Abstract
Retinal photomontages, which are constructed by aligning and integrating multiple fundus images, are useful in diagnosing retinal diseases affecting peripheral retina. We present a novel framework for constructing retinal photomontages that fully leverage recent deep learning methods. Deep learning based object detection is used to define the order of image registration and blending. Deep learning based vessel segmentation is used to enhance image texture to improve registration performance within a two step image registration framework comprising rigid and non-rigid registration. Experimental evaluation demonstrates the robustness of our montage construction method with an increased amount of successfully integrated images as well as reduction of image artifacts.
1. Introduction
Retinal fundus images can be acquired non-invasively, with high-resolution and high quality, in order to observe the state of the retina. Acquisition is simple, with relatively low-cost equipment, which makes them ubiquitous in routine screenings and clinical examinations. Because they enable close observation and assessment of the retina, fundus images can be used in the diagnosis of retinal degenerative diseases and cardiovascular complications, including age related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy [1], cerebral disorders [2], and hypertention [3].
Yet, the accurate diagnosis of diseases using fundus imaging is mainly done manually by clinicians. In order to improve their convenience, more recent software, such as the works by Son et al. [4,5], have leveraged machine learning technology, in particular, deep learning methods that are based on convolutional neural networks (CNN).
Most fundus images have a limited field of view, commonly within an angle of 30 to 50 degrees, depending on the parameters of the imaging equipment. This limitation may not hinder diagnoses of diseases that are localized in a small portion of the retina. However, for retinal diseases mainly affecting peripheral retina, such as diabetic retinopathy or retinal breaks, a wider angle of view is required, because it may be necessary to check the entire retina, including the optic disc, the surrounding of the fovea, and the peripheral regions all at once. For instance, in the work by Wykoff et al. [6], the severity of diabetes is measured using seven to nine fundus images continuously photographed in various directions to cover a wide angle of view. While these images do cover the wider field of view, the clinician needs to aggregate the information either mentally, or by image registration. An automatic method to integrate and visualize these multiple images would definitely benefit the clinician during examinations.
The photomontage technique does exactly this by aligning multiple images through image registration, and then stitching and blending them into a single image [7,8,9,10,11]. In the work of Mahurkar et al. [7], without many techniques for registration, background subtracted images are warped using a polynomial function that is based on guided matches. In Can et al. [8], a fully automated method that is based on a hierarchical matching scheme with a model of weak perspective camera, rigid motion, and approximate quadratic surface of the retina was proposed. In Cattin et al. [9], the improved SURF keypoint matching method [12] was used to improve the matching and, thus, the montage. In Lee et al. [10], the primary focus is on the modeling and validating the geometry of the eye. In a more recent work by Feng et al. [11], deep learning is indeed used as a CNN, but only to segment the vessel map from which bifurcation features are localized and matched for registration.
There are several issues that still can be improved within the frame of integrating retinal fundus images to achieve a wider field of view. One is the order and combination of the image alignment. As the number of images to be integrated increase, the combinatorial space of optimally aligning the images may become very large. As most image registration methods, such as feature point based methods [13], operate on pairs of images, it is simple to sequentially register the next image to the montage one-by-one. Here, determining the optimal order of images to be subsequently added arises as one key problem. Another issue is the accuracy of image registration and image warping during alignment and stitching. As the images are from the retina, distortion from projecting the three-dimensional spherical shape into two-dimensions increase as the stitched images are positioned farther from the center of the montage. The image registration and warping must be as accurate as possible in order to minimize artifacts.
In this paper, we present a novel framework for constructing photomontages of the retina from multiple fundus images that fully leverages recent deep learning methods. We apply a deep learning based object detection method [14] to detect the optic disc and retinal fovea, which is then used as reference landmarks to determine the order of image registration and alignment. We also adopt a recently proposed two step image registration framework [15,16] comprising rigid and non-rigid registration, but with key modifications to improve robustness for images in the peripheral of the retina. Here, CNN based vessel segmentation is used as the basis to maximize the accuracy of both rigid and non-rigid registration. Figure 1 depicts the overview of the proposed framework comprising the landmark detection, order determination, and iterative registration.
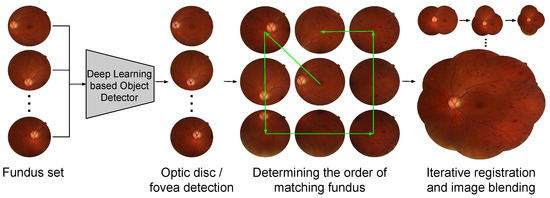
Figure 1.
