Abstract
Understanding light transportation in skin tissues can help improve clinical efficacy in the laser treatment of dermatosis, such as port-wine stains (PWS). Patient-specific cross-bridge PWS vessels are structurally complicated and considerably influence laser energy deposition due to shading effects. The shading effect of PWS vessels is investigated using a tetrahedron-based Monte Carlo (MC) method with extended boundary condition (TMCE). In TMCE, body-fitted tetrahedra are generated in different tissues, and the precision of photon–surface interaction can be considerably improved via mesh refinement. Such improvement is difficult to achieve with the widely used voxel-based MC method. To fit the real physical boundary, the extended boundary condition is adapted by extending photon propagation to the semi-infinite tissue layers while restricting the statistics of photon propagation in the computational domain. Results indicate that the shading parameters, such as the cross angle, vessel distance, and geometric shadow (GS), of cross-bridge blood vessel pairs determine the peak characteristics of photon deposition in deep vessels by affecting the relative deposition of collimated and diffused light. Collimated light is shaded, attenuated, and partially transformed into diffused light due to the increase in vessel distance and GS of vessel pairs, resulting in difficulty in treating deep and shallow vessels with one laser pulse. The TMCE method can be used for the individualized and precise forecasting of laser energy deposition based on the morphology and embedding characteristics of vascular lesions.
1. Introduction
Understanding light transportation in skin tissues can help improve clinical efficacy in the laser treatment of dermatosis, such as port-wine stains (PWS) [1]. As an effective and easy-to-parallelize technique [2], the Monte Carlo (MC) method has been successfully used in modeling light transportation in biological tissues. In this method, a “random walk” with a sufficient number of photon packets is traced to build reliable trends of light transportation on the basis of their statistical scattering and absorption.
Non-uniform energy distribution via selective photothermolysis [3] is caused by various optical properties in different skin tissues, leading to preferential absorption in blood vessels instead of in other skin tissues, including epidermis, dermis, and hair follicles [4]. Moreover, patient-specific PWS vessels are typically structurally complicated in terms of computation. Multilayered PWS vessels, particularly cross-bridge vessels, considerably influence laser propagation due to shading effects [5,6] (Figure 1). Therefore, an unknown deposition of light energy always appears in PWS vessels [7]. The effect of the adaptability of complicated vessel structures has elicited considerable attention from researchers in MC simulation.
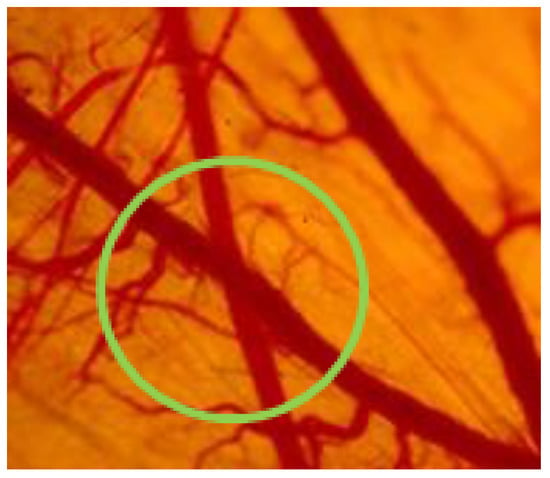
Figure 1.
Cross-bridge vessels [8].
Wang et al. [9] developed the MC method in multilayered tissues (MCML) and applied it to a succession of homogeneous layers with different optical properties that are parallel to one another. MCML has been extended to adapt to the cylindrical surface of blood vessels by using Snell’s law in the curved interface to trace the transport of light. This algorithm is called the geometric Monte Carlo (GMC) [10,11] because all tissue structures and their interfaces require geometric descriptions. However, GMC is limited in the burdensome mathematical definitions of complicated tissue structures.
In terms of light propagation in arbitrarily complex 3D heterogeneous tissue morphology, the voxel-based Monte Carlo (VMC) algorithm has attracted considerable attention among scholars [12,13,14,15]. In VMC, the computational domain is divided into voxels by using a cuboid mesh with a simple connection relationship. Photon radiation is investigated by assigning certain optical properties to each voxel [13]. However, the round or oblique boundaries between neighboring tissues are approximated via serrated surfaces due to the fixed mesh connection. Consequently, large errors (80–120%) of photon intensity occur in boundary voxels [7]. Moreover, mesh refinement does not change the shape and arrangement of grids, and thus is unable to improve the description of light reflection and refraction at curved boundaries. Therefore, errors exist even with fine discretization [16].
