Abstract
Cold-adapted esterases are attracting increasing attention owing to their prospective use in biotechnology. In this study, a novel cold-adapted family Ⅳ esterase EstDR4 was identified and obtained from extremophile Deinococcus radiodurans (D. radiodurans). EstDR4 displayed significant substrate preference towards short and medium chain monoesters (C2–C12). It also showed regioselectivity, enantioselectivity and degradation effects on four insecticides. The optimum temperature and pH for EstDR4 activity were 30 °C and pH 8, respectively. Additionally, EstDR4 exhibited relatively high catalytic activity at 0 °C and high stability from 10–40 °C, with over 80% of its initial activity retained after 1 h of incubation. Moreover, EstDR4 activity was stimulated by Tween 80 and Triton X-100, and inhibited by metal ions such as Co2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ and several organic solvents. Thus, this enzyme shows development potential for many industrial biotechnological applications, including the manufacture of thermolabile pharmaceutical products, cold-wash detergents and insecticide biodegradation.
1. Introduction
As an important group of the most utilitarian biocatalysts, lipolytic enzymes, with their ability to catalyze the cleavage and synthesis of ester bonds, have been widely used in many applications including pharmaceuticals, paper, biofuels, and detergent manufacturing [1]. The two main categories of lipolytic enzymes, esterases and lipases, are differentiated by their substrate preference. Esterases prefer hydrolyzing small esters with short fatty acid side chains (≤C10), conversely, lipase prefers long fatty acid chains triglycerides (>C10). Esterases and lipases can also be distinguished according to their substrate hydrophobicity, interfacial activation, solvent stability and enantioselectivity [2,3]. The tertiary structure of lipolytic enzymes is highly conserved with a typical α/β hydrolase fold structure. The catalytic amino acid triplet from esterases of different sources generally consists of Ser-Asp-His, usually with a conserved motif (Gly-x-Ser-x-Gly) around the active site serine. Microbial lipolytic enzymes have been classified into eight families according to their conservative amino acid sequence motifs and biochemical event properties. Among them, lipases belong to family Ⅰ, which can be divided into 6 subfamilies, and esterases belong to families Ⅱ-Ⅷ [4]. Generally, esterases demonstrate optimal reaction temperatures around 30 °C and those that display catalytic activity even at 0 °C are called cold-adapted esterases. Cold-adapted esterases always have high catalytic activity and low activation energy in low temperature environments, which advantageously can prevent product decomposition, structural damage and save energy cost. Additionally, chemical processes such as bioremediation, fermentation, and biomass conversion are best performed at low temperatures to reduce energy consumption and risk of contamination by mesophiles. Therefore, the development and application of cold-adapted esterase have important research values to broaden the industrial applications of esterases [5,6,7].
To date, many different lipolytic enzymes have been reported. Esterases with special properties have a more and broad application prospect: detergent-resistant esterases are applied as detergent additives; cold-adapted esterases are important in the manufacture of thermolabile pharmaceutical products; organic solvent-stable esterases are necessary for biotransformation processes in organic solvents such as biodiesel production. However, few esterases with specific properties have been reported, implying the necessity to find more novel esterases. This discovery process yields additional information regarding the structural and functional adaptation of lipolytic enzymes. The aim of the current study was to identify the gene encoding lipolytic enzymes in D. radiodurans (ATCC 13939), an extremophilic bacterium, and then purify and biochemically characterize the corresponding enzyme to provides a potential biocatalyst for industrial biotechnological applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Analysis and Homology Modeling of EstDR4
The complete sequence of D. radiodurans can be downloaded from the NCBI GenBank database (CP015081.1). The protein sequence of EstDR4 was published in the NCBI GenBank database (ANC71385.1). Databases were searched for similarity and alignment using the BLAST tool of NCBI. The molecular weight and extinction coefficient of EstDR4 were analyzed by ProtParam on the ExPASy Server. The tertiary structure of EstDR4 was predicted by the Phyre2 server. The PDB file of EstDR4 was visualized and edited with VMD version 1.9.3 software. A phylogenetic tree was built using MEGA version 7.0 software with the neighbor-joining method, using the amino acid sequences of bacterial lipolytic enzymes from eight families, as published by Arpigny and Jaeger [4].
2.2. Construction of Prokaryotic Expression Recombinant Plasmid
The estDR4 gene, including 939 DNA base pairs and encoding 312 amino acids, was amplified by PCR from the D. radiodurans genome. The primers utilized are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The restriction enzyme sites BamHⅠ and HindⅢ were added at both ends of the fragment. The estDR4 gene was directly cloned into the pET28a (+) plasmid to generate the pET28a-estDR4 vector using the ClonExpress Ultra One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme Biotech, Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The pET28a (+) plasmid was fused with His-tag for detection and purification. The plasmid was then transformed into E. coli strain BL21 (DE3) for further expression and purification.
2.3. Protein Expression and Purification
E. coli cells with the pET28a-estDR4 vector were cultured in LB medium with 50 μg·mL−1 kanamycin. EstDR4 expression was induced by adding 0.1 mM of isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) when the OD600 of the bacteria solution reached 0.6~0.8. The bacteria were harvested through centrifugation after bacteria were grown for nearly an additional 6 h at 28 °C, and 15 mL of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8) was added. The bacteria were then disrupted by sonifierand centrifuged at 11,000× g for 50 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was retained as the crude enzyme solution.
