The Diagonal Arch Bridge, a Particular Case of Spatial Arch Bridges
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
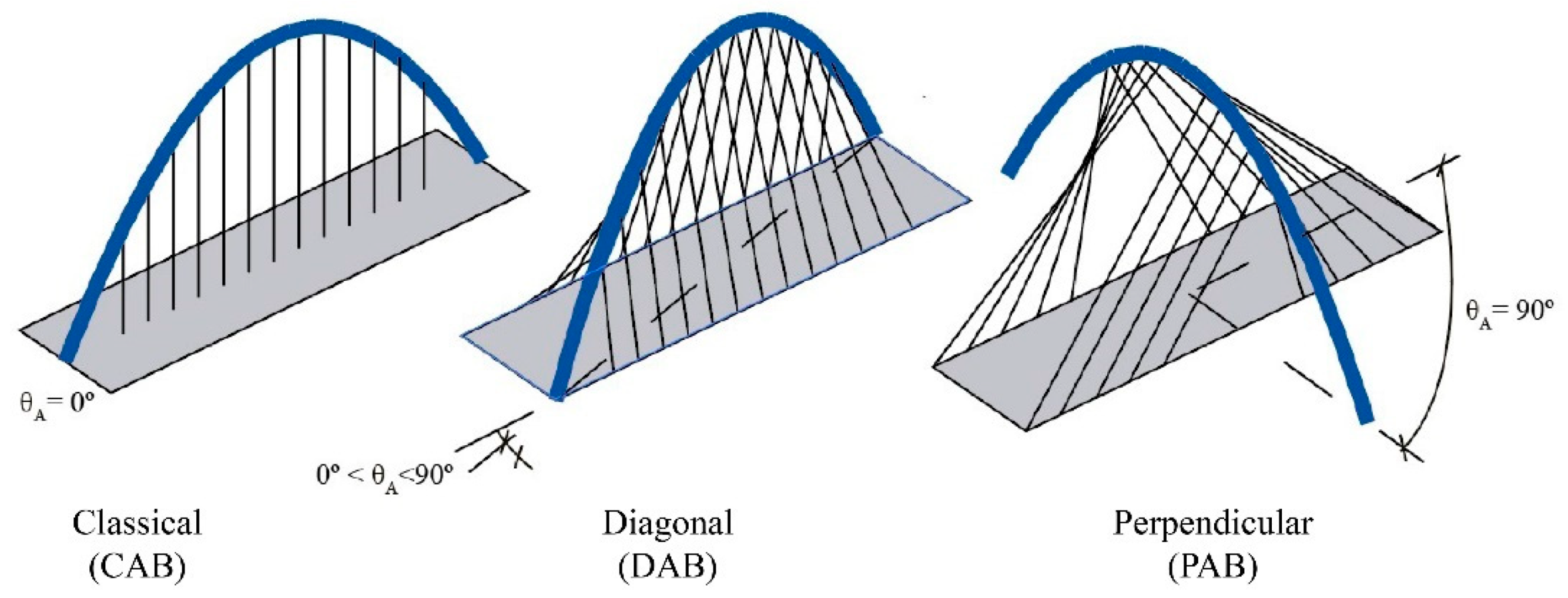
1.1. The Spatial Arch Bridge
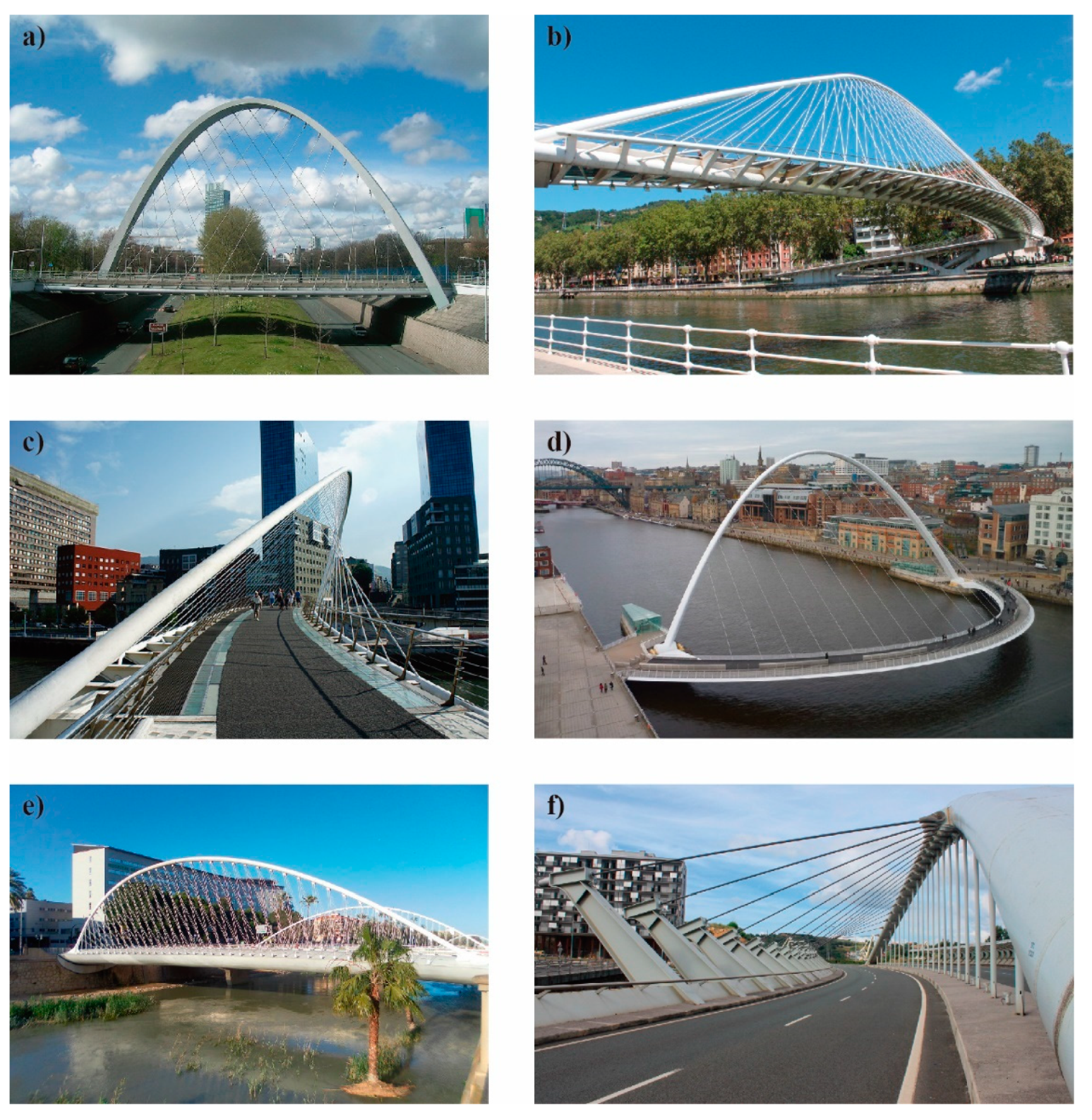
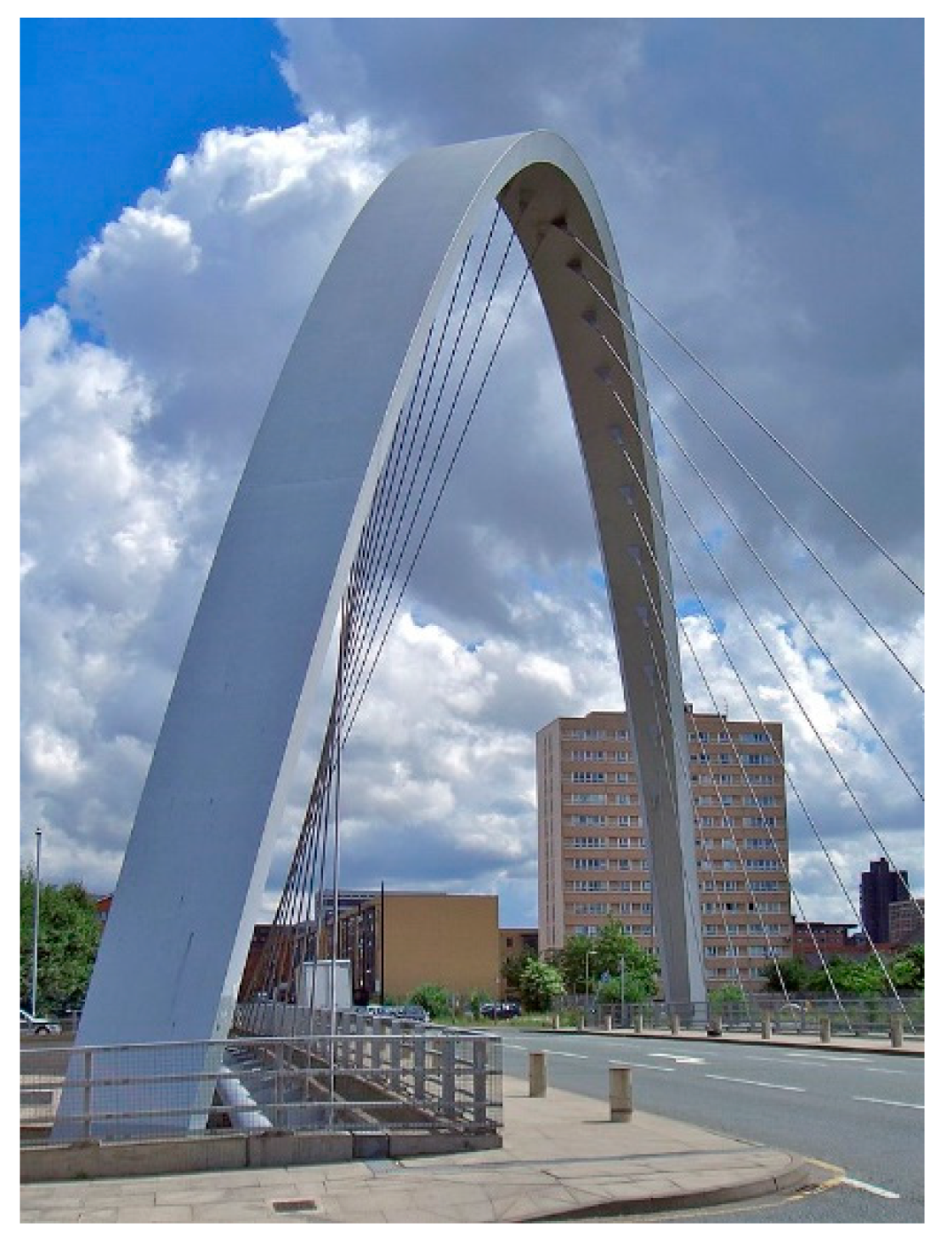
