Impact Response of Composite Sandwich Cylindrical Shells
Abstract
1. Introduction
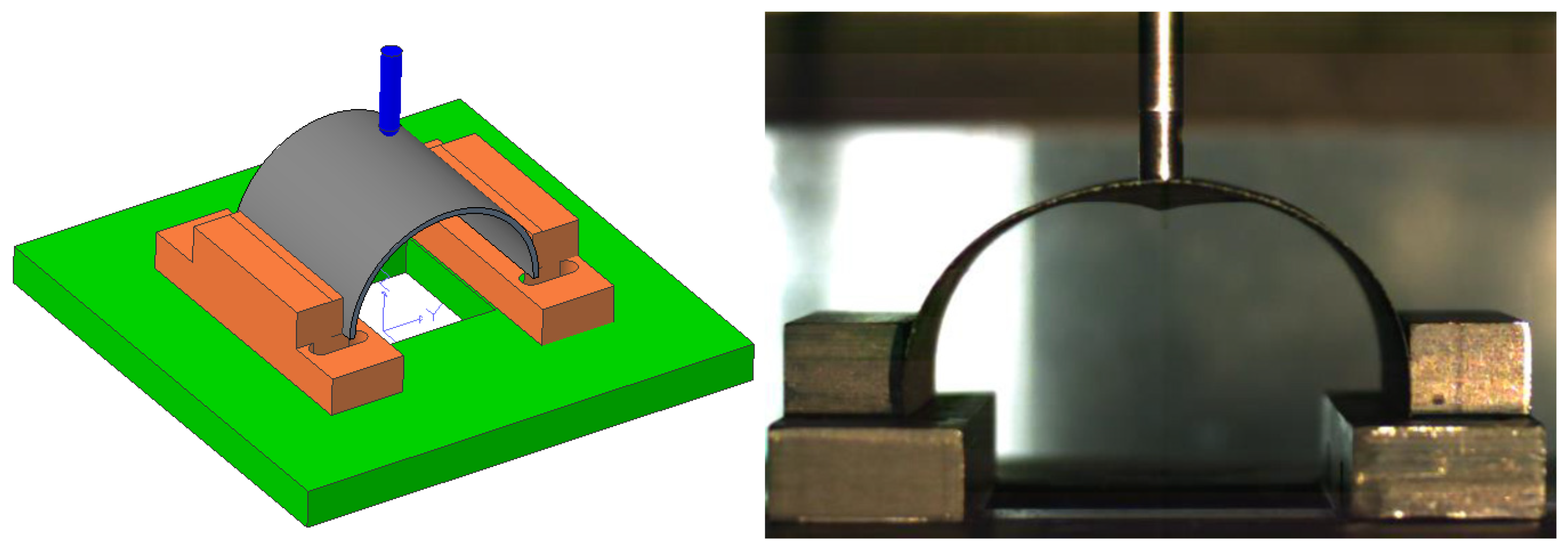
2. Material and Experimental Procedure
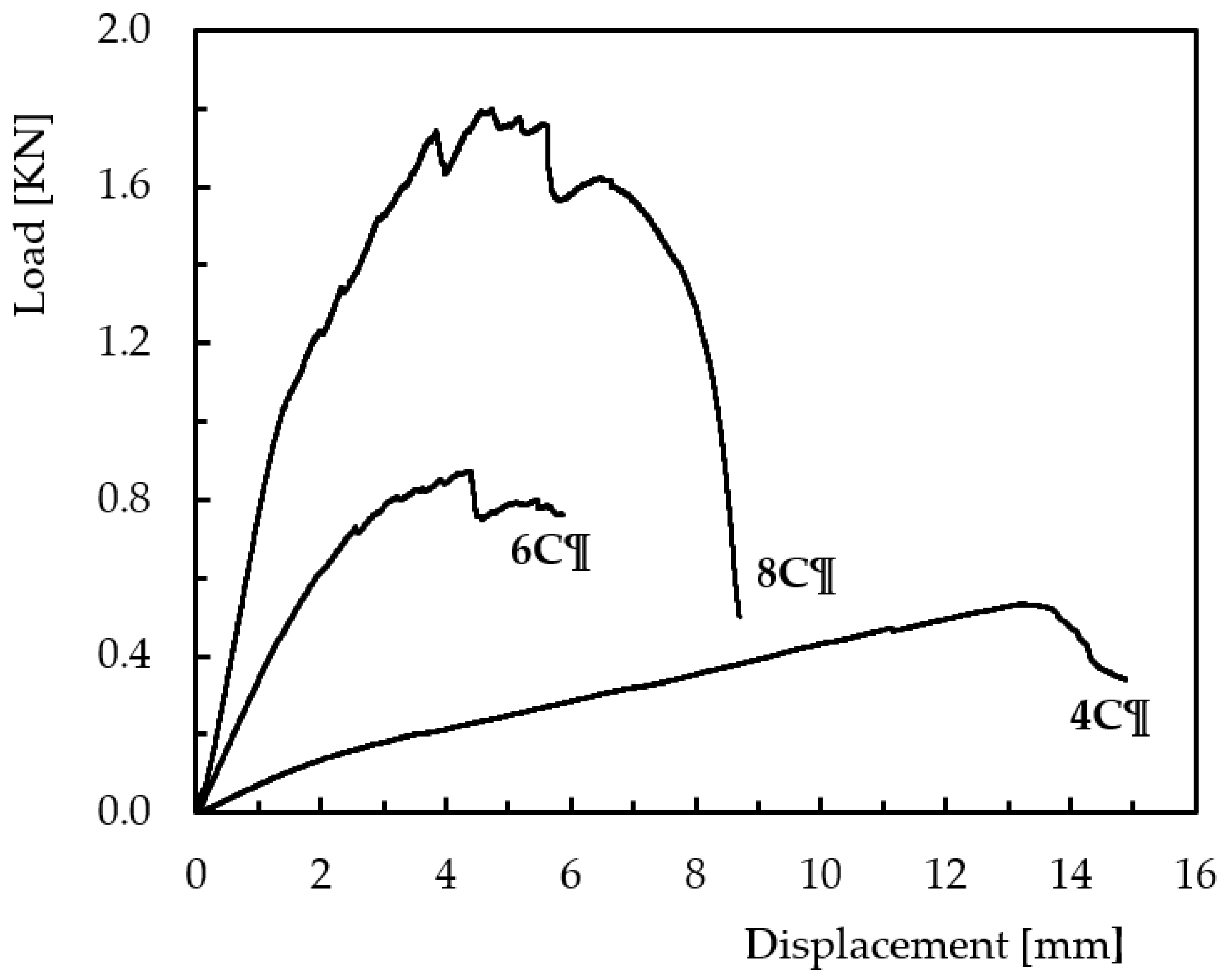
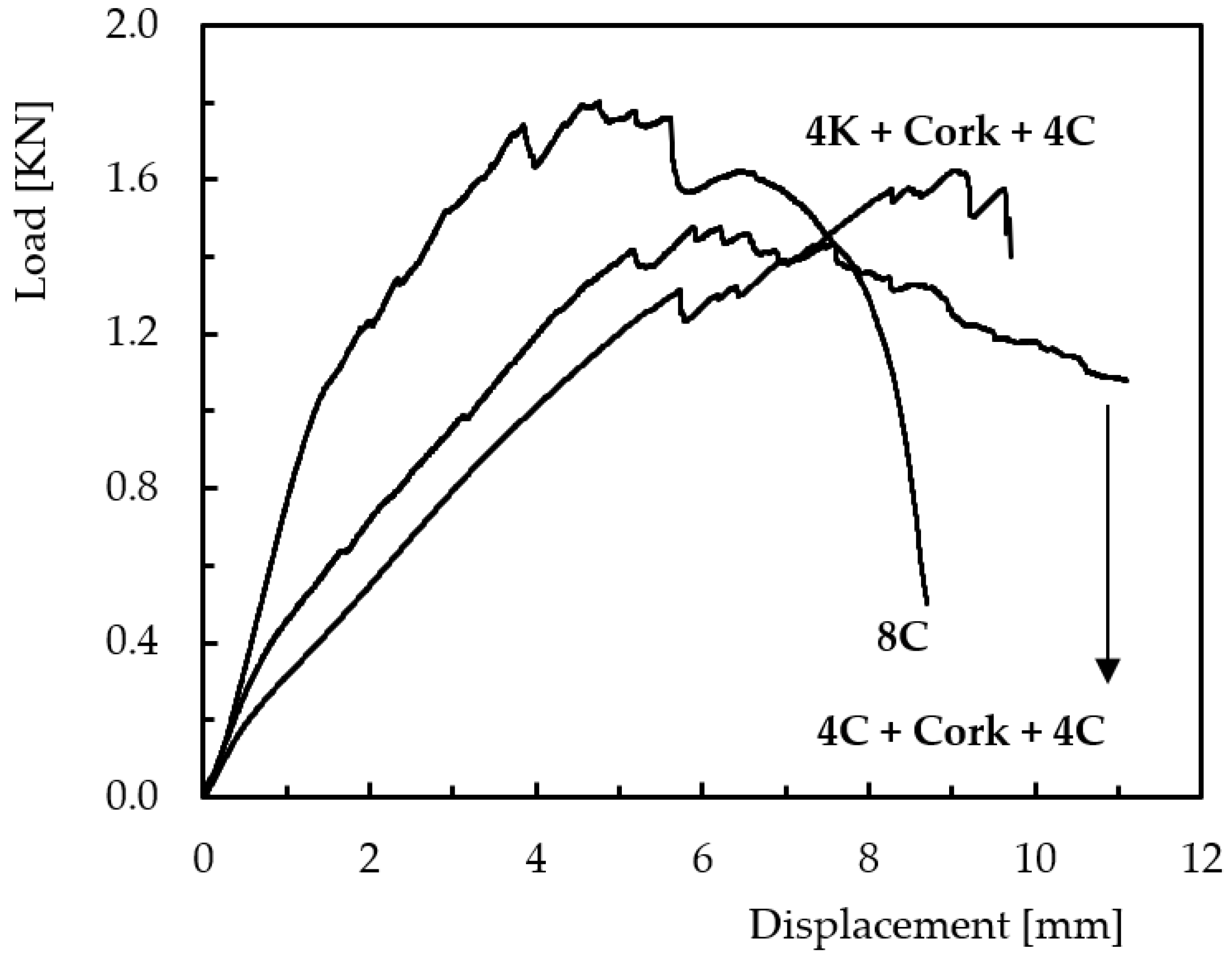
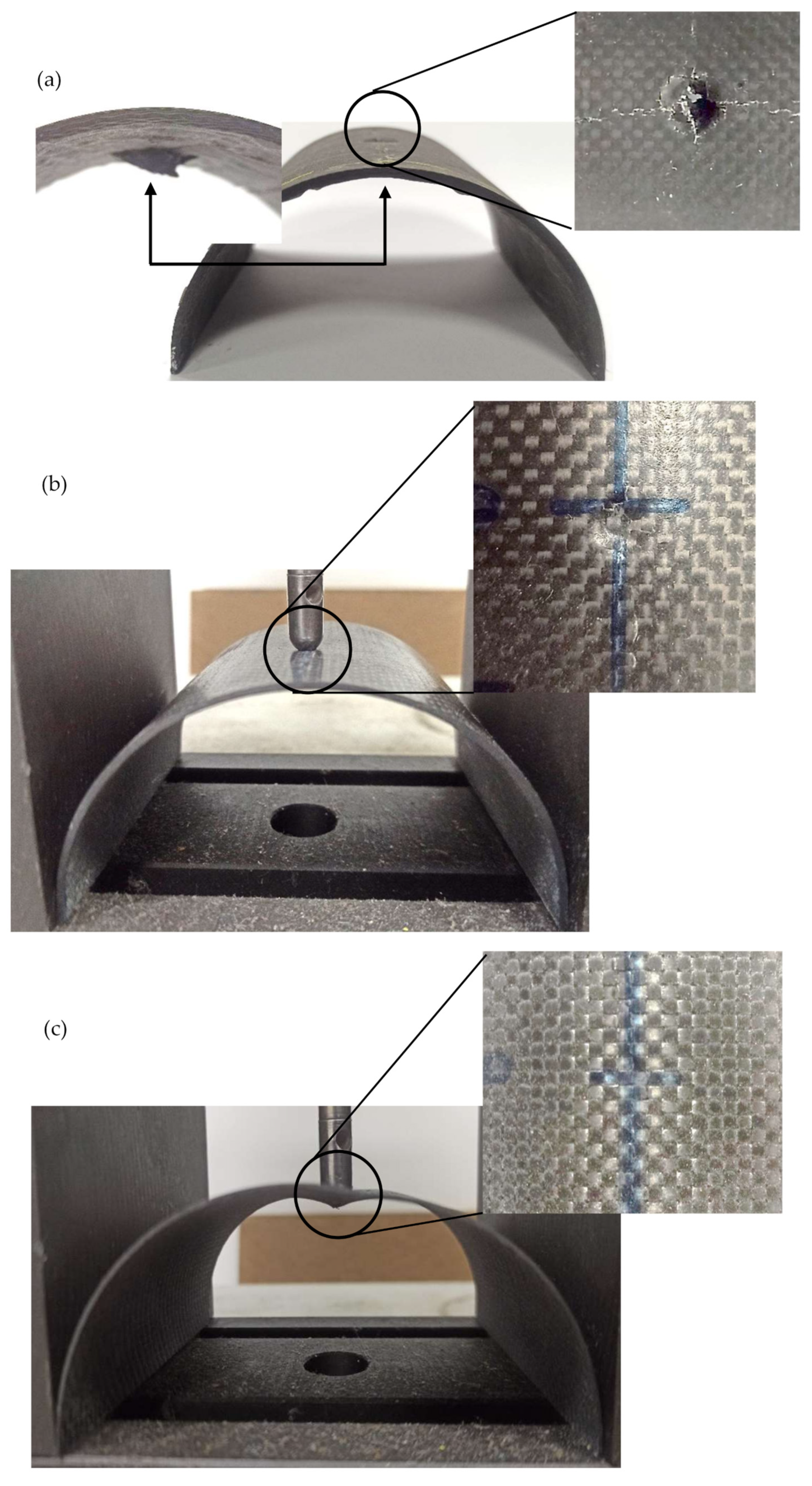
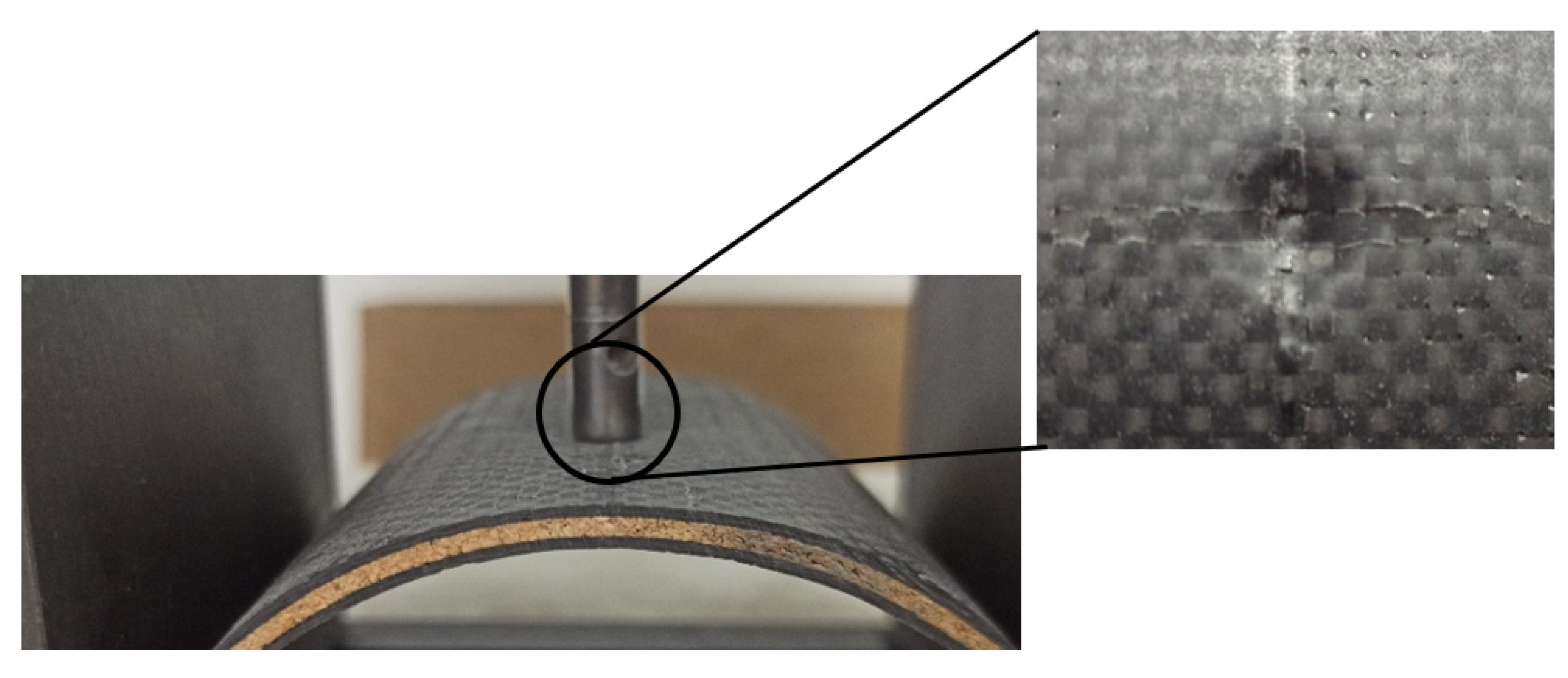
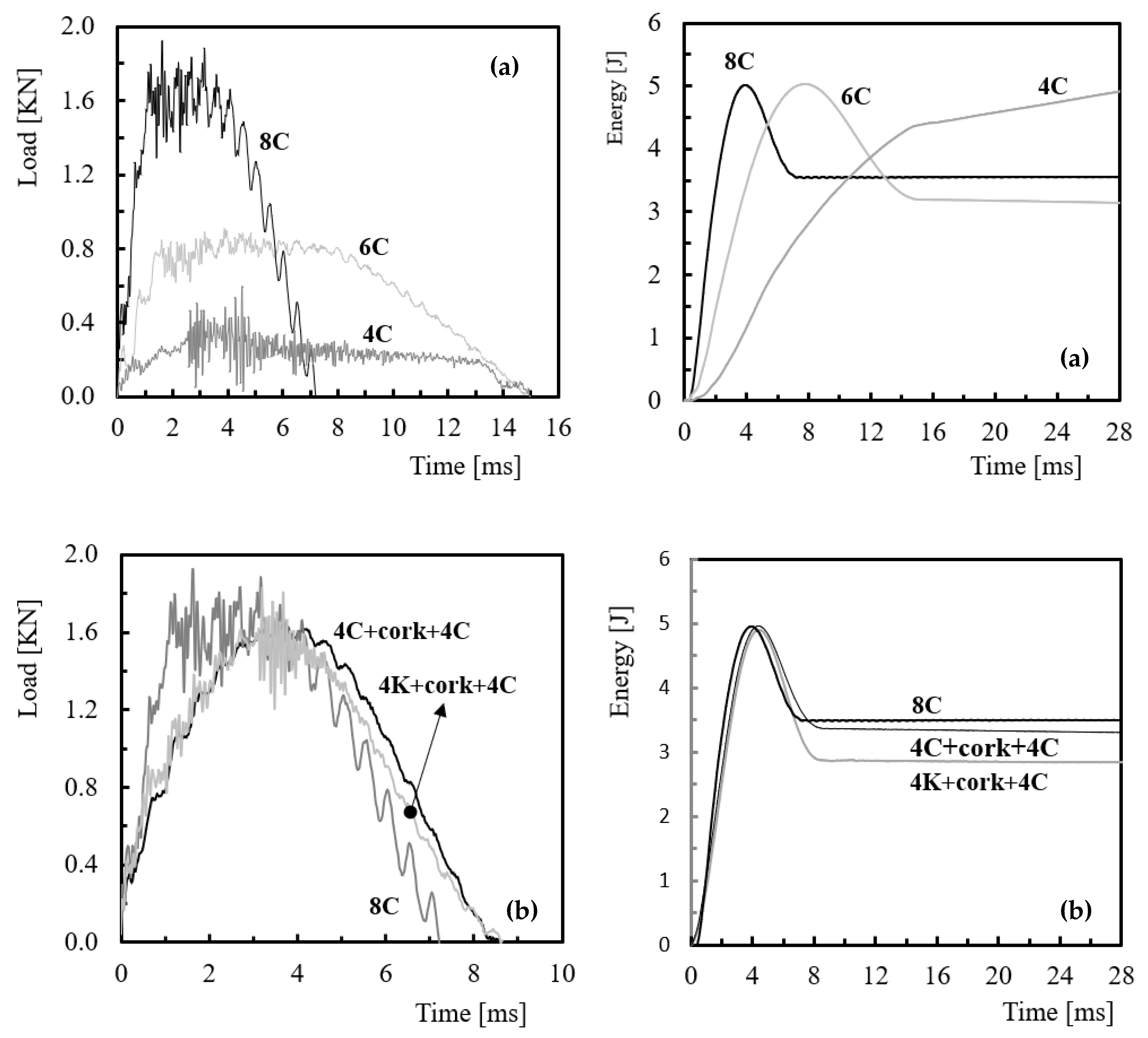
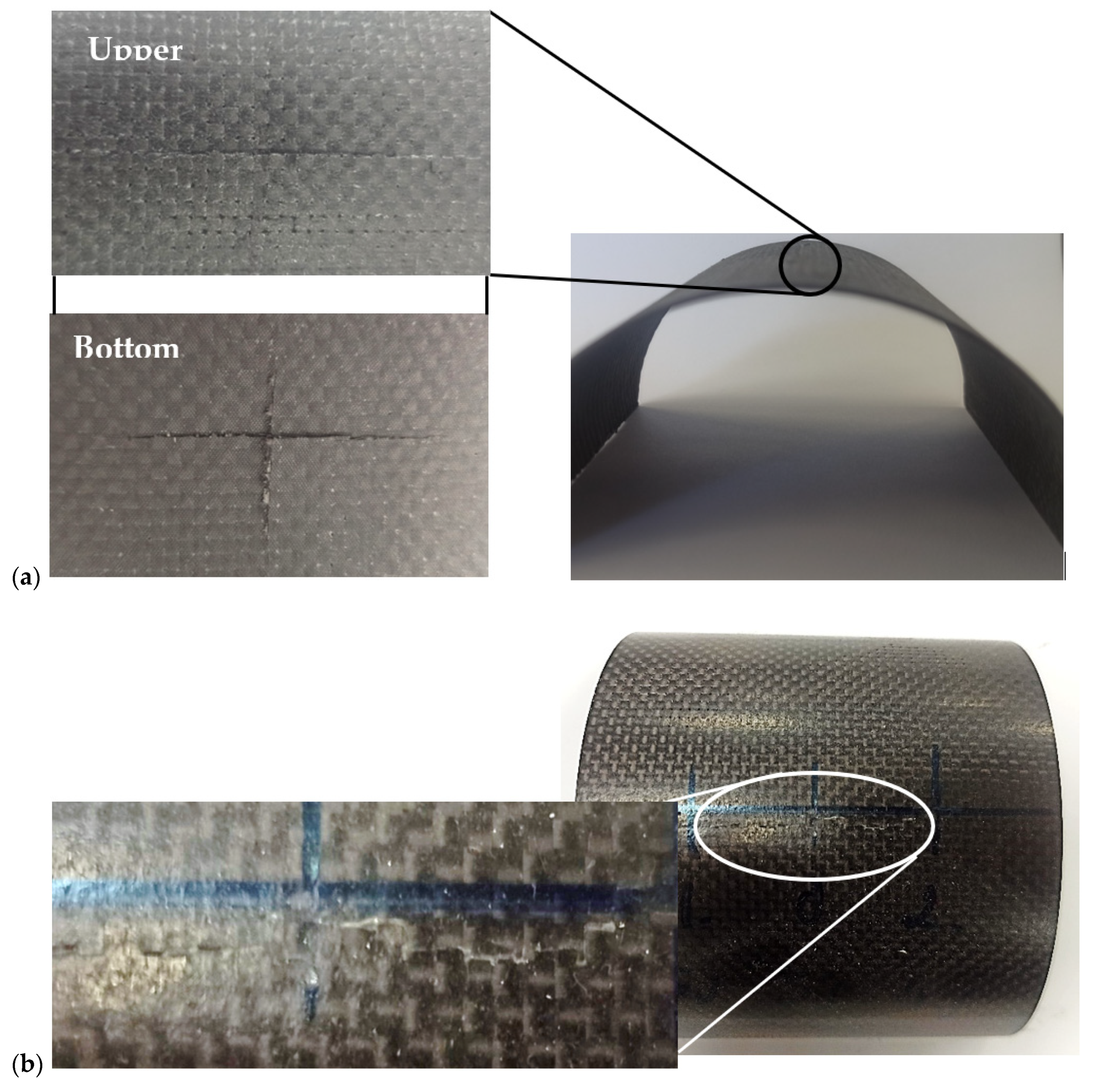
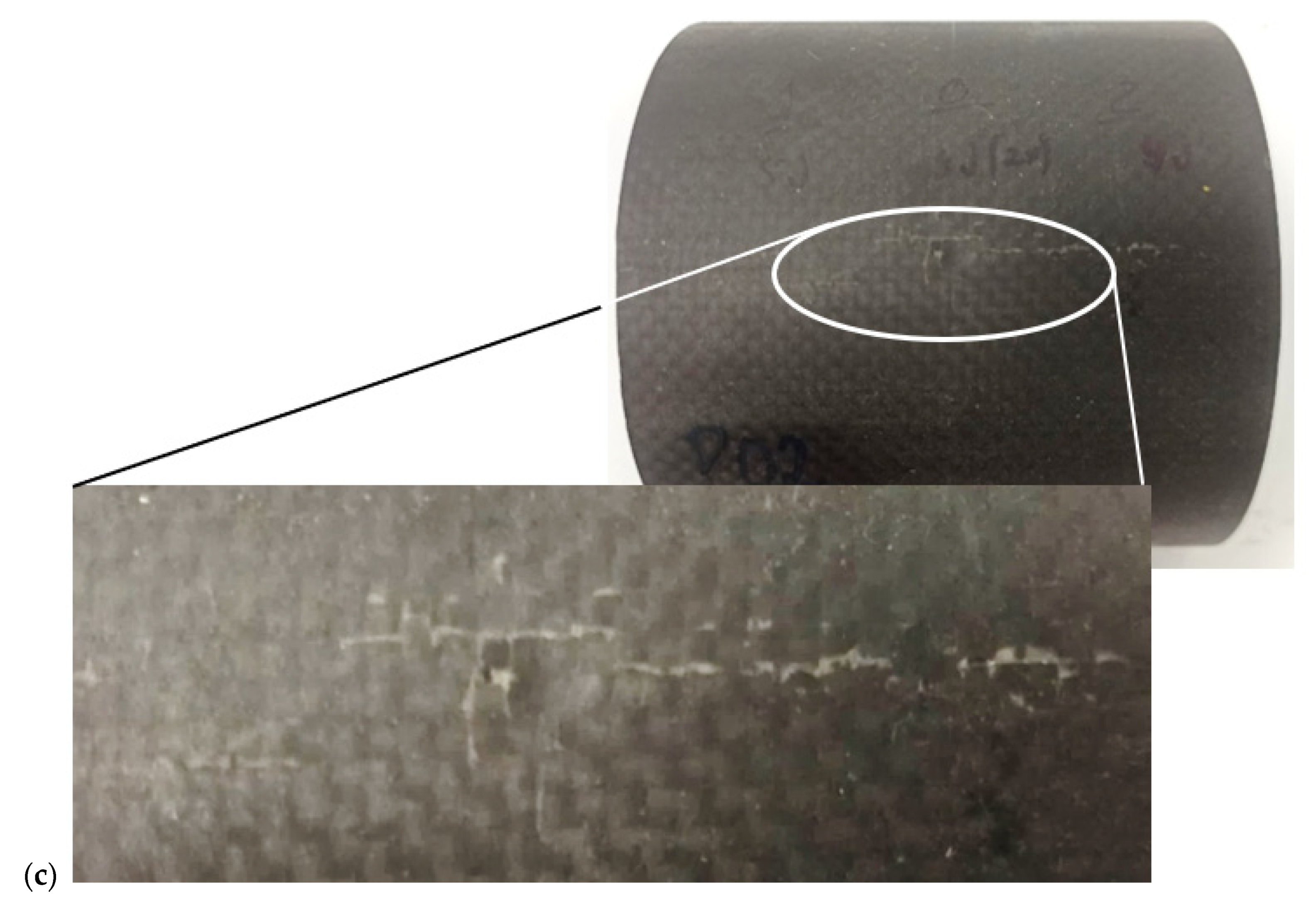
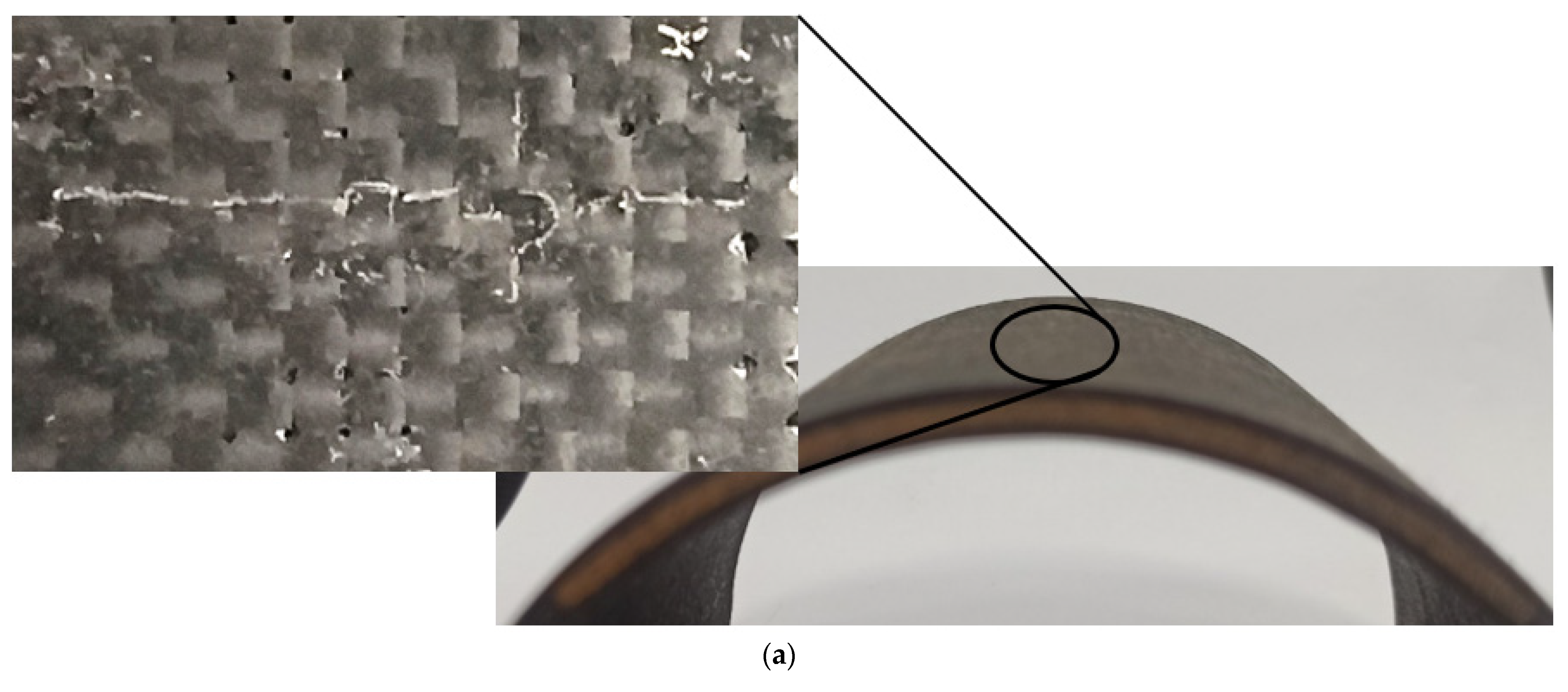
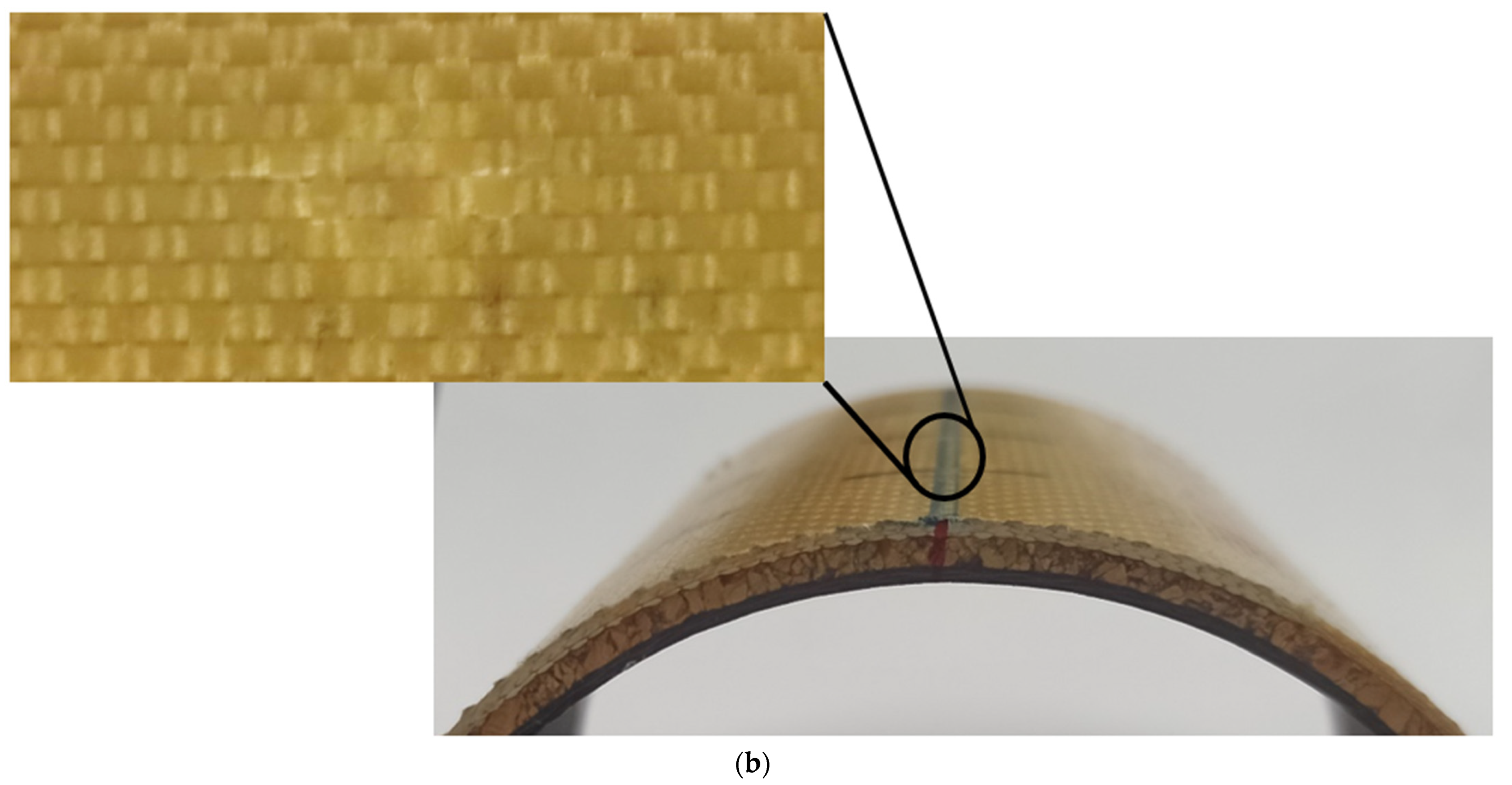
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, R.D.; Cawley, P.D.R.D. A review of defects types and non-destructive testing techniques for composites and bonded joints. NDT E Int. 1998, 21, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; de Moura, M.F.S.F.; Santos, J.B. Damage detection on laminated composite materials using several NDT techniques. Insight 2012, 54, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, M.F.S.F.; Marques, A.T. Prediction of low velocity impact damage in carbon-epoxy laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2002, 33, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Antunes, F.V.; Richardson, M.O.W. Effect of interlayer delamination on mechanical behavior of carbon/epoxy laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 2609–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; de Moura, M.F.S.F.; Reis, P.N.B. Residual strength after low velocity impact in carbon-epoxy laminates. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 514–516, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; de Moura, M.F.S.F. Delamination effect on bending behaviour in carbon-epoxy composites. Strain 2011, 47, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.O.W.; Wisheart, M.J. Review of low-velocity impact properties of composite materials. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 1996, 27, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Río, T.G.; Zaera, R.; Barbero, E.; Navarro, C. Damage in CFRPs due to low velocity impact at low temperature. Compos. Part B Eng. 2005, 36, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Atas, C.; Icten, B.M.; Karakuzu, R. An experimental investigation of the impact response of composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2009, 87, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.N.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Bennett, N.; Reis, P.N.B. Low-velocity impact response of nonwoven hemp fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites: Influence of impactor geometry and impact velocity. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 2756–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.D.; Goel, R.; Naik, N.K. Effect of back pressure on impact and compression after-impact characteristics of composites. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; de Moura, M.F.S.F.; Neto, M.A. Influence of multi-impacts on GFRP composites laminates. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 52, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; Neto, M.A.; Louro, C. Effects of alkaline and acid solutions on glass/epoxy composites. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2013, 98, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortas, N.; Er, O.; Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M. Effect of corrosive solutions on composites laminates subjected to low velocity impact loading. Compos. Struct. 2014, 108, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; Neto, M.A. Experimental study of temperature effects on composite laminates subjected to multi-impacts. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 98, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosur, M.V.; Adbullah, M.; Jeelani, S. Studies on the low-velocity impact response of woven hybrid composites. Compos. Struct. 2005, 67, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorsen, A.; Salehi-Khojn, A.; Mahinfalah, M.; Nakhaei-Jazar, R. Temperature effects on the impact behavior of fiberglass and fiberglass/Kevlar sandwich composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2006, 13, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Khojin, A.; Mahinfalaha, M.; Bashirzadeh, R.; Freeman, B. Temperature effects on Kevlar/hybrid and carbon fiber composite sandwiches under impact loading. Compos. Struct. 2007, 78, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, A.F.; Soares, M.I.; Neto, A.S. A study on nanostructured laminated plates behavior under low-velocity impact loadings. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2007, 34, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Khan, S.-U.; Munir, A.; Kim, J.-K. Impact damage resistance of CFRP with nanoclay-filled epoxy matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Santos, P.; Richardson, M.O.W.; Santos, J.B. Impact response of Kevlar composites with filled epoxy matrix. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Benameur, T.; Richardson, M.O.W. Impact response of Kevlar composites with nanoclay enhanced epoxy matrix. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 46, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Benameur, T.; Richardson, M.O.W. Impact strength of composites with nano-enhanced resin after fire exposure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silva, S.P.; Sabino, M.A.; Fernandes, E.M.; Correlo, V.M.; Boesel, L.F.; Reis, R.L. Cork: Properties, capabilities and applications. Int. Mater. Rev. 2005, 50, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, J.F. The viscoelastic properties of cork. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.E.; Fortes, M.A. Deformation and fracture of cork in tension. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Silva, P.A.A. Mechanical behaviour of composites filled by agro-waste materials. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Bouvet, C.; Bergerot, A.; Barrau, J.J. Impact and compression after impact experimental study of a composite laminate with a cork thermal shield. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 3286–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.G.A.; de Moura, M.F.S.F.; Magalhães, A.G. Low velocity impact behaviour of a hybrid carbon-epoxy/cork laminate. Strain 2017, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; Ivañez, I.; Sánchez-Saez, S.; Garcia-Castillo, S.K.; Barbero, E. The High-velocity impact behaviour of Kevlar composite laminates filled with cork powder. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Costa, J.D.M.; Santos, M.J. Fatigue performance of Kevlar/epoxy composites with filled matrix by cork powder. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivañez, I.; Sánchez-Saez, S.; Garcia-Castillo, S.K.; Barbero, E.; Amaro, A.; Reis, P.N.B. High-velocity impact behaviour of damaged sandwich plates with agglomerated cork core. Compos. Struct. 2020, 248, 112520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Toh, S.; Shim, V. The elastic response of orthotropic laminated cylindrical shells to low-velocity impact. Compos. Eng. 1994, 4, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, K.; Mahajan, P.; Mittal, R. Impact response and damage in laminated composite cylindrical shells. Compos. Structur. 2003, 59, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, K.; Mahajan, P.; Mittal, R. A parametric study of the impact response and damage of laminated cylindrical composite shells. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, L. Experimental investigation of the impact response of cylindrically curved laminated composite panels. In Proceedings of the 35th Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Hilton Head, SC, USA, 18–20 April 1994; pp. 2292–2297, AIAA paper, 94-1604-CP. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kistler, L.S.; Waas, A.M. Experiment and analysis on the response of curved laminated composite panels subjected to low velocity impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1998, 21, 711–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Cho, C. Damage initiation and propagation in composite shells subjected to impact. Compos. Struct. 