Purification of EstDR4 was performed using the affinity chromatography technique described by Ganasen et al. [8] using a HisTrap 1 mL column (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA). Buffer A was 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8) and buffer B was 50 mM Tris-HCl with 500 mM imidazole (pH 8). The bound EstDR4 was eluted by gradually increasing the proportion of buffer B. Fractions containing EstDR4 were confirmed through SDS-PAGE. The purified solution of EstDR4 was concentrated, and imidazole was removed by ultrafiltration with the 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer solution without imidazole. The obtained solution was stored at 4 °C for further characterization.
2.4. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of the Catalytic Triplet
The predicted catalytic triplet was mutated to aspartic acid using a Fast Mutagenesis Kit (Vazyme Biotech, Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The wild-type plasmid was used as a template to expand plasmids with primers containing mutant nucleotides. The primer pairs utilized are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The PCR products were digested by DpnI and transformed into BL21 after cyclization. These mutated strains (S156A, D253A and H283A) were expressed along with the wild type EstDR4. The resulting crude enzymes were used for detecting esterase activity.
2.5. Determination of Substrate Specificity
Unless otherwise described, 42 μg·mL–1 of purified EstDR4 in 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8) was used for all testing. Substrate specificity on chain length of EstDR4 was determined at 30 °C using pNP esters with various acyl chain lengths as substrates, including p-nitrophenyl acetate (pNPC2), p-nitrophenyl butyrate (pNPC4), p-nitrophenyl caprylate (pNPC8), p-nitrophenyl laurate (pNPC12), and p-nitrophenyl palmitate (pNPC16). Esterase activity was determined by measuring hydrolysis production of ρ-nitrophenol (pNP) based on spectrophotometric analysis at 410 nm. Regioselectivity determination of EstDR4 was used 1-naphthyl acetate (α-NA) and 2-naphthyl acetate (β-NA) as substrates, by measuring hydrolysis production of naphthol based on spectrophotometric analysis at 315 nm. Enantioselectivity determination of EstDR4 was used (R)-methyl 3-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoate ((R)-MHM) and (S)-methyl 3-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoate ((S)-MHM) as substrates with pH shift method. In addition, other substrates such as 2-methylbutyl acetate (2-MA), tert-butyl acetate (TA), linalyl acetate (LA), glyceryl tributyrate (GTB), glyceryl trioctanoate (GTO) and olive oil (OO) were also measured by pH shift method.
2.6. Determination of Temperature, pH, Optimum and Stability
The optimum temperature was determined at temperatures from 0–70 °C using pNPC8 at pH 8. The effect of temperature on EstDR4 stability was determined at various temperatures (10 °C, 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C) for 1 to 6 h, followed by a residual enzyme activity assay at 30 °C and pH 8. The optimum pH was determined between pH 5–11 with pNPC8 at 30 °C. The impact of pH on EstDR4 stability was tested by incubation at pH 5–11 for 1 h at 30 °C followed by a residual enzyme activity assay at 30 °C and pH 8.
2.7. Effects of Metal Ions, Organic Solvents, and Detergents on Enzyme Activity
EstDR4 was subjected to esterase activity assays after treatment with 1 mM and 5 mM metal ions (Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+) for 1 h at 30 °C. The impact of organic solvents on esterase activity was determined with 25% (v/v) of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), methanol, ethanol, acetone, isopropanol, 1-butanol, isoamyl alcohol, chloroform, methylbenzene, and n-hexane for 1 h at 30 °C. The influence of detergents on EstDR4 activity was assayed by adding 1% (w/v) of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 1% (v/v) of Tween 20, Tween 80, and Triton X-100 to the reaction solutions for 1 h at 30 °C. The controls were determined at 30 °C and pH 8 without any metal ions, detergents or organic solvents in the reaction mixture.
2.8. Kinetic Parameters
The kinetic parameters were determined with various concentrations (10~700 µM) of pNPC8 as the substrate. The hydrolysis reactions were carried out in 96-well plate at 30 °C and pH 8. The initial reaction velocity was measured by detecting the rate of pNP released according to the absorbance at 410 nm. The kinetic parameters Vmax and Km were confirmed via the enzyme kinetics–Michaelis–Menten function in Origin version 2018 software (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA). The kcat and kcat/ Km values were calculated using the data obtained.
2.9. Determination of Insecticide Degradation
The four insecticides including carbaryl, fenpropathrin, α-cypermethrin and deltamethrin were tested by mass spectrometric quantification. The concentration of EstDR4 and insecticides in the hydrolysate were 42 μg·mL−1 and 5 μg·mL−1. The reaction solution was incubated at 30 °C for 8 h, and then extracted by equivalent volume ethyl acetate. The solution was freeze-dried and redissolved in methanol to detect the remaining content of carbaryl by liquid chromatographic-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (LC-QqQ-MS/MS, Agilent Technologies, Co., Ltd., Palo Alto, CA, USA). Separation occurred on an Agilent Poroshell 120 SB-C18 column (2.1 mm × 75 mm, 2.7 μm particle size). Data acquisition was performed in Dynamic MRM mode with positive ESI, the mass spectrometry parameters as list: gas temperature 350 °C, gas flow 12 L·min−1, nebulizer pressure 35 psi, capillary voltage: 3500 V.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with SPSS Statistics 19.0.0 software (IBM SPSS Statistics, Armonk, NY, USA) in a completely randomized design. Differences in means between groups were compared for statistical significance at p < 0.05 using Duncan’s multiple range tests.
