SNR Analysis for Quantitative Comparison of Line Detection Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Streamlined derivation of the SNRs of line detectors including the derivation of correlations among noises after smoothing; derivations of signal and noise strengths of elementary operators; combination of SNRs for line detectors; and application of a penalty function for considering the influence of blurring, smoothing, and line width on line detectors.
- Analytical quantification of the SNRs of line detectors using error propagation and visualization of the quantity of the derived values including signal strengths, noise strengths, and SNRs.
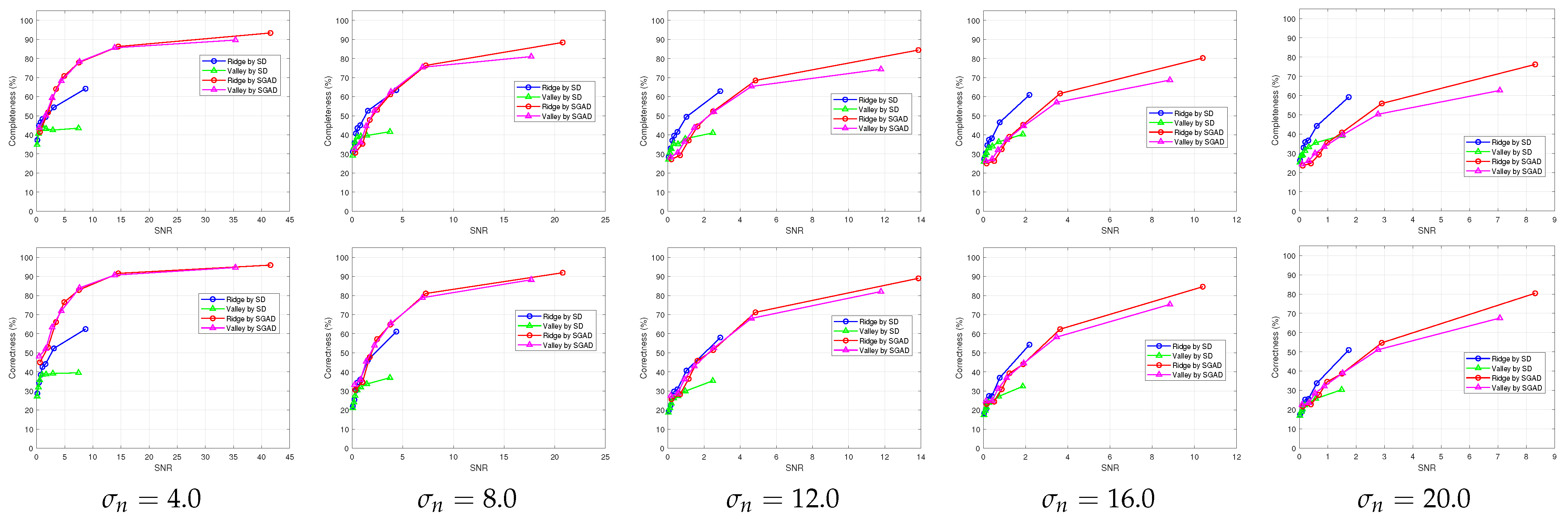
- Verification of the validity of the SNRs derived for the SD- and SGAD-based line detectors by investigating the relationship of the SNRs with completeness and correctness of their line detection results.
2. Related Work
3. Method—SNR of ED and SD for Line Detection
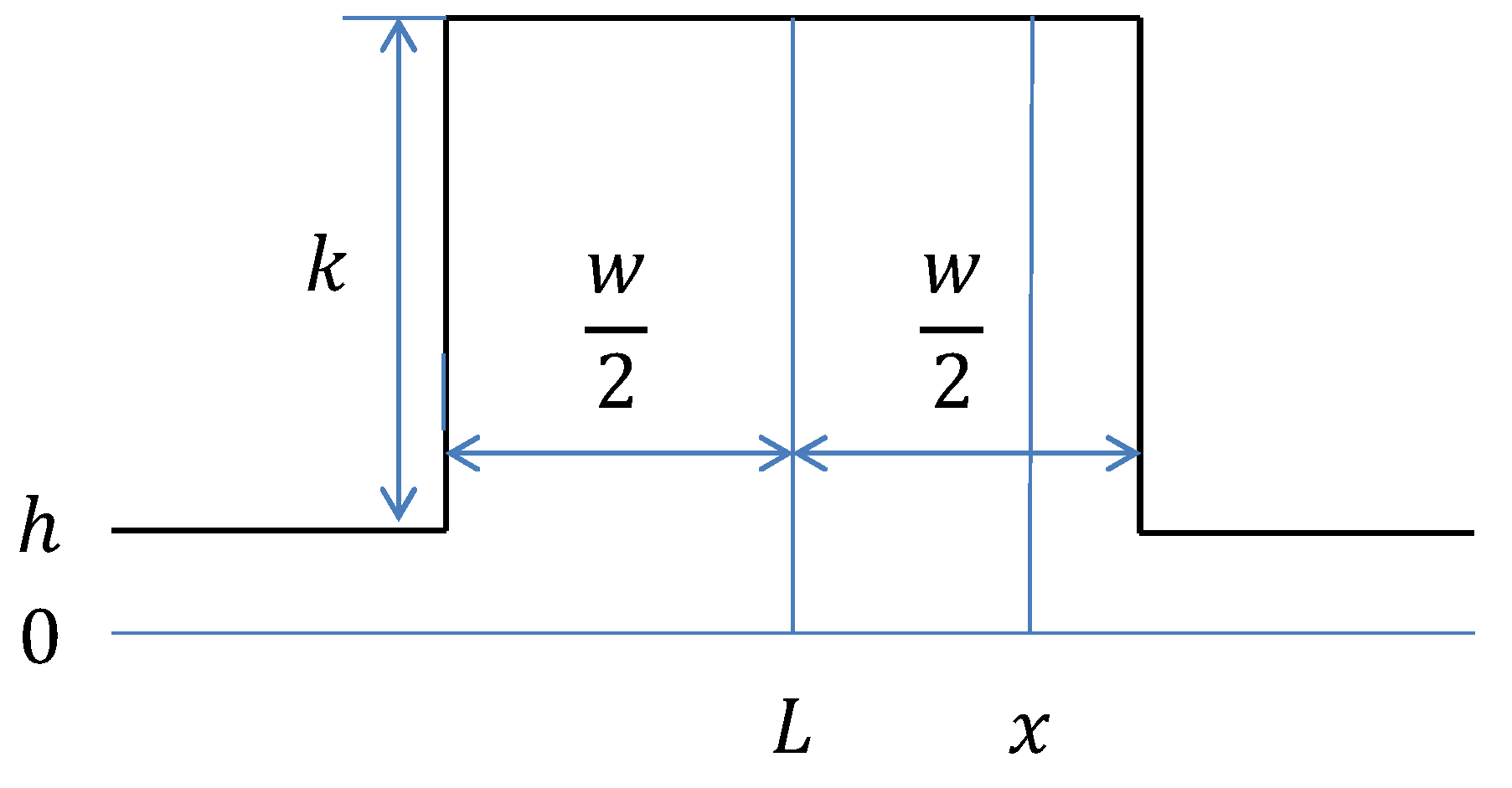
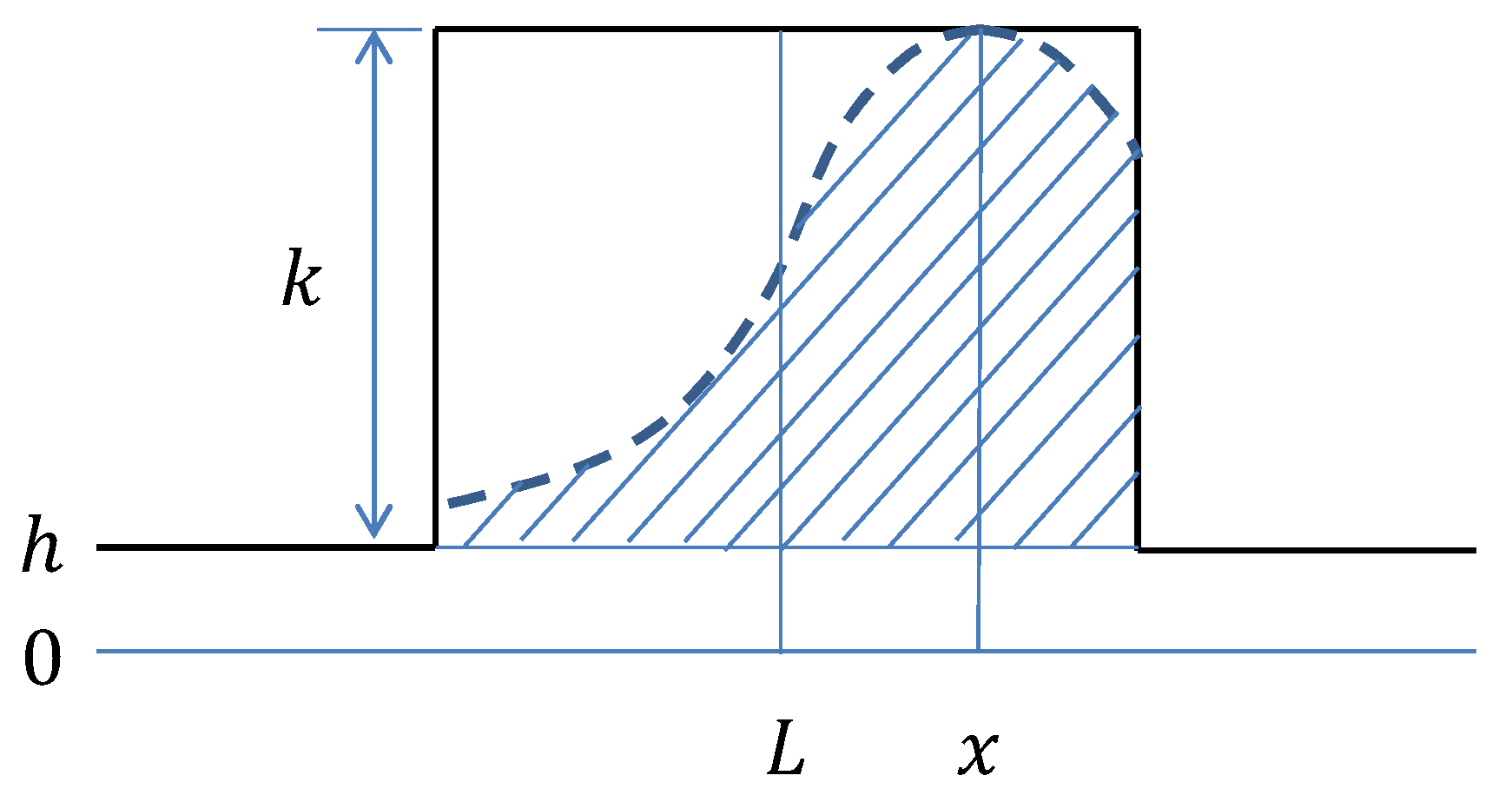
3.1. Line Model and Derivation of Its Derivatives
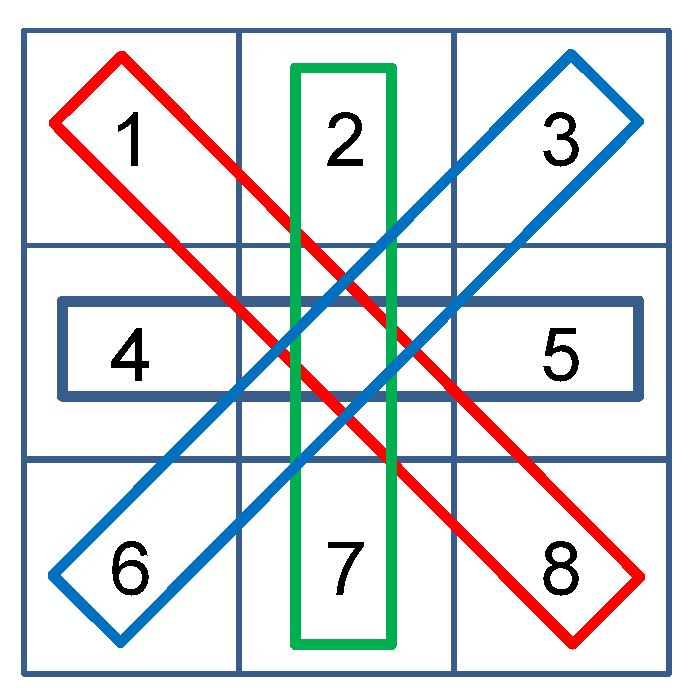
3.2. Measure of Signal Strengths
3.3. Measure of Noise Strengths
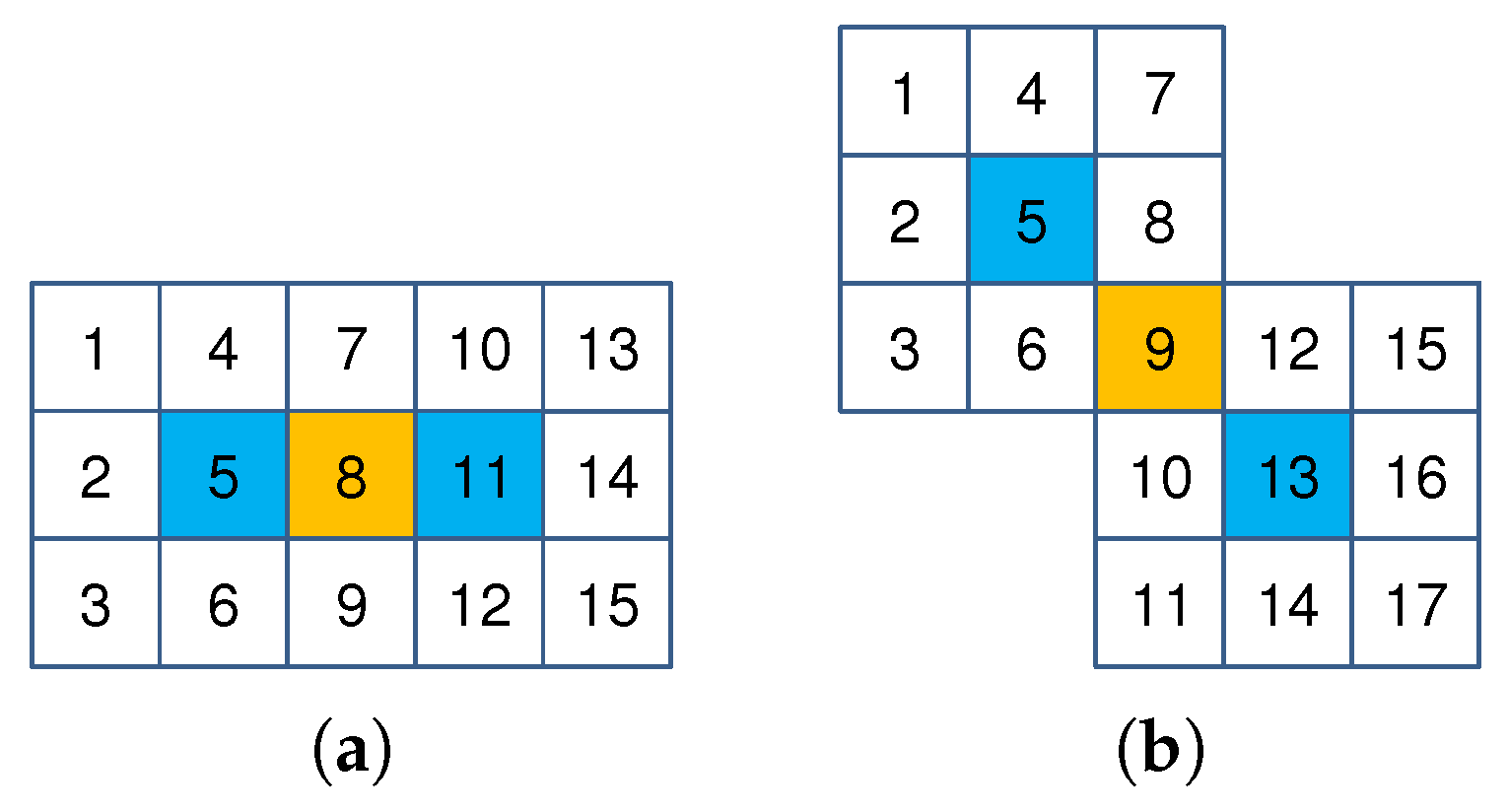
3.3.1. Correlation of Noises in Smoothed Images
