Protective Effects of Echinacea purpurea Ethanol Extract on Male Reproductive Dysfunction in Obese Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Echinacea Purpurea Ethanol Extract (EPE)
2.2.2. In Vivo Analysis
2.2.3. Sperm and Testis Sample Collection
2.2.4. Adipose Tissue Diameter and Morphology
2.2.5. Determination of Glucose and Testosterone Level in Plasma
2.2.6. Determination of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Catalase, and Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx)
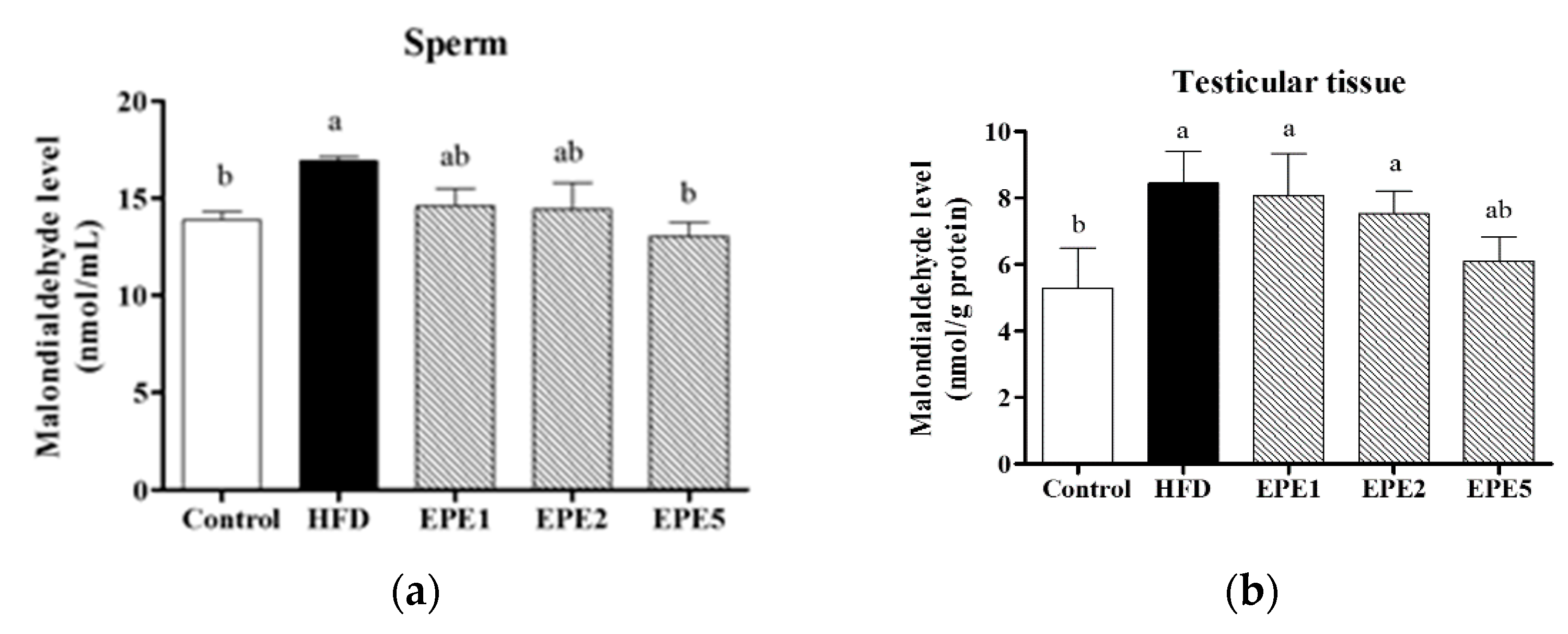
2.2.7. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Analysis in Testes and Sperm
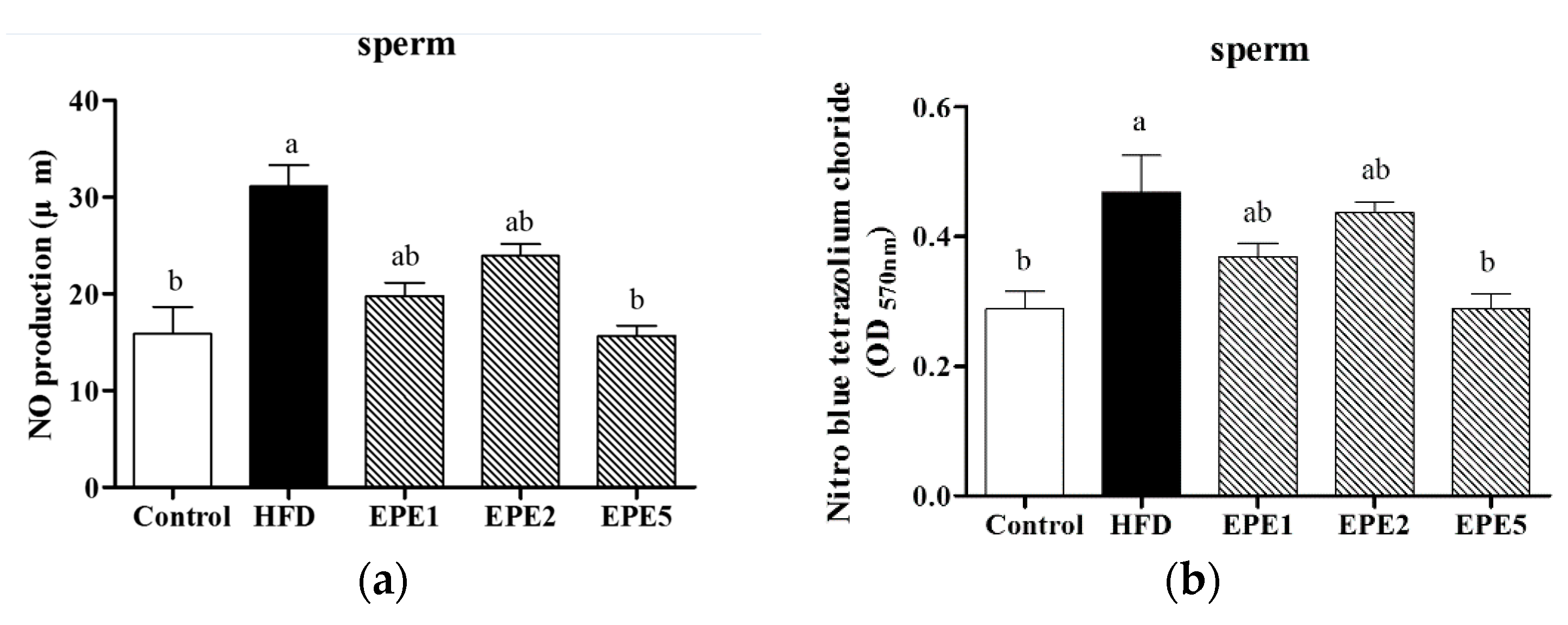
2.2.8. Determination of Nitric Oxide (NO) Production
2.2.9. Determination of ROS Production
2.2.10. Determination of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) and Interleukin (IL)-6 Levels
2.2.11. Determination of Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Urea, and Creatinine Levels
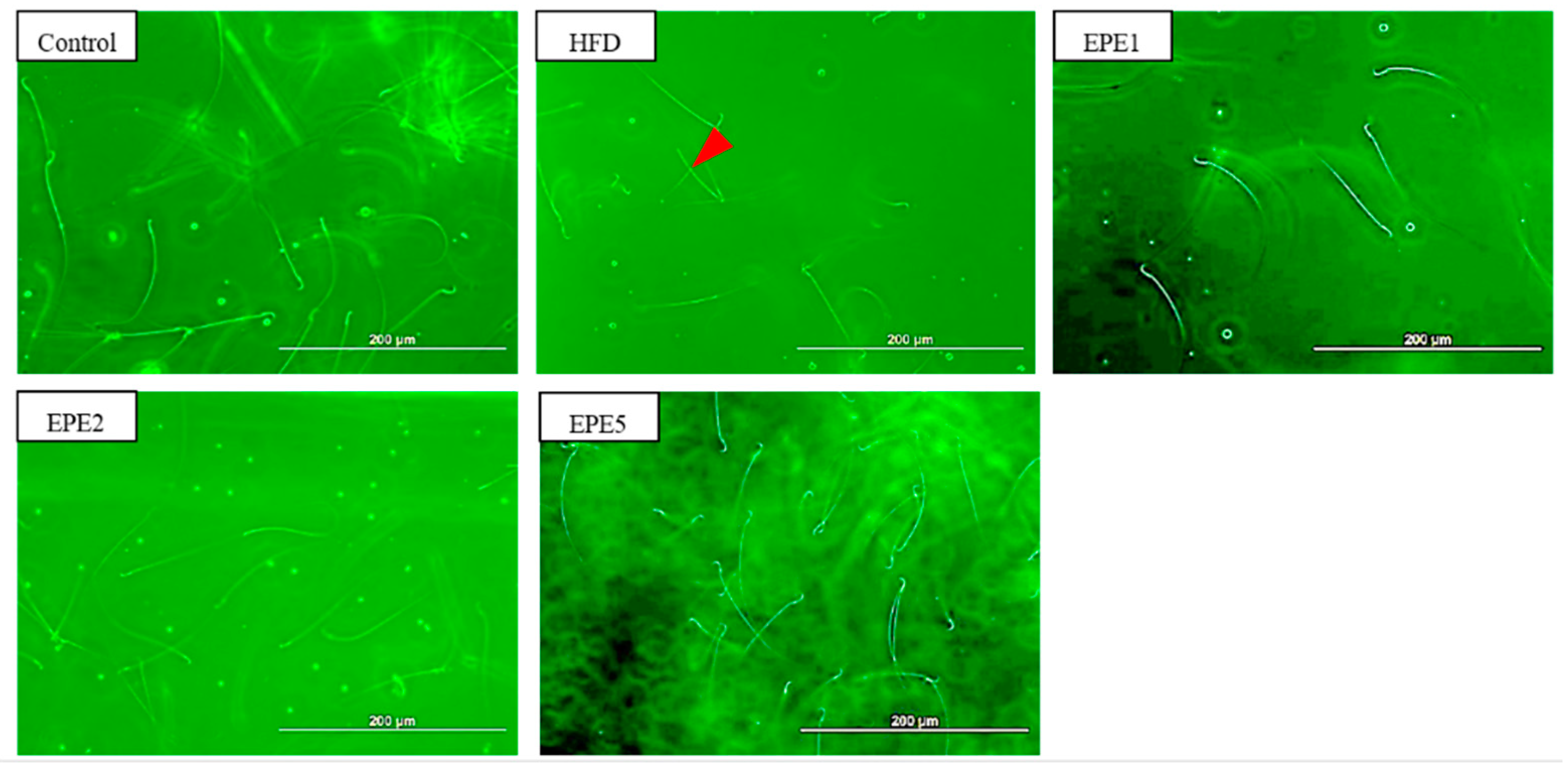
2.2.12. Determination of Sperm Count, Motility, and Abnormal Sperm Count
2.2.13. Sperm Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.2.14. Acridine Orange (AO) Assay
2.2.15. Tissue Sectioning and Staining
2.2.16. Western Blot Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
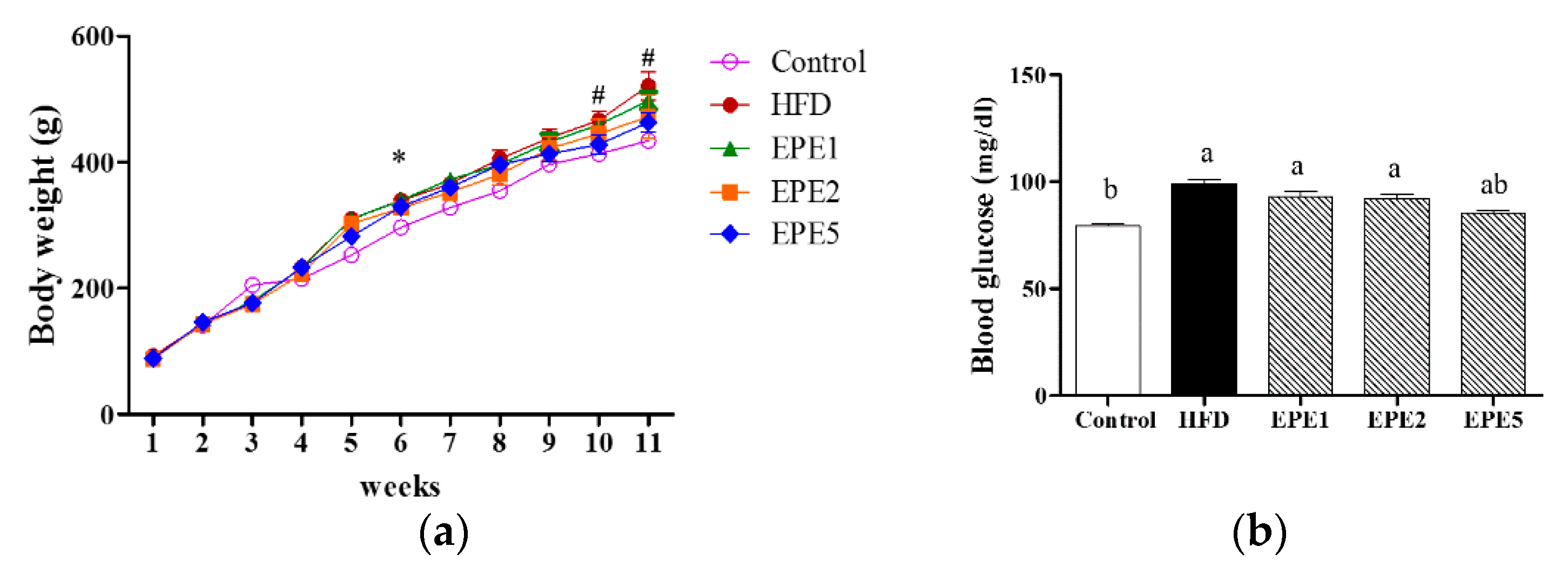
3.1. Body Weight Change and Blood Glucose Level
3.2. Adipocyte Morphology
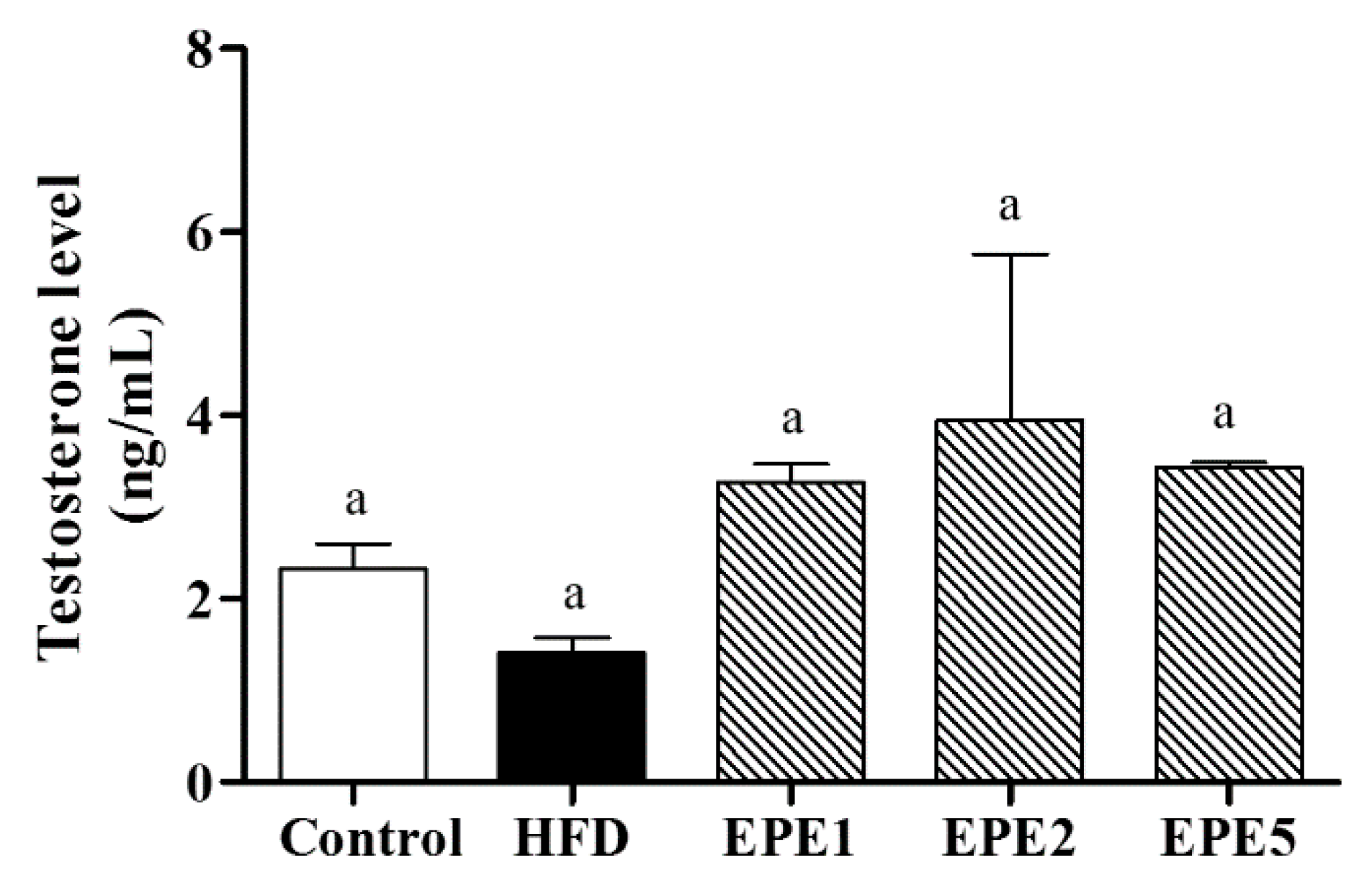
3.3. Plasma Testosterone Level
3.4. Weight of Testes and Epididymis
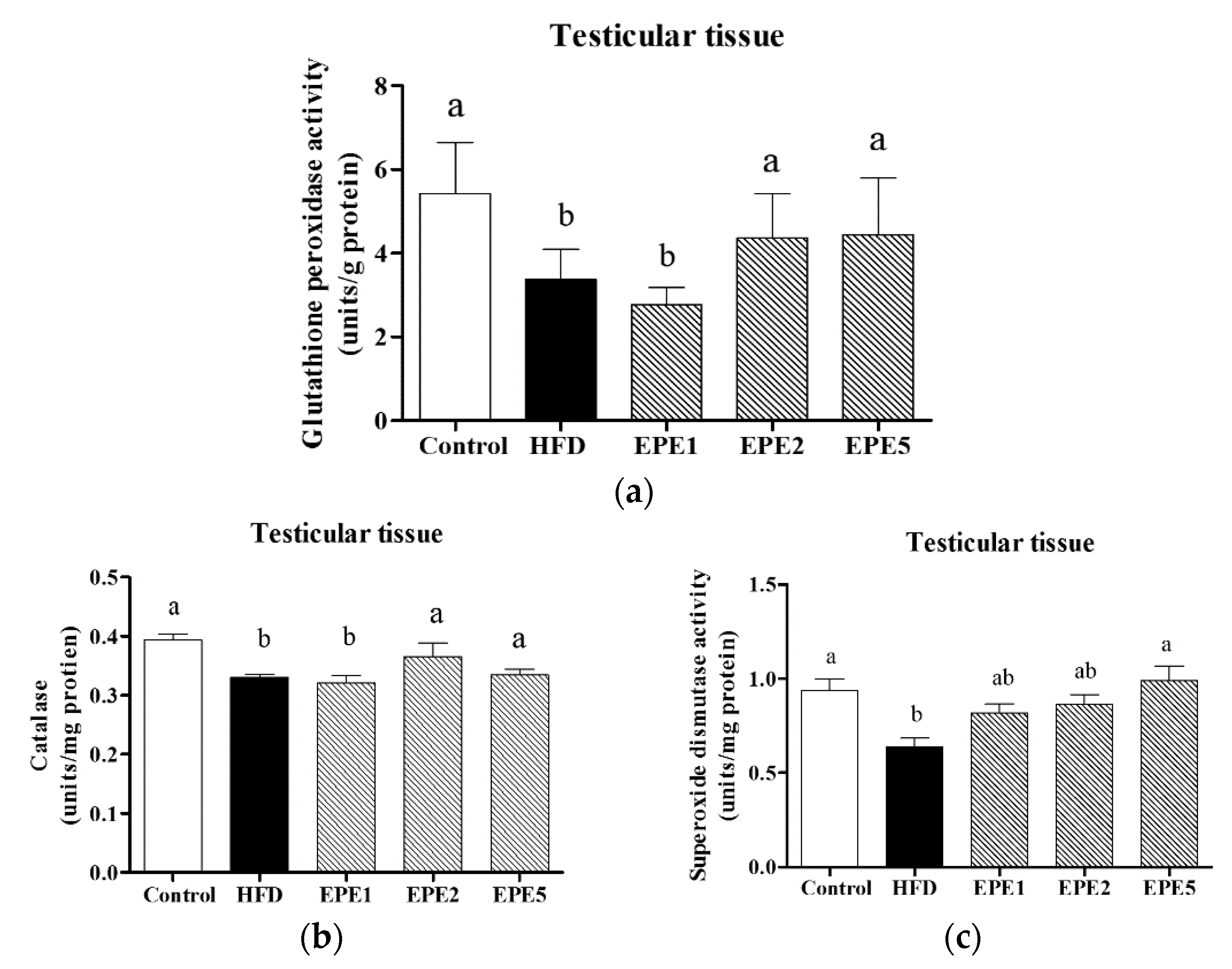
3.5. Determination of Antioxidant Level
3.6. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Production
3.7. Nitric Oxide (NO) Production and Nitroblue Tetrazolium (NBT) Assay
3.8. Proinflammatory Cytokines Level
3.9. Alanine Transaminase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Urea, and Creatinine Level
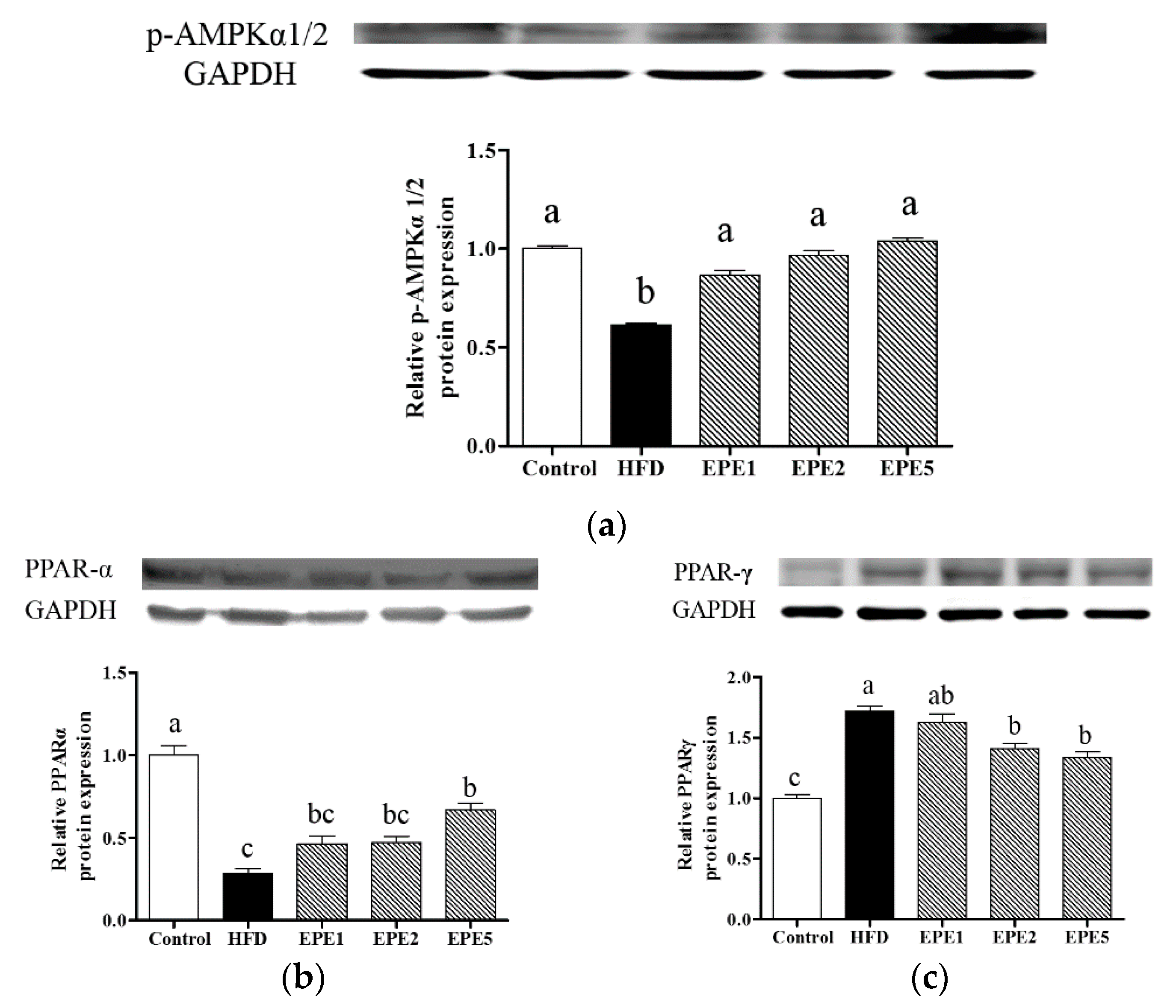
3.10. Liver Protein Expression of Phospho-Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Alpha 1/2 (p-AMPKα1/2), Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha (PPAR-α), and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma (PPAR-γ)
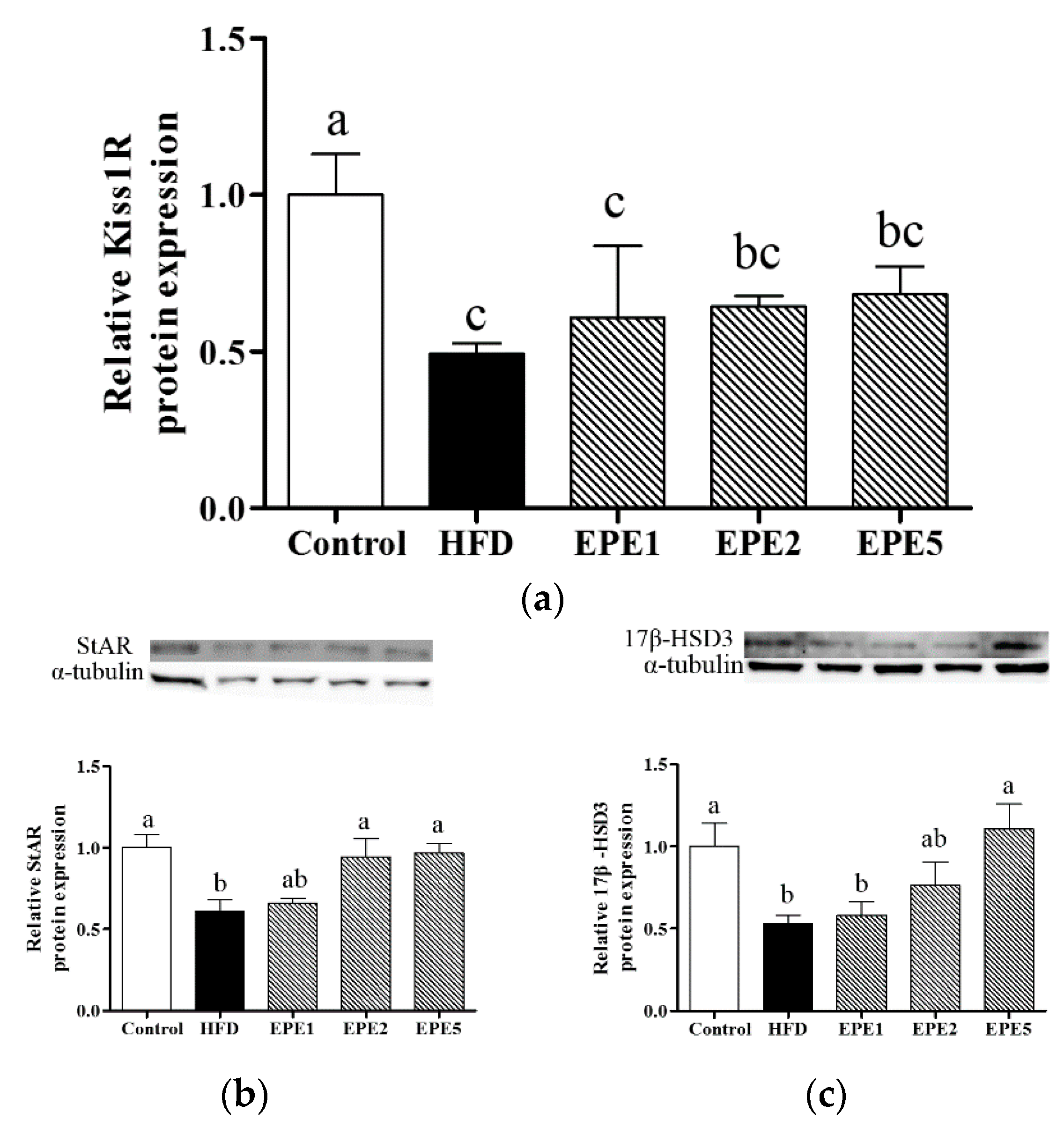
