Evaluating the Effect of Intensity Standardisation on Longitudinal Whole Brain Atrophy Quantification in Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
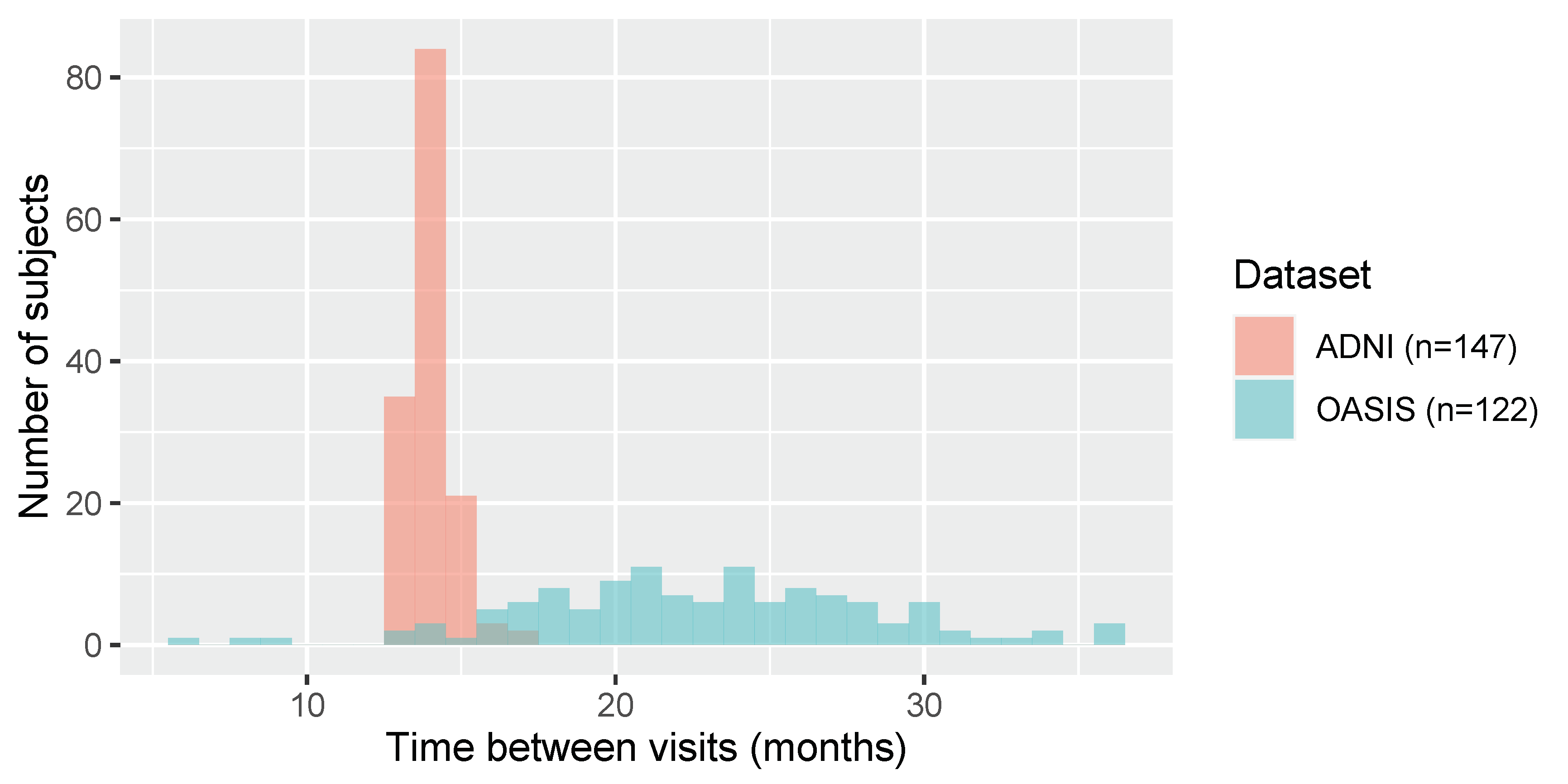
2.1. Datasets
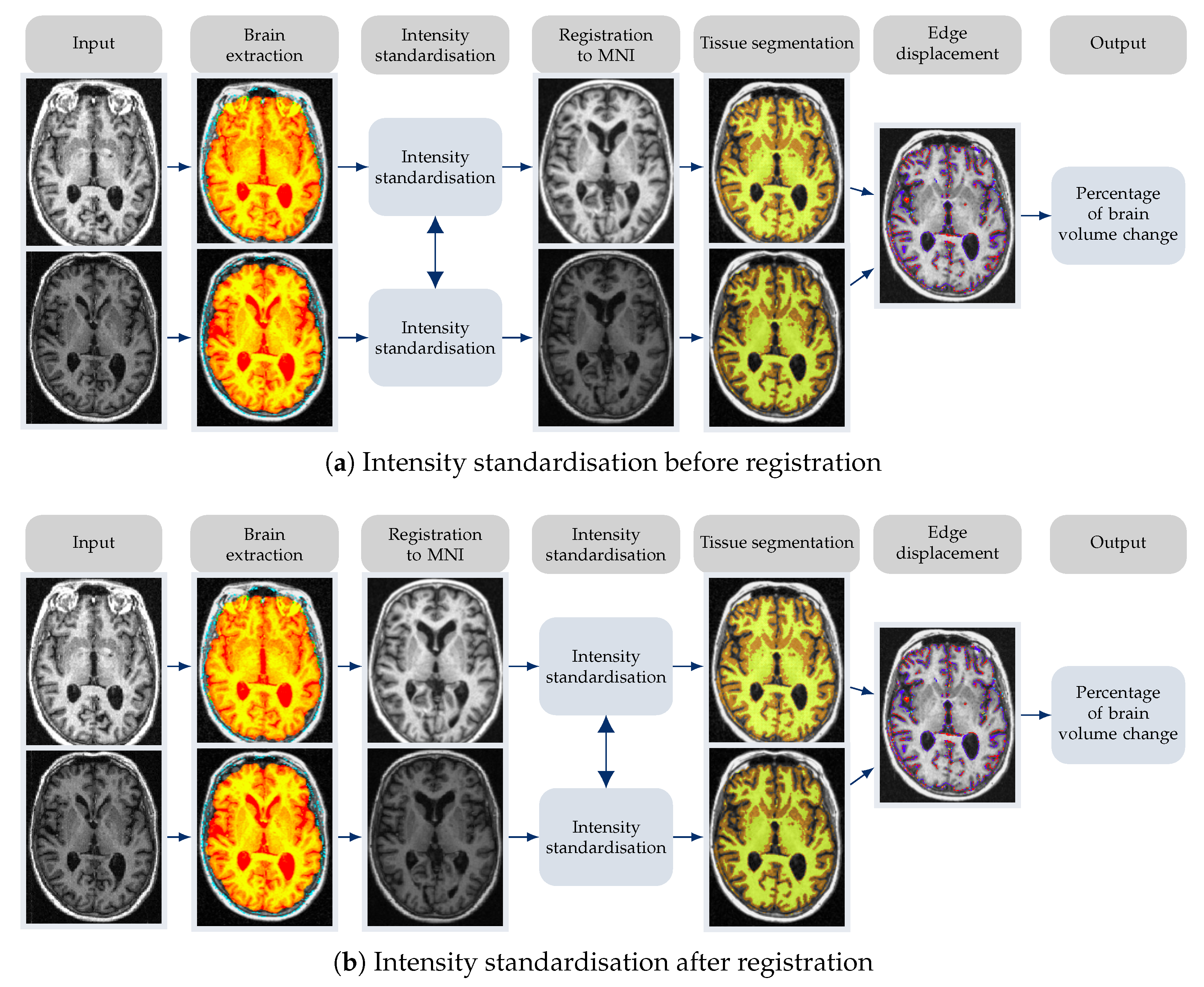
2.2. Equipping FSL-SIENA with Intensity Standardisation
2.3. Considered Intensity Standardisation Techniques
2.3.1. z-Score
2.3.2. Fuzzy c-Means-Based Standardisation
2.3.3. Gaussian Mixture Model-Based Standardisation
2.3.4. WhiteStripe
2.3.5. Kernel Density Estimation Based Standardisation
2.3.6. Piecewise Linear Histogram Matching
2.4. Evaluation Analysis and Measures
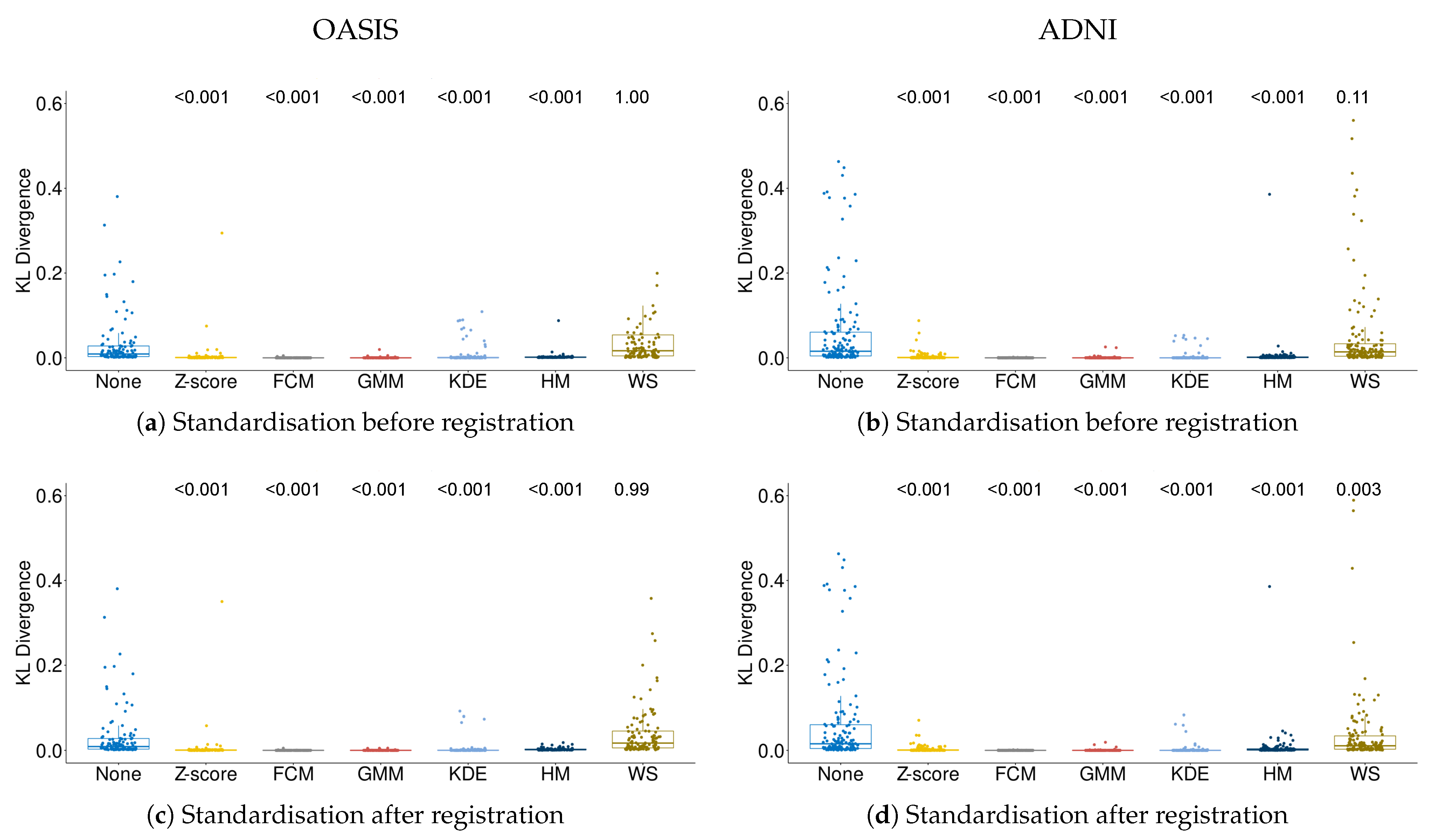
2.4.1. Quality of Intensity Standardisation
2.4.2. Scan–Rescan Repeatability
2.4.3. Testing for Atrophy Differences between Alzheimer’s Disease and Normal Control Subjects
2.5. Implementation Details
3. Results
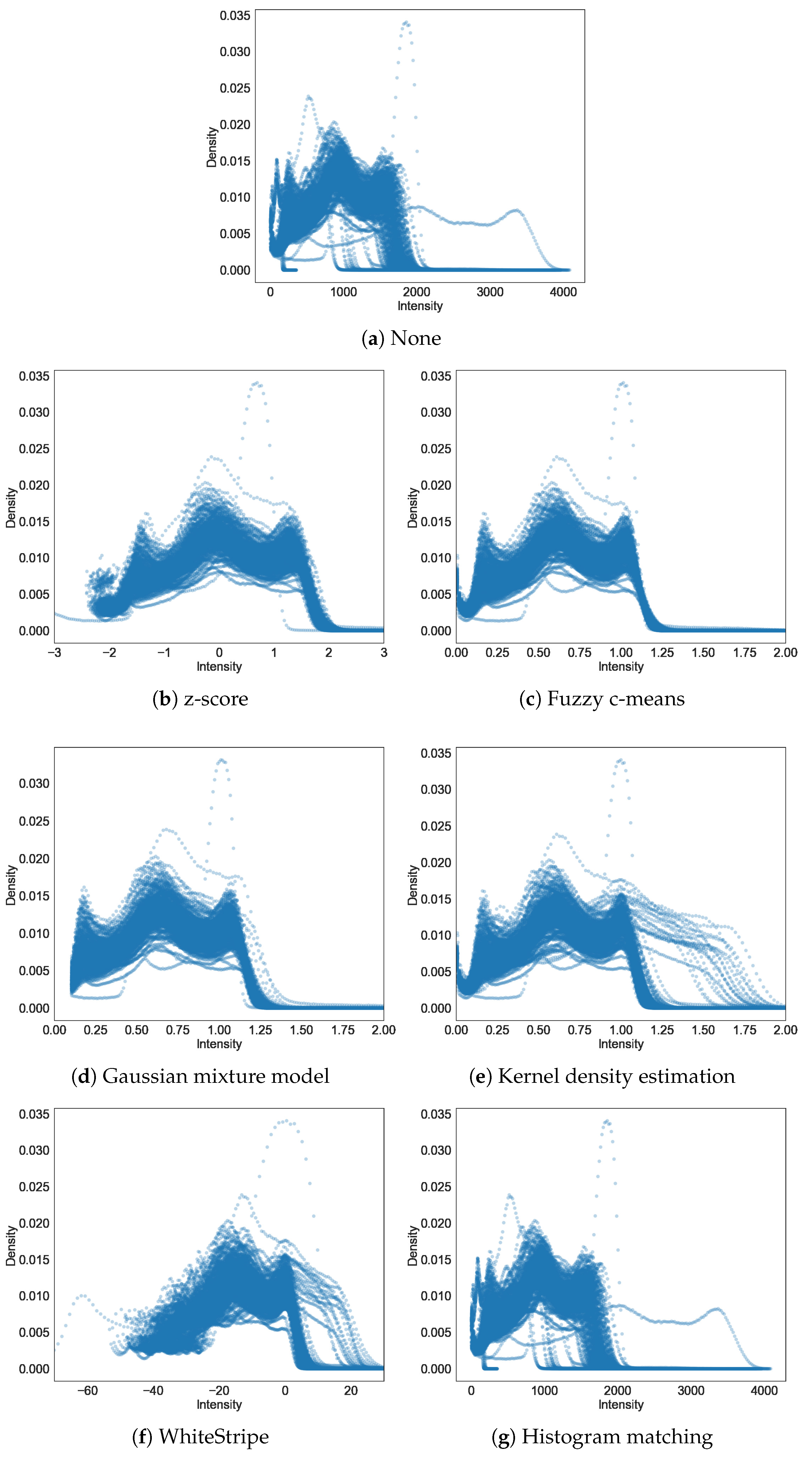
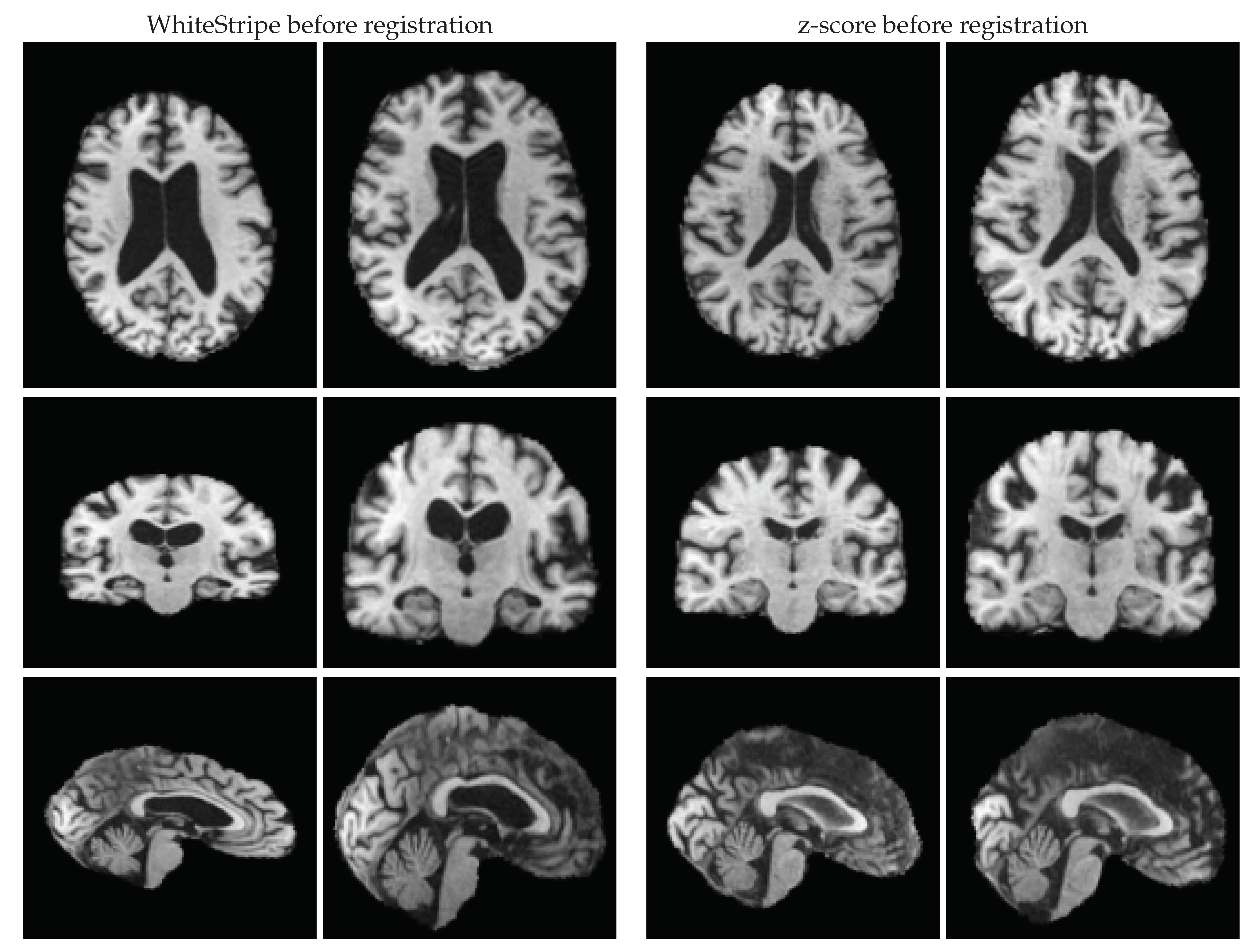
3.1. Quality of Intensity Standardisation
3.2. Scan–Rescan Repeatability
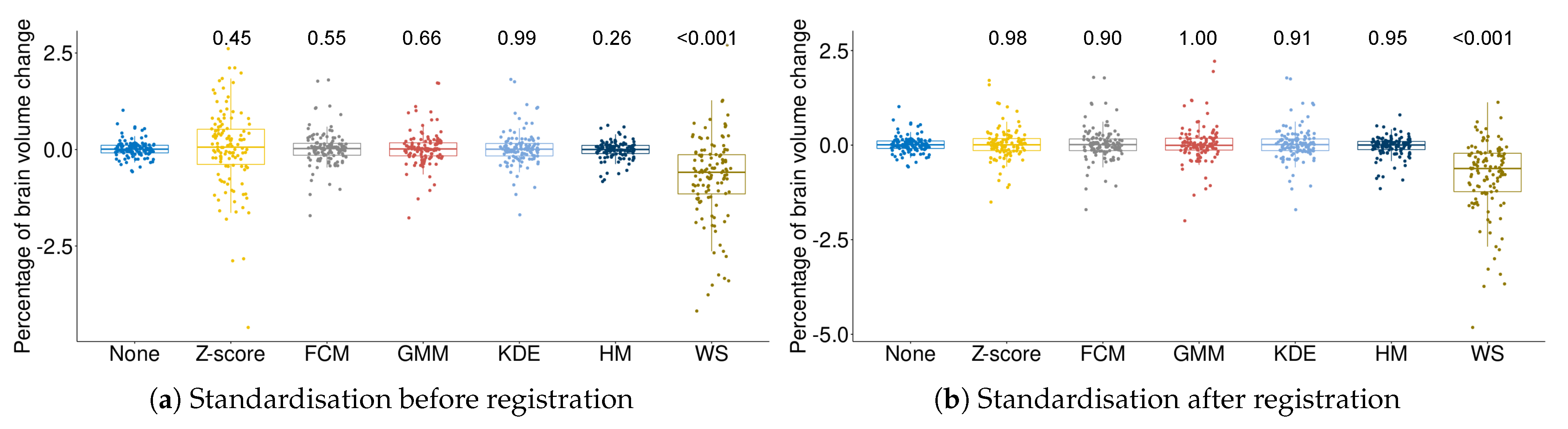
3.3. Effect of Intensity Standardisation on Atrophy Differences between Alzheimer’s Disease and Normal Control Subjects
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ADNI | Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| FCM | Fuzzy c-means |
| FSL-BET | Brain Extraction Tool |
| FSL-SIENA | Structural Image Evaluation, using Normalization, of Atrophy |
| GMM | Gaussian mixture model |
| HM | Histogram matching |
| KDE | Kernel density estimation |
| KL | Kullback–Leibler |
| MNI | Montreal Neurological Institute |
| MP-RAGE | Magnetization Prepared-RApid Gradient Echo |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NC | Normal control |
| OASIS | Open Access Series of Imaging Studies |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| WS | WhiteStripe |