3.3.2. Measure of Noise in Derivatives
3.4. Derivation of SNRs
4. Method—SNR of SGAD for Line Detection
4.1. Definition of SGAD
4.2. Dispersion of Gradient Angle Differences
4.3. Derivation of SNRs
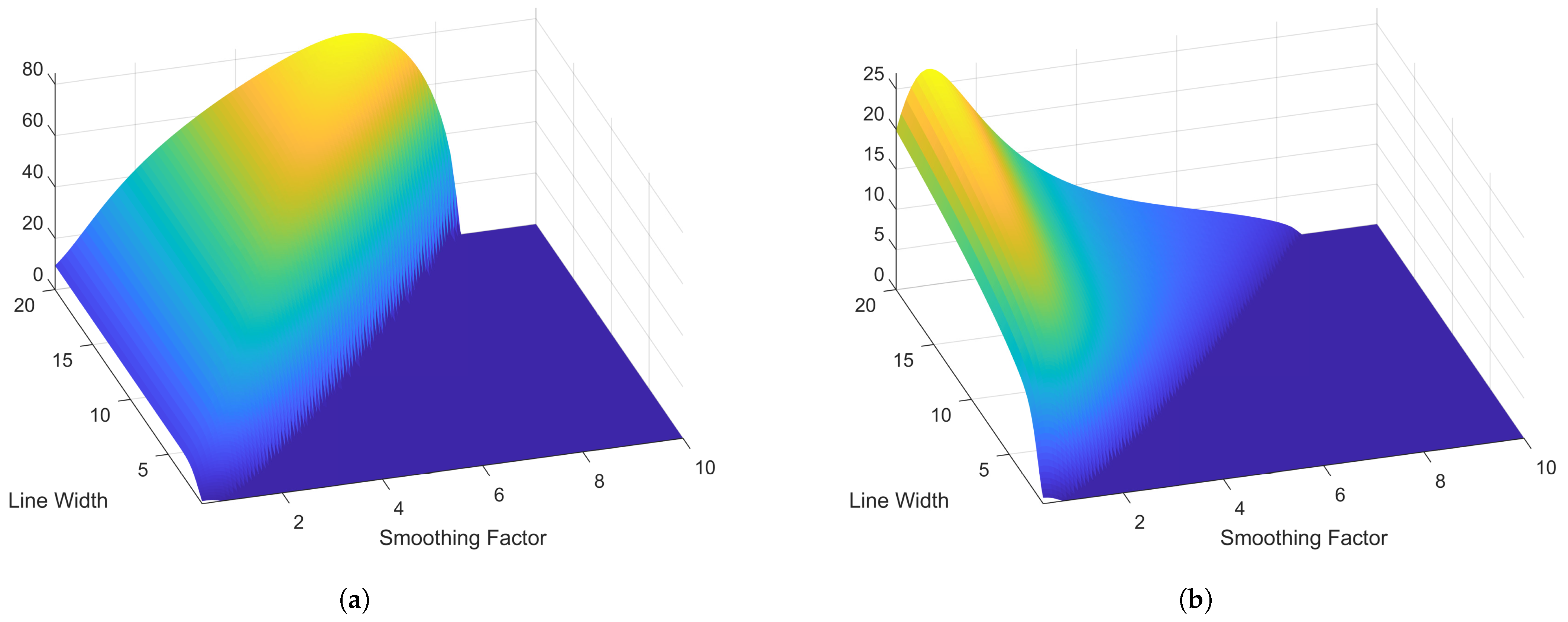
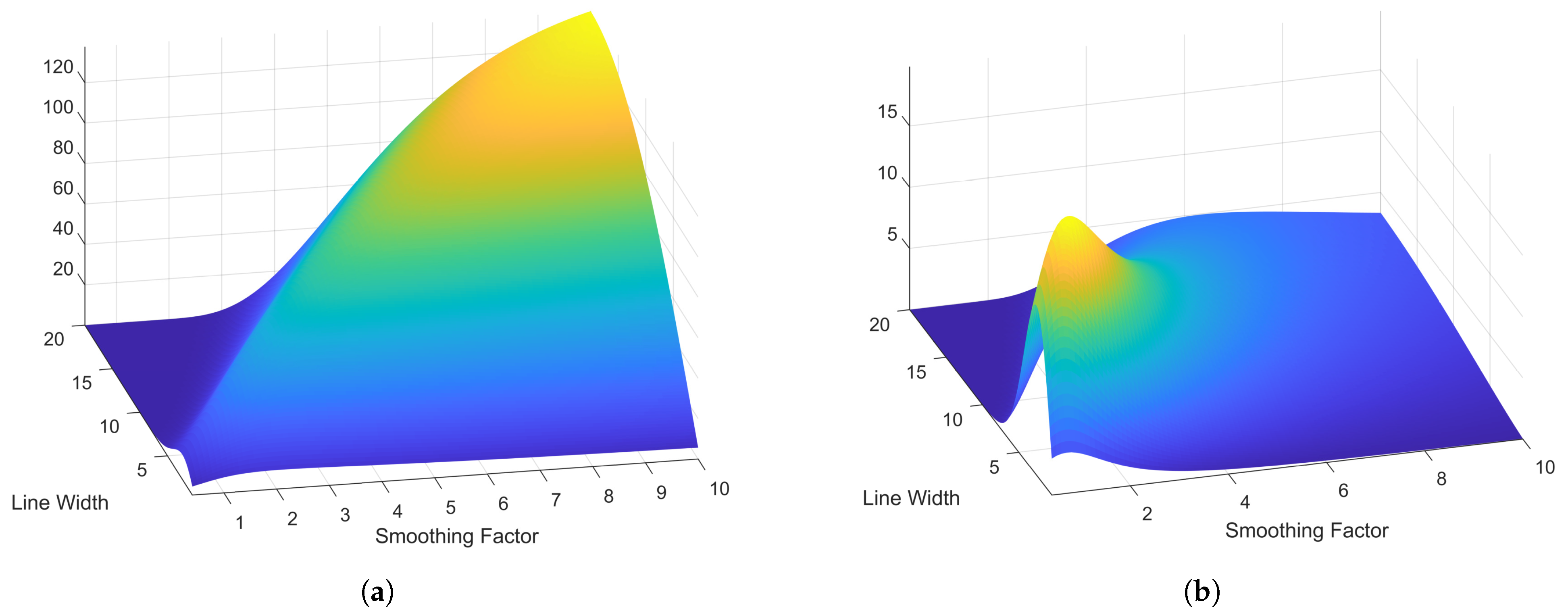
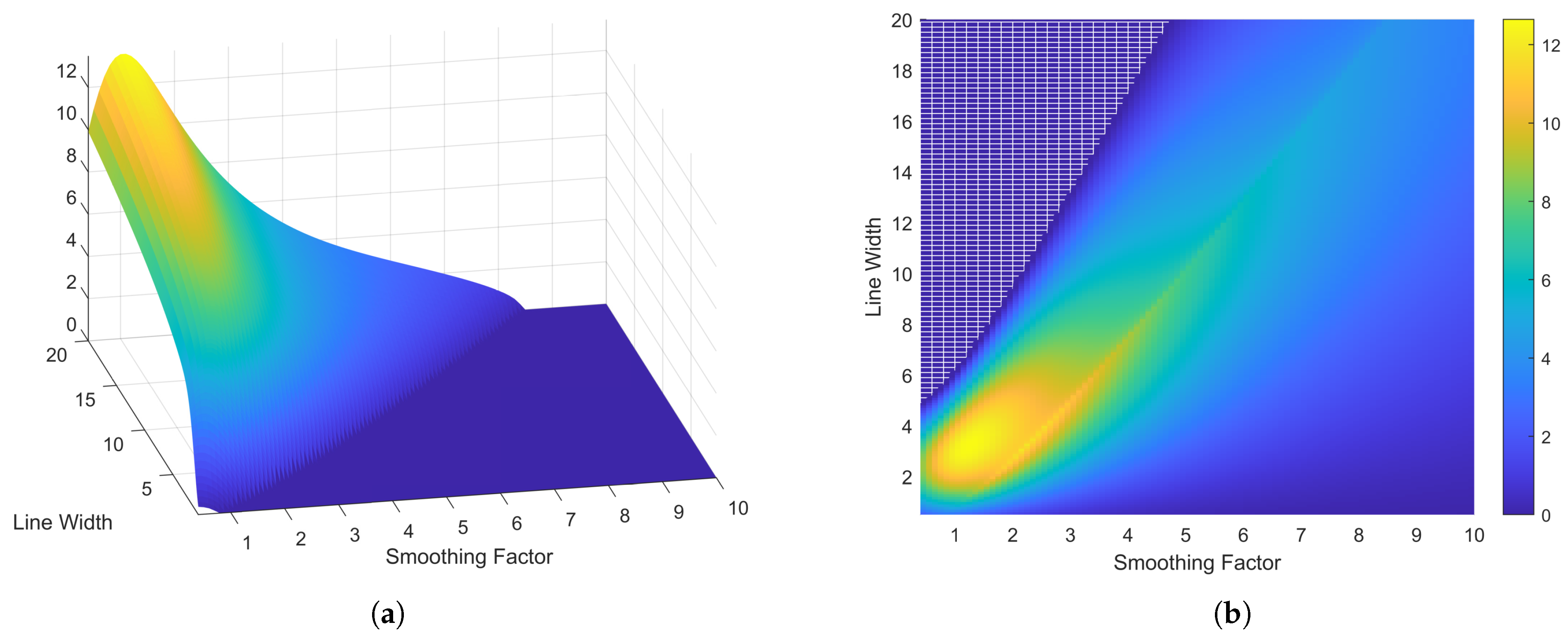
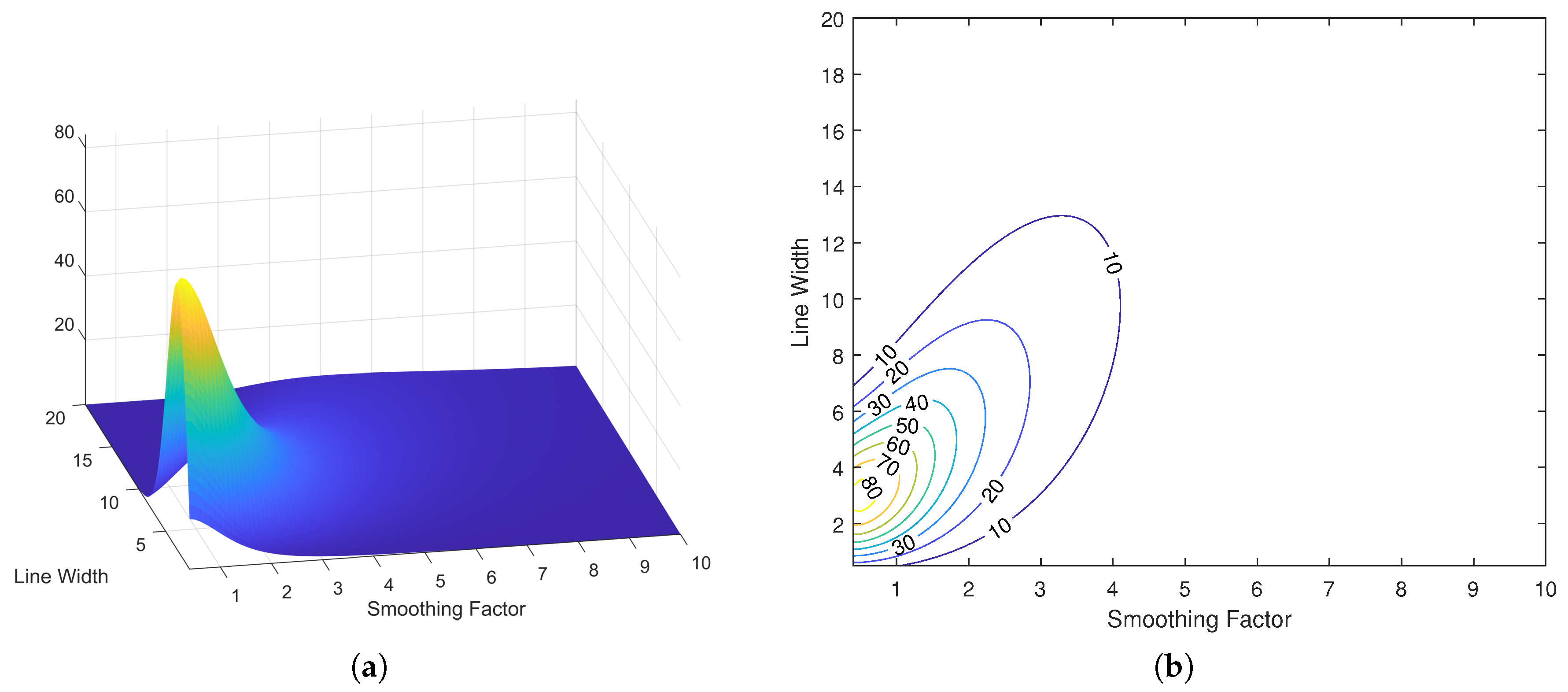
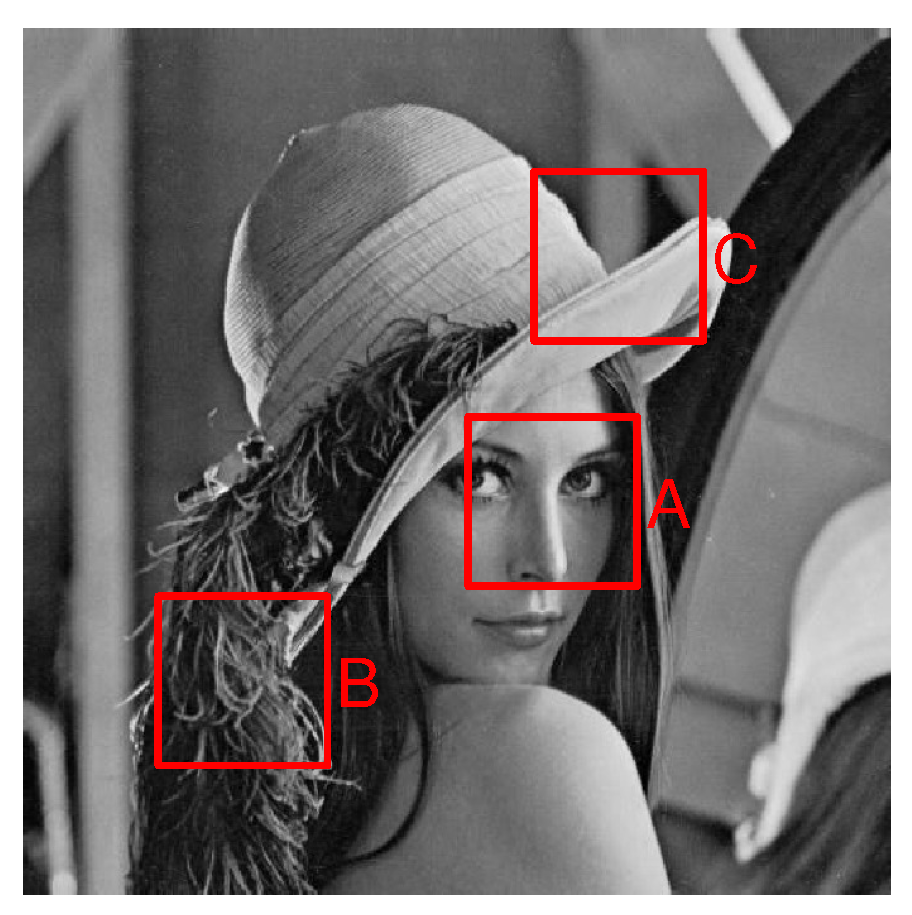
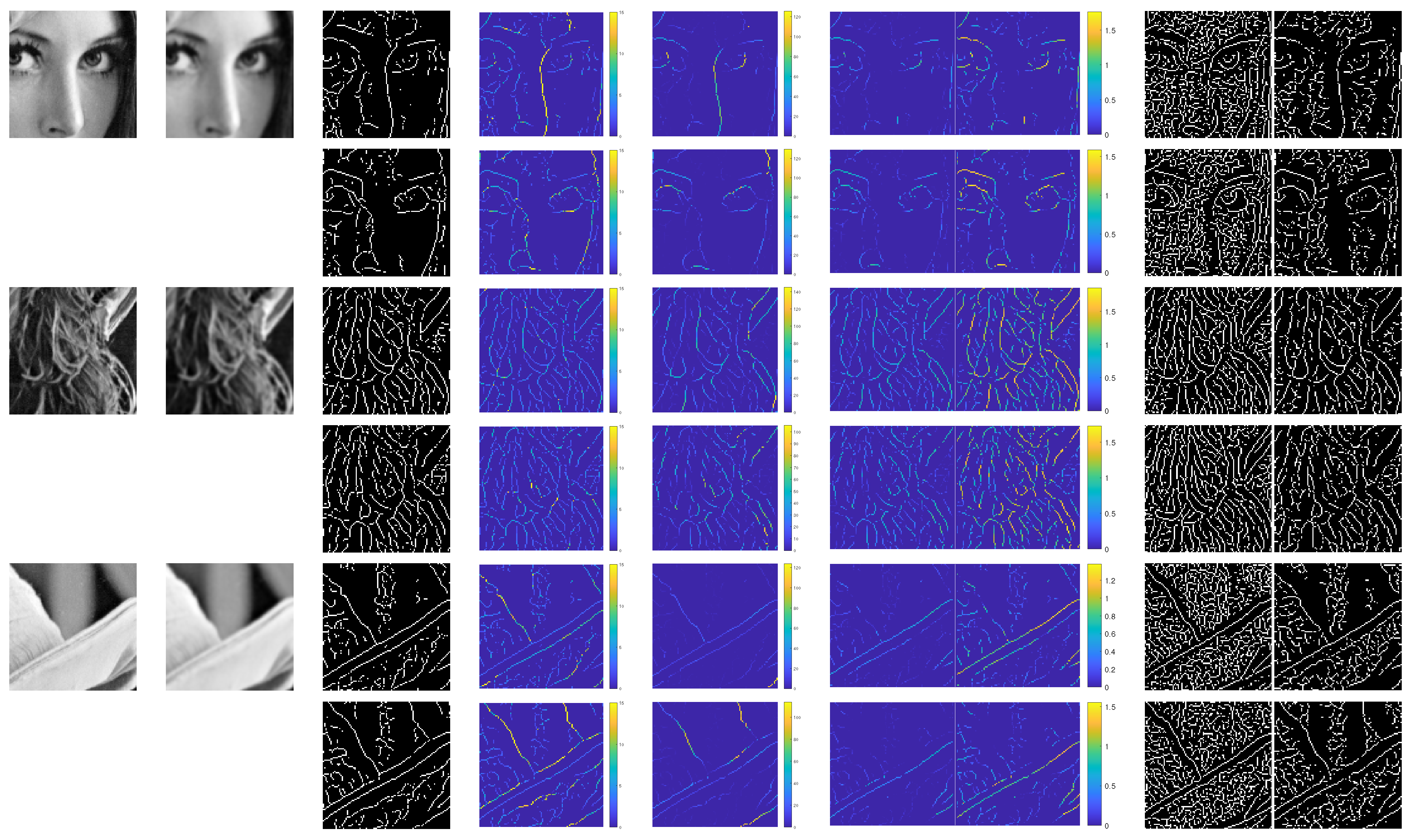
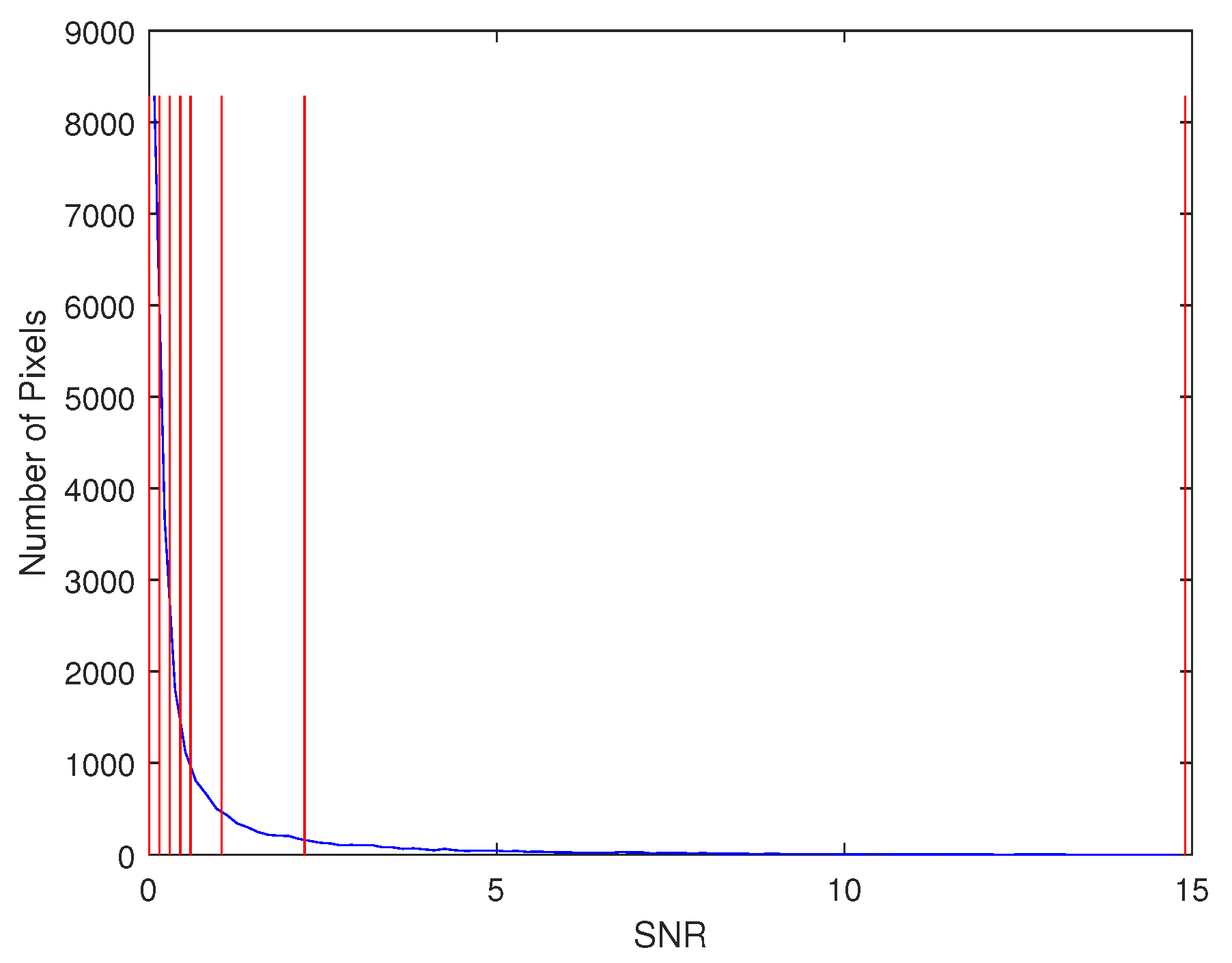
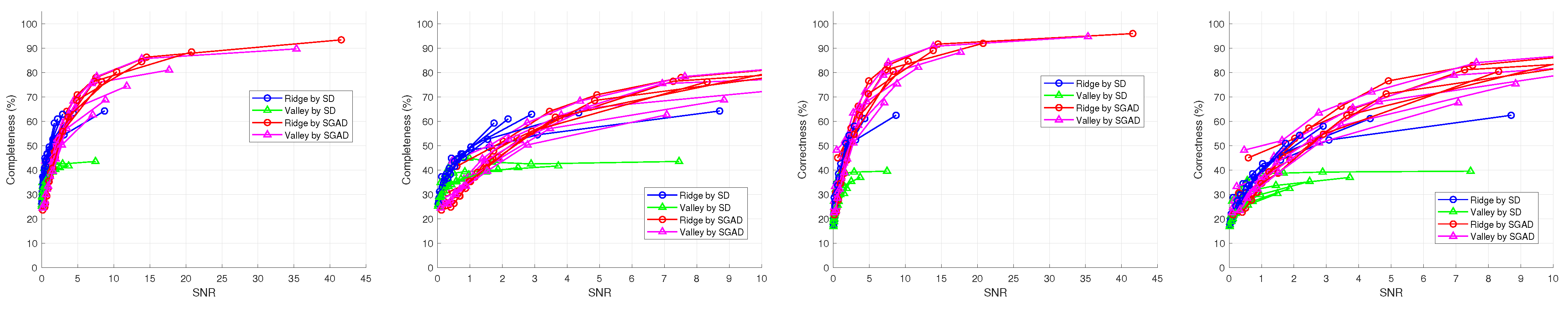
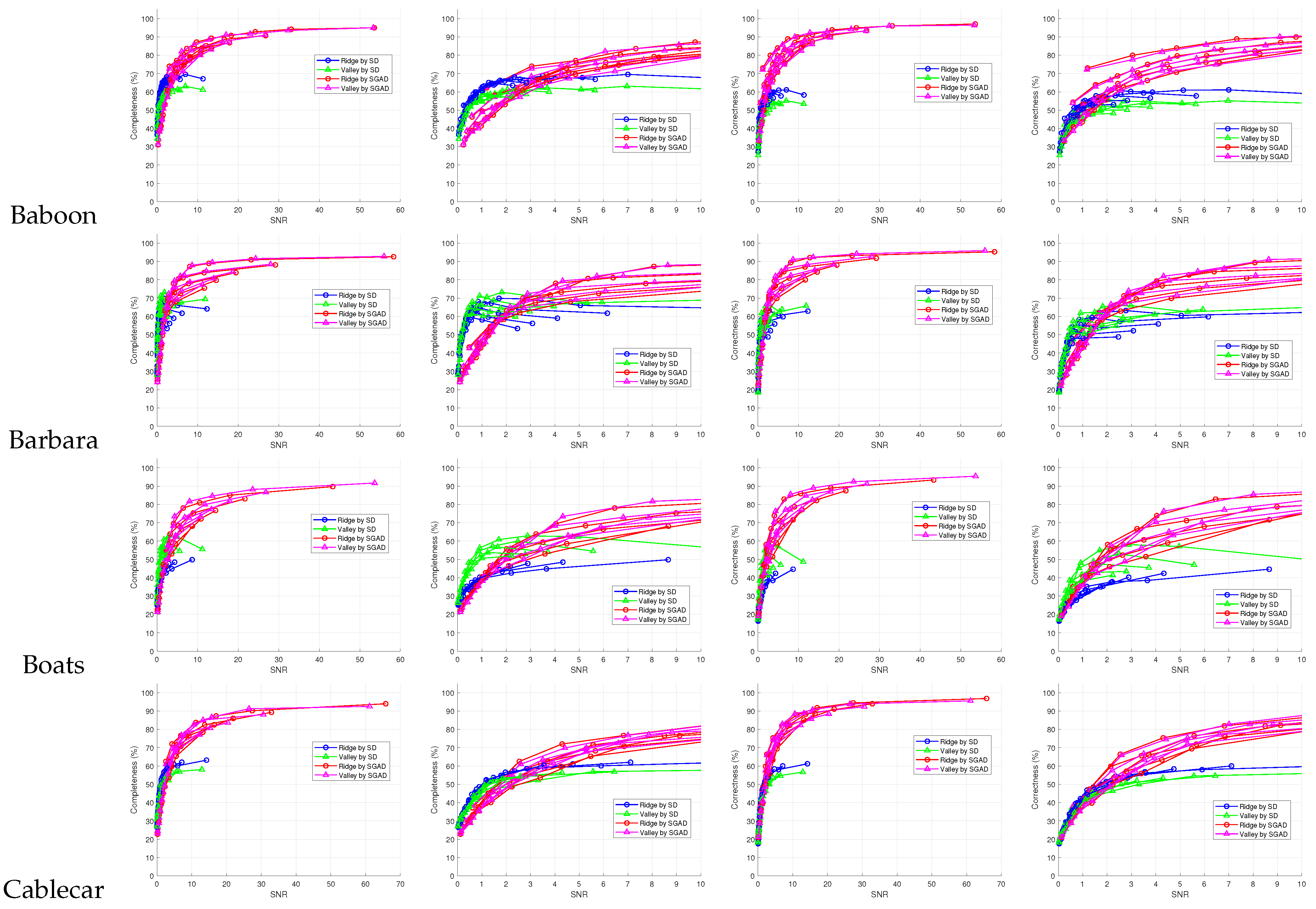
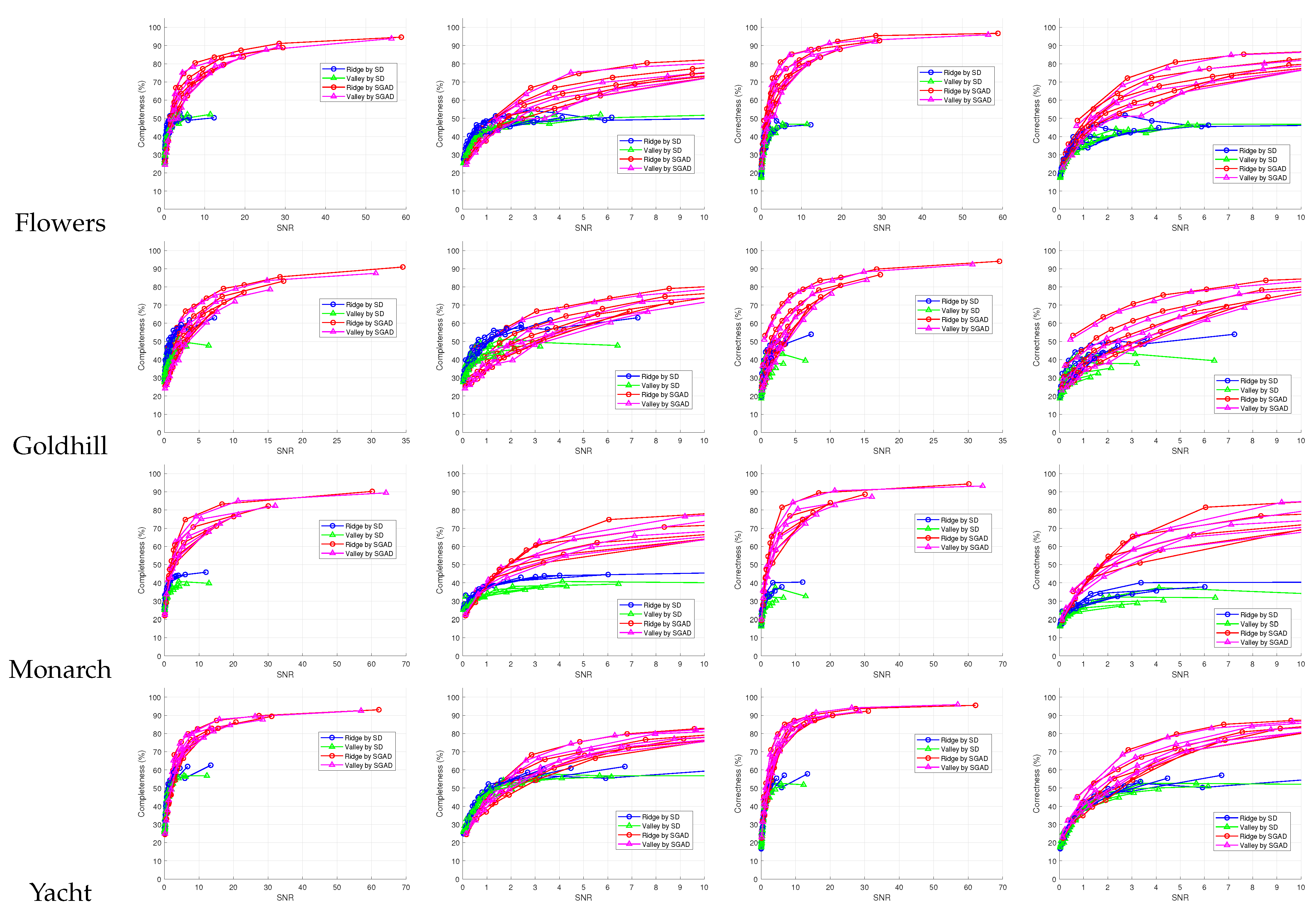
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haralick, R.M. Ridges and valleys on digital images. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1983, 22, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauch, J.M.; Pizer, S.M. Multiresolution analysis of ridges and valleys in grey-scale images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1993, 15, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrat, J.; Lopez, A.; Lloret, D. On ridges and valleys. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Barcelona, Spain, 3–7 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rashe, C. Rapid contour detection for image classification. IET Image Process. 