Abstract
Exercise is good for health, quality of life, and maintenance of human muscles. Dumbbells are popular indoor exercise equipment with several benefits such as low cost, high flexibility in space and time, easy operation, and suitability for people of all ages. Facilitated by advances in the Internet of Things, smart dumbbells that provide automatic counting and motion monitoring functions have been developed. To perform these tasks, the key process is identification of exercise mode. This study proposes a method to identify essential muscle groups’ (biceps, triceps, and deltoids) exercise modes of a dumbbell using an inertial measurement unit to provide three-axis angular velocities and accelerations. The motion angles were estimated from the axial acceleration and angular velocity. Phase diagrams and time plots of the axial angle, angular velocity, and acceleration were used to extract significant features of each exercise. Machine Learning and weighting functions were developed to combine these features into an identification index value for accurate identification and classification of the exercise modes. An algorithm was developed to verify the exercise mode identification. The results show that the proposed method and weighting function can successfully identify the six exercise modes. The identification algorithm was 99.5% accurate. The exercise mode identification of the dumbbell is confirmed.
1. Introduction
Physical exercise is important for the human immune system and can help to reduce a person’s risk of infection. It may also prevent bacterial infections of the lungs that result in diseases such as cold, flu, and others [1,2]. Exercise is also one contribution in clinical implications that could help exercise as a diagnostic tool-non/invasive technique. For example, human data show that during each exercise bout, transient immune changes occurred that over time may improve immunosurveillance against pathogens, thereby reducing upper respiratory tract infection [3,4]. In addition, Ostman has shown that exercise training enhances the human body, cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome [5]. Some experts also pointed out that high physical exercise was associated with favorable results for most health-related quality of life scale scores, including disability, frailty, and exhaustion, in dialysis patients [6]. Dumbbells, which are popular indoor sports equipment, are widely used for resistance training to increase the strength of the skeletal muscular system; it improves bone density, enhances lean mass, and increases metabolism [7,8]. Currently, the conventional dumbbell exercise equipment has unrecordable training information, and as it involves repetitive steps, creates a feeling of boredom. Therefore, the device has been unhelpful to people who need accurate control of exercises and want to manage their health data. Liu et al. developed an intelligent dumbbell [9] that can monitor fitness activity; however, the device only obtains the raw acceleration signal from MPU6050 with no filter to denoise unwanted signals. The human interface machine recorded three-axis acceleration data and provided information about the angle to an observer on the Mobile Application (APP). Catching up with the trend, Xiaomi has successfully developed Smart Dumbbells and commercialized the market. However, this product only guides people to practice according to the preset program available in the application.
Smart dumbbells are created by combining a traditional dumbbell and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensor, which consists of gyroscopes and accelerometers, enabling translational movements and tracking of rotation. This sensor is an improvement in technology for developing microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) with low power and cost that can be applied to many smart tracking devices in gloves, tennis or golf. The initial idea to use an acceleration sensor to track free-weight exercises was proposed by Chang and Chen [10]. They used the naive Bayes and hidden Markov model methods to identify nine modes of exercise; yet, their results have a problem with imposing similar acceleration responses and the effect reaches approximately 90%. Li et al. used the same acceleration signal to identify and resolve this problem faced by previous research using a combination of a fifth order Butterworth filter to remove noise [11]. Artificial neural networks (ANNs), support vector machines (SVMs), statistical dynamic time warping (SDTW), and improved dynamic time warping (IDTW) methods were applied to compare their performances. The recognition accuracy of the ANN is not acceptable, but the IDTW method has a high efficiency of approximately 96%, which is better compared to 77% for SVMs and 81% for SDTW. In recent years, fusion sensors with artificial intelligence (AI) have contributed significantly to tracking and classifying modes of exercise [12,13,14]. However, there are various issues in accurately determining features from raw data of the fusion sensor: all of these methods require big data and need a lot of computer memory. So far, the identification accuracy using deep learning was 99.96% [12]; however, no real-time testing has been conducted in this research study. In addition, the fusion sensor contains a lot of noise; thus, we need to have an excellent denoising filter. This has resulted in many studies revolving around filter development. The Kalman filter, complementary filter, and gradient descent are popular methods for denoising raw data [15,16,17,18,19]; existing results show that the Kalman filter is better than the others under the condition of a simple system with no multiple state variables. Many dumbbell workouts focus on different parts of the body, which can be divided into different primary groups: those vital involving the biceps, deltoids, and triceps. In this study, we selected six acts for each muscle named bicep, deltoid, tricep, shoulder, squat, side and lunge actions.