Overview of the proposed framework for constructing retinal fundus photomontages. Through deep learning based object detection, we are able to apply prior knowledge of the fovea and optic disc to determine the optimal order in which to integrate the images into the montage. Deep learning is also leveraged to reduce errors in registration.
The idea behind using object detection is based on two observations. The first is that the fovea is anatomically close to the center of the retina. Thus, it can be a good reference point to center the photomontage. However, because it has fairly vague features, in the form of a slightly darker spot on the retina, it is not easy to use it as a reference in image alignment. Our second observation is about the optic disc, in that it has characteristic appearances. This makes feature point matching easier around the optic disc, and it can be exploited as a reference for more reliable image registration. Based on these observations, we categorize the images based on the existence of the fovea and the optic disc. Namely, (i) images containing both, (ii) images containing only the optic disc, (iii) images containing only the fovea, and (iv) images containing neither. Each category of images is integrated into the montage in this order, based on the positions of the fovea and/or optic disc within the image. For images with neither the fovea nor the optic disc, we rely on keypoint matching to determine the order.
When constructing the montage, we not only apply an accurate registration method, but also include a criterion for rejecting possible mismatched images. If the rigid transform and non-rigid displacement vectors computed during registration turn out to be excessively large distortions, we consider that the registration process might have failed and exclude that image from the montage. Combining these components, our framework can be repeatedly applied to all the image frames to generate the final montage.
By applying the detected positions of the fovea and optic disc, we effectively incorporate prior knowledge in the process, thereby resulting in a more robust montage construction with reduced failures. In addition, we can also improve the efficiency by avoiding the need to compare many image pairs in order to determine the best image to integrate next. We also improve the robustness of the image integration by maximizing the accuracy of image registration. We provide experimental evaluation on 62 retinal image sets to demonstrate the robustness, efficiency, and accuracy of the proposed framework.
2. Methods
We assume that the given set of fundus images are of varying viewing angles of the retina, with all images partially overlapping at least one other image. Henceforth, we refer to an image within a set as a frame. The process to determine the order of frame registration, or frame sorting, into the montage comprises fovea and optic disc detection and frame categorization, montage center frame selection, and per-frame sorting. The photomontage is initialized by the montage center frame, and then expanded by iteratively matching and blending the images into the montage one-by-one. Here, only images that have passed a validity test are included and those that do not are excluded. Details of each subprocess are described in the following subsections.
2.1. Frame Sorting
2.1.1. Disc and Fovea Detection and Frame Categorization
We apply the Faster R-CNN [14] method, depicted in Figure 2, since it has a good balance between efficiency in computation and storage, and detection performance. It comprises a CNN for feature extraction, a region proposal network (RPN) for exploring the bounding box location of object candidates, and a Fast R-CNN classifier for the object candidates, and it is combined in an end-to-end fashion. For the CNN, we used the ResNet-50 [17], which was pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset [18]. We applied transfer learning by fine-tuning the network on 13,000 images that were centered on either the optic disc or the fovea, sampled from our private dataset described in Section 3.1. For the RPN, we fixed the size of the object bounding boxes, since the size of the optic disc and fovea are generally constant in the fundus images. The results are given as the 2-D position and size of the bounding box, and confidence score for each object class, namely the fovea and optic disc. Here, we select the object with maximum confidence if there are more than one detection, as well as apply a threshold value of 0.9 on the confidence score, in order to determine the fovea and optic disc, respectively. For the detected fovea and optic disc, we often only use their point coordinate that is defined as the center coordinate of the bounding box.
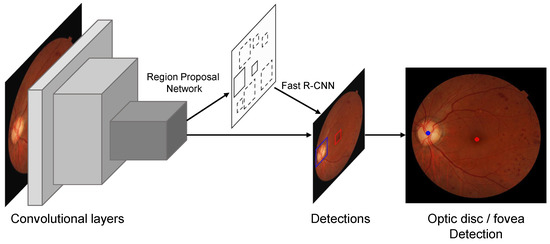
Figure 2.
Network diagram for disc and fovea detection. We apply the Faster R-CNN [14] method which is a two-step method comprising a region proposal network for detecting object candidates and a Fast RCNN network for classifying and localizing the bounding boxes for detection.
