High-Resolution LiDAR Digital Elevation Model Referenced Landslide Slide Observation with Differential Interferometric Radar, GNSS, and Underground Measurements
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
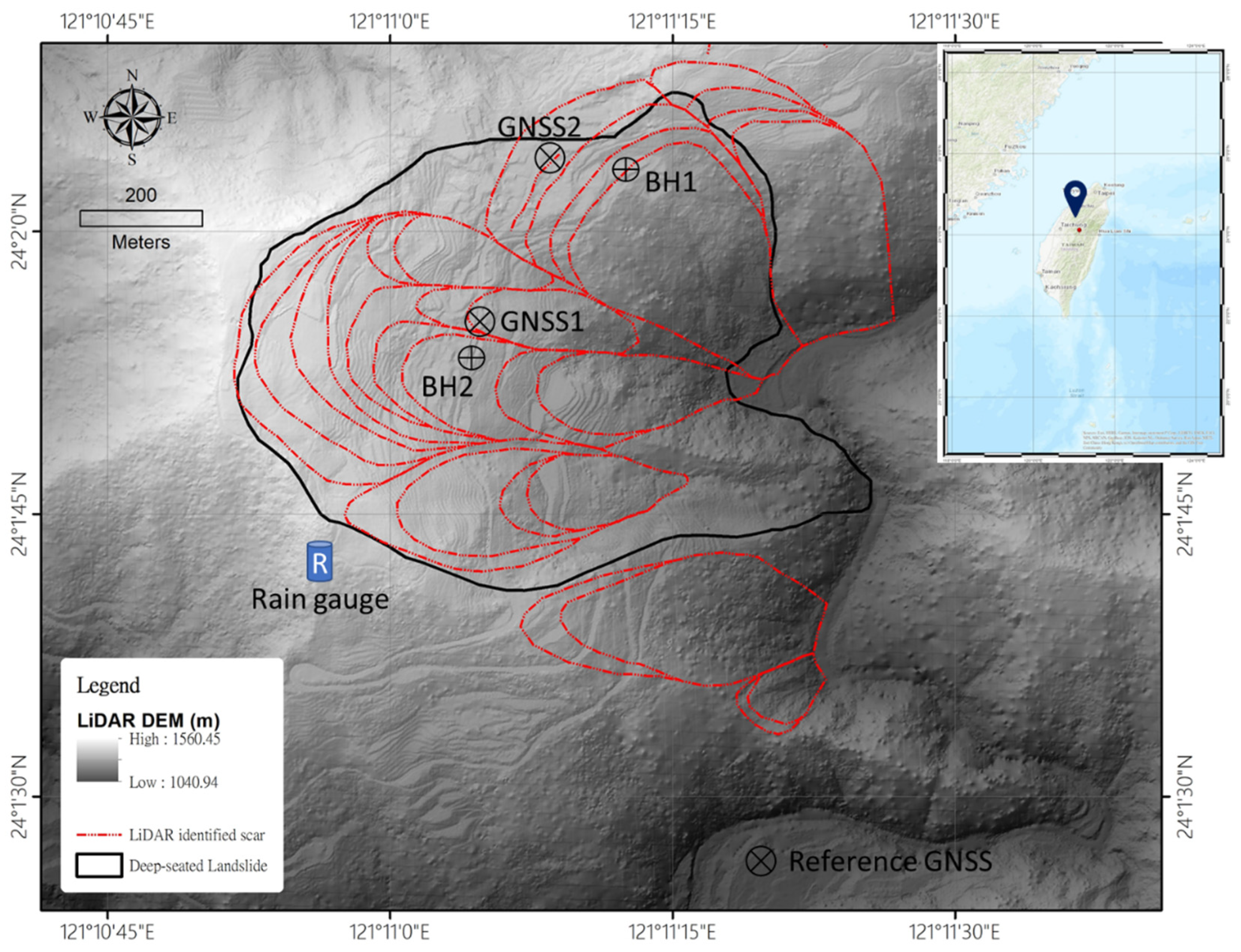
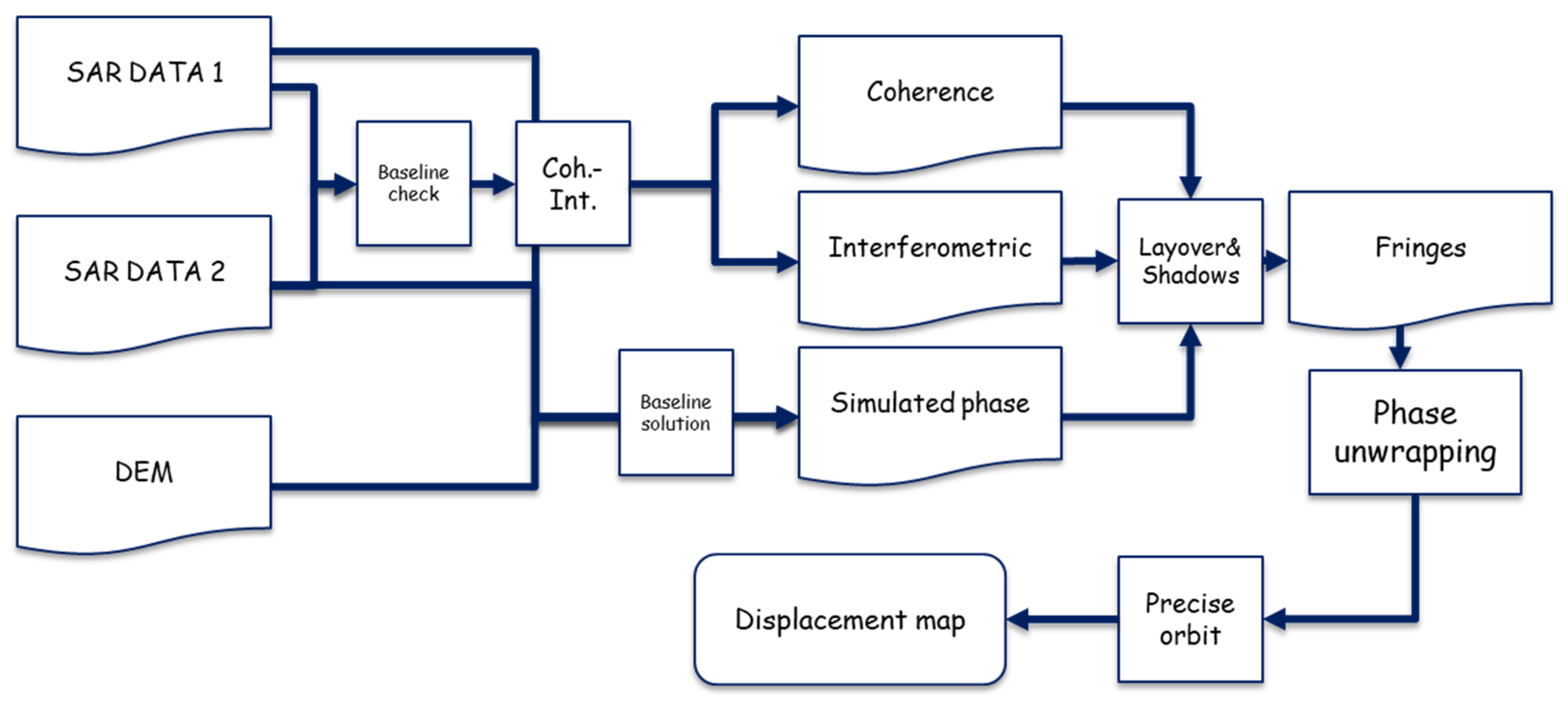
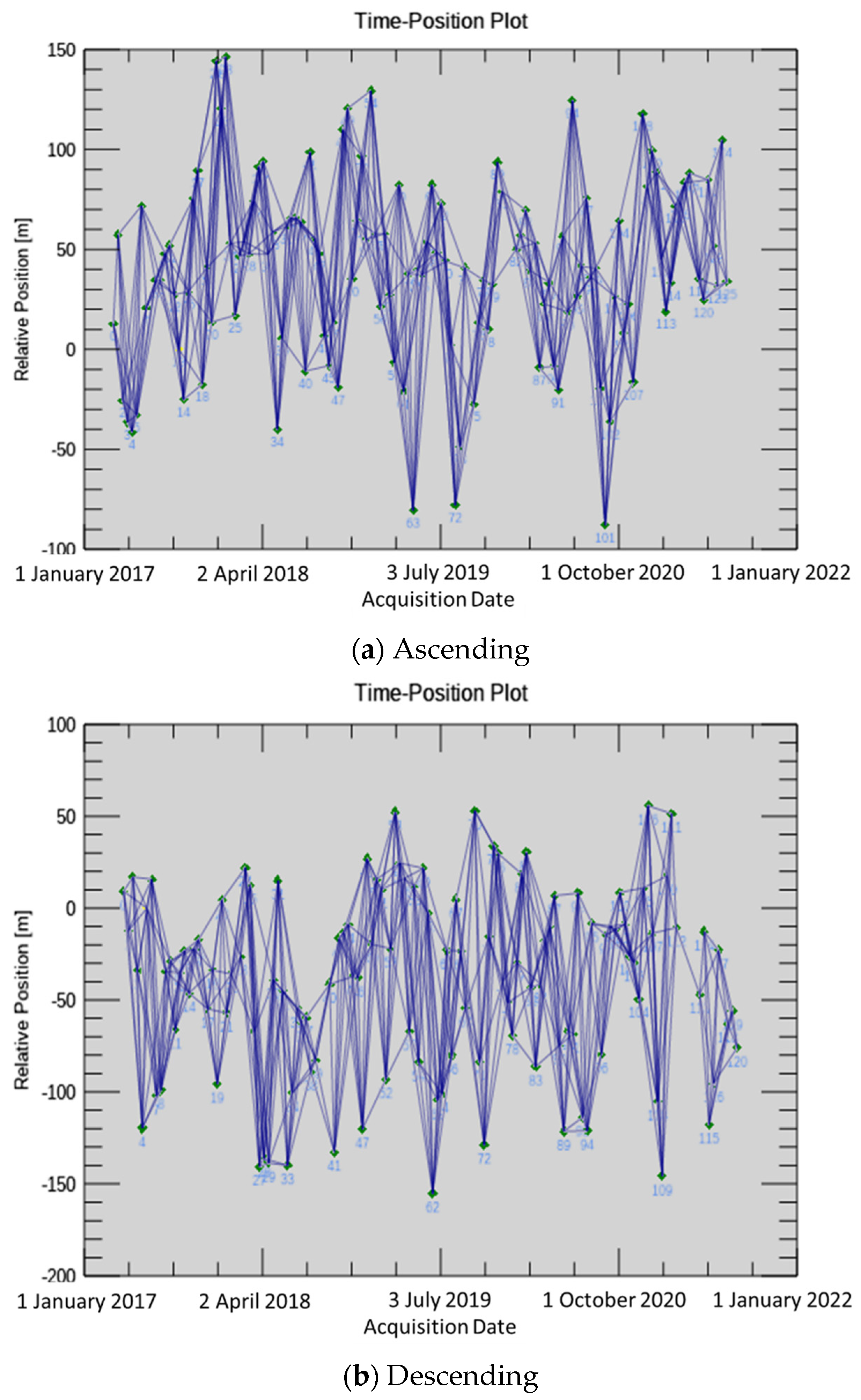
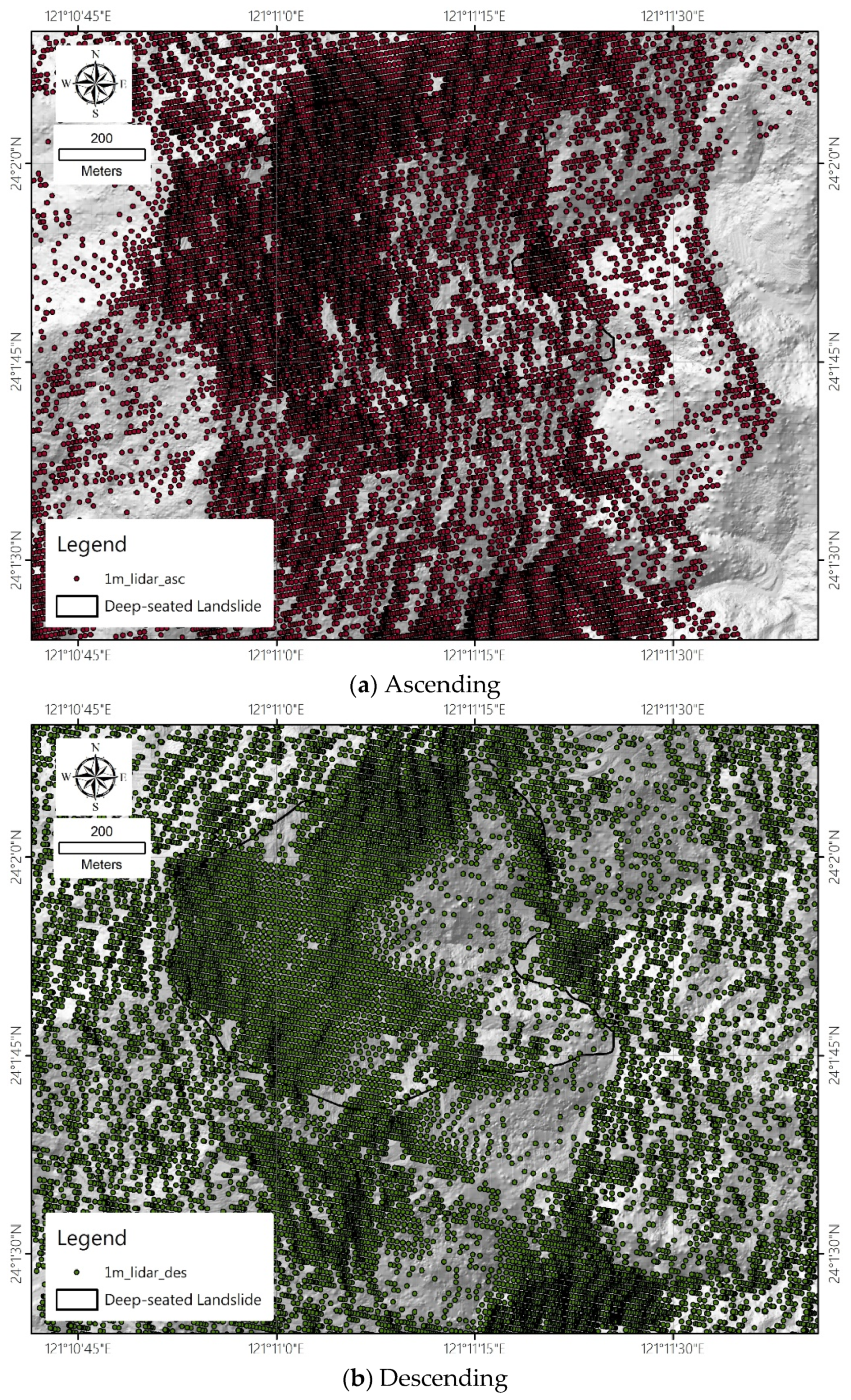
2. Materials and Methods
