysis (RQ-4).
2.7. Validity Evaluation
3. Results
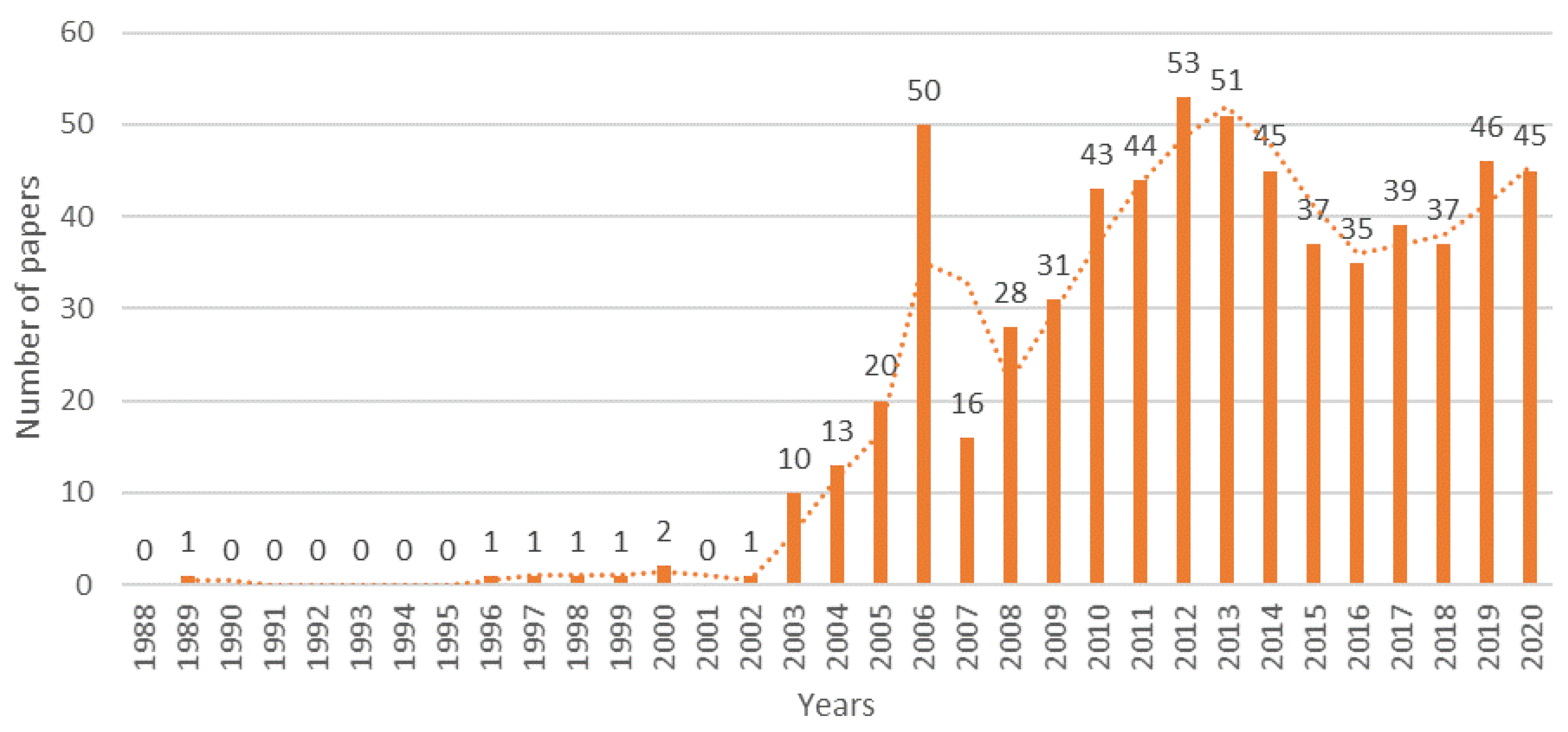
3.1. Chronological Distribution Analysis (RQ-1)
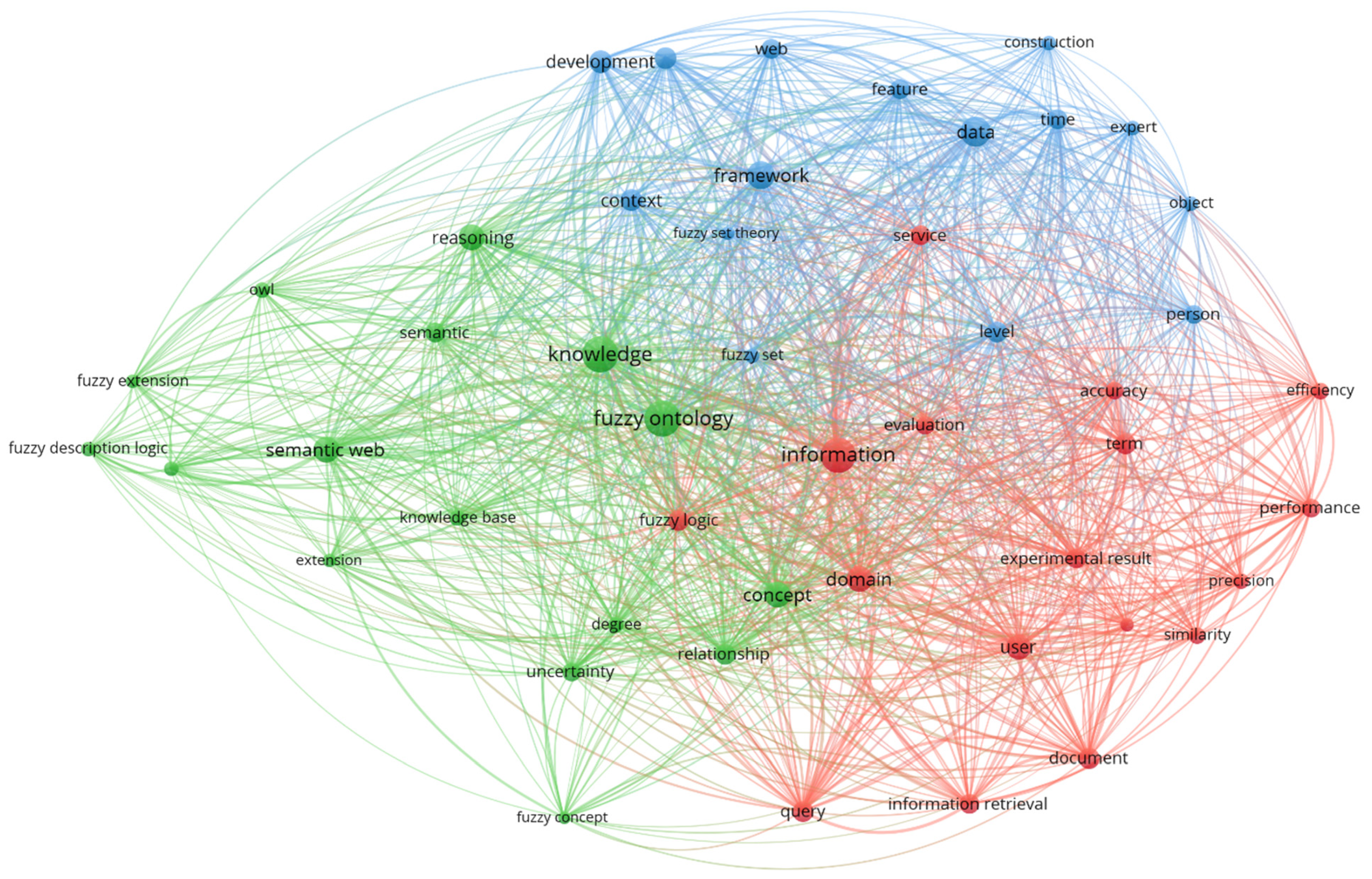
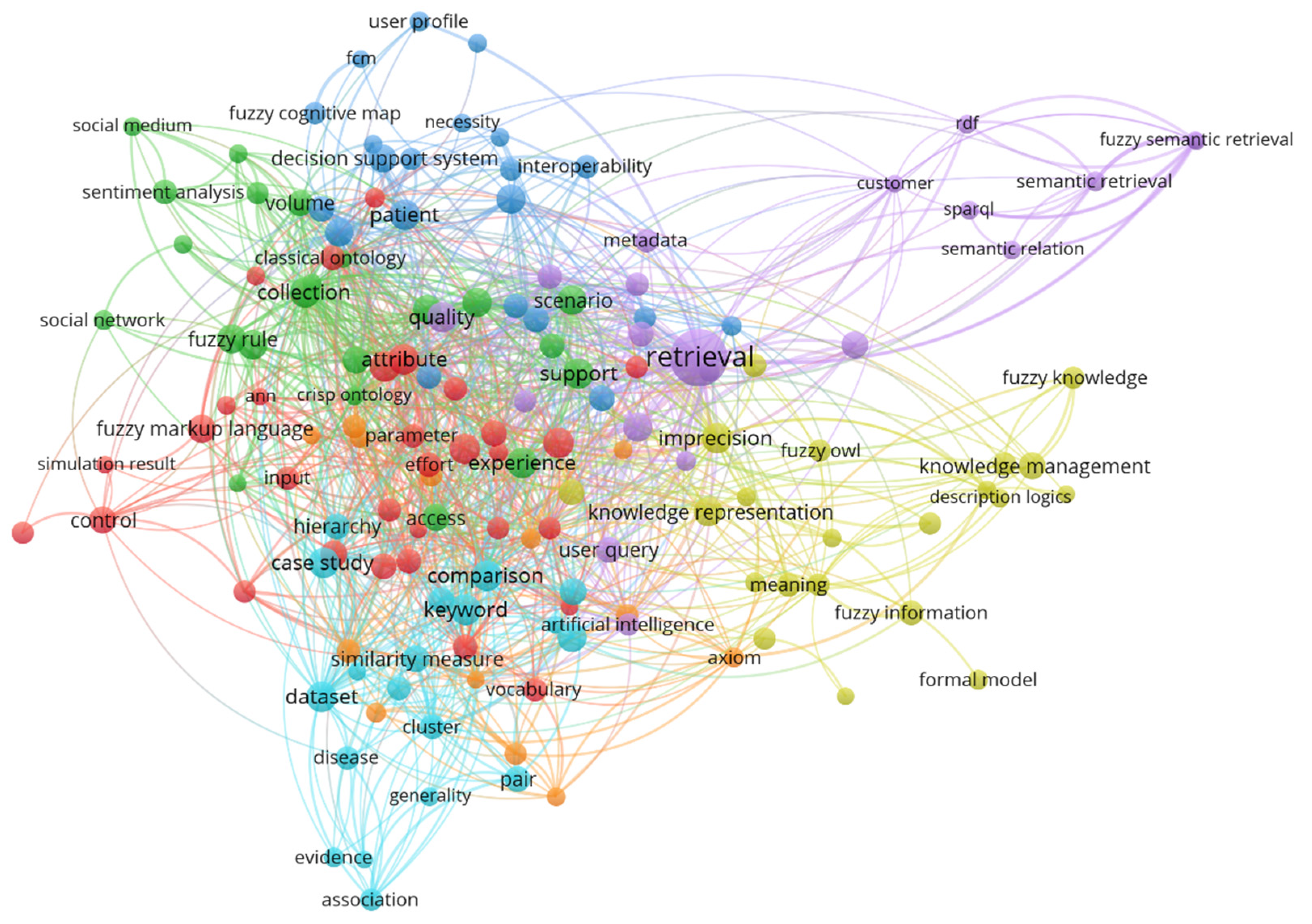
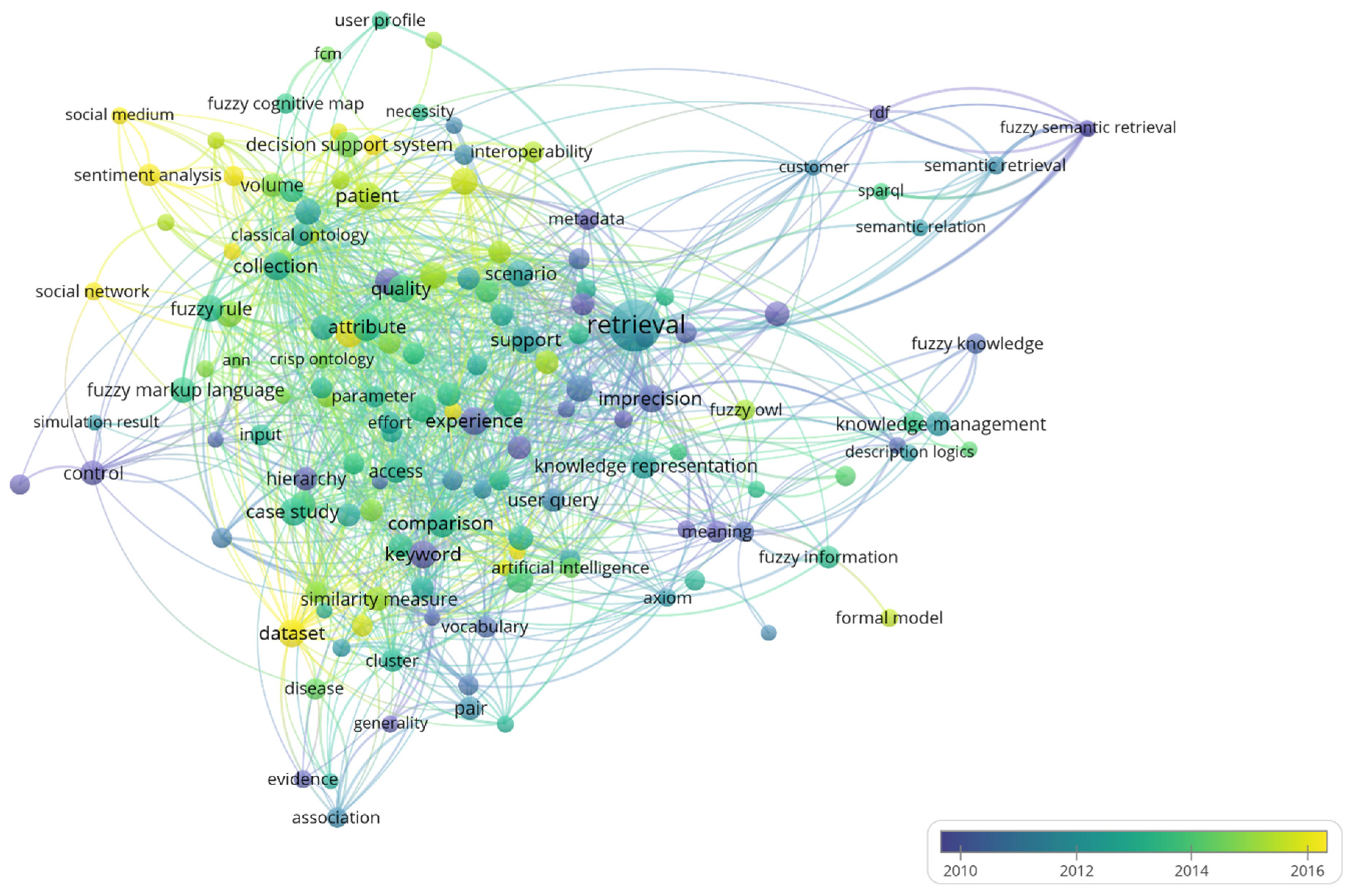
3.2. Keywords Occurrence Analysis (RQ-2 and RQ-3)
3.2.1. The Most Occurring Keywords
3.2.2. The Moderately Occurring Keywords
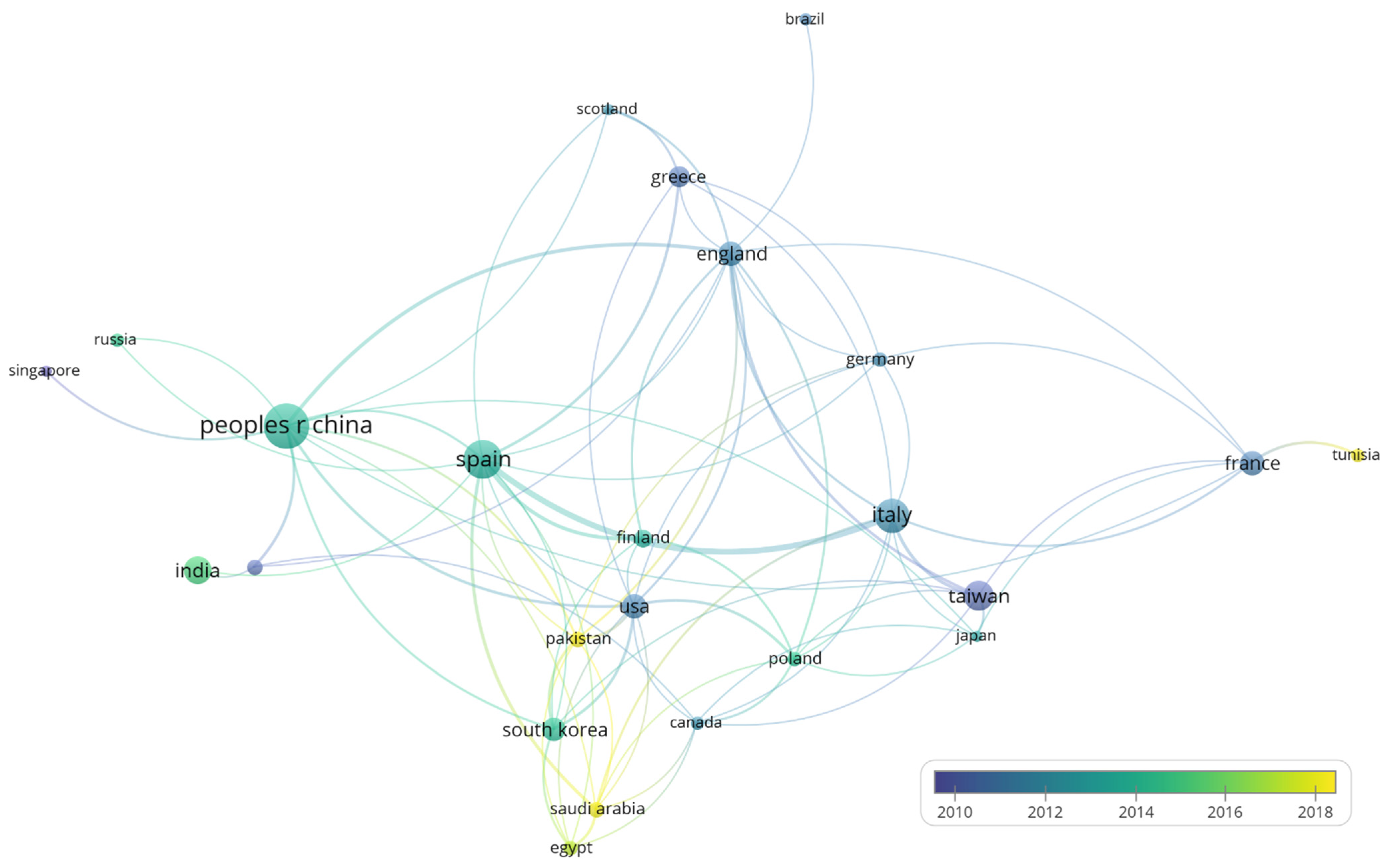
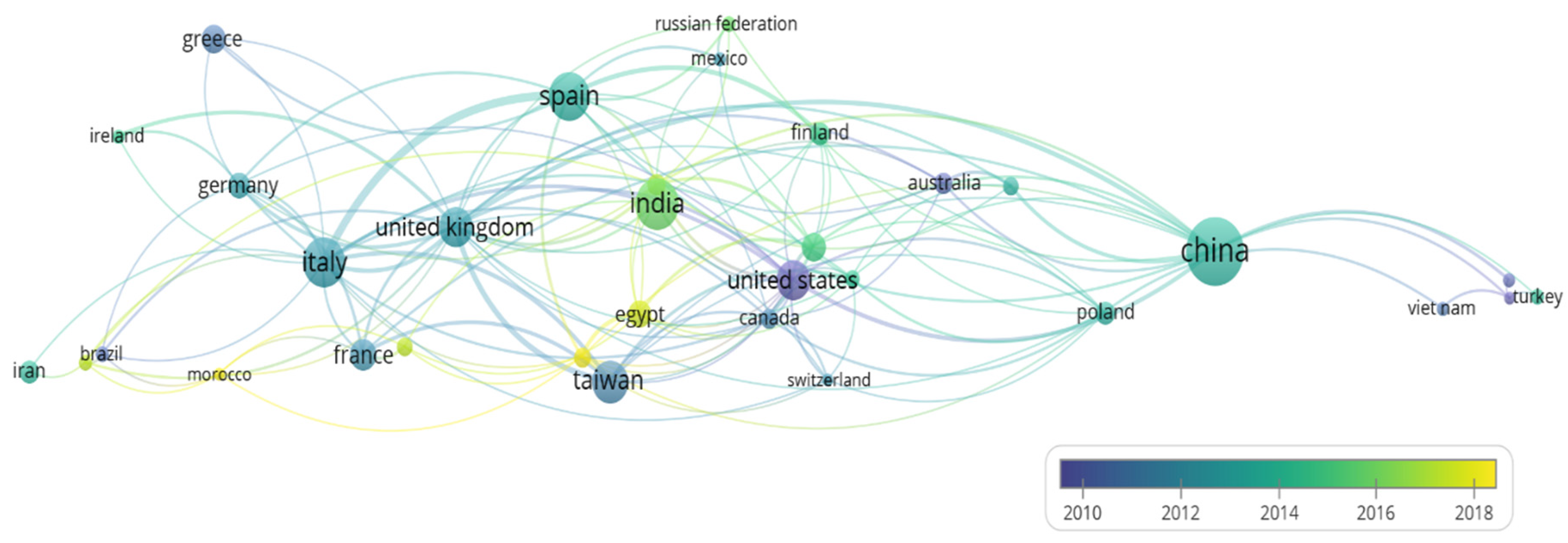
3.3. Countries Participating in the Study (RQ-4)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balke, W.; Mainzer, K. Knowledge representation and the embodied mind: Towards a philosophy and technology of personalized informatics. In Professional Knowledge Management; Althoff, K., Dengel, A., Bergmann, R., Nick, M., Roth-Berghofer, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3782, pp. 586–597. [Google Scholar]
- Qasim, I.; Alam, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Malik, K.; Saleem, M.; Bukhari, S. A comprehensive review of type-2 fuzzy ontology. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 1187–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonck, M.; Gailly, F.; Pergl, R.; Guizzardi, G.; Martins, B.; Pastor, O. Comparing traditional conceptual modeling with ontology-driven conceptual modeling: An empirical study. Inf. Syst. 2019, 81, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corea, C.; Delfmann, P. Detecting Compliance with Business Rules in Ontology-Based Process Modeling. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop of Wirtschaftsinformatik (WI 2017), St. Gallen, Switzerland, 12–15 February 2017; Leimeister, J.M., Brenner, W., Eds.; pp. 226–240. [Google Scholar]
- Karagiannis, D.; Buchmann, R. A proposal for deploying hybrid knowledge bases: The ADOxx-to-GraphDB interoperability case. In Proceedings of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hilton Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 3 January 2018; pp. 4055–4064. [Google Scholar]
- Wand, Y.; Weber, R. On the ontological expressiveness of information systems analysis and design grammars. Inf. Syst. J. 1993, 3, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.; Gutheil, M.; Kiko, K. On the relationship of ontologies and models. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Meta-Modelling (WoMM 2006), Karlsruhe, Germany, 12–13 October 2006; pp. 