Compared with voxel-based medium discretization, a tetrahedron-based approach is ideally adaptable to modeling targets with curved boundaries or locally refined structures. Shen and Wang [17] proposed a tetrahedron-based inhomogeneous MC optical simulator (TIM-OS) using tetrahedral meshes for MC simulations. Although TIM-OS was validated by MCML, its computational domains are mostly regular regions with less complexity. Jia et al. [18] developed a tetrahedron-based MC (TMC) solver that is suitable for computing photon energy deposition in complicated domains with a body-fitted tetrahedron mesh. The error caused by confused optical parameters between neighboring cells when photons are incident along the cell boundary can be avoided in TMC by introducing the distance threshold [18,19]. The influence of discretization on light propagation was discussed to compare the relative errors of VMC and TMC with the benchmark of GMC. A comparative study showed that energy deposition error via TMC in the interfacial region is one-tenth to one-fourth that via VMC; thus, the former yields a more accurate computation of photon transportation [18]. In TMC, the escape boundary condition (BC) is applied to computational surfaces. However, this approach is suitable only for the treatment of skin surrounded by air [20]. To overcome this problem, an approach that addresses tissue BC should be developed. Only one study has been conducted on simply arranged PWS vessels. Therefore, further studies are necessary to extend the TMC method to laser propagation in the complex structures of PWS vessels.
In the present study, a TMC with extended BC (TMCE) solver is developed. TMCE is suitable for computing photon energy deposition in complex domains with a body-fitted tetrahedron mesh. The applicability of TMCE in skin optics is validated by comparing its results with those of GMC. Skin models with parallel and cross-bridge vessels are investigated via TMCE to identify regulations of photon transport in complex tissue regions.
2. Materials and Methods
In TMCE, tetrahedra are generated along the interface, yielding a polyhedron approximation to match the real interface [18]. A photon randomly propagates into a series of tetrahedra and repeatedly interacts with triangular surfaces until it loses all its weight or escapes the object. With mesh refinement, the TMCE method demonstrates its superiority by modifying the shape and arrangement of tetrahedral meshes to fit the real boundary, increasing the accuracy of photon reflection and refraction (Figure 2). In such situations, identifying photon–surface interactions when tracing a photon through tetrahedral meshes is a challenging task.
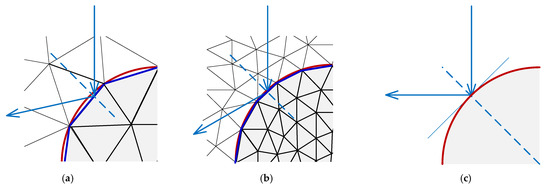
Figure 2.
Photon reflection on vessel–dermis boundary. (a) Tetrahedron-based Monte Carlo method with extended boundary condition (TMCE) with relatively sparse mesh, (b) TMCE with refined mesh, and (c) real physical process.
2.1. Photon–Surface Interaction in TMCE
Our simulation of light propagation in PWS skin is conducted on the basis of the weighted-photon MC technique [9]. In this approach, a large number of energy packets (“photons”) propagate through tissues and deposit a fraction of their energy into specific volume elements in accordance with local absorption properties. Stochastic relations are used to determine each photon’s random trajectory on the basis of the physical laws of light scattering, reflection, and refraction. The step size of the photon is calculated based on a sampling of the probability distribution for the photon’s free path. Integrating the interaction coefficient (sum of the absorption and scattering coefficient) along the photon trajectory determined by a random number can obtain the step size [18]. The implementation of photon–interface interaction in TMCE is presented as follows.
Suppose that P is the position of the photon, U is the unit direction of photon movement, and N is the inward unit normal vector of the triangle surface. For a photon with P in the current tetrahedron, a judgment of N·U < 0 will be performed on each of the four triangular surfaces to identify a possible photon–triangle interaction. In general, two or three of the triangles satisfy the judgment, as shown in Figure 3.
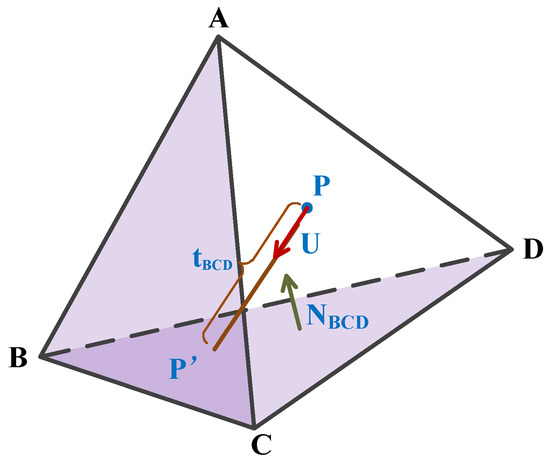
Figure 3.
