Time-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Subjects with Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
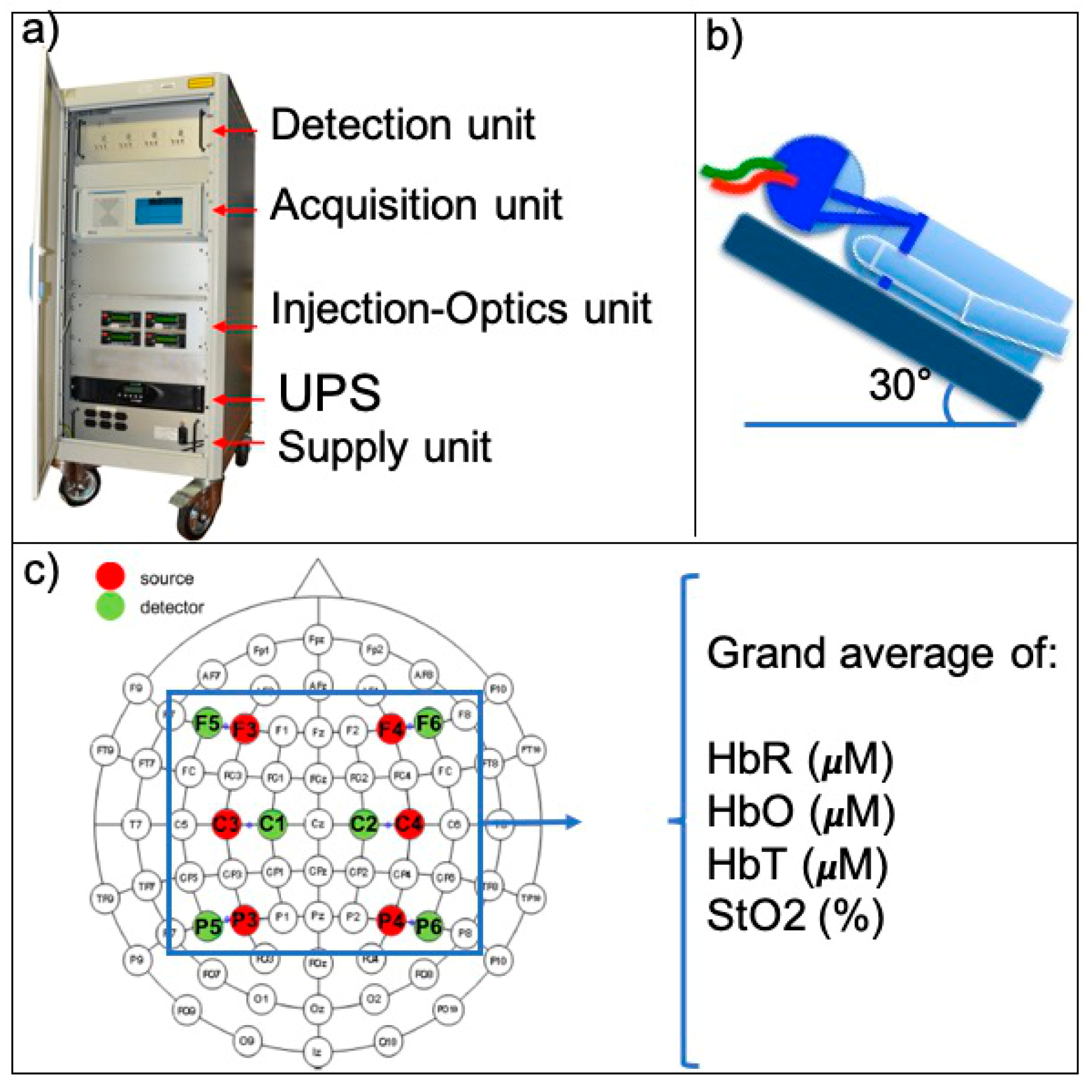
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, L.; Engedal, T.S.; Moreton, F.; Hansen, M.B.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Dalkara, T.; Markus, H.S.; Muir, K.W. Cerebral small vessel disease: Capillary pathways to stroke and cognitive decline. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2016, 36, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.D.; Regenhardt, R.W.; Vernooij, M.W.; Blacker, D.; Charidimou, A.; Viswanathan, A. Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Insights from Population-Based Studies. J. Stroke 2019, 21, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, S.E.; Longstreth, W.T.; Koudstaal, P.J. Silent brain infarcts: A systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Cordonnier, C.; Viswanathan, A.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Warach, S.; Launer, L.J.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Breteler, M.M. Microbleed Study Group Cerebral microbleeds: A guide to detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, N.D.; Scheltens, P. White matter hyperintensities, cognitive impairment and dementia: An update. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerma, R.A. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1987, 8, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusto, A.; D’Andrea, C.; Spinelli, L.; Contini, D.; Torricelli, A.; Martelli, F.; Zaccanti, G.; Cubeddu, R. Monitoring absorption changes in a layered diffusive medium by white-light time-resolved reflectance spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, G.; Zanoletti, M.; Contini, D.; Re, R.; Spinelli, L.; Roveri, L.; Torricelli, A. Cerebral time domain-NIRS: Reproducibility analysis, optical properties, hemoglobin species and tissue oxygen saturation in a cohort of adult subjects. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallacoglu, B.; Sassaroli, A.; Wysocki, M.; Guerrero-Berroa, E.; Schnaider Beeri, M.; Haroutunian, V.; Shaul, M.