Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Characteristics over the Ocean Relevant to Astronomy and Atmospheric Physics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Methodology
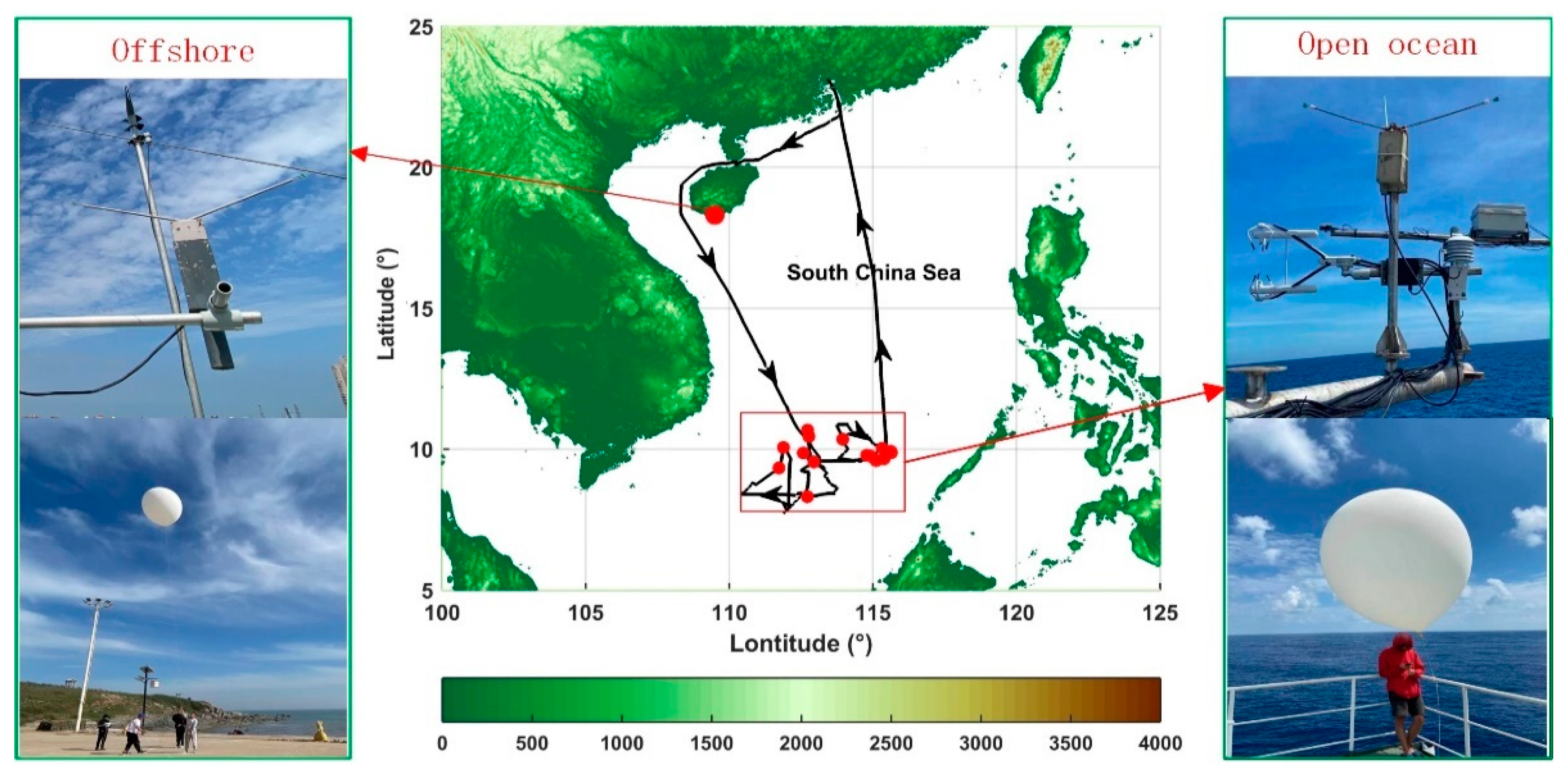
2.1. Experiment Details
2.2. Principle of Measurement
2.3. Estimation Model