After the fovea and the optic disc are detected, we categorize the frames into four categories, namely, frames containing both the fovea and optic disc, frames containing only the fovea, frames containing only the optic disc, and peripheral frames that do not contain either one.
2.1.2. Montage Center Frame Selection and Per-Frame Sorting
We denote the center frame of the montage as . Because of the proximity of the fovea and the optic disc, images where the fovea can be located near the center also contain the optic disc. Thus, we select the initial frame among the frames. More specifically we select as the frame among with the minimum distance between the fovea center coordinate and the image center coordinate.
For the per-frame sorting, we first sort the frame categories in the order of , , , and . For both and , we sort the frames in the order of the relative distances between the optic disc coordinates within the frame and that of . That is, if we denote the pixel coordinate of the optic disc within and the frames as and , respectively, we sort the indices of based on the Euclidean distance . We apply this simple criterion, because frames that have similar optic disc coordinates have higher overlap.
We apply a similar approach to frames in , but based on the coordinates of the fovea instead of the optic disc. For the frames shownin we use the number of successful keypoint matches with the montage as the criterion for selecting the next frame.
Because the montage must be constructed at the point when selecting the next frame from , sorting is actually performed in a frame-by-frame manner, so that the next frame is iteratively determined, at which point registration is performed for that image and then integrated into the montage.
2.2. Frame Integration
We propose a modified version of the registration framework of Noh et al. [15,16], combining keypoint matching based rigid registration, CNN based vessel segmentation, and B-spline based non-rigid registration. Our modification stems from the need to enhance the number of keypoints in the rigid registration for the peripheral frames with less amount of texture when compared to frames containing the optic disc. Thus, we perform vessel segmentation first, and then use the vessel map in a preprocessing scheme to enhance the frame appearance. Figure 3 depicts a visual summary of this registration pipeline. Each frame is iteratively registered with, and blended into, the montage, in the order determined, as described in the previous subsection. In the following, we review each subprocess along with the process for blending new frames into the montage.
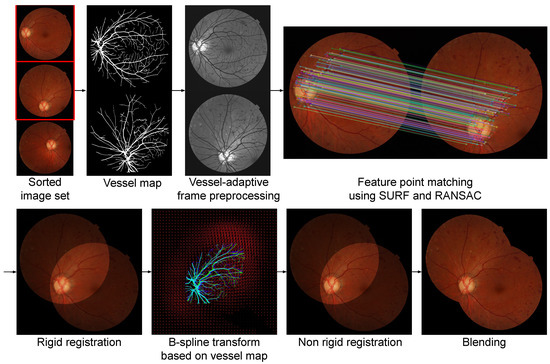
Figure 3.
A visual summary of the frame integration pipeline, including a two-step rigid and non-rigid registration method adapted from [15], together with image blending.
2.2.1. Vessel Segmentation and Frame Preprocessing
Unique landmarks are vital for image registration, for which vessels are an important and reliable source. However, often in fundus images, the vessels have very low contrast and they are unclear, especially for those in the peripheral that mostly contains thin vessels. Thus, we propose a preprocessing method to enhance the contrast that is based on vessel segmentation.
We apply the SSANet that was proposed by Noh et al. [19], which incorporates a layer for scale-space approximation to better deal with vessels of various widths, in order to generate a pixelwise vessel probability map for each frame. We then construct a binary mask from the map through thresholding, which is then used as a stencil for enhancing the frame contrast. Specifically, we simply increase pixel values by for non-vessel pixels, while maintaining the values of vessel pixels. Because vessel pixels consistently have lower intensities, this enhances the contrast. Figure 4 depicts a visualization of this process. We note that we train the SSANet on 554 images that were sampled from our private dataset described in Section 3.1, with ground truth being generated by the method of Noh et al. [15,16], based on the registered vessels of corresponding fluorescein angiography (FA) images, with minor manual corrections.
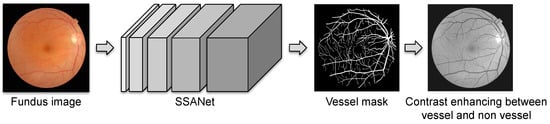
Figure 4.
Visual description of the proposed preprocessing scheme based on vessel segmentation using the SSANet of [19].