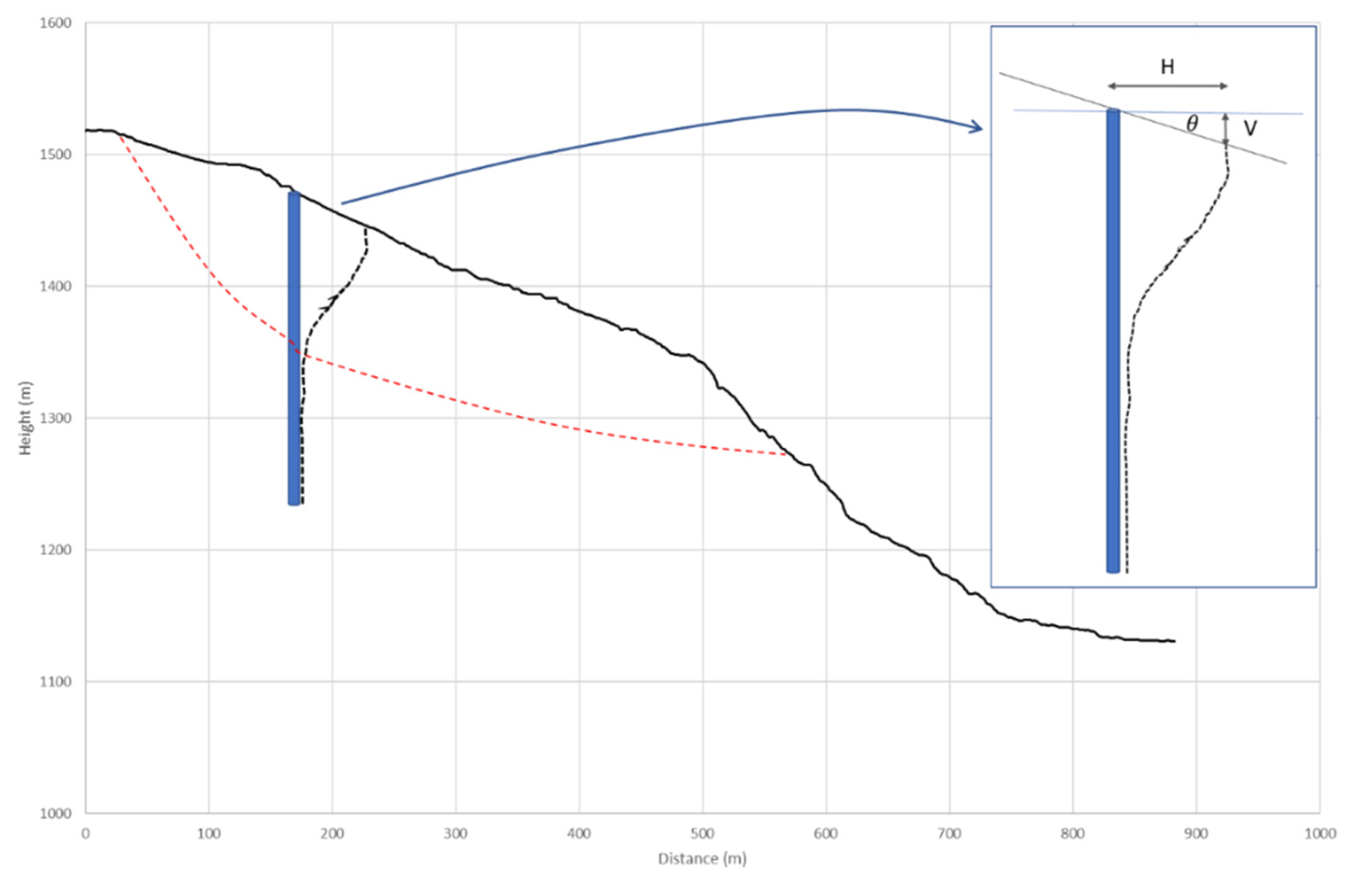
Vertical Deformation from DInSAR
3. Results
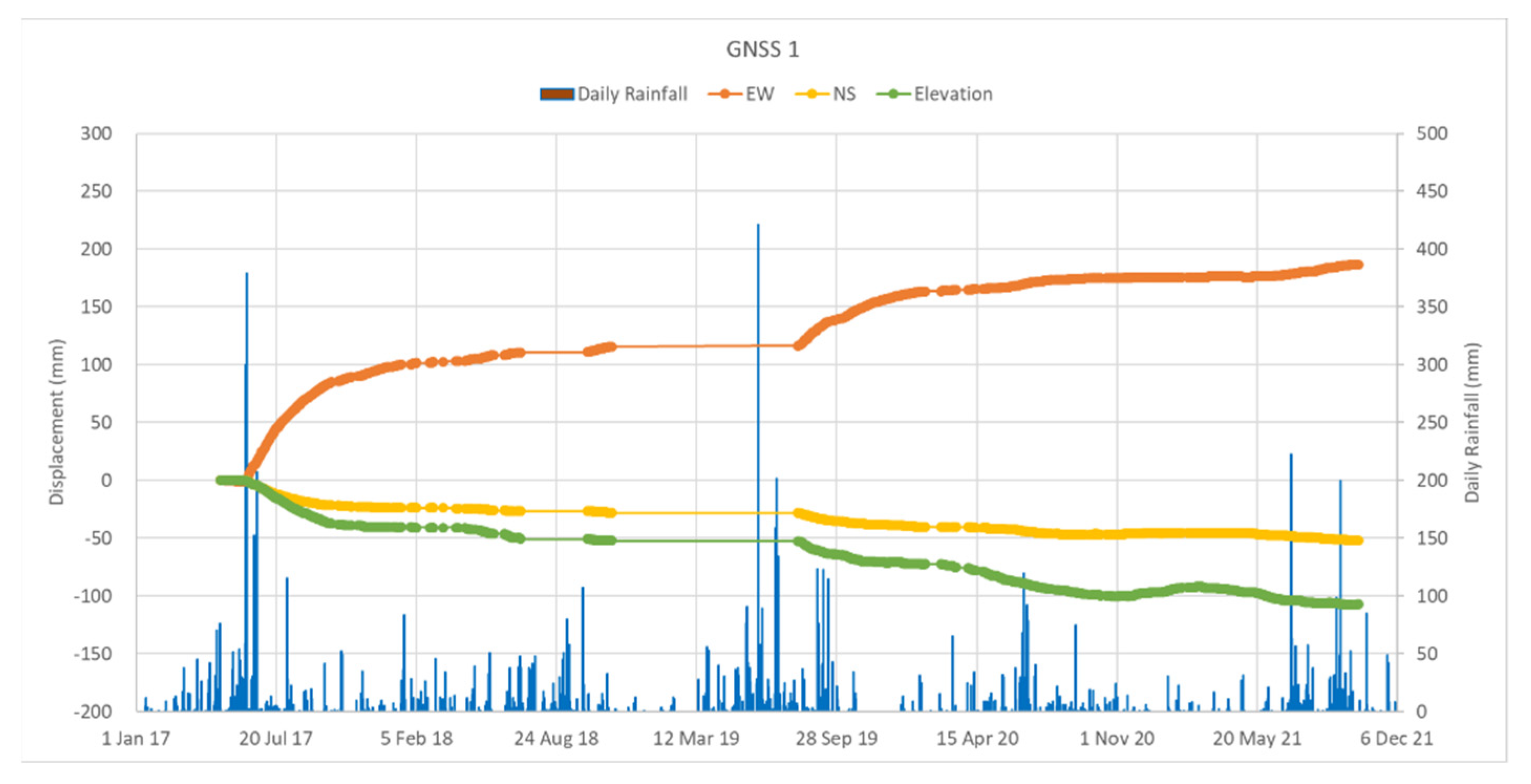
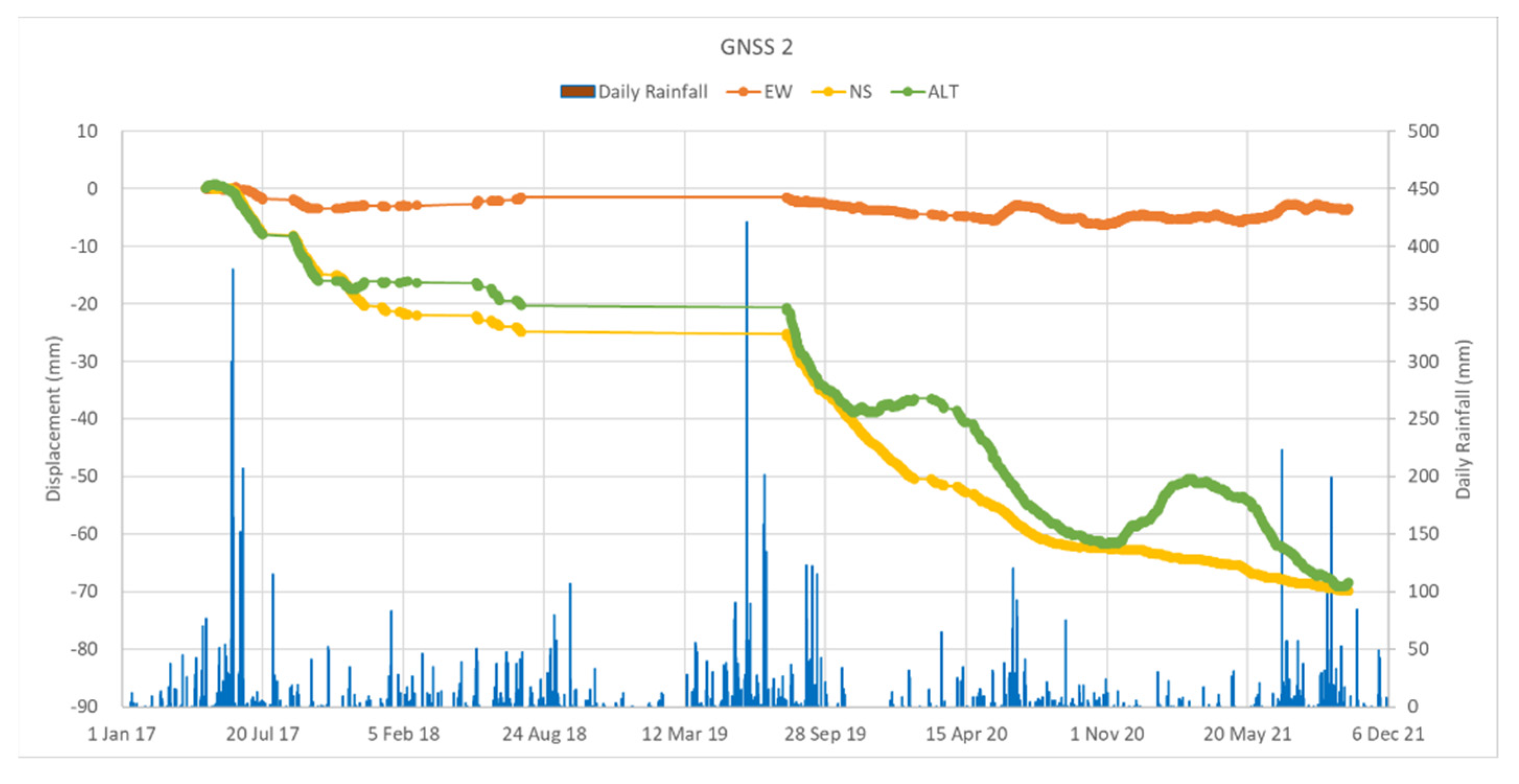
3.1. GNSS Measurement