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson-Sellers, B. On the Mathematics of Modelling, Metamodelling, Ontologies and Modelling Languages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilecas, O.; Kalibatiene, D.; Guizzardi, G. Towards a formal method for the transformation of ontology axioms to ap-plication domain rules. Inf. Technol. Control. 2009, 38, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kalibatienė, D.; Vasilecas, O. Application of the Ontology Axioms for the Development of OCL Constraints from PAL Constraints. Informatica 2012, 23, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalibatiene, D.; Vasilecas, O. Ontology-based application for domain rules development. CSIT 2010, 756, 9–32. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, N. Formal ontology and information systems. In Proceedings of the FOIS’98, Trento, Italy, 6–8 June 1998; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, N.; Welty, C. A formal ontology of properties. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference EKAW 2000, Juan-les-Pins, France, 2–6 October 2000; Dieng, R., Corby, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, H. Fuzzy Set Theory—And Its Applications, 4th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; p. 525. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.-Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, N. Information structures and uncertainty measures in a fully fuzzy information system. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2018, 101, 119–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, C.; Jensen, R.; Hurtado, G.; Ślezak, D. Attribute selection with fuzzy decision reducts. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 1990, 17, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Dai, J.; Chen, J.; Fujita, H. Measures of uncertainty based on Gaussian kernel for a fully fuzzy information system. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 196, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Ma, J.; Lei, J.; Li, C. A Fuzzy Approach for Measuring the Semantic Similarity Between words in WordNet. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2009, 6, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, S.; Inuiguchi, M.; Slowinski, R. Fuzzy rough sets and multiple-premise gradual decision rules. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2006, 41, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaszczyński, J.; Słowiński, R.; Szeląg, M. Sequential covering rule induction algorithm for variable consistency rough set approaches. Inf. Sci. 2011, 181, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryszkiewicz, M. Rules in incomplete information systems. Inf. Sci. 1999, 113, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-Z. Attribute reduction based on evidence theory in incomplete decision systems. Inf. Sci. 2008, 178, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Pedrycz, W.; Yu, D.; Lang, J. Selecting Discrete and Continuous Features Based on Neighborhood Decision Error Minimization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part. B (Cybernetics) 2010, 40, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Liang, J.; Pedrycz, W.; Dang, C. Positive approximation: An accelerator for attribute reduction in rough set theory. Artif. Intell. 2010, 174, 597–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thangavel, K.; Pethalakshmi, A. Dimensionality reduction based on rough set theory: A review. Appl. Soft Comput. 2009, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhan, J.; Xu, Z. A novel decision-making approach based on three-way decisions in fuzzy information systems. Inf. Sci. 2020, 541, 362–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Cai, M.; Dai, J.; Li, Q. A novel approach to predictive analysis using attribute-oriented rough fuzzy sets. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Characterizations and uncertainty measurement of a fuzzy information system and related results. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 12753–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Xie, N.; Lin, F. cc-reduction in a fully fuzzy information system. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 6589–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyaswamy, V.; Manogaran, G.; Logesh, R.; Vijayakumar, V.; Chilamkurti, N.; Malathi, D.; Senthilselvan, N. An ontology-driven personalized food recommendation in IoT-based healthcare system. J. Supercomput. 2019, 75, 3184–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz, J.A.; Cánovas-García, M.; Valencia-García, R. Ontology-driven aspect-based sentiment analysis classification: An infodemiological case study regarding infectious diseases in Latin America. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 112, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, J.; Guizzardi, G. Individual determinacy and identity criteria in ontology-driven information systems. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Formal Ontologies and Information Systems (FOIS 2018), Cape Town, South Africa, 17–21 September 2018; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ruy, F.B.; Guizzardi, G.; Falbo, R.A.; Reginato, C.C.; Santos, V.A. From reference ontologies to ontology patterns and back. Data Knowl. Eng. 2017, 109, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, J.; Ma, Z. A survey on fuzzy ontologies for the Semantic Web. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2016, 31, 278–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulaish, M.; Dey, L. Information extraction and imprecise query answering from web documents. WIAS 2006, 4, 407–429. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L.; Huang, L.; Wu, C.; Chen, S. Fuzzy Knowledge Management through Knowledge Engineering and Fuzzy Logic. J. Converg. Inf. Technol. 2010, 5, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Satler, M.; Romero, F.; Menendez-Dominguez, V.; Zapata, A.; Prieto, M. Fuzzy ontologies-based user profiles applied to enhance e-learning activities. Soft Comput. 2012, 16, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, A.C.; Kim, Y.-G.; Bukhari, S.A.C. Integration of a secure type-2 fuzzy ontology with a multi-agent platform: A proposal to automate the personalized flight ticket booking domain. Inf. Sci. 2012, 198, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, C.; Ching-López, A.; Lefranc, G.; Loia, V.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Sharing notes: An academic social network based on a personalized fuzzy linguistic recommender system. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Vakkalanka, S.; Kuzniarz, L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaki, A.A.; Rasoolzadegan, A.; Bafghi, A.G. A Systematic Mapping Study on Intrusion Alert Analysis in Intrusion Detection Systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnenluecke, M.K.; Marrone, M.; Singh, A.K. Conducting systematic literature reviews and bibliometric analyses. Aust. J. Manag. 2020, 45, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Budgen, D. What Do We Know about the Effectiveness of Software Design Patterns? IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2011, 38, 1213–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B.A.; Budgen, D.; Brereton, O.P. Using mapping studies as the basis for further research—A participant-observer case study. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2011, 53, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering (EBSE 2007-001); Technical Report; Keele University: Keele, UK; Durham University: Durham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dybå, T.; Dingsøyr, T. Empirical studies of agile software development: A systematic review. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2008, 50, 833–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalibatienė, D.; Miliauskaitė, J. A Hybrid Systematic Review Approach on Complexity Issues in Data-Driven Fuzzy Inference Systems Development. Informatica 2021, 32, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchenham, B. Procedures for Performing Systematic Reviews; Joint Technical Report TR/SE-0401; Keele University: Keele, UK; Australian Technology Park: Sydney, Australia, 2004; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, M.; Martínez, M.; Gutiérrez-Salcedo, M.; Fujita, H.; Herrera-Viedma, E. 25 years at Knowledge-Based Systems: A bibliometric analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 80, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Kong, X.; Hong, S.; Li, J.; He, Z. Global ontology research progress: A bibliometric analysis. Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 2015, 67, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilutiene, T.; Kalibatiene, D.; Hosseini, M.R.; Pellicer, E.; Zavadskas, E.K. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Structural Engineering: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Literature. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L.; Noyons, E.C.M.; Buter, R.K. Automatic term identification for bibliometric mapping. Science 2010, 82, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalil, G.; Gotway Crawford, C. A bibliometric analysis of US-based research on the behavioral risk factor surveillance system. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 48, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eck, N.; Waltman, L. Manual for VOS Viewer Version 1.6.10; CWTS, Universiteit Leiden: Leiden, Holland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adeniji, B. A Bibliometric Study on Learning Analytics. Master’s Thesis, Long Island University, New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Waltman, L.; van Eck, N.J.; Noyons, E.C. A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. J. Inf. 2010, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakeel, Y.; Krüger, J.; von Nostitz-Wallwitz, I.; Lausberger, C.; Durand, G.; Saake, G.; Leich, T. Literature analysis—Threats and experiences. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 13th International Workshop on Software Engineering for Science (SE4Science), Gothenburg, Sweden, 2 June 2018; pp. 20–27. [Google Scholar]