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Troen, A.M.; Fantini, S. Absolute measurement of cerebral optical coefficients, hemoglobin concentration and oxygen saturation in old and young adults with near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 081406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, A.C.; Bhandari, S.G.; Cullen, S.P.; Reddy, A.V.; Hsu, D.P.; Rao, V.A.; Patel, M.; Pombra, J.; Edwards, N.J.; Chan, S.L. Detection of anterior circulation large artery occlusion in ischemic stroke using noninvasive cerebral oximetry. Stroke 2018, 49, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritzenthaler, T.; Cho, T.H.; Mechtouff, M.; Ong, E.; Turjman, F.; Robinson, F.; Berthezène, Y.; Nighoghossian, N. Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy a potential approach for thrombectomy monitoring. Stroke 2017, 48, 3390–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Mederos, R.; Gregori-Pla, C.; Zirak, P.; Blanco, I.; Dinia, L.; Marín, R.; Durduran, T.; Martí-Fàbregas, J. Transcranial diffuse optical assessment of the microvascular reperfusion after thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durduran, T.; Zhou, C.; Edlow, B.L.; Yu, G.; Choe, R.; Kim, M.N.; Cucchiara, B.L.; Putt, M.E.; Shah, Q.; Kasner, S.E.; et al. Transcranial optical monitoring of cerebrovascular hemodynamics in acute stroke patients. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 3884–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregori-Pla, C.; Blanco, I.; Camps-Renom, P.; Zirak, P.; Serra, I.; Cotta, G.; Maruccia, F.; Prats-Sánchez, L.; Martínez-Domeño, A.; Busch, D.R.; et al. Early microvascular cerebral blood flow response to head-of-bed elevation is related to outcome in acute ischemic stroke. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregori-Pla, C.; Delgado-Mederos, R.; Cotta, G.; Giacalone, G.; Maruccia, F.; Avtzi, S.; Prats-Sánchez, L.; Martínez-Domeño, A.; Camps-Renom, P.; Martí-Fàbregas, J.; et al. Microvascular cerebral blood flow fluctuations due to periodic apneas in acute ischemic stroke. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, G.; Zanoletti, M.; Re, R.; Germinario, B.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A.; Roveri, L. Time-domain near-infrared spectroscopy in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatu, L.; Moulin, T.