Diagram of photon–tetrahedron interaction. Planes ABC and BCD satisfy the judgment. tBCD represents the photon propagation distance to plane BCD, and NBCD denotes the inward unit normal vector of plane BCD.
The description of photon propagation should be presented to determine the photon–interaction plane from two or three triangles. The path of the photon to hit a triangle can be described as the following line function:
where t is the distance from the photon’s current location to the intersection point. For the potential triangle of photon collision, the following equation is derived in accordance with the plane function:
where Q is a point on the plane, and d is a scalar. The propagation distance t can be solved by combining Equations (1) and (2) as follows:
The plane marked by the minimum t is the target plane of photon propagation. If the minimum t (t’) among the potential planes is larger than the photon step size ts (generated by a random number), then the photon transports within the current tetrahedron; otherwise, the photon will hit the related triangular surface and continue to propagate until the step size is covered. In the preceding procedure of photon–triangle interaction, when a photon hits an interface (triangular surface) between two media, the photon is either reflected or refracted as determined by the Fresnel formulas connected with a random number [18]. The reflection and refraction directions are determined from the reflection law and Snell’s law [18]. When the photon reaches the destination of the current step size, the energy carried in the photon is attenuated by the absorption and scattering effect. Subsequently, the next step size will be generated.
2.2. Boundary Conditions
The three primary BCs in the TMCE models are reflecting, escape, and extended BCs. A reflecting BC describes a perfectly reflecting situation wherein all the photon energy is recycled to the computational domain via reflection (as shown in Figure 4a). This approach considerably accelerates computation and yields acceptable results for wide-beam irradiation, such that its diameter is significantly larger than the computational domain.
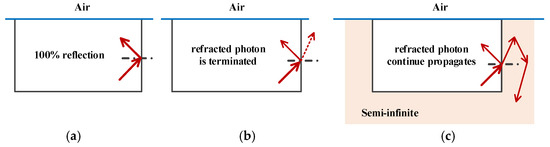
Figure 4.
Three boundary conditions (BCs) for laser transportation. The computational domain is marked by a black rectangle. (a) Reflecting BC, (b) Escape BC and (c) Extended BC. The red dashed line represents the terminated photon.
In the escape BC, the probability of photon reflection or refraction is determined by the Fresnel coefficients when hitting a boundary. The photon is terminated when it exits the boundary via refraction, as shown in Figure 4b.
In the extended BC, photons are launched in accordance with the profile of the laser beam intensity and propagate in laterally infinite tissue layers until they deposit all their energy or escape into the air (Figure 4c). In this approach, photons exiting the finely discretized computational domain are propagated further in semi-infinite tissue layers until they return to the computational domain, escape into the air, or lose all their energy.
In this study, a small-diameter laser beam is adopted to simulate light transport in skin with complex vessel structures. Therefore, reflecting BC is unsuitable. The cuboid domain has six boundaries (Figure 4). Escape BC is applied to the top surface, which is a real physical boundary connected to the air. The principle of extended BC is applied to the bottom and the four side boundaries.
2.3. Validation of TMCE
To validate the TMCE algorithm, we initially compared TMCE and TMC with GMC [10] by recording the energy deposition in the skin model (Figure 5), which is composed of two layers of media: 60 μm-thick epidermis and 940 μm-thick dermis underneath. In the dermis, a single cylindrical PWS vessel with a diameter of 120 μm is buried at 250 μm. The laser spot with top hat profile was irradiated at the center of the incident plane with a diameter of 1.0 mm and energy fluence of 1 J/cm2. A 1.4 mm × 1.4 mm × 1.0 mm domain was used because it was sufficiently large and no evident fluence variation occurred at the tissue boundary when the computation space was expanded. The total photon number was 108.
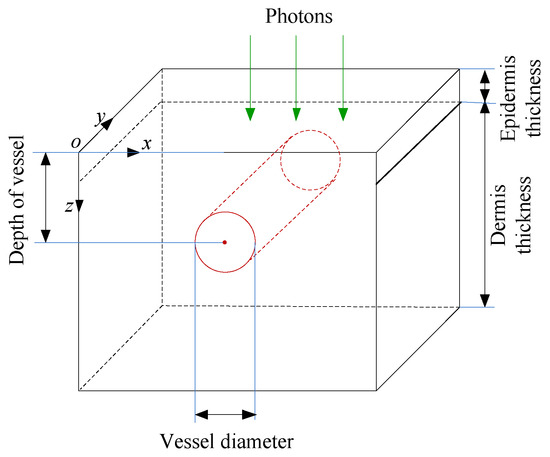
Figure 5.