The aim of this study is to create a new smart dumbbell that can monitor and identify the user’s state as well as manage the accuracy of the dumbbell movement. We improved the identification quality of Support Vector Machine (SVM) in the Machine Learning method and proposed a new algorithm to recognize the modes of exercises with high efficiency. The proposed new algorithm could keep tracking and classifying the movement of the dumbbell in order to correctly and effectively train certain muscles in real time.
2. The Mode Training and Identification of Data
The dumbbell that is used is called a hex dumbbell, as shown in Figure 1. We attached the IMU sensor to one side. There are many IMU products that output 6-axis or 9-axis sensor data. The device is designed by incorporating an accelerometer and a gyroscope (6DoF) in the first case; alternatively, another accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer (9DoF) are integrated on a printed circuit board.
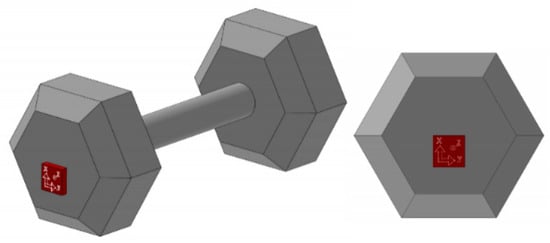
Figure 1.
Prototype of hex dumbbell.
In this study, we use a 9DoF Razor IMU on the dumbbell, which includes the sensors and control process unit onboard. Different parts of the muscles are used while exercising; however, the person training with the dumbbell focuses on biceps, deltoids, and triceps. Six types of actions with dumbbell exercises were selected and classified into two categories, namely simple and complex actions. In terms of simple actions, the dumbbell bicep curl was selected to develop the bicep muscle in the biceps’ mode. It is an action in which humans turn their palm up while simultaneously bringing the dumbbell to align with their shoulders. The second mode is the deltoids mode, in which the elbow is slightly bent, and this position is maintained in order to raise the arm until it is parallel to the floor [20,21]. The third method is the triceps mode. On the other hand, complex mode actions include the dumbbell shoulder modes that enable the improvement of the supraspinatus, teres major and infraspinatus muscles. The fifth one is squat and press mode, which will develop quadriceps, biceps and deltoids muscle. The final one is side lunge mode. Figure 2 presents the simple versions of the three modes and positions of the active muscles for these modes. Figure 3 shows the three complex modes of exercise that are used in our research.
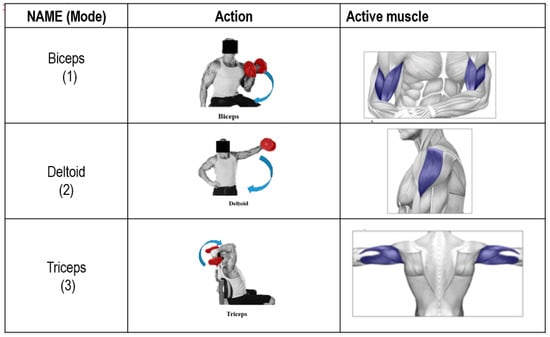
Figure 2.
Three simple modes and groups of muscles in dumbbell training.
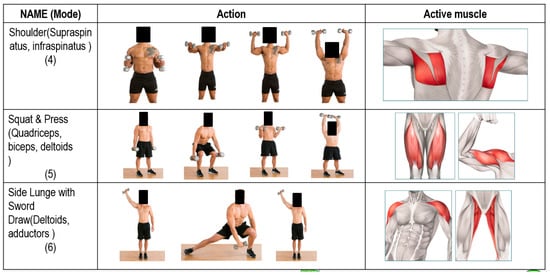
Figure 3.