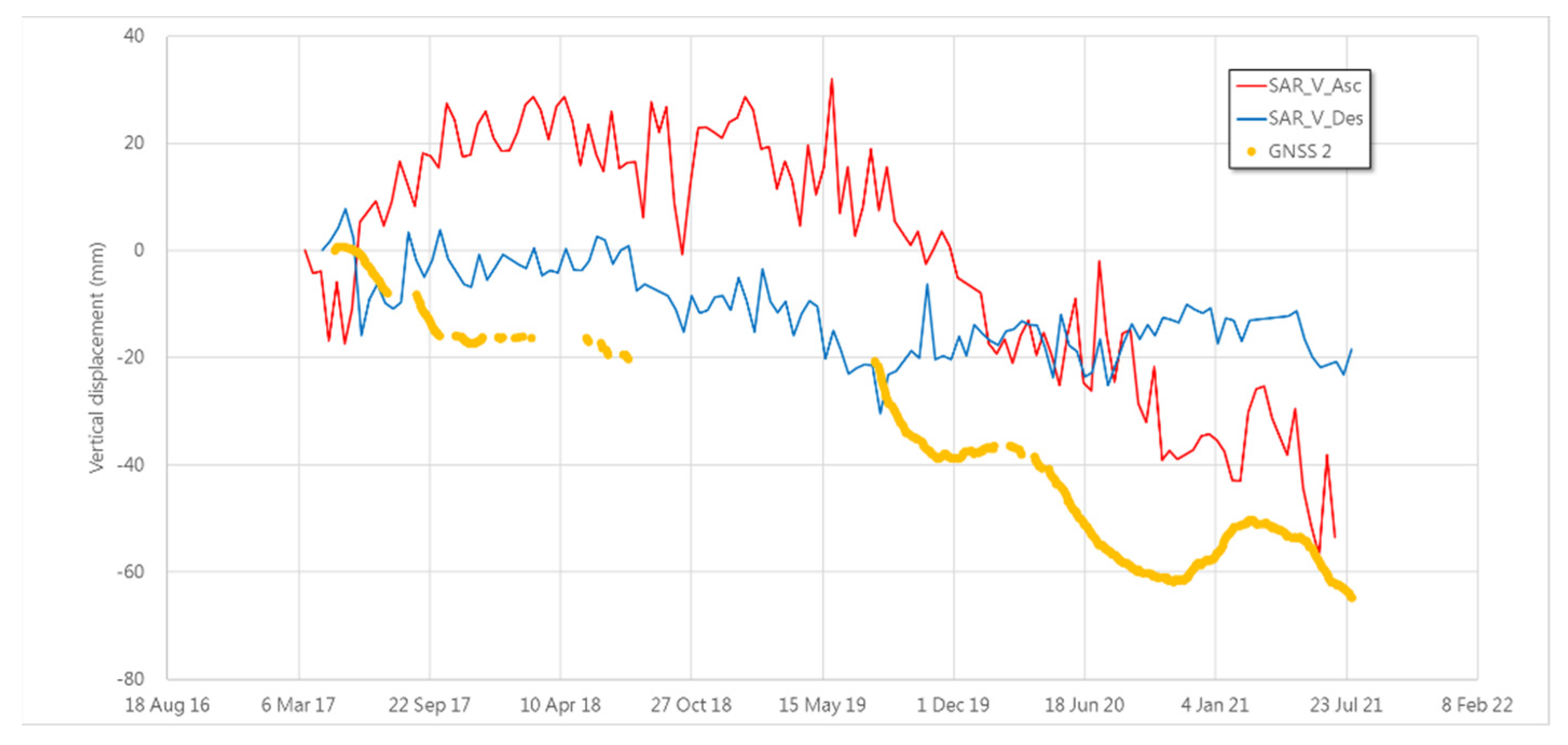
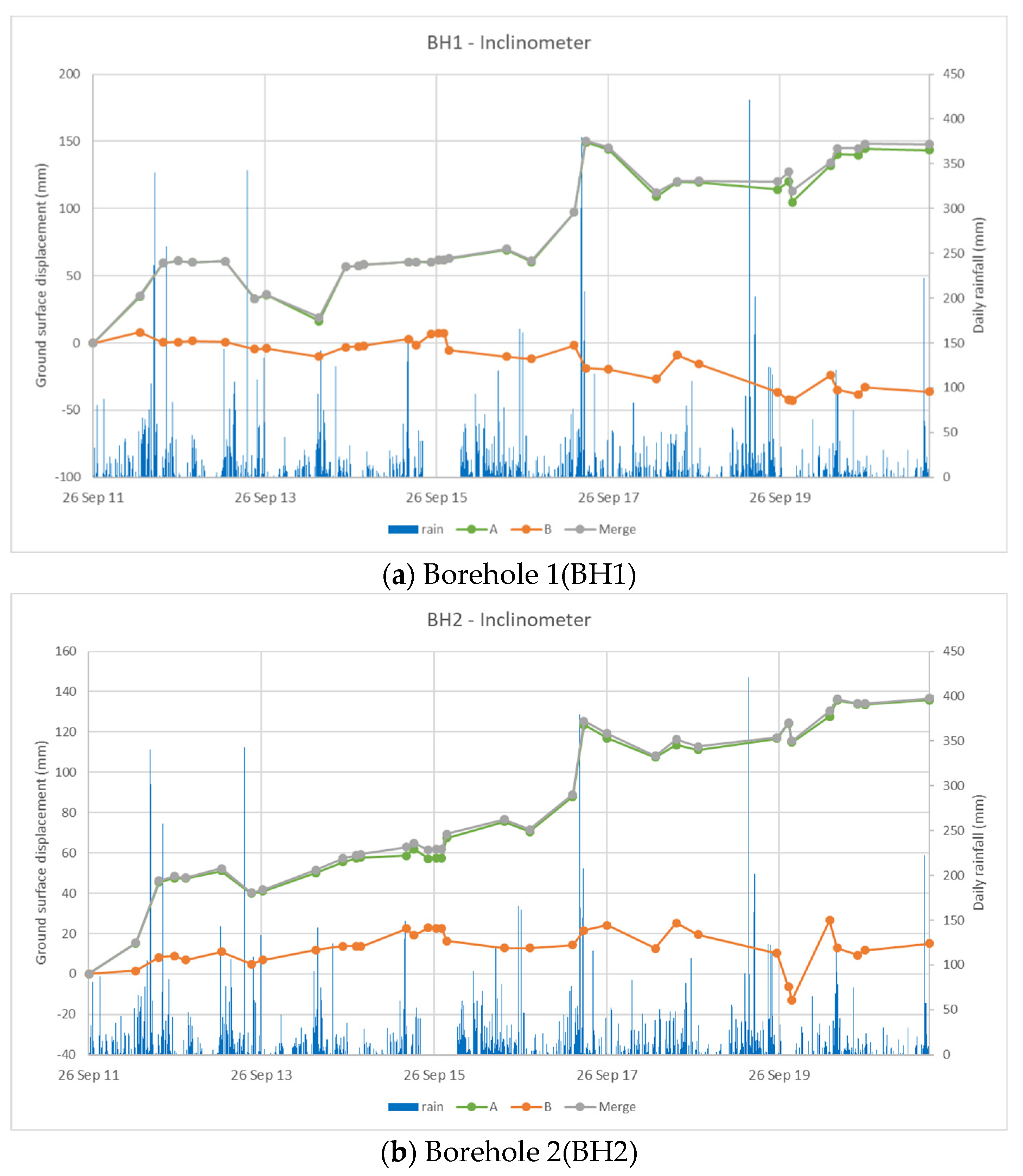
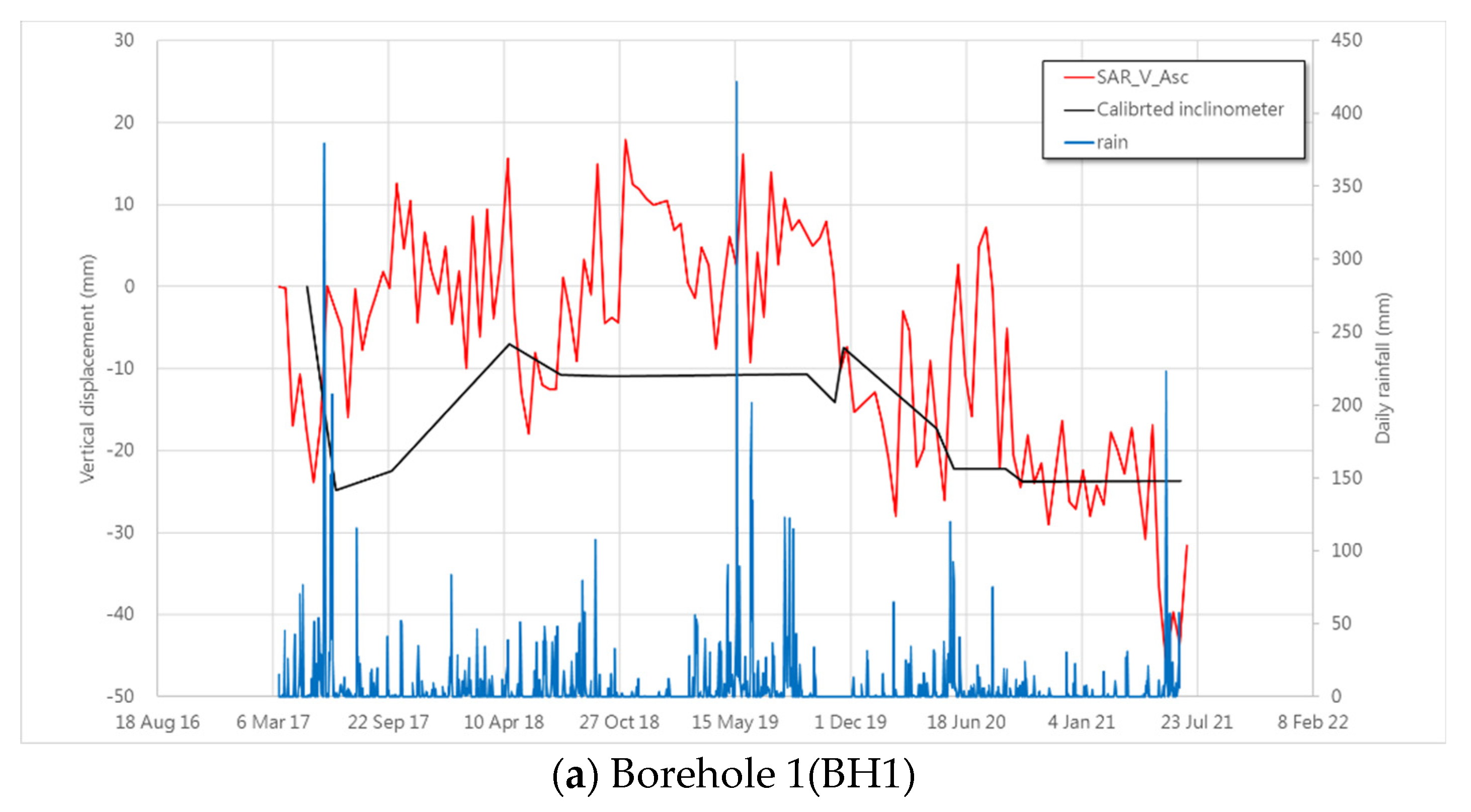
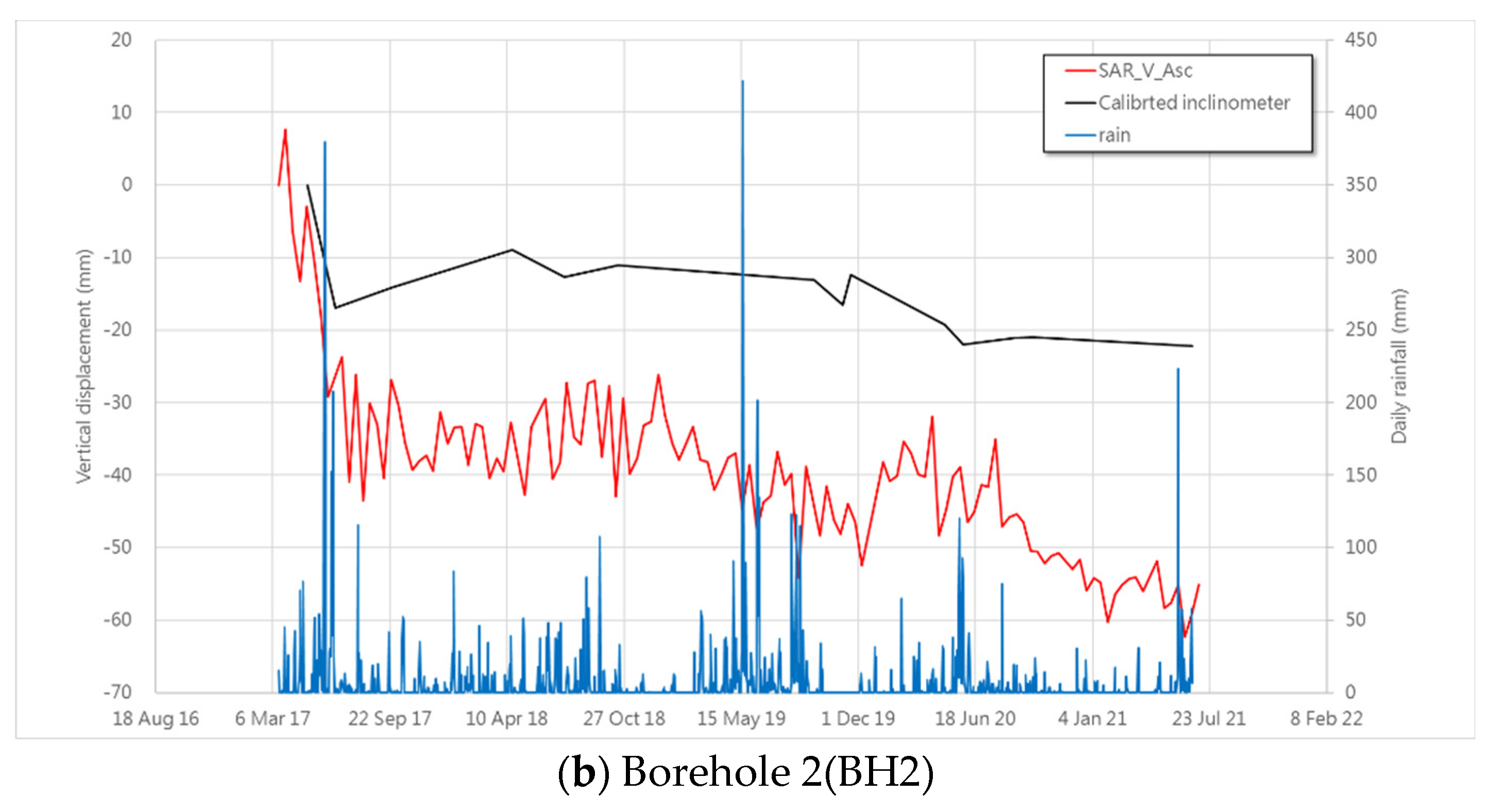
3.2. The Sliding Behavior Comparing with Slope Inclinometer
