Producing Synthetic Dataset for Human Fall Detection in AR/VR Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We implemented a physical model of digital humans to simulate the fall of a person and their interaction with the environment with inverse kinematics for producing various fall dynamics;
- (2)
- We took into account the coordinates of impact with the object of interaction in the process of registering a digital human fall to improve the segmentation ability of the hit mask;
- (3)
- We implemented the integration of digital human behaviour simulation for automatic “playing” of various scenarios of interactions and falls in a 3D scene automatically;
- (4)
- We apply the deep learning approach to examine the ability for training with synthetic data to recognize the real datasets.
2. Related Works
2.1. Human Fall Detection
2.2. Existed Training Sets
3. Proposed Digital Human Falling Dataset Generation Pipeline
- Three-dimensional scene generation for various textures, meshes, skeleton physics, etc. (Section 3.1, Section 3.2 and Section 3.3);
- Various behaviour simulation of a digital human (Section 3.4);
- Masks of digital human hit registration with a 3D scene environment (Section 3.5).
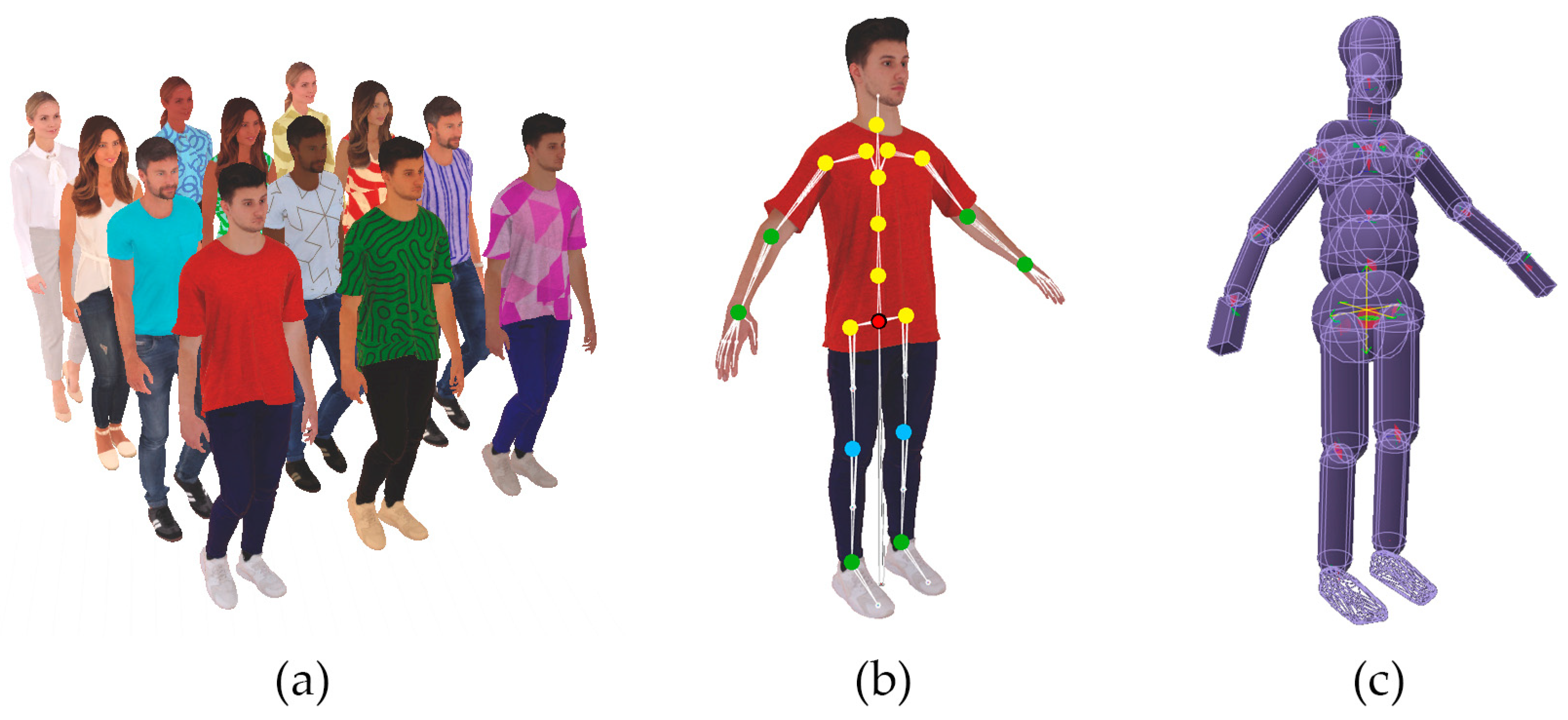
3.1. Digital Human Construction
3.2. Physical Modeling
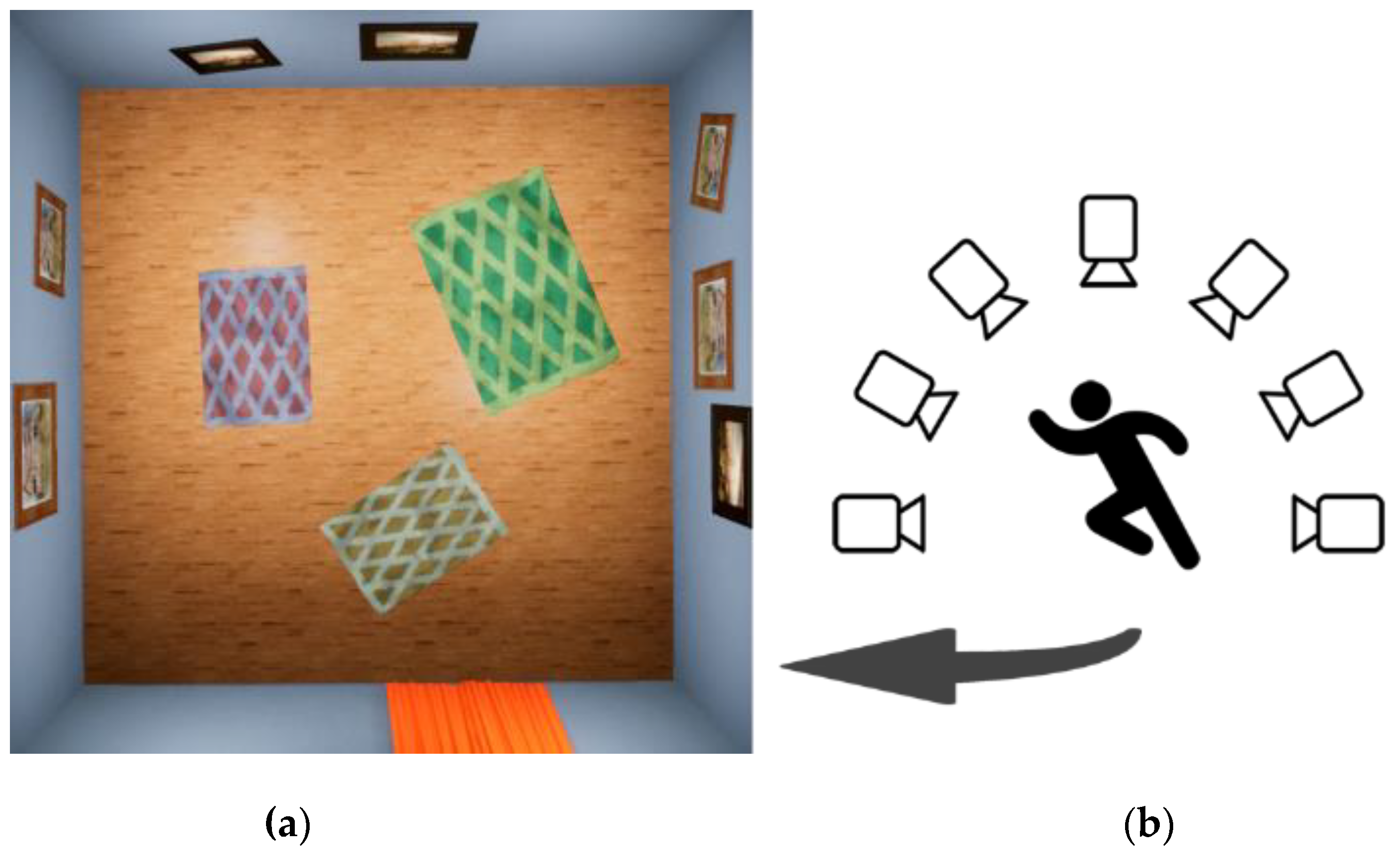
3.3. Background and Rendering
3.4. Digital Human Behavior Simulation
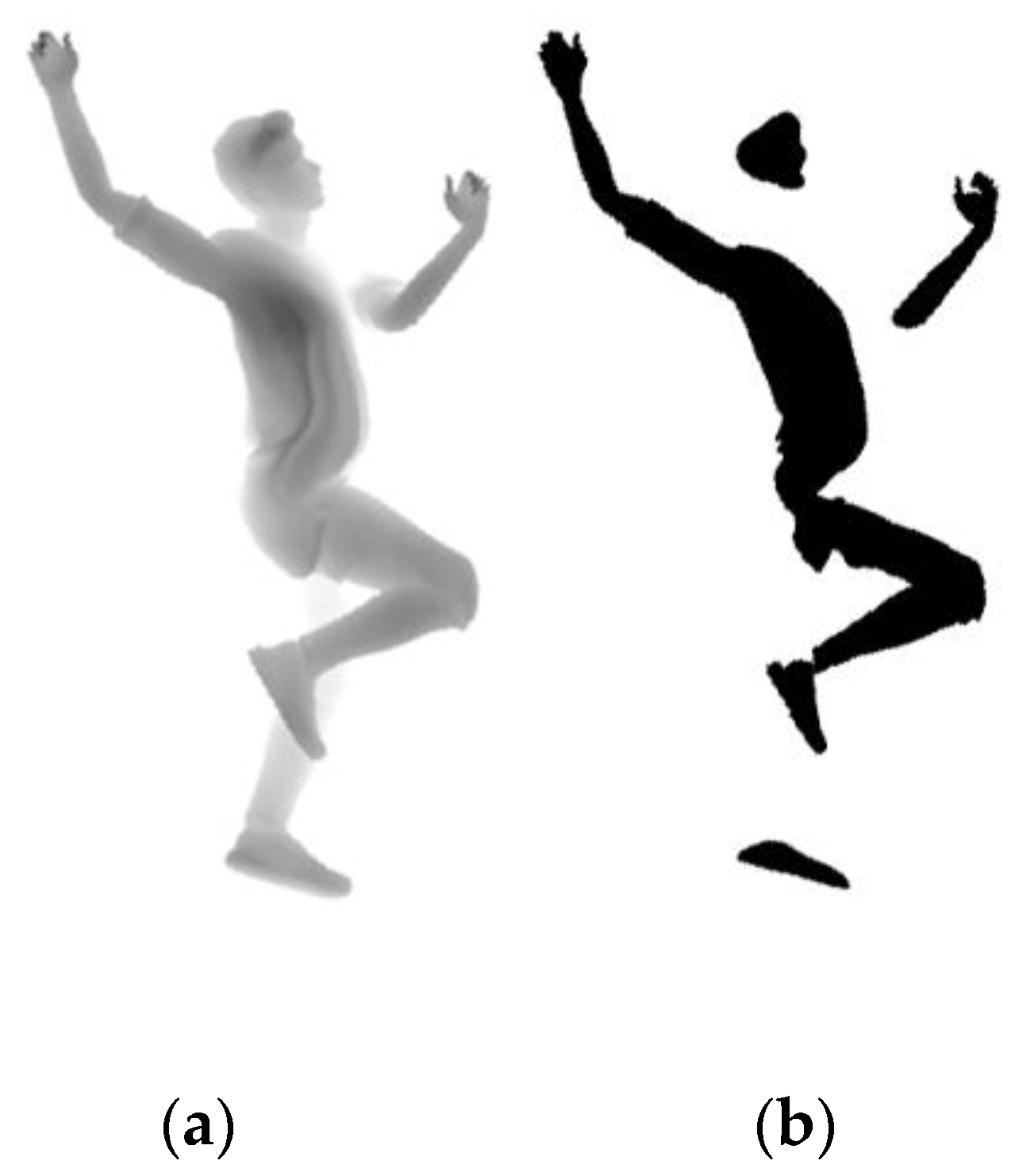
3.5. Hit Masks and Visualisation
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
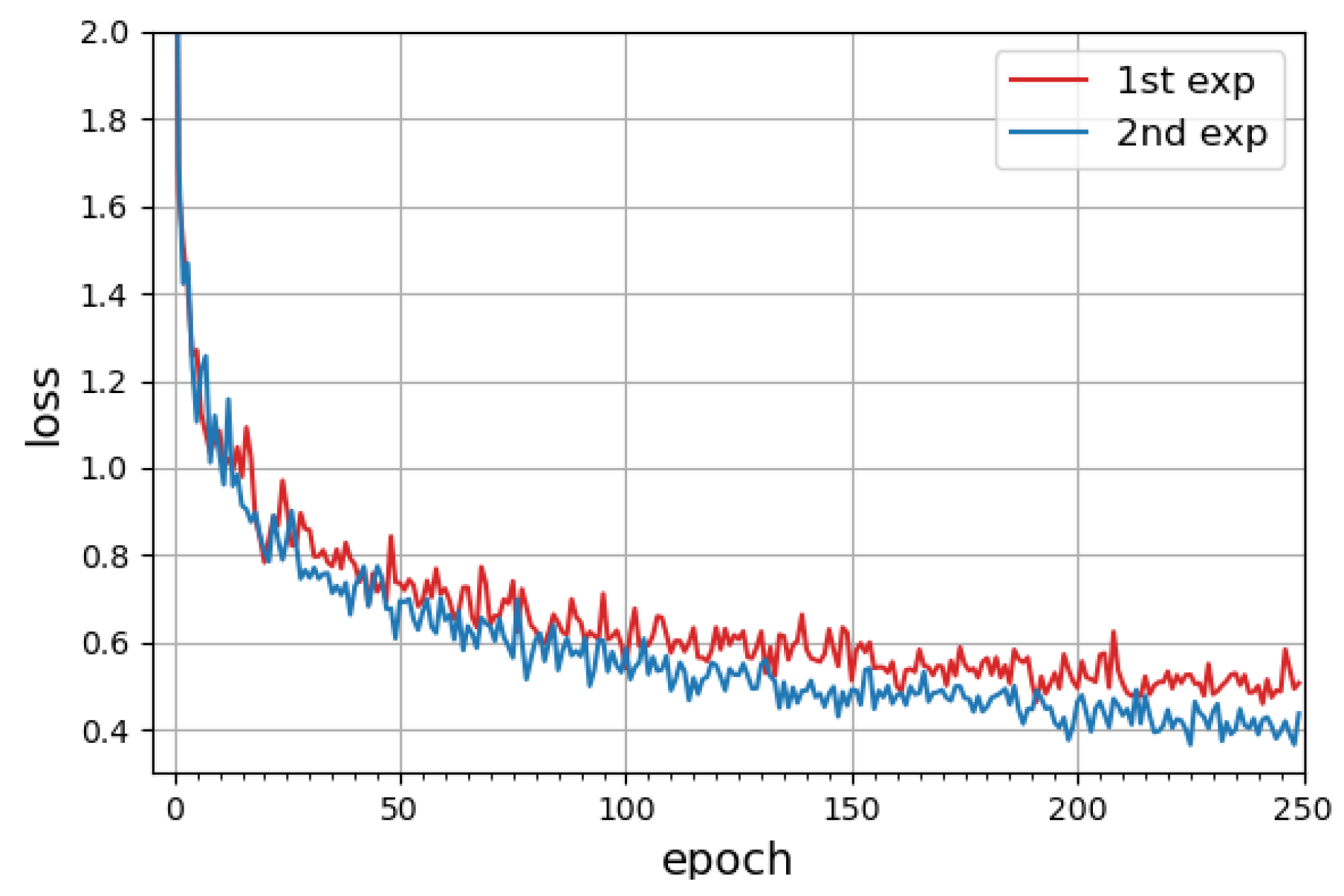
4.2. CNN Training
4.3. Recognition Results
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le, T.; Baydin, A.; Zinkov, R.; Wood, F. Using synthetic data to train neural networks is model-based reasoning. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 3514–3521. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep visual domain adaptation: A survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Yue, J.; Dong, Y.; He, S.; Wang, H.; Ning, S. A synthetic dataset for Visual SLAM evaluation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 124, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ball, J.E.; Tang, B.; Carruth, D.W.; Doude, M.; Islam, M.A. Semantic Segmentation with Transfer