Three complex modes with groups of muscles in dumbbell train.
The data of the IMU from the person who was performing the exercise with the dumbbell was collected. Figure 4 shows the range of mode motions with dumbbells performed by the angle (Roll, Pitch, Yaw of IMU). It is easy to identify modes through the different range of angle distributions. In the research, the threshold range of motion (ROM) and SVM in Machine Learning is focused to identify actions. The range of motions which are used determines the range of parameters the IMU uses to define the action mode. Furthermore, the data could be used for the training model in which the label is the action mode. The vector variables is the signal from the IMU.
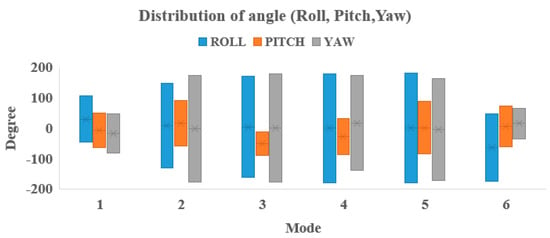
Figure 4.
Distribution of angle parameters for six modes (1 = Bicep, 2 = Deltoid, 3 = Tricep, 4 = Shoulder, 5 = Squat, 6 = Side and lunge).
3. Methodology
3.1. Estimation of Sensor Fusion
The raw data from the output of the IMU contain many errors; therefore, we used the Kalman filter to reduce the noise. It includes two steps to process the data, i.e., prediction and update [22,23,24]. The equations of the algorithm are summarized as follows:
Prediction:
Update:
where F is the transition matrix of state, B is control-input matrix, uk−1 is the control vector, P is called state error covariance, Kk is the Kalman gain, is the measurement residual. These equations are used to create the filter after denoising in order to obtain the output angle. During model testing, the accuracy of the Kalman filter was used as an encoder to verify the results. We obtained a root mean square (RMS) value of 3.5998. The estimated angle using a Kalman filter is shown in Figure 5.
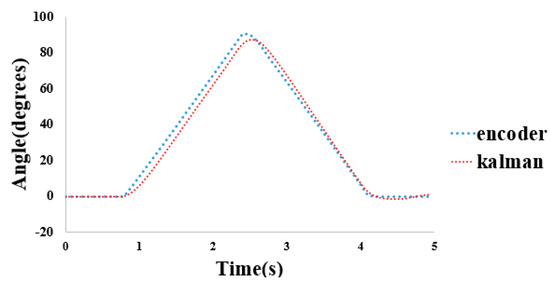
Figure 5.
Comparison between estimated angles using encoder and Kalman filter.
3.2. Determination of the Exercise Cycle
From Figure 6, we observe certain features of the biceps’ mode. The signal can be divided into five steps.
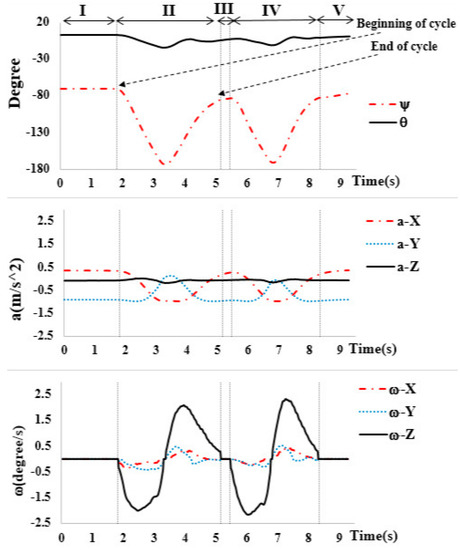
Figure 6.
Signal from the IMU sensor working on two cycles.