2018, 12, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S. Subpixel line localization with normalizaed sums of gradients and location linking with straightness and omni-directionality. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 180155–180167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S. Line-detection based on the sum of gradient angle differences. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Kelber, C. Lane following and lane departure using a linear-parabolic model. Image Vis. Comput. 2005, 23, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Shang, E.; Song, J.; Li, J.; He, H. Real-time lane departure warning system based on a single FPGA. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2013, 38, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Chang, C.; Lin, C. Lane mark extraction for automobiles under complex conditions. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 2756–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Yoo, H.; Kim, S.; Sohn, K. Real-time illumination invariant lane detection for lane departure warning system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasulu, B. Automatic extraction of retinal blood vessels: A software implementation. Eur. Sci. J. 2012, 8, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, J.; Kundu, D.; Tewary, S.; Ghosh, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Gupta, S. An automated graphical user interface based system for the extraction of retinal blood vessels using Kirsch’s template. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2015, 6, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Cao, T.; Eklund, P. A review of road extraction from remote sensing images. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2016, 3, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L. Machine perception of three-dimensional solids. In Optical and Electro-Optical Information Processing; Tippet, J., Berkowitz, D., Clapp, L.C., Koester, C.J., Alexander Vanderburgh, J., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1965; pp. 159–197. [Google Scholar]
- Pingle, K. Visual perception by computer. In Automatic Interpretation and Classification of Images; Grasselli, A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Prewitt, J. Object enhancement and extraction. In Picture Processing and Psychophysics; Rosenfeld, A., Lipkin, B., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970; pp. 75–149. [Google Scholar]