Diagram of the skin model with single port-wine stain (PWS) vessel.
In the model, melanin is assumed to be homogeneously distributed throughout the epidermis. The epidermal absorption coefficient, μa,epi, is calculated using the following equations [20]:
where μa,mel is the absorption coefficient of melanosome, and μa,base is the average baseline value for the skin. In this study, the laser wavelength λ is 585 nm and fmel is 5%. These values correspond to Asian skin. Other optical properties corresponding to the wavelength of 585 nm was used similar with that in Table 2 in [15].
In the TMCE and TMC methods, a tetrahedron mesh is generated using the commercial software GAMBIT 2.4. Body-fitted tetrahedra are generated along the vessel–tissue interface. The total number of cells is 144,783. In the simulation, energy deposition is recorded with respect to depth at the beam center. The energy deposited in the column of cubes directly below the center of the beam (0.7 mm) via GMC, TMCE, and TMC is illustrated in Figure 6. The line graph includes four parts: epidermis, dermis, blood vessel, and dermis (Figure 6). The result of TMCE agrees well with that of GMC. By contrast, errors appear at the epidermis–dermis and vessel–dermis boundaries in TMC. This finding is attributed to the accurate boundary description of TMCE.
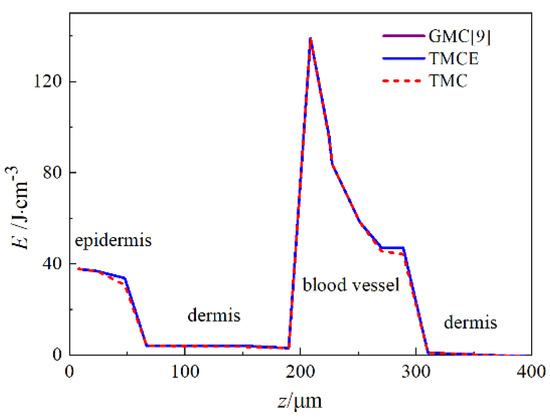
Figure 6.
Line graph of energy deposition vs. depth at the beam center for simulations of skin with a single blood vessel.
To further compare the accuracy of the three methods, we assessed photon deposition distribution in the central cross-section of the vascular region in the blood vessel (Figure 7). Figure 7a shows that in GMC the photon that transmits to the vessel from the top half should be mostly deposited near the vessel wall, forming the crescent of high deposition region. The results computed by TMCE show a more similar crescent shape to Figure 7a than that by TMC.
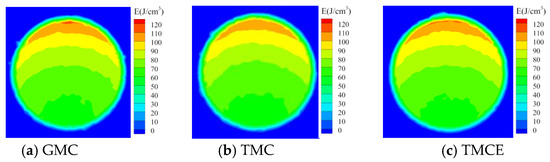
Figure 7.
Photon deposition (J/cm3) in the central cross-section of the vascular region.
Deposition errors in the annular cylinder close to the inner wall of the vessel was segmented by Δr of 5 μm and θ of 1° (Figure 8a). The deposition in the 1° annular cylinder computed by GMC, TMC, and TMCE was collected. The relative error KTMC and KTMCE of TMC, and TMCE are calculated with GMC as a benchmark, as follows:
where E is the photon deposition in each 1° annular cylinder.
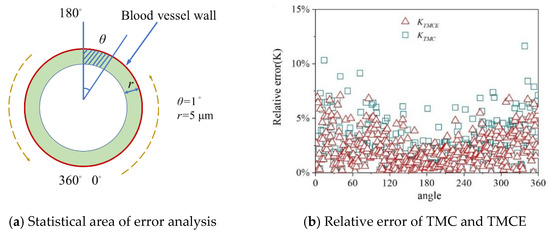
Figure 8.
Relative error distribution in 1° annular cylinder region.
Figure 8b presents the relative error distribution in each 1° annular cylinder. We can see a KTMC larger than 8% was observed at 0°–60° and 330°–360°, whereas KTMCE maintained less than 7.5%, not sensitive to angles.
3. Results
In this section, the shading effects on the energy deposition of parallel and cross-bridge vessels are systematically studied using the TMCE method. The laser spot assumed a flat top profile as described in Section 2.3. Given the high absorption in the epidermis and blood vessels, local refinement is implemented in these regions [18].