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis and Expression of EstDR4
The estDR4 gene (939 bp) that encodes the 312-amino-acid protein EstDR4 from D. radiodurans was inserted into pET-28a for overexpression in E. coil BL21(DE3). BLASTP analysis revealed that EstDR4 had greater than 50% amino acid sequence similarity with some uncharacterized hydrolases, including an α/β hydrolase from Deinococcus wulumuqiensis (81.35%), a lipase from Deinococcus swuensis (67.74%), and an acetyl hydrolase from Alphaproteobacteria bacterium 65–37 (50.00%). EstDR4 showed significant amino acid sequence similarity with esterases from family IV, such as Est8 from a metagenomic library (PDB ID 4YPV, 44.30%), EstDL136 from a metagenome (PDB ID 6AAE, 42.24%), and LipP from Pseudomonas sp. B11-1 (AAC38151.1, 44.59%). A phylogenetic tree including the EstDR4 protein and representative members of eight lipolytic bacterial enzyme families was constructed to obtain further insight into the evolutionary relationships of EstDR4 (Figure 1a). Phylogenic analysis revealed that EstDR4 and its homologs belonged to family Ⅳ, of which most of esterases display a striking amino acid sequence similarity to hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), thus, lipolytic enzyme family Ⅳ is also called the HSL family. Multiple sequence alignments of EstDR4 with LipP (AAC38151.1) and Est8 (PDB 4YPV) revealed that the conserved motifs HGGG and GXSXG, which exist in lipolytic enzyme family Ⅳ, were also present in EstDR4 (Figure 1b).
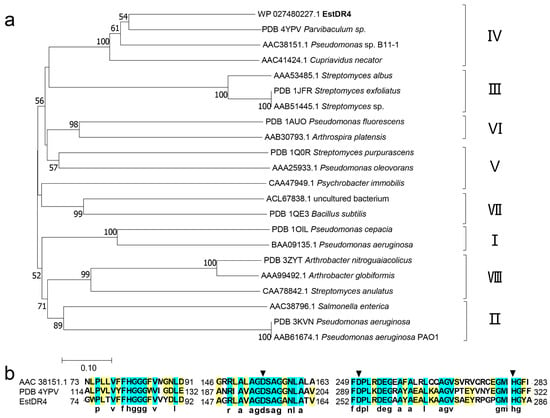
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of EstDR4 and homologous sequence alignment. (a) Phylogenetic evolutionary tree of EstDR4 constructed using 21 amino acid sequences of lipolytic enzymes from different families and EstDR4. The protein ID at NCBI or the protein databank (PDB) are shown before the name of the strain that was the enzyme source. (b) Homologous sequence alignment constructed using the amino acid sequences of EstDR4, Pseudomonas sp. lipase (AAC38151.1), and Parvibaculum sp. esterase (PDB ID 4YPV), which all belong to family IV. The catalytic triads are marked by black arrows.
Recombinant EstDR4 with N-terminal His-tag was successfully expressed and purified (Figure 2b). The tertiary structure of EstDR4 was modeled in accordance with the structure of Est8 (PDB 4YPV, 44.3%) using the Phyre2 server. The model comprised an α/β hydrolase fold and a cap domain. The predicted catalytic amino acid triad residues, Ser156, Asp253, and His283, were in spatial proximity to each other (Figure 2a). Three mutant strains were constructed to experimentally confirm the putative catalytic residues; as expected, all three mutants, S156A, D253A, and H283A, showed negligible activity compared to the wild type (Figure 2c).
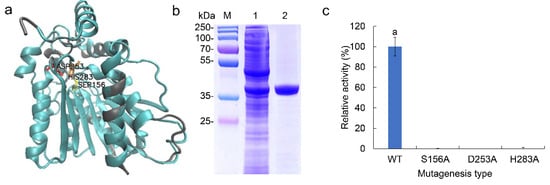
Figure 2.
Tree dimensional structure, purification and enzyme activity of the mutants of EstDR4. (a) The predicted three-dimensional structural model of EstDR4. The tertiary structure of EstDR4 (blue ribbon) was modeled on that of Est8 (PDB 4YPV, gray ribbon). Potential catalytic triad residues (Ser156, Asp253 and His283) are marked on the figure. (b) SDS-PAGE electrophoresis of EstDR4. Lane M: marker, lane 1: crude, lane 2: purified EstDR4. The EstDR4 protein band at ~35 kDa, was in accordance with the prediction that EstDR4 (33 kDa) added with the HisTag. (c) WT is the wild type EstDR4, the mutants are S156A, D253A and H283A. The different letters between each condition indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.2. Substrate Specificity of EstDR4
The substrate specificity of EstDR4 was determined by using pNP esters of various chain lengths as substrates (C2~C16) (Figure 3a). The results revealed that EstDR4 preferentially hydrolyzes short and medium chain monoesters. EstDR4 displayed maximum hydrolytic activity toward pNPC8. Additionally, EstDR4 exhibited high activity toward short chain esters C2 (40.16%) and C4 (57.80%), weak activity toward C12 (11.68%), and negligible activity toward C16 (2.03%). Thus, EstDR4 is best classified as an esterase (EC3.1.1.1) according to the substrate preference.