3.11. Kisspeptin 1-Derived Peptide Receptor (Kiss1R), Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR), and 17β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase 3 (17β-HSD3) mRNA Expressions
3.12. Sperm Morphology and Sperm Parameters
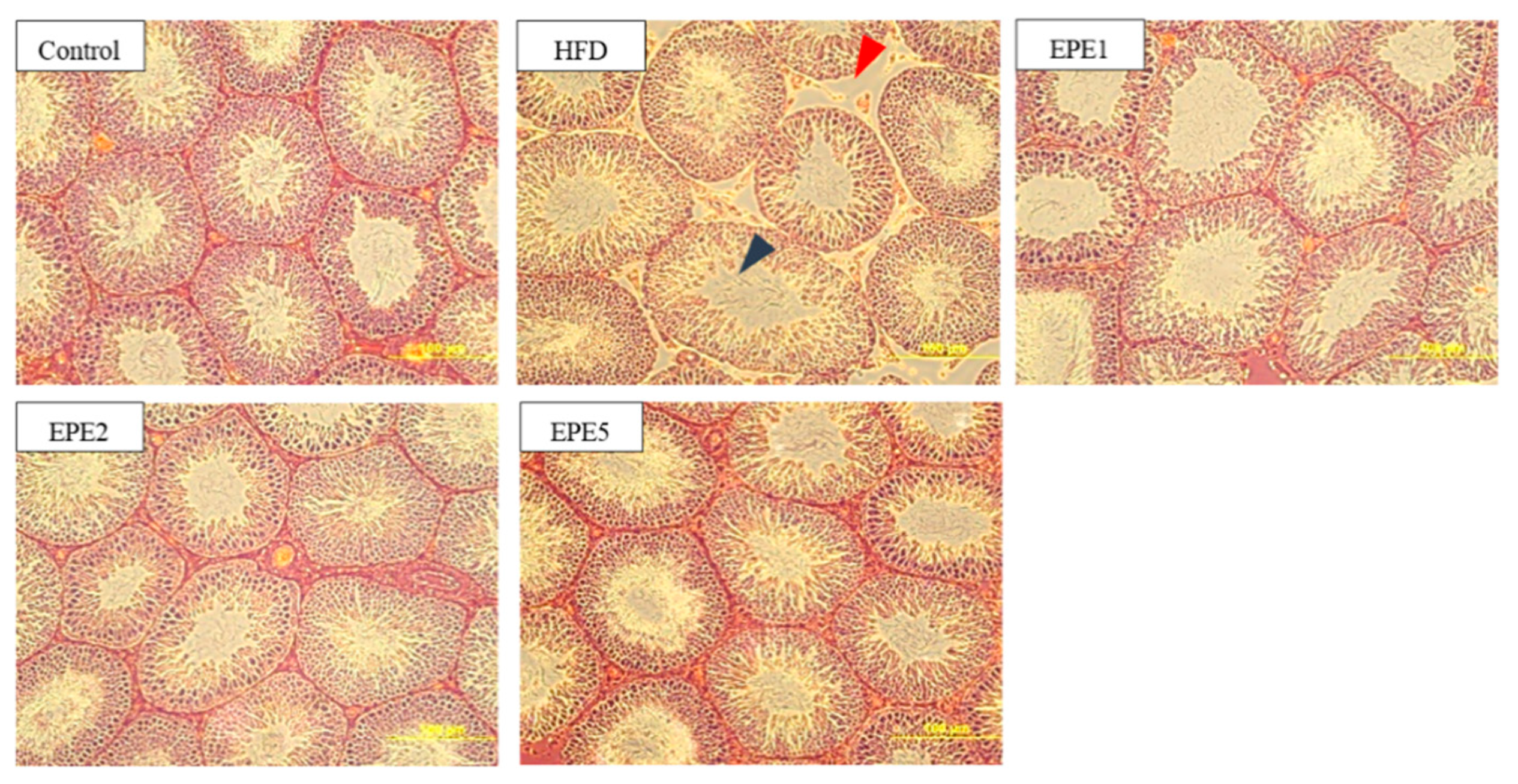
3.13. Histopathological Evaluation of Testes
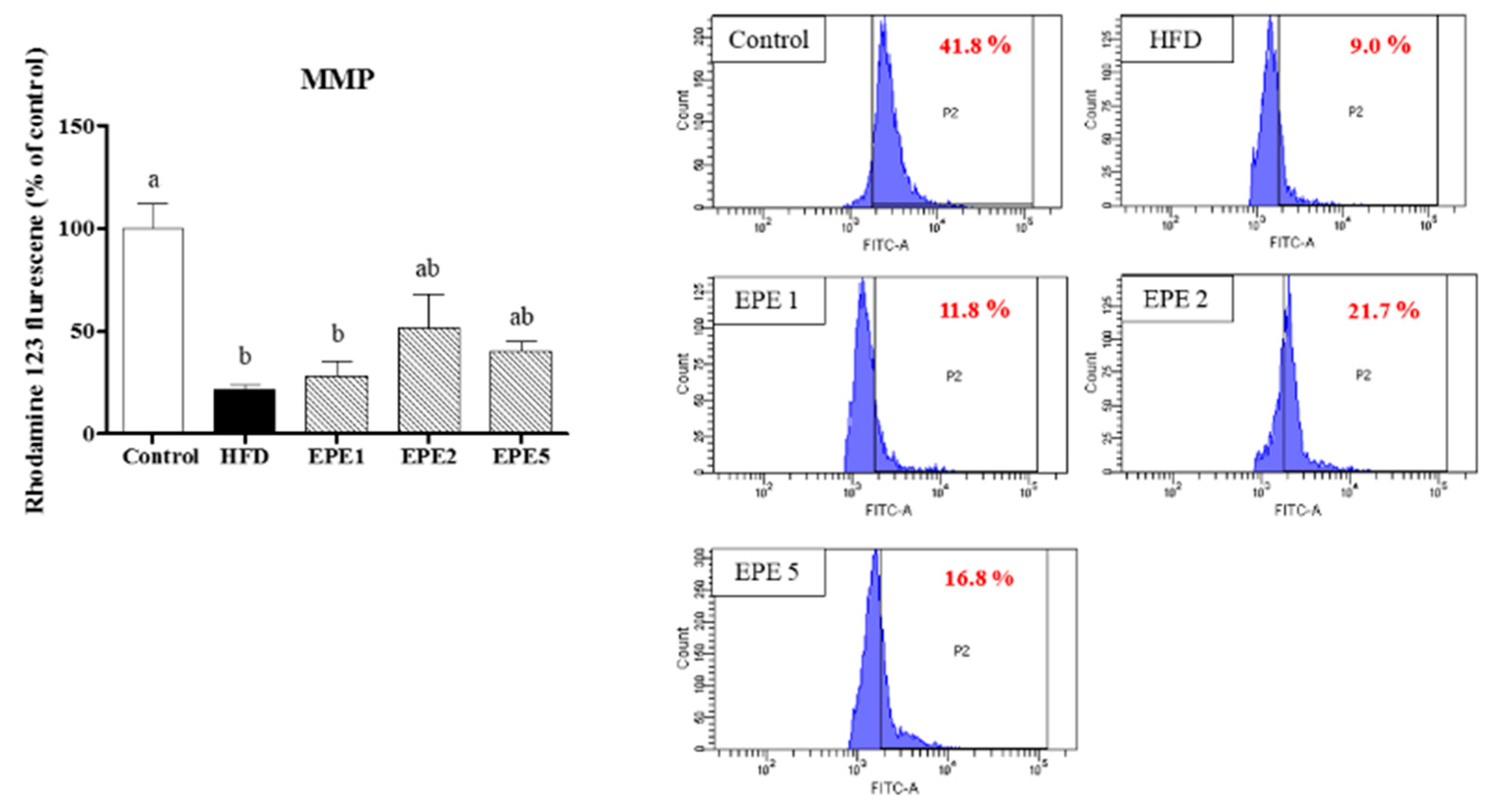
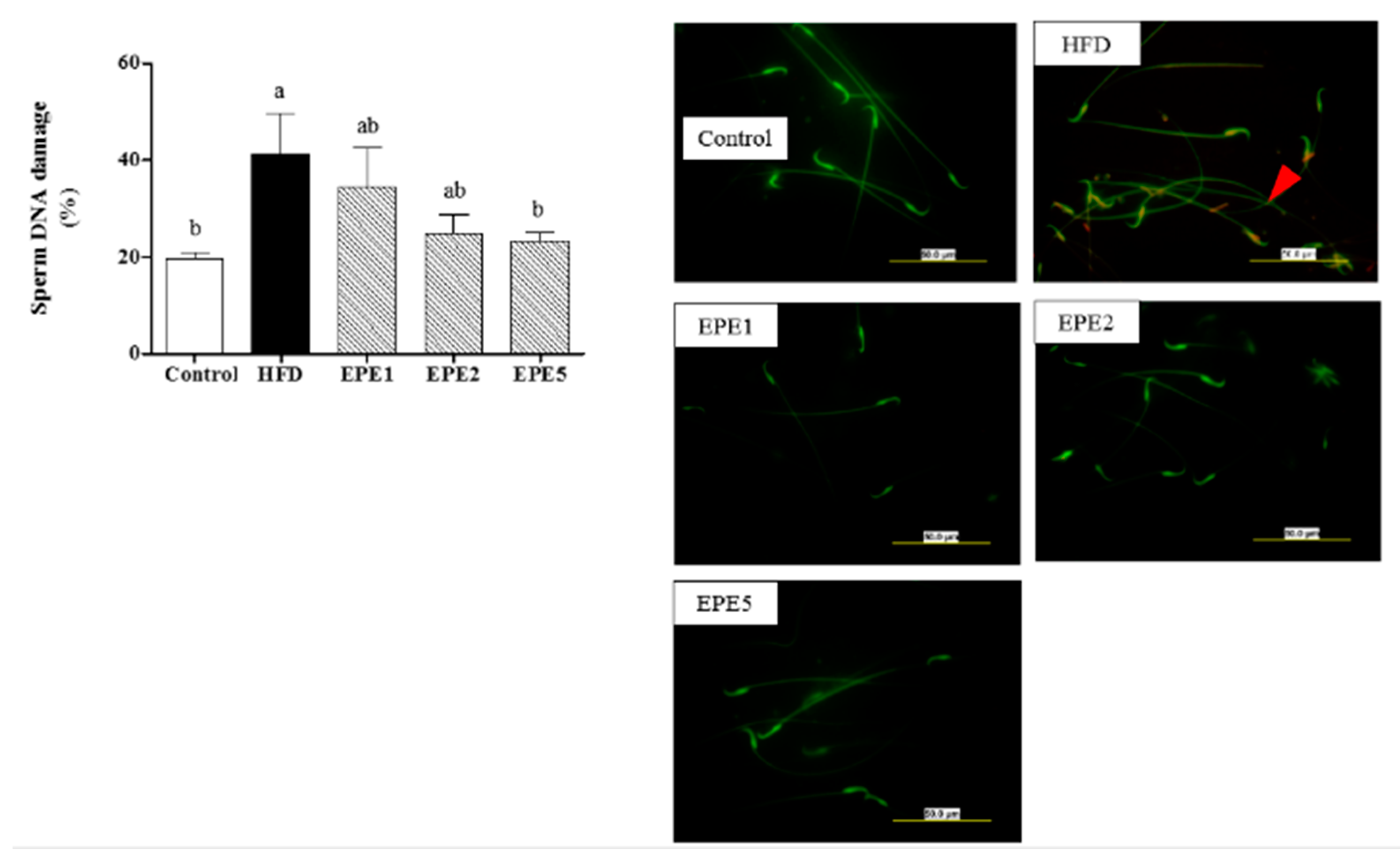
3.14. Sperm Mitochondrial Potential (MMP) and Sperm DNA Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The epidemiology of obesity: A big picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djalalinia, S.; Qorbani, M.; Peykari, N.; Kelishadi, R. Health impacts of obesity. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 31, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Jambocus, N.G.S.; Ismail, A.; Khatib, A.; Mahomoodally, F.; Saari, N.; Mumtaz, M.W.; Hamid, A.A. Morinda citrifolia L. leaf extract prevent weight gain in Sprague-Dawley rats fed a high fat diet. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Cho, B.O.; Jang, S.I. Anti-obesity effects of Diospyros lotus leaf extract in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, L.H.C.; Souza, I.L.L.; Pinheiro, L.S.; Silva, B.A. Ion channels in obesity: Pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets. Front Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, T.A.; Woods, S.C. Overview of animal models of obesity. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2012, 58, 5.61.1–5.61.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C.D.B.; Bellentani, F.F.; Fernandes, G.S.A.; Perobelli, J.E.; Favareto, A.P.A.; Nascimento, A.F.; Cicogna, A.C.; Kempinas, W.D.G. Diet-induced obesity in rats leads to a decrease in sperm motility. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalca, R.; Fica, S. The impact of obesity on the male reproductive axis. J. Med. Life 2014, 7, 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Suleiman, J.; Bahiyah, A.; Abu Bakar, A.; Mohamed, M. Review on effects of obesity on male reproductive system and the role of natural products. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, H.A.; Sahib, N.G.; Saari, N.; Abas, F.; Ismail, A.; Mumtaz, M.W.; Hamid, A.A. Anti-obesity effect of ethanolic extract from Cosmos caudatus Kunth leaf in lean rats fed a high fat diet. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manayi, A.; Vazirian, M.; Saeidnia, S. Echinacea purpurea: Pharmacology, phytochemistry and analysis methods. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.B. Applications of the phytomedicine Echinacea purpurea (Purple Coneflower) in infectious diseases. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, B.; Ricordi, C. Anti-inflammatory nutrition as a pharmacological approach to treat obesity. J. Obes. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.; Cheng, S.C.; Tsou, D.; Kong, Z.L. Attenuation of reproductive dysfunction in diabetic male rats with timber cultured Antrodia cinnamomea ethanol extract. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.-L.; Johnson, A.; Ko, F.-C.; He, J.-L.; Cheng, S.-C. Effect of Cistanche Tubulosa extracts on male reproductive function in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.-F.; Zhang, X.-R.; Johnson, A.; He, J.-L.; Kong, Z.-L. Modulation of diabetes mellitus-induced male rat reproductive dysfunction with micro-nanoencapsulated Echinacea purpurea Ethanol Extract. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javvaji, P.K.; Dhali, A.; Francis, J.R.; Kolte, A.P.; Mech, A.; Roy, S.C.; Mishra, A.; Bhatta, R. An efficient nitroblue tetrazolium staining and bright-field microscopy based method for detecting and quantifying intracellular reactive oxygen species in oocytes, cumulus cells and embryos. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idriss, H.T.; Naismith, J.H. TNFα and the TNF receptor superfamily: Structure-function relationship(s). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 50, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspec.T Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, D.; Nagrajappa, A.K.; Ravi, K.S. Assessment and correlation of urea and creatinine levels in saliva and serum of patients with chronic kidney disease, diabetes and hypertension—A research study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC58–ZC62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, B.T.; Tafere, G.G.; Wondafrash, D.Z.; Gidey, M.T. The bewildering effect of AMPK activators in alzheimer’s disease: Review of the current evidence. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.; Ling, Y.; Kuang, H. Reproductive functions of Kisspeptin/KISS1R Systems in the Periphery. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, S.; Bellemare, V.; Pelletier, G.; Labrie, F.; Luu-The, V. Expression and localization of estrogenic type 12 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the cynomolgus monkey. BMC Biochem. 2007, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, S.; Gupta, P.; Saini, A.S.; Kaushal, C.; Sharma, S. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor: A family of nuclear receptors role in various diseases. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Sui, X.; Cao, S.; Li, X.; Ning, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, L.; Zhi, X. Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) overexpression reduces inflammation and insulin resistance in obese mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 3932–3942. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, P.; Wafer, R.; Minchin, J.E.N. Adipose morphology and metabolic disease. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jackson, G.; Jones, T.H.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Nehra, A.; Perelman, M.A.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Traish, A.; Zitzmann, M.; Cunningham, G. Low testosterone associated with obesity and the metabolic syndrome contributes to sexual dysfunction and cardiovascular disease risk in men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungheim, E.S.; Travieso, J.L.; Carson, K.R.; Moley, K.H. Obesity and reproductive function. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 39, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, A.; Busetto, L.; Vettor, R.; Rossato, M. Obesity, male reproductive function and bariatric surgery. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.D.; Majzoub, A.; Agawal, A. Metabolic syndrome and male fertility. World J. Mens Health 2019, 37, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Tai, Y.; Yang, X.; Hu, F.; Xie, Z. Anti-inflammatory effects of essential oil in Echinacea purpurea L. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 26, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Montan, P.D.; Sourlas, A.; Olivero, J.; Silverio, D.; Guzman, E.; Kosmas, C.E. Pharmacologic therapy of obesity: Mechanisms of action and cardiometabolic effects. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Goblan, A.S.; Al-Alfi, M.A.; Khan, M.Z. Mechanism linking diabetes mellitus and obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2014, 7, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, J.; Tchernof, A. Depot- and obesity-related differences in adipogenesis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2012, 7, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelusi, C.; Pasquali, R. The significance of low testosterone levels in obese men. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2012, 1, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Obesity, oxidative stress, adipose tissue dysfunction, and the associated health risks: Causes and therapeutic strategies. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2015, 13, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susantiningsih, T.; Perdani, R.R.W.; Berawi, K.; Hadi, S. The Effect of treadmill treatment on oxidative stress markers and endogenous antioxidant status in obesity mice. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-J.; McAllister, M.J.; Slusher, A.L.; Webb, H.E.; Mock, J.T.; Acevedo, E.O. Obesity-related oxidative stress: The impact of physical activity and diet manipulation. Sports Med. Open 2015, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, O.; Thompson, J.; Tremellen, K. Development of the NBT assay as a marker of sperm oxidative stress. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Gu, N.; Chen, L.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Pang, L.; Guo, X.; Ji, C.; et al. IL-6 and TNF-α induced obesity-related inflammatory response through transcriptional regulation of miR-146b. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanavari, T.; Giannogonas, P.; Karalis, K.P. TNF-alpha and obesity. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, B.A.; Doumatey, A.