Identifying Engineering Undergraduates’ Learning Style Profiles Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Student Learning Profiles
2.2. Student Learning Styles
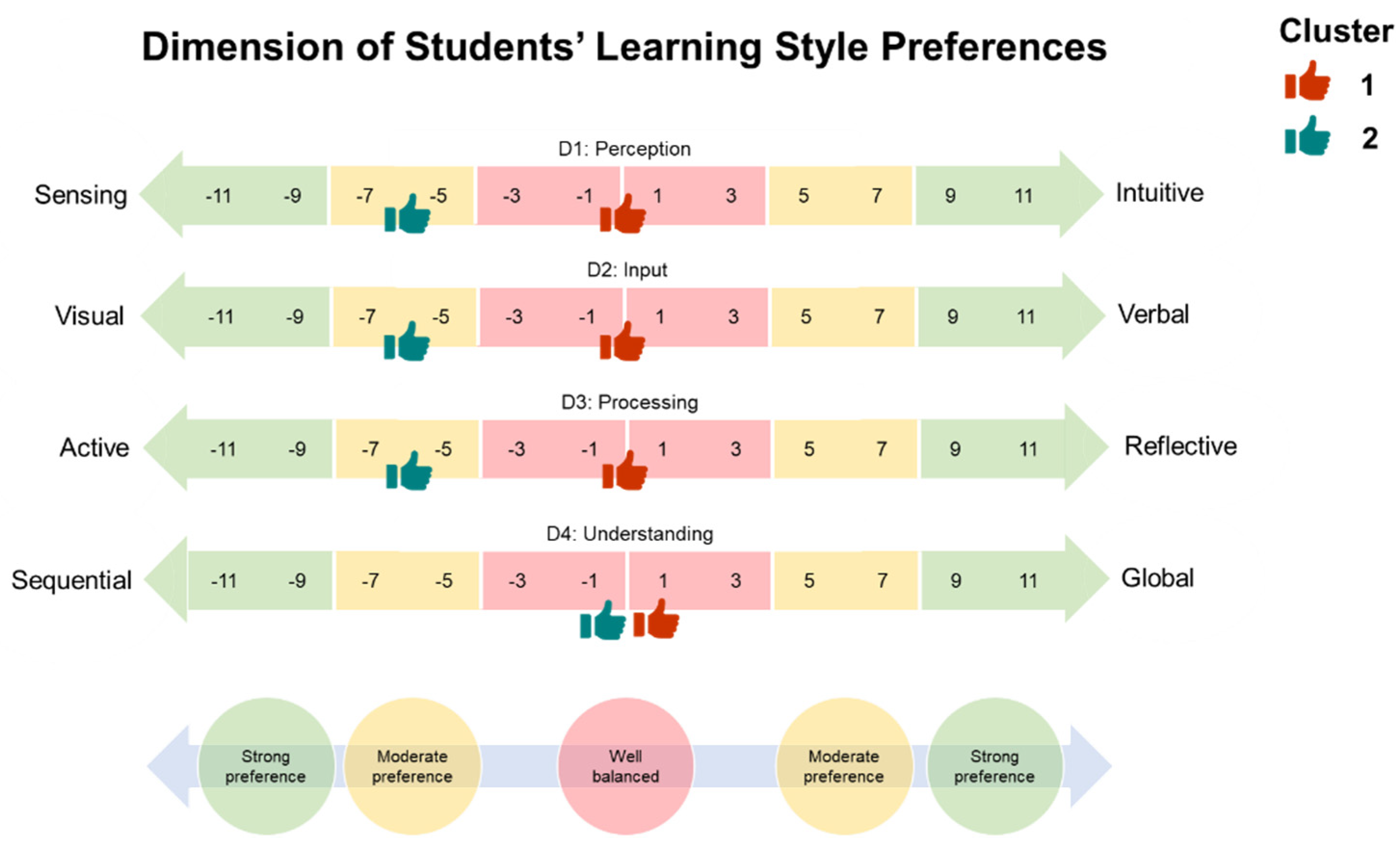
- D1—Perception: sensing (concrete thinker, practical, oriented towards facts and procedures) or intuitive (abstract thinker, innovative, oriented towards theories and underlying meanings).
- D2—Input: visual (learners prefer visual representations of material presented, such as pictures, diagrams, and flow charts) or verbal (learners prefer written and spoken explanations).