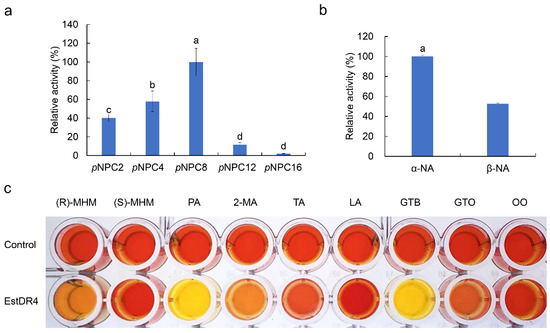
Figure 3.
Substrate specificity of EstDR4. (a) Substrate specificity of EstDR4 toward pNPC2, pNPC4, pNPC8, pNPC12, and pNPC16. The maximum activity measured towards pNPC8 was taken as 100%. (b) Substrate specificity of EstDR4 toward α-NA and β-NA. The different letters between each condition in (a,b) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). (c) Substrate specificity of EstDR4 toward (R)-MHM, (S)-MHM, PA, 2-MA, TA, LA, GTB, GTO, OO.
We also measured the regioselectivity and enantioselectivity of the EstDR4. The regioselectivity was determined by using α-NA and β-NA as substrates. As shown in Figure 3b, EstDR4 had a stronger substrate preference for α-NA compare with β-NA, the hydrolysis rate of EstDR4 on α-NA was almost twice that of β-NA. (R)-MHM and (S)-MHM were used as the substrates to detected the enantioselectivity of EstDR4 by the pH shift method. The cleavage of the ester bond will generate acid, and the reaction solution added with phenol red will also change color with the change of pH. The darker the yellow, the more acid was generated in the solution. As shown in Figure 3c, EstDR4 displayed a substrate preference for (R)-MHM over (S)-MHM, weak hydrolytic activity toward (R)-MHM and negligible activity toward (S)-MHM, thus, the enantioselectivity of EstDR4 can be confirmed. According to the results shown in Figure 3c, EstDR4 also had a hydrolysis effect on phenyl ester, tertiary alcohols and triglycerides, including PA, 2-MA, TA, GTB and GTO. However, EstDR4 still displayed negligible hydrolytic activity toward long-chain tertiary alcohols and glycerides such as LA and OO.
3.3. Effects of Temperature and pH on EstDR4
The optimum temperature of EstDR4 was tested from 0–70 °C using pNPC8 as the substrate. EstDR4 displayed maximum catalytic activity at 30 °C and retained 26.77% and 44.98% relative activity at 0 °C and 5 °C, respectively. The activity increased consistently from 0–30 °C and decreased rapidly at higher temperatures; the enzyme was almost inactivated at 70 °C (Figure 4a). EstDR4 exhibited high stability from 10–40 °C, with over 80% residual activity detected after 1 h of incubation, and the enzyme retained 66.32% residual activity after 6 h incubation at 40 °C. However, EstDR4 residual activity was sharply reduced to approximately 56.31% after incubation at 50 °C for 1 h (Figure 4b).
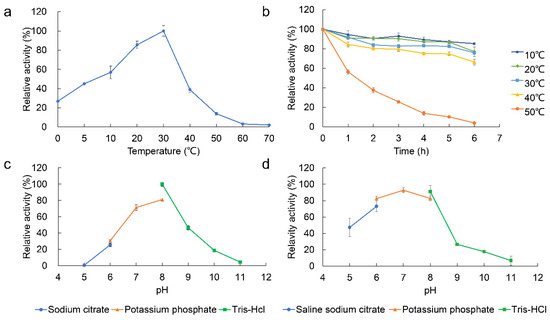
Figure 4.
Effect of temperature and pH on enzyme activity. (a) Effect of temperature on esterase activity using pNPC8 as a substrate from 0–70 °C. (b) Temperature stability of EstDR4 at various temperatures (10 °C, 20 °C, 30 °C, 40 °C and 50 °C) for 1 to 6 h with esterase activity assayed every hour at 30 °C and pH 8. (c) Effect of pH on enzymatic activity, measured from pH 5–11. (d) Stability of EstDR4 at different pH values (pH 5–11) for 1 h at 30 °C followed by esterase activity assayed at 30 °C and pH 8. All-results are shown in relative activity, the maximum activity measured was taken as 100%.
The optimum pH of EstDR4 was determined by testing its activity from pH 5–11 at 30 ℃ using pNPC8 as the substrate. The suitable hydrolytic environment for EstDR4 was neutral and slightly alkaline between pH 7–9, with an optimum pH of 8 based on enzyme activity (Figure 4c). Furthermore, EstDR4 showed high pH stability from pH 6–8, with approximately 80% residual activity retained after incubation for 1 h at this pH range. A considerable loss in EstDR4 activity was observed after 1 h of incubation at pH 9 (Figure 4d).
