Simulation Design of Incremental Leg Tapered Birdcage Coil for Head Imaging at 4.7T MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
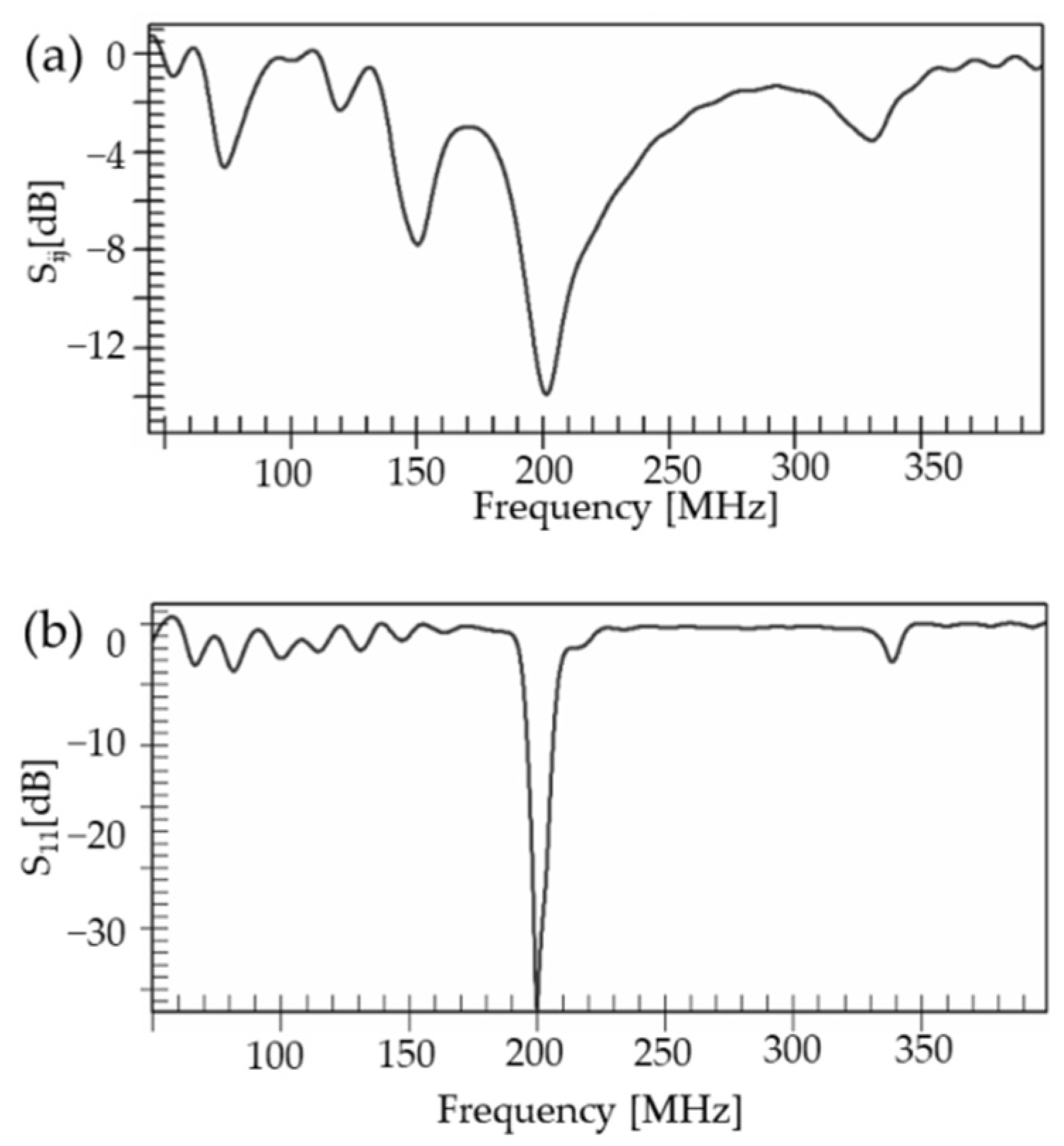
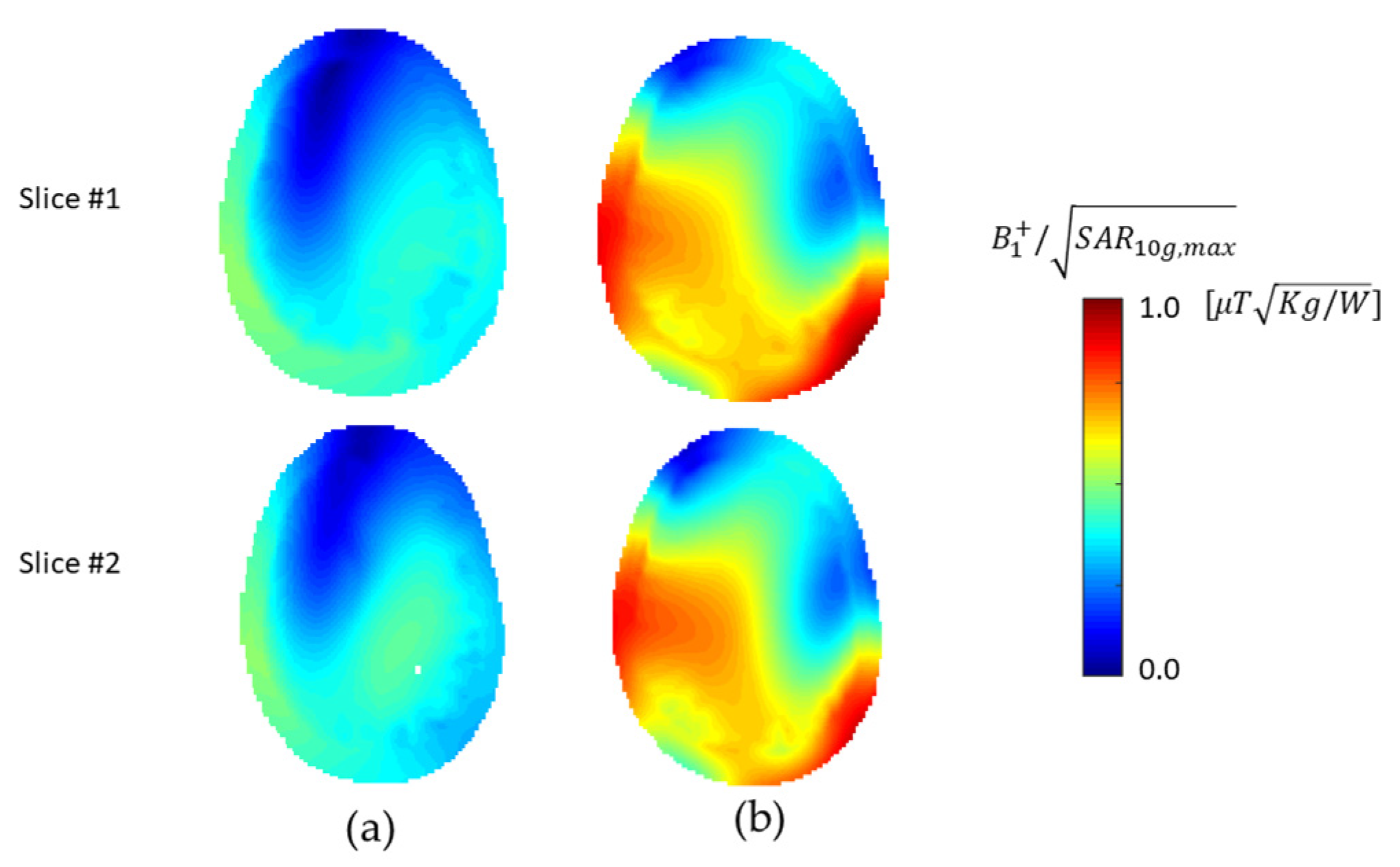
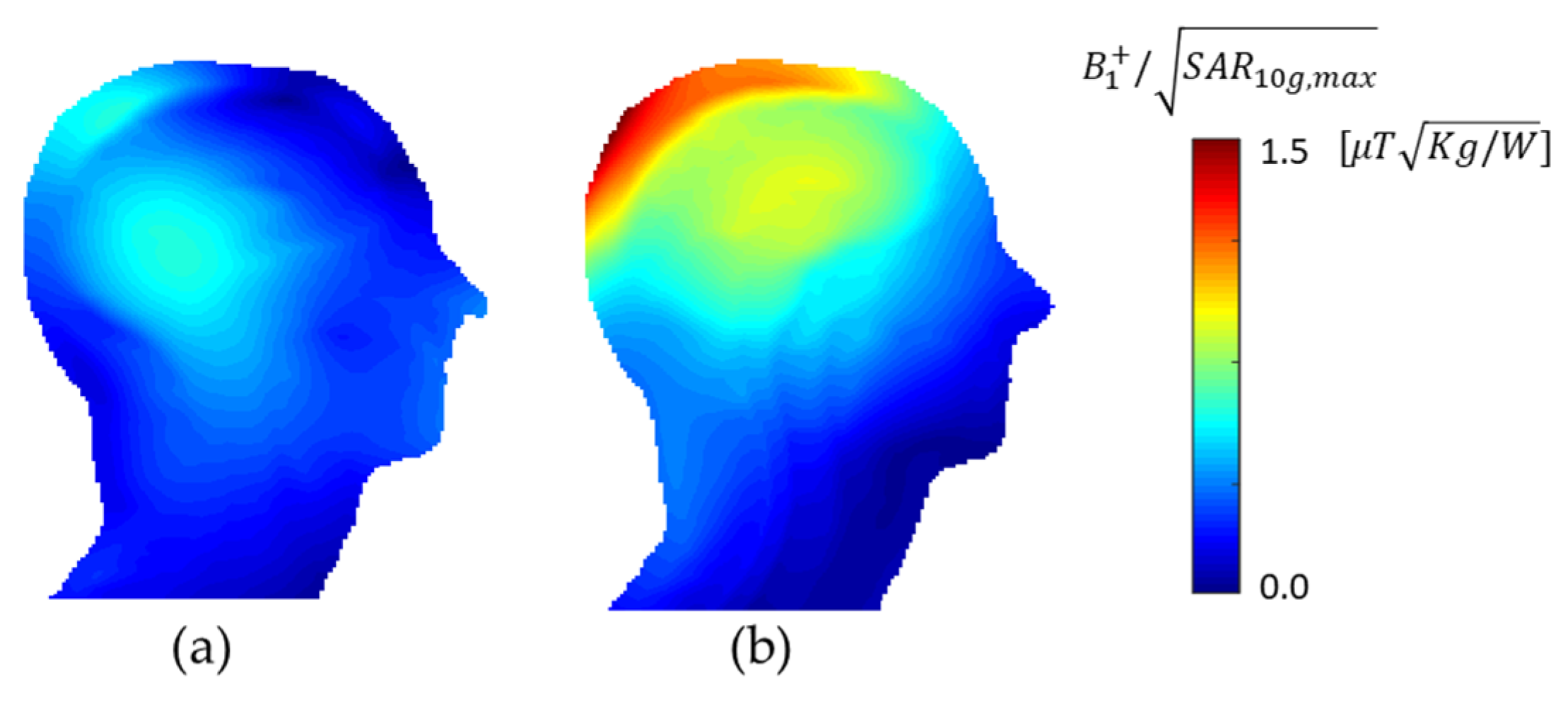
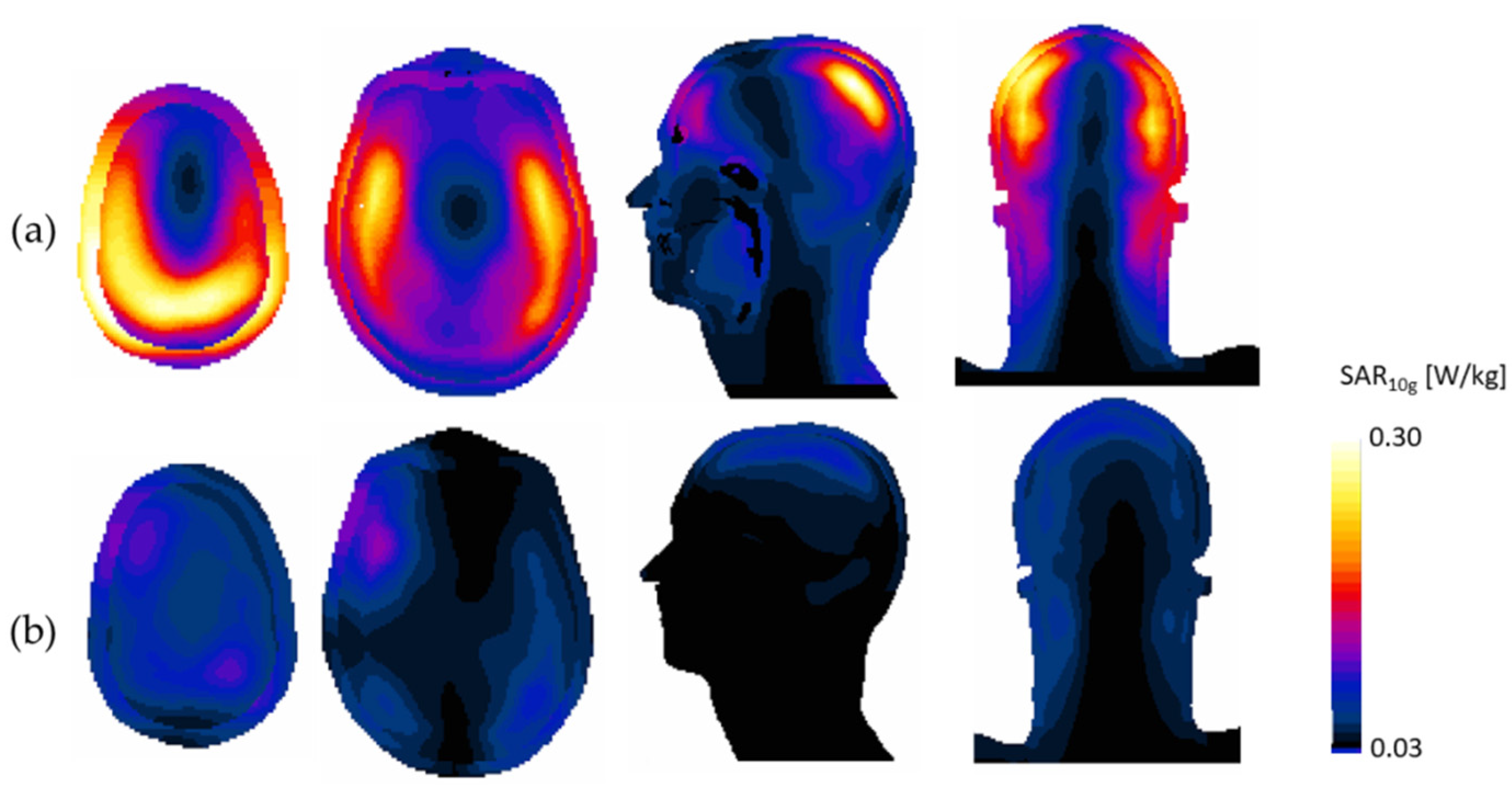
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ipek, Ö. Radio-frequency coils for ultra-high field magnetic resonance. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 529, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.M.; DelaBarre, L.; Gopinath, A.; Vaughan, J.T. RF head coil design with improved RF magnetic near-fields uniformity for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory. Tech. 2014, 62, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, J.T.; Adriany, G.; Snyder, C.J.; Tian, J.; Thiel, T.; Bolinger, L.; Liu, H.; DelaBarre, L.; Ugurbil, K. Efficient high-frequency body coil for high-field MRI. Magn. Reason. Med. 2004, 52, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissoles, P.; Caloz, G. Magnetic Field Properties in a Birdcage Coil. 2006. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00020757 (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Tomanek, B.; Volotovskyy, V.; Gruwel, M.L.; Mckenzie, E.; King, S.B. Double-frequency birdcage volume coils for 4.7 T and 7T. Concepts Magn. Reason. Part B Magn. Reason. Eng. 2005, 26, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanche, N.D. Birdcage Volume Coil