| Database | Search String | Document Type | Language | Categories | Search Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WoS | (“ontolog*” AND “fuzzy”) | article OR review | English | Computer Science OR Engineering | 508 |
| Scopus | (“ontolog*” AND “fuzzy”) | article OR review | English | Computer Science OR Engineering | 647 |
| Total 1: | 1155 | ||||
| Keywords | Feature | Framework | Fuzzy Extension | Fuzzy Logic | Fuzzy Ontology | Fuzzy Set | Fuzzy Set Theory | Information | Information Retrieval | Knowledge | Knowledge Base | User |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| accuracy | 6 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| concept | 7 | 17 | 4 | 7 | 23 | 5 | 6 | 32 | 10 | 29 | 6 | 16 |
| context | 5 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 20 | 4 | 14 | 4 | 12 |
| data | 12 | 25 | 0 | 8 | 26 | 8 | 3 | 32 | 6 | 30 | 5 | 15 |
| degree | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 13 | 2 | 5 |
| development | 4 | 14 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 2 | 5 | 13 | 3 | 16 | 2 | 4 |
| document | 2 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 1 | 5 | 17 | 16 | 14 | 4 | 12 |
| domain | 8 | 14 | 3 | 9 | 26 | 3 | 6 | 28 | 6 | 37 | 5 | 13 |
| experimental result | 5 | 5 | 0 | 7 | 15 | 2 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 20 | 5 | 11 |
| expert | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 12 | 1 | 1 |
| feature | 0 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 13 | 3 | 3 | 15 | 3 | 19 | 1 | 6 |
| framework | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 21 | 5 | 4 | 26 | 9 | 22 | 2 | 14 |
| fuzzy logic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 20 | 6 | 20 | 1 | 10 |
| fuzzy ontology | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 38 | 11 | 46 | 10 | 14 |
| information | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 42 | 8 | 38 |
| information retrieval | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 6 | 9 |
| knowledge | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 16 |
| Keywords | Retrieval | Search Engine | Semantic Query Expansion | Semantic Relation | Semantic Retrieval | Semantic Similarity | Similarity Measurement | Social Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| collection | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| dataset | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| fuzzy semantic retrieval | 3 