Appendix A. Histograms of Intensity before and after Intensity Standardisation

References
- Rovira, À.; Wattjes, M.P.; Tintoré, M.; Tur, C.; Yousry, T.A.; Sormani, M.P.; De Stefano, N.; Filippi, M.; Auger, C.; Rocca, M.A.; et al. Evidence-based guidelines: MAGNIMS consensus guidelines on the use of MRI in multiple sclerosis-clinical implementation in the diagnostic process. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenwijk, M.D.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Daams, M.; Tijms, B.M.; Wink, A.M.; Balk, L.J.; Tewarie, P.K.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J.; Barkhof, F.; Vrenken, H.; et al. Cortical atrophy patterns in multiple sclerosis are non-random and clinically relevant. Brain 2016, 139, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Ciccarelli, O.; De Stefano, N.; Evangelou, N.; Kappos, L.; Rovira, A.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; Tintorè, M.; Frederiksen, J.L.; et al. MRI criteria for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: MAGNIMS consensus guidelines. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, L.; Rocca, M.A.; Pagani, E.; Van Hecke, W.; Horsfield, M.A.; De Stefano, N.; Rovira, A.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; Palace, J.; Sima, D.; et al. Measurement of Whole-Brain and Gray Matter Atrophy in Multiple Sclerosis: Assessment with MR Imaging. Radiology 2018, 288, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushibar, K.; Valverde, S.; González-Villà, S.; Bernal, J.; Cabezas, M.; Oliver, A.; Lladó, X. Automated sub-cortical brain structure segmentation combining spatial and deep convolutional features. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 48, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, J.; Kushibar, K.; Cabezas, M.; Valverde, S.; Oliver, A.; Lladó, X. Quantitative Analysis of Patch-Based Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Tissue Segmentation on Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 89986–90002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, L.; Pievani, M.; Bocchetta, M.; Altomare, D.; Bosco, P.; Cavedo, E.; Galluzzi, S.; Marizzoni, M.; Frisoni, G.B. Brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s Disease and aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 30, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, K.S.; van Schijndel, R.A.; van Dijk, B.W.; Redolfi, A.; Knol, D.L.; Frisoni, G.B.; Barkhof, F.; Vrenken, H.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Assessing the reproducibility of the SIENAX and SIENA brain atrophy measures using the ADNI back-to-back MP-RAGE MRI scans. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2011, 193, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haijma, S.V.; Van Haren, N.; Cahn, W.; Koolschijn, P.C.M.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E.; Kahn, R.S. Brain volumes in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis in over 18 000 subjects. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 39, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Mechanisms of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: Insights from neuroimaging. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erp, T.G.; Hibar, D.P.; Rasmussen, J.M.; Glahn, D.C.; Pearlson, G.D.; Andreassen, O.A.; Agartz, I.; Westlye, L.T.; Haukvik, U.K.; Dale, A.M.; et al. Subcortical brain volume abnormalities in 2028 individuals with schizophrenia and 2540 healthy controls via the ENIGMA consortium. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, M.A.; Battaglini, M.; Benedict, R.H.; De Stefano, N.; Geurts, J.J.; Henry, R.G.; Horsfield, M.A.; Jenkinson, M.; Pagani, E.; Filippi, M. Brain MRI atrophy quantification in MS: From methods to clinical application. Neurology 2016, 88, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Jenkinson, M.; Chen, J.; Matthews, P.; Federico, A.; De Stefano, N. Accurate, robust, and automated longitudinal and cross-sectional brain change analysis. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglini, M.; Jenkinson, M.; De Stefano, N.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. SIENA-XL for improving the assessment of gray and white matter volume changes on brain MRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Nakamura, K.; Narayanan, S.; Brown, R.A.; Arnold, D.L.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Estimating and accounting for the effect of MRI scanner changes on longitudinal whole-brain volume change measurements. NeuroImage 2019, 184, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Xiao, Y.; Subbanna, N.; Francis, S.; Arnold, D.L.; Collins, D.L.; Arbel, T. Evaluating intensity normalization on MRIs of human brain with multiple sclerosis. Med. Image Anal. 2011, 15, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, R.T.; Sweeney, E.M.; Goldsmith, J.; Shiee, N.; Mateen, F.J.; Calabresi, P.A.; Jarso, S.; Pham, D.L.; Reich, D.S.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; et al. Statistical normalization techniques for magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 6, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, J.C.; Dewey, B.E.; Carass, A.; Prince, J.L. Evaluating the impact of intensity normalization on MR image synthesis. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2019, Image Processing. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 15 March 2019; Volume 10949, p. 109493H. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, D.S.; Fotenos, A.F.; Csernansky, J.G.; Morris, J.C.; Buckner, R.L. Open access series of imaging studies: Longitudinal MRI data in nondemented and demented older adults. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bernstein, M.A.; Fox, N.C.; Thompson, P.; Alexander, G.; Harvey, D.; Borowski, B.; Britson, P.J.; Whitwell, J.L.; Ward, C.; et al. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 27, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bağcı, U.; Udupa, J.K.; Bai, L. The role of intensity standardization in medical image registration. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Eskildsen, S.F.; Narayanan, S.; Arnold, D.L.; Collins, D.L.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Improving the SIENA performance using BEaST brain extraction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.E.; Liu, C.Y.; Thompson, P.M.; Tu, Z. Robust brain extraction across datasets and comparison with publicly available methods. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Kwitt, R.; Aylward, S.; Bakas, S.; Menze, B.; Asturias, A.; Vespa, P.; Van Horn, J.; Niethammer, M. Brain extraction from normal and pathological images: A joint PCA/image-reconstruction approach. NeuroImage 2018, 176, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J.C. A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters. J. Cybern. 1973, 3, 32–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyúl, L.G.; Udupa, J.K.; Zhang, X. New variants of a method of MRI scale standardization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2000, 19, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, R.; Vrooman, H.A.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij, M.W.; Breteler, M.M.; van der Lugt, A.; Niessen, W.J. Accuracy and reproducibility study of automatic MRI brain tissue segmentation methods. NeuroImage 2010, 51, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.P.; Sweeney, E.M.; Muschelli, J.