2.2.2. Keypoint Matching Based Rigid Registration
Rigid registration that is based on keypoint matches is first applied to account for large scale differences in the viewing direction between frames. We apply the SURF keypoint detector and descriptor [12] among many possible methods due to its balance of efficiency and robustness. The transform between the subsequent frame with the montage is modeled as a two-dimensional perspective homography and RANSAC (random sample consensus) is applied to disregard the outliers [20].
Inadequacy in applying a 2-D homography to represent the view transform of a 3-D spherical object and limited number of matched keypoints stemming from small overlap or insufficient texture may cause failures. Figure 5 depicts an example of erroneous registration and subsequent warping, which occurs when feature matching between overlapped images is not done properly. We add a simple validity test to exclude integrating an erroneously registered frame into the mosaic to avoid this. In particular, we measure the difference in pixel area before and after the determined homography transform. If the difference is larger than 10%, we exclude the frame. Here, the threshold value of 10% was empirically set based on the particular dataset in our experiments.

Figure 5.
An example case of rigid registration failure that occurred because too few keypoint matches were established. We include a validity test, based on the difference of pixel area before and after the transform, so that frames, such as these, are not integrated into the mosaic.
2.2.3. Non-Rigid Registration
We apply non-rigid registration to supplement simple rigid registration, which is likely to have limited accuracy due to the distortions that occur from projecting the original three-dimensional (3-D) shape as a two-dimensional (2-D) surface.
We perform pixel-wise non-rigid registration on the vessel probability maps to ensure sufficient amount of landmarks. The deformable transform is modeled as a B-spline transform model, and similarity is measured by normalized cross-correlation. The optimization of the deformation is determined by the gradient based L-BFGS-B [21] algorithm.
When integrating each frame into the montage, this non-rigid registration is applied between each frame and the current montage. Thus, we must construct and store the vessel map montage as well as the photomontage. Accordingly, while rigid registration does not depend on the vessel maps, we use the homography obtained at that step to perform rigid-registration on the vessel maps before we apply the non-rigid registration of the vessel maps. After the B-spline optimization, we apply the displacement vectors from the vessel map registration to the original frame to expand the photomontage.
2.2.4. Blending
The color intensity in the outer light, its scattering, and the opening of the eyelid are just a few factors that affect the achieved fundus image. Because the variations that occur, there are differences in the intensity, color, and contrast of the frame appearance. When different frames are registered, the overlapping regions have different pixel values due to these variations, and must be resolved to construct a visually pleasing photomontage.
To address this, we use the multi-resolution spline method [22] at the overlapping regions and boundaries of the frames, as depicted in the final step in Figure 3. Multi-resolution splines can minimize image intensity differences between each layer by applying weights around the center of the image pair and then applying the Gaussian filter and Laplacian filter.
2.3. Algorithm Summary
Here, we summarize the overall framework shown in Algorithm 1 to show how the frame sorting and frame integration is actually combined in an effective and efficient manner. Note that a montage of the vessel segmentation results must also be constructed and stored to perform non-rigid registration during the photomontage construction.
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Dataset and Experimental Environment
We used fovea–centered retinal fundus images from the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Retina Image Archive (SBRIA), which contains images that were obtained at the health screening center and ophthalmology outpatient clinic at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital obtained from 1 June 2003, through 30 June 2016, using various fundus cameras (CF60Uvi and CR6-45NM [Canon, Utsunomiya, Japan]; VX-10, VX-10a, nonmyd 7, and GENESIS-D [Kowa Optimed, Tokyo, Japan]) [5,16,23]. Our experimental test dataset comprises 62 image sequences that were collected from both eyes of 31 patients, where each image subset has a minimum of six to maximum nine frames, totalling 454 images, or 7.32 frames per subset. Each image is of resolution .
Experiments were performed on a system with 3.50 GHz i9-9900x CPU [Intel, Santa Clara, USA] and two GeForce RTX 2080ti GPUs [Nvidia, Santa Clara, USA]. We used the TorchVision package of PyTorch [24] as the implementation of the Faster R-CNN in disc and fovea detection, and the OpenCV implementation of SURF [25], and the SimpleITK implementation of B-spline registration [26]. PlantCV python-based opencv and PlantCV libraries were used to perform the technique. PlantCV is an opencv source library and it is used to find branch points in blood vessel images. All code was implemented in Python 3.