Learning for Off-Road Autonomous Driving. Sensors 2019, 19, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, J.; Xu, R.; Sun, S.; Li, C. Simulation of an Autonomous Mobile Robot for LiDAR-Based In-Field Phenotyping and Navigation. Robotics 2020, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Kapoor, A.; Scherer, S. TartanAir: A Dataset to Push the Limits of Visual SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Antonini, A.; Guerra, W.; Murali, V.; Sayre-McCord, T.; Karaman, S. The Blackbird Dataset: A Large-Scale Dataset for UAV Perception in Aggressive Flight. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Experimental Robotics; Xiao, J., Kröger, T., Khatib, O., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Advanced Robotics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, A.; Raychowdhury, A. Autonomous Navigation via Deep Reinforcement Learning for Resource Constraint Edge Nodes Using Transfer Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 26549–26560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, G.; Barrado, C.; Çetin, E.; Salami, E. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Drone Delivery. Drones 2019, 3, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Saeedi, S.; McCormac, J.; Clark, R.; Tzoumanikas, D.; Ye, Q.; Leutenegger, S. InteriorNet: Mega-scale Multi-sensor Photo-realistic Indoor Scenes Dataset. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00716. [Google Scholar]
- Danielczuk, M.; Matl, M.; Gupta, S.; Li, A.; Lee, A.; Mahler, J.; Goldberg, K. Segmenting Unknown 3D Objects from Real Depth Images using Mask R-CNN Trained on Synthetic Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7283–7290. [Google Scholar]
- McCormac, J.; Handa, A.; Leutenegger, S.; Davison, A. SceneNet RGB-D: Can 5M Synthetic Images Beat Generic ImageNet Pre-training on Indoor Segmentation? In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2678–2687. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Choe, G.; Nadir, Z.; Nabil, O.; Lee, S.-J.; Sheikh, H.; Yoo, Y.; Polley, M. Sensor-realistic Synthetic Data Engine for Multi-frame High Dynamic Range Photography. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Virtual, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 516–517. [Google Scholar]