2.4. Integrated Astroclimatic Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
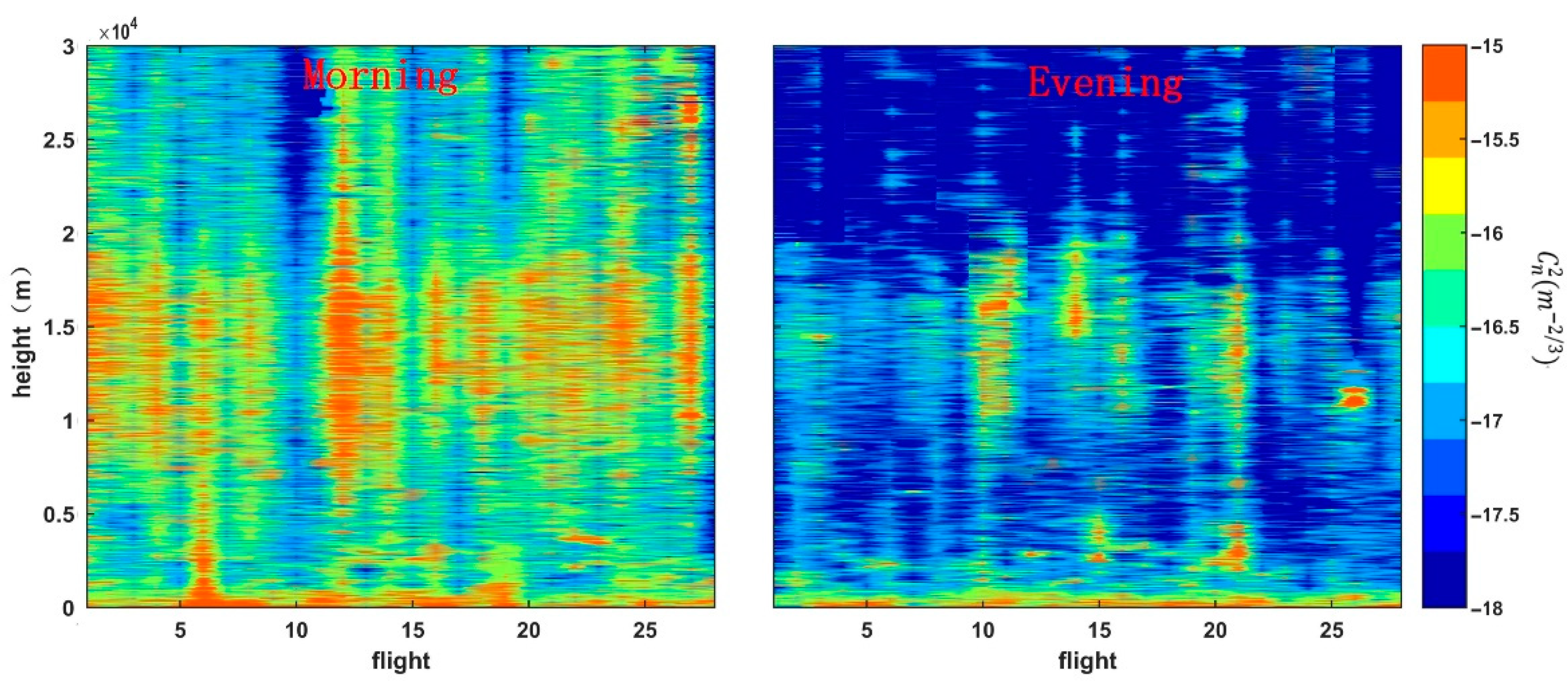
3.1. Evolution Trend
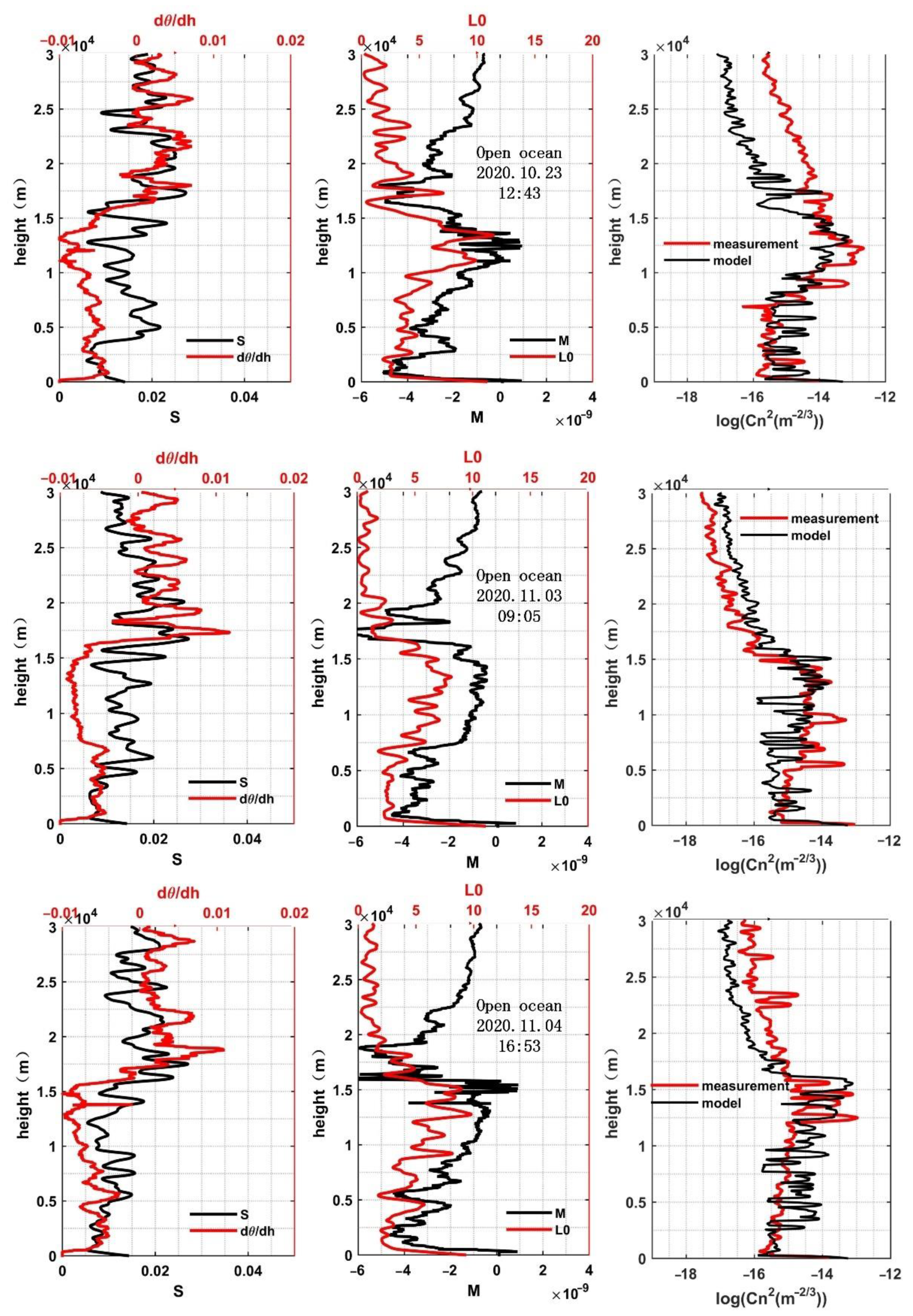
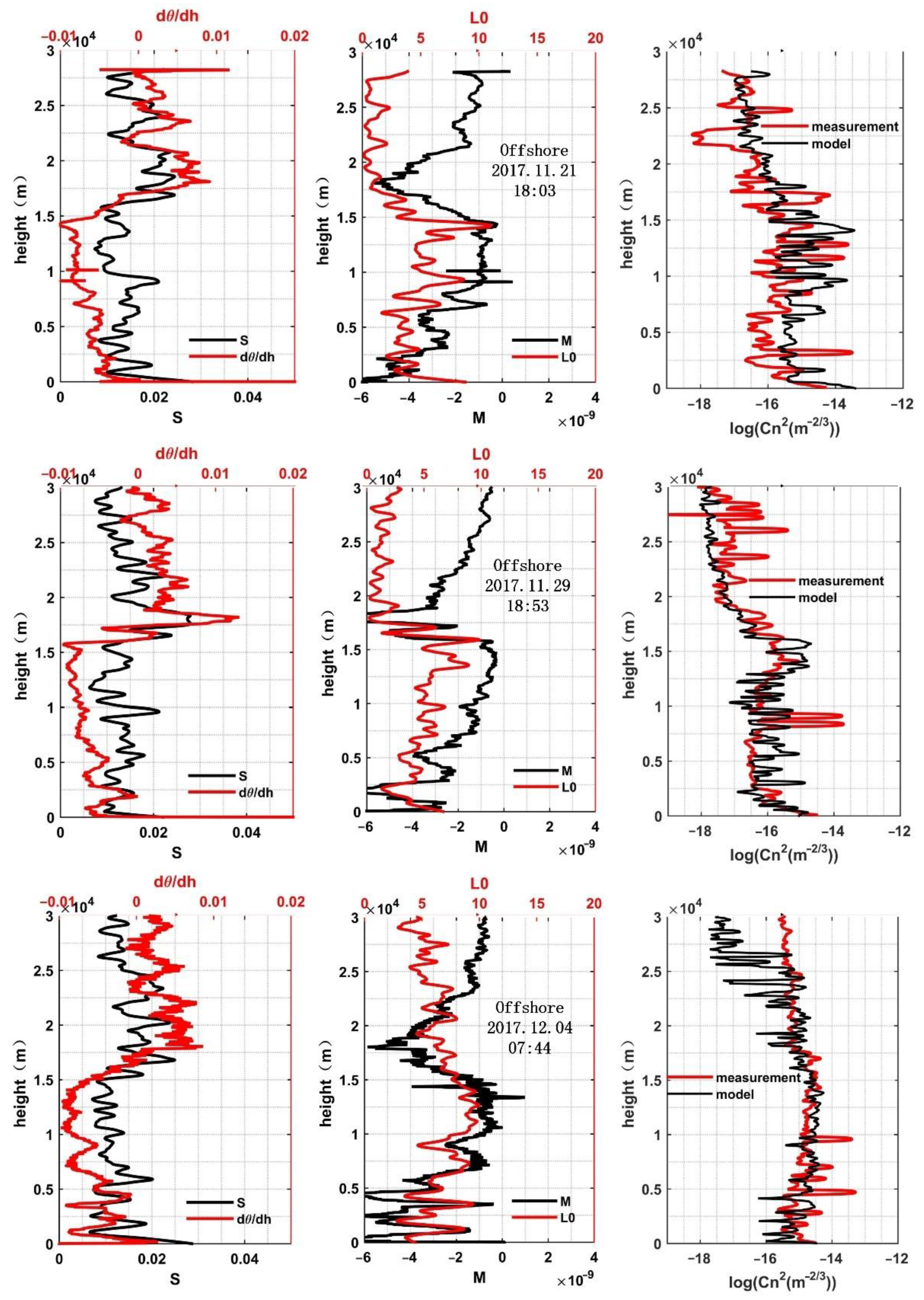
3.2. Analysis of Influencing Factors
3.3. Integrated Astroclimatic Parameters
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The refractive index structure constant has a relatively typical ‘seesaw’ feature near the ocean surface in the offshore area, which disappears farther than 160 km away from the coast. The optical turbulence strength from the ground up to 30 km is strongest at noon with a maximum value close to 5 × 10−13 m−2/3, and relatively weak at morning and dusk even near the magnitude of 10−19 m−2/3 over the open ocean. For turbulence strength profiles of the offshore area, the value of in the morning is larger than that in the evening.