First, Section I denotes the period at the beginning of the exercise with no movement. Section II denotes the period during which one cycle (or repetition) of exercise is performed in the biceps’ mode. Third, Section III denotes the short time of rest before execution of the next repetition in Section IV. Finally, Section V denotes the completion of the exercise. The dumbbell is not moved at the beginning (I) and the end (III, V) of the exercise, and only the gravitational force acts on the sensor (mostly on the Y-axis (a-Y)). We can also see the corresponding angular velocity profiles (ω-X, ω-Y, ω-Z). The movement contains a steady rotation around the Z-axis (yaw (ψ)).
Then, we can detect the cycle of exercise, which is the duration of movement to finish one repetition using the gyroscope sensor and the angle between the forearm and the upper arm. As all actions of the mode using dumbbells require time to stop the movement to transform the direction, it is a period of time to make the signal from the gyroscope sensor reach zero. In addition, we need to combine the angle (yaw angle in biceps’ mode) to verify that it is the end of the cycle. Based on this phenomenon, we detect the start and endpoints of single repetitions, as shown in Figure 6. In contrast, a previous study described in [4], only used accelerometer sensors and captured a cycle of the time series based on raw acceleration signals. In the proposed method, it is difficult to maintain a constant value for the stopped period of time when the position of the human that performs each exercise mode is different. Furthermore, the proposed method is robust and stable in all modes, resulting in faster and more memory-efficient execution.
3.3. Range of Motion Response for Exercise Modes
In this section, we discuss the different exercises from the results of the IMU sensor, which serves as a method to create an algorithm to detect the mode of use. We could look at the data resulting from the IMU sensor of the six-mode exercise when humans perform it. From the properties of the accelerometer and gyroscope, we focus on movement from different modes with regard to acceleration and gyroscope behavior in different axes and values. Further, we created criteria to evaluate the ability of each mode to be correct. These are maximum (max), minimum (min), and in the range of nine variables as well as six from two signals from the IMU, which are acceleration and gyroscope (ω-X, ω-Y, ω-Z) of the X, Y, and Z-axes. The rest is the angle of the X, Y, and Z-axes, which are called sequentially roll (ϕ), pitch (θ), and yaw (ψ).
Figure 7 presents the distribution values of the gyroscope in each region corresponding to the criteria of the exercise modes. For example, if we calculate the maximum gyroscope of X axes (GX) in one cycle of the biceps’ mode, it will be located in the region of −1.35 to 1.34 degrees/s. Similarly, in the other modes, the location of the maximum gyroscope of each mode is different.
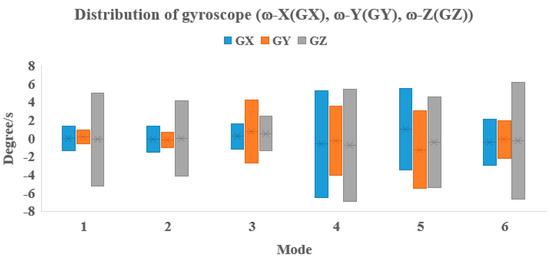
Figure 7.
Distribution of gyroscope parameters for six modes (1 = Bicep, 2 = Deltoid, 3 = Tricep, 4 = Shoulder, 5 = Squat, 6 = Side and lunge).
In Figure 8, we can clearly see the difference of each mode through the distribution of acceleration that can help identify the method of exercise.
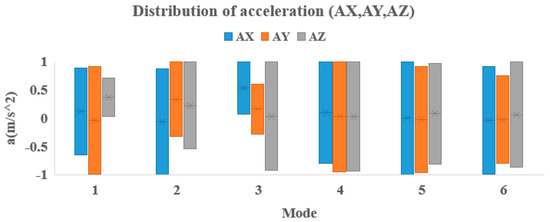
Figure 8.
Distribution of acceleration parameters for six modes (1 = Bicep, 2 = Deltoid, 3 = Tricep, 4 = Shoulder, 5 = Squat, 6 = Side and lunge).
4. Algorithm Design
4.1. The General Mathematics for Identification of Modes Action
The features of each mode in the distribution value of the IMU signal are shown in Figure 4, Figure 7 and Figure 8, above. We define the rules to identify the mode. Each rule has a point in evaluating these modes and it is expressed in the following equations:
where i is the number of the mode, xij is the criterion j (parameter of IMU sensor) of the mode i and k are the point of criterion j.