2007, 78, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Analysis of impact response and damage in laminated composite shell involving large deformation and material degradation. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 2008, 3, 1741–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchige, B.; Ghasemnejad, H.; Augousti, A.T. Theoretical approach to predict transverse impact response of variable-stiffness curved composite plates. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 89, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arachchige, B.; Ghasemnejad, H. Post impact analysis of damaged variable-stiffness curved composite plates. Compos. Struct. 2017, 166, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.A.C.P.; Navalho, F.V.P.; Reis, P.N.B. Impact response of laminate cylindrical shells. Frat. Integrita Strutt. 2019, 48, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; Magalhães, A.; De Moura, M.F.S.F. The Influence of the Boundary Conditions on Low-Velocity Impact Composite Damage. Strain 2011, 47, e220–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.A.; Hsia, R.L. Effect of thickness on the large elastic deformation behavior of laminated shells. Compos. Struct. 1998, 43, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimn, D.; Chaudhuri, R.A. Effect of Thickness on Buckling of Perfect Cross-Ply Rings under External Pressure. Compos. Struct. 2007, 81, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.A. Effects of thickness and fibre misalignment on compression fracture in cross-ply (very) long cylindrical shells under external pressure. Proc. R. Soc. A 2015, 471, 20150147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Antunes, F.V.; Costa, J.D.M. Flexural behaviour of hybrid laminated composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.P.; Santos, P.; Sousa, N.N.; Reis, P.N.B. Strain rate effect on composites with epoxy matrix filled by cork powder. Mater. Des. Process Comm. 2019, 1, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Silva, M.P.; Santos, P.; Parente, J.M.; Bezazi, A. Viscoelastic behaviour of composites with epoxy matrix filled by cork powder. Compos. Struct. 