- Ros, G.; Sellart, L.; Materzynska, J.; Vazquez, D.; Lopez, A. The SYNTHIA Dataset: A Large Collection of Synthetic Images for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3234–3243. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, S.; Hayder, Z.; Koltun, V. Playing for Benchmarks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2213–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Khalid, S.; Xiao, W.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Towards Semantic Segmentation of Urban-Scale 3D Point Clouds: A Dataset, Benchmarks and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4977–4987. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, S.; Athanasiou, N.; Kocabas, M.; Black, M.J. Learning to Regress Bodies from Images using Differentiable Semantic Rendering. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11250–11259. [Google Scholar]
- Quirós-Ramírez, M.A.; Streuber, S.; Black, M.J. Red shape, blue shape: Political ideology influences the social perception of body shape. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2021, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Black, M.J.; Tang, S. PLACE: Proximity Learning of Articulation and Contact in 3D Environments. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Fukuoka, Japan, 25–28 November 2020; pp. 642–651. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, G.; Romero, J.; Martin, X.; Mahmood, N.; Black, M.J.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Learning from Synthetic Humans. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Pishchulin, L.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. 2D human pose estimation: New benchmark and state of the art analysis. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 3686–3693. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, D.; Tzionas, D.; Black, M.J.; Tang, S. Learning to Train with Synthetic Humans. In Proceedings of the 2019 German Conference on Pattern Recognition (GCPR), Dortmund, Germany, 11–13 September 2019; pp. 609–623. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart Williams, J.; Kowal, P.; Hestekin, H.; O’Driscoll, T.; Peltzer, K.; Wu, F.; Arokiasamy, P.; Chatterji, S. Prevalence, risk factors and disability associated with fall-related injury in older adults in low- and middle-incomecountries: Results from the WHO Study on global AGEing and adult health (SAGE). BMC Med. 2015, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taheri, O.; Ghorbani, N.; Black, M.J.; Tzionas, D. GRAB: A Dataset of Whole-Body Human Grasping of Objects. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.11200. [Google Scholar]
