An Analytical Model for Almost Conformal Spherical Contact Problems: Application to Total Hip Arthroplasty with UHMWPE Liner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Application to Total Hip Arthroplasty with UHMWPE Liner
3.1. Determination of the Foundation Modulus
3.2. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- 1.
- It provides acceptable results regardless of the liner thickness and also for Poisson’s ratios larger than 0.45.
- 2.
- It provides very simple closed-form analytical solutions for both the pressure distribution and the dependencies between macroscopic contact quantities.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Symbol | Symbol Name |
| a | Contact radius |
| A | Contact area |
| C1, C2, C3 | Coefficients for fitting foundation modulus |
| δ | Contact/indentation depth |
| Radial clearance | |
| ε | Half-contact angle |
| E1 | Elastic modulus of head material |
| E2, E | Elastic modulus of liner material |
| Effective elastic modulus | |
| FN | Normal force |
| K | Foundation modulus |
| Dimensionless foundation modulus | |
| KB | Foundation modulus introduced by Bartel et al. |
| KBL | Foundation modulus of the bonded-layer-model |
| L | Liner thickness |
| µ | Coefficient of friction |
| ν1 | Poisson ratio of head material |
| ν2, ν | Poisson ratio of liner material |
| Maximum contact pressure | |
| Radial contact pressure | |
| Radius of femoral head | |
| Inner radius of acetabular cup | |
| Effective radius of curvature | |
| ur | Radial displacement of Winkler foundation |
References
- Zhou, Z.R.; Jin, Z.M. Biotribology: Recent progresses and future perspectives. Biosurface Biotribol. 2015, 1, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arzt, E.; Quan, H.; McMeeking, R.M.; Hensel, R. Functional surface microstructures inspired by nature–From adhesion and wetting principles to sustainable new devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 120, 100823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; Sicilia, A. Lubrication modeling and wear calculation in artificial hip joint during the gait. Tribol. Int. 2020, 142, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basdogan, C.; Giraud, F.; Levesque, V.; Choi, S. A review of surface haptics: Enabling tactile effects on touch surfaces. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2020, 13, 450–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakis, A.I.; Yastrebov, V.A.; Scheibert, J.; Nicola, L.; Dini, D.; Minfray, C.; Ciavarella, M. Modeling and simulation in tribology across scales: An overview. Tribol. Int. 2018, 125, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heß, M. Über die Exakte Abbildung Ausgewählter Dreidimensionaler Kontakte auf Systeme mit Niedrigerer Räumlicher Dimension. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Göttingen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, V.L.; Heß, M. Method of Dimensionality Reduction in Contact Mechanics and Friction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-642-53875-9. [Google Scholar]
- Argatov, I.; Heß, M.; Popov, V.L. The extension of the method of dimensionality reduction to layered elastic media. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech. Z. Für Angew. Math. Und Mech. 2018, 98, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimaki, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.I.; Chai, Y.S.; Popov, V.L. Rapid simulation procedure for fretting wear on the basis of the method of dimensionality reduction. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 4215–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsbach, F. Stress Tensor and Gradient of Hydrostatic Pressure in the Half-Space Beneath Axisymmetric Bodies in Normal and Tangential Contact. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A. On the Stress Distribution of Cylindrical Elastic Bodies in Contact; Chalmers University of Technology: Göteborg, Sweden, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, L.E.; Keer, L.M. The contact stress problem for an elastic sphere indenting an elastic cavity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1965, 1, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Puccio, F.; Mattei, L. Biotribology of Artificial Hip Joints. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.J.; Palmer, A.J.; Taylor, A.; Porter, M.L.; Malchau, H.; Glyn-Jones, S. Hip replacement. Lancet 2018, 392, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.M. A general axisymmetric contact mechanics model for layered surfaces, with particular reference to artificial hip joint replacements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2000, 214, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.L.; Burstein, A.H.; Toda, M.D.; Edwards, D.L. The effect of conformity and plastic thickness on contact stresses in metal-backed plastic implants. J. Biomech. Eng. 1985, 107, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imado, K.; Kido, Y.; Miyagawa, H. A method of calculation for contact pressure between femoral head and cup of artificial hip joint. Tribol. Trans. 2005, 48, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.M.; Dowson, D.; Fisher, J. A parametric analysis of the contact stress in ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular cups. Med. Eng. Phys. 1994, 16, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.N.; Himeno, S.; Tsumura, H.; Kawai, T.; Chao, E.Y.S. Pressure distribution on articular surfaces: Application to joint stability evaluation. J. Biomech. 1990, 23, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Y.; Fregly, B.J. Multibody dynamic simulation of knee contact mechanics. Med. Eng. Phys. 2004, 26, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abraham, C.L.; Maas, S.A.; Weiss, J.A.; Ellis, B.J.; Peters, C.L.; Anderson, A.E. A new discrete element analysis method for predicting hip joint contact stresses. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.R.; Won Choi, K.; Negrut, D.; Thelen, D.G. Efficient computation of cartilage contact pressures within dynamic simulations of movement. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2018, 6, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, E.; Andersen, M.S. A closed-form formulation for the conformal articulation of metal-on-polyethylene hip prostheses: Contact mechanics and sliding distance. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2018, 232, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.S.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L. Normal force-displacement relationship of spherical joints with clearances. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2006, 1, 160–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, P.A. Joint Replacement Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Plank, G.R.; Estok, D.M.; Muratoglu, O.K.; Oconnor, D.O.; Burroughs, B.R.; Harris, W.H. Contact stress assessment of conventional and highly crosslinked ultra high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular liners with finite element analysis and pressure sensitive film. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Villarraga, M.L.; Herr, M.P.; Bergström, J.S.; Rimnac, C.M.; Edidin, A.A. Thermomechanical behavior of virgin and highly crosslinked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene used in total joint replacements. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3681–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.M. 1-A primer on UHMWPE. In UHMWPE Biomaterials Handbook: Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene in Total Joint Replacement and Medical Devices; Andrew, W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Sakamoto, M.; Chao, E.Y. A comparison of different methods in predicting static pressure distribution in articulating joints. J. Biomech. 1997, 30, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Galvin, A.; Jin, Z.; Fisher, J. A new formulation for the prediction of polyethylene wear in artificial hip joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2010, 225, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikko, V. Effect of contact area on the wear and friction of UHMWPE in circular translation pin-on-disk tests. ASME