- D3—Processing: active (learners prefer to learn by trying things out, enjoy working in groups) or reflective (learners prefer to learn by thinking things through, such as working alone or with a single familiar partner).
- D4—Understanding: sequential (learners prefer to learn using a linear thinking process, learn in small incremental steps) or global (learners prefer to learn using a holistic thinking process, learn in giant leaps).
2.3. Predictive Analysis with Decision Trees
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Scales and Attributes
3.2. Data
4. Results
4.1. Cluster Analysis
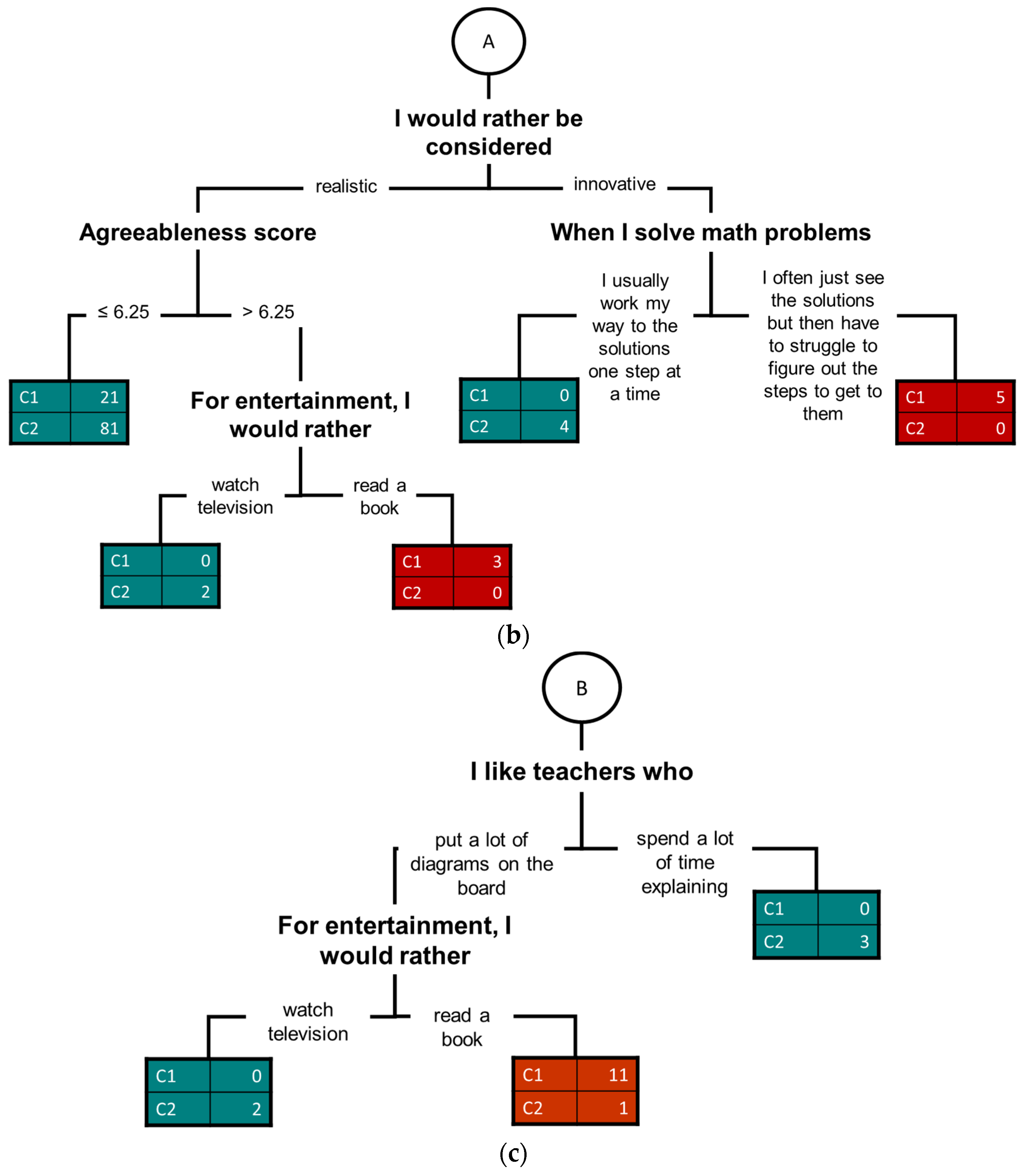
4.2. Predictive Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mok, K.H.; Xiong, W.; Ke, G.; Cheung, J.O.W. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on international higher education and student mobility: Student perspectives from mainland China and Hong Kong. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2021, 105, 101718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawk, T.F.; Shah, A.J. Using learning style instruments to enhance student learning. Decis. Sci. J. Innov. Educ. 2007, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baticulon, R.E.; Sy, J.J.; Alberto, N.R.I.; Baron, M.B.C.; Mabulay, R.E.C.; Rizada, L.G.T.; Tiu, C.J.S.; Clarion, C.A.; Reyes, J.C.B. Barriers to Online Learning in the Time of COVID-19: A National Survey of Medical Students in the Philippines. Med. Sci. Educ. 2021, 31, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willingham, D.T.; Hughes, E.M.; Dobolyi, D.G. The Scientific Status of Learning Styles Theories. Teach. Psychol. 2015, 42, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, R.; Silverman, L. Learning and teaching styles in engineering education. Eng. Educ. 1988, 78, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ora, A.; Sahatcija, R.; Ferhataj, A. Learning Styles and the Hybrid Learning: An Empirical Study about the Impact of Learning Styles on the Perception of the Hybrid Learning. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2018, 9, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar-Concha, C.; Ramírez-Correa, P. Predicting the Intention to Donate Blood among Blood Donors Using a Decision Tree Algorithm. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagci, M. Development of an Artificial Intelligence Based Computerized Adaptive Scale and Applicability Test. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Applied Mathematics in Engineering, Antalya, Turkey, 18–20 April 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 292–303. [Google Scholar]