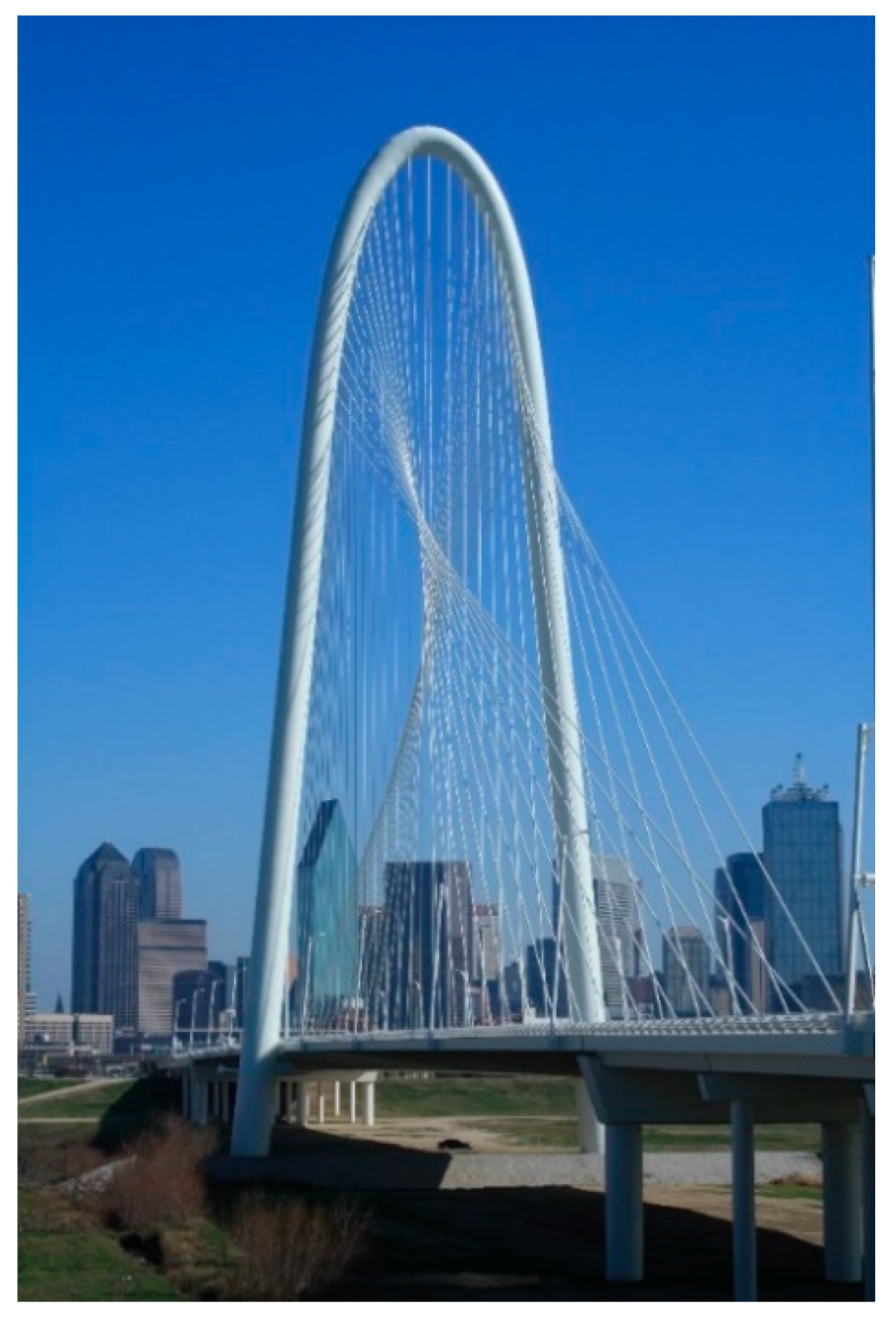
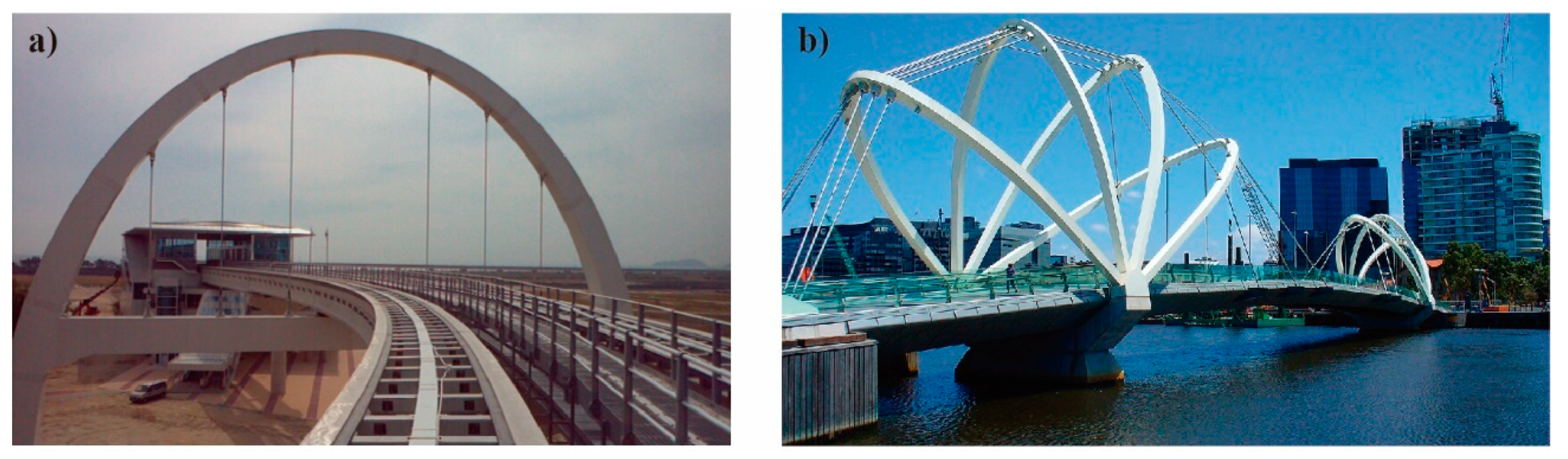
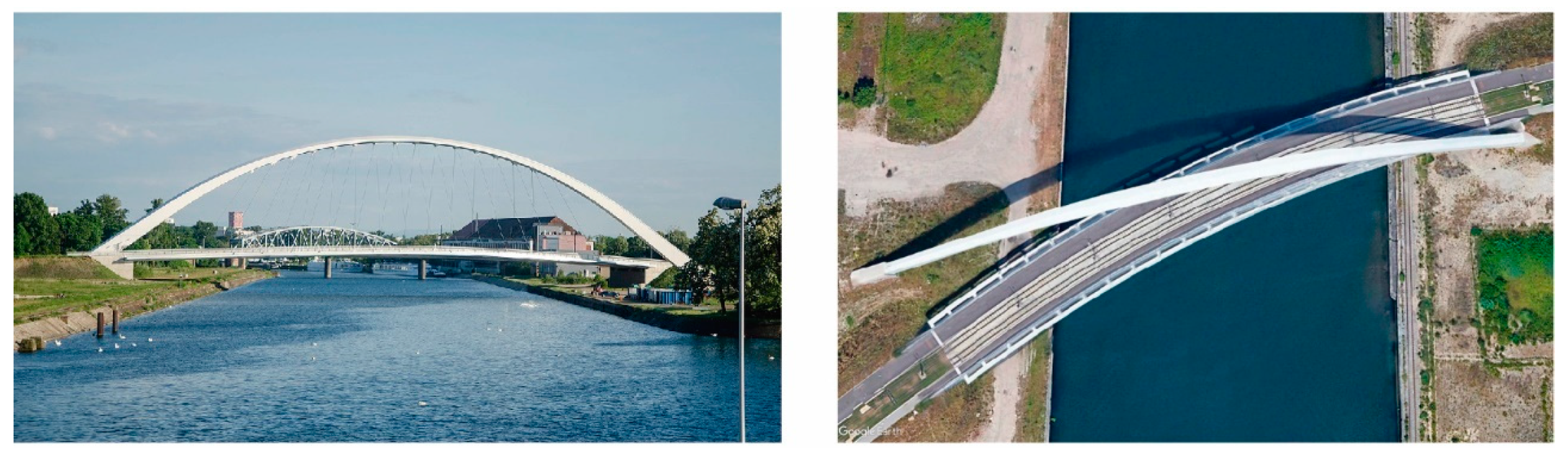
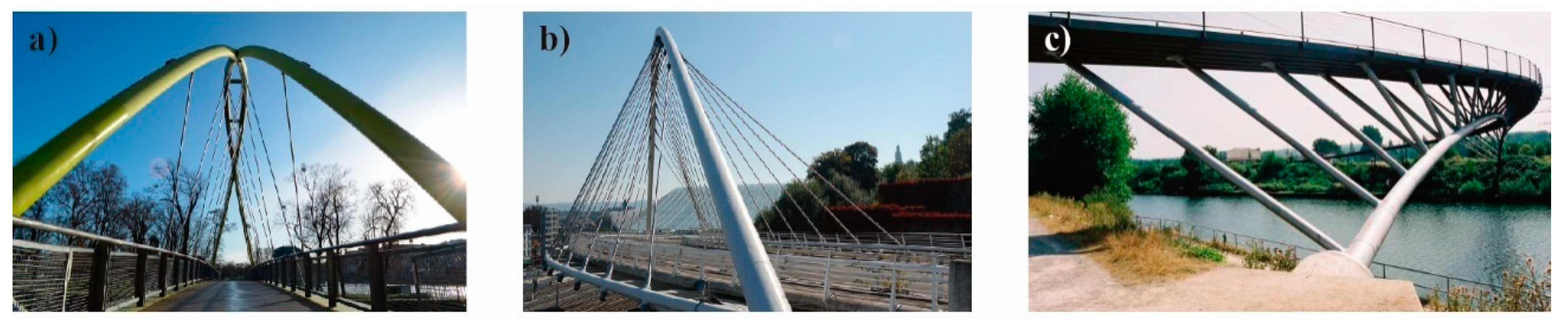
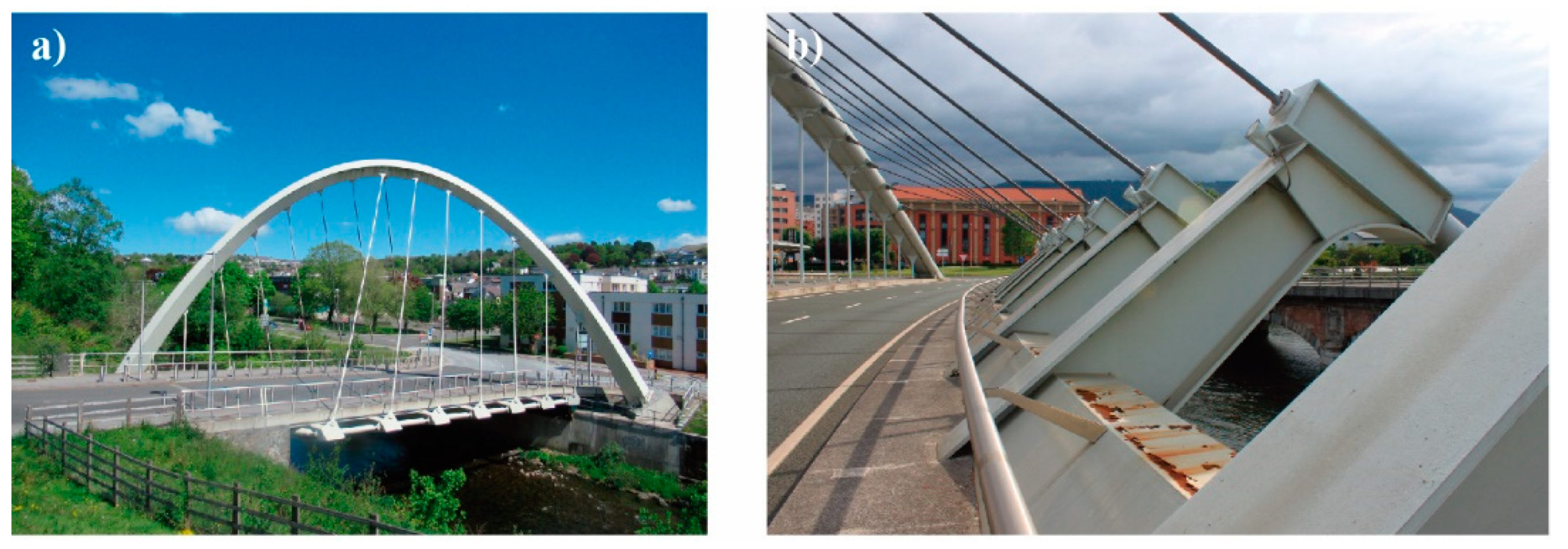
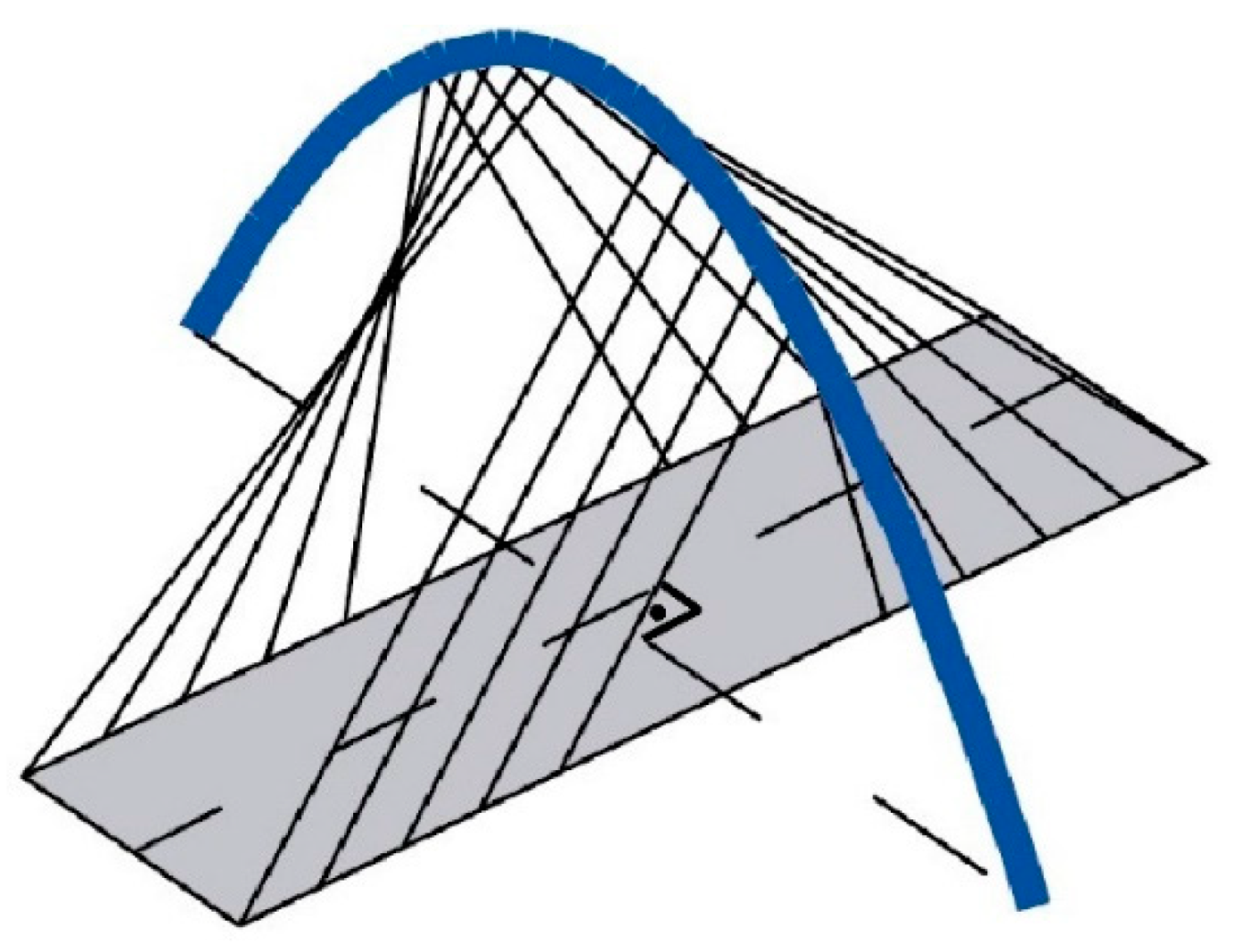