- Harrou, F.; Zerrouki, N.; Sun, Y.; Houacine, A. An Integrated Vision-Based Approach for Efficient Human Fall Detection in a Home Environment. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 114966–114974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ramamoorthy, V.; Gal, U.; Guez, A. Possible Life Saver: A Review on Human Fall Detection Technology. Robotics 2020, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Wei, Z.; Wang, S. Learning Spatiotemporal Representations for Human Fall Detection in Surveillance Video. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 59, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, U.; Mashford, B.; Cavallar, S.; Yohanandan, S.; Roy, S.; Tang, J.; Harrer, S. Privacy Preserving Human Fall Detection using Video Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 Machine Learning for Health NeurIPS Workshop, PMLR, Virtual Conference, 11 December 2020; pp. 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Rahmani, H.; Akhtar, N.; Mian, A. Learning Human Pose Models from Synthesized Data for Robust RGB-D Action Recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clever, H.; Erickson, Z.; Kapusta, A.; Turk, G.; Liu, K.; Kemp, C. Bodies at rest: 3d human pose and shape estimation from a pressure image using synthetic data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6215–6224. [Google Scholar]
- Min, W.; Zou, S.; Li, J. Human fall detection using normalized shape aspect ratio. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 14331–14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villaseñor, L.; Ponce, H.; Brieva, J.; Moya-Albor, E.; Núñez-Martínez, J.; Peñafort-Asturiano, C. UP-Fall Detection Dataset: A Multimodal Approach. Sensors 2019, 19, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, K.; Wang, P.; Zhuang, S. Human fall detection using slow feature analysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 