3.1. Parallel Blood Vessels
First, we studied the skin model with parallel vessels because it is the basis for investigating other increasingly complex shading. A skin model with two cylindrical parallel vessels with a diameter of 120 μm is shown in Figure 9. The axes of the two vessels are along the y-axis. The angle between the center–center line of the two circles and the horizontal line is defined as the shading angle (0 ≤ θshad ≤ 90°) (Figure 9a). Parallel vessel pairs are represented by θshad and the vessel distance Hshad (Figure 7a). The position of the superficial vessel is fixed at z = 250 μm, x = 700 μm to explore the effect of the deep vessel’s position. For a convenient comparison, the energy deposition of a deep vessel before and after shading was calculated when Hshad changed from 150 μm to 350 μm or θshad from 0° to 90°. The deep vessel is fully shaded at θshad = 90°.
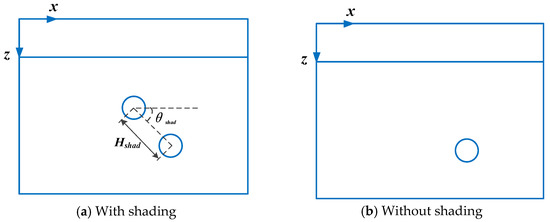
Figure 9.
Cross-sectional view of the skin model with parallel PWS vessels.
Figure 10 shows the ratio of deep vessel deposition with shading to that without shading at different shading angles and distances. The shading effect is apparent with a large θshad and a low Hshad. For example, energy loss in the deep vessel with shading is only 8% (ω = 8%) at θshad = 0° and Hshad = 350 μm. By contrast, it increases to 37% (ω = 63%) at θshad = 90° and Hshad = 150 μm (Figure 10). This phenomenon can be explained by scattering theory. When incident light enters a turbid biological tissue, it will scatter and deviate from the original direction. For the shading angle, more photon energy is absorbed by the shallow blood vessel as θshad increases. Subsequently, energy deposition in the deep blood vessel decreases. Consequently, the scattered light transmits randomly and is less likely to propagate around the superficial vessel and be absorbed by the deep vessel. As the energy loss caused by the shading effect increases, the deep vessel receives insufficient thermal damage. Therefore, high laser fluence is required to rupture deeply buried or (and) fully shaded blood vessels.
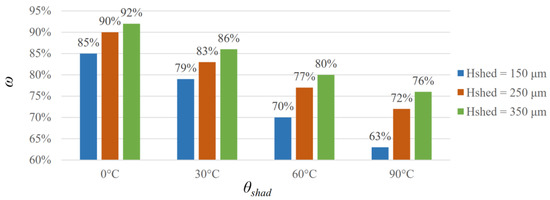
Figure 10.
Ratio (ω) of vessel energy deposition with shading to that without shading using a superficial vessel.
Figure 11 shows the energy deposition directly below the center of the beam at θshad = 90° with Hshad of 150, 250, and 350 μm. When the two vessels are arranged along the z direction, photon deposition in the deep vessels decreases gradually from 5.4% to 4.1% with an increase in Hshad from 150 μm to 350 μm (not shown) because photon energy attenuates less by scattering before reaching the relatively shallow-buried vessel. However, the absorption peak of the deep vessels is only approximately 60 J/cm3 regardless of Hshad. This value is considerably less than 140 J/cm3 in the shallow vessel. This finding indicates that the deep vessel is difficult to damage through complete shading (θshad = 90°) of the shallow vessel.
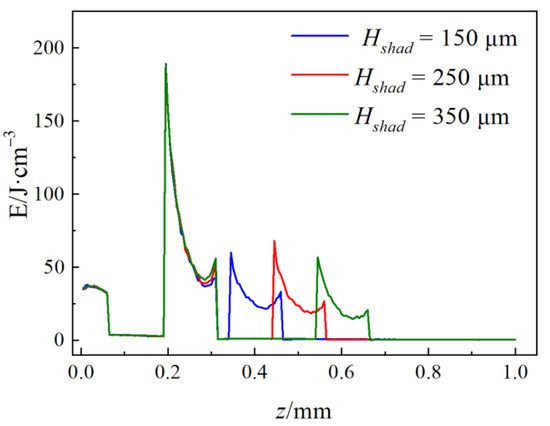
Figure 11.
Line graph of energy deposition vs. depth at the beam center for simulations of skin with parallel blood vessels with different Hshad values at θshad = 90°.
3.2. Cross-Bridge Blood Vessels
The skin tissues with cross-bridge vessels can be simplified into the model shown in Figure 12. The angle between the axes of the two vessels is defined as the crossing angle α0, and the distance between them is defined as the vessel distance Hcshad. The laser treatment of the cross-bridge PWS vessels faces tremendous challenges due to the diversity of α0 and Hcshad.