2020, 234, 111669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Silva, M.P.; Santos, P.; Parente, J.M.; Valvez, S.; Bezazi, A. Mechanical performance of an optimized cork agglomerate core-glass fibre sandwich panel. Compos. Struct. 2020, 245, 112375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Rosa, M.E.; Pereira, E. Variability of the compression properties of cork. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.P.; Santos, P.; Parente, J.; Valvez, S.; Reis, P.N.B. Effect of harsh environmental conditions on the impact response of carbon composites with filled matrix by cork powder. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancaspro, J.W.; Papakonstantinou, C.G.; Balaguru, P.N. Flexural Response of Inorganic Hybrid Composites with E-Glass and Carbon Fibers. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2010, 132, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.S.; Duong, J.; Davies, I.J. Flexural properties of S-2 glass and TR30S carbon fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Davies, I.J. Optimal design for the flexural behaviour of glass and carbon fibre reinforced polymer hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2012, 37, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeppner, G.A.; Abrate, S. Delamination threshold loads for low velocity impact on composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2000, 31, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belingardi, G.; Vadori, R. Low velocity impact of laminate Glass-Fiber-Epoxy matrix composite materials plates. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2002, 27, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; de Moura, M.; Santos, J.B. Influence of the specimen thickness on low velocity impact behavior of composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2012, 32, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.G.; Velmurugan, R.; Gupta, N.K. Energy absorption and ballistic limit of targets struck by heavy projectile. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 3, 21–39. [Google Scholar]