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| image | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| information retrieval system | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| keyword | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| relevance | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| retrieval | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| semantic query expansion | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Countries 1 | Australia | Brazil | Canada | Egypt | England | Finland | France | Germany | Greece | India | Italy | Japan | Pakistan | Peoples R China | Poland | Russia | Saudi Arabia | Scotland | South Korea | Spain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egypt | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| England | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Finland | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| France | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Germany | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Greece | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| India | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Italy | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Japan | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Pakistan | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Peoples R China | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Poland | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Russia | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Saudi Arabia | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Scotland | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Singapore | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| South Korea | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Spain | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Taiwan | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Tunisia | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||
| USA | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Countries 1 | Australia | Brazil | Canada | China | Egypt | Finland | France | Germany | Greece | Hong Kong | India | Iran | Ireland | Italy | Japan | Malaysia | Mexico | Morocco | New Zeeland | Pakistan | Poland | Russian Federation | Saudi Arabia | Singapore | South Korea | Spain | Switzerland | Taiwan | United Kingdom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Egypt | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Finland | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Germany | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greece | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hong Kong | 3 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| India | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ireland | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Italy | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japan | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malaysia | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mexico | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morocco | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| New Zeeland | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pakistan | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poland | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian Federation | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saudi Arabia | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Singapore | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| South Korea | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spain | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Switzerland | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taiwan | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tunisia | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turkey | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United Kingdom | 2 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 9 | ||||||||
| United States | 2 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Vietnam | 2 | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalibatiene, D.; Miliauskaitė, J. A Systematic Mapping with Bibliometric Analysis on Information Systems Using Ontology and Fuzzy Logic. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073003
Kalibatiene D, Miliauskaitė J. A Systematic Mapping with Bibliometric Analysis on Information Systems Using Ontology and Fuzzy Logic. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073003
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalibatiene, Diana, and Jolanta Miliauskaitė. 2021. "A Systematic Mapping with Bibliometric Analysis on Information Systems Using Ontology and Fuzzy Logic" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073003
APA StyleKalibatiene, D., & Miliauskaitė, J. (2021). A Systematic Mapping with Bibliometric Analysis on Information Systems Using Ontology and Fuzzy Logic. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073003