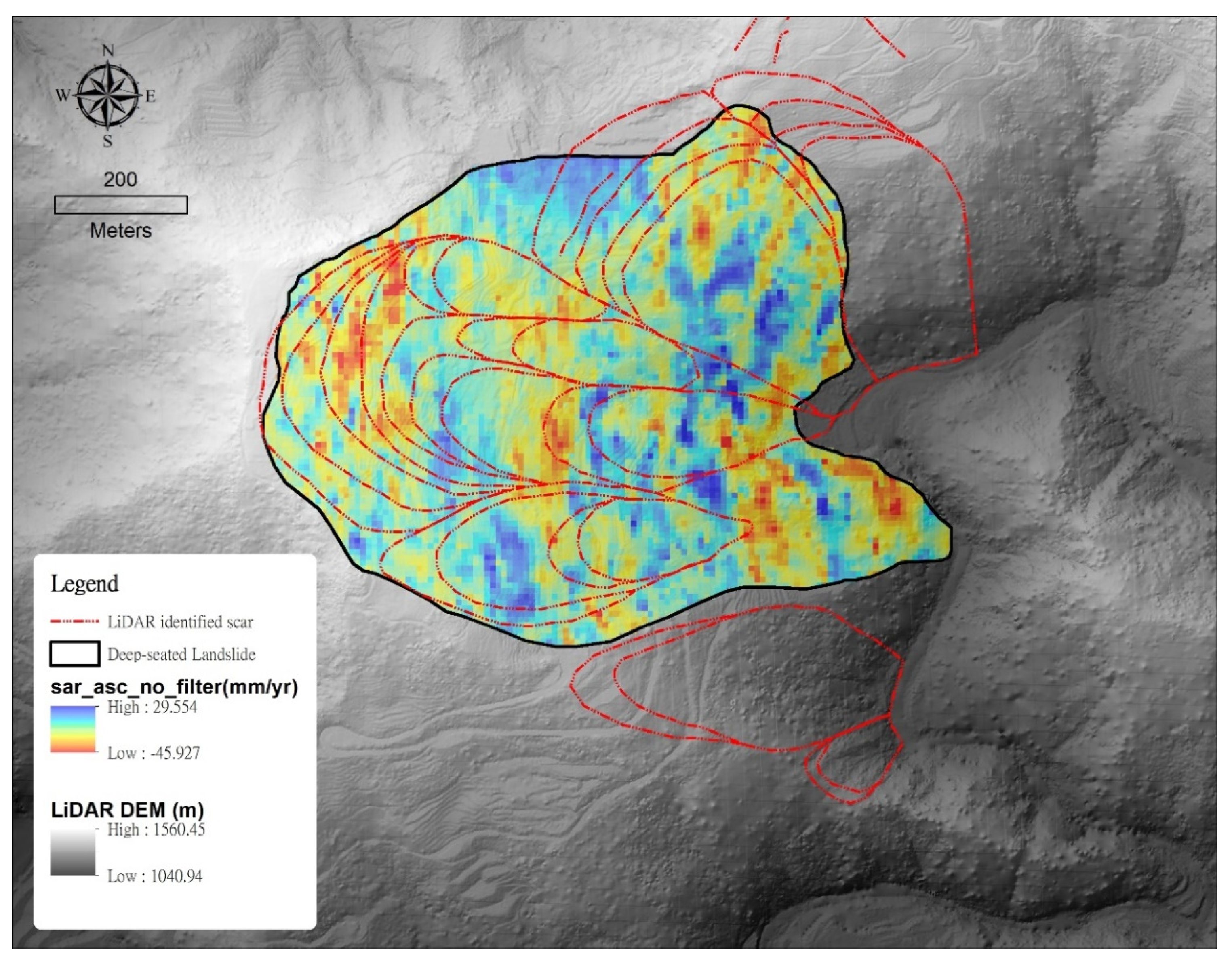
3.3. Potential Landslide Scar Mapping from SBAS Method
- 1.
- Calculate vertical displacement from LOS displacement after SBAS analysis.
- 2.
- Interpolate vertical displacement to raster format.
- 3.
- Overlap raster vertical displacement with shaded hill derived from the digital elevation model.
- 4.
- Compare displacement with LiDAR identified scars.