J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 061606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, D.; Spector, M. Effects of contact area and stress on the volumetric wear of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Wear 2003, 254, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M. A JKR solution for a ball-in-socket contact geometry as a bi-stable adhesive system. Acta Mech. 2018, 229, 2835–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
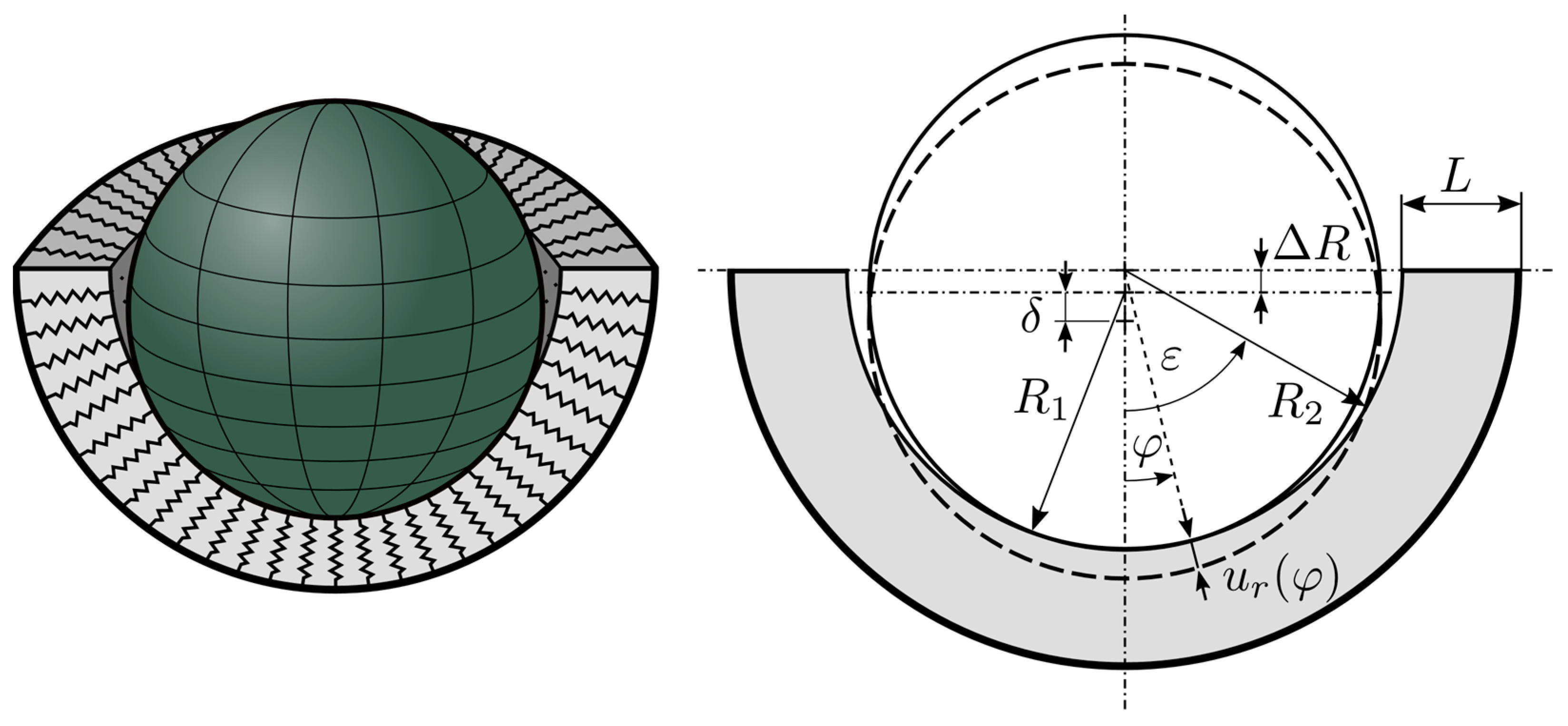

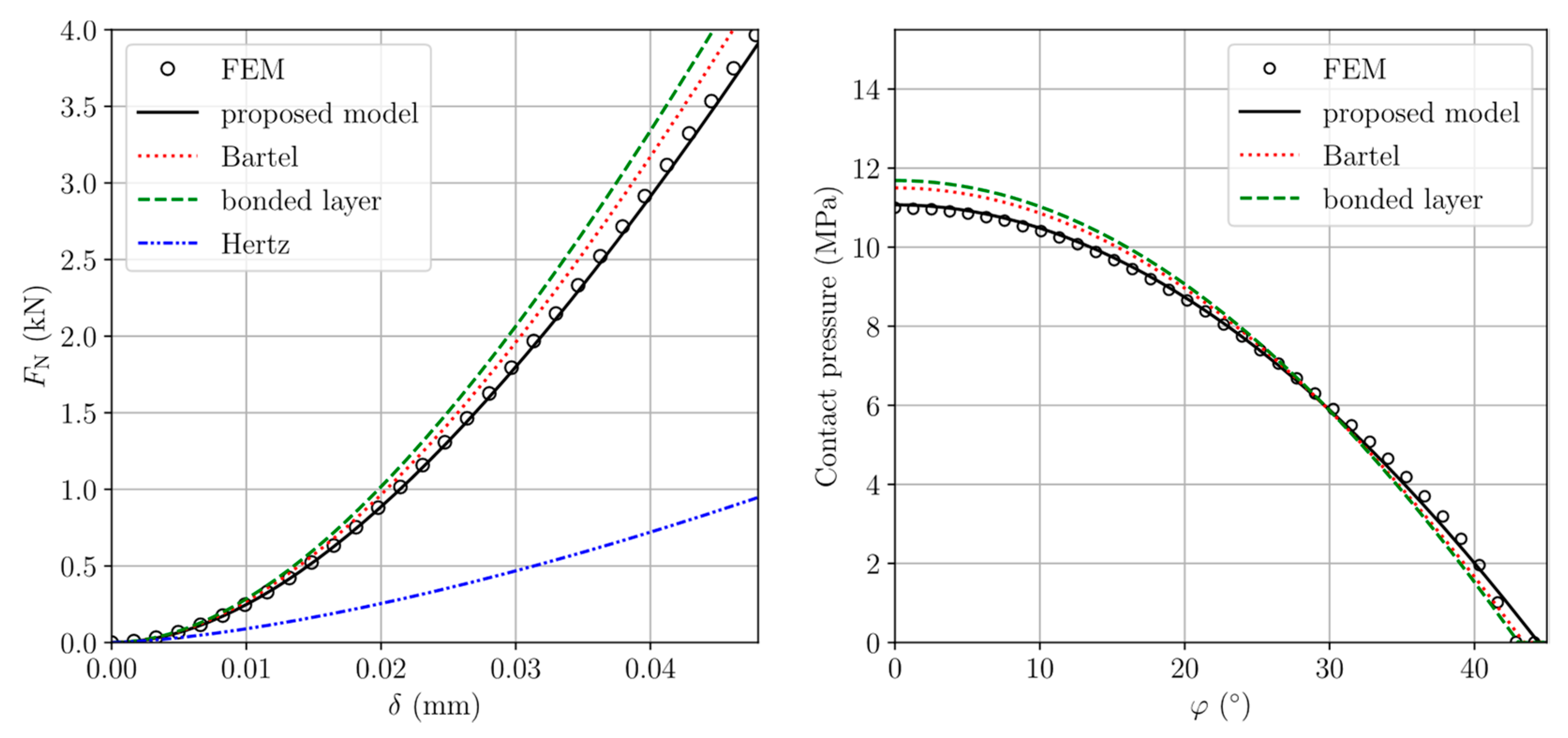
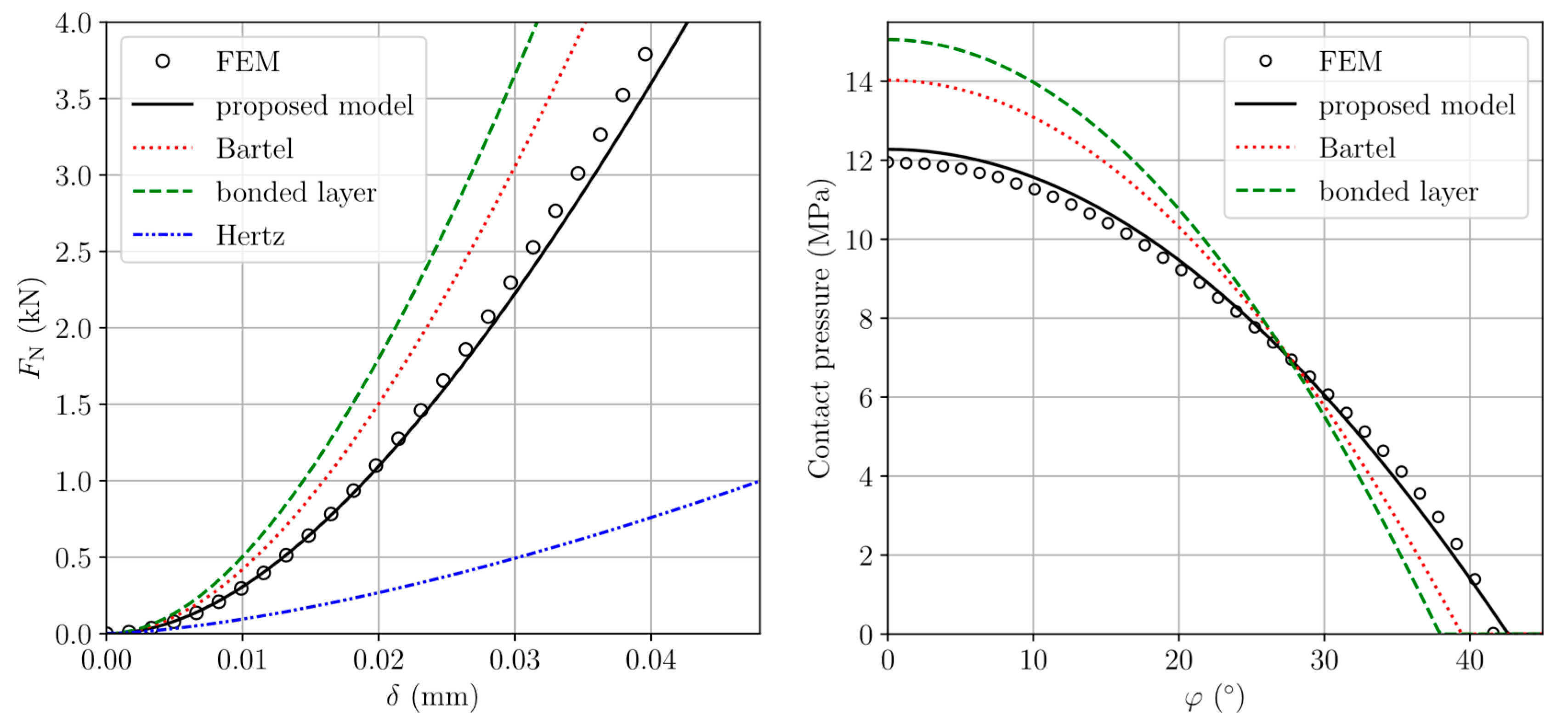
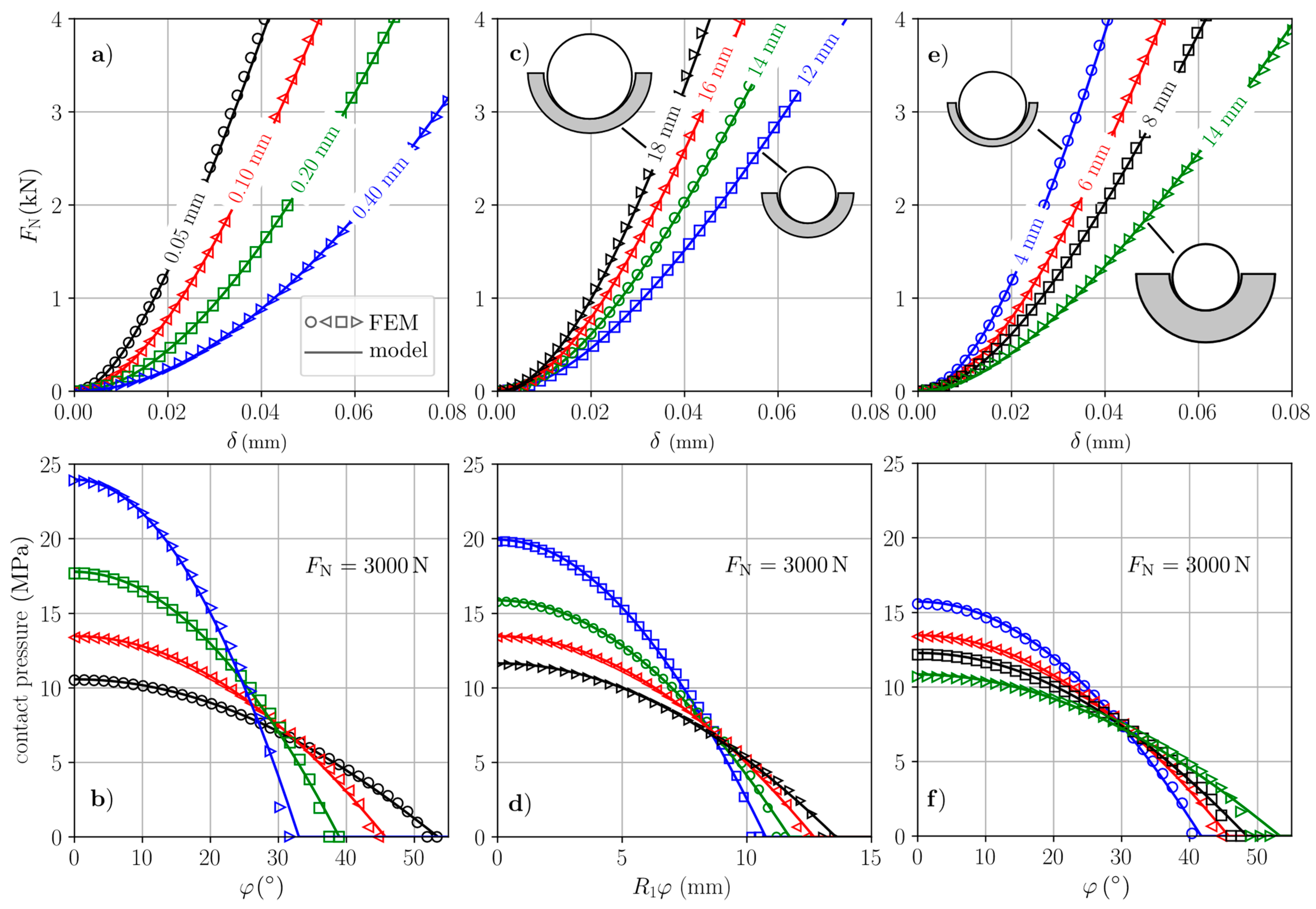

| Head Radius | Liner Thickness | Radial Clearance | Outer Cup Radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11–23 mm | 3–15 mm | 0.05–0.2 mm | 16–26 mm |
| Material | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | 230 | 0.3 |
| UHMWPE | 1 | 0.4, 0.45 |
| 1.14 | 1.10 | 1.06 | 0.99 | 0.96 | |
| 0.97 | 1.07 | 1.23 | 1.51 | 1.79 | |
| 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heß, M.; Forsbach, F. An Analytical Model for Almost Conformal Spherical Contact Problems: Application to Total Hip Arthroplasty with UHMWPE Liner. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311170
Heß M, Forsbach F. An Analytical Model for Almost Conformal Spherical Contact Problems: Application to Total Hip Arthroplasty with UHMWPE Liner. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(23):11170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311170
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeß, Markus, and Fabian Forsbach. 2021. "An Analytical Model for Almost Conformal Spherical Contact Problems: Application to Total Hip Arthroplasty with UHMWPE Liner" Applied Sciences 11, no. 23: 11170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311170
APA StyleHeß, M., & Forsbach, F. (2021). An Analytical Model for Almost Conformal Spherical Contact Problems: Application to Total Hip Arthroplasty with UHMWPE Liner. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311170