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, G.; Shriner, D.; Adeyemo, A.; Rotimi, C.N. The roles of IL-6, IL-10, and IL-1RA in obesity and insulin resistance in African-Americans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E2018–E2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; He, C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 44, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, G.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Grulich-Henn, J.; Teufel, U. Alanine aminotransferase elevation in obese infants and children: A marker of early onset non alcoholic Fatty liver disease. Hepat. Mon. 2014, 14, e14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, S.; Desai, P.B.; Hull, V.V.; Math, A.A.K.; Vernekar, S.N.; Kulkarni, S.S. A review on laboratory liver function tests. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2009, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirmiran, P.; Gaeini, Z.; Bahadoran, Z.; Azizi, F. Elevated serum levels of aminotransferases in relation to unhealthy foods intake: Tehran lipid and glucose study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.H. Overview of urea and creatinine. J. Lab. Med. 2014, 45, e19–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Hellberg, K.; Chaix, A.; Wallace, M.; Herzig, S.; Badur, M.G.; Lin, T.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Pinto, A.F.M.; Ross, D.S.; et al. Genetic liver-specific AMPK activation protects against diet-induced obesity and NAFLD. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 192–208.e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, S.; Foretz, M.; Viollet, B.; Du, M. Obesity impairs skeletal muscle regeneration through inhibition of AMPK. Diabetes 2016, 65, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corrales, P.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Medina-Gómez, G. PPARs and metabolic disorders associated with challenged adipose tissue plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, F.; Atika, B.; Ullah, F.; Shahab, M.; Behr, R. Metabolic impact on the hypothalamic kisspeptin-Kiss1r signaling pathway. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Ziarniak, K.; Sliwowska, J.H. Kisspeptin and metabolism: The brain and beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.R.; Dyson, M.T.; Stocco, D.M. Regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene expression: Present and future perspectives. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindnich, R.; Haller, F.; Halbach, F.; Moeller, G.; Angelis, M.H.d.; Adamski, J. Androgen metabolism via 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 in mammalian and non-mammalian vertebrates: Comparison of the human and the zebrafish enzyme. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, P.M.; Seierøe, K.; Pakkenberg, B. The total number of Leydig and Sertoli cells in the testes of men across various age groups—A stereological study. J. Anat. 2015, 226, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.K.; Agrawal, A.K.; Hakim, B.A.; Vishwakarma, A.L.; Narender, T.; Sachan, R.; Sachdev, M. Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) regulates sperm motility. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2016, 52, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, C.; Faure, C.; Sermondade, N.; Boubaya, M.; Eustache, F.; Clément, P.; Briot, P.; Berthaut, I.; Levy, V.; Cedrin-Durnerin, I.; et al. Obesity leads to higher risk of sperm DNA damage in infertile patients. Asian J. Androl. 2013, 15, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
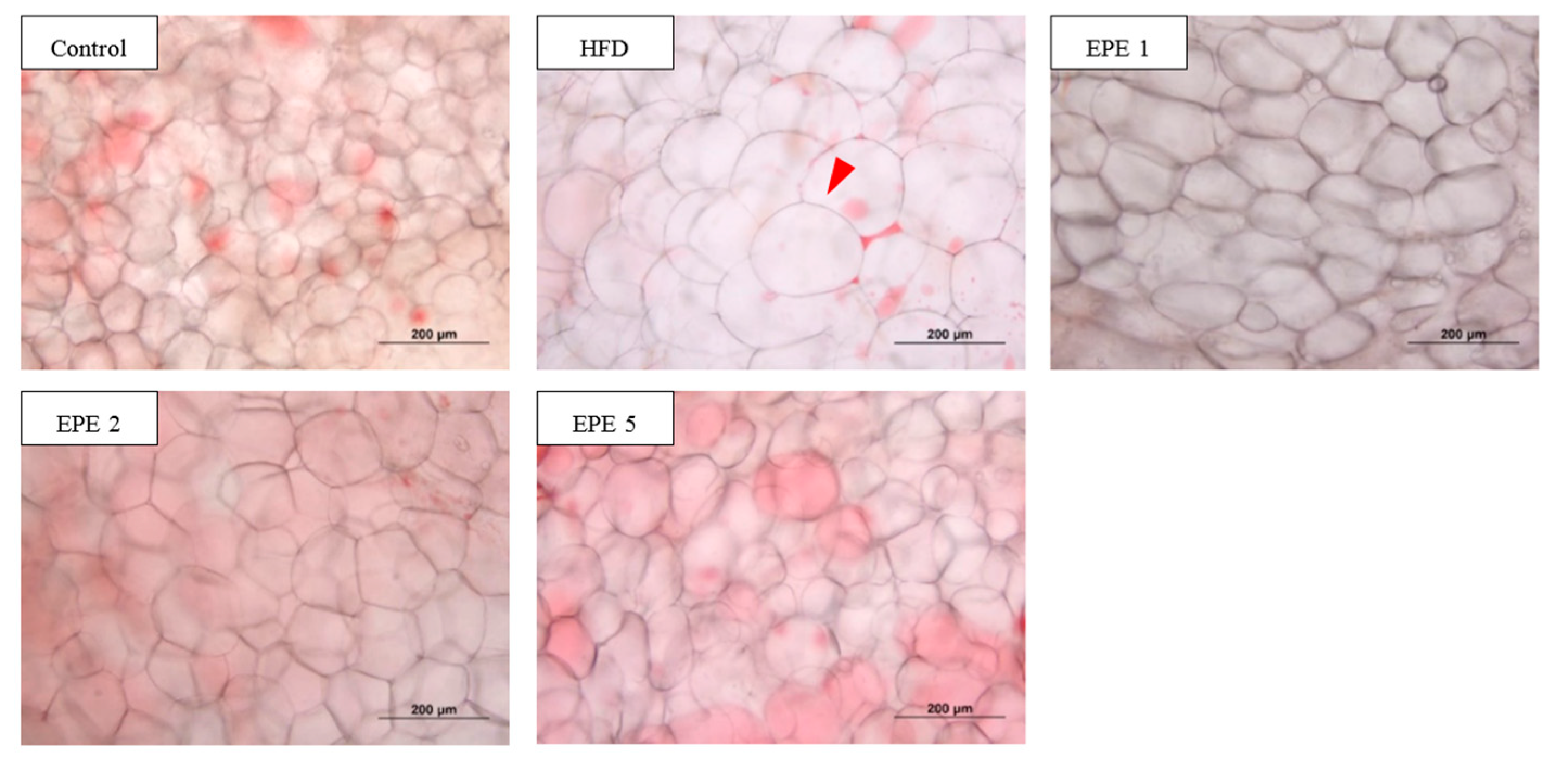
| Diameter μm (%) | Control | HFD | EPE1 | EPE2 | EPE5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 50 | 32 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 24 |
| 100 | 46 | 11 | 30 | 53 | 48 |
| 150 | 17 | 56 | 58 | 39 | 25 |
| 200 | 1 | 33 | 9 | 2 | 2 |
| Average (μm) | 90.5 | 161 | 136.25 | 118.25 | 101.75 |
| Control | HFD | EPE1 | EPE2 | EPE5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testes | Weight (g/100 g body weight) | 0.74 ± 0.01 a | 0.63 ± 0.04 b | 0.70 ± 0.04 ab | 0.69 ± 0.02 ab | 0.71 ± 0.03 ab |
| length (cm) | 2.18 ± 0.04 a | 2.08 ± 0.07 a | 2.24 ± 0.05 a | 2.24 ± 0.02 a | 2.22 ± 0.06 a | |
| Weight/ length (g/cm) | 1.51 ± 0.03 a | 1.46 ± 0.04 a | 1.48 ± 0.03 a | 1.50 ± 0.02 a | 1.53 ± 0.03 a | |
| Epididymis | Weight (g/100 g body weight) | 0.29 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 c | 0.26 ± 0.01 bc | 0.27 ± 0.01 ab | 0.27 ± 0.01 ab |