- Mwamikazi, E.; Fournier-Viger, P.; Moghrabi, C.; Barhoumi, A.; Baudouin, R. An adaptive questionnaire for automatic identification of learning styles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3–6 June 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 399–409. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Y.P.; Li, B.; Chen, N.; Li, X.F.; Hu, J.; Zhu, F. The discrimination of learning styles by Bayes-based statistics: An extended study on ILS system. Control Intell. Syst. 2015, 43, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, C.A.; Brighton, C.; Hertberg, H.; Callahan, C.M.; Moon, T.R.; Brimijoin, K.; Conover, L.A.; Reynolds, T. Differentiating instruction in response to student readiness, interest, and learning profile in academically diverse classrooms: A review of literature. J. Educ. Gift. 2003, 27, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomlinson, C.A. How TO Differentiate Instruction in Mixed-Ability Classrooms; ASCD: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2001; ISBN 0871209179. [Google Scholar]
- Sapounidis, T.; Stamovlasis, D.; Demetriadis, S. Latent class modeling of children’s preference profiles on tangible and graphical robot programming. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2018, 62, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikainen, H.; Salmela-Aro, K.; Parpala, A.; Katajavuori, N. Learning profiles and their relation to study-related burnout and academic achievement among university students. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2020, 78, 101781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, O.H.T.; Huang, A.Y.Q.; Huang, J.C.H.; Lin, A.J.Q.; Ogata, H.; Yang, S.J.H. Applying learning analytics for the early prediction of Students’ academic performance in blended learning. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 220–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.M. Extending the expectation-confirmation model with quality and flow to explore nurses’ continued blended e-learning intention. Inf. Technol. People 2014, 27, 230–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Do personality traits make a difference in teaching styles among Chinese high school teachers? Pers. Individ. Dif. 2007, 43, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Armstrong, S.J. The relationship between Kolb’s experiential learning styles and Big Five personality traits in international managers. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2015, 86, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foroozandehfar, L.; Khalili, G.F. On the relationship between Iranian EFL learners’ reading fluency, their personality types and learning styles. Cogent Arts Humanit. 2019, 6, 1681347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffield, F.; Moseley, D.; Hall, E.; Ecclestone, K. Should we be using Learning Styles? Learn. Ski. Res. Cent. 2004, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, R.M.; Spurlin, J. Applications, reliability and validity of the Index of Learning Styles. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2005, 21, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, R.M.; Brent, R. Understanding student differences. J. Eng. Educ. 2005, 94, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Correa, P.E.; Rondan-Cataluña, F.J.; Arenas-Gaitán, J.; Alfaro-Perez, J.L. Moderating effect of learning styles on a learning management system’s success. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.M.; Smith, T.; Kalmar, E.L.; Burgoon, J.M. What type of learner are your students? Preferred learning styles of undergraduate gross anatomy students according to the index of learning styles questionnaire. Anat. Sci. Educ. 2018, 11, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of Decision Trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzberg, S.L. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning by J. Ross Quinlan. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc., 1993. Mach. Learn. 1994, 16, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Kumar, V.; Ross, Q.J.; Ghosh, J.; Yang, Q.; Motoda, H.; McLachlan, G.J.; Ng, A.; Liu, B.; Yu, P.S.; et al. Top 10 algorithms in data mining. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2008, 14, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, E.; Villar, P.; Gómez-Fraguela, J.A.; López-Romero, L. Measuring personality traits with ultra-short scales: A study of the Ten Item Personality Inventory (TIPI) in a Spanish sample. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2012, 53, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, R.K. Predicting students’ learning style using learning analytics: A case study of business management students from India. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2018, 37, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troussas, C.; Krouska, A.; Sgouropoulou, C.; Voyiatzis, I. Ensemble learning using fuzzy weights to improve learning style identification for adapted instructional routines. Entropy 2020, 22, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.M.C.; do Freixo Pereira, J.M.; Dias, R.M.T.S.; Noronha, A.B. Learning Styles in Business Management students: An empirical study in Portuguese Higher Education. Adm. Ensino Pesqui. 2020, 21, 348–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasina, I.; Bayram, G.; Labib, W.; Abdelhadi, A.; Nurunnabi, M. Clustering students into groups according to their learning style. MethodsX 2019, 6, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.; Rousseeuw, P.J. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hobeken, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 344, ISBN 0470317485. [Google Scholar]
- Tulsi, P.K.; Poonia, M.P.; Priya, A. Learning Styles of Engineering Students. J. Eng. Educ. Transform. Citeseer 2016, 30, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, G. De Learning styles, culture and inclusive instruction in the multicultural classroom: A business and management perspective. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2001, 38, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxeda, R.J.; Moore, D.A. Using learning-styles data to design a microbiology course. J. Coll. Sci. Teach. 