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; Shinohara, R.T.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Removing inter-subject technical variability in magnetic resonance imaging studies. NeuroImage 2016, 132, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bresser, J.; Portegies, M.P.; Leemans, A.; Biessels, G.J.; Kappelle, L.J.; Viergever, M.A. A comparison of MR based segmentation methods for measuring brain atrophy progression. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, J.; Valverde, S.; Kushibar, K.; Cabezas, M.; Oliver, A.; Lladó, X. Generating Longitudinal Atrophy Evaluation Datasets on Brain Magnetic Resonance Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Segmentation Priors. Neuroinformatics 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaçali, B.; Davatzikos, C. Simulation of tissue atrophy using a topology preserving transformation model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2006, 25, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, B.; Ayache, N.; Pennec, X. Simulating longitudinal brain MRIs with known volume changes and realistic variations in image intensity. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyes, R.G.; Rueckert, D.; Aljabar, P.; Whitwell, J.; Schott, J.M.; Hill, D.L.; Fox, N.C. Cerebral atrophy measurements using Jacobian integration: Comparison with the boundary shift integral. NeuroImage 2006, 32, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Guizard, N.; Fonov, V.S.; Narayanan, S.; Collins, D.L.; Arnold, D.L. Jacobian integration method increases the statistical power to measure gray matter atrophy in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 4, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | OASIS | ADNI |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence | MP-RAGE | MP-RAGE |
| Repetition time (ms) | 9.7 | 3000 |
| Echo time (ms) | 4.0 | – |