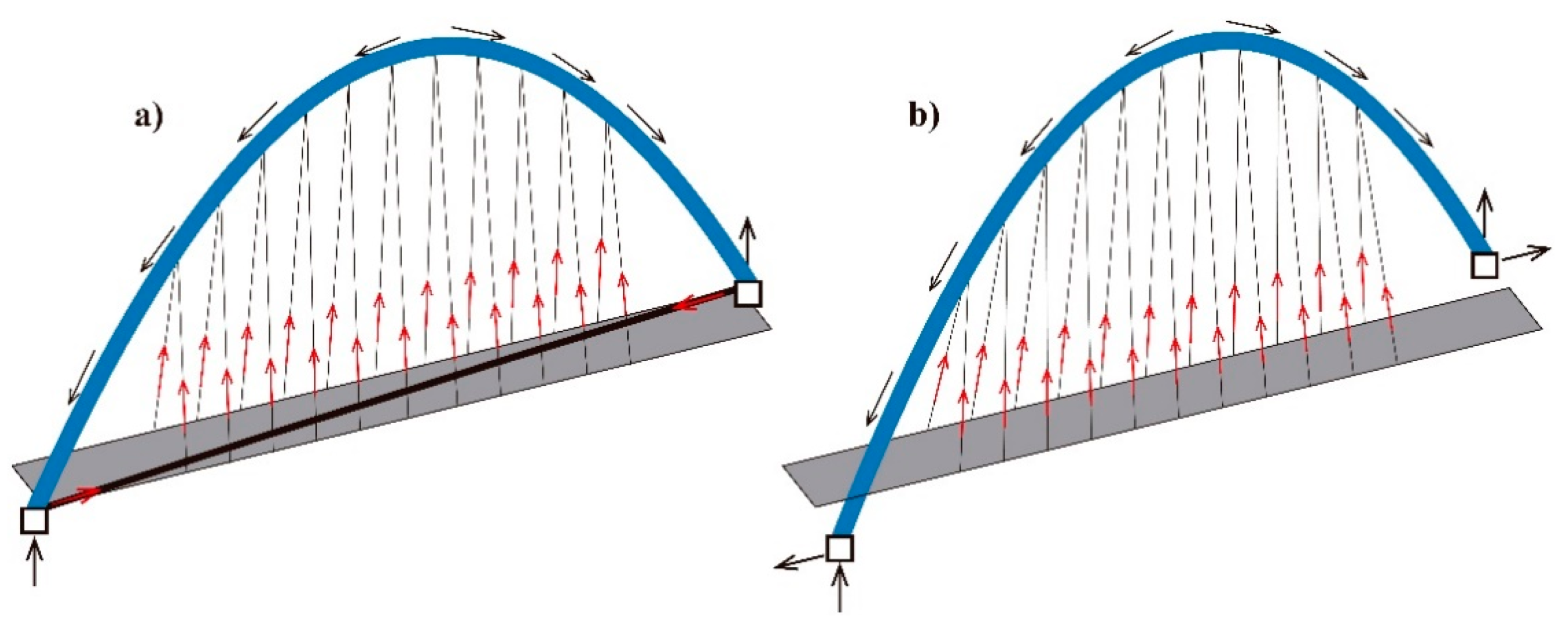
1.2. The Diagonal Arch bridge
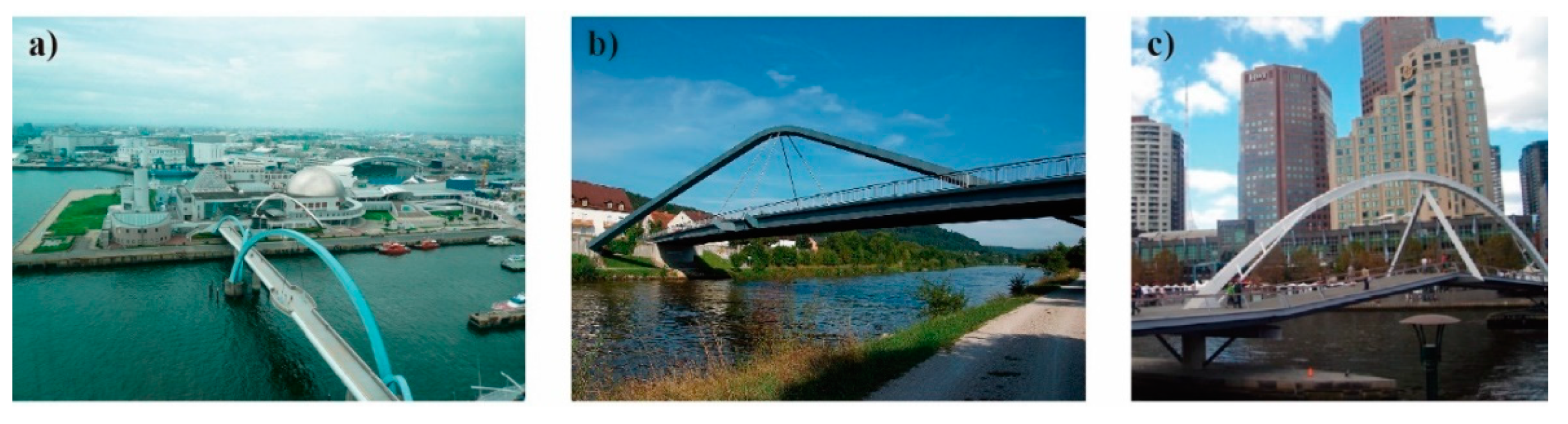
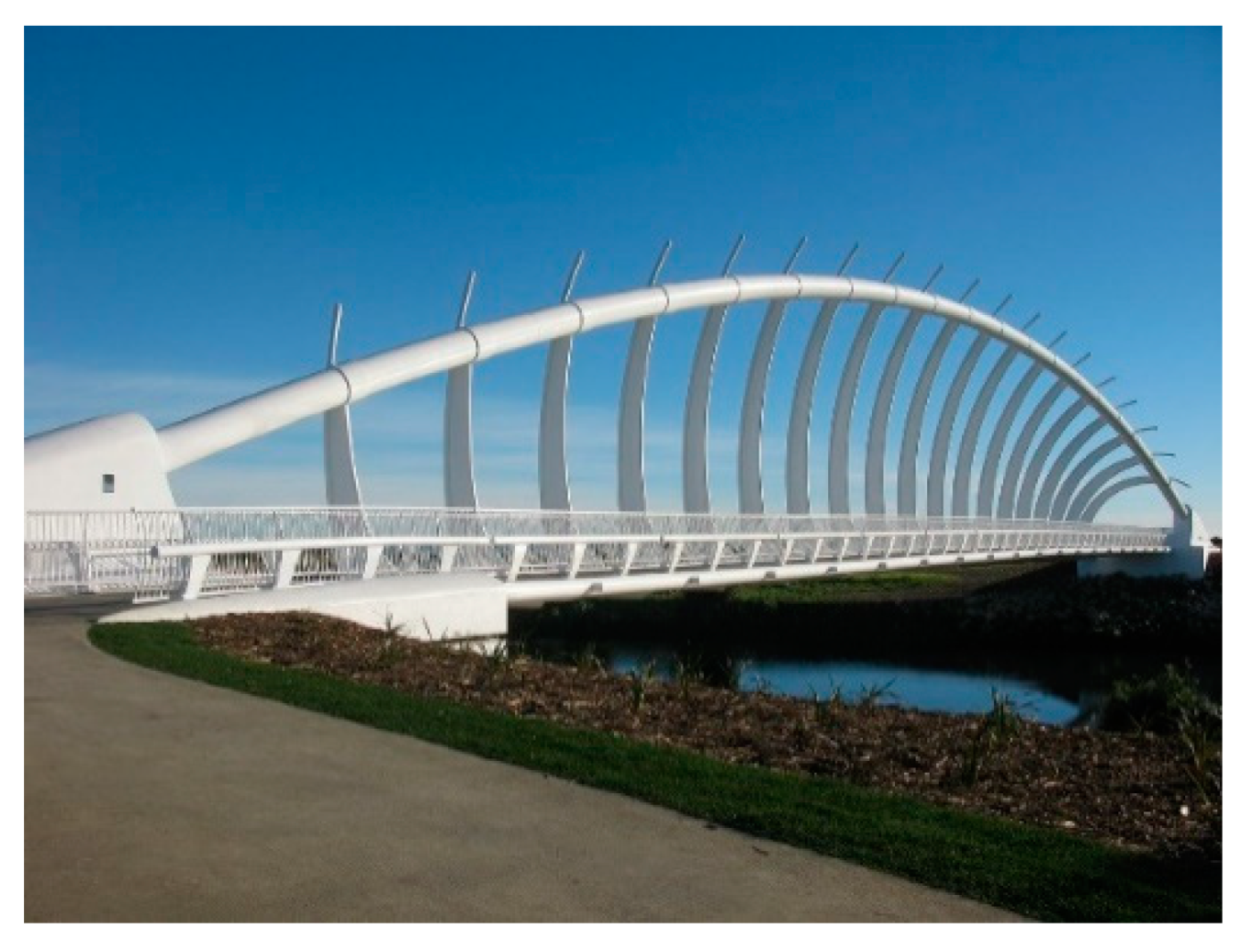
1.3. The Perpendicular Arch bridge
1.4. Recent Studies
1.5. Paper Structure
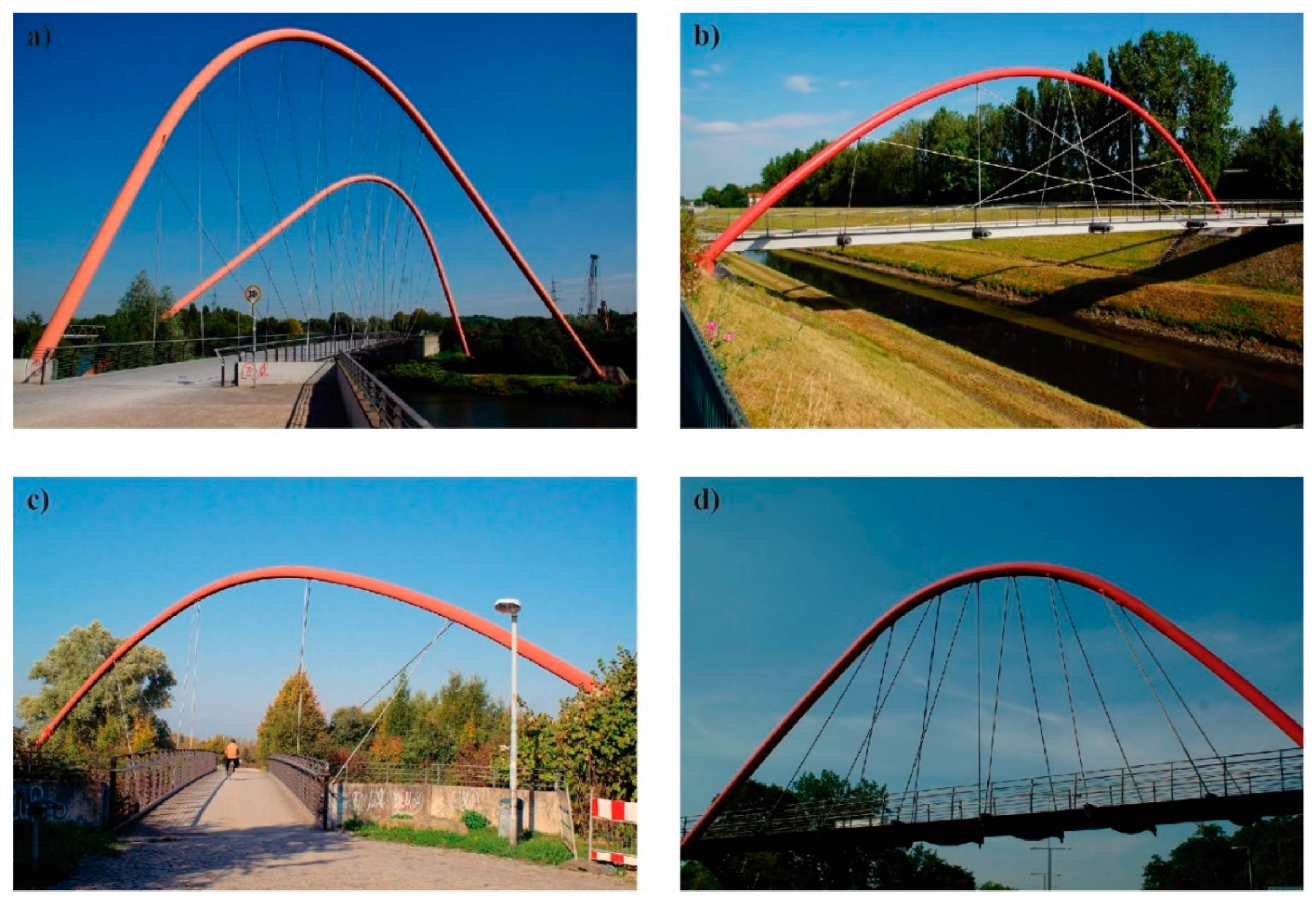