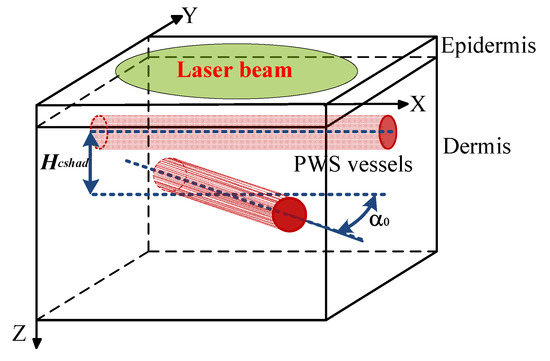
Figure 12.
Simplified skin model embedded with cross-bridge vessels.
The energy absorbed by biological tissues originates from two contributors: collimated light (propagates parallel to the direction of the incident beam) and diffused light (with random propagation direction). Diffused light increasingly contributes to photon deposition with an increase in photon propagation depth due to tissue scattering. Consequently, light scattering weakens the shading effect. The shape and structure of cross-bridge vessels also considerably influence the proportion of collimated and scattered light deposited into blood vessels. Therefore, the shading effects of α0 and Hcshad and the shape of the cross section of blood vessels are investigated in this section.
3.2.1. Cross Angle
Figure 13 shows the distribution of energy deposition along the axis direction of the cylindrical deep vessel with an increase in α0 from 0° to 90° at an Hcshad of 250 μm. The vessel diameters are 120 μm, and the shallow vessel is buried at 250 μm. As shown in Figure 13a, the deep blood vessel is completely shaded at α0 = 0°. Consequently, the collimated light is mostly absorbed by the superficial blood vessel and only scattered light is deposited into the deep vessel. Hence, photon deposition appears as a single smooth peak. Collimated laser light becomes diffused because of scattering. When α0 is greater than 20°, the photon energy exhibits a bimodal characteristic because the collimated light with reflection and refraction through the wall of the superficial blood vessel is concentrated on the two sides of the deep blood vessel (as shown in Figure 13b). With the increase in α0, the bimodal characteristic of energy deposition is enhanced gradually and reaches the highest value at α0 = 90°.
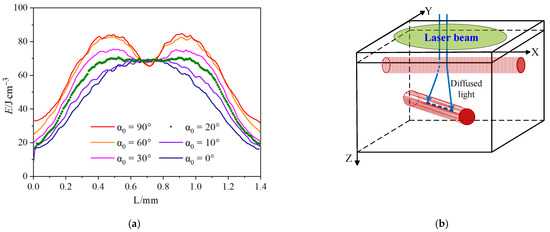
Figure 13.
Effect of cross angle (α0) on energy deposition in the axis of the deep blood vessel at D = 120 μm and Hcshad = 250 μm. (a) Energy deposition along the vessel axis. (b) Diagram of energy deposition in the deep vessel at α0 > 20° and Hcshad = 250 μm.
3.2.2. Vessel Distance
Figure 14 shows the distribution of energy deposition along the axis direction of the cylindrical deep vessel with an increase in Hcshad from 150 μm to 450 μm at α0 = 30°. Vessel diameter is 120 μm, and the shallow vessel is buried at 250 μm. As shown in Figure 14 when Hcshad is small (150 μm), a large amount of collimated light is deposited in the deep vessel and forms the significant characteristic of double peaks. The dermal layer between the two vessels becomes thicker with an increase in Hcshad. The collimated light partially becomes diffused light with additional random propagation direction due to additional attenuation via scattering in the dermis. Therefore, the double peak characteristic of photon deposition in the deep blood vessel gradually weakens until it disappears.
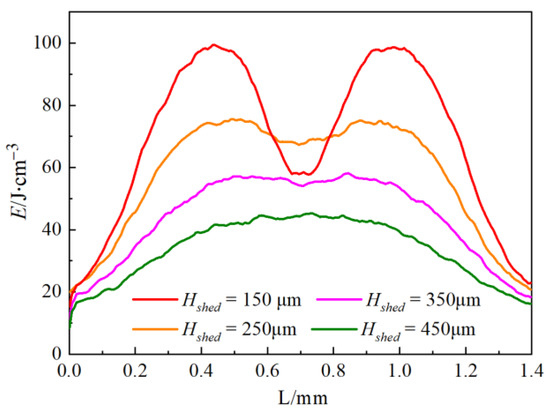
Figure 14.
Effect of vessel distance to energy deposition on the axis of the deep blood vessel at D = 120 μm and α0 = 30°.
3.2.3. Shape of Vessel Cross Section
The cross section of real blood vessels is depicted as more elliptical than an ideal circle. As shown in Figure 15 the semimajor axis a and semiminor axis b define an elliptical section of a vessel. Geometric shadow (GS), which is defined as the width of the cross section of the vessel, is used to study the effect of vessel shape (Figure 15) when the area of the cross section and α0 remain unchanged. Therefore, the only difference between Cases A, B, C, and D in Figure 13 is that the GSs are 80, 120, 160, and 200 μm, respectively.