3.2. Quantitative Evaluation
We measure quantitative performance in two terms: (1) the number and portion of successfully integrated frames for each sequence and (2) the target registration error (TRE) based on landmark points. A frame is deemed as successfully integrated into the montage unless the keypoint matching based rigid registration fails, even with the safeguard measure, which is determined by manual inspection. Landmark points for which TRE is measured are defined as vessel bifurcation points that are automatically detected from the vessel segmentation map using the PlantCV library [27]. We note that, since the registration results vary considerably for each comparative method, TRE could not be measured on the same keypoints or the same image pairs. Thus, we only provide an aggregate comparison of the average TRE. Because the number of integrated frames are compared within an identical setup, we believe that these results present a more straightforward comparison of the performance between methods.
| Algorithm 1: Retinal Fundus Photomontage Construction Using Deep Learning. |
| Input: Set of fundus image frames , Trained Faster R-CNN for detecting optic disc and fovea Trained SSANet for vessel segmentation Output: Constructed photomontage , vessel map montage  |
Table 1 presents the quantitative evaluation. As to serve as an ablation study, we provide a comparison with the results when using the greedy approach that is based on the number of keypoint matches for sorting all frames to show the effect of our object detection based frame sorting method. We also provide a comparison between the results for other preprocessing methods, including a simple approach to normalize the minimum and maximum pixel intensities, and a more complex modified morphological top-hat transform by Li et al. [28], which was particularly proposed for retinal images. While each component contributes to slightly decrease TRE, the number of correctly integrated increases considerably. When compared to the method using min/max normalization and keypoint match sorting, our method with the proposed frame sorting and the preprocessing results in a photomontage with, on average, more frames, increased from 3.83 to 6.34, equivalent to an increase of 34.38 percentage points. In terms of TRE, there is a reduction. We also provide statistical analysis of the difference of the number of frames integrated into the montage as the P-value of the paired t-test, which supports the effectiveness of the proposed method that is based on significant improvements.

Table 1.
Comparison of preprocessing frame sorting methods for constructing a photomontage on 62 image sequences.
3.3. Qualitative Evaluation
We first present a qualitative comparison between a sample result for the different preprocessing methods in Figure 6. The min/max normalization can in this case increase their differences due to the presence and absence of the optic disc in the frame pair, which results in insufficient keypoint matches. For the modified top-hat transform of [28], the preprocessing mostly enhances local textures, which are not distinctive enough to be used as keypoint matches. The proposed preprocessing method is not affected by the presence or absence of the optic disc, and it enhances vessel textures that are suitable to be applied as keypoints.
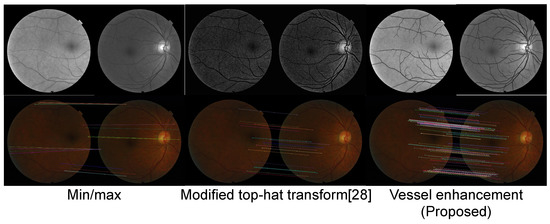
Figure 6.
Qualitative comparison of results from different preprocessing methods: min/max normalization where pixel values are rescaled, so that the minimum and maximum values of each image are normalized, modified top-hat transform proposed in [28], and the proposed method. The lower row shows the results of applying the SURF method [12] for keypoint matching on the corresponding input frame pairs above.
We present comparative qualitative evaluations for three methods, namely, the montage function of KOWA’s VK-2 [29], the AutoStitch application [30], and the proposed method. Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the results where all of the methods generate montages of similar size, but with differences in the quality of the generated montage. Overall, all three methods seem to generate similar montages, as depicted in (a–c); we can see that the proposed method reduces artifacts that occur in other methods, as depicted in the zoomed view of local artifact regions in (d–g). Figure 7d and Figure 8d, ghosting artifacts are visible from the results of the KOWA VK-2 montage, which are corrected in the results of the proposed method in Figure 7e and Figure 8e. Similarly, in Figure 7f and Figure 8f, misalignment causes ghosting of the same blood vessel from the results of AutoStitch, which are corrected in Figure 7g and Figure 8g.
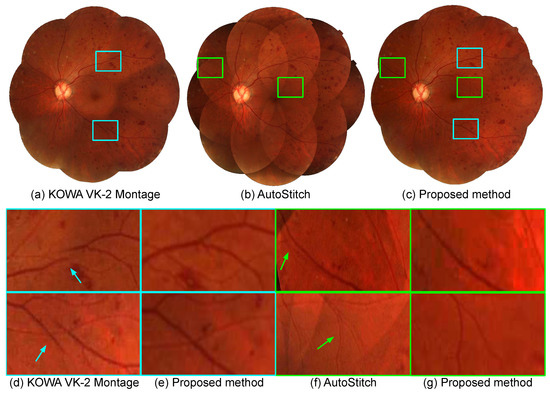
Figure 7.