3.4. Effects of Various Metal Ions, Organic Solvents and Detergents on EstDR4
Four metal ions (Li+, Na+, K+, and Mg2+) showed no or negligible effects on EstDR4 activity at concentrations of 1 mM and 5 mM in our assays (p > 0.05) (Figure 5a). EstDR4 activity was substantially enhanced by 1 mM Cs+, Ca2+, and Sr2+, and 5 mM Cs+. However, EstDR4 activity was significantly inhibited by 1 mM and 5 mM Co2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+, and 5 mM Ca2+, Sr2+, and Mn2+ (p < 0.05). Among these, 1 mM Cu2+ had the greatest inhibitory effect on esterase activity; almost all enzyme activity was lost at this concentration. Interestingly, EstDR4 activity was significantly enhanced by 1 mM Sr2+, increasing to 123.27% of the initial activity (p ˂ 0.05), whereas 5 mM Sr2+ significantly inhibited the activity of EstDR4.
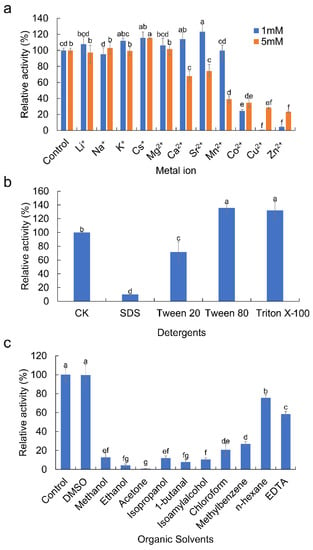
Figure 5.
Effect of metal ions, detergents and organic solvents on esterase activity of EstDR4. (a) Effect of metal ions (1 and 5 mM) on EstDR4 activity: Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+. (b) Effect of detergents on enzyme activity: SDS, Tween 20, Tween 80 and Triton X-100. (c) Effect of organic solvents (25% v/v) on EstDR4 activity: dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), methanol, ethanol, acetone, isopropanol, 1-butanol, isoamyl alcohol, chloroform, methylbenzene and n-hexane. The relative activity of the control without metal ions, detergents and organic solvents was regarded as 100%. The different letters between each condition indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
The tolerance of EstDR4 toward most organic solvents was generally low (Figure 5c); the enzyme was almost inactivated in 25% (v/v) ethanol and acetone, and had weak activity in methanol, isopropanol, 1-butanal, isoamyl alcohol, chloroform and methylbenzene (residual activity 7%~27%). However, DMSO and n-hexane only slightly diminished the activity to approximately 99.59% and 75.59% of the initial activity, respectively.
As for detergents, EstDR4 was significantly activated by 1% of Tween 80 and Triton X-100 exhibiting 135.47% and 132.22% of original activity, respectively (p ˂ 0.05). However, EstDR4 activity was inhibited by SDS, in which it exhibited less than 10% residual activity compared with the original level. Additionally, 1% Tween 20 diminished the activity to approximately 71.74% of the original level (Figure 5b).
3.5. Enzyme Kinetics
The kinetic parameters of EstDR4 were determined using different concentrations (10~700 µM) of pNPC8 as substrate. The apparent Km and Vmax values were calculated to be 372.50 µM and 45.91 µM·min−1, respectively. Therefore, the kcat and kcat/ Km values for EstDR4 were 28.34 s−1 and 76.08 s−1mM−1, respectively (Figure 6).
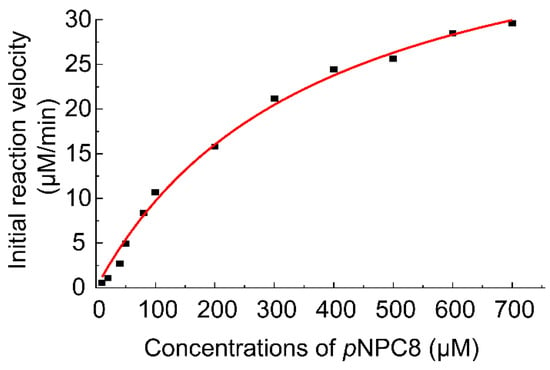
Figure 6.
Michaelis–Menten kinetics of EstDR4. Enzymatic reaction kinetics of EstDR4 were tested with various concentrations (10~700 µM) of pNPC8 as substrate.
3.6. Degradation Properties of EstDR4 to Insecticides
The degradation of EstDR4 to four insecticides (carbaryl, fenpropathrin, α-cypermethrin and deltamethrin) were measured by LC-MS, and the results are shown in Figure 7. Under the conditions of this study, EstDR4 was able to degrade all the insecticides tested, and a significant change in the residual content of carbaryl was observed that EstDR4 almost hydrolyzed all the carbaryl in the solution compared with the control group. Furthermore, the degradation rate of fenpropathrin by EstDR4 is 85.19%, and the following are α-cypermethrin and deltamethrin, with 54.19% and 34.23% degradation rates in turn.
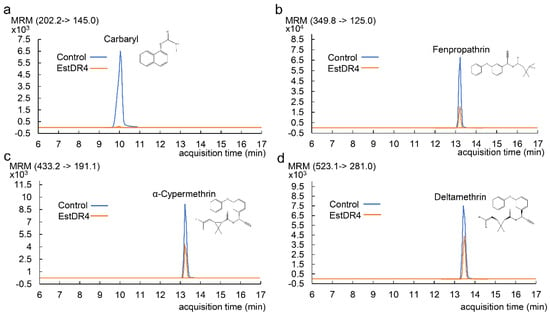
Figure 7.
Degradation of insecticides by EstDR4. (a) carbaryl; (b) fenpropathrin; (c) α-cypermethrin; (d) deltamethrin. The initial concentration of carbaryl was 5 μg·mL−1, the concentration of EStDR4 in the experimental group was 42 μg·mL−1, while the control group was replaced with the same concentration of boiled inactivated EstDR4.