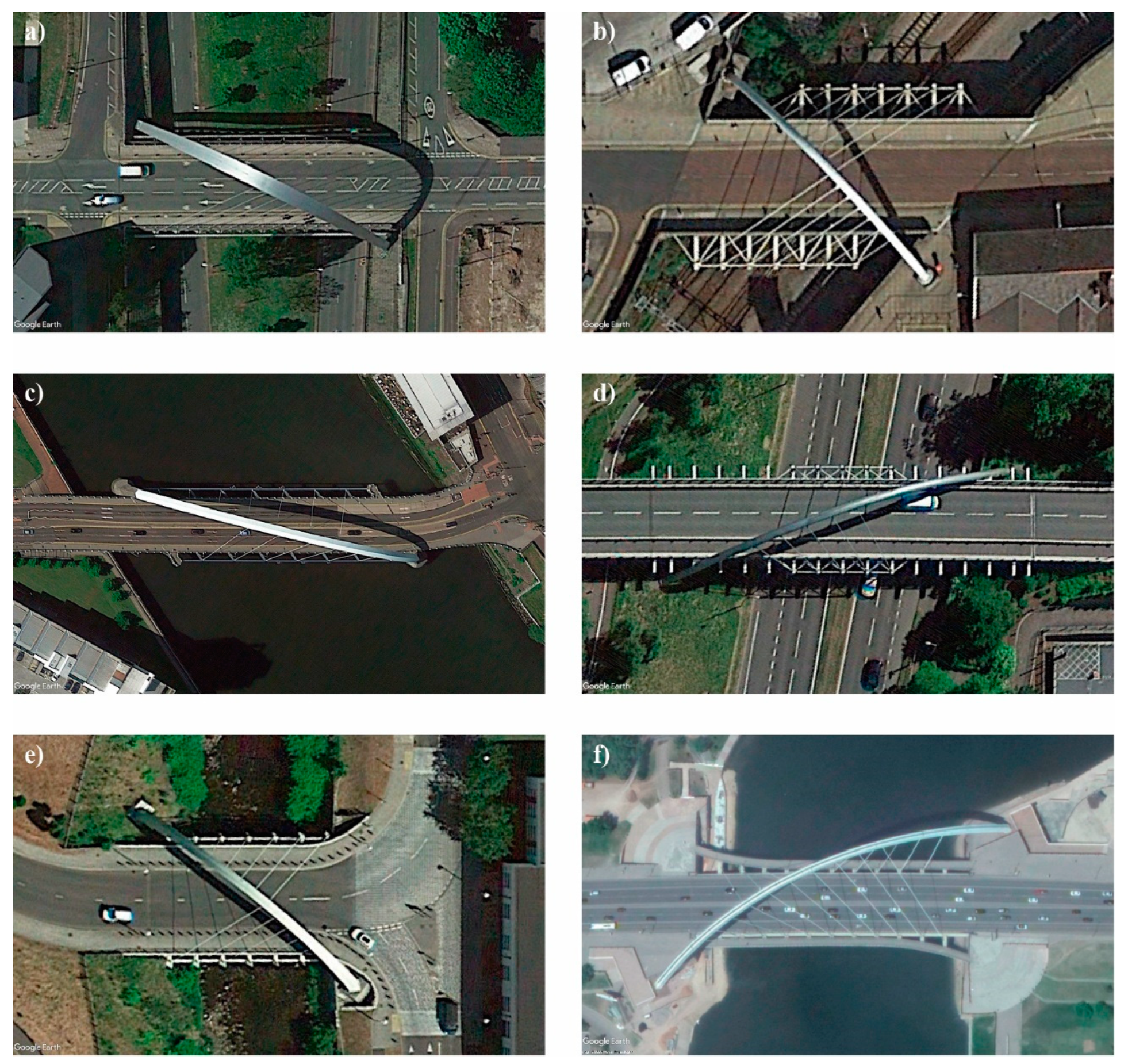
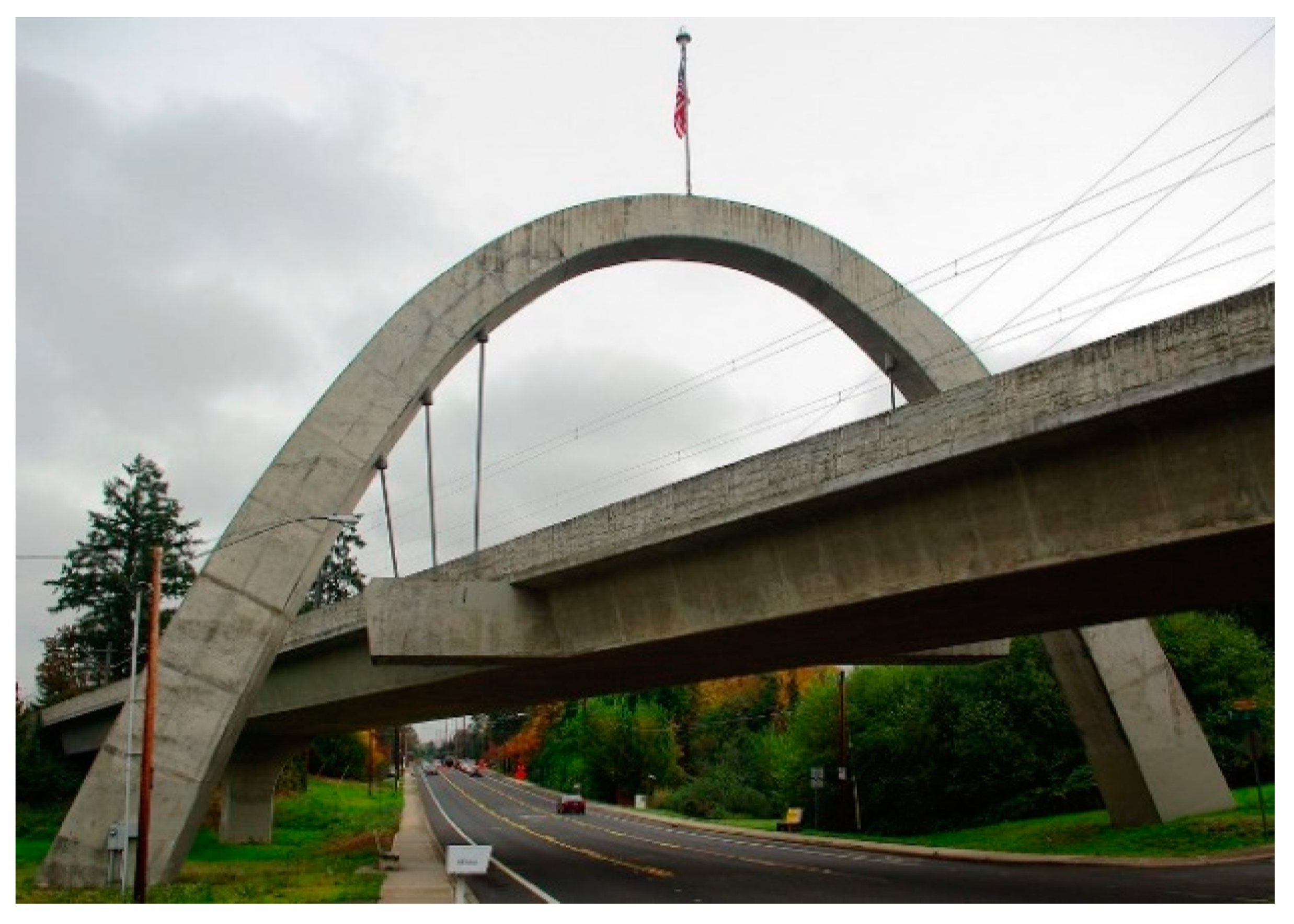
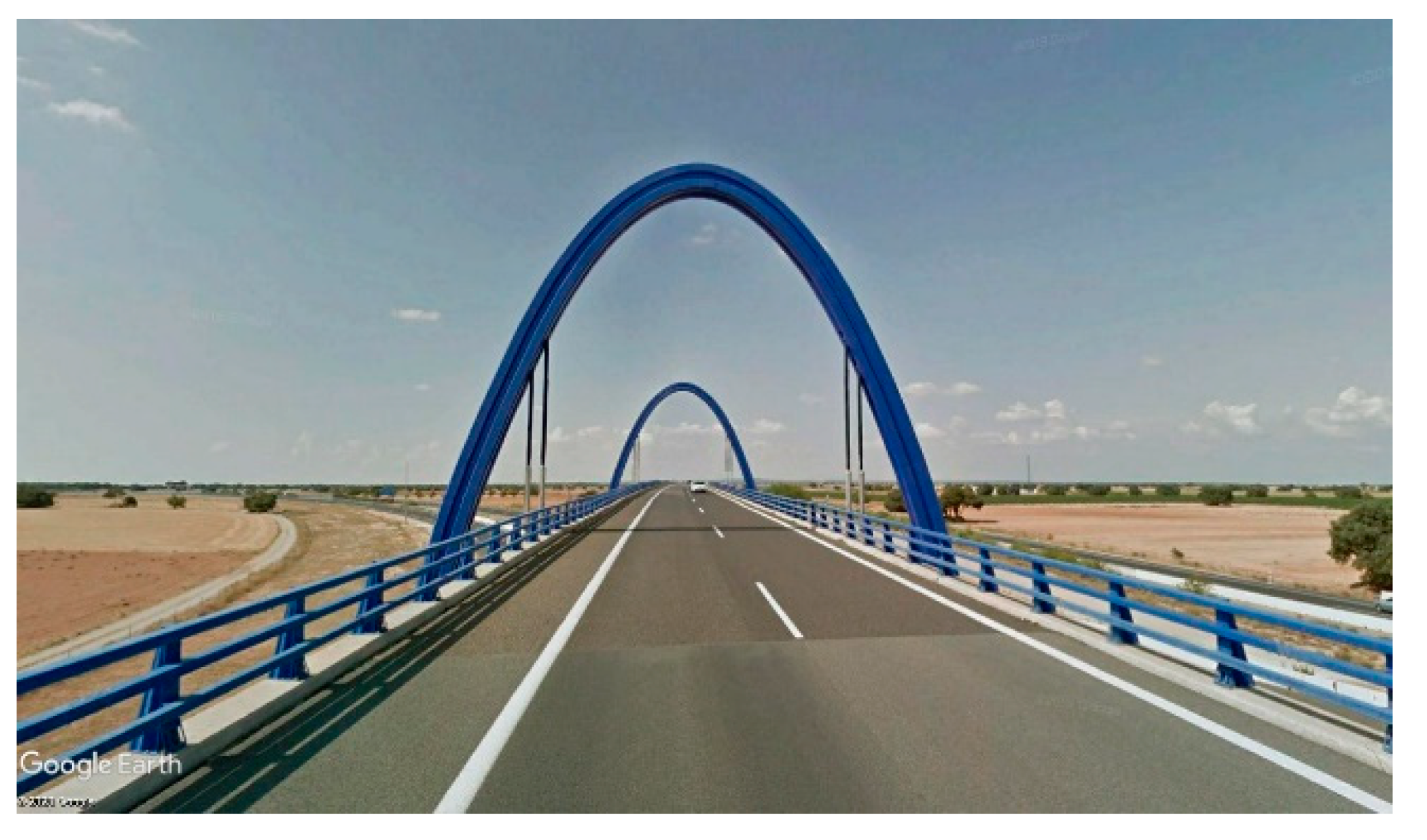
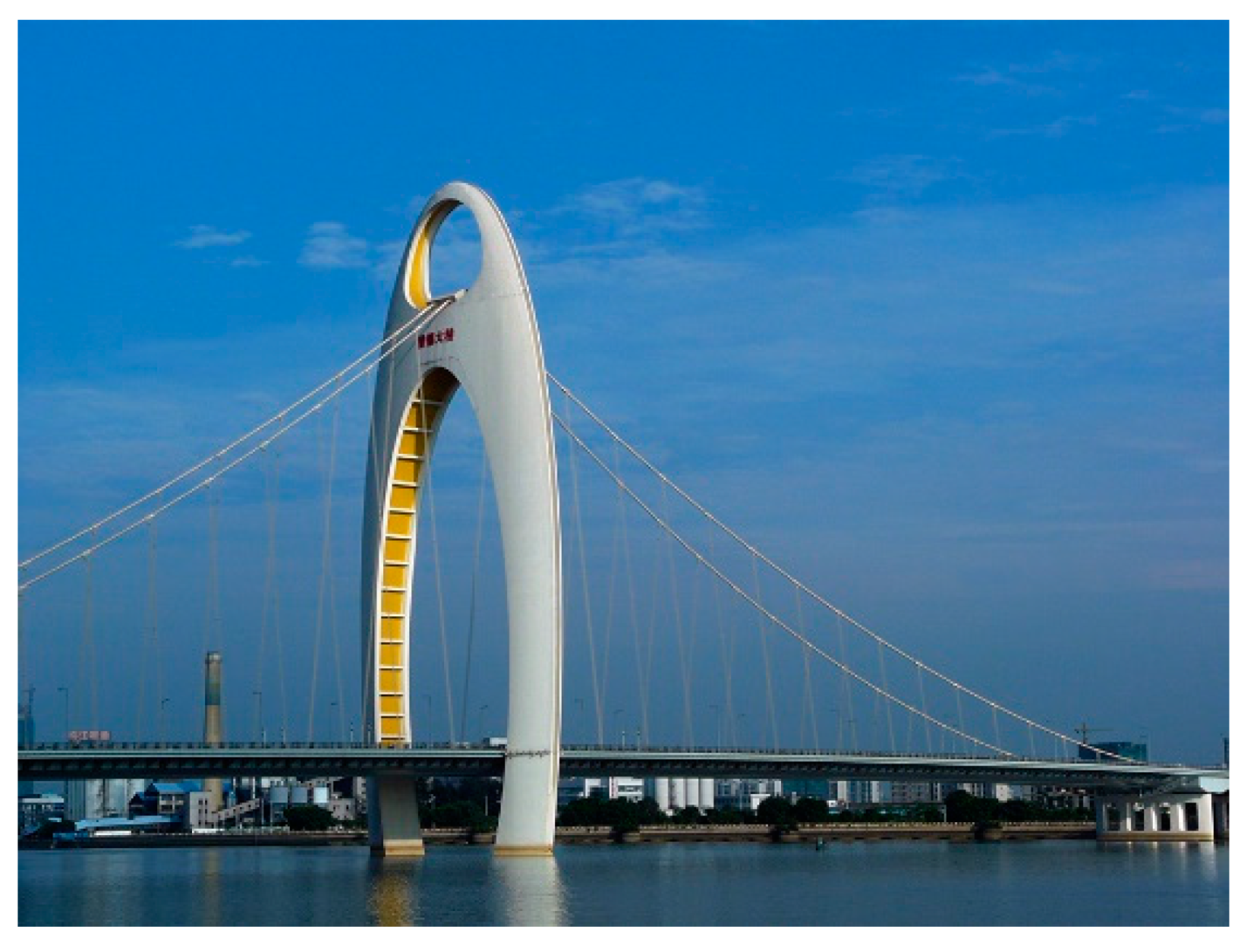
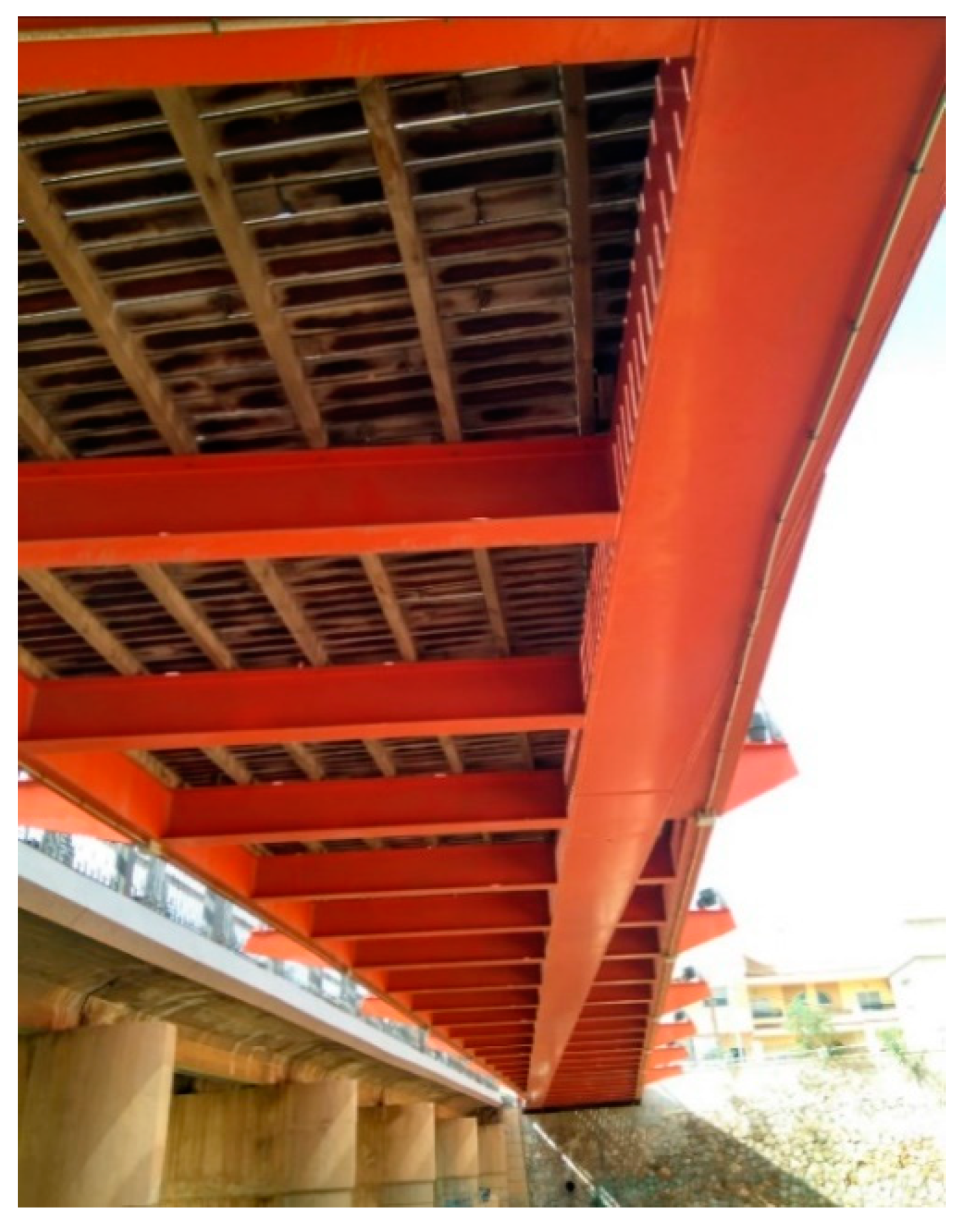
2. Brief Historical Review: Examples and Evolution
3. Definition and Typological Classification