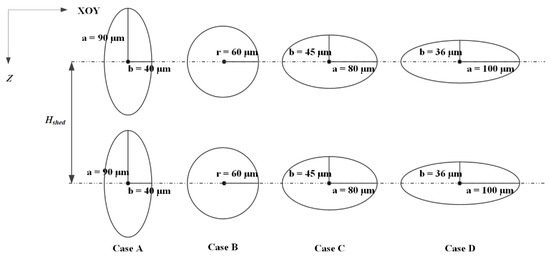
Figure 15.
Representation of the cross section of the four vessel pairs (α0 = 30°).
Table 1 provides the photon energy deposition in deep vessels with shading (WS) and without shading (OS) using the superficial vessel. The ratio between WS and OS at different vessel distances and GSs is also presented in this table. An increase in GS and vessel distance reduces the ratio from 73% to 64%. The scattering attenuation of the collimated light in the dermis is significant when Hcshad is equal to 450 μm, and the ratio of energy deposition is inevidently affected by the GS of blood vessels.

Table 1.
Energy deposition (J·cm−3) in deep vessels with different Hcshad values and geometric shadows (GSs).
Figure 16 shows the distribution of energy deposition in the deep vessel with the vessel distance ranging from shallow to deep in Cases B, C, and D. The large GS of the elliptical vessels indicates the evident shading effect of the shallow vessels on the collimated light. Consequently, the value of the double peaks of deep vessel deposition decreases significantly.
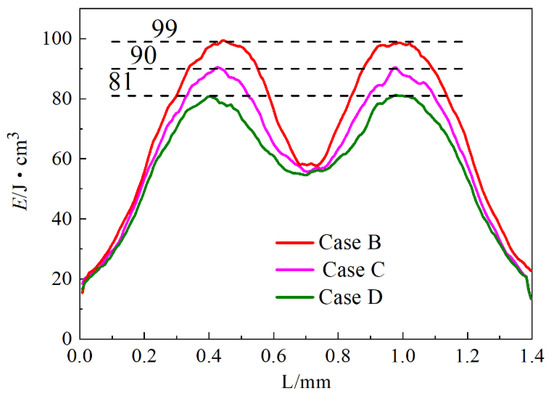
Figure 16.
Effect of vessel cross section on energy deposition in the axis of the deep blood vessel at Hcshad = 150 μm and α0 = 30°.
In summary, an increase in cross angle, a decrease in vessel distance, or a decrease in vessel GS increases the deposition of collimated light into deep vessels in cross-bridge vessels. Consequently, the energy distribution characteristic of deep vessels changes from single peak to double peak with a continuous decrease in value. The effect with two peaks exhibits the greatest difference in laser energy deposition between cross-bridge and parallel vessels. A high deposition rate of collimated light is beneficial for the injury of deep vessels. However, an increase in vessel distance and GS attenuates collimated light, making single-laser treatment of deep and shallow vessels difficult. Double-laser treatment should be considered to damage shallow and deep vascular lesions. Therefore, therapy expenses and the number of cycles will increase. The results provide guidance for reasonable treatment strategies based on the morphology and embedding characteristics of vascular lesions.
4. Conclusions
The presented 3D TMCE model is developed as a flexible and accurate approach for predicting light propagation in skin tissues. Body-fitted tetrahedra are generated to avoid photon reflection and refraction errors in the interface cells. A direct comparison shows that the results of TMCE are consistent with the energy deposition map in GMC.
The shading effect of two parallel blood vessels irradiated with 585 nm pulsed dye laser was investigated using the TMCE method. The results showed that the shading effect is more significant with an increase in shading angle θshad or a decrease in vessel distance Hshad. When θshad = 90° and Hshad = 150 μm, the energy deposition of deep vessels after shading decreases to 63% compared with that without shading, and the peak deposition is 80 J/cm3, which is lower than that of the shallow vessel. The findings show that the penetration depth of a 585 nm laser is shallow and photon deposition in deep vessels is insufficient. A deeper penetration laser wavelength (e.g., 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser) is suggested to treat deep PWS vessels.