| Flip angle | 10 | 8 |
| Inversion time (ms) | 20 | 1000 |
| Orientation | Sagittal | Sagittal |
| Thickness (mm) | 1.25 | 1.20 |
| Slice number | 128 | 184–208 |
| Resolution | 256 × 256 | 192 × 192 |
| 1 × 1 mm | 1.25 × 1.25 mm |
| None | z-Score | Fuzzy c-Means | Gaussian Mixture Model | Kernel Density Estimation | WhiteStripe | Histogram Matching | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OASIS (n = 122) | Before | Mean (CI), AD % | −0.61 (−0.85, −0.37) | −0.94 (−1.65, −0.23) | −1.00 (−1.51, −0.49) | −0.99 (−1.49, −0.49) | −0.98 (−1.49, −0.48) | −0.94 (−0.59, −1.28) | −0.59 (−0.79, −0.40) |
| Mean (CI), NC % | −0.10 (−0.35, 0.17) | 0.48 (−0.30, 1.26) | 0.06 (−0.50, 0.62) | 0.04 (−0.50, 0.60) | 0.10 (−0.46, 0.67) | −0.01 (0.38, −0.41) | −0.27 (−0.49, −0.06) | ||
| Cohen’s d | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.30 | ||
| p-value | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.10 | ||
| After | Mean (CI), AD % | −0.61 (−0.85, −0.38) | −1.01 (−1.49, −0.53) | −1.01 (−1.51, −0.50) | −1.05 (−1.62, −0.49) | −1.01 (−1.52, −0.50) | −0.83 (−1.18, −0.49) | −0.60 (−0.81, −0.39) | |
| Mean (CI), NC % | −0.09 (−0.35, 0.17) | 0.03 (−0.49, 0.56) | 0.03 (−0.53, 0.59) | 0.08 (−0.54, 0.71) | 0.02 (−0.53, 0.59) | −0.04 (−0.42, 0.34) | −0.35 (−0.58, −0.11) | ||
| Cohen’s d | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.23 | ||
| p-value | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.20 | ||
| ADNI (n = 147) | Before | Mean (CI), AD % | −0.89 (−1.10, −0.69) | −2.42 (−3.78, −1.07) | −1.43 (−1.76, −1.09) | −1.42 (−1.75, −1.09) | −1.44 (−1.77, −1.10) | −1.03 (−2.29, 0.21) | −0.77 (−0.95, −0.59) |
| Mean (CI), NC % | −0.27 (−0.45, −0.08) | 0.19 (−1.03, 1.42) | −0.44 (−0.75, −0.14) | −0.44 (−0.74, −0.14) | −0.45 (−0.75, −0.14) | −0.78 (−1.92, 0.36) | −0.28 (−0.44, 0.12) | ||