- Garcıía-Castillo, S.K.; Sánchez-Sáez, S.; Barbero, E. Influence of areal density on the energy absorbed by thin composite plates subjected to high-velocity impacts. J. Strain Anal. 2012, 47, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.M. Penetration and perforation of thick FRP laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.K.; Shrirao, P.; Reddy, B.C.K. Ballistic impact behavior of woven fabric composites: Parametric Studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process 2005, 412, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, B.A.; Gillespie, J.W. Punch shear based penetration model of ballistic impact of thick-section composites. Compos. Struct. 2008, 86, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujicic, M.; Glomski, P.S.; He, T.; Arakere, G.; Bell, W.C. Material modelling and ballistic-resistance analysis of armor-grade composites reinforced with high-performance fibers. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Goldsmith, W.; Dharan, C.K.H. Penetration of laminated Kevlar by projectiles-II. Analytical model. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1992, 29, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wen, H.M.; Qin, Y. Penetration and perforation of FRP laminates struck transversely by conical-nosed projectiles. Compos. Struct. 2007, 81, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.A.O.; Pascoal, R.J.S.; Alves de Sousa, R.J. Modelling impact response of agglomerated cork. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Stacking Sequence | Schematic Lay-Up | Thickness (mm) Average Value (Standard Deviation) |
|---|---|---|
| 8C |  | 2.53 (0.15) |
| 6C |  | 1.58 (0.03) |
| 4C |  | 0.92 (0.02) |
| 4C + Cork + 4C |  | 4.23 (0.09) |
| 4K + Cork + 4C |  | 4.11 (0.03) |