4. Discussion
Extremophiles that thrive in extreme adverse environmental conditions are regarded as valuable sources of novel enzymes required in industrial applications [9]. As a polyextremophile bacterium, D. radiodurans is well known for its radiation resistance [10], and can withstand oxidative stress, pressure, and low temperatures [11,12,13]. With interest in isolating lipolytic enzymes from extremophiles, one of the putative lipolytic enzyme genes (estDR4) in D. radiodurans was cloned, expressed and characterized.
Sequence analysis indicated that EstDR4 belongs to family IV of bacterial lipolytic enzymes, also called the HSL family. The predicted catalytic amino acid triad residues, Ser156, Asp253 and His283, were confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis. Two of the catalytic residues, Ser156 and Asp253, were located in the typical motifs of HSL family esterases, pentapeptide GDSAG and C-terminal conserved motif DPLR, respectively. The catalytic residue His283 was located in HGY, which differs from the common type HGF in HSL family esterases; the functional significance of this variant is currently unknown. Moreover, this study has confirmed that EstDR4 has a weak hydrolysis effect on TA. EstDR4 contained a GGGX type (82HGGG85) oxyanion hole, which has been proposed to be responsible for the ability of these enzymes to hydrolyze tertiary alcohol esters [14,15]. This motif is also present in esterases from other sources such as RmEstA from Rhizomucor miehei and γ-PLE, an isomerase of pig liver esterase [16,17].
The tertiary structure of EstDR4 was modeled according to the structure of Est8 (PDB 4YPV), an alkaline esterase from a metagenomic library [18]. The tertiary structure of EstDR4 exhibited a cap domain and α/β hydrolase fold. Lipolytic enzymes of HSL family have various substrate preferences, such as LipU from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv toward pNPC4, Est06 from a forest soil metagenome toward pNPC5, and thermal stability lipase Blip from Bacillus halodurans prioritizes medium to long chain fatty acyl esters [19,20,21]. Est8 shares 44.3% amino acid sequence similarity with EstDR4, although they have quite different substrate preferences, with EstDR4 favoring pNPC8, and Est8 favoring pNPC2. Similar to Est8, the tertiary structure of EstDR4 revealed spatially adjacent catalytic residues, which might not accommodate long-chain esters. Thus, the difference in substrate preference may be due to differences in substrate channel and cap domain. Two aromatic residues in Est8, Met213 and Phe217, were observed to block the substrate channel, and mutations Met213Gly and Phe217Val led to increasing relative activity against C4 and C5 [18]. The corresponding residues in EstDR4 are Met212 and Gly216, and a smaller side chain in site 216 might be a reason for mid-chain substrate preference. Moreover, the cap domain of EstDR4 contains two shorter α-helices than in Est8 (Supplementary Figure S1), which may allow longer substrates to enter the active center. EstDR4 catalyzes the hydrolysis of a variety of substrates containing phenyl ester, tertiary alcohol and triglyceride, and the regioselectivity and enantioselectivity were identified by asymmetrical hydrolysis of α-NA, β-NA, (R)-MHM and (S)-MHM. These identify EstDR4 for potential use in a wide range of industrial applications.
EstDR4 showed optimum activity at 30 °C, which concurs with the reported maximum activity of other cold-adapted esterases, such as EstT1-39 from the psychotolerant Pseudomonas sp. T1-39, EstLiu from Zunongwangia profunda, PMGL3 from the permafrost microbial community and rEstSL3 from Alkalibacterium sp. SL3 [22,23,24,25]. While EstDR4 had higher relative activity at an environment below 10 °C compared with cold-adapted esterase PMGL3 [24] and PsyEst from Psychrobacter sp. Ant300, another cold-active esterase [26]. The activity of cold-adapted enzymes at low temperatures depends on the flexibility of the protein structure, which has rendered cold-adapted enzymes susceptible to denaturation by heat at ambient temperatures compared with their mesophilic counterparts. However, EstDR4 exhibited high stability from 10–40 °C, and retained over 80% residual activity after 1 h of incubation. The half-lives of EstDR4 at 40 ℃ and 50 °C were 10.13 h and 1.29 h, respectively, significantly higher than those reported cold-adapted esterases PLM3, PsyEst, Est684 and MtEst45 [24,26,27,28]. EstDR4 can be classified as an alkaline esterase, not only because its optimum pH was 8, but it also exhibited high stability at pH 8, with over 80% residual activity after 1 h at pH 8. In comparison, an esterase from Bacillus circulans was maximally active only between pH 8–9 and stable between pH 6–8 [29]. Similarly, Est1 from a compost metagenome exhibited maximum activity at pH 7 and retained more than 95% activity between pH 6–8 [30]. Moreover, EstDR4 better performed hydrolysis in the presence of some detergents like Tween 80 and Triton X-100. The effect of detergent or surfactant on enzyme activity may be due to the interaction between enzyme, detergent and substrate [31]. EstDR4 activation by Tween 80 and Triton X-100 may be attributed to an increased substrate solubility and probability of entering the substrate pocket [32]. However, EstDR4 activity was inhibited by SDS due to the nonspecific binding between SDS and proteins, which results in the formation of complexes and unfolding of proteins [20]. These characteristics demonstrate the potential value of EstDR4 as a low temperature catalytic industrial use, such as processes involving food ingredients, manufacture of thermolabile pharmaceutical products, and cold-wash detergents [33].