During the training exercise, the criteria xij ∈ {0, 1}, which depends on the value of xij, belongs to the range of motion [ai;bi] as true or false. It returns to zero if the value does not belong to a specified region, and vice versa. Subsequently, Gi is calculated using Equation (5). If Gi has a value of the highest, the mode will be selected based on the i index. The algorithm program on LabVIEW was used to demonstrate the accuracy of each model. It is worth noting that the values of the criteria determination were calculated in a cycle.
4.2. Support Vector Machine for Classification of Modes Action
SVM aims to solve the problem of the optimal separating hyperplane between label classes by the margin criterion. Assuming that (1) training vector xi ∈ Rd, i = 1, 2, 3 …, l exported from the parameter of IMU sensor, which is the triad of acceleration, gyro and angle rotation (Roll, Pitch, Yaw); (2) label vector yi ∈ {1, …, k} is the number of the action mode or class of xi. The mth SVM is trained with the positive labels including the negative labels in the mth class. It is important to note that the purpose of the presence of the parameters ξ is to adjust errors of classification. The problem is solved based on the cost function [25,26]:
where the vector xi is mapped to a higher dimensional space by the function ϕ and C is the penalty parameter. In addition, w is the vector of hyperplane coefficients, while b is the bias term. After function (6) is solved, the value for the decision function will be obtained. The vector x belongs to the class that has the largest value of the decision function.
There are many kinds of kernel function ϕ (for example, radial basis function (rbf), linear function, polynomial function kernel, and linear Support Vector Classifier (SVC)) that will affect the accuracy of the model [27,28]. Figure 9 shows the decision boundary of four methods, in which various colors are designed with the aim to match each action and present its trajectory. As shown in the figure, the data is nonlinearly separable; therefore, it can be concluded that the RBF function or polynomial kernel is a good method to classify the label. The data transformation from non-linearly separable into linearly separable can be observed from this figure as well. The RBF function is applied for classifying modes of action in our research.
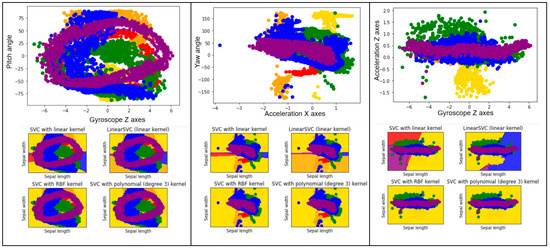
Figure 9.
The decision surface for four different SVM classifiers of mode dumbbell exercises (red = Bicep, orange = Deltoid, lack = Tricep, green = Shoulder, blue = Squat, purple = Side and lunge).
5. Results and Discussion
A human interface machine was created using LabVIEW to verify our algorithm. Figure 10 shows the parameters during the exercise. These are the repetition, set, power, and percentage completion of the task. We processed personal training with a dumbbell. Each person took a dumbbell, and the initial conditions of the dumbbell were the same. After performing the exercise for 15 times, the person rested.
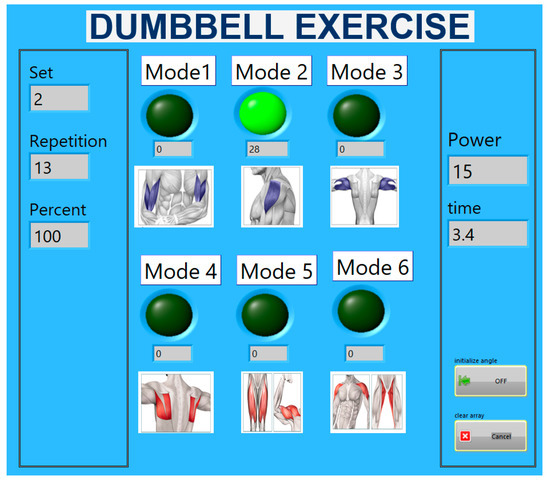
Figure 10.