3.1. Definition
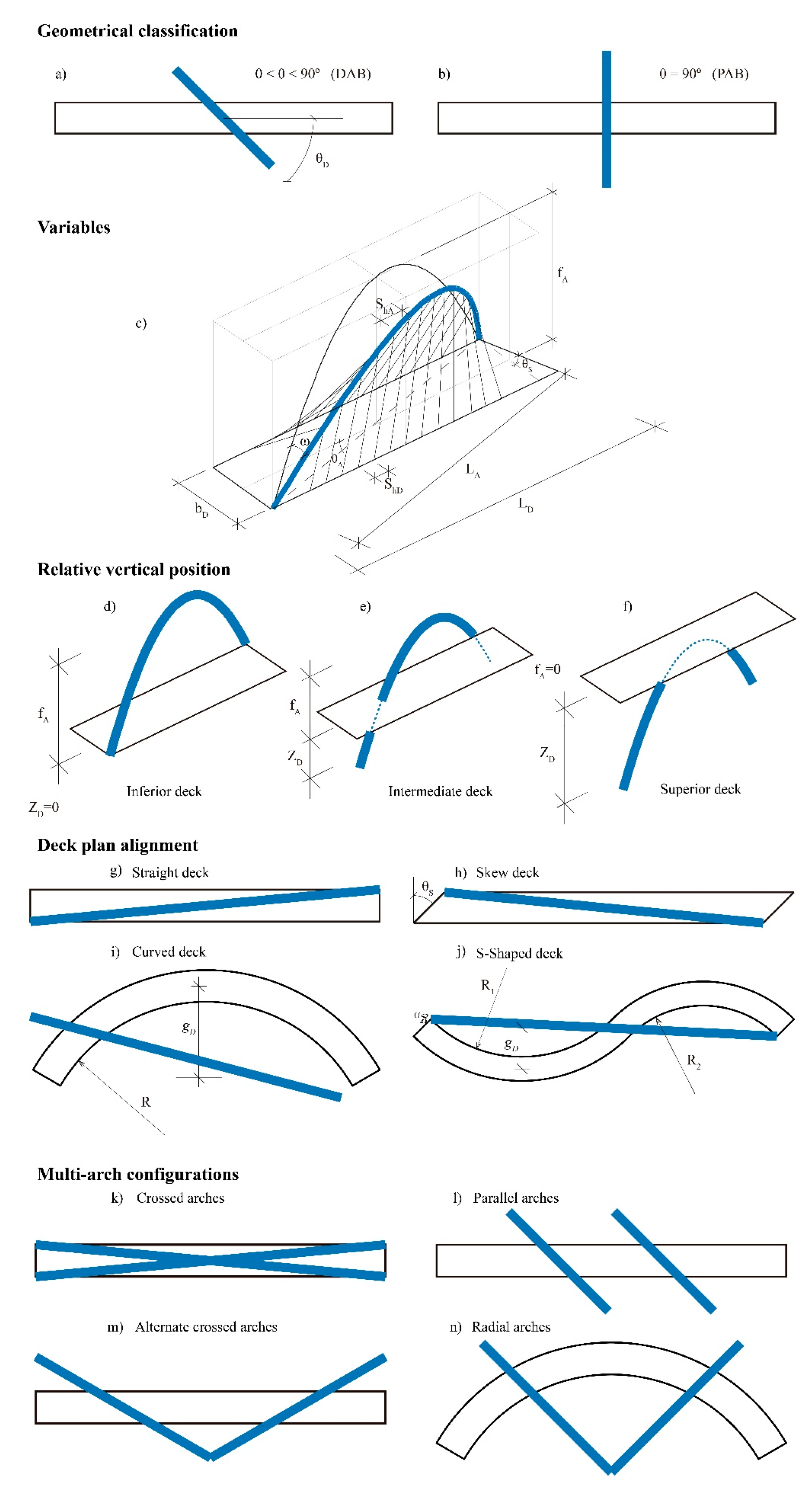
3.2. Main Geometrical Variables
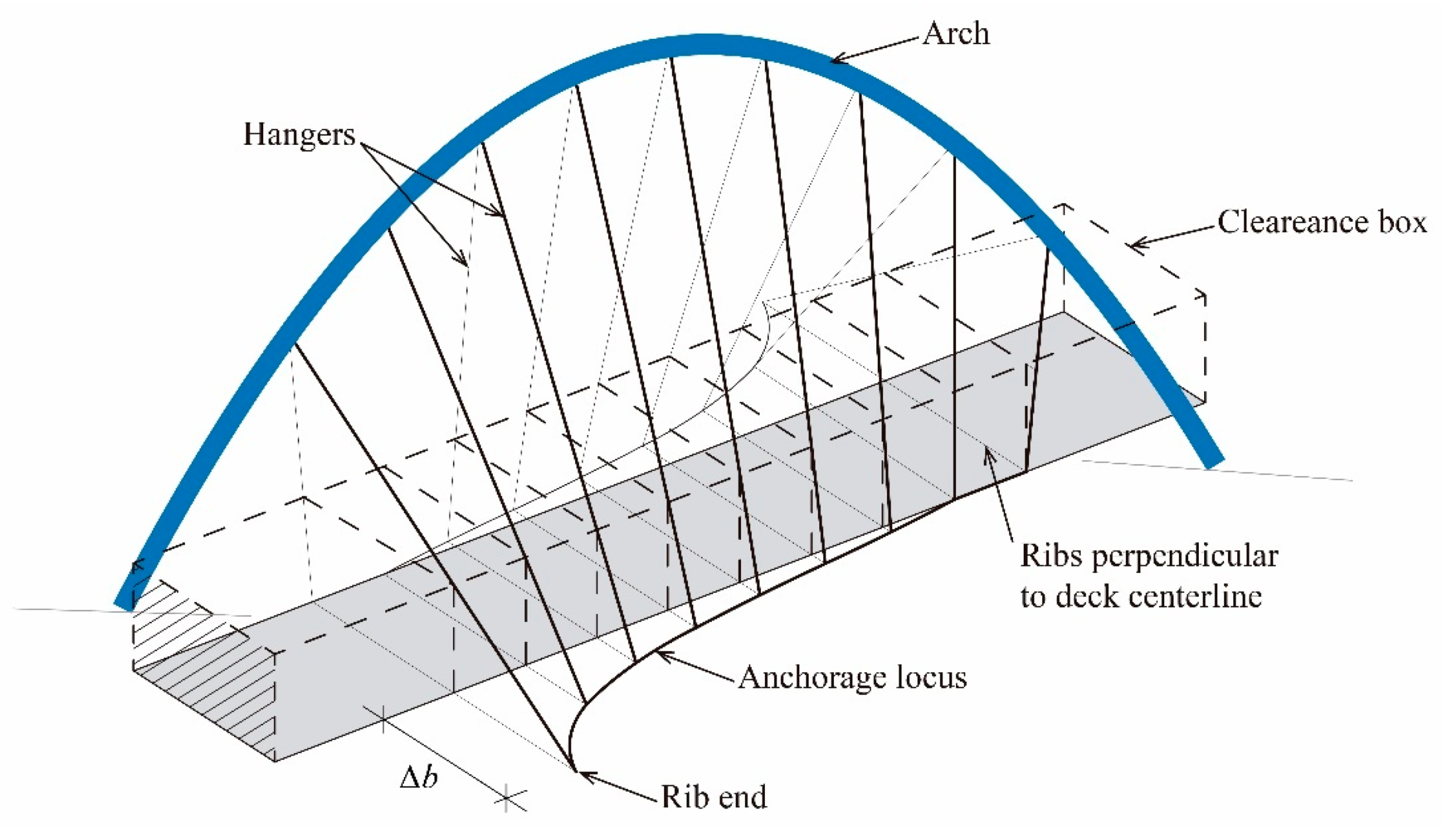
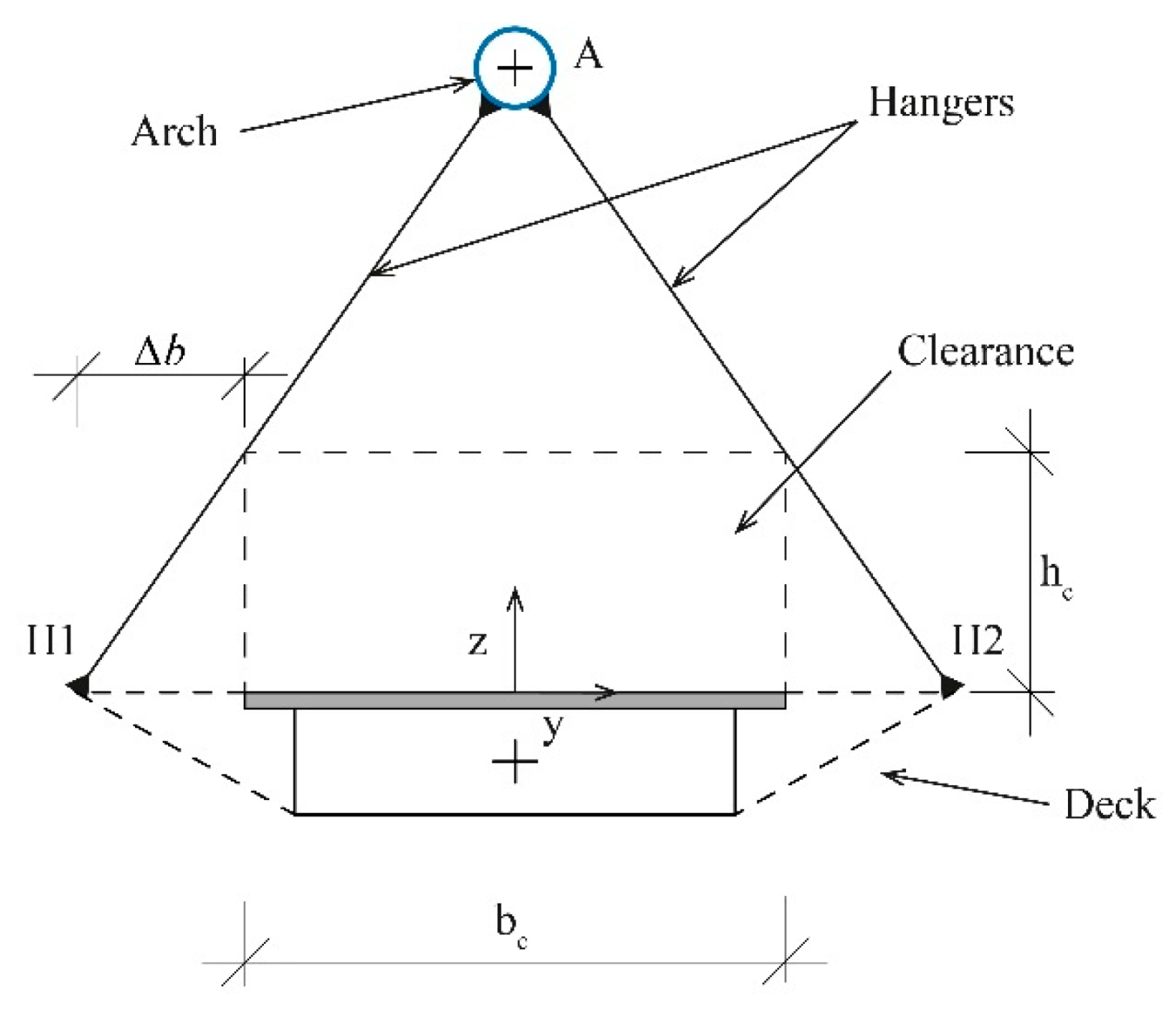
- LA: Span of the arch, defined as the length between the springs of the arch.