9101–9128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Levine, M.D.; Wen, G.; Qiu, S. A deep neural network for real-time detection of falling humans in naturally occurring scenes. Neurocomputing 2017, 260, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmahboub, B.; Samavi, S.; Karimi, N.; Shirani, S. Automatic monocular system for human fall detection based on variations in silhouette area. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparrini, S.; Cippitelli, E.; Spinsante, S.; Gambi, E. A depth-based fall detection system using a kinect® sensor. Sensors 2014, 14, 2756–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvinet, E.; Multon, F.; Saint-Arnaud, A.; Rousseau, J.; Meunier, J. Fall Detection With Multiple Cameras: An Occlusion-Resistant Method Based on 3-D Silhouette Vertical Distribution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 15, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfi, I.; Miteran, J.; Dubois, J.; Atri, M.; Tourki, R. Optimized spatio-temporal descriptors for real-time fall detection: Comparison of support vector machine and adaboost-based classification. J. Electron. Imaging 2013, 22, 041106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, U.; Cavallar, S.; Tang, J.; Harrer, S. SSHFD: Single Shot Human Fall Detection with Occluded Joints Resilience. In Proceedings of the 2020 European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 29 August–8 September 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, H.; Mahmood, A.; Huynh, D.; Mian, A. Histogram of oriented principal components for cross-view action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 2430–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bak, S.; Carr, P.; Lalonde, J.F. Domain adaptation through synthesis for unsupervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2014; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.; Wang, G. NTU RGB+D: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1010–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C.; Papava, D.; Olaru, V.; Sminchisescu, C. Human3.6M: Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3D human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiourt, C.; Koutsoudis, A.; Pavlidis, G. DynaMus: A fully dynamic 3D virtual museum framework. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 22, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unreal Engine 4. Available online: https://www.unrealengine.com/en-US/what-is-unreal-engine-4 (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- RenderPeople—A Photorealistic Human 3D Models. Available online: https://renderpeople.com/ (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Millington, I. Game Physics Engine Development: How to Build a Robust Commercial-Grade Physics Engine for Your Game; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aristidou, A.; Lasenby, J.; Chrysanthou, Y.; Shamir, A. Inverse Kinematics Techniques in Computer Graphics: A Survey. Comput. Graph. Forum 2017, 37, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovino, M.; Scukins, E.; Styrud, J.; Ögren, P.; Smith, C. A Survey of Behavior Trees in Robotics and AI. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.05842. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Kwolek, B.; Kepski, M. Human fall detection on embedded platform using depth maps and wireless accelerometer. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 117, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Marcos, A.; Azkune, G.; Arganda-Carreras, I. Vision-based fall detection with convolutional neural networks. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 9474806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fallon, M.; Riem, M.; Kunst, L.; Kop, W.; Kupper, N. Multi-modal responses to the Virtual Reality Trier Social Stress Test: Acomparison with standard interpersonal and control conditions. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 161, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garduño, H.; Martínez, M.; Castro, M. Impact of Virtual Reality on Student Motivation in a High School Science Course. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





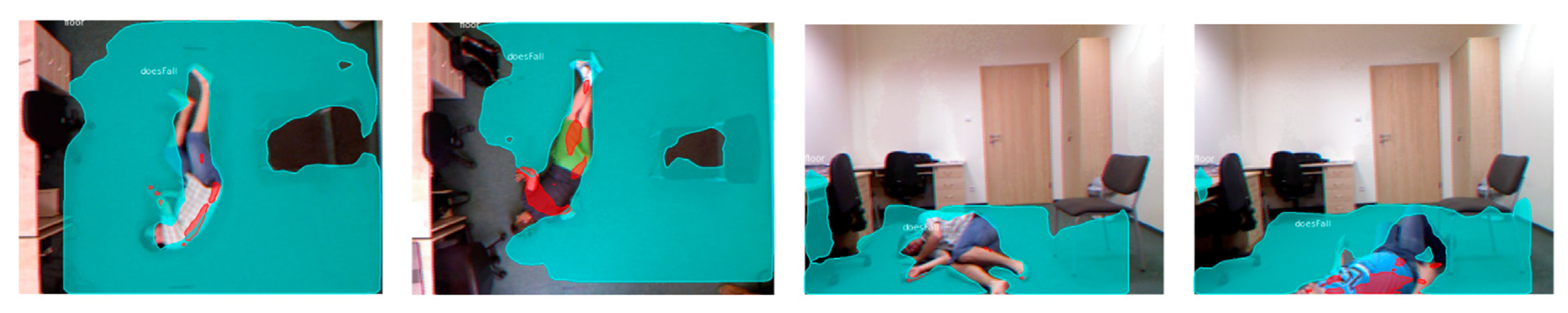

| Fall Type | GT | Predicted Map, 1st Exp | Predicted Map, 2nd Exp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward fall (Camera #2) |  |  | 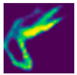 |
| Forward fall (Camera #2) |  | 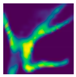 |  |
| Forward fall (Camera #11) |  | 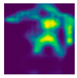 | 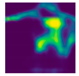 |
