Synchronized Motion Profiles for Inverse-Dynamics-Based Online Control of Three Inextensible Segments of Trunk-Type Robot Actuators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Approximate Inverse Kinematics Solution for Imposed End-Effector State
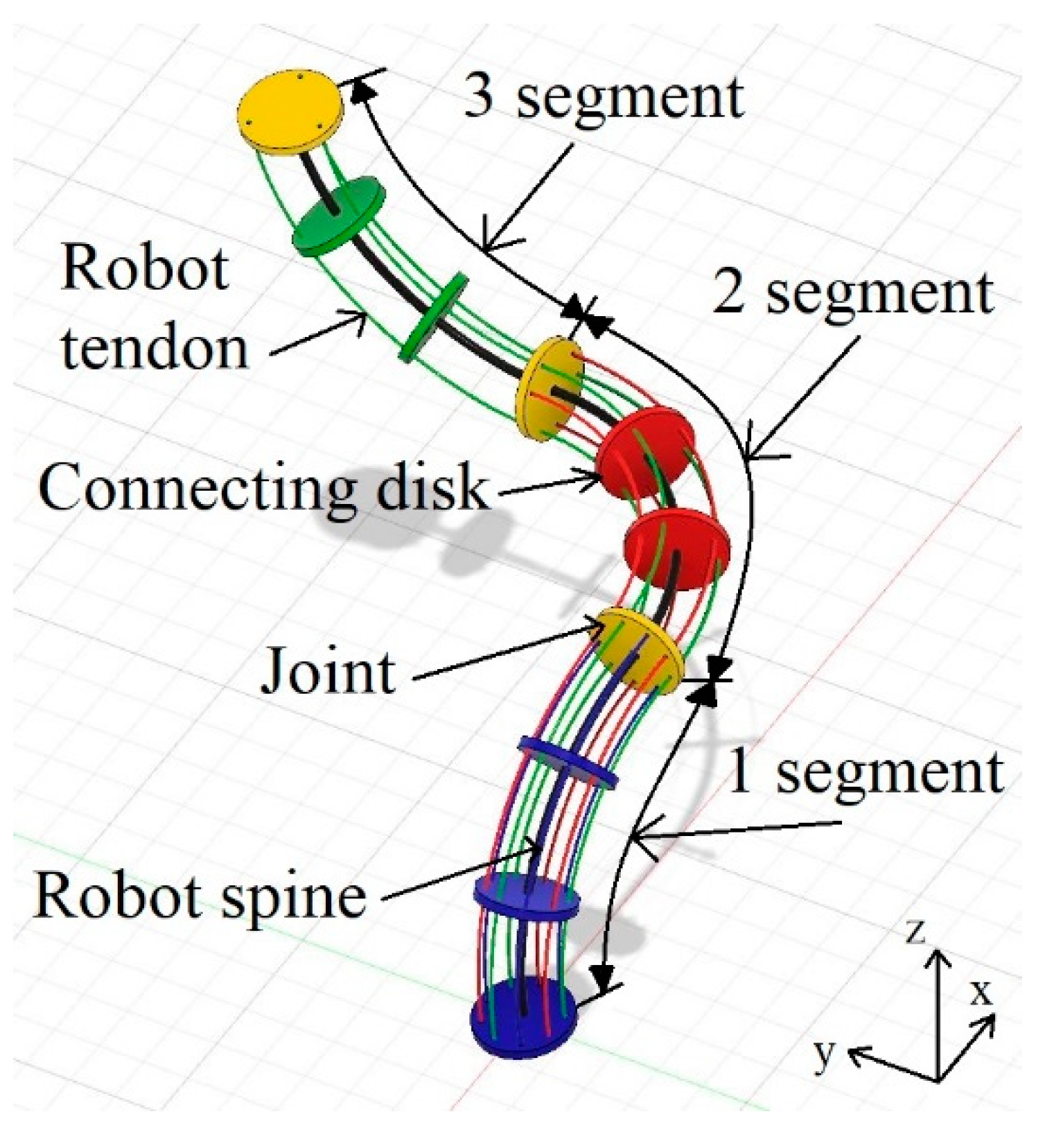
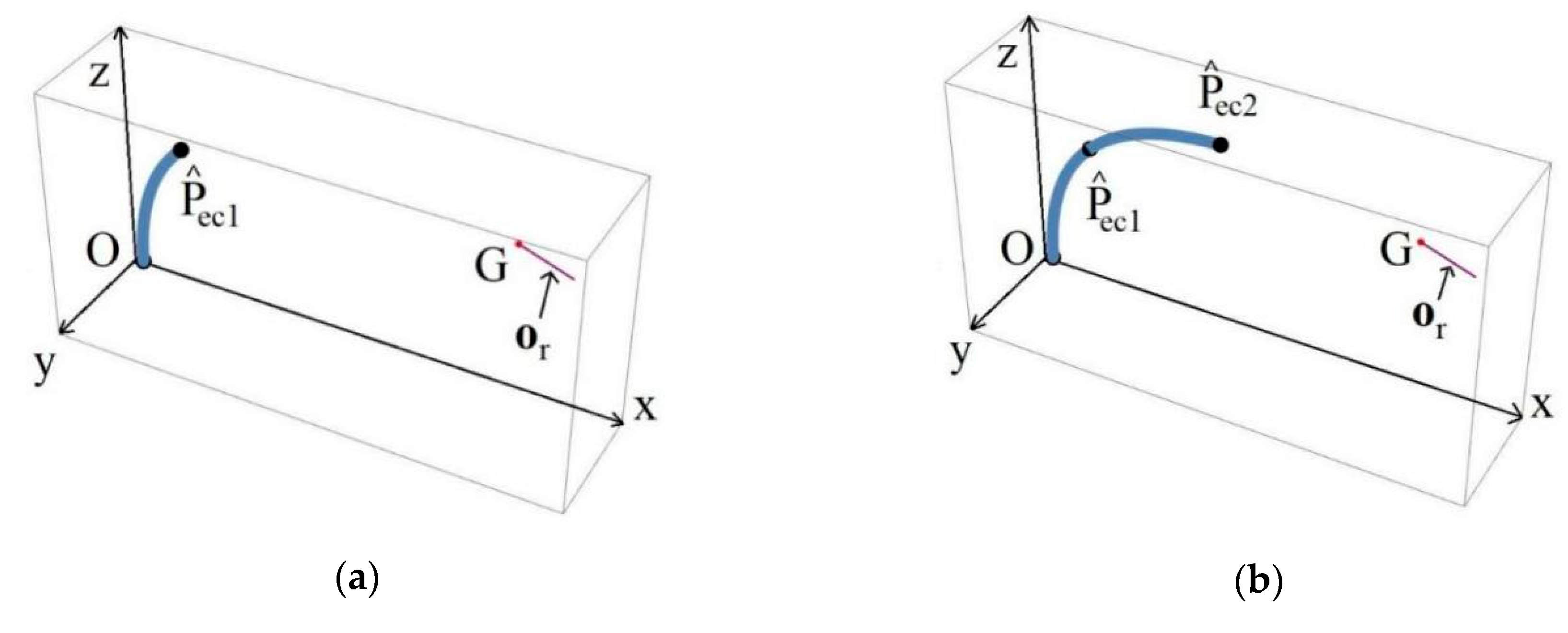
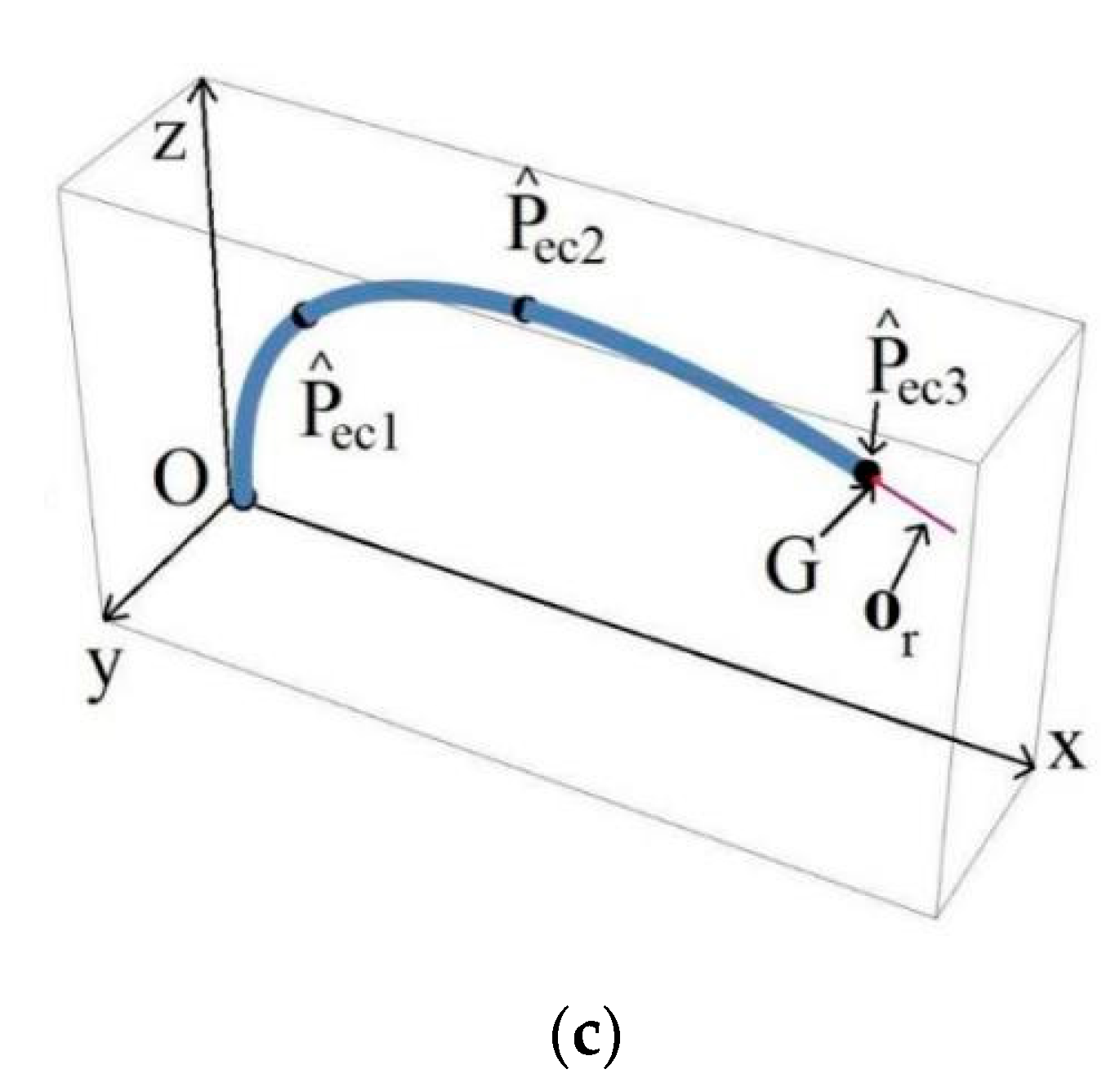
- Trunk-type robot bent spine curve approximation in the 3D Cartesian coordinate system.
- The bending angles calculation for each robot segment.
- Segments’ endpoints’ x, y, and z coordinates in the Cartesian coordinate system, and sections’ endpoint orientation computation.
- Robot metal wire (tendon) lengths’ calculation according to robot spine curvature and segments’ orientations.