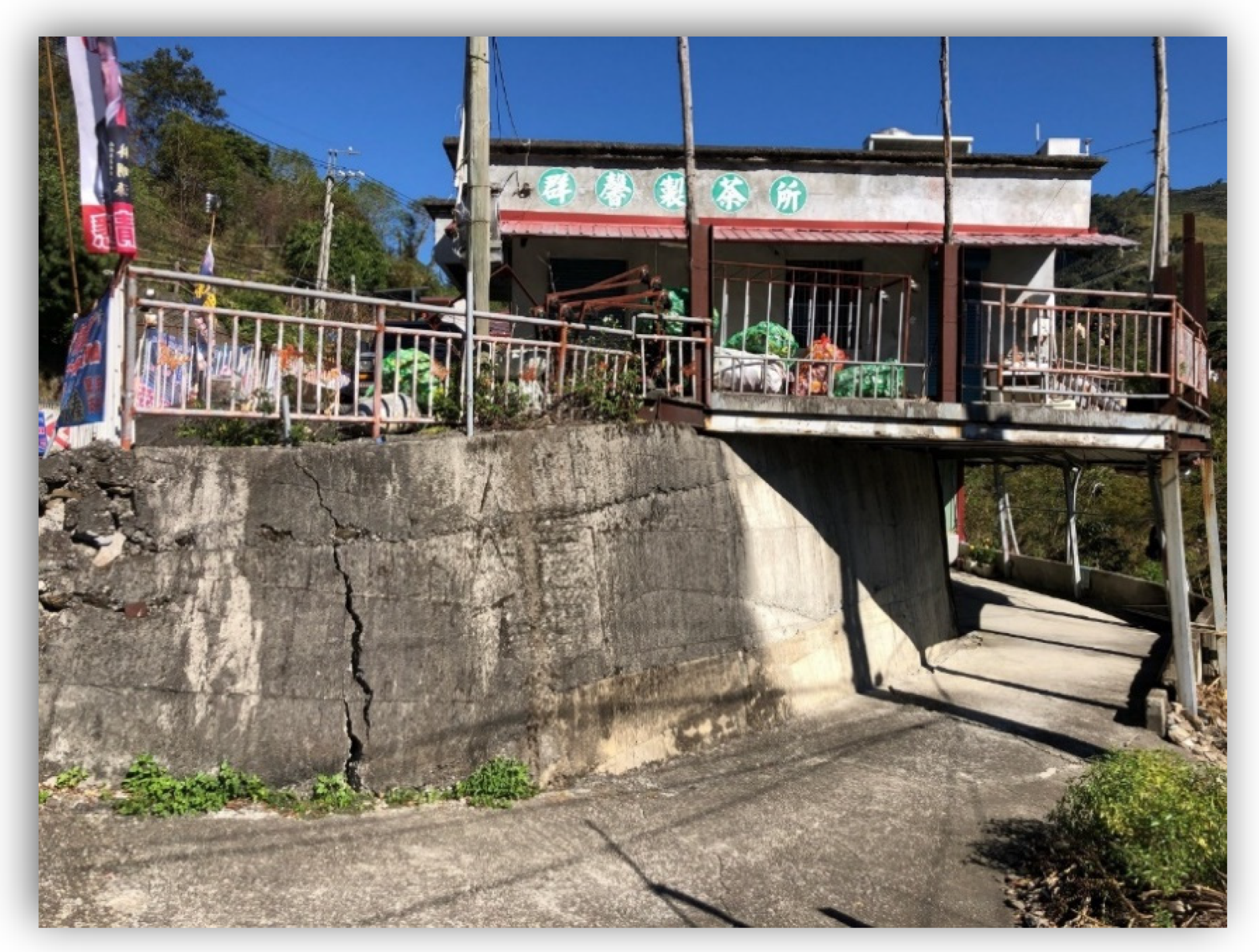
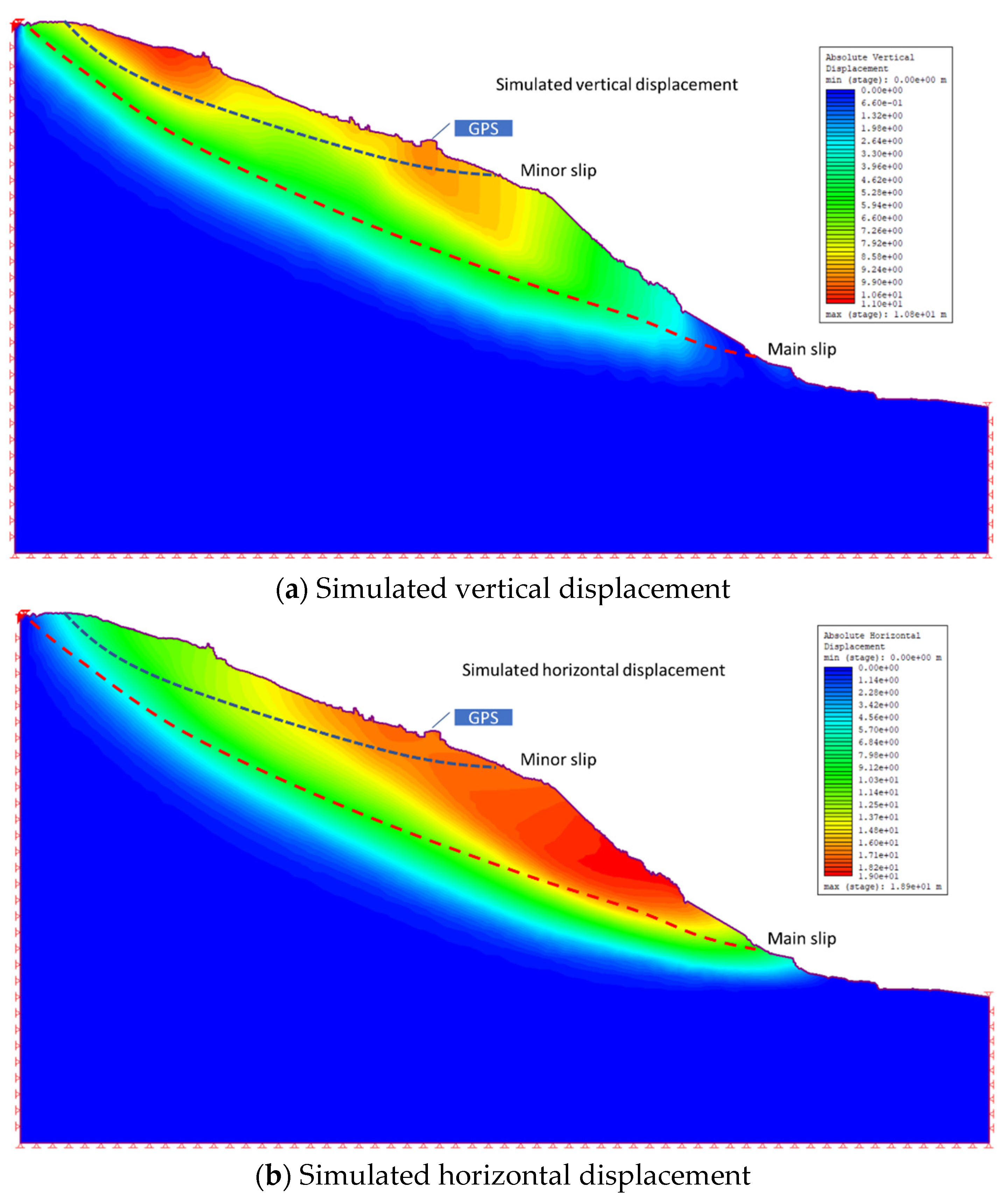
3.4. Numerical Simulation and Field Investigation of Uplift Condition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yen, J.-Y.; Lu, C.H.; Chang, C.P.; Hooper, A.J.; Chang, Y.H.; Liang, W.T.; Chang, T.Y.; Lin, M.S.; Chen, K.S. Investigating the active deformation in the northern longitudinal valley and hualien city of eastern taiwan by using persistent scatterer and small-baseline sar interferometry. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2012, 22, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, W.C.; Hwang, C.H.; Chen, Y.A.; Chang, C.P.; Yee, J.Y.; Andrew, H.; Yang, C.Y. Surface deformation from persistent scatterers SAR Interferometry and fusion with leveling data: A case study over the Choushui River Alluvial Fan, Taiwan. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F.; Tofani, V. Persistent scatterers interferometry hotspot and cluster analysis (PSI-HCA) for detection of extremely slow-moving landslides. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 466–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Fuente, J. Large-area landslide detection and monitoring with ALOS/PALSAR imagery data over Northern California and Southern Oregon, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champenois, J.; Fruneau, B.; Pathier, E.; Deffontaines, B.; Lin, K.-C.; Hu, J.-C. Monitoring of active tectonic deformations in the Longitudinal Valley (Eastern Taiwan) using Persistent Scatterer InSAR method with ALOS PALSAR data, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 337–338, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.; Hu, J.-C. Assessments of serious anthropogenic land subsidence in Yunlin County of central Taiwan from 1996 to 1999 by Persistent Scatterers InSAR. Tectonophysics 2012, 578, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyłucka, M.; Herrera, G.; Graniczny, M.; Colombo, D.; Béjar-Pizarro, M. Combination of conventional and advanced DInSAR to monitor very fast mining subsidence with TerraSAR-X Data: Bytom City (Poland). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5300–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krawczyk, A.; Grzybek, R. An evaluation of processing InSAR Sentinel-1A/B data for correlation of mining subsidence with mining induced tremors in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin (Poland). E3S Web Conf. 2018, 26, 00003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Ng, A.H.M. Subsidence monitoring in the Ordos basin using integrated SAR differential and time-series interferometry techniques. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, S.; Sigmundsson, F.; Carstensen, J. Three-dimensional surface motion maps estimated from combined interferometric synthetic aperture Radar and GPS data. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.G.; Bian, Z.F.; Lei, S.G.; Liu, D.L.; Sowter, A. Evaluation of PS-DInSAR technology for subsidence monitoring caused by repeated mining in mountainous area. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Du, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, C. Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring subsidence induced by longwall mining activity using Radarsat-2, Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 61, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Solari, L.; Giannecchini, R.; Galanti, Y.; Moretti, S. Evaluation of subsidence induced by long-lasting buildings load using InSAR technique and geotechnical data: The case study of a Freight Terminal Tuscany, Italy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 82, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.S.; Ojha, C.; Deo, R. Persistence scatterer interferometry for surface movement mapping over Himalayan region. In Proceedings of the 2011 3rd International Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Seoul, Korea, 26–30 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, S.C.; Zêzere, J.L.; Catalão, J.; Nico, G. The contribution of PSInSAR interferometry to landslide hazard in weak rock-dominated areas. Landslides 2015, 12, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Lagomarsino, D.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Landslide susceptibility map refinement using PSInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastaoglu, K.O. Comparing the results of PSInSAR and GNSS on slow motion landslides, Koyulhisar, Turkey. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 786–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Frodella, W.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Analysis of building deformation in landslide area using multisensor PSInSAR™ technique. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2014, 33, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Frodella, W.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. The effectiveness of high-resolution LiDAR data combined with PSInSAR data in landslide study. Landslides 2015, 13, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateos, R.M.; Azanon, J.M.; Roldan, F.J.; Notti, D.; Perez-Pena, V.; Galve, J.P.; Perez-Garcia, J.L.; Colomo, C.M.; Gomez-Lopez, J.M.; Montserrat, O.; et al. The combined use of PSInSAR and UAV photogrammetry techniques for the analysis of the kinematics of a coastal landslide affecting an urban area (SE Spain). Landslides 2017, 14, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, G.; González, P.J.; Mateos, R.M.; Roldán, F.J.; Herrera, G.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Fernández, J. A-DInSAR Monitoring of Landslide and Subsidence Activity: A Case of Urban Damage in Arcos de la Frontera, Spain. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonielli, B.; Mazzanti, P.; Rocca, A.; Bozzano, F.; Dei Cas, L. A-DInSAR Performance for Updating Landslide Inventory in Mountain Areas: An Example from Lombardy Region (Italy). Geosciences 2019, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Lu, Z. Ground settlement monitoring based on temporarily coherent points between two SAR acquisitions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE TGRS 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduto, D.; Santoro, M.; Aceto, L.; Borrelli, L.; Gullà, G. Full integration of geomorphological, geotechnical, A-DInSAR and damage data for detailed geometric-kinematic features of a slow-moving landslide in urban area. Landslides 2021, 18, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Integration of DInSAR and SBAS Techniques to Determine Mining-Related Deformations Using Sentinel-1 Data: The Case Study of Rydułtowy Mine in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Pieraccini, M.; Casagli, N.; Luzi, G.; Tarchi, D.; Mecatti, D.; Noferini, L.; Atzeni, C. Landslide monitoring by ground-based radar interferometry: A field test in Valdarno (Italy). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarchi, D.; Casagli, N.; Moretti, S.; Leva, D.; Sieber, A.J. Monitoring landslide displacements by using ground-based synthetic aperture radar interferometry: Application to the Ruinon landslide in the Italian Alps. J. Geophys. Res. Sol. Earth 2013, 108, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzzetti, F.; Manunta, M.; Ardizzone, F.; Pepe, A.; Cardinali, M.; Zeni, G.; Reichenbach, P.; Lanari, R. Analysis of Ground Deformation Detected Using the SBAS-DInSAR Technique in Umbria, Central Italy. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2009, 166, 1425–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cal, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Castaldo, R.; Lollino, P.; Tizzani, P.; Guzzetti, F.; Lanari, R.; Manunta, M. Landslide Analysis through the Multi-Sensor SBAS-DInSAR Approach: The Case Study of Assisi, Central Italy. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 2916–2919. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.K.; Chen, R.; Shao, Y.F.; Xu, W.; Xiao, D. Monitoring of ground deformation in Beijing using SBAS-DInSAR technique. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Tsukuba, Japan, 23–27 September 2013; pp. 300–303. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, B.F.; Gomez, W.; Zhou, M.A.; Mooney, B.H.; Grasmick, J. High resolution displacement monitoring of a slow velocity landslide using ground based radar interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2013, 166, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebur, M.N.; Pradhan, B.; Tehrany, M.S. Tehrany, Using ALOS PALSAR derived high-resolution DInSAR to detect slow-moving landslides in tropical forest: Cameron Highlands, Malaysia. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2015, 6, 741–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, P.; Chen, F.; Guo, H.; Tian, B.; Wang, X.; Ishwaran, N. Large-Area Landslides Monitoring Using Advanced Multi-Temporal InSAR Technique over the Giant Panda Habitat, Sichuan, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casagli, N.F.; Cigna, S.; Bianchini, D.; Hölbling, P.; Füreder, G.; Righini, S.; Del Conte, B.; Friedl, S.; Schneiderbauer, C.; Iasio, J.; et al. Landslide mapping and monitoring by using radar and optical remote sensing: Examples from the EC-FP7 project SAFER. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlemann, S.; Smith, A.; Chambers, J.; Dixon, N.; Dijkstra, T.; Haslam, E.; Meldrum, P.; Merritt, A.; Gunn, D.; Mackay, J. Assessment of ground-based monitoring techniques applied to landslide investigations. Geomorphology 2016, 253, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| GNSS1 Location | ||
| Slope (degree) | Aspect (degree) | |
| 15.6 | 88.9 | |
| Ascending orbit | Descending orbit | |
| Error Mean (mm) | 13.21 | 84.74 |
| Error Standard Deviation (mm) | 10.14 | 37.82 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.95 | −0.69 |
| GNSS2 Location | ||
| Slope (degree) | Aspect (degree) | |
| 19.8 | 169.8 | |
| Ascending orbit | Descending orbit | |
| Error Mean (mm) | 24.43 | 25.76 |
| Error Standard Deviation (mm) | 15.17 | 17.52 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.51 | −0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.-L.; Lin, J.-T.; Chu, H.-K.; Chen, C.-W.; Lu, C.-H.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lin, H.-H.; Chi, C.-C. High-Resolution LiDAR Digital Elevation Model Referenced Landslide Slide Observation with Differential Interferometric Radar, GNSS, and Underground Measurements. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311389
Wang K-L, Lin J-T, Chu H-K, Chen C-W, Lu C-H, Wang J-Y, Lin H-H, Chi C-C. High-Resolution LiDAR Digital Elevation Model Referenced Landslide Slide Observation with Differential Interferometric Radar, GNSS, and Underground Measurements. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(23):11389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311389
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kuo-Lung, Jun-Tin Lin, Hsun-Kuang Chu, Chao-Wei Chen, Chia-Hao Lu, Jyun-Yen Wang, Hsi-Hung Lin, and Chung-Chi Chi. 2021. "High-Resolution LiDAR Digital Elevation Model Referenced Landslide Slide Observation with Differential Interferometric Radar, GNSS, and Underground Measurements" Applied Sciences 11, no. 23: 11389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311389
APA StyleWang, K.-L., Lin, J.-T., Chu, H.-K., Chen, C.-W., Lu, C.-H., Wang, J.-Y., Lin, H.-H., & Chi, C.-C. (2021). High-Resolution LiDAR Digital Elevation Model Referenced Landslide Slide Observation with Differential Interferometric Radar, GNSS, and Underground Measurements. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311389