Human interface machine with dumbbell exercise.
Table 1 and Table 2 demonstrate the matrix fusion results of the two methods. The ROM method reached 100%, exactly, for the simple actions’ mode but complex action was lower than 90%. The SVM method was highly efficient with six actions, the results were smallest at 97% accuracy. When a person uses a dumbbell to perform an action, the properties of the IMU could help to recognize the action by changing the axes. Moreover, the action of humans was movement and rotation. The limit angle rotation (Roll, Pitch, Yaw) of each action mode could make the map see different ranges. However, there are huge movements in each action, which makes it difficult for the method threshold range of motion to find the feature of the parameter by threshold number. For the Support Vector Machine, the kernel function RBF is considered to be the best method to recognize the complex action mode. The large number of calculations in SVM leads to real-time difficulty responding to high-frequency movements of the simple mode. On the contrary, it is favorable for the complex mode because the cycle time of the mode is long enough for the calculation.

Table 1.
The matrix fusion of the range of motion threshold method.

Table 2.
The matrix fusion of Support vector machine method.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, two methods of classification were used to identify the modes of dumbbell exercise in real time. Working of these methods has successfully implemented these algorithms, and combination of the two methods resulted in perfect results. For the ROM method, monitoring the activity of each mode was based on the behavior of the person performing the dumbbell exercise. The SVMs with a non-linear kernel are extremely powerful classifiers. The results showed that the accuracy rates of six mode detections were 100%, 98%, 100%, 99%, 100%, and 97%, respectively. Additionally, we developed an estimated cycle for a task using a small amount of data to detect the action. Further, we have not only used the acceleration and velocity of the angle but also the angle of the Kalman filter to create an algorithm that may obtain an accuracy result of 100%. The classification of the action mode has a significant benefit for dumbbell exercises in that humans will not be bored by interacting with each mode of motion. In the future, it may replace the personal trainer for assisting human training of dumbbell exercisers.
In future research, we aim to work on creating an algorithm for all modes of exercise with dumbbells. Additionally, we would like to allow people to correct the activity through following a guide on the monitor of the human interface machine. The research may open a new direction in which exercise testing can be considered a non/invasive diagnostic technique applied in clinical practice. Through the recognition of motion status with dumbbells, the increase/decrease of movement speed or parameters of action can be analyzed. As a result, abnormal data associated with repeatedly wrong movements is detected, which may contribute to clinical implications in diagnosing the disorder symptoms including exercise-induced asthma, growth hormone deficiency, congenital heart defects, and so on.
Author Contributions
In this paper, the author contributions were: conceptualization, Y.S.; methodology, Y.S. and T.H.; software, T.H. and P.-Y.C.; validation, Y.S. and T.H.; formal analysis, Y.S. and T.H.; investigation, T.H. and P.-Y.C.; data curation, T.H. and P.-Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, T.H.; writing—review and editing, Y.S.; supervision, Y.S.; project administration, Y.S.; funding acquisition, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Taiwan, grant number 108-2622-8-027-005.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to all subject involved in this study being authors or lab members.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from all subjects to publish this paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank the financial support from Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Taiwan (Project number: MOST 108-2622-8-027-005 and 108-2221-E-027-097.)
