Exact Scan Patterns of Rotational Risley Prisms Obtained with a Graphical Method: Multi-Parameter Analysis and Design
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Scanners with Pairs of Rotational Risley Prisms
3. Linear Deviations of the Four Scanner Configurations
3.1. Linear Deviations of the Scanner (a) ab-ab
3.2. Linear Deviations of the Scanner (b) ab-ba
3.3. Linear Deviations of the Scanner (c) ba-ba
3.4. Linear Deviations of the Scanner (d) ba-ab
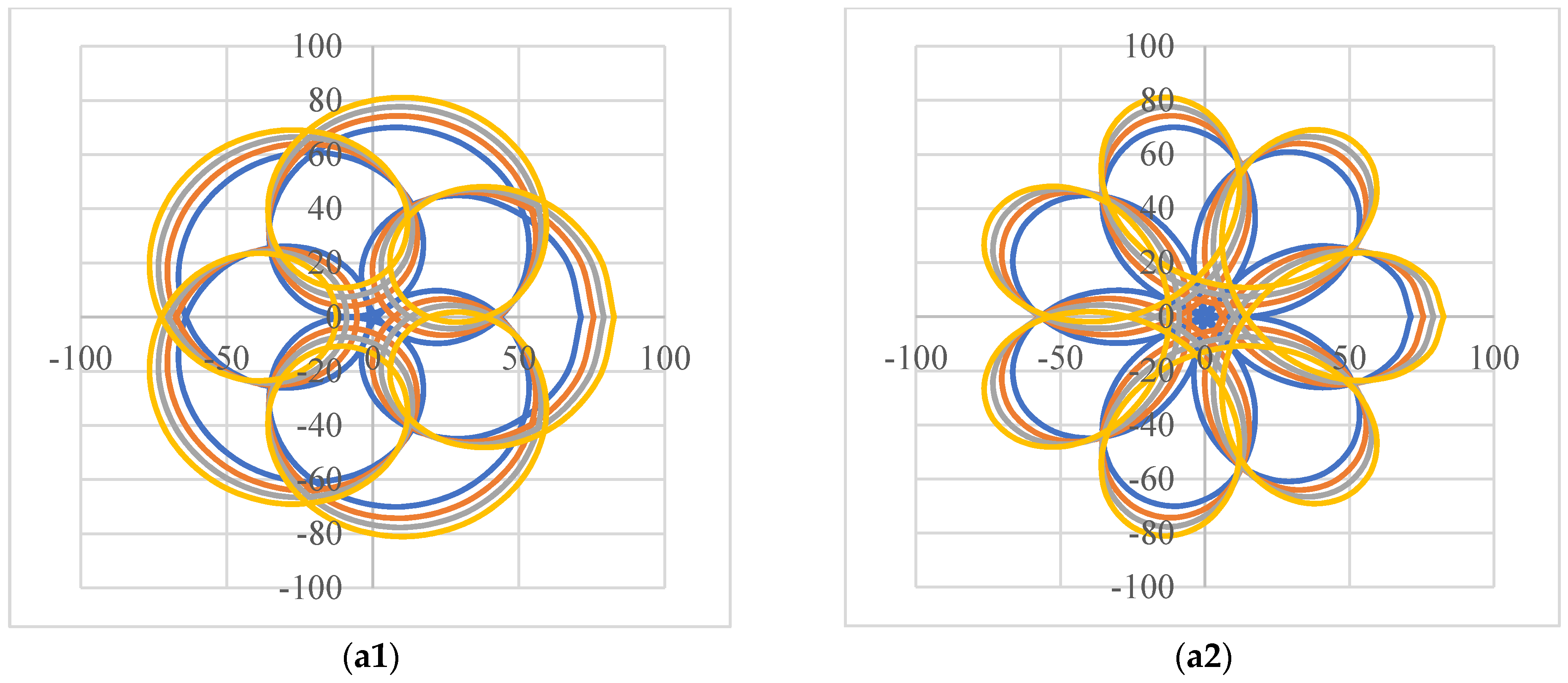
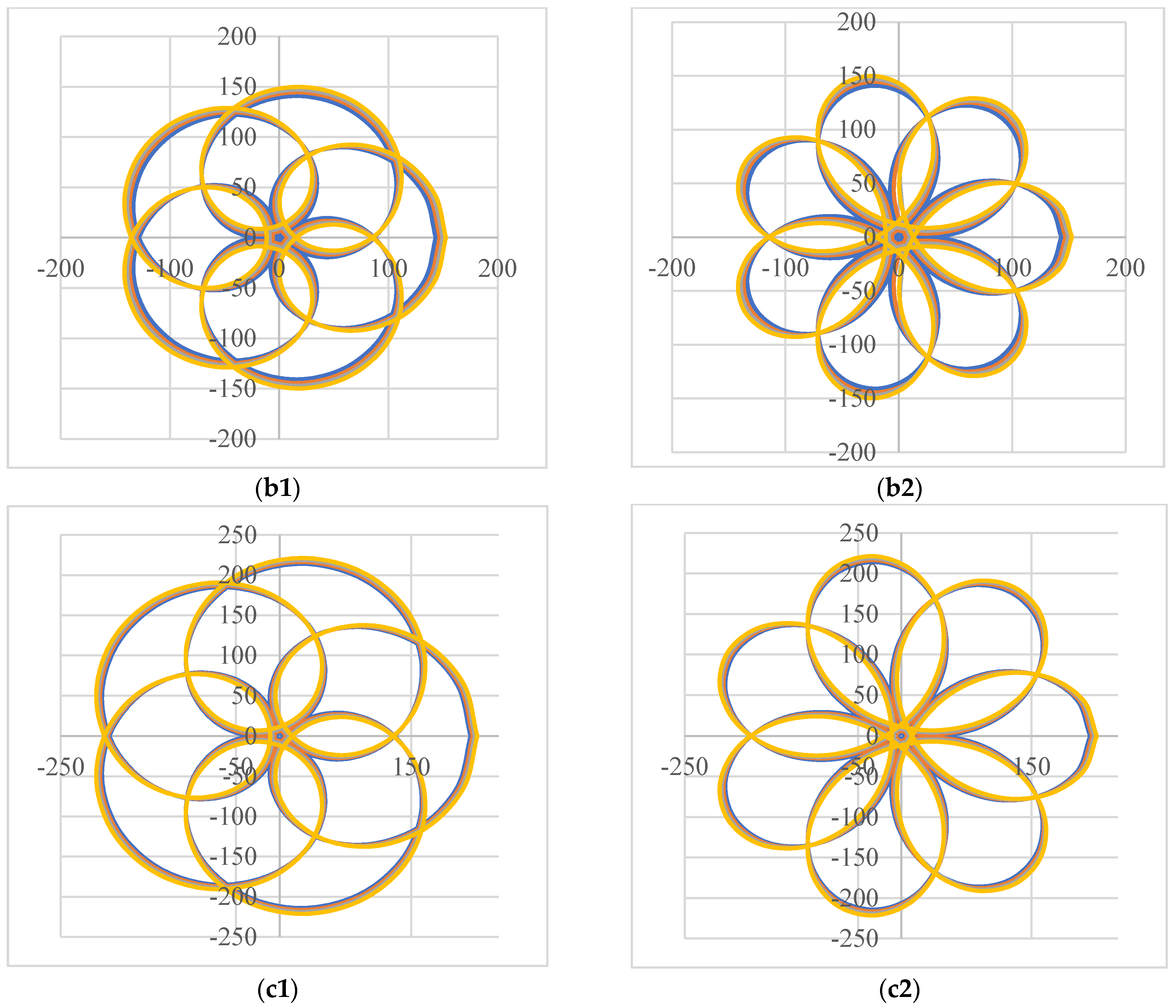
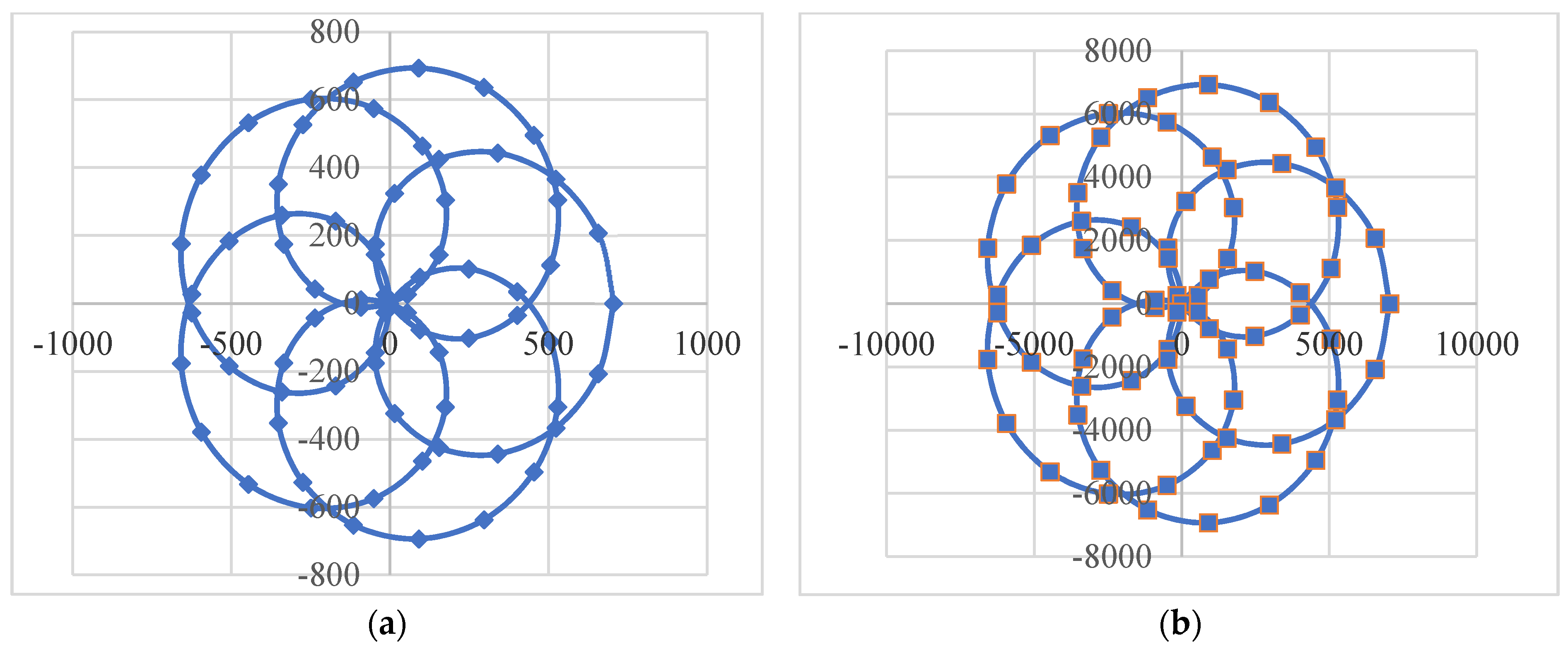