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Duvernoy, H. Arterial territories of the human brain: Cerebral hemispheres. Neurology 1998, 50, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koessler, L.; Maillard, L.; Benhadid, A.; Vignal, J.P.; Felblinger, J.; Vespignani, H.; Braun, M. Automated cortical projection of EEG sensors: Anatomical correlation via the international 10-10 system. Neuroimage 2009, 46, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, H.; Akima, M.; Hatori, T.; Nagayama, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ihara, F. Microvasculature of the human cerebral white matter: Arteries of the deep white matter. Neuropathology 2003, 23, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.S.; Guo, Z.N.; Ou, Y.B.; Yu, Y.N.; Zhang, X.C.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Lou, M. Cerebral venous collaterals: A new fort for fighting ischemic stroke? Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 163–164, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Berghold, A.; Jokinen, H.; Gouw, A.A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Petrovic, P.; Madureira, S.; Verdelho, A.; et al. White matter lesion progression in LADIS: Frequency, clinical effects, and sample size calculations. Stroke 2012, 43, 2643–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, E.J.; Prins, N.D.; Vrooman, H.A.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Breteler, M.M.B. Progression of cerebral small vessel disease in relation to risk factors and cognitive consequences: Rotterdam scan study. Stroke 2008, 39, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Torricelli, A.; Bargigia, I.; Spinelli, L.; Cubeddu, R.; Foschum, F.; Jäger, M.; Simon, E.; Fugger, O.; Kienle, A.; et al. In vivo Multilaboratory investigation of the optical properties of the human head. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 2609–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| noWMHs n = 6 | pvWMHs n = 5 | d+pvWMHs n = 9 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 59 (56–61) | 68 (67–78) | 70 (70–77) | 0.015 |
| Gender (M/F) | 83/17% | 80/20% | 44/56% | 0.22 |
| Arterial hypertension | 17% | 20% | 67% | 0.09 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0% | 40% | 33% | 0.23 |