| Back fall (Camera #9) |  | 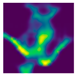 | 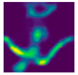 |
| Back fall (Camera #1) |  |  | 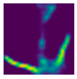 |
| Back fall (Camera #4) |  | 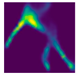 |  |
| Side fall (Camera #1) |  | 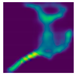 | 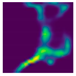 |
| Side fall (Camera #6) |  | 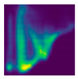 | 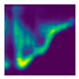 |
| Side fall (Camera #1) |  |  |  |
| Data Generation | 1st Exp (577 Simulations) 1 Random Character, 1 Random Room | 2nd Exp (271 Simulations) 2 Random Characters, 4 Random Rooms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fall type | fw | back | side | fw | back | side |
| Total simulations | 191 | 196 | 190 | 89 | 90 | 92 |
| Total images | 27,476 | 12,698 | ||||
| DICE (%) | 71.9 | 62.1 | 59.7 | 75.0 | 69.3 | 66.7 |
| IoU (%) | 55.5 | 48.0 | 44.7 | 59.7 | 52.3 | 49.4 |
| Camera Type | Camera1 (Filming Top-Down) | Camera0 (Filming Side) |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 97.9% | 87.5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zherdev, D.; Zherdeva, L.; Agapov, S.; Sapozhnikov, A.; Nikonorov, A.; Chaplygin, S. Producing Synthetic Dataset for Human Fall Detection in AR/VR Environments. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11938. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411938
Zherdev D, Zherdeva L, Agapov S, Sapozhnikov A, Nikonorov A, Chaplygin S. Producing Synthetic Dataset for Human Fall Detection in AR/VR Environments. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(24):11938. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411938
Chicago/Turabian StyleZherdev, Denis, Larisa Zherdeva, Sergey Agapov, Anton Sapozhnikov, Artem Nikonorov, and Sergej Chaplygin. 2021. "Producing Synthetic Dataset for Human Fall Detection in AR/VR Environments" Applied Sciences 11, no. 24: 11938. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411938
APA StyleZherdev, D., Zherdeva, L., Agapov, S., Sapozhnikov, A., Nikonorov, A., & Chaplygin, S. (2021). Producing Synthetic Dataset for Human Fall Detection in AR/VR Environments. Applied Sciences, 11(24), 11938. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411938