- fA: Rise of the arch in the vertical plane. Despite the plan of the arch is diagonal, its elevation has a vertex at the crown of the arch (0, fA) and passes through its springs (-LA/2, 0) and (LA/2, 0).
- θA: Arch rotation angle, or angle between the horizontal projection of the centerline of the arch and the deck. θA = atan(b/L) when the arch crosses the deck diagonally.
- ω: Inclination of the plan of the arch with respect to the vertical plane.
- LD: Span of the deck.
- bD: Width of the deck.
- θS: Angle of skew of the deck. Angle between the axis of the deck and the line of supports.
- gD: Horizontal sagitta of the horizontally curved deck (Figure 21). For S-shaped decks, gD changes its sign when the curvature of the deck changes.
- R: Radius in the deck axis, for curved and S-shaped decks (Figure 21).
- shD: Distance between hangers measured in the deck plan.
- shA: Distance between hangers measured over the developed length of the arch.
- ZD = 0, inferior deck.
- fA ≥ ZD > 0, intermediate deck.
- ZD ≥ fA, superior deck.
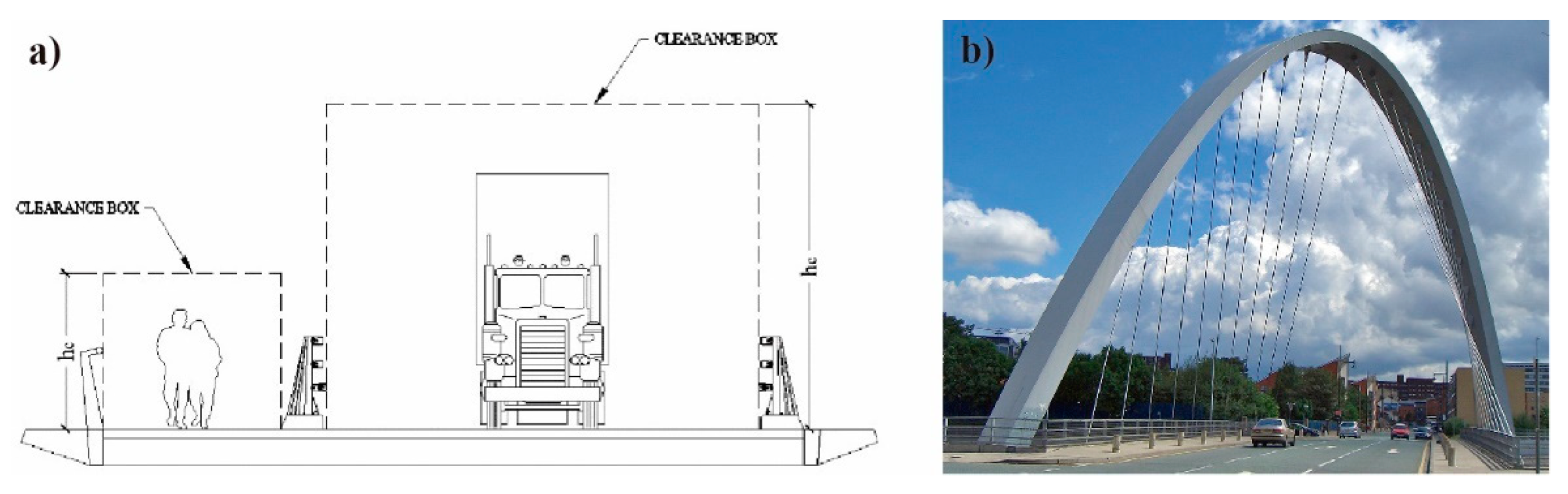
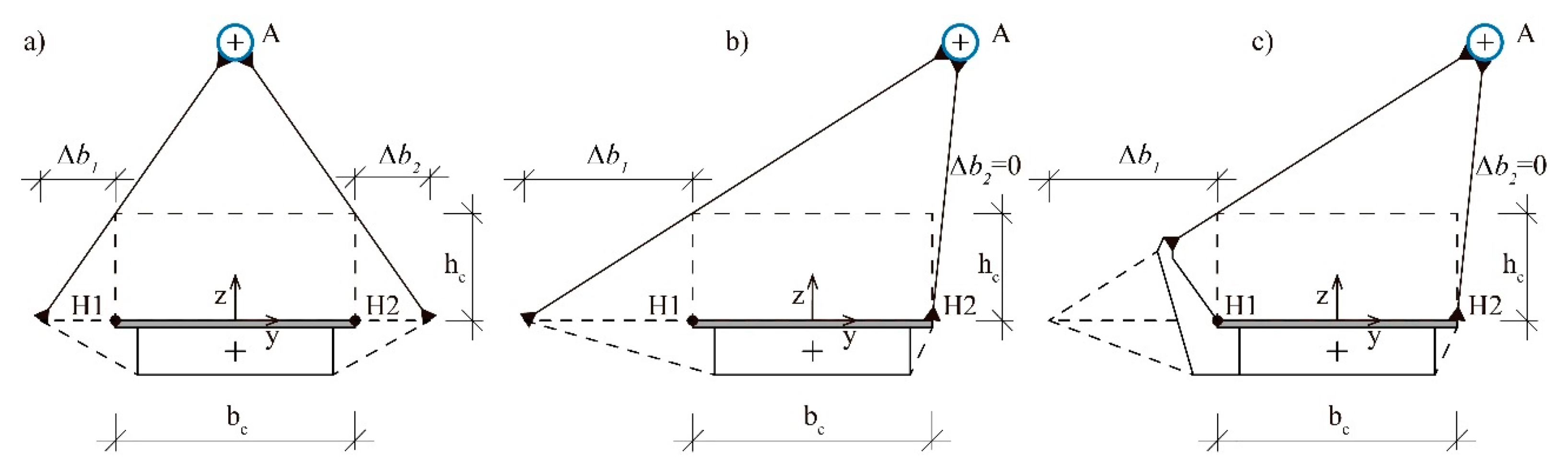
3.3. Clearance Requirements
3.4. Tied Diagonal Arch Bridge
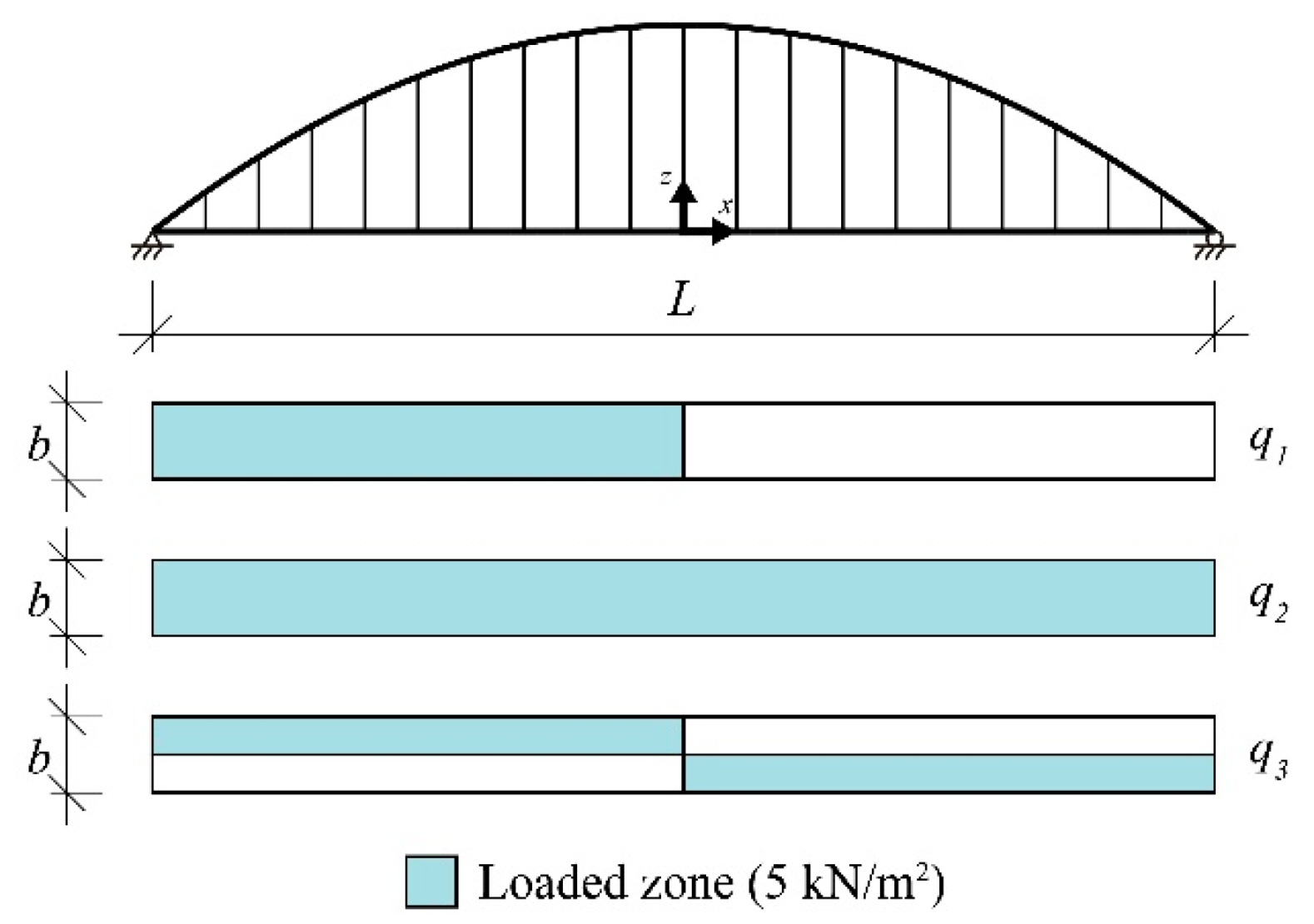
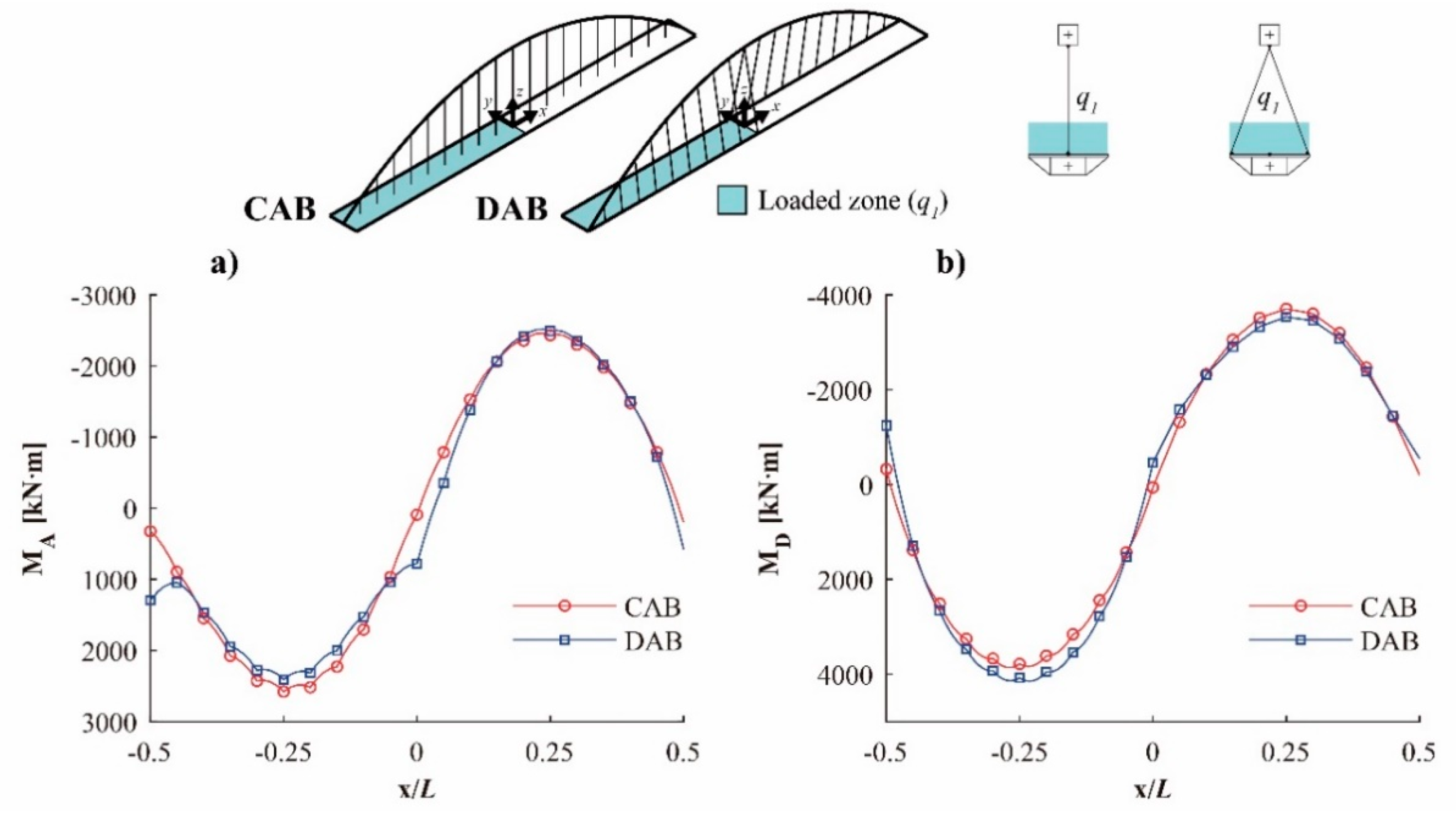
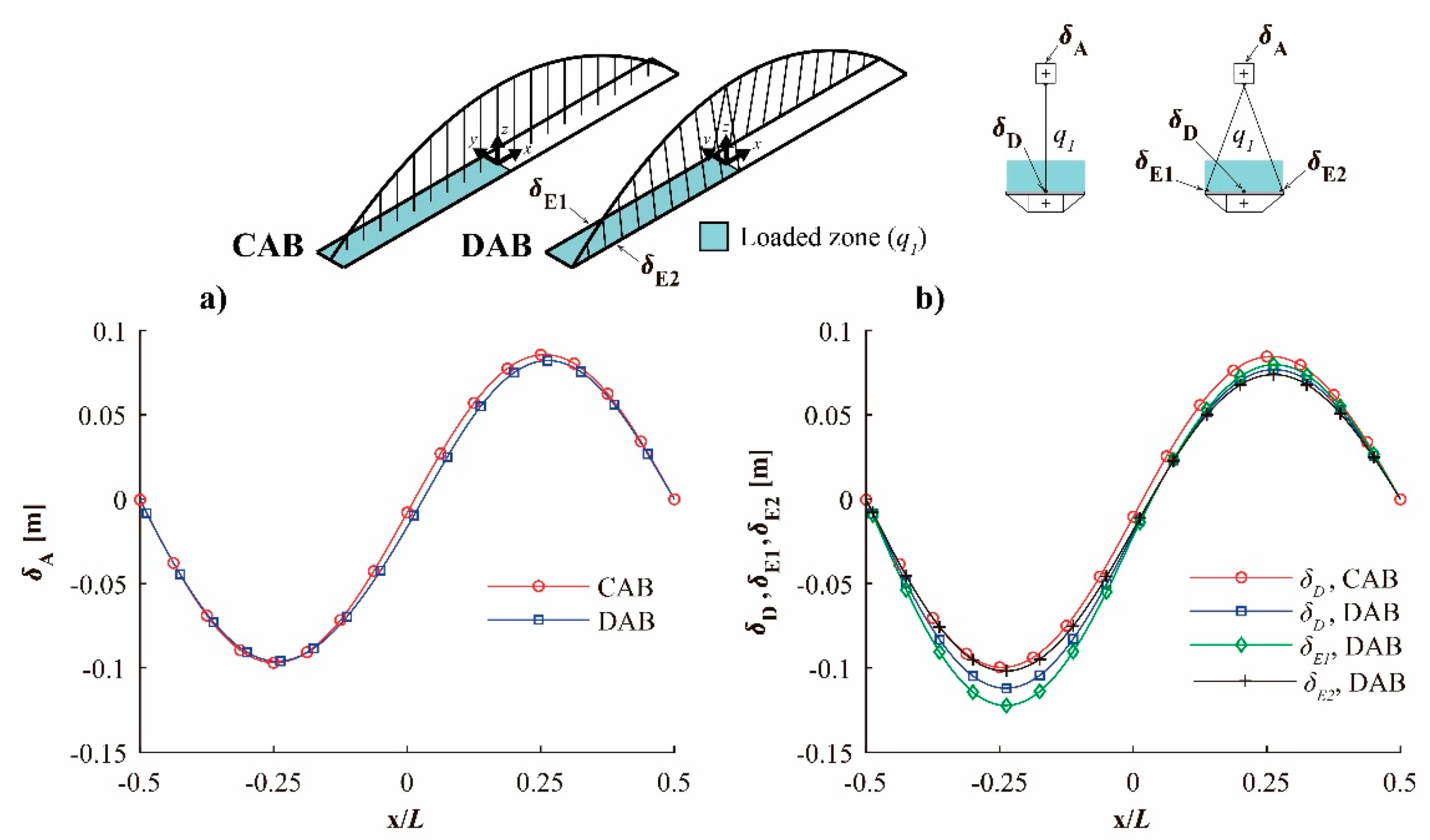
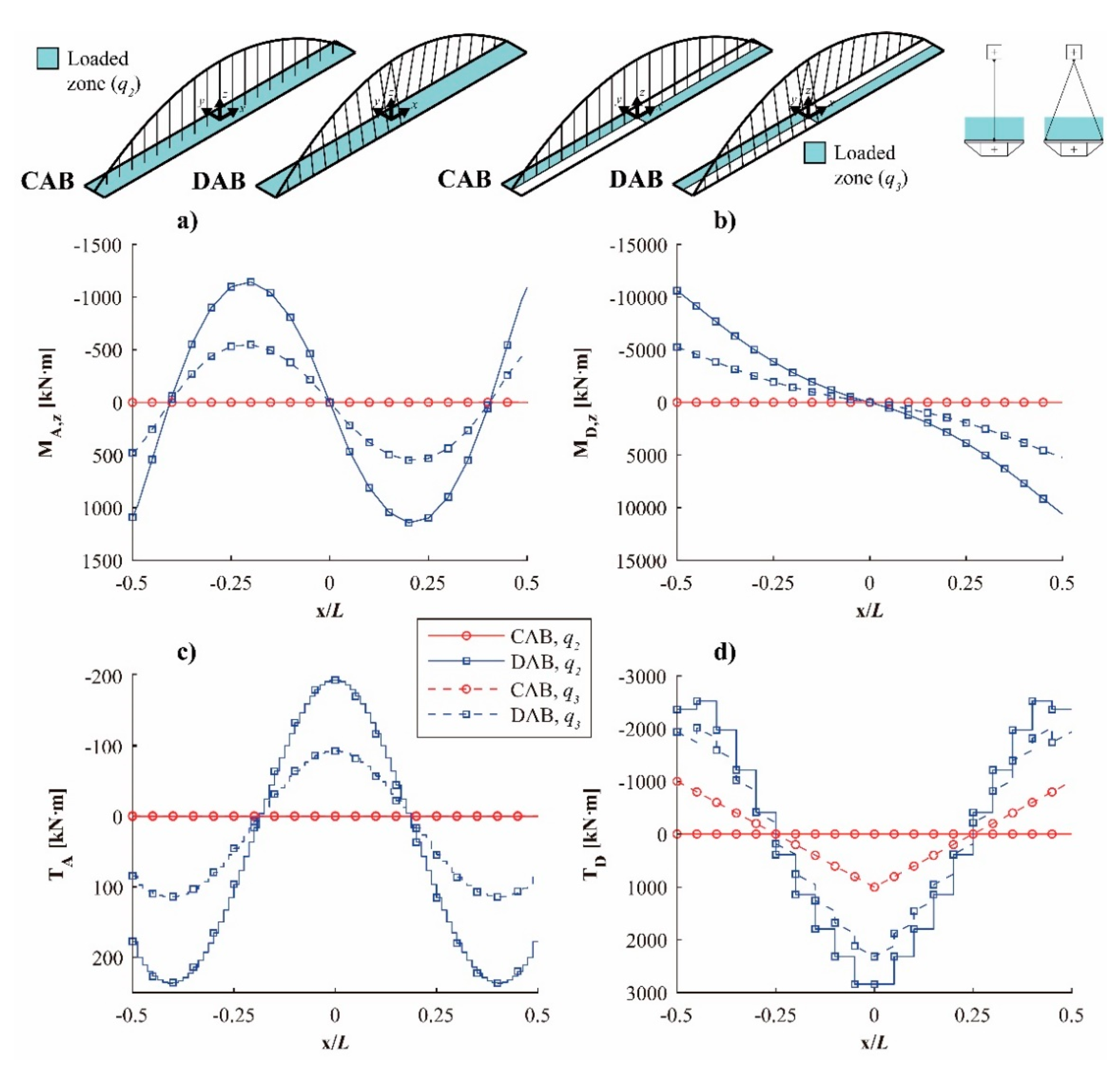
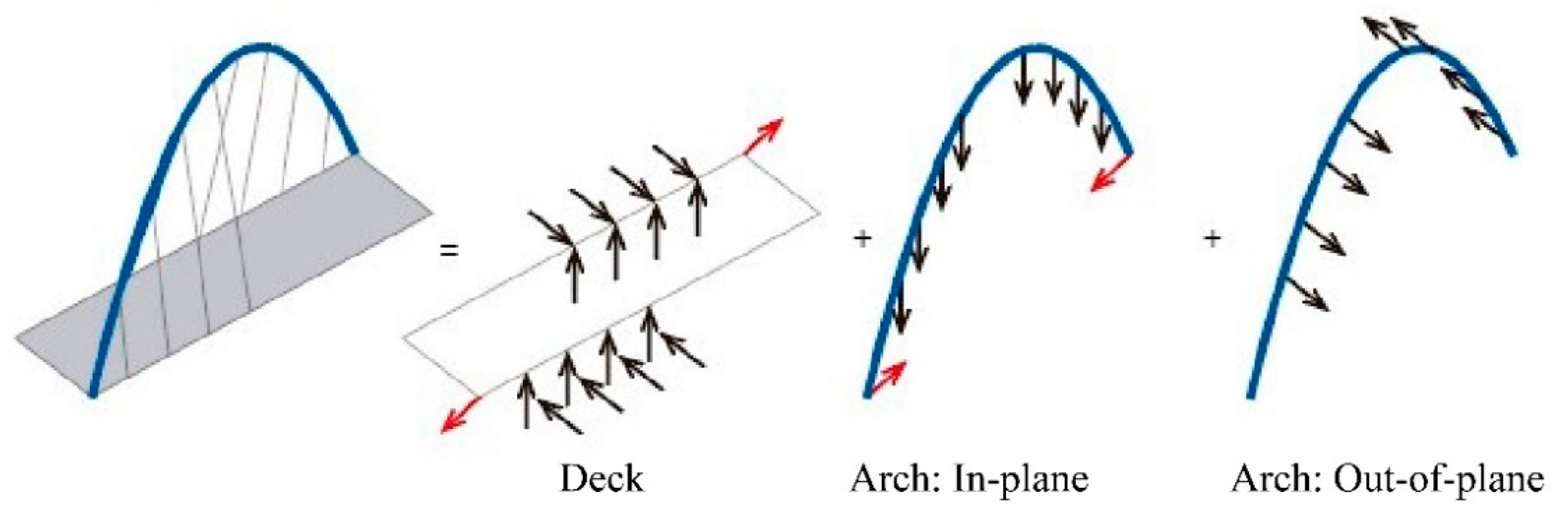
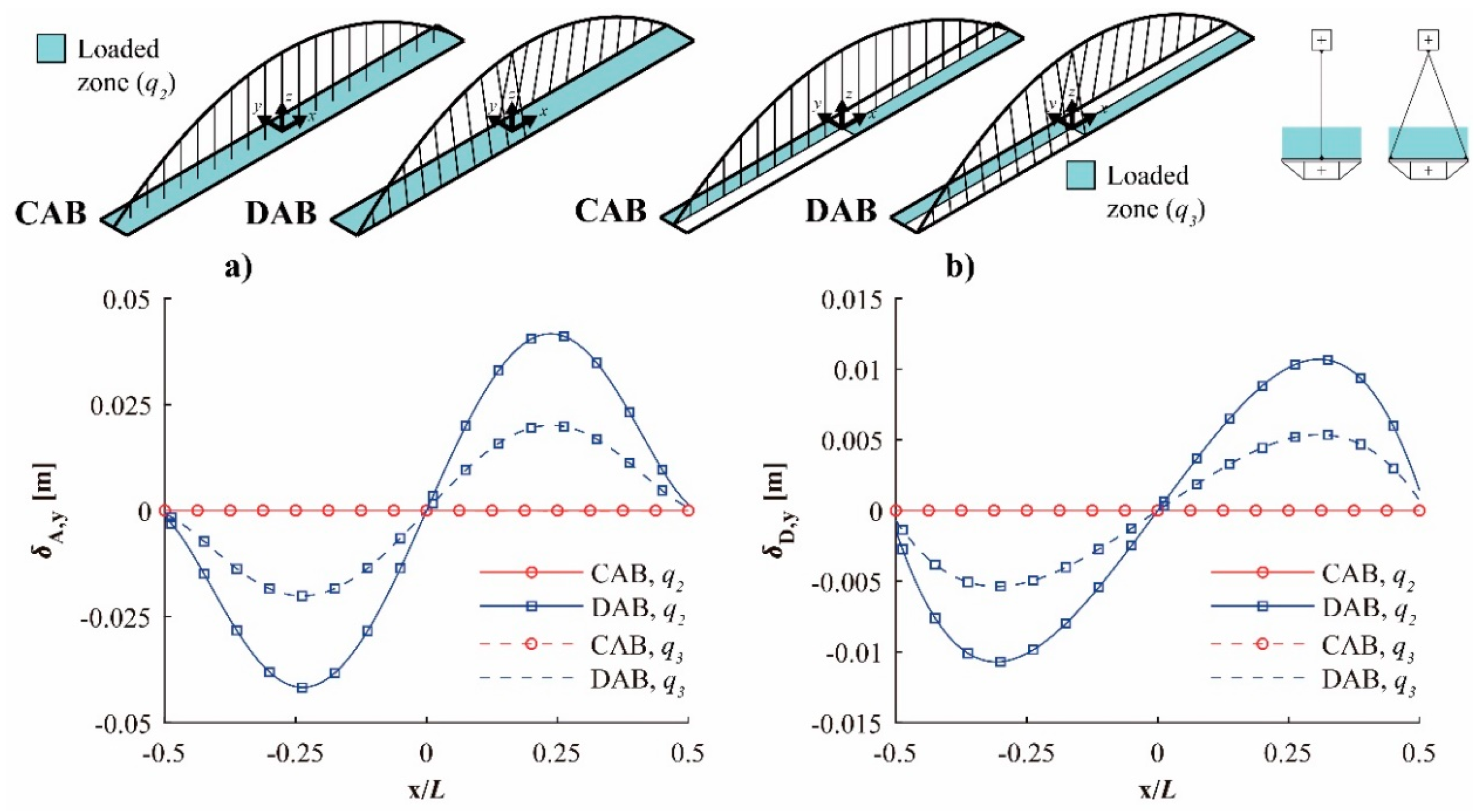
4. Structural Behavior
- The self-weight (SW) of the bridge, evaluated for a specific weight of 78.5 kN/m3, and a dead load (DL), with a value of 3 kN/m2.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jorquera-Lucerga, J.J. A Study on Structural Behaviour of Spatial Arch Bridges (Estudio del Comportamiento Resistente de los Puentes Arco Espaciales). Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2007. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento, M. Structural Behaviour and Design Criteria of Spatial Arch Bridges. Ph.D. Thesis, Polytechnic University of Catalonia, Barcelona, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- García-Guerrero, J.M. The Spatial Arch Bridge as a Typological Evolution (El Puente Arco Espacial como una Evolución Tipológica). Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Cartagena, Cartagena, Spain, 2018. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Hudecek, M. Structural Behaviour of Spatial Arch Bridges. Ph.D. Thesis, Calgary University, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vande Walle, P. Skew Placement of Arches for Single Span Road Bridges. Master’s Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, N.; Wilson, I. The Hulme Arch Bridge, Manchester. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Civ. Eng. 1999, 132, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, L.B. A critical analysis of the Hulme arch bridge, Manchester. In Proceedings of the Bridge Engineering 2 Conference 2009, Bath, UK, 16–23 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Hu, H.; Li, J. Axis optimisation of arch-shaped pylons for high-speed railway cable-stayed bridges. Eng. Struct. 2021, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.-L.; Kao, C.-S.; Kou, C.-H.; Tsai, J.-L.; Yang, G. Stability Analysis of Special-Shape Arch Bridge. Tamkang J. Sci. Eng. 2010, 13, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, X.N.; Gui, X. 3D Finite Element Analysis of Single Span Special-Shape Arch Bridge with Diagonal Crossing Arch Rib and Curved Girder. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 63, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z. Model Test Study on a Single Diagonal-Span Arch Bridge with Curved Beam. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2010, 44, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.-J.; Han, L.-Z. Analysis of Geometric Nonlinearity of Special-Shaped Arch Bridges. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fadón Martínez, S.; Herrero-Beneitez, J.E.; Bajo-Pavía, C.; Loscos-Areoso, P. Tablero suspendido de arcos en el enlace de la roda AP36. In Proceedings of the IV Congreso de la Asociación Científico-Técnica del Hormigón Estructural—Congreso Internacional de Estructuras, Valencia, Spain, 24–27 November 2008. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Tarquis-Alfonso, F.; Hue-Ibargüen, P. Puente Juscelino Kubistchek (JK). In Proceedings of the III Congreso de ACHE de puentes y estructuras, Zaragoza, Spain, 14–17 November 2005. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Baus, U.; Slaich, M. Footbridges: Construction, Design, History; Birkhäuser Verlag AG: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Romo, J. Managing constraints in footbridge design: Conceptual design and context. In Proceedings of the Footbridge 2014, 5th International Conference, London, UK, 16–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt, F. Bridges (Brücken); The Architectural Press: London, UK, 1982; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, H. Cable-Stayed Bridges: 40 Years of Experience Worldwide; Wilhelm Ernst & Sohn: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lebet, J.P.; Hirt, M.A. Steel Bridges; EPFL Press: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 461–488. ISBN 9781466572973. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN). Eurocode 1: Actions on Structures—Part. 2: Traffic Loads on Bridges; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Computers and Structures, Inc. Analysis Reference Manual for SAP2000® v 16; CSI: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer Tension Members. Available online: https://www.pfeifer.de/emag/PFEIFER-Zugglieder/index (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN). Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures—Part. 1-11: Design of Structures with Tension Components; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- García-Guerrero, J.M.; Jorquera-Lucerga, J.J. Effect of Stiff Hangers on the Longitudinal Structural Behavior of Tied-Arch Bridges. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Guerrero, J.M.; Jorquera-Lucerga, J.J. Influence of stiffened hangers on the structural behavior of all-steel tied-arch bridges. Steel Compos. Struct. 2019, 32, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Guerrero, J.M.; Jorquera-Lucerga, J.J. Improving the Structural Behavior of Tied-Arch Bridges by Doubling the Set of Hangers. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





















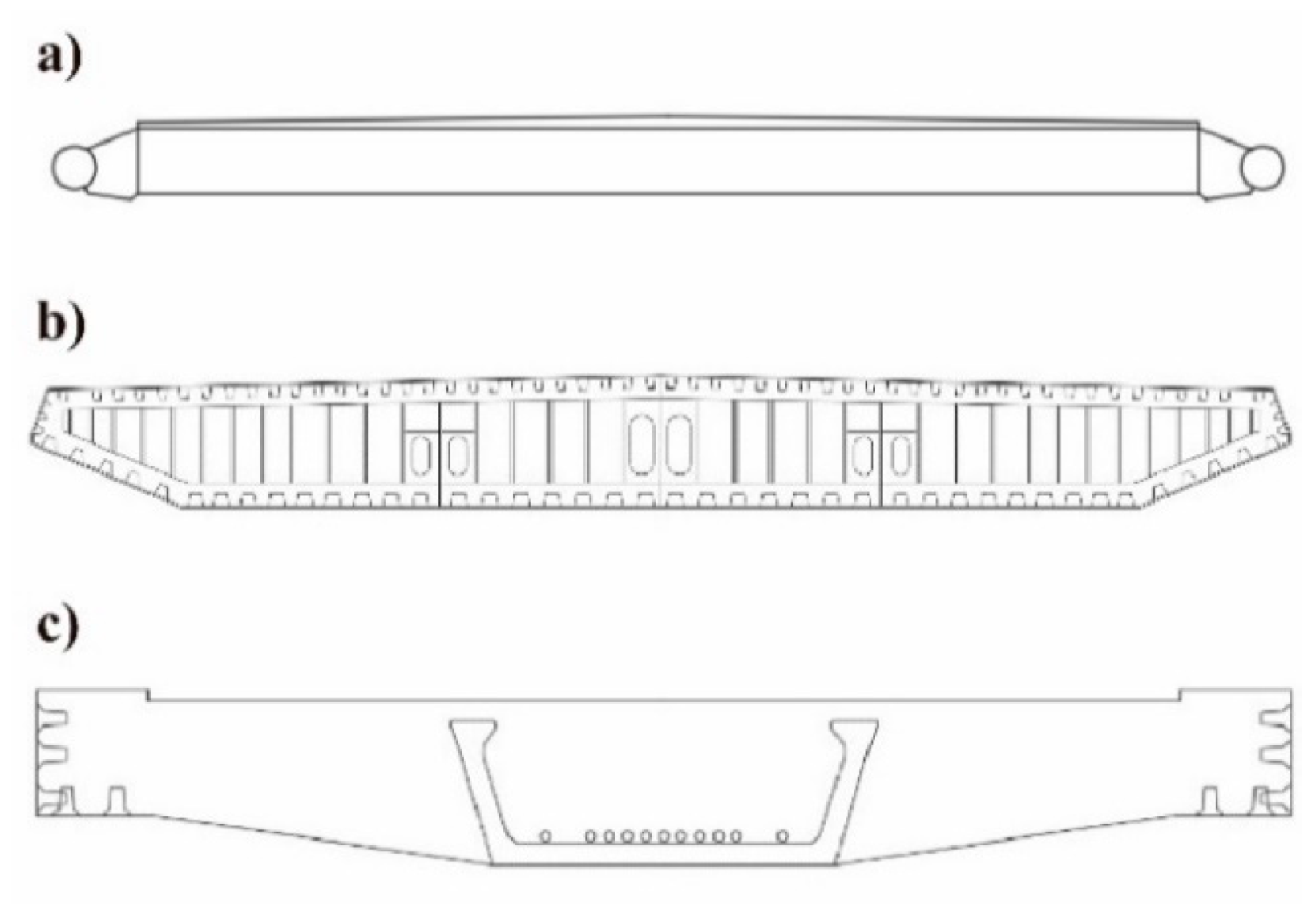



| Structural Element | Cross-Sections | Size 1 | Young’s Modulus (N/mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arch | Square hollow-box | 1250 × 1250 mm, tf = tw = 30 mm | 2.0 × 105 |
| Hangers | Solid circular | Ø 80 mm | 1.6 × 105 |
| Deck | Rectangular hollow-box | 5000 × 1000 mm, tf = tw = 20 mm | 2.0 × 105 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilar-Jiménez, J.; García-Guerrero, J.M.; Jorquera-Lucerga, J.J. The Diagonal Arch Bridge, a Particular Case of Spatial Arch Bridges. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041869
Aguilar-Jiménez J, García-Guerrero JM, Jorquera-Lucerga JJ. The Diagonal Arch Bridge, a Particular Case of Spatial Arch Bridges. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041869
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilar-Jiménez, Jesús, Juan Manuel García-Guerrero, and Juan José Jorquera-Lucerga. 2021. "The Diagonal Arch Bridge, a Particular Case of Spatial Arch Bridges" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041869
APA StyleAguilar-Jiménez, J., García-Guerrero, J. M., & Jorquera-Lucerga, J. J. (2021). The Diagonal Arch Bridge, a Particular Case of Spatial Arch Bridges. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041869