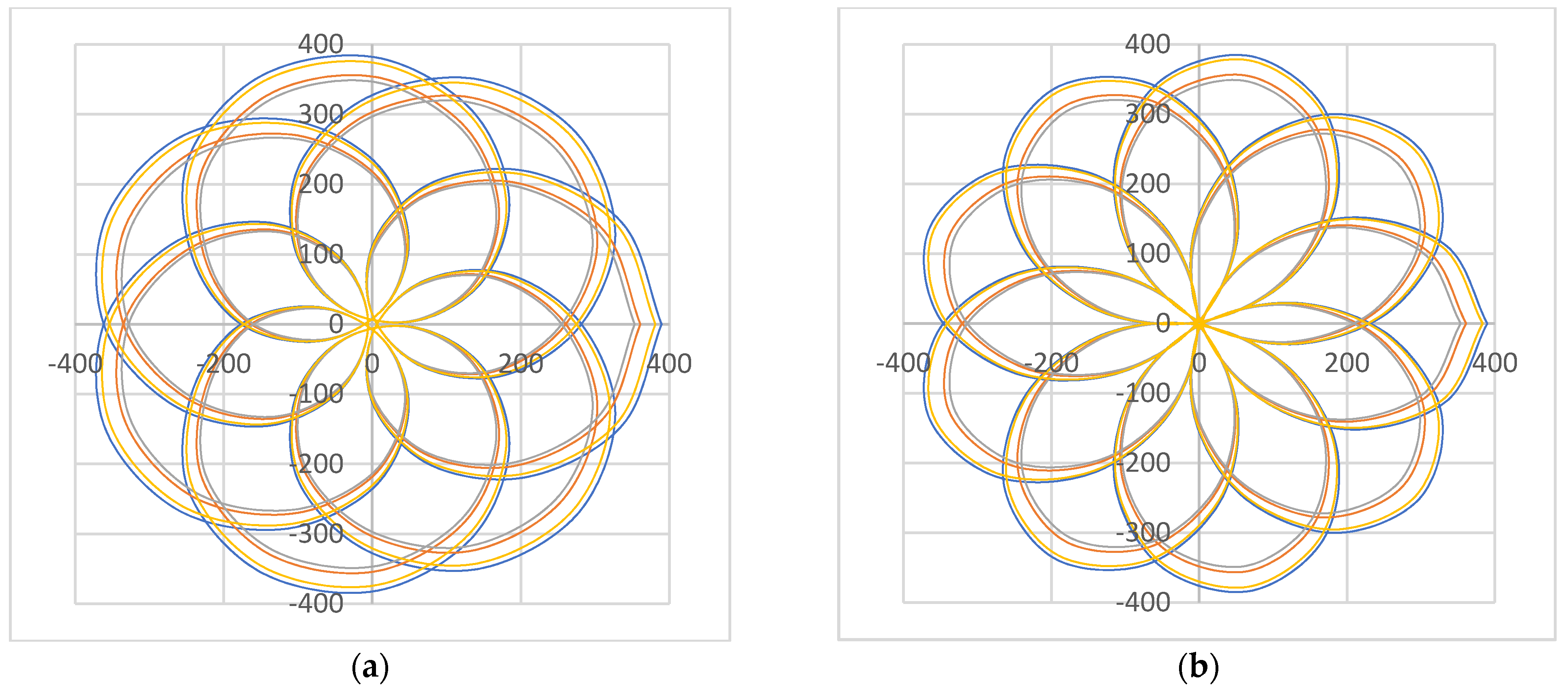
4. Results of Modeling and Simulations: Shapes of the Scan Patterns
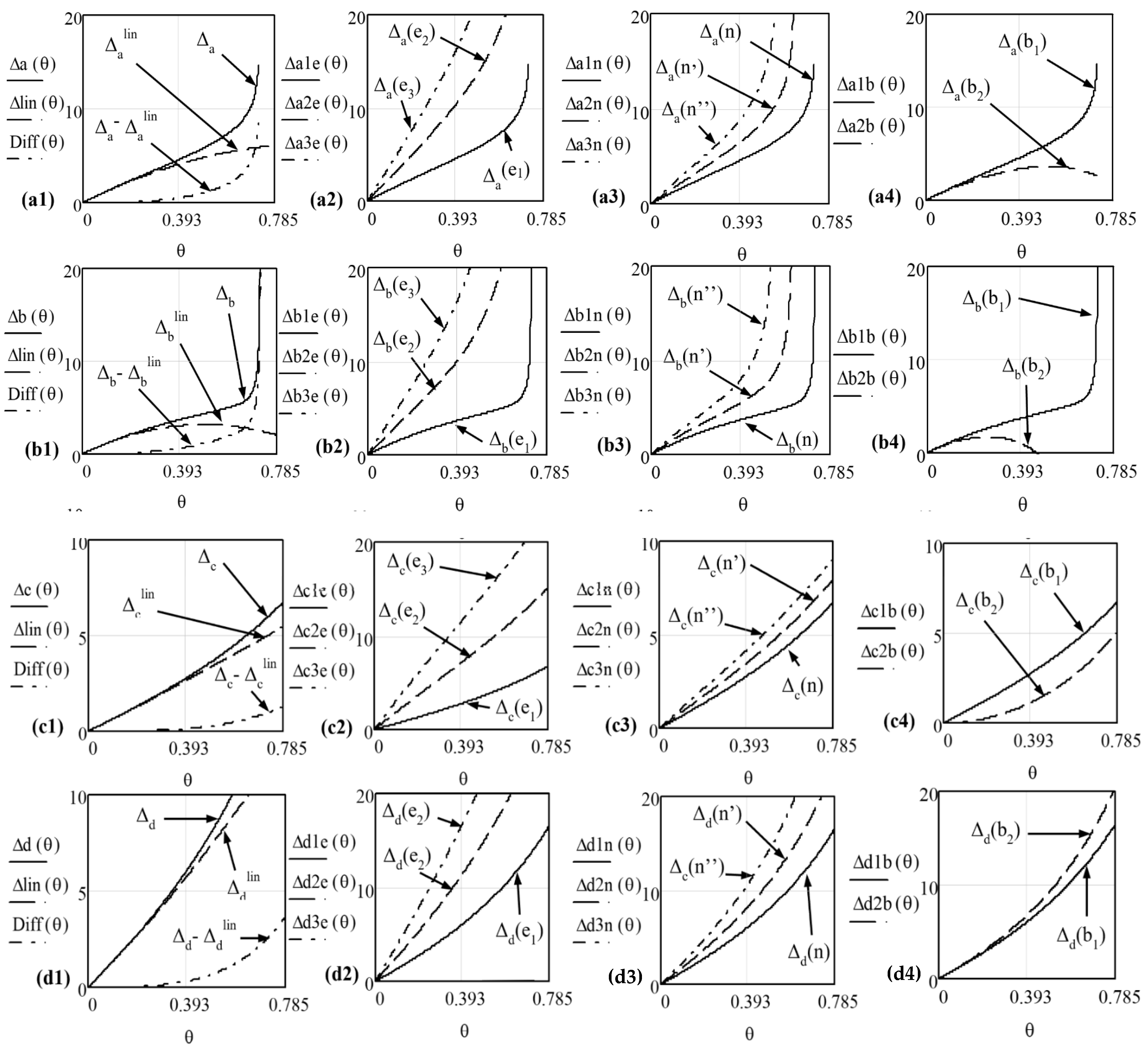
5. Multi-Parameter Analysis of Angular and Linear Deviations