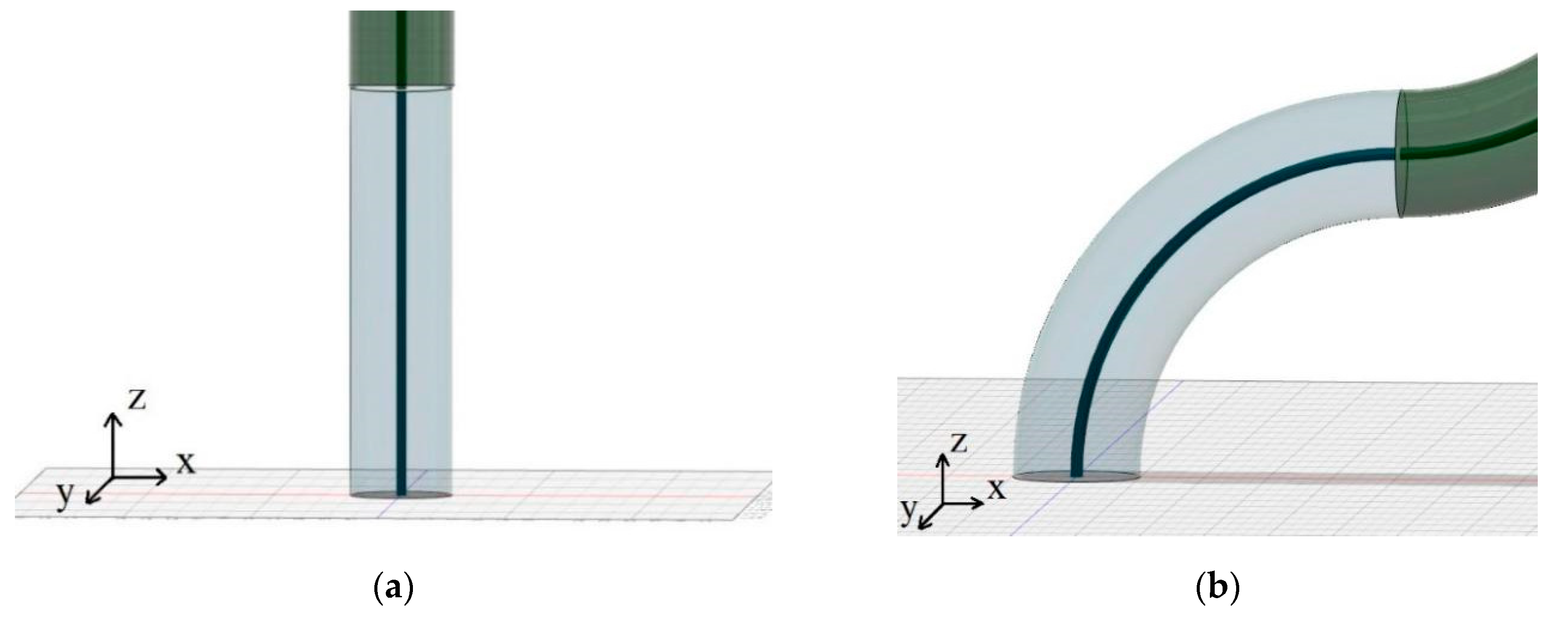
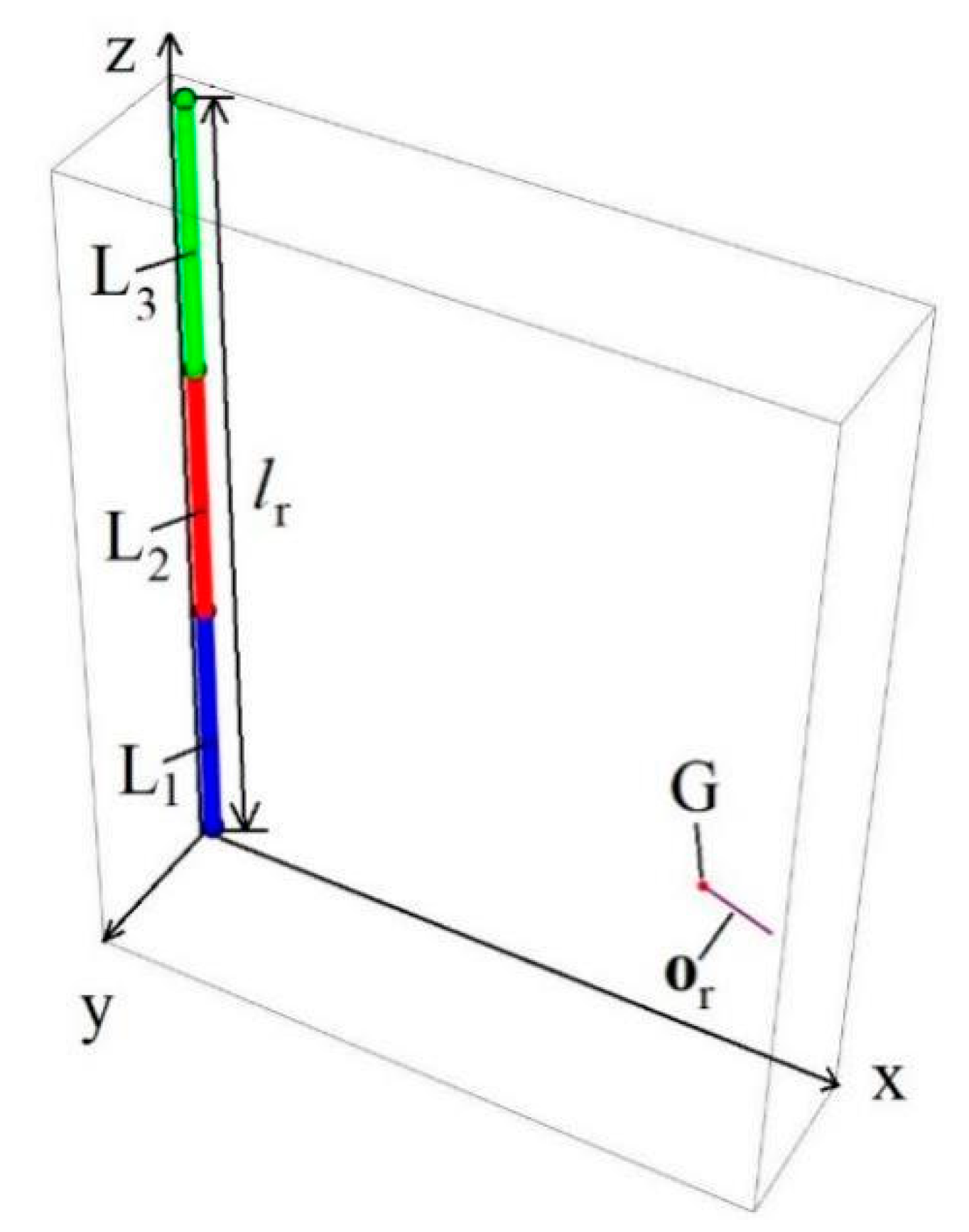
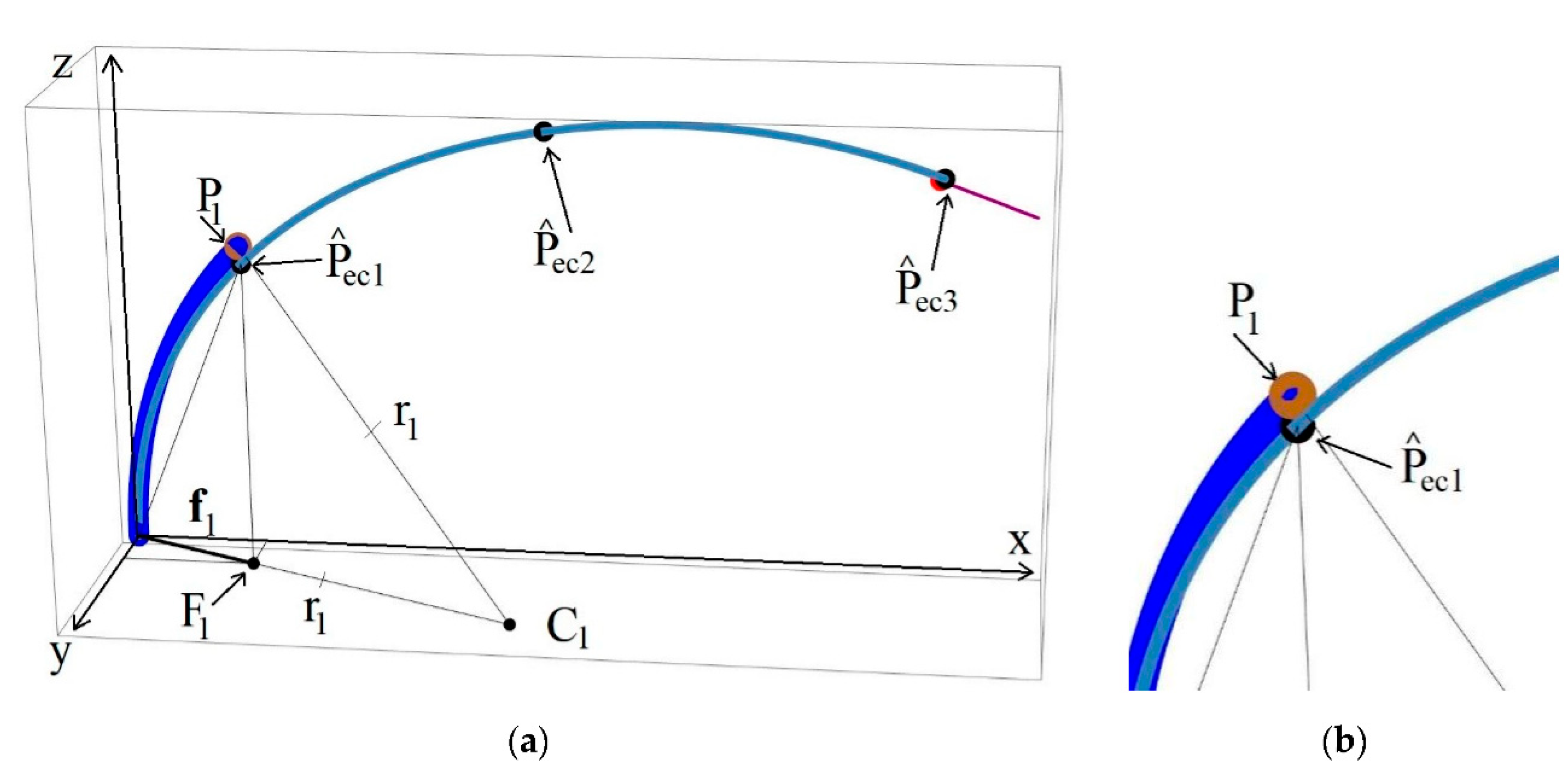
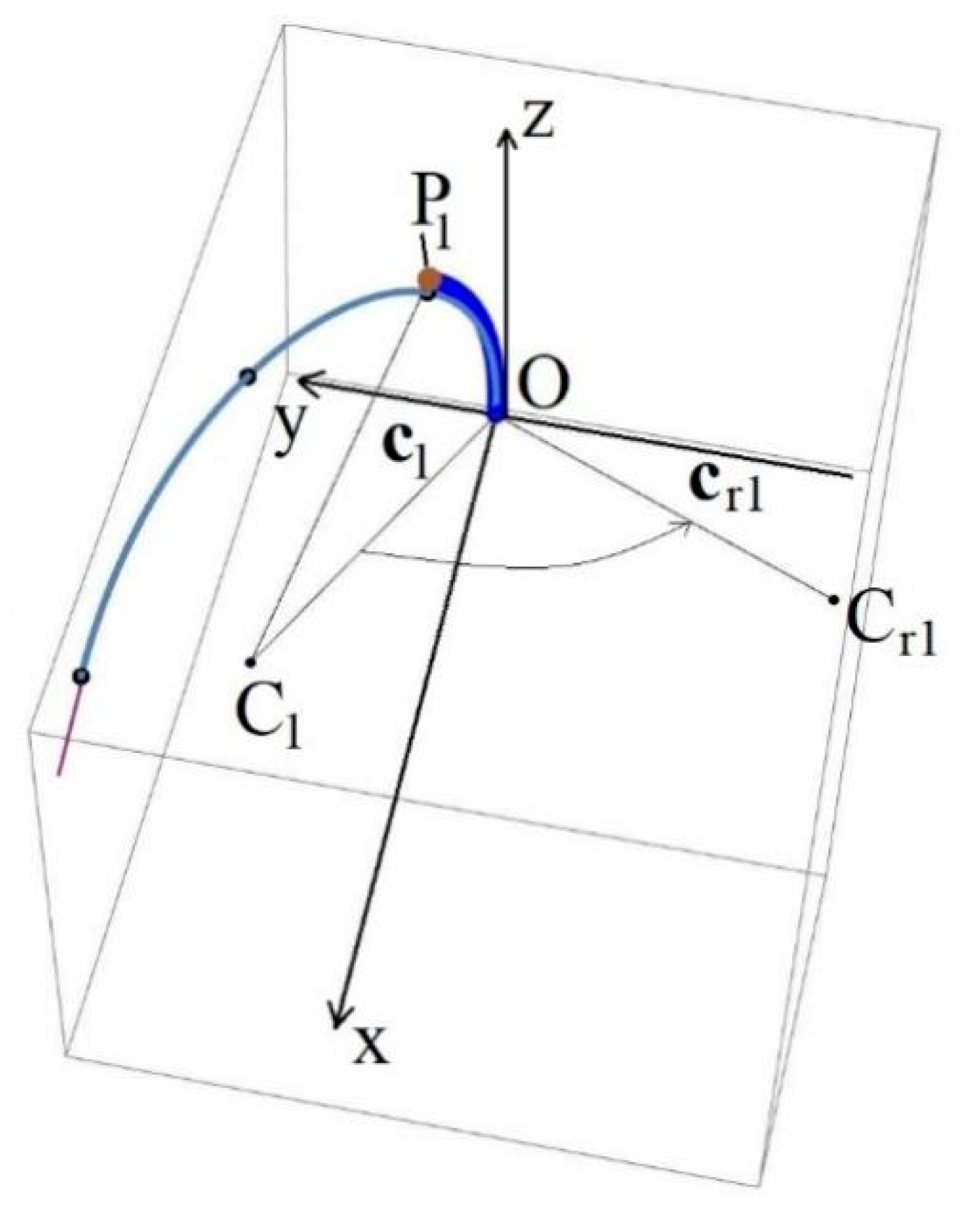
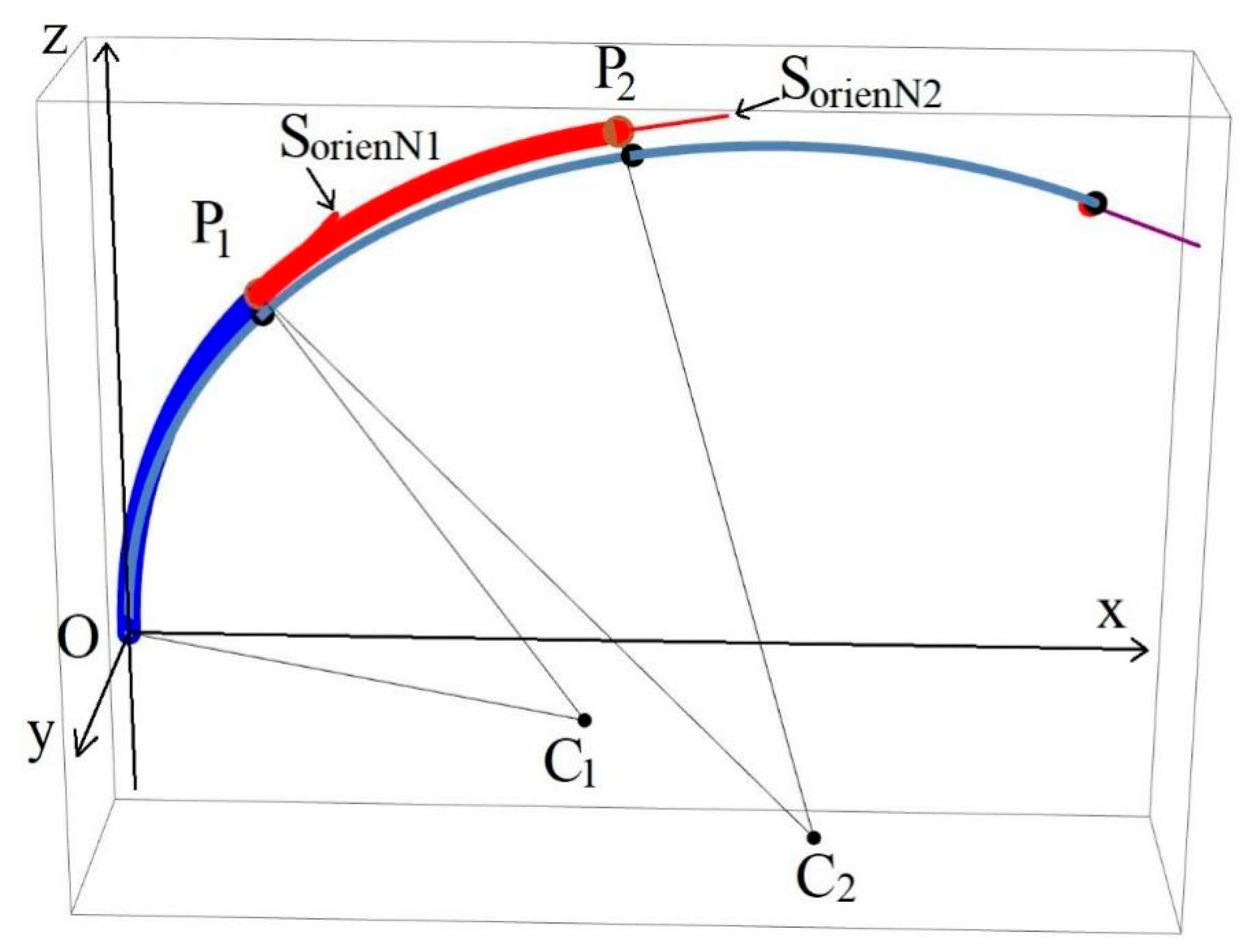
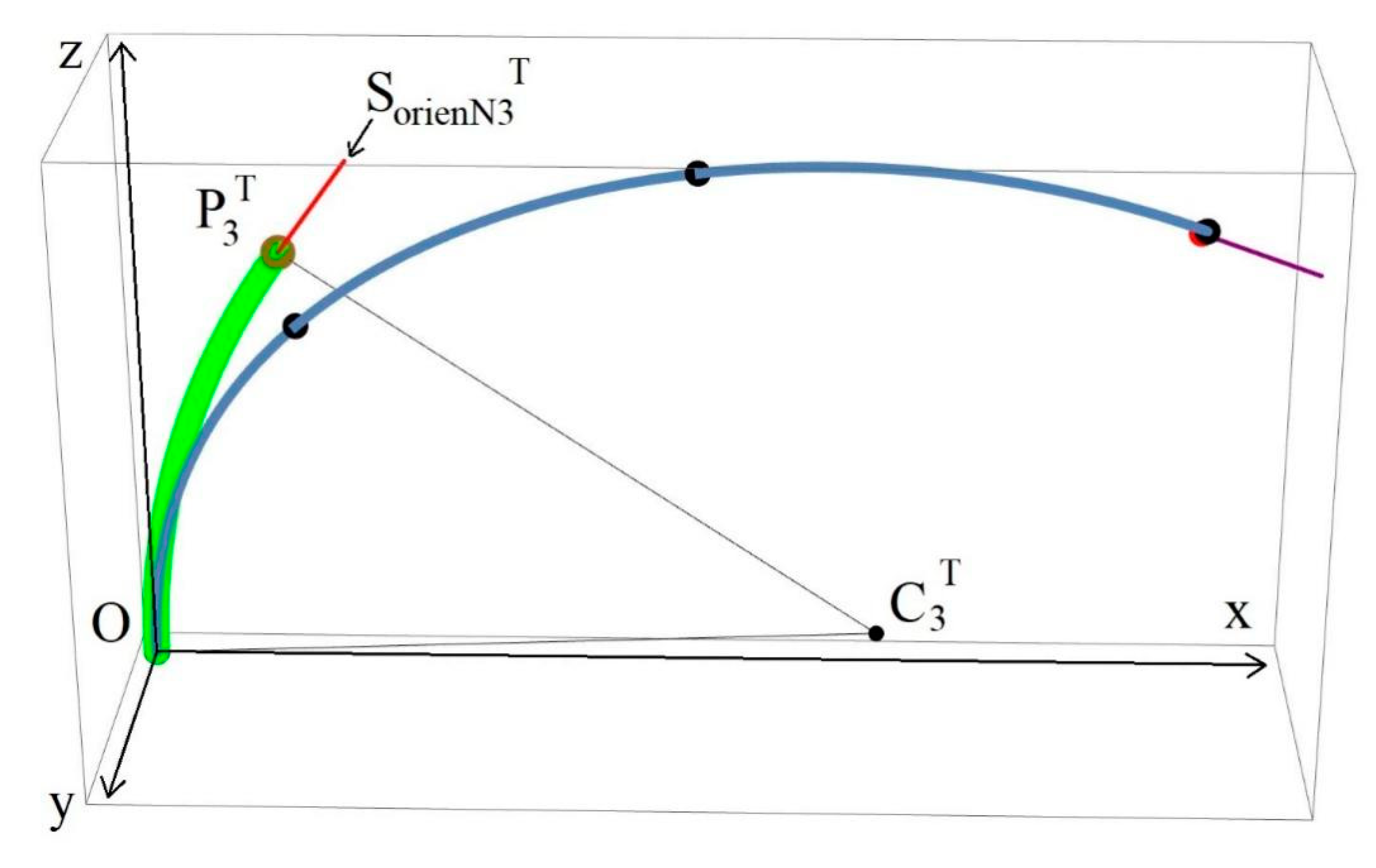
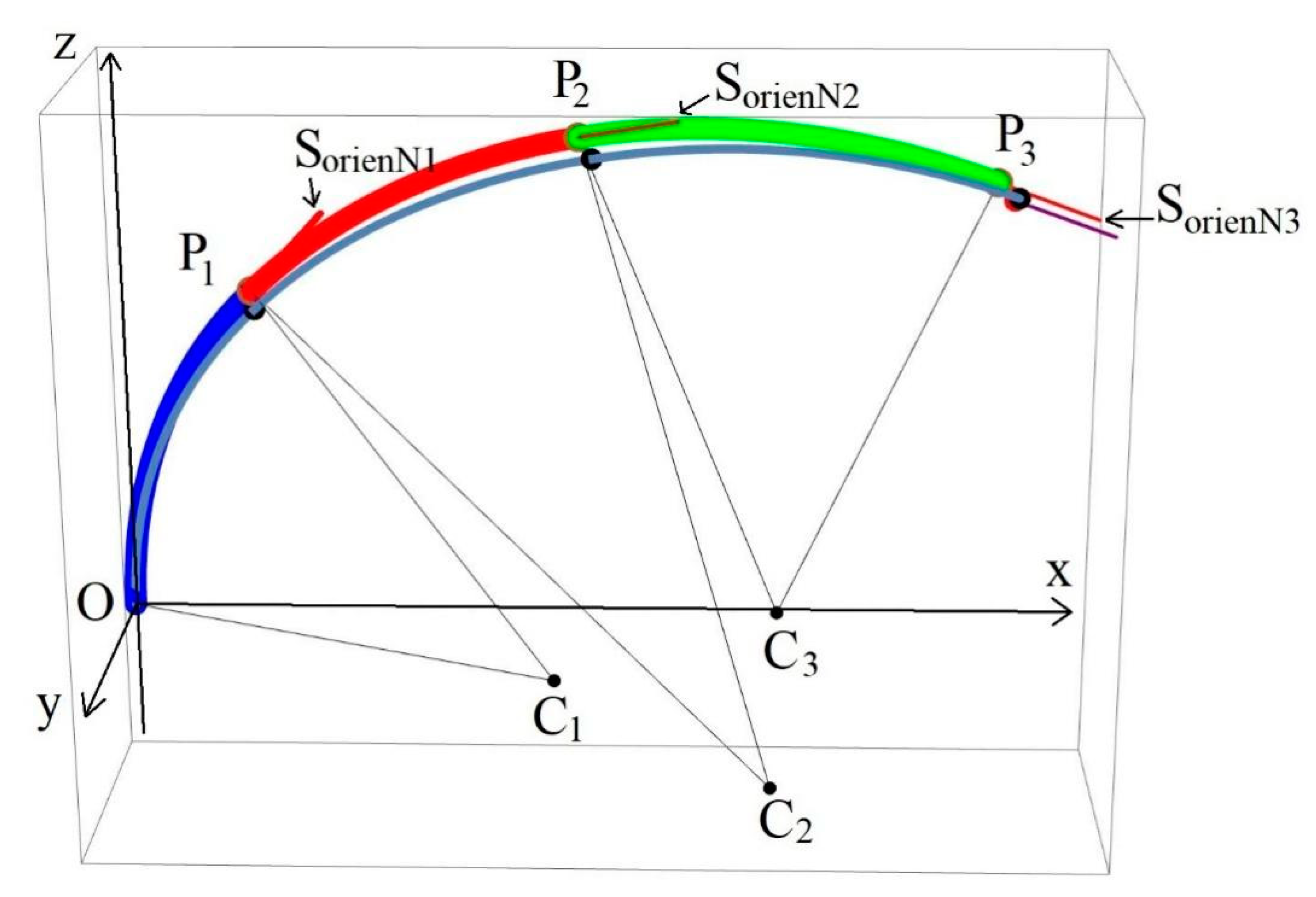
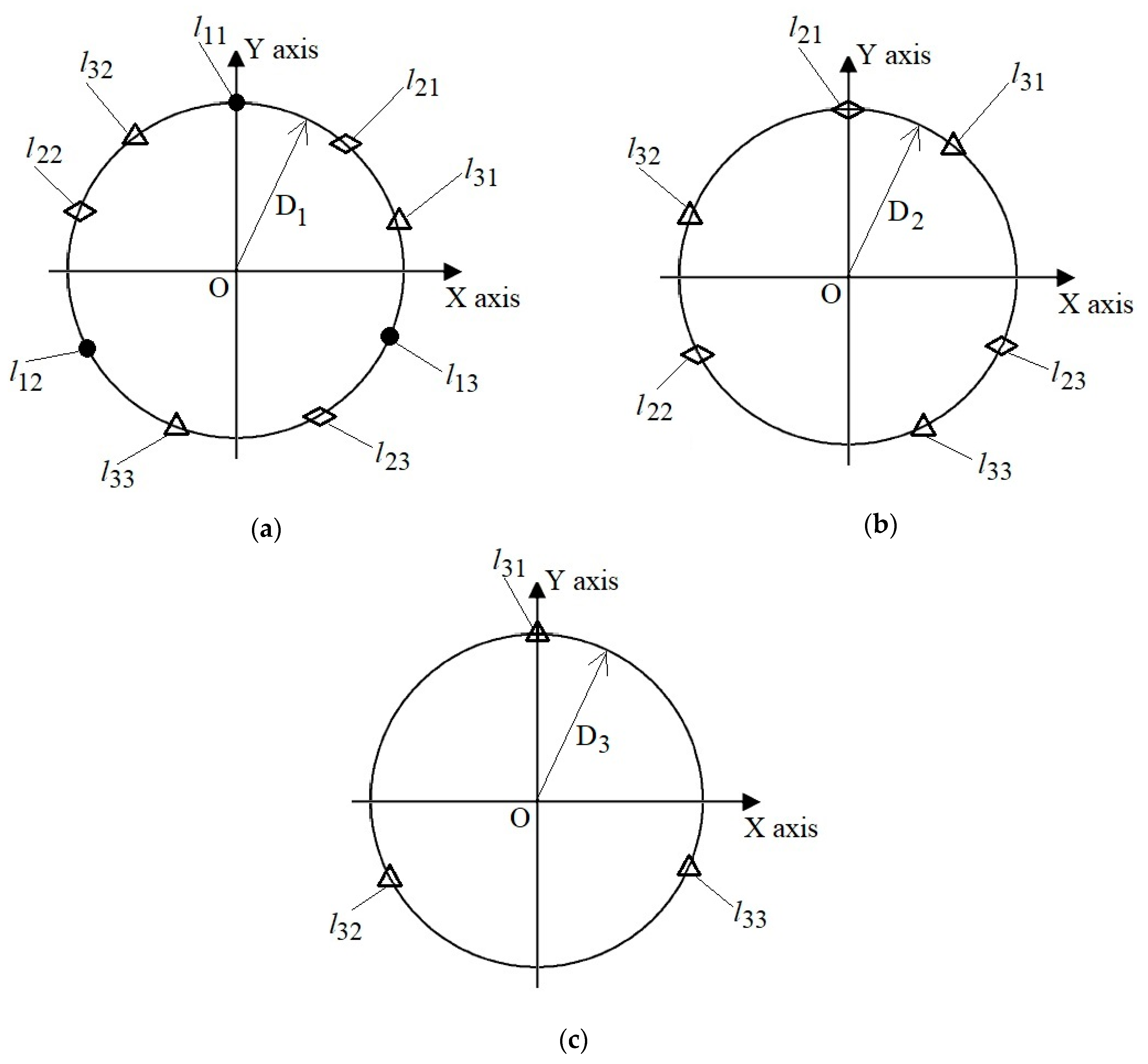
3.1. Determination of Approximate Robot Spine State Configuration
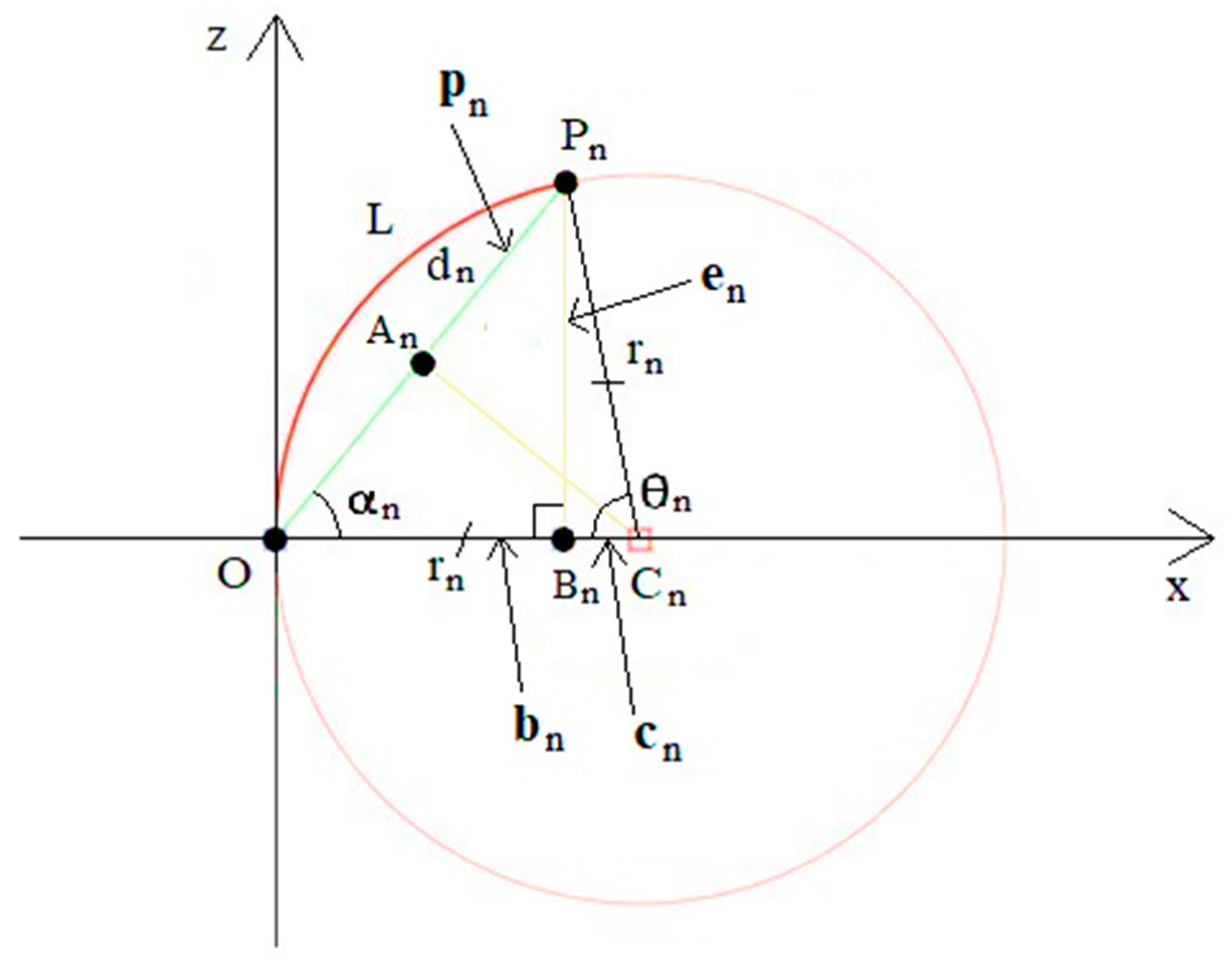
3.2. Segment’s Bending Angles Calculation
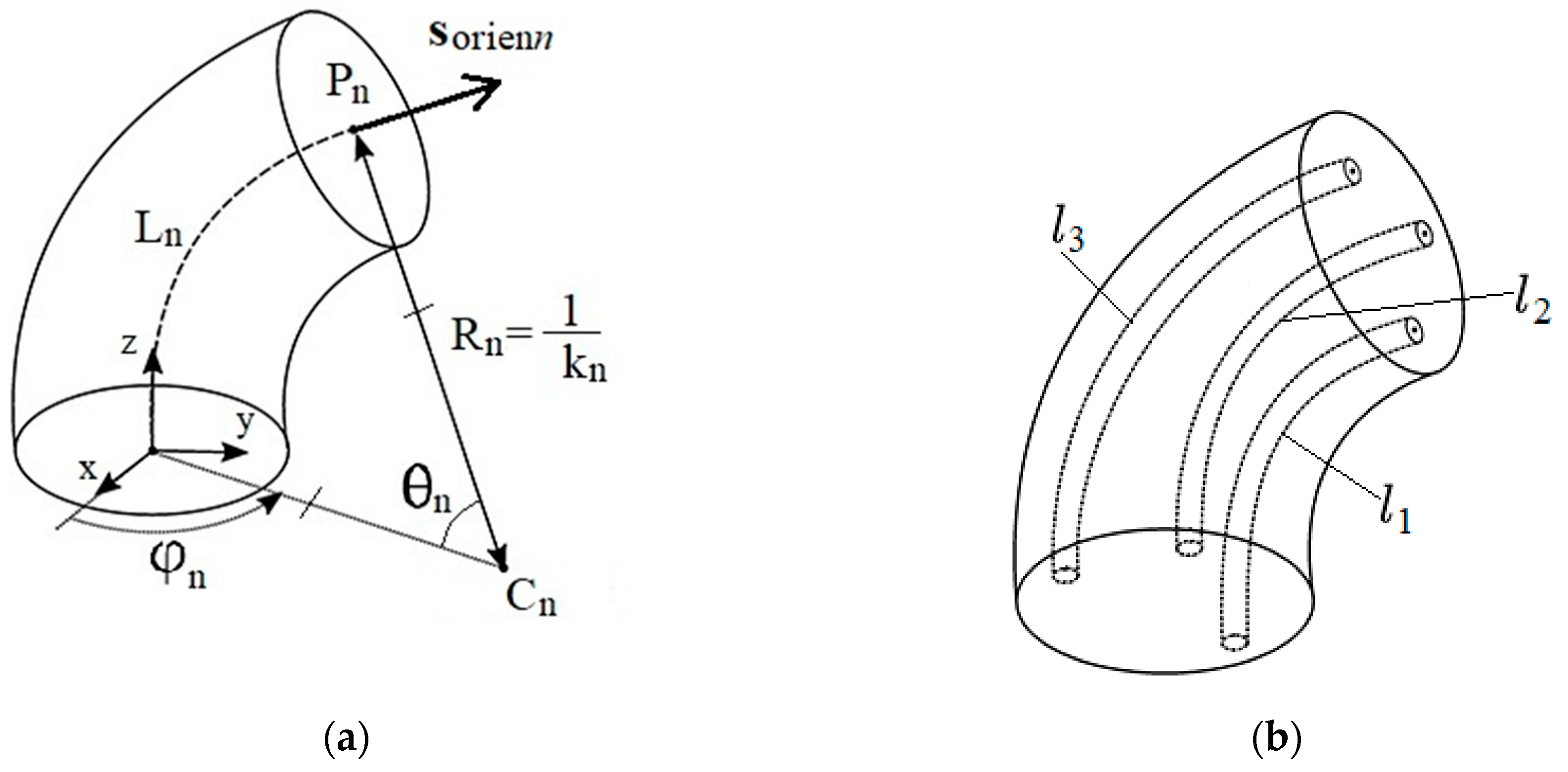
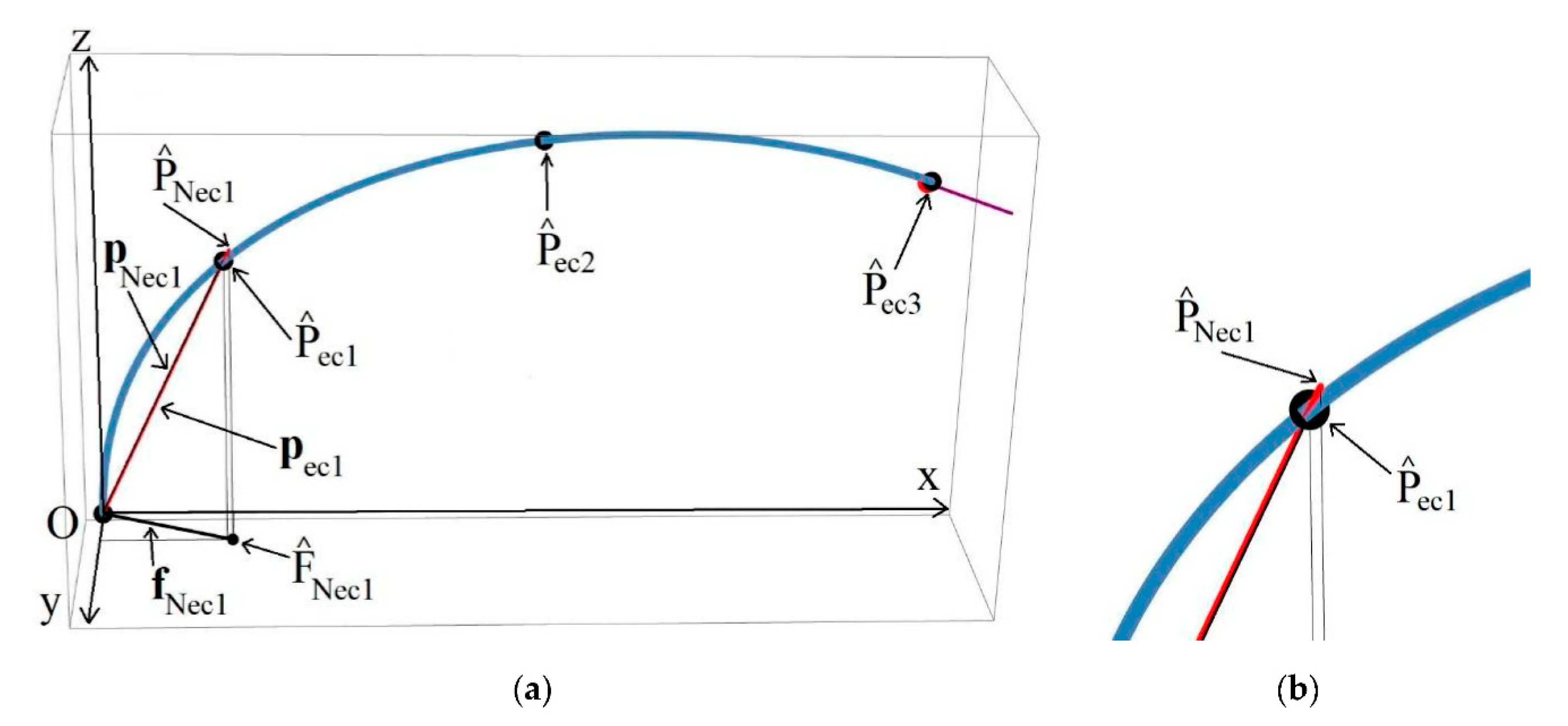
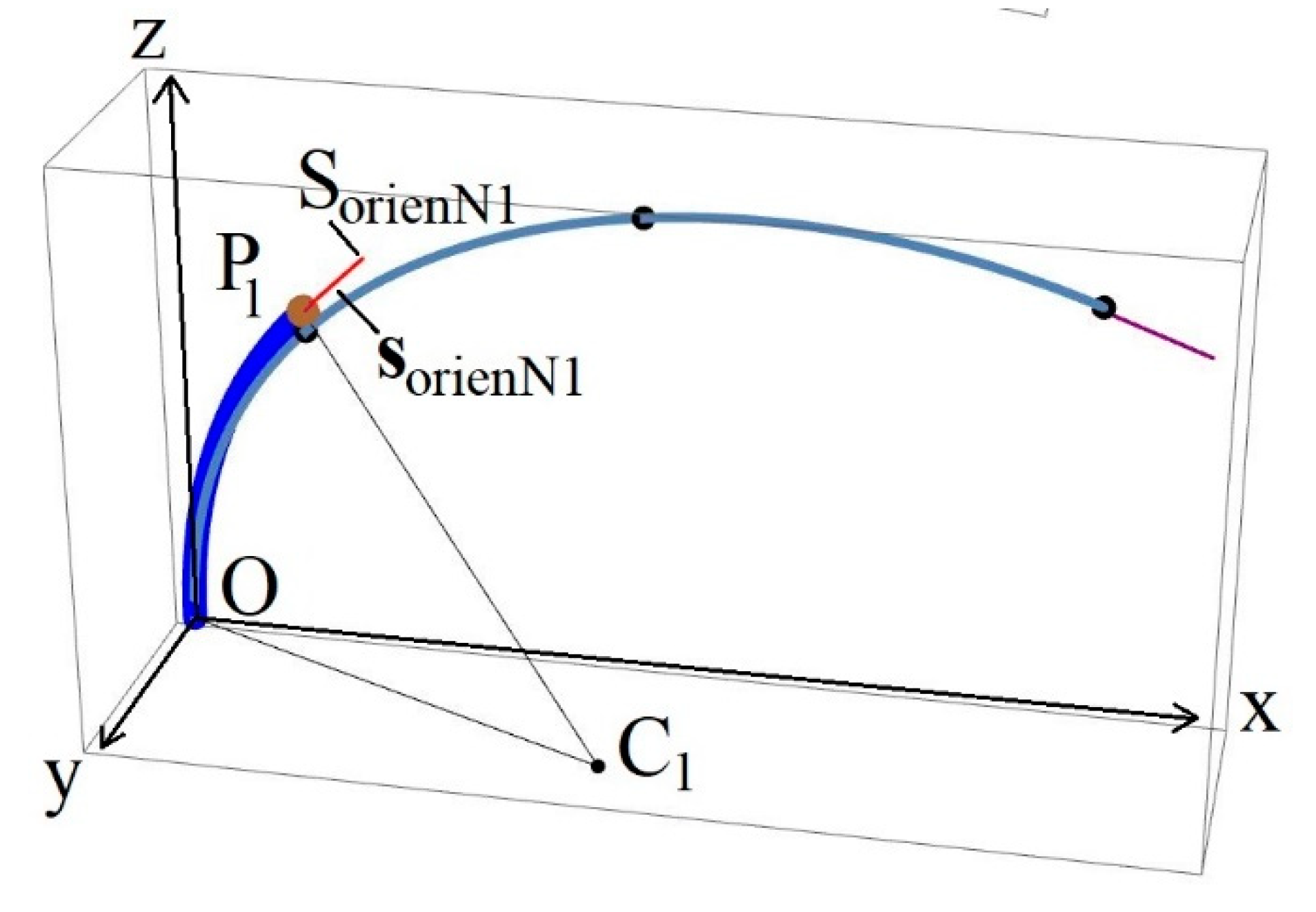
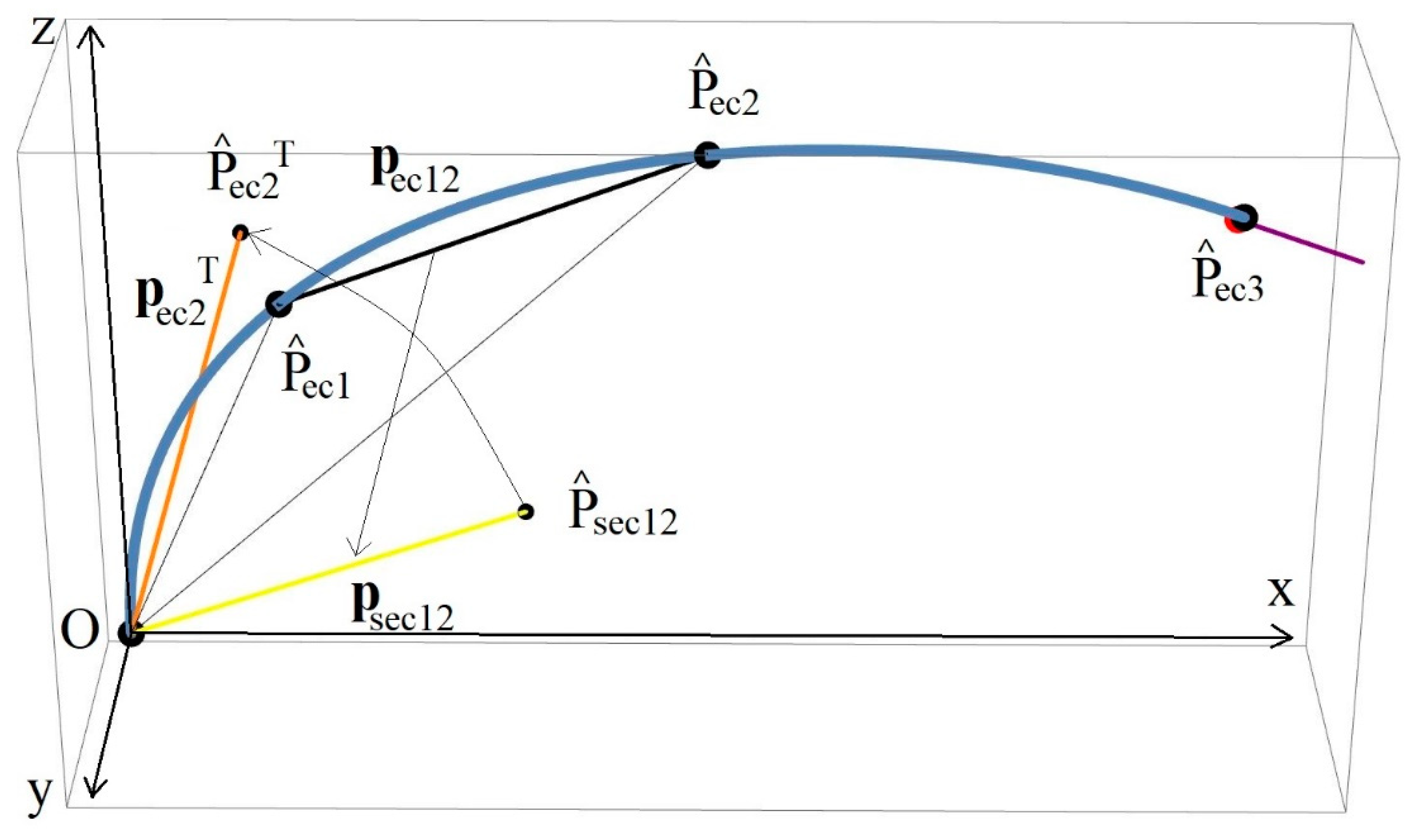
3.3. Calculation of Arc Segments’ Endpoints and Orientations
3.4. Robot Cables’ (Tendons’) Length Calculation According to the Robot Spine Curvature
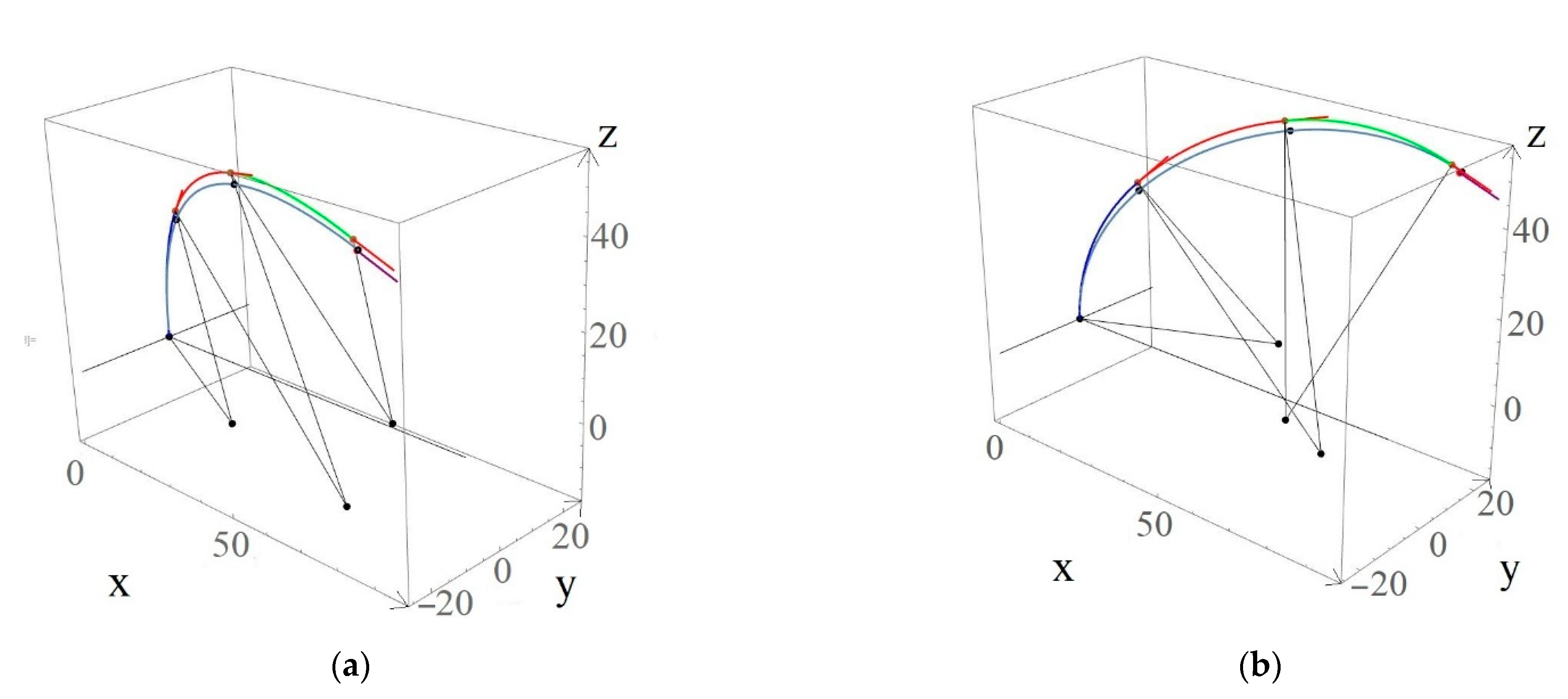
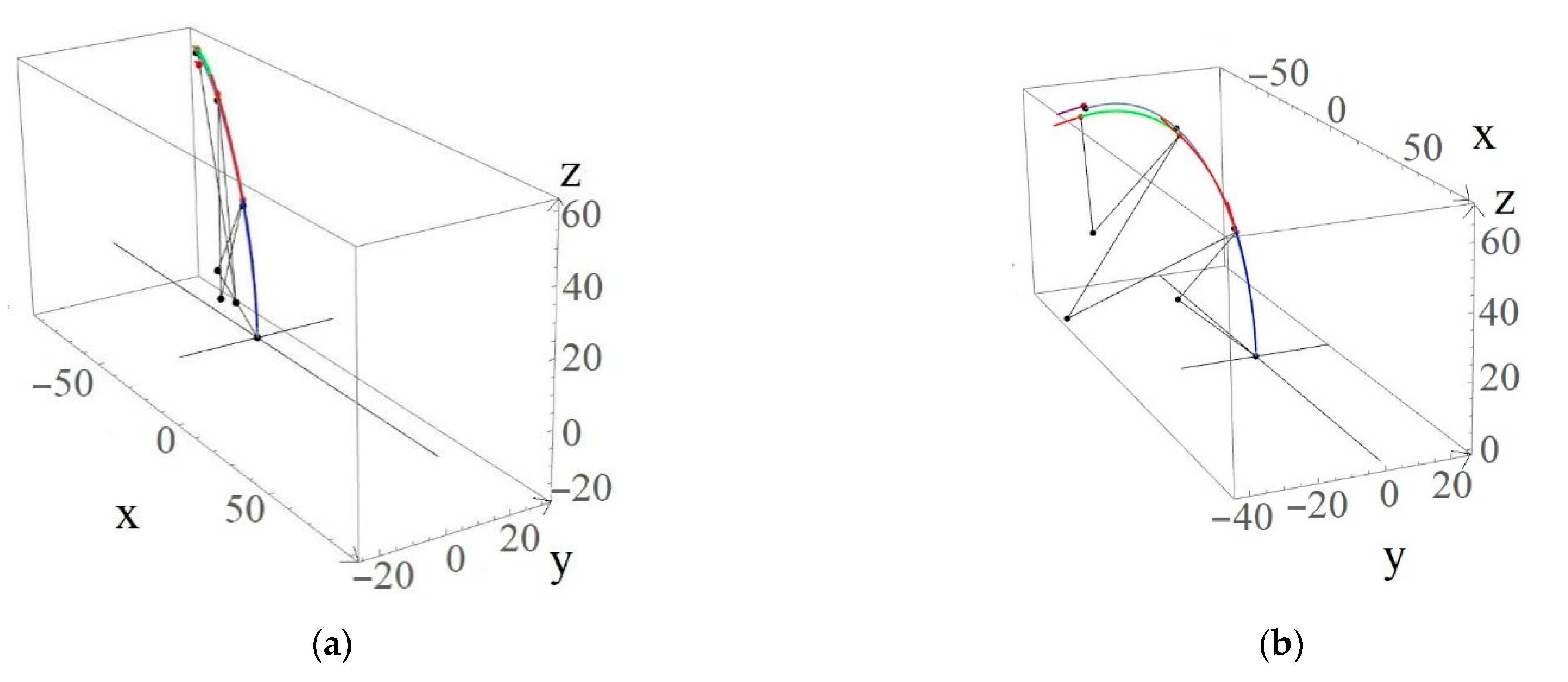
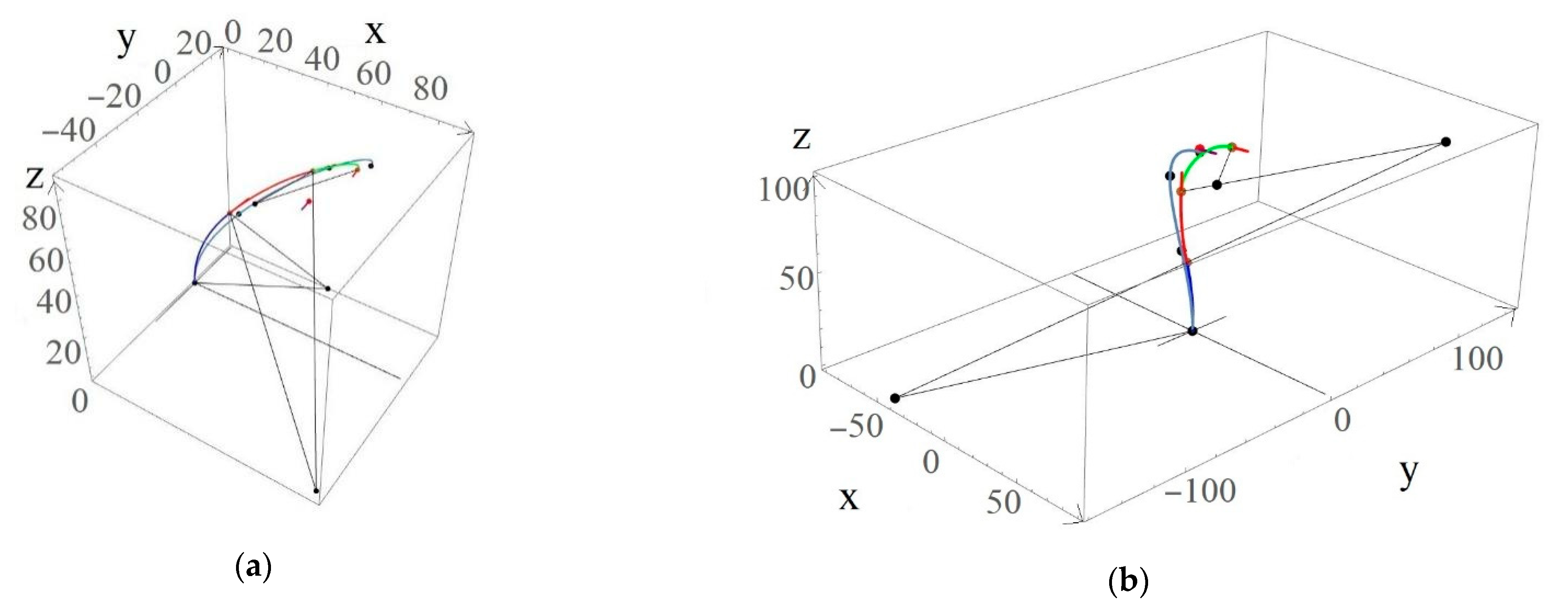
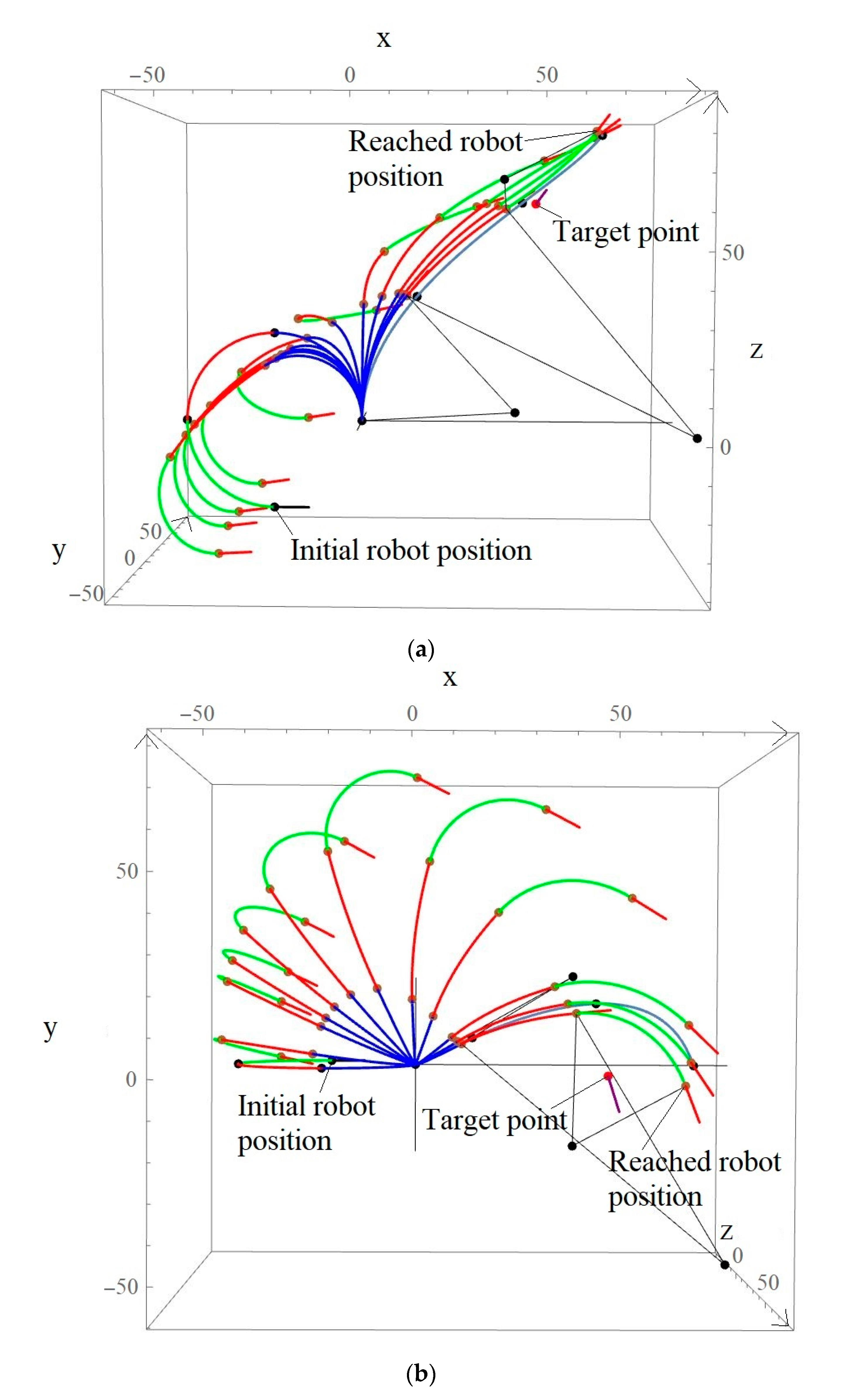
4. Robot Bending Simulation Results
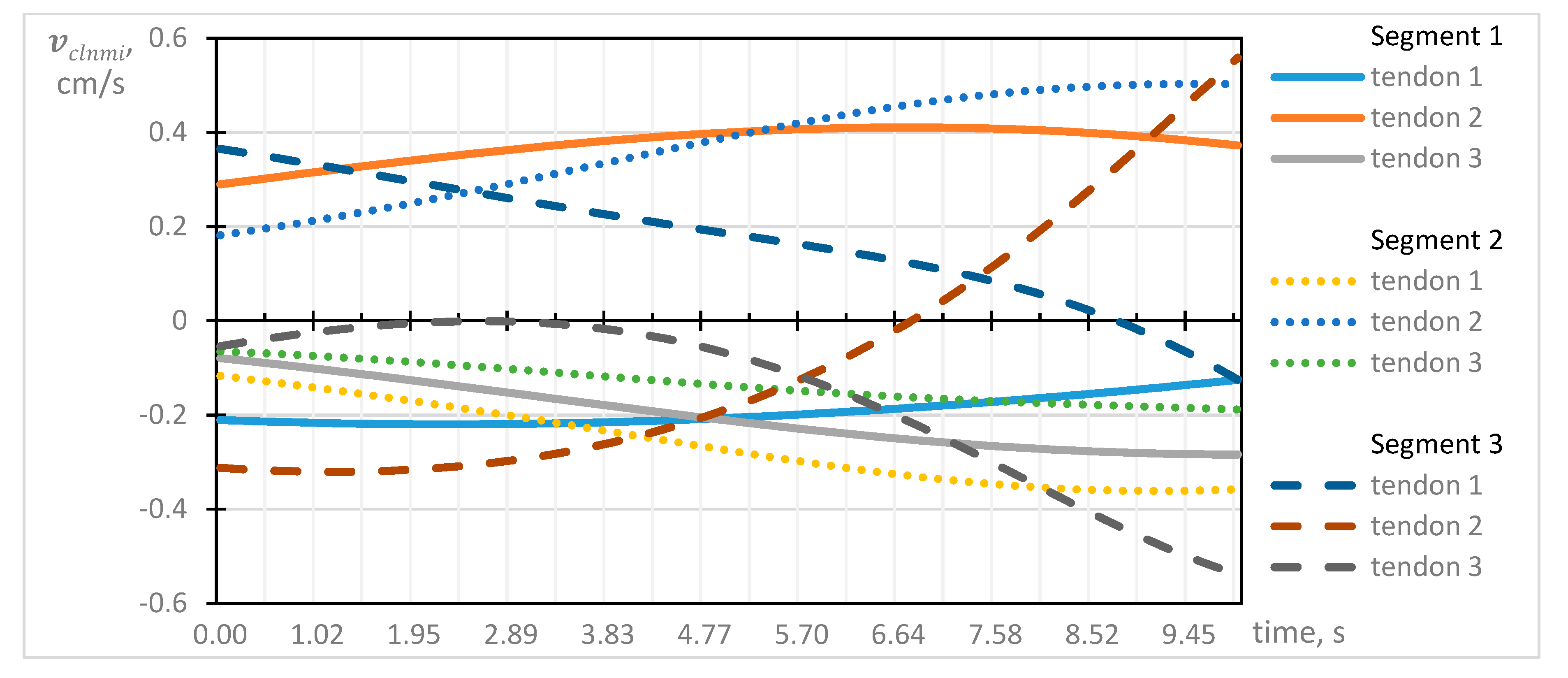
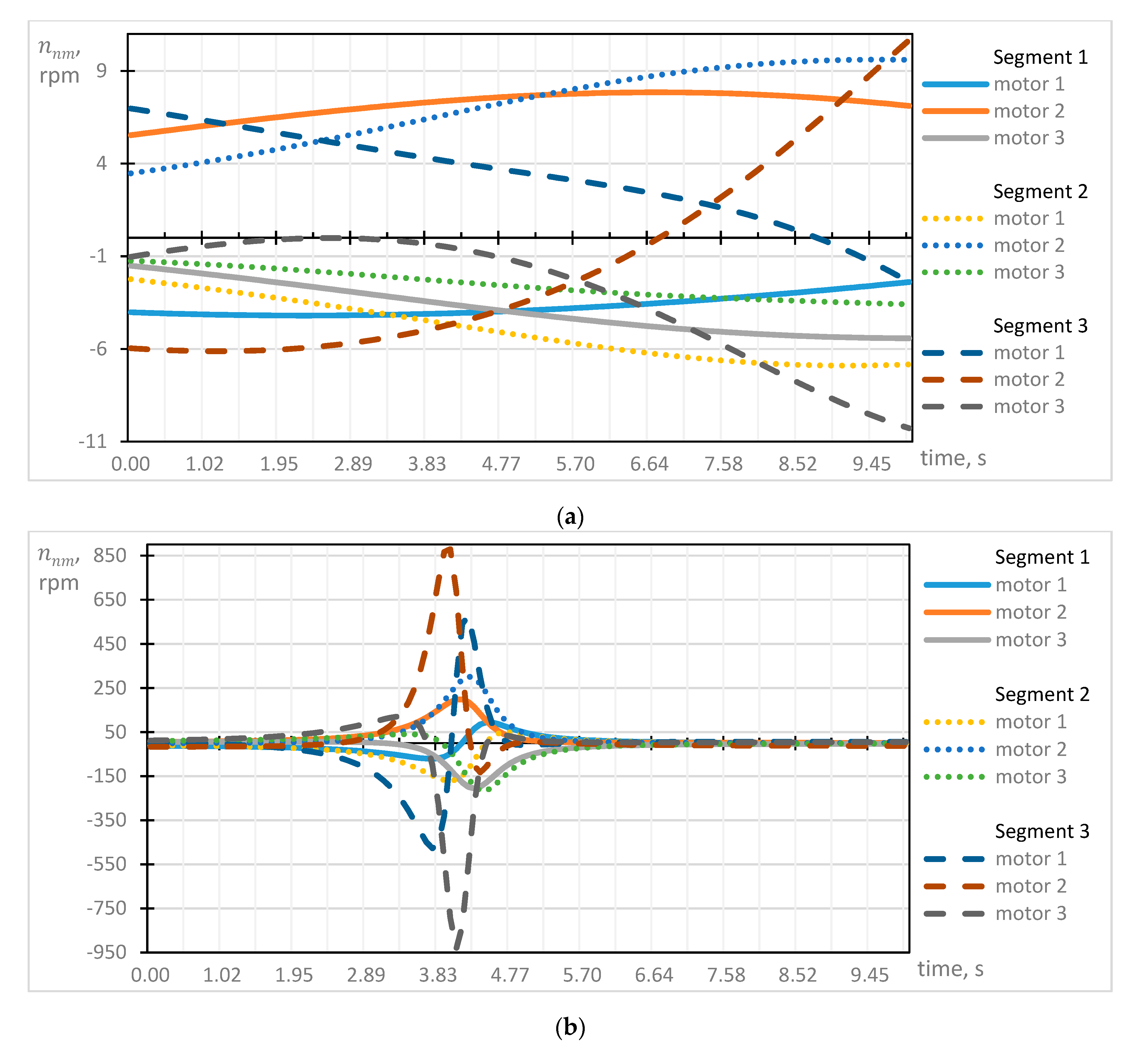
5. Electric Motor Speed Control Profiles
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Li, M.; Kang, R.; Geng, S.; Guglielmino, E. Design and Control of a Tendon-Driven Continuum Robot. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2018, 40, 3263–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppalli, S.; Jones, B.A. Design, Construction, and Analysis of a Continuum Robot. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runciman, M.; Darzi, A.; Mylonas, G.P. Soft Robotics in Minimally Invasive Surgery. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.; Ram Chauhan, N. A Review on Snake-like Continuum Robots for Medical Surgeries. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 691, 012093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, D. Design of a Three-Segment Continuum Robot for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Robot. Biomim. 2016, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piltan, F.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, J.-M. Adaptive Fuzzy-Based Fault-Tolerant Control of a Continuum Robotic System for Maxillary Sinus Surgery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.Z.; Yuan, G.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Forward and Inverse Kinematic of Continuum Robot for Search and Rescue. AMR 2013, 712–715, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, D.M. New Technologies and Emerging Spaces of Care; ROUTLEDGE: MiltonPark, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-1-138-25006-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Axinte, D.; Palmer, D.; Cobos, S.; Raffles, M.; Rabani, A.; Kell, J. Development of a Slender Continuum Robotic System for On-Wing Inspection/Repair of Gas Turbine Engines. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2017, 44, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dong, X.; Ba, W.; Mohammad, A.; Axinte, D.; Norton, A. Design, Modelling and Validation of a Novel Extra Slender Continuum Robot for In-Situ Inspection and Repair in Aeroengine. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.04572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouri, A.; Mahfoudi, C.; Zaatri, A. Dynamic Modeling of a Spatial Cable-Driven Continuum Robot Using Euler-Lagrange Method. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2020, 10, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Branson, D.T.; Dai, J.S. Design of a Pneumatic Muscle Based Continuum Robot with Embedded Tendons. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J.; Romano, J.M.; Cowan, N.J. Mechanics of Precurved-Tube Continuum Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Branson, D.T.; Zheng, T.; Guglielmino, E.; Caldwell, D.G. Design, Modeling and Control of a Pneumatically Actuated Manipulator Inspired by Biological Continuum Structures. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 036008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarillo, D.B.; Milne, C.F.; Carlson, C.R.; Zinn, M.R.; Salisbury, J.K. Mechanics Modeling of Tendon-Driven Continuum Manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, R.; Robinson, M.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Berg, D.R. Design and Preliminary Testing of a Continuum Assistive Robotic Manipulator. Robotics 2019, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J.; Jones, B.A. Design and Kinematic Modeling of Constant Curvature Continuum Robots: A Review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazelle, C.G.; Kapadia, A.; Walker, I. Developing a Kinematically Similar Master Device for Extensible Continuum Robot Manipulators. J. Mech. Robot. 2018, 10, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-D.; Burgner-Kahrs, J. A Tendon-Driven Continuum Robot with Extensible Sections. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshmukhametov, A.; Koganezawa, K.; Yamamoto, Y. A Novel Discrete Wire-Driven Continuum Robot Arm with Passive Sliding Disc: Design, Kinematics and Passive Tension Control. Robotics 2019, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgilas, I.; Tourassis, V. From the Human Spine to Hyperredundant Robots: The ERMIS Mechanism. ISRN Robot. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffin, A.; Urniezius, R. The Kalman Filter Revisited Using Maximum Relative Entropy. Entropy 2014, 16, 1047–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffin, A.; Urniezius, R. Simultaneous State and Parameter Estimation Using Maximum Relative Entropy with Nonhomogenous Differential Equation Constraints. Entropy 2014, 16, 4974–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urniežius, R.; Mohammad-Djafari, A.; Bercher, J.-F.; Bessiére, P. Online Robot Dead Reckoning Localization Using Maximum Relative Entropy Optimization with Model Constraints; American Institute of Physics: Chamonix, France, 2011; pp. 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A. An O(n) -Algorithm for the Higher-Order Kinematics and Inverse Dynamics of Serial Manipulators Using Spatial Representation of Twists. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins-Valls, D.; Xu, J.; Waytowich, N.; Allen, P. Learning Your Way Without Map or Compass: Panoramic Target Driven Visual Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 5816–5823. [Google Scholar]
- Norberto Pires, J. Industrial Robots Programming; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-23325-3. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Yang, S.; Walker, I.D.; Ju, Z. Elephant’s Trunk Robot: An Extremely Versatile Under-Actuated Continuum Robot Driven by a Single Motor. J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 11, 051008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X. A Hyper-Redundant Elephant’s Trunk Robot with an Open Structure: Design, Kinematics, Control and Prototype. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 33, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G. Motion Planning and Control for Endoscopic Operations of Continuum Manipulators. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2019, 12, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, J.; Han, S. Kinematic Model and Real-Time Path Generator for a Wire-Driven Surgical Robot Arm with Articulated Joint Structure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustaitis, A.; Jurėnas, V. Dynamics of Trunk Type Robot with Spherical Piezoelectric Actuators. IJRA 2020, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.A.; Walker, I.D. Kinematics for Multisection Continuum Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga-Casanovas, A.; Rodriguez y Baena, F. Kinematics of Continuum Robots with Constant Curvature Bending and Extension Capabilities. J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 11, 011010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppalli, S.; Csencsits, M.A.; Jones, B.A.; Walker, I. A Geometrical Approach to Inverse Kinematics for Continuum Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 3565–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wagner, J.; Frazelle, C.G.; Walker, I.D. Continuum Robot Control Based on Virtual Discrete-Jointed Robot Models. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Abbena, E.; Salamon, S. Modern Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces with Mathematica, 3rd ed.; Studies in advanced mathematics; Chapman & Hall CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-1-58488-448-4. [Google Scholar]
- Urniezius, R.; Giffin, A. Iteration Free Vector Orientation Using Maximum Relative Entropy with Observational Priors. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1443, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Lee, T.; Sklar, D. Precalculus: A Problems-Oriented Approach, 6th ed.; Thomson-Brooks/Cole: Belmont, CA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-534-40212-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lipschutz, S.; Spiegel, M.R.; Lipschutz, S.; Spellman, D. Vector Analysis and an Introduction to Tensor Analysis, 2nd ed.; Schaum’s outline series; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-07-161545-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhao, B.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, P.; Meng, M.Q.-H. Hybrid Adaptive Control Strategy for Continuum Surgical Robot Under External Load. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, K.; Urniezius, R. Research and Development of a Gesture-Controlled Robot Manipulator System. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), Baden-Baden, Germany, 19–21 September 2016; pp. 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

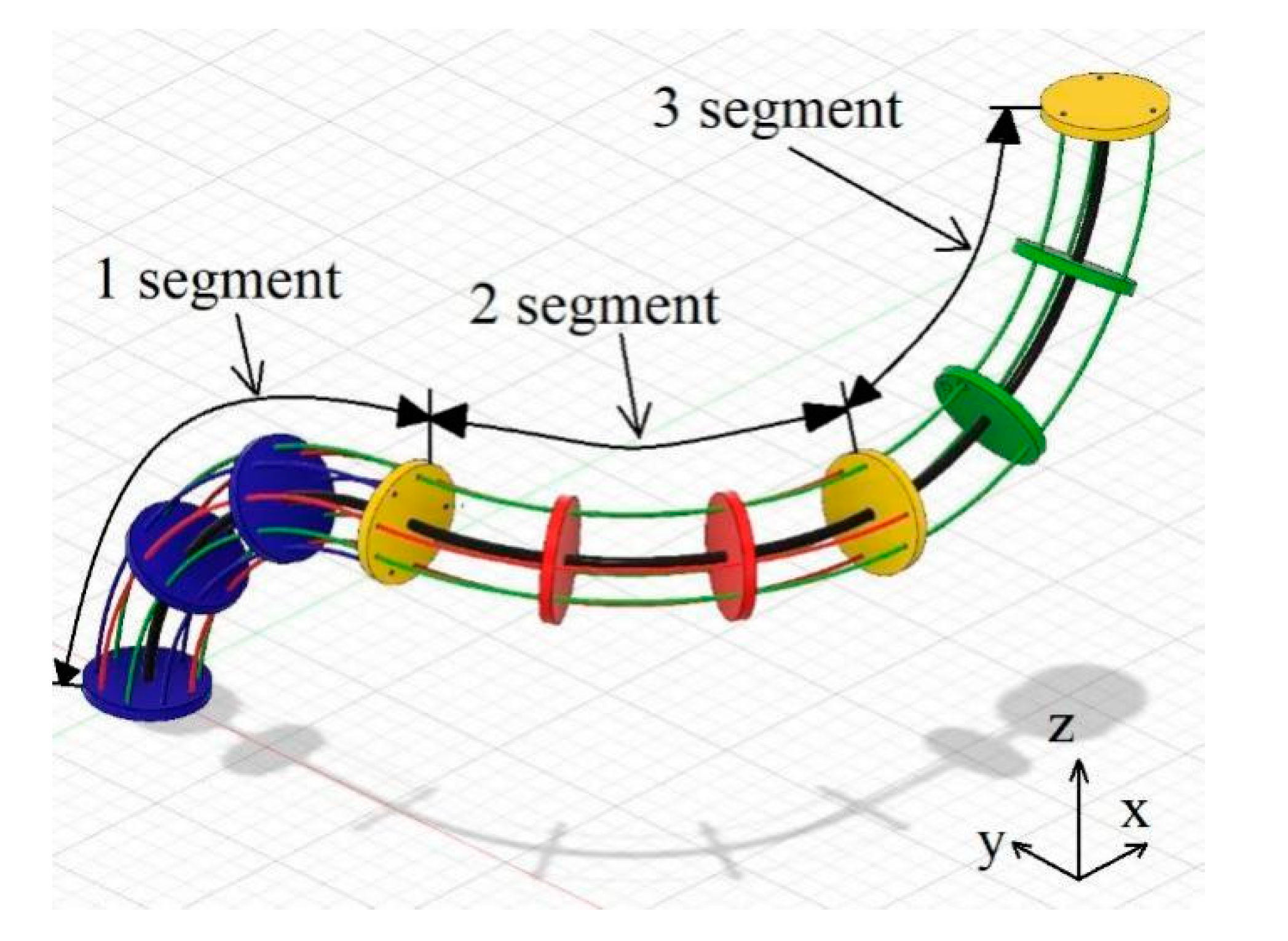
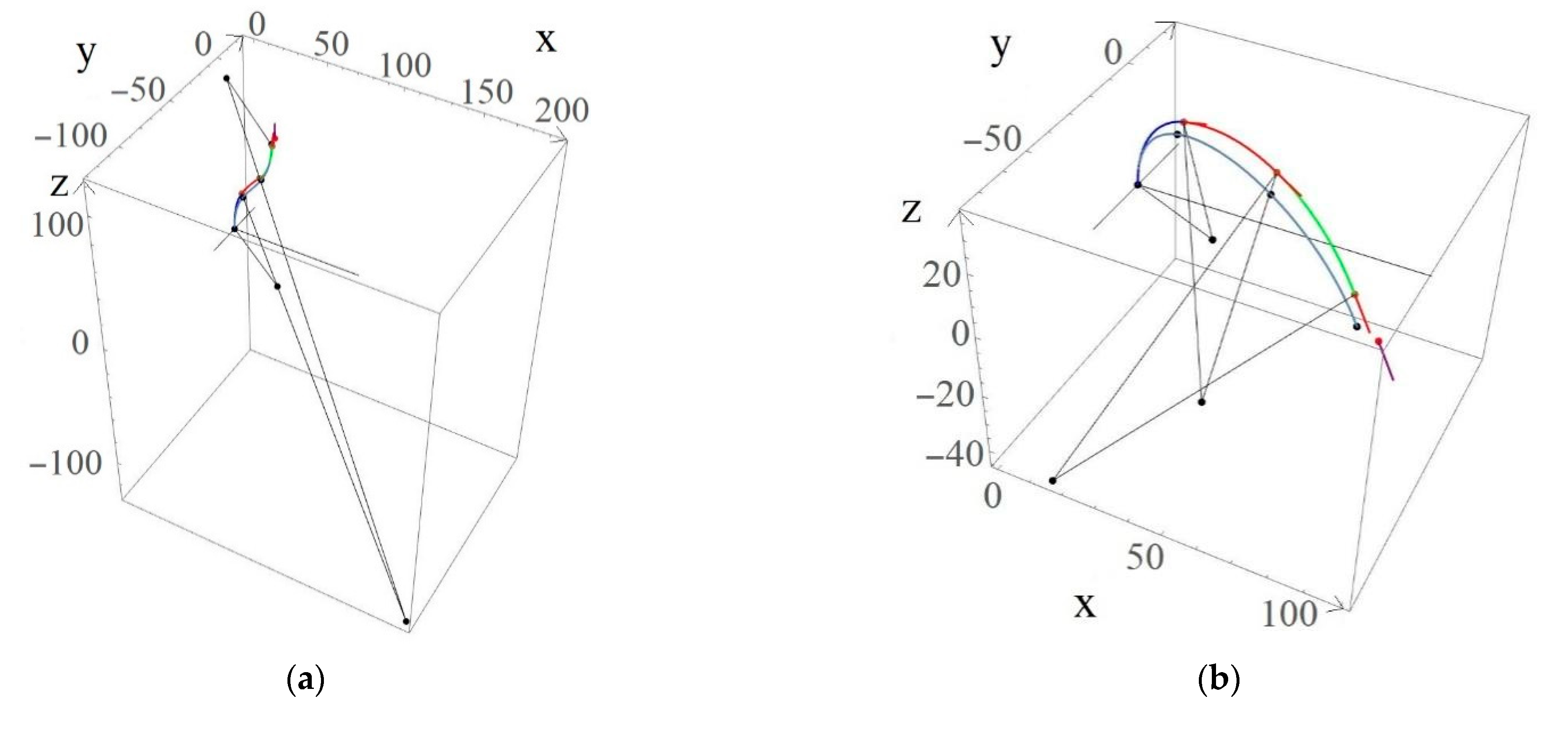
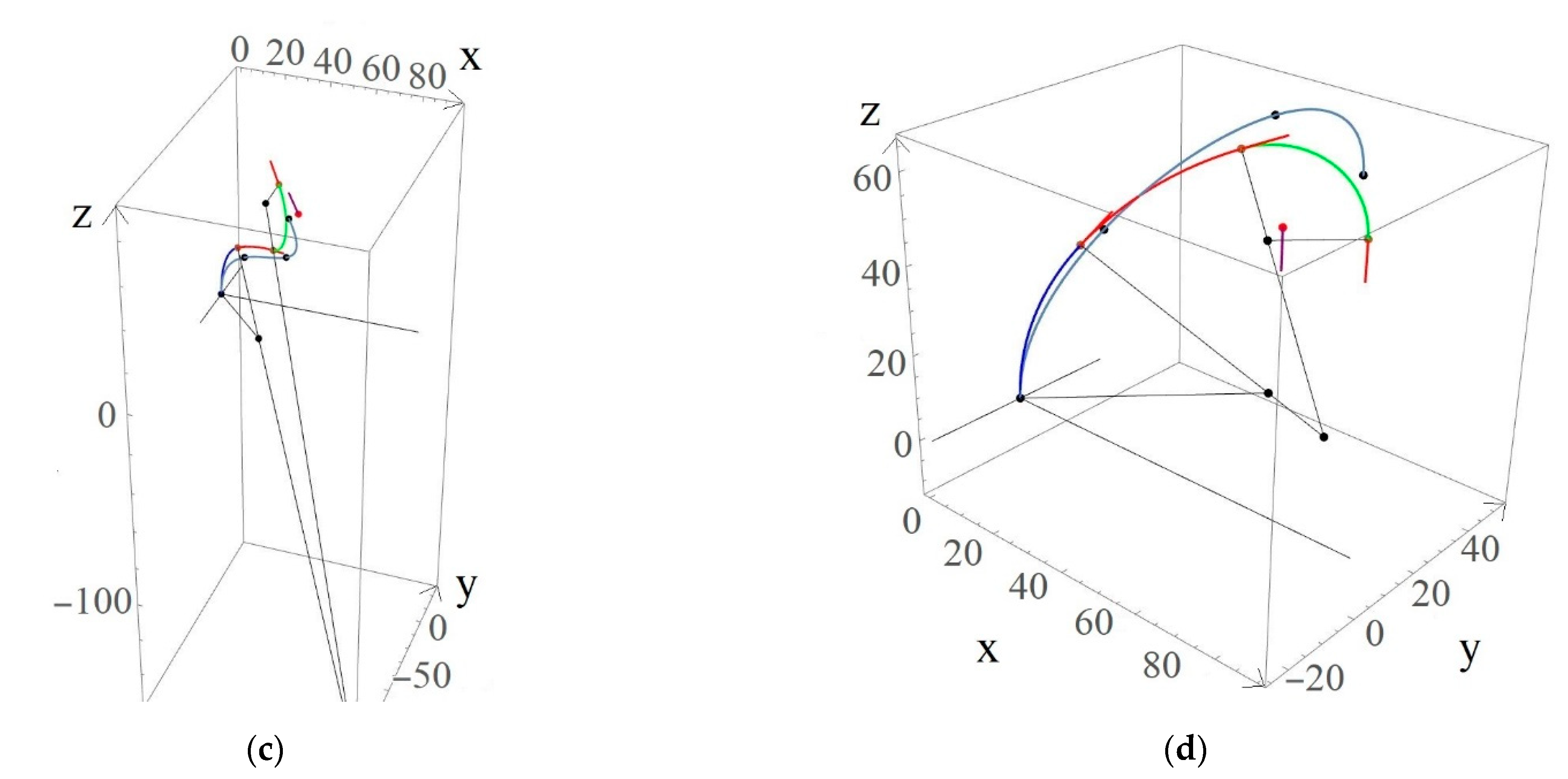
| Specification | Segment 1 | Segment 2 | Segment 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| (cm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
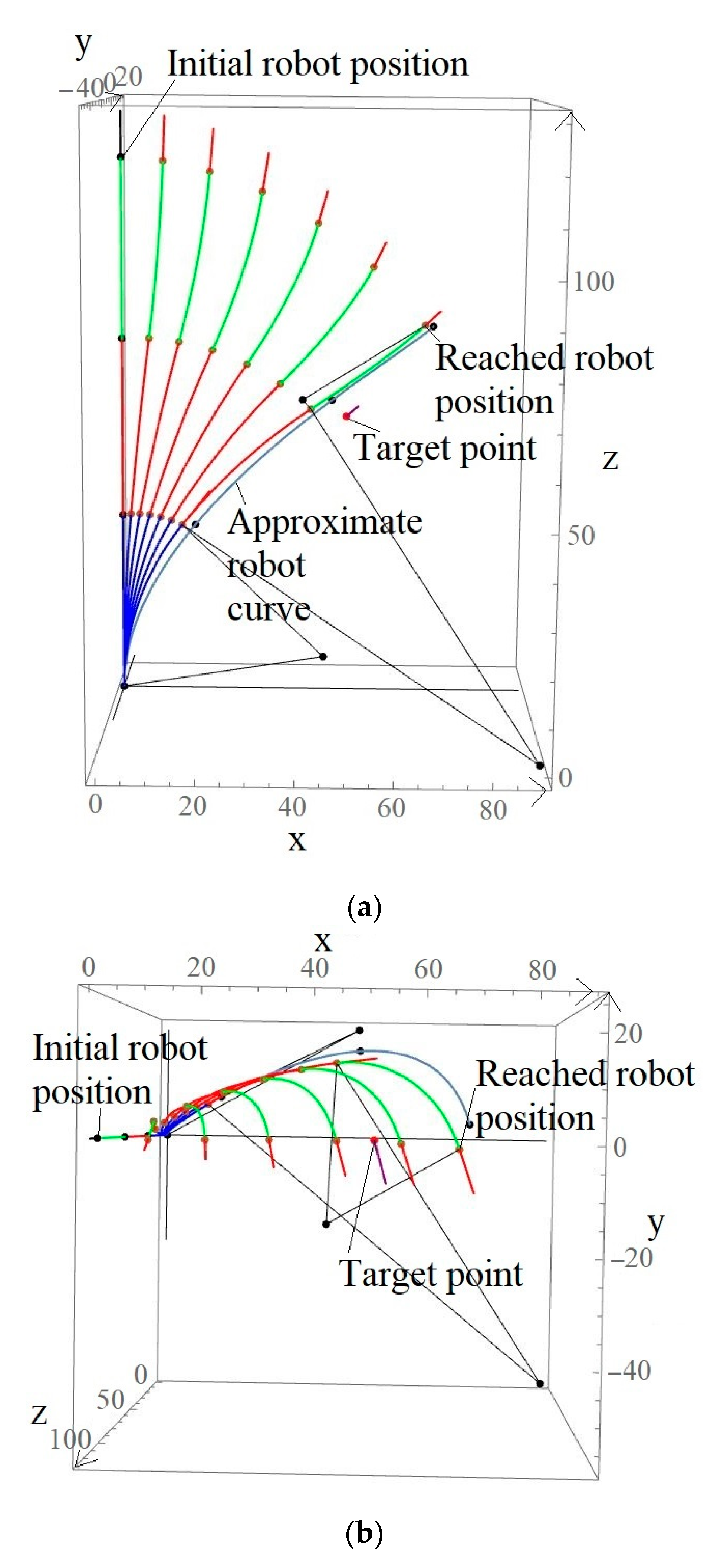
| Simulation No | Target Point | Reached Point | Position Error(cm) | Desired Orientation | Reached Orientation | Orientation Error(°) |
| 1 | (87.30, −25, 49.81) | (85.79, −24.33, 51.33) | 2.242 | (0.94, 0, −0.342) | (0.938, 0.015, −0.346) | 0.91 |
| 2 | (87.30, 25, 49.81) | (85.79, 24.33, 51.33) | 2.242 | (0.94, 0, −0.342) | (0.938, 0.015, −0.346) | 0.9101 |
| 3 | (−80.30, 27.5, 55.81) | (−82.54, 28.24, 60.01) | 4.817 | (−0.913, 0.365, −0.183) | (, 0.362, −0.183) | 0.2195 |
| 4 | (−74.19, −29.46, 67.64) | (−72.67, −31.09, 64.44) | 3.903 | (−0.549, −0.768, −0.329) | (−0.567, −0.753, −0.334) | 1.3826 |
| 5 | (50, 0, 63) | (67.21, −1.35, 83.795) | 27.028 | (0.254, −0.889, 0.381) | (0.289, −0.858, 0.424) | 3.617 |