Many metal ions reportedly have inhibitory or activation effects on esterases [34]. In this work, EstDR4 activity was substantially inhibited by Cu2+ and Zn2+, a similar phenomenon has been observed in AMS8 from antarctic Pseudomonas and EstATII from a Red Sea brine pool metagenomic [8,35]. Most tested organic solvents in the current study induced inhibitory effects on the catalytic activity of EstDR4. Only DMSO and n-hexane slightly diminished the esterase activity to 99.59% and 75.59% of the initial activity, respectively. Generally, organic solvents affect the catalytic activity of enzymes due to disruption of the balance between organic solvent phase and enzyme surface, disruption of core hydrophobic interactions that lead to a conformational change of the enzyme molecule, and competition for substrate binding [36]. As an example, Ganasen et al. [8] discovered that AMS8 lipase loses its helix formation due to hydrogen bond formation interference in the presence of ethanol, 2-propanol, and DMSO, causing the loss of lipase activity. Protein engineering may enhance the organic solvent stability of enzymes in three manners: modification to increase the stabilizing interactions of surface residues, modification of residue flexibility, and surface charge alteration. Lipase T6 from Geobacillus stearothermophilus achieved enhanced stability in methanol by substituting charged surface residues with hydrophobic residues, which led to extensive formation of new hydrogen bonds [37]. Yagonia et al. [38] confirmed that modulating the flexibility within the hydrophilic solvent-affecting region can enhance the organic solvent stability of Candida Antarctica lipase B.
Due to the frequent use of insecticides in agriculture and other environments, the pollution caused by insecticides has been gradually noticed. While the biodegradation of insecticides has been recognized for its advantages of high efficiency and energy saving. Esterase has a potential degradation effect on insecticides [39], which has been confirmed for EstDR4 in this study. However, esterases have different substrate specificity for insecticides, the esterase EstSt7 from Sulfolobus tokadaii that hydrolyzed various pyrethroids, and enpropathrin served as preferred substrate as compared to the other pyrethroids tested [40]. In this study, EstDR4 was shown a maximum degradation to carbaryl compared with fenpropathrin, α-cypermethrin and deltamethrin, this may due to the contrasting substrate affinity.
5. Conclusions
We identified a new esterase EstDR4 from extremophile D. radiodurans. As a newly identified member of family Ⅳ esterases, EstDR4 contains typical motifs GDSAG and HGGG. It exhibited maximum catalytic activity at 30 °C and pH 8 and outstanding catalytic activity at cold conditions, even at 0 ℃. EstDR4 also demonstrated good compatibility with detergent and versatile substrate preferences toward short and medium chain monoesters, phenyl ester, tertiary alcohol and triglyceride. In addition, EstDR4 was able to hydrolyze various insecticides. These identify EstDR4 for potential use in a wide range of industrial applications and warrants further research.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/11/4/1864/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z., Z.L., M.L. and Z.Z.; methodology, Y.Z.; validation, Y.Z.; formal analysis, Y.Z.; investigation, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z., W.L., Z.Z., W.Z., M.C., M.L., Z.L. and J.W.; supervision, Z.L. and Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFA0901003), the National Transgenic Major Program of China (No. 2019ZX08010-004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31930004 and 31500063) and Fundamental Research Fund for Central Non-Profit Scientific Institution (1610392019006). We also appreciate the support of the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of CAAS.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks go to Min Lin, Zhu Liu and Zhengfu Zhou for their constructive suggestions on the revision of the article and other authors for their excellent technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sarmah, N.; Revathi, D.; Sheelu, G.; Yamuna Rani, K.; Sridhar, S.; Mehtab, V.; Sumana, C. Recent advances on sources and industrial applications of lipases. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 34, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornscheuer, U.T. Microbial carboxyl esterases: Classification, properties and application in biocatalysis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahiniana, H.; Sarda, L. Distinction between esterases and lipases: Comparative biochemical properties of sequence-related carboxylesterases. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpigny, J.L.; Jaeger, K.E. Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: Classification and properties. Biochem. J. 1999, 343, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangla, V.; Ravi, B.; Mehra, S.; Mehrotra, S.; Mehrotra, R. Biofuels: An overview with special emphasis on biodiesel and the role of lipase enzyme in its synthesis. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2013, 7, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.D.; Verger, R. Lipases: Interfacial enzymes with attractive applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1998, 37, 1608–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Organic solvent tolerant lipases and applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 625258, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasen, M.; Yaacob, N.; Rahman, R.N.; Leow, A.T.; Basri, M.; Salleh, A.B.; Ali, M.S. Cold-adapted organic solvent tolerant alkalophilic family I.3 lipase from an Antarctic Pseudomonas. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, B.V.D. Extremophiles as a source for novel enzymes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmaso, G.Z.; Lage, C.A.; Mazotto, A.M.; Dias, E.P.; Caldas, L.A.; Ferreira, D.; Vermelho, A.B. Extracellular peptidases from Deinococcus radiodurans. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, C.; Dalmaso, G.; Teixeira, L.; Bendia, A.; Paulino-Lima, I.; Galante, D.; Janot-Pacheco, E.; Abrevaya, X.; Azúa-Bustos, A.; Pellizari, V.; et al. Mini-Review: Probing the limits of extremophilic life in extraterrestrial environment-simulated experiments. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2012, 11, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Airo, A.; Chan, S.L.; Martinez, Z.; Platt, M.O.; Trent, J.D. Heat shock and cold shock in Deinococcus radiodurans. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 40, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, D.; Radman, M. Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 133–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehdorf, J.; Behrens, G.A.; Nguyen, G.S.; Kourist, R.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Pseudomonas putida esterase contains a GGG(a)x-motif confering activity for the kinetic resolution of tertiary alcohols. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, E.; Pleiss, J.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Activity of lipases and esterases towards tertiary alcohols: Insights into structure-function relationships. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3211–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yan, Q.; Yang, S.; Duan, X.; Jiang, Z. Biochemical characterization of a first fungal esterase from Rhizomucor miehei showing high efficiency of ester synthesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77856. [Google Scholar]
- Hasenpusch, D.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Langel, W. Simulation on the structure of pig liver esterase. J. Mol. Model. 2011, 17, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pereira, M.R.; Maester, T.C.; Mercaldi, G.F.; de Macedo Lemos, E.G.; Hyvönen, M.; Balan, A. From a metagenomic source to a high-resolution structure of a novel alkaline esterase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 4935–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Ren, S.; Li, P.; Xie, J. Characterization and function of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv Lipase Rv1076 (LipU). Microbiol. Res. 2017, 196, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukunde, A.; Schneider, D.; Lu, M.; Brady, S.; Daniel, R. A novel, versatile family IV carboxylesterase exhibits high stability and activity in a broad pH spectrum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, A.; Gupta, R. Functional characterization of hormone sensitive-like lipase from Bacillus halodurans: Synthesis and recovery of pNP-laurate with high yields. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 871–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Gasmalla, M.A.A.; Zhao, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Yang, R. Characterization of a cold-adapted esterase and mutants from a Psychotolerant pseudomonas sp. strain. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Culsum, U.; Tang, W.; Zhang, S.W.; Wu, G.; Liu, Z. Characterization of a novel cold active and salt tolerant esterase from Zunongwangia profunda. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 85, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovskaya, L.E.; Novototskaya-Vlasova, K.A.; Gapizov, S.S.; Spirina, E.V.; Durdenko, E.V.; Rivkina, E.M. New member of the hormone-sensitive lipase family from the permafrost microbial community. Bioengineered 2017, 8, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Q.; Lin, X.; Bun Ng, T.B.; Yan, R.; Lin, J.; Ye, X. A novel cold-adapted and highly salt-tolerant esterase from Alkalibacterium sp. SL3 from the sediment of a soda lake. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kulakova, L.; Galkin, A.; Nakayama, T.; Nishino, T.; Esaki, N. Cold-active esterase from Psychrobacter sp. Ant300: Gene cloning, characterization, and the effects of Gly→Pro substitution near the active site on its catalytic activity and stability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1696, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Identification and immobilization of a novel cold-adapted esterase, and its potential for bioremediation of pyrethroid-contaminated vegetables. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-Suk, L. Isolation and characterization of a novel cold-adapted esterase, MtEst45, from Microbulbifer thermotolerans DAU221. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Kademi, A.; Ait-Abdelkader, N.; Fakhreddine, L.; Baratti, J.C. Characterization of a new thermostable esterase from the moderate thermophilic bacterium Bacillus circulans. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2000, 10, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Dukunde, A.; Daniel, R. Biochemical profiles of two thermostable and organic solvent-tolerant esterases derived from a compost metagenome. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Lupilov, N.; Leichert, L.I. Characterization of ML-005, a novel metaproteomics-derived esterase. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, V.; Dhouib, R.; Canaan, S.; Fotiadu, F.; Carrière, F.; Cavalier, J.F. Effects of surfactants on lipase structure, activity, and inhibition. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siso, M.I.G.; Cerdan, M.E.; Lopez-Lopez, O. New extremophilic lipases and esterases from metagenomics. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 445–455. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Gupta, N.; Rathi, P. Bacterial lipases: An overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Y.M.; Ghazy, M.A.; Sayed, A.; Ouf, A.; El-Dorry, H.; Siam, R. Isolation and characterization of a heavy metal-resistant, thermophilic esterase from a Red Sea Brine Pool. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, P.; Tan, Y.; Kinsella, G.K.; Henehan, G.T.; Ryan, B.J. Solvent stable microbial lipases: Current understanding and biotechnological applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, A.; Kanteev, M.; Kagan, I.; Gihaz, S.; Shahar, A.; Fishman, A. Structural insights into methanol-stable variants of lipase T6 from Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 9449–9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagonia, C.F.J.; Park, H.J.; Hong, S.Y.; Yoo, Y.J. Simultaneous improvements in the activity and stability of Candida antarctica lipase B through multiple-site mutagenesis. Biotechnol. Bioproc. E 2015, 20, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Bhatt, K.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Chen, S. Esterase is a powerful tool for the biodegradation of pyrethroid insecticides. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Feng, S.; Shen, Y.; He, P.; Ma, G.; Yu, X.; Zhang, F.; Mao, D. Characterization of a novel thermophilic pyrethroid-hydrolyzing carboxylesterase from Sulfolobus tokodaii into a new family. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 97, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).