| Control | HFD | EPE1 | EPE2 | EPE5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 8.68 ± 1.25 b | 13.90 ± 1.55 a | 12.07 ± 1.87 ab | 10.75 ± 1.15 ab | 8.83 ± 0.56 b |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 10.74 ± 1.99 b | 22.09 ± 3.78 a | 16.47 ± 1.70 ab | 16.44 ± 1.14 ab | 14.40 ± 1.46 b |
| (mg/dl) | Control | HFD | EPE1 | EPE2 | EPE5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT | 31.43 ± 2.14 a | 27.59 ± 3.96 a | 27.94 ± 2.14 a | 35.97 ± 3.77 a | 34.22 ± 7.08 a |
| AST | 33.52 ± 0.86 a | 41.03 ± 2.42 a | 37.71 ± 2.11 a | 44.23 ± 2.25 a | 33.87 ± 8.80 a |
| Urea | 14.89 ± 3.78 b | 38.37 ± 16.60 a | 26.06 ± 19.61 ab | 18.64 ± 6.25 b | 12.43 ± 5.39 b |
| Creatinine | 0.29 ± 0.10 a | 0.38 ± 0.06 a | 0.31 ± 0.13 a | 0.28 ± 0.12 a | 0.27 ± 0.11 a |
| Control | HFD | EPE1 | EPE2 | EPE5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counts (106) | 30.68 ± 1.61 ab | 26.78 ± 8.27 b | 31.52 ± 1.43 a | 29.50 ± 8.95 ab | 30.78 ± 3.11 ab |
| Mobility (%) | 31.89 ± 2.38 a | 12.55 ± 1.37 b | 17.89 ± 1.85 b | 25.31 ± 3.03 ab | 24.95 ± 3.95 ab |
| Abnormality (%) | 9.11 ± 0.40 a | 18.70 ± 2.07 c | 14.31 ± 0.80 b | 12.70 ± 1.40 ab | 13.09 ± 0.71 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Z.-L.; Johnson, A.; Ting, T.-L.; Cheng, P.-J.; Mao, C.-F. Protective Effects of Echinacea purpurea Ethanol Extract on Male Reproductive Dysfunction in Obese Rats. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052392
Kong Z-L, Johnson A, Ting T-L, Cheng P-J, Mao C-F. Protective Effects of Echinacea purpurea Ethanol Extract on Male Reproductive Dysfunction in Obese Rats. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Zwe-Ling, Athira Johnson, Tzu-Ling Ting, Po-Jen Cheng, and Chien-Feng Mao. 2021. "Protective Effects of Echinacea purpurea Ethanol Extract on Male Reproductive Dysfunction in Obese Rats" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052392
APA StyleKong, Z.-L., Johnson, A., Ting, T.-L., Cheng, P.-J., & Mao, C.-F. (2021). Protective Effects of Echinacea purpurea Ethanol Extract on Male Reproductive Dysfunction in Obese Rats. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052392