Retinal photomontages constructed by (a) the montage function of KOWA VK-2 [29], (b) AutoStitch [30], and (c) the proposed method, respectively. Local regions highlighted as boxes in (a–c) are enlarged in (d–g). (d) and (f) show the comparison between KOWA VK-2 montage and the proposed method, and (e,g) show the comparison between AutoStitch and the proposed method, respectively.
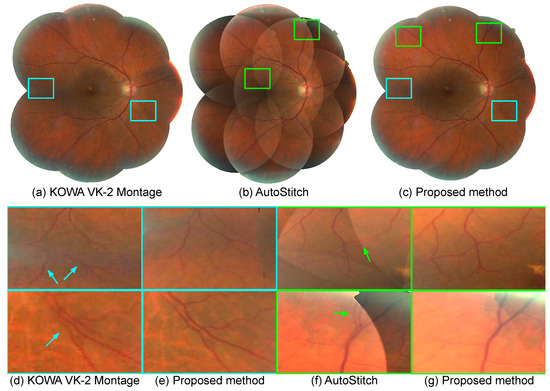
Figure 8.
Retinal photomontages constructed by (a) the montage function of KOWA VK-2 [29], (b) AutoStitch [30], and (c) the proposed method, respectively. Local regions highlighted as boxes in (a–c) are enlarged in (d–g). (d) and (f) show the comparison between KOWA VK-2 montage and the proposed method, and (e,g) show the comparison between AutoStitch and the proposed method, respectively.
In Figure 9, we present more challenging image sets where the comparative methods fails, leading to insufficient coverage of the montage and various artifacts. For the montages of the KOWA VK-2, many artifacts are evident, even within the insufficiently formed montage. For the results of AutoStitch, fewer artifacts are visible, but it seems that only two or three frames have been integrated. The proposed method is able to generate a more complete montage when compared to these methods.
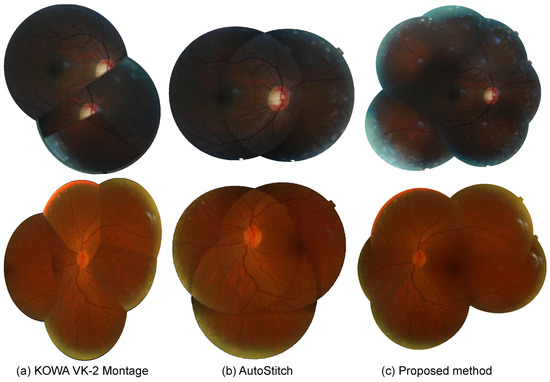
Figure 9.
Comparison of Mosaic images constructed by different application. (a) KOWA software. (b) AutoStitch. (c) proposed.
4. Discussion
We present a new method to construct retinal photomontages that apply recently developed deep learning methodologies for object detection and segmentation. Not only do we adopt a recent registration method, but we also propose an improved frame sorting for sequencing frame integration helps to improve the registration accuracy, which can be observed by the reduction of TRE. We also propose an improved preprocessing method utilizing the results of the vessel segmentation that is required in non-rigid registration, to enable more robust feature keypoint matching in rigid registration. For future works, we plan to clinically apply our process in the early diagnosis and treatment of various retinal diseases as well as degenerative diseases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L., S.J.P., K.J.N. and J.K.; methodology, S.L., S.J.P., K.J.N. and J.K.; software, S.L., K.J.N. and J.K.; validation, S.L. and J.K.; formal analysis, S.L., S.J.P. and J.K.; investigation, S.L., S.J.P. and J.K.; resources, S.J.P.; data curation, S.J.P. and J.K.; Writing—Original draft preparation, J.K.; Writing—Review and editing, S.L., S.J.P., S.G. and J.K.; visualization, J.K.; supervision, S.L. and S.J.P.; project administration, S.L. and S.J.P.; funding acquisition, S.J.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2018R1D1A1A09083241, 2020R1F1A1051847).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the institutional review board at Seoul National Bundang Hospital (institutional review board identifier, X-1509-316-903) and was conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the institutional review board because of the retrospective nature of the study, conducted on a preconstructed de-identified dataset.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to IRB restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cunha-Vaz, J.G. Pathophysiology of diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1978, 62, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.K.; De Jong, F.J.; Van Dijk, E.J.; Prins, N.D.; Hofman, A.; Breteler, M.M.B.; De Jong, P.T.V.M. Retinal vessel diameters and cerebral small vessel disease: The Rotterdam Scan Study. Brain 2005, 129, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritt, M.; Schmieder, R.E. Wall-to-Lumen ratio of retinal arterioles as a tool to assess vascular changes. Hypertension 2009, 54, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.; Shin, J.Y.; Chun, E.J.; Jung, K.H.; Park, K.H.; Park, S.J. Predicting high coronary artery calcium score from retinal fundus images with deep learning algorithms. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.; Shin, J.Y.; Kim, H.D.; Jung, K.H.; Park, K.H.; Park, S.J. Development and Validation of Deep Learning Models for Screening Multiple Abnormal Findings in Retinal Fundus Images. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Eichenbaum, D.A.; Roth, D.B.; Hill, L.; Fung, A.E.; Haskova, Z. Ranibizumab induces regression of diabetic retinopathy in most patients at high risk of progression to proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2018, 2, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahurkar, A.A.; Vivino, M.A.; Trus, B.L.; Kuehl, E.M.; Datiles, M.B., 3rd; Kaiser-Kupfer, M.I. Constructing retinal fundus photomontages. A new computer-based method. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Can, A.; Stewart, C.V.; Roysam, B. Robust hierarchical algorithm for constructing a mosaic from images of the curved human retina. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Fort Collins, CO, USA, 23–25 June 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Cattin, P.C.; Bay, H.; Van Gool, L.; Székely, G. Retina mosaicing using local features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Reinhardt, J.M.; Cattin, P.C.; Abràmoff, M.D. Objective and expert-independent validation of retinal image registration algorithms by a projective imaging distortion model. Med. Image Anal. 2010, 14, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Cai, G.; Gou, X.; Yun, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, W. Retinal Mosaicking with Vascular Bifurcations Detected on Vessel Mask by a Convolutional Network. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Surf: Speeded up robust features. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Matas, C.; Zabulis, X.; Argyros, A.A. An experimental evaluation of the accuracy of keypoints-based retinal image registration. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object eetection with region proposal networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Garnett, R., Eds.; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Volume 28, pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, K.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S. Fine-Scale vessel extraction in fundus images by registration with fluorescein angiography. In Proceedings of International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI); Shen, D., Liu, T., Peters, T.M., Staib, L.H., Essert, C., Zhou, S., Yap, P.T., Khan, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 779–787. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, K.J.; Kim, J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S. Multimodal registration of fundus images With fluorescein angiography for fine-scale vessel segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 63757–63769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, K.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S. Scale-space approximated convolutional neural networks for retinal vessel segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 178, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.; Nocedal, J.; Zhu, C. A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization. Siam J. Sci. Comput. 1995, 16, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, P.J.; Adelson, E.H. A multiresolution spline with application to image mosaics. Acm Trans. Graph. (TOG) 1983, 2, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Shin, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Son, J.; Jung, K.H.; Park, K.H. A Novel Fundus Image Reading Tool for Efficient Generation of a Multi-dimensional Categorical Image Database for Machine Learning Algorithm Training. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32; Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Bradski, G. The opencv library. Dr Dobb’s J. Softw. Tools 2000, 25, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lowekamp, B.C.; Chen, D.T.; Ibáñez, L.; Blezek, D. The design of SimpleITK. Front. Neuroinform. 2013, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehan, M.A.; Fahlgren, N.; Abbasi, A.; Berry, J.C.; Callen, S.T.; Chavez, L.; Doust, A.N.; Feldman, M.J.; Gilbert, K.B.; Hodge, J.G.; et al. PlantCV v2: Image analysis software for high-throughput plant phenotyping. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C.; Yin, T.; Liu, C.; Yang, J. Robust Retinal Image Enhancement via Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform and Morphology-Based Method. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47303–47316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowa American Corporation. KOWA VK-2 Image Filing System: Features; 2021. Available online: https://ophthalmic.kowa-usa.com/products/software/vk-2-image-filing-system-features (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Brown, M.; Lowe, D.G. Automatic Panoramic Image Stitching using Invariant Features. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).