Design; eMagRes: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, C.E.; Edelstein, W.A.; Schenck, J.F.; Mueller, O.M.; Eash, M. An efficient, highly homogeneous radiofrequency coil for whole-body NMR imaging at 1.5 T. J. Magn. Reson. 1985, 63, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, G.; Landini, L.; Santarelli, M.F.; Positano, V. A fast and accurate simulator for the design of birdcage coils in MRI. MAGMA 2002, 15, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.H.; Kwong, K.K.; Huang, I.J.; Belliveau, J.W.; Wald, L.L. Degenerate mode birdcage volume coil for sensitivity-encoded imaging. Magn. Reason. Med. 2003, 50, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifer, M.C. Resonant modes of the birdcage coil. J. Magn. Reason. 1997, 124, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-H.; Han, S.-D.; Kim, K.-N. Investigation of the B1 field distribution and RF power deposition in a birdcage coil as functions of the number of coil legs at 4.7 T, 7.0 T, and 11.7 T. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2015, 66, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, A.G.; Collins, C.M. Parallel transmit and receive technology in high-field magnetic resonance neuroimaging. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2010, 20, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, J.C.; Mao, W.; Liu, W.; Smith, M.B.; Collins, C.M. SAR and temperature: Simulations and comparison to regulatory limits for MRI. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2007, 26, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.T.; Wang, Z.; Loew, W.; Vogel, M.W.; Hancu, I. Local specific absorption rate in high-pass birdcage and transverse electromagnetic body coils for multiple human body models in clinical landmark positions at 3T. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2011, 33, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Guo, R.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J. Impacts of RF shimming on local SAR caused by MRI 3T birdcage coil near femoral plate implants. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–14 July 2017; pp. 1005–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Shen, G.X. B1 field, SAR, and SNR comparisons for birdcage, TEM, and microstrip coils at 7T. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2006, 24, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.M.; Li, S.; Smith, M.B. SAR and B1 field distributions in a heterogeneous human head model within a birdcage coil. Magn. Reason. Med. 1998, 40, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, W.M.; Dumoulin, C.L. Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center. Asymmetric Birdcage Coil for a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). U.S. Patent Application 16/437,234, 22 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wetterling, F.; Corteville, D.M.; Kalayciyan, R.; Rennings, A.; Konstandin, S.; Nagel, A.M.; Stark, H.; Schad, L.R. Whole body sodium MRI at 3T using an asymmetric birdcage resonator and short echo time sequence: First images of a male volunteer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dregely, I.; Ruset, I.C.; Wiggins, G.; Mareyam, A.; Mugler, J.P., III; Altes, T.A.; Meyer, C.; Ruppert, K.; Wald, L.L.; Hersman, F.W. 32-channel phased-array receive with asymmetric birdcage transmit coil for hyperpolarized xenon-129 lung imaging. Magn. Reason. Med. 2013, 70, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zanche, N.; Chhina, N.; Teh, K.; Randell, C.; Pruessmann, K.P.; Wild, J.M. Asymmetric quadrature split birdcage coil for hyperpolarized 3He lung MRI at 1.5 T. Magn. Reason. Med. 2008, 60, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Han, S.D.; Seo, J.H.; Heo, P.; Yoo, D.; Im, G.H.; Lee, J.H. An Asymmetric Birdcage Coil for Small-animal MR Imaging at 7T. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2017, 16, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reisker, T.J.; Monski, W.J.; Reid, E.D.; Misic, G.J.; Bayer Medical Care Inc. Tapered Birdcage Resonator for Improved Homogeneity in MRI. U.S. Patent 6,344,745, 5 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Avdievich, N.I.; Hetherington, H.P.; Kuznetsov, A.M.; Pan, J.W. 7T head volume coils: Improvements for rostral brain imaging. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2009, 29, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim4Life, ZMT. Available online: https://www.zmt.swiss (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Christ, A.; Kainz, W.; Hahn, E.G.; Honegger, K.; Zefferer, M.; Neufeld, E.; Rascher, W.; Janka, R.; Bautz, W.; Chen, J.; et al. The Virtual Family—Development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 55, N23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Coil Type | SAR10g | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean [µT] | RU [%] | Mean [µT√Kg/W] | Max [W/Kg] | Mean [W/Kg] | |
| BC coil | 0.14 | 38.8 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.06 |
| Yurt coil | 0.15 | 40.4 | 0.48 | 0.09 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.; Kim, K.-N.; Hernandez, D. Simulation Design of Incremental Leg Tapered Birdcage Coil for Head Imaging at 4.7T MRI. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052064
Song H, Kim K-N, Hernandez D. Simulation Design of Incremental Leg Tapered Birdcage Coil for Head Imaging at 4.7T MRI. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052064
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Hyunwoo, Kyoung-Nam Kim, and Daniel Hernandez. 2021. "Simulation Design of Incremental Leg Tapered Birdcage Coil for Head Imaging at 4.7T MRI" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052064
APA StyleSong, H., Kim, K.-N., & Hernandez, D. (2021). Simulation Design of Incremental Leg Tapered Birdcage Coil for Head Imaging at 4.7T MRI. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052064