This study on the shading effect of cross-bridge blood vessels shows that the cross angle, vessel distance, and GS of vessels determine the peak characteristics of photon deposition in the deep vessel by affecting the relative deposition of collimated and diffused light. In particular, the axis distribution of energy deposition of the deep vessel changes from a gentle single peak to a steep double peak due to an increase in shading angle and a decrease in vessel distance and vessel GS. This condition benefits the injury of deep vessels. By contrast, an increase in vessel distance and GS shades and attenuates a portion of collimated light, making the treatment of deep and shallow vessels using only one laser pulse difficult. Therefore, two pulses should be considered to damage deep and shallow vascular lesions, resulting in an increase in therapy expense and time. The numerical results of this work can be used for individualized and precise treatment based on the morphology and embedding characteristics of vascular lesions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.J. and B.C.; methodology, H.J.; software, H.J.; validation, D.L; formal analysis, B.C.; investigation, H.J.; resources, B.C.; data curation, H.J.; writing—original draft preparation, H.J.; writing—review and editing, B.C.; visualization, D.L.; supervision, B.C.; project administration, H.J.; funding acquisition, H.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51727811), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LZ15E090002) and Science Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (ZSTU) (19022101-Y, 11130231711926).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available upon request. Please email Hao Jia at jiahao@zstu.edu.cn.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lucassen, G.W.; Verkruysse, W.; Keijzer, M.; Gemert, M.J.V. Light distributions in a port wine stain model containing multiple cylindrical and curved blood vessels. Lasers Surg. Med. 1996, 18, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q. Mesh-based Monte Carlo method using fast ray-tracing in Plücker coordinates. Biomed. Opt. Express 2010, 1, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.R.; Parrish, J.A. Selective photothermolysis: Precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science 1983, 220, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillermo, A.; Bernard, C.; Mans, B.; Yang, O.; Yang, B.; Pedram, G.; Chen, J.K.; Rick, B.; Stuart, N.J.; Margreet, V.D.A. An Overview of Three Promising Mechanical, Optical, and Biochemical Engineering Approaches to Improve Selective Photothermolysis of Refractory Port Wine Stains. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 486–506. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Farshidi, D.; Wang, G.X.; He, Y.L.; Kelly, K.M.; Wu, W.J.; Chen, B.; Ying, Z.X. A comparison of microvascular responses to visible and near-infrared lasers. Lasers Surg. Med. 2014, 46, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonya-Ananta, T.; Rodriguez, A.J.; Ajmal, A.; Le, V.N.D.; Hansen, A.K.; Hutcheson, J.D.; Ramella-Roman, J.C. Synthetic photoplethysmography (PPG) of the radial artery through parallelized Monte Carlo and its correlation to body mass index (BMI). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binzoni, T.; Leung, T.S.; Giust, R.; Fenacht, D.; Gandjbakhche, A.H. Light transport in tissue by 3D Monte Carlo: Influence of boundary voxelization. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2008, 89, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, B.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, G.X.; He, Y.L.; Ying, Z.X. Experimental study on the vascular thermal response to visible laser pulses. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 35–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jacques, S.L.; Zheng, L. MCML—Monte Carlo modeling of light transport in multi-layered tissues. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 1995, 47, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, D.; Wang, X.G. Efficient and Accurate Simulation of Light Propagation in Bio-Tissues Using the Three-Dimensional Geometric Monte Carlo Method. Numerical Heat Transf. 2015, 68, 827–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, J. Numerical study on 3-d light and heat transport in biological tissues embedded with large blood vessels during laser-induced thermotherapy. Numerical Heat Transf. 2004, 45, 415–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.K.; Boas, D.A.; Stott, J.J.; Culver, J.P. Three dimensional Monte Carlo code for photon migration through complex heterogeneous media including the adult human head. Opt. Express 2002, 10, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Boas, D.A. Monte Carlo simulation of photon migration in 3D turbid media accelerated by graphics processing units. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 20178–20190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronin, A.; Meglinski, I. Online object oriented Monte Carlo computational tool for the needs of biomedical optics. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dremin, V.; Zherebtsov, E.; Bykov, A.; Popov, A.; Doronin, A.; Meglinski, I. Influence of blood pulsation on diagnostic volume in pulse oximetry and photoplethysmography measurements. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 9398–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premru, J.; Milanič, M.; Majaron, B. Monte Carlo simulation of radiation transfer in human skin with geometrically correct treatment of boundaries between different tissues. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2013, 8579, 85790Z. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Wang, G. A tetrahedron-based inhomogeneous Monte Carlo optical simulator. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Chen, B.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y. Boundary discretization in the numerical simulation of light propagation in skin tissue: Problem and strategy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 25007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Xue, C.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, L. Photon penetration depth in human brain for light stimulation and treatment: A realistic Monte Carlo simulation study. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2017, 10, 1743002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanic, M.; Majaron, B. Three-dimensional Monte Carlo model of pulsed-laser treatment of cutaneous vascular lesions. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 128002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).