1999, 29, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Palou, E. Learning Styles of Mexican Food Science and Engineering Students. J. Food Sci. Educ. 2006, 5, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seery, N.; Gaughran, W.F.; Waldmann, T. Multi-Modal Learning in Engineering Education. In Proceedings of the 2003 ASEE Conference and Exposition, Nashville, TN, USA, 22–25 June 2003; American Society for Engineering Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Kuri, N.P.; Truzzi, O.M.S. Learning styles of freshmen engineering students. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Engineering Education, Manchester, UK, 18–21 August 2002; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
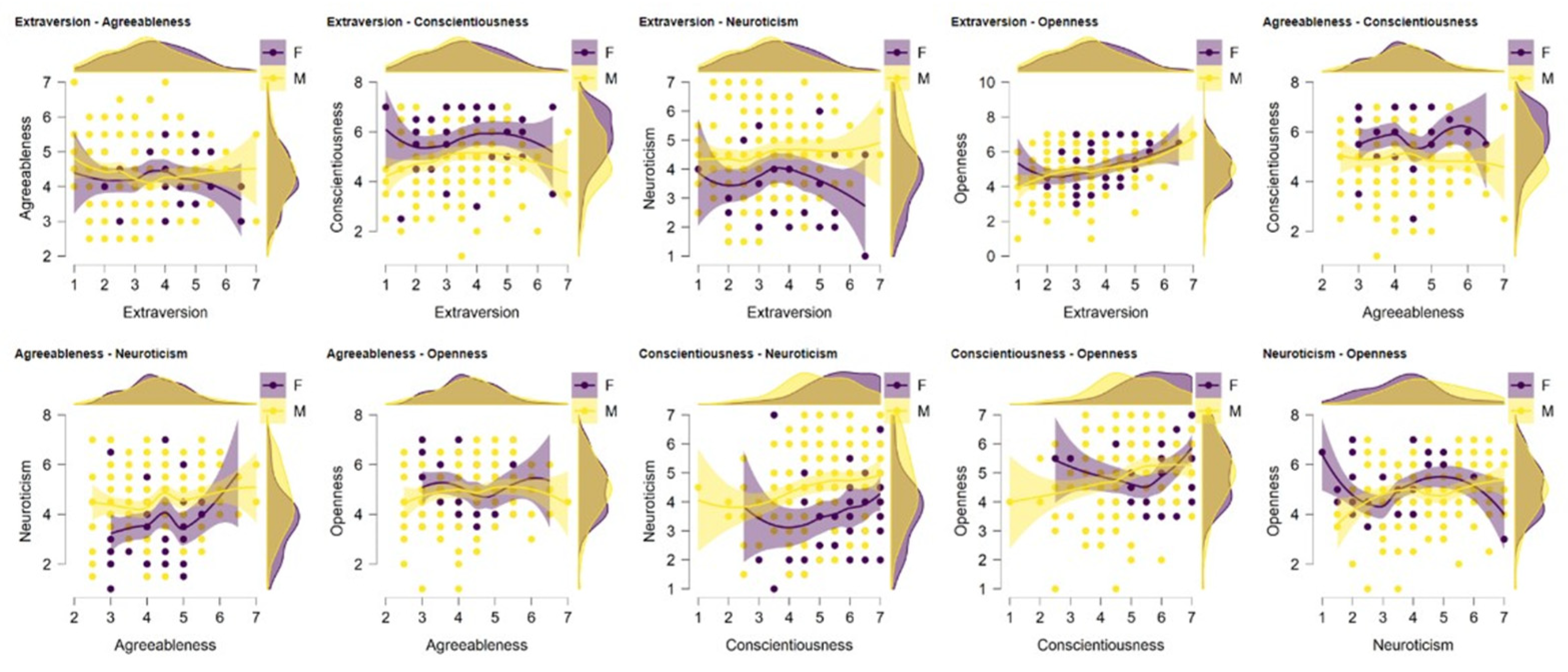


| Attribute | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | 198 | 74 | |
| Female | 70 | 26 | |
| Learning style that the student was skilled at | |||
| Reading | 11 | 4 | |
| Writing | 43 | 16 | |
| Listening | 26 | 10 | |
| Doing | 188 | 70 | |
| Total | 268 | 100 | |
| Age | Mean 20.9 ± 2.6 | ||
| Range 18–46 years |
| Cluster 1 (56.4%) | Cluster 2 (43.6%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-Score | Mean | SD | Z-Score | Mean | SD | |
| D1: Perception | 0.138 | −1.694 | 3.093 | −0.471 | −5.167 | 2.804 |
| D2: Input | 0.547 | −0.919 | 3.043 | −0.487 | −4.153 | 2.188 |
| D3: Processing | 0.565 | 0.097 | 3.096 | −0.474 | −3.250 | 2.546 |
| D4: Understanding | 0.550 | 0.145 | 2.876 | −0.431 | −2.597 | 2.360 |
| Accuracy: 72.20% | Cluster 1 (True) | Cluster 2 (True) | Class Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 (pred.) | 89 | 35 | 71.77% |
| Cluster 2 (pred.) | 33 | 87 | 72.50% |
| Class recall | 72.95% | 71.31% |
| Accuracy: 82.93% | Cluster 1 (True) | Cluster 2 (True) | Class Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 (pred.) | 15 | 3 | 83.33% |
| Cluster 2 (pred.) | 4 | 19 | 82.61% |
| Class recall | 78.95% | 86.36% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Correa, P.; Alfaro-Pérez, J.; Gallardo, M. Identifying Engineering Undergraduates’ Learning Style Profiles Using Machine Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210505
Ramírez-Correa P, Alfaro-Pérez J, Gallardo M. Identifying Engineering Undergraduates’ Learning Style Profiles Using Machine Learning Techniques. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210505
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Correa, Patricio, Jorge Alfaro-Pérez, and Mauricio Gallardo. 2021. "Identifying Engineering Undergraduates’ Learning Style Profiles Using Machine Learning Techniques" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210505
APA StyleRamírez-Correa, P., Alfaro-Pérez, J., & Gallardo, M. (2021). Identifying Engineering Undergraduates’ Learning Style Profiles Using Machine Learning Techniques. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210505