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miller, M.D.; Thompson, S.R. Infectious Diseases in the Athlete. In DeLee, Drez, & Miller’s Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Principles and Practice, 5th ed.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4557-4376-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bopp, C.M.; Phillips, K.D.; Fulk, L.J.; Hand, G.A. Clinical implications of therapeutic exercise in HIV/AIDS. J. Assoc. Nurses AIDS Care 2003, 14, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C. Clinical implications of exercise immunology. J. Sport Health Sci. 2012, 1, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehrman, J.K.; Gordon, P.M.; Visich, P.S.; Keteyian, S.J. (Eds.) Clinical Exercise Physiology; Human Kinetics Publishers: Champaign, IL, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781492546467. [Google Scholar]
- Ostman, C.; Smart, N.A.; Morcos, D.; Duller, A.; Ridley, W.; Jewiss, D. The effect of exercise training on clinical outcomes in patients with the metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.H.; Do, J.Y.; Jeong, H.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.C. The clinical significance of physical activity in maintenance dialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.E.; Sherwood, H.S.; Rogers, N.L.; Bohlken, R.M. Effects of dumbbell and elastic band training on physical function in older inner-city African-American women. Women Health 2002, 36, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, A.; Maruyama, T.; Naito, H.; Sinclair, P.J. Effects of exhaustive dumbbell exercise after isokinetic eccentric damage: Recovery of static and dynamic muscle performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hsu, C.-L.; Liu, Y. An intelligent dumbbell designed for fitness activity monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computation, Communication and Engineering (ICCCE), Longyan, Fujian, China, 8–10 November 2019; International Institute of Knowledge Innovation and Invention (IIKII): Singapore, 2019; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.; Chen, M.Y.; Canny, J. Tracking free-weight exercises. In UbiComp 2007: Ubiquitous Computing; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4717, pp. 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Fei, M.; Hu, H.; Qi, Z. Free weight exercises recognition based on dynamic time warping of acceleration data. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2013, 355, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, A.; Brunner, G.; Tanner, S.; Wattenhofer, R. Recognition and repetition counting for complex physical exercises with deep learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crema, C.; Depari, A.; Flammini, A.; Sisinni, E.; Haslwanter, T.; Salzmann, S. IMU-Based Solution for automatic detection and classification of exercises in the fitness scenario. In Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Glassboro, NJ, USA, 13–15 March 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausberger, P.; Fernbach, A.; Kastner, W. IMU-based smart fitness devices for weight training. In Proceedings of IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 5182–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madgwick, S.O.H.; Harrison, A.J.L.; Vaidyanathan, R. Estimation of IMU and MARG orientation using a gradient descent algorithm. In Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Fourati, H.; Li, R. Fast complementary filter for attitude estimation using low-cost MARG sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6997–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, P.; Tang, L.; Mukhopadhyay, S. MEMS based IMU for tilting measurement: Comparison of complementary and kalman filter based data fusion. In Proceedings of 2015 IEEE 10th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Auckland, New Zealand, 15–17 June 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Bang, H. Introduction to kalman filter and its applications. In Introduction and Implementations of the Kalman Filter; Govaers, F., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narasimhappa, M.; Mahindrakar, A.D.; Guizilini, V.C.; Terra, M.H.; Sabat, S.L. An improved sage husa adaptive robust kalman filter for de-noising the MEMS IMU drift signal. In Proceedings of the 2018 Indian Control Conference (ICC), Kanpur, India, 4–6 January 2018; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R. Freeweight Training Anatomy: An Illustrated Guide to the Muscles Used While Exercising with Dumbbells, Barbells, and Kettlebells and More; Chou, L., Ed.; Ulysses Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781612435350. [Google Scholar]
- Stoppani, J. Encyclopedia of Muscle & Strength, 2nd ed.; Klug, J., Ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2014; ISBN 1450459749. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, R.; Ji, K.; Dai, W. Kalman Filter and Its Application. In Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Conference on Intelligent Networks and Intelligent Systems (ICINIS), Tianjin, China, 1–3 November 2015; pp. 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Valade, A.; Acco, P.; Grabolosa, P.; Fourniols, J.Y. A Study about Kalman Filters Applied to Embedded Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, S. Quaternion-based unscented kalman filter for accurate indoor heading estimation using wearable multi-sensor system. Sensors 2015, 15, 10872–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivapragasam, C.; Liong, S.-Y.; Pasha, M.F.K. Rainfall and runoff forecasting with SSA–SVM approach. J. Hydroinform. 2001, 3, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; ISBN 9780521780193. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Cao, J. Random radial basis function kernel-based support vector machine. J. Franklin Inst. 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Sun, C.; Chen, X. Sparse representation theory for support vector machine kernel function selection and its application in high-speed bearing fault diagnosis. ISA Trans. 2021, 118, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).