| 6 | (0, 0, 100) | (5.08, 17.79, 97.99) | 18.613 | (0.254, 0.889, −0.381) | (0.254, 0.888, −0.382) | 0.08424 |
| 7 | (50, −33, 110) | (47.20, −31.15, 102.41) | 8.298 | (0, 0, 1) | (0.119, −0.079, 0.99) | 8.146 |
| 8 | (94, −54, 20) | (85.29, −48.46, 26.44) | 12.168 | (0.651, −0.651, −0.391) | (0.66, −0.634, −0.403) | 1.278 |
| 9 | (55, −55, 80) | (42.36, −42.36, 84.06) | 18.325 | (−0.615, 0.615, 0.492) | (−0.539, , 0.647) | 10.658 |
| 10 | (40, 40, 40) | (53, 53, 37.04) | 18.624 | (0, 0, −1) | (0, 0, −1) | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matukaitis, M.; Urniezius, R.; Masaitis, D.; Zlatkus, L.; Kemesis, B.; Dervinis, G. Synchronized Motion Profiles for Inverse-Dynamics-Based Online Control of Three Inextensible Segments of Trunk-Type Robot Actuators. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072946
Matukaitis M, Urniezius R, Masaitis D, Zlatkus L, Kemesis B, Dervinis G. Synchronized Motion Profiles for Inverse-Dynamics-Based Online Control of Three Inextensible Segments of Trunk-Type Robot Actuators. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072946
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatukaitis, Mindaugas, Renaldas Urniezius, Deividas Masaitis, Lukas Zlatkus, Benas Kemesis, and Gintaras Dervinis. 2021. "Synchronized Motion Profiles for Inverse-Dynamics-Based Online Control of Three Inextensible Segments of Trunk-Type Robot Actuators" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072946
APA StyleMatukaitis, M., Urniezius, R., Masaitis, D., Zlatkus, L., Kemesis, B., & Dervinis, G. (2021). Synchronized Motion Profiles for Inverse-Dynamics-Based Online Control of Three Inextensible Segments of Trunk-Type Robot Actuators. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072946