- Marr, D.; Hildreth, E. Theory of edge detection. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1980, 207, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canny, J. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steger, C. An unbiased detector of curvilinear structures. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiggelaar, R.; Astely, S.M.; Boggis, C.R.M.; Taylor, C.J. Linear structures in mammographic images: Detection and classification. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2004, 23, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.M.; Lumbreras, F.; Serrat, J.; Villanueva, J.J. Evaluation of methods for ridge and valley detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, K. Picture description using Legendre polynomials. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1975, 4, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Mehrotra, R. Detection of comosite edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1994, 3, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, T. Edge detection and ridge detection with automatic scale selection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1998, 30, 117–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laptev, I.; Mayer, H.; Lindeberg, T.; Eckstein, W.; Steger, C.; Baumgartner, A. Automatic extraction of roads from aerial images based on scale space and snakes. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2000, 12, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.K.; Jang, J.H.; Hong, K.S. Road detection in spaceborne SAR images using a genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Molina, C.; de Ulzurrun, G.V.D.; Baetens, J.; den Bulcke, J.V.; Baets, B.D. Unsupervised ridge detection using second order anisotropic Gaussian kernels. Signal Process. 2015, 116, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, B.; Ruzic, T.; Gezels, E.; Doomes, A.; Pizurica, A.; Platisa, L.; Cornelis, J.; Martens, M.; Mey, M.D.; Daubechies, I. Crack detection and impainting for virtual restoration of paintings: The case of the Ghent Altarpiece. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Shao, B.; Zhao, H.; Ning, R.; Zhang, Y. 3D room layout estimation from a single RGB image. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 22, 3014–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagendijk, R.L.; Tekalp, A.M.; Biemond, J. Maximum likelihood image and blur identification: A unifying approach. Opt. Eng. 1990, 29, 422–435. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, S.J.; Mersereau, R.M. Blur identification by the method of generalized cross-validation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1992, 1, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savakis, A.E.; Trussell, H.J. Blur identification by residual spectral matching. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1993, 2, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundur, D.; Hatzinakos, D. Blind image deconvolution. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1996, 13, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitzhaky, Y.; Kopeika, N.S. Identification of blur parameters from motion blurred images. Graph. Model. Image Process. 1997, 59, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yap, K.H. Efficient discrete spatial techniques for blur support identification in blind image deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lin, W.; Xie, S.; Lu, Z.; Ong, E.P.; Yao, S. Blind blur assessment for vision-based applications. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2009, 20, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. PSF estimation via gradient domain correlation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Cho, S.; Pan, C. Automatic blur-kernel-size estimation for motion deblurring. Vis. Comput. 2015, 31, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S. Edge modeling by two blur parameters in varying contrast. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2701–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromiley, P.A. Products and Convolutions of Gaussian Probability Density Functions; TINA: Manchester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S. Subpixel edge localization based on adaptive weighting of gradients. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 5501–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, S. SNR Analysis for Quantitative Comparison of Line Detection Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10088. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110088
Seo S. SNR Analysis for Quantitative Comparison of Line Detection Methods. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(21):10088. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110088
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Suyoung. 2021. "SNR Analysis for Quantitative Comparison of Line Detection Methods" Applied Sciences 11, no. 21: 10088. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110088
APA StyleSeo, S. (2021). SNR Analysis for Quantitative Comparison of Line Detection Methods. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 10088. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110088