| Smoking | 33% | 0% | 0% | 0.07 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 17% | 20% | 11% | 0.9 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0% | 0% | 22% | 0.26 |
| Migraine | 0% | 20% | 11% | 0.54 |
| MAP (mmHg) * | 95 (88–97) | 90 (87–90) | 90 (87–103) | 0.63 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) * | 64 (60–70) | 65(60–73) | 71 (65–82) | 0.60 |
| SpO2 (%) * | 99 (98–99) | 97 (96–97) | 98 (98–99) | 0.06 |
| Hb (g/dl) * | 13.9 (1.4) | 13.9 (0.5) | 13.2 (1.2) | 0.56 |
| noWMHs n = 6 | pvWMHs n = 5 | d+pvWMHs n = 9 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbR (µM) | 23.7 (22.1–25.3) | 19.0 (18.6–19.1) | 23.0 (17.9–25.8) | 0.32 |
| HbO (µM) | 34.1 (31.9–35.6) | 29.8 (26.5–35.2) | 26.9 (25.7–29.3) | 0.26 |
| HbT (µM) | 57.5 (54.8–61.0) | 48.8 (45.2–54.3) | 51.1 (44.2–55.1) | 0.28 |
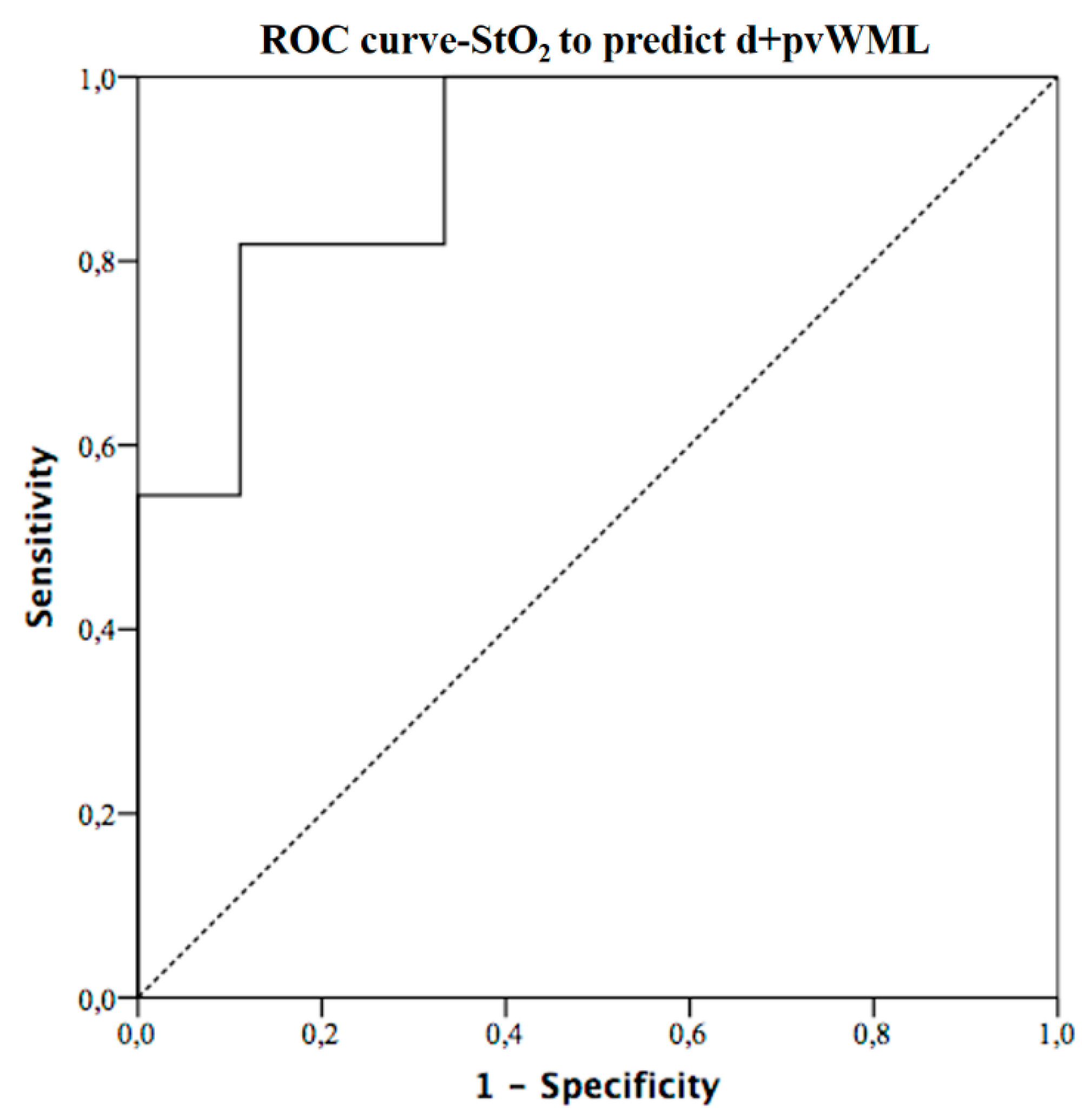
| StO2 (%) | 58.8 (57.5–59.5) | 61.1 (58.6–61.6) | 54.8 (53.2–57.3) | 0.007 |
| Independent Variables | t | Beta | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| StO2 | −2.5 | −0.96 (−0.18–−0.015) | 0.023 |
| Age | 3.7 | 0.06 (0.025–0.093) | 0.002 |
| Arterial hypertension | 2.3 | 0.55 (0.040–1.01) | 0.037 |
| Smoking | −1.5 | −0.63 (−1.5–0.26) | 0.152 |
| SpO2 | 2.0 | 0.21 (−0.01–0.43) | 0.066 |
| Constant | −1.6 | −18.1 (−42.9–6.7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giacalone, G.; Zanoletti, M.; Re, R.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A.; Roveri, L. Time-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Subjects with Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052407
Giacalone G, Zanoletti M, Re R, Contini D, Spinelli L, Torricelli A, Roveri L. Time-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Subjects with Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052407
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiacalone, Giacomo, Marta Zanoletti, Rebecca Re, Davide Contini, Lorenzo Spinelli, Alessandro Torricelli, and Luisa Roveri. 2021. "Time-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Subjects with Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052407
APA StyleGiacalone, G., Zanoletti, M., Re, R., Contini, D., Spinelli, L., Torricelli, A., & Roveri, L. (2021). Time-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Subjects with Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052407