| Cohen’s d | 0.43 | 0.27 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.02 | 0.39 | ||
| p-value | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 0.02 | ||
| After | Mean (CI), AD % | −0.89 (−1.10, −0.69) | −1.47 (−1.79, −1.14) | −1.45 (−1.78, −1.12) | −1.51 (−1.87, −1.14) | −1.45 (−1.78, −1.12) | −1.19 (−1.44, −0.93) | −0.71 (−0.89, −0.55) | |
| Mean (CI), NC % | −0.27 (−0.45, −0.08) | −0.45 (−0.75, −0.15) | −0.45 (−0.75, −0.15) | −0.46 (−0.80, −0.12) | −0.44 (−0.75, −0.14) | −0.36 (−0.59, −0.13) | −0.27 (−0.41, −0.10) | ||
| Cohen’s d | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.36 | ||
| p-value | 0.01 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.007 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvajal-Camelo, E.E.; Bernal, J.; Oliver, A.; Lladó, X.; Trujillo, M.; Initiative, T.A.D.N. Evaluating the Effect of Intensity Standardisation on Longitudinal Whole Brain Atrophy Quantification in Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041773
Carvajal-Camelo EE, Bernal J, Oliver A, Lladó X, Trujillo M, Initiative TADN. Evaluating the Effect of Intensity Standardisation on Longitudinal Whole Brain Atrophy Quantification in Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041773
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvajal-Camelo, Emily E., Jose Bernal, Arnau Oliver, Xavier Lladó, María Trujillo, and The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. 2021. "Evaluating the Effect of Intensity Standardisation on Longitudinal Whole Brain Atrophy Quantification in Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041773
APA StyleCarvajal-Camelo, E. E., Bernal, J., Oliver, A., Lladó, X., Trujillo, M., & Initiative, T. A. D. N. (2021). Evaluating the Effect of Intensity Standardisation on Longitudinal Whole Brain Atrophy Quantification in Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041773