- (2)
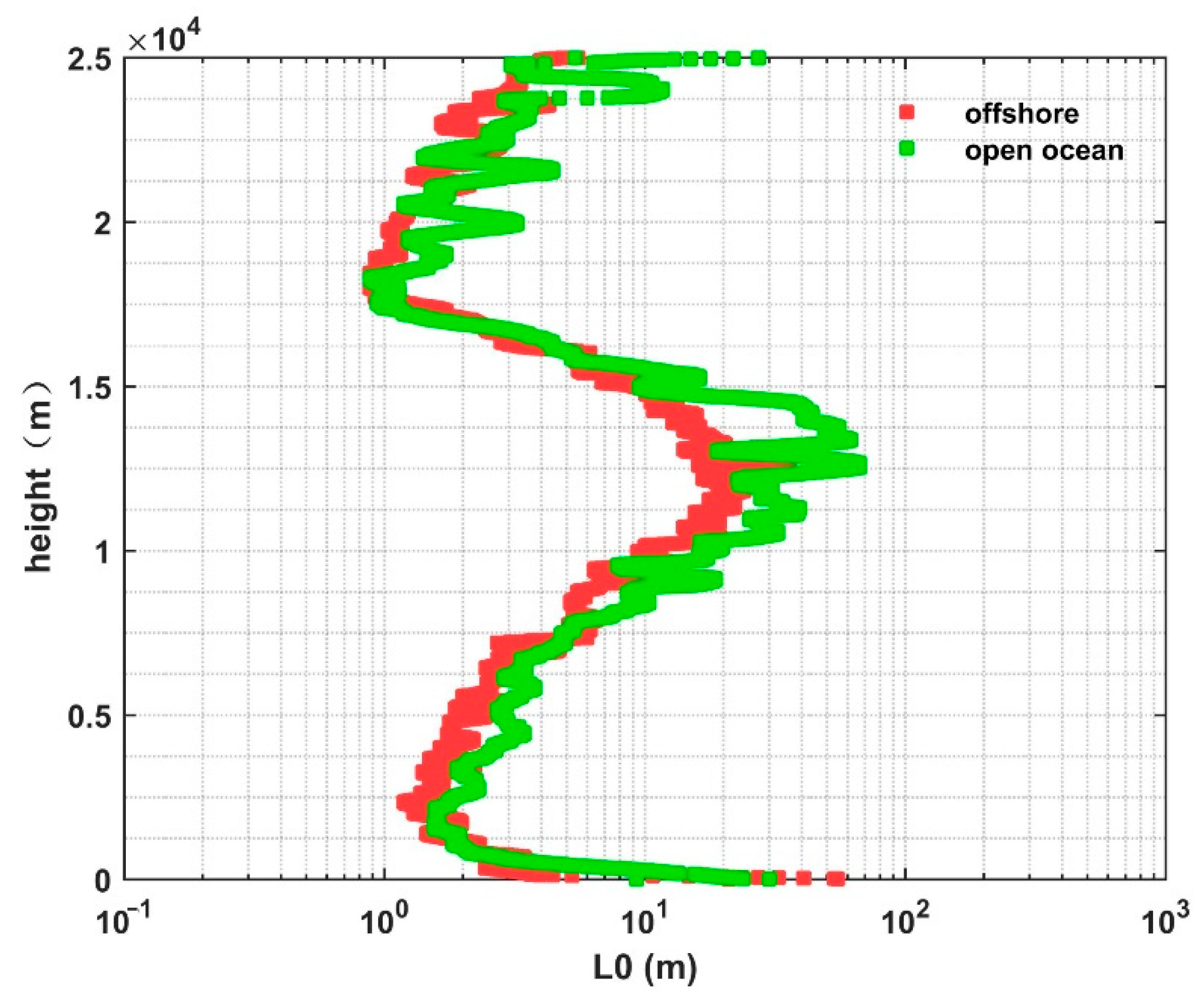
- Over the offshore and open ocean areas, the variance trends of the profiles are similar near the same height, and the outer scale has the biggest influence weight among influence factors. It is reasonable to use the HMNSP99 model to estimate profiles, although there is still room for improvement. Furthermore, the value of the outer scale of the offshore area is smaller than that of the open ocean overall, which may be caused by the difference in the location and the release time of the balloons.