| Laminates | Maximum Load (N) | Displacement at Max. Load (mm) | Stiffness (N/mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Std. | Average | Std. | Average | Std. | |
| 8C | 1801 | 212 | 3.9 | 0.7 | 812 | 29 |
| 6C | 873 | 121 | 4.4 | 1.0 | 354 | 41 |
| 4C | 533 | 101 | 13.2 | 2.1 | 71,7 | 8 |
| Laminates | Maximum Load (N) | Displacement at Max. Load (mm) | Stiffness (N/mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Std. | Average | Std. | Average | Std. | |
| 8C | 1801 | 212 | 4.7 | 1.1 | 812 | 29 |
| 4C + Cork + 4C | 1476 | 121 | 5.9 | 1.9 | 484 | 37 |
| 4K + Cork + 4C | 1623 | 101 | 9.1 | 2.3 | 256 | 32 |
| Laminates | Peak Load (N) | Max Displacement (mm) | Elastic Recuperation (J) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Std. | Average | Std. | Average | Std. | |
| 8C | 1959 | 50 | 4.2 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 0.38 |
| 6C | 924 | 12 | 7.8 | 0.19 | 1.71 | 0.19 |
| 4C | 589 | 4 | - | - | - | - |
| Laminates | Peak Load [N] | Max Displacement [mm] | Elastic Recuperation [J] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Std. | Average | Std. | Average | Std. | |
| 8C | 1959 | 50 | 4.2 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 0.38 |
| 4C + Cork + 4C | 1755 | 92 | 4.7 | 0.05 | 1.68 | 0.01 |
| 4K + Cork + 4C | 1653 | 21 | 4.9 | 0.13 | 2.03 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reis, P.N.B.; Coelho, C.A.C.P.; Navalho, F.V.P. Impact Response of Composite Sandwich Cylindrical Shells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210958
Reis PNB, Coelho CACP, Navalho FVP. Impact Response of Composite Sandwich Cylindrical Shells. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210958
Chicago/Turabian StyleReis, Paulo N. B., Carlos A. C. P. Coelho, and Fábio V. P. Navalho. 2021. "Impact Response of Composite Sandwich Cylindrical Shells" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210958
APA StyleReis, P. N. B., Coelho, C. A. C. P., & Navalho, F. V. P. (2021). Impact Response of Composite Sandwich Cylindrical Shells. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210958