- (3)
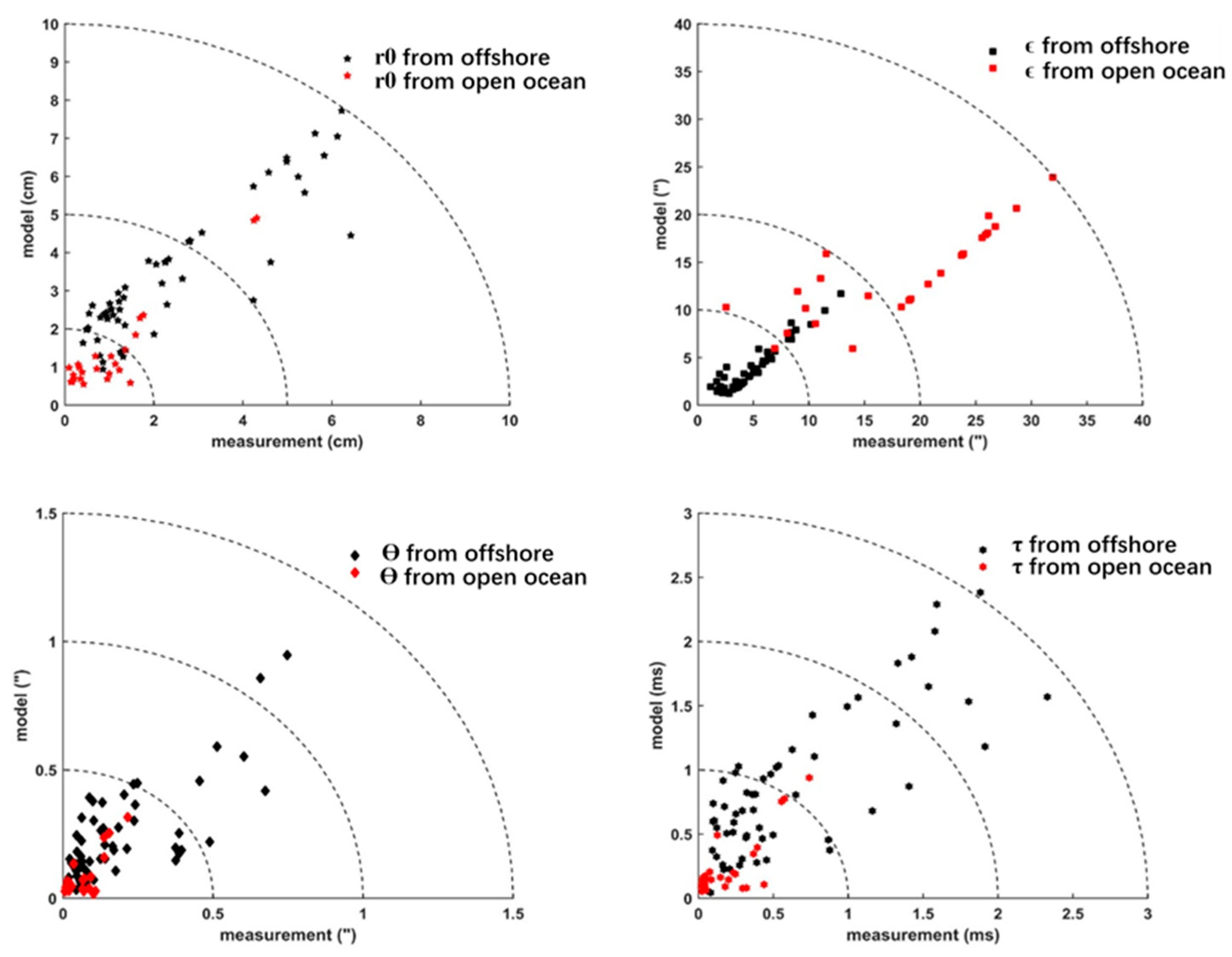
- The mean from the radiosonde measurement at the open ocean area is smaller than offshore, which agrees with the finding that the optical turbulence of the open ocean from the ground up to 30 km is stronger than offshore. Otherwise, the characteristics of the coherence time present that the turbulence strength develops faster over the open ocean. The establishment of astronomical observation sites on the ocean has certain limitations. The results we have achieved provide potential supports for the application of adaptive optics systems and astronomical observation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, L.; Phillips, R. Laser Beam Propagation through Random Media; SPIE Optical Engineering Press: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, L.H. Modeling and measurement of atmospheric optical turbulence over land. Opt. Eng. 1999, 38, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarski, V.I.; Silverman, R.A.; Chako, N. Wave Propagation in a Turbulent Medium. Phys. Today 1961, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azouit, M.; Vernin, J. Optical Turbulence Profiling with Balloons Relevant to Astronomy and Atmospheric Physics. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2005, 117, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-L.; Huang, J.; Wu, L.; Zeng, Q.-C. Structures and characteristics of the windy atmospheric boundary layer in the South China Sea region during cold surges. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Qin, F.; Xu, M.; Liu, Q.; Han, Y.; Xu, Z. Temporal and spatial variation of refractive index structure coefficient over South China sea. Results Eng. 2021, 9, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R. Subseasonal variability during the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 34, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abahamid, A.; Jabiri, A.; Vernin, J.; Benkhaldoun, Z.; Azouit, M.; Agabi, A. Optical turbulence modeling in the boundary layer and free atmosphere using instrumented meteorological balloons. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 416, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, C.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Qiao, C.; Rao, R.; Mei, H. Use of weather research and forecasting model outputs to obtain near-surface refractive index structure constant over the ocean. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 13303–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolbasova, L.A.; Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Kopylov, E.A.; Selin, A.A.; Lukin, V.P.; Kovadlo, P.G. Daytime optical turbulence and wind speed distributions at the Baikal Astrophysical Observatory. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 482, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Wen, Z. Variations of latent heat flux during tropical cyclones over the South China Sea. Meteorol. Appl. 2014, 21, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, N.; Hon, K.K.; Chan, P.W.; Wang, S.; Chan, J.C.L.; Lee, T.C.; Toumi, R. Aircraft Observations of Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer Turbulence over the South China Sea. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 76, 3773–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, V.P. Outer scale of turbulence and its influence on fluctuations of optical waves. Phys.-Uspekhi 2021, 64, 280–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, C.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, W. Performance analysis of weather research and forecasting model for simulating near-surface optical turbulence over land. Optik 2019, 188, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wu, X.; Luo, T.; Wu, S.; Qing, C. Adaptive niche-genetic algorithm based on backpropagation neural network for atmospheric turbulence forecasting. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 3699–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, D.L.; Mevers, G.E.; Keister, M.P. Measurements of Laser-Beam Scintillation in the Atmosphere. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1967, 57, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beland, R.R. Propagation through atmospheric optical turbulence. In The Infrared and Electro-Optical Systems Handbook; Infrared Information Analysis Center: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1993; pp. 157–232. [Google Scholar]
- Bufton, J. Correlation of Microthermal Turbulence Data with Meteorological Soundings in the Troposphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Qin, F.; Liu, Q.; Xu, M.; Cheng, X. Turbulent Structure Function Analysis Using Wireless Micro-Thermometer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 123929–123937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.S.; Ochs, G.R.; Clifford, S.F. Measurements of Atmospheric Turbulence Relevant to Optical Propagation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1970, 60, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, X.; Luo, T.; Qing, C.; Yang, Q.; Jin, X.; Liu, N.; Wu, S.; Su, C. New Cn2 statistical model based on first radiosonde turbulence observation over Lhasa. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2020, 37, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, C.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Luo, T.; Su, C.; Zhu, W. Mesoscale optical turbulence simulations above Tibetan Plateau: First attempt. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 4571–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, Q.; Nana, L.; Zhang, K.; Qing, C.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Luo, T. Analysis of wind-speed profiles and optical turbulence above Gaomeigu and the Tibetan Plateau using ERA5 data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 501, 4692–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, F.H.; Debenedictis, F.H. Forecasting optical turbulence from mesoscale numerical weather prediction models. In Proceedings of the DoD High Performance Modernization Program Users Group Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 10–14 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Roddier, F.; Gilli, J.M.; Lund, G. On the origin of speckle boiling and its effects in stellar speckle interferometry. J. Opt. 2000, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, D.L. Optical Resolution Through a Randomly Inhomogeneous Medium for Very Long and Very Short Exposures. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1966, 56, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, A.; Kovadlo, P.; Lukin, V.; Nosov, V.; Kiselev, A.; Kolobov, D.; Kopylov, E.; Shikhovtsev, M.; Avdeev, F. Statistics of the Optical Turbulence from the Micrometeorological Measurements at the Baykal Astrophysical Observatory Site. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauer, B.; Wang, Q.; Alvarenga, O.; Yamaguchi, R.; Kalogiros, J.; Alappattu, D.P.; Cauble, G. Observations of optical turbulence in the marine atmospheric surface layer during CASPER-West. In Proceedings of the Laser Communication and Propagation through the Atmosphere and Oceans VII, San Diego, CA, USA, 1 September 2018; p. 107700H. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, C.; Qian, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Luo, T.; Wu, X.; Qing, C. Estimating and measurement of atmospheric optical turbulence accordingto balloon-borne radiosonde for three sites in China. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2020, 37, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciadri, E.; Lascaux, F.; Fini, L. MOSE: Operational forecast of the optical turbulence and atmospheric parameters at European Southern Observatory ground-based sites—I. Overview and vertical stratification of atmospheric parameters at 0–20 km. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 1968–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, P.N.; Mauter, H.A.; Smartt, R. Technical Report. Day-time seeing statistics at Sacramento Peak Observatory. Astron. Astrophys. 1987, 26, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Irbah, A.; Laclare, F.; Merlin, G.; Borgnino, J. Solar diameter measurements with Calern Observatory astrolabe and atmospheric turbulence effects. Sol. Phys. 1994, 149, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristidi, E.; Agabi, A.; Fossat, E.; Azouit, M.; Martin, F.; Sadibekova, T.; Travouillon, T.; Vernin, J.; Ziad, A.J.A. Site testing in summer at Dome C, Antarctica. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 444, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, R.D.; Vernin, J.; Azouit, M.; Manigault, J.F.; Clevelin, C. Measurement of optical seeing on the high antarctic plateau. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1999, 134, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Shao, S.; Weng, N.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Characteristics over the Ocean Relevant to Astronomy and Atmospheric Physics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210548
Xu M, Shao S, Weng N, Zhou L, Liu Q, Zhao Y. Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Characteristics over the Ocean Relevant to Astronomy and Atmospheric Physics. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210548
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Manman, Shiyong Shao, Ningquan Weng, Liangping Zhou, Qing Liu, and Yuefeng Zhao. 2021. "Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Characteristics over the Ocean Relevant to Astronomy and Atmospheric Physics" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210548
APA StyleXu, M., Shao, S., Weng, N., Zhou, L., Liu, Q., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Characteristics over the Ocean Relevant to Astronomy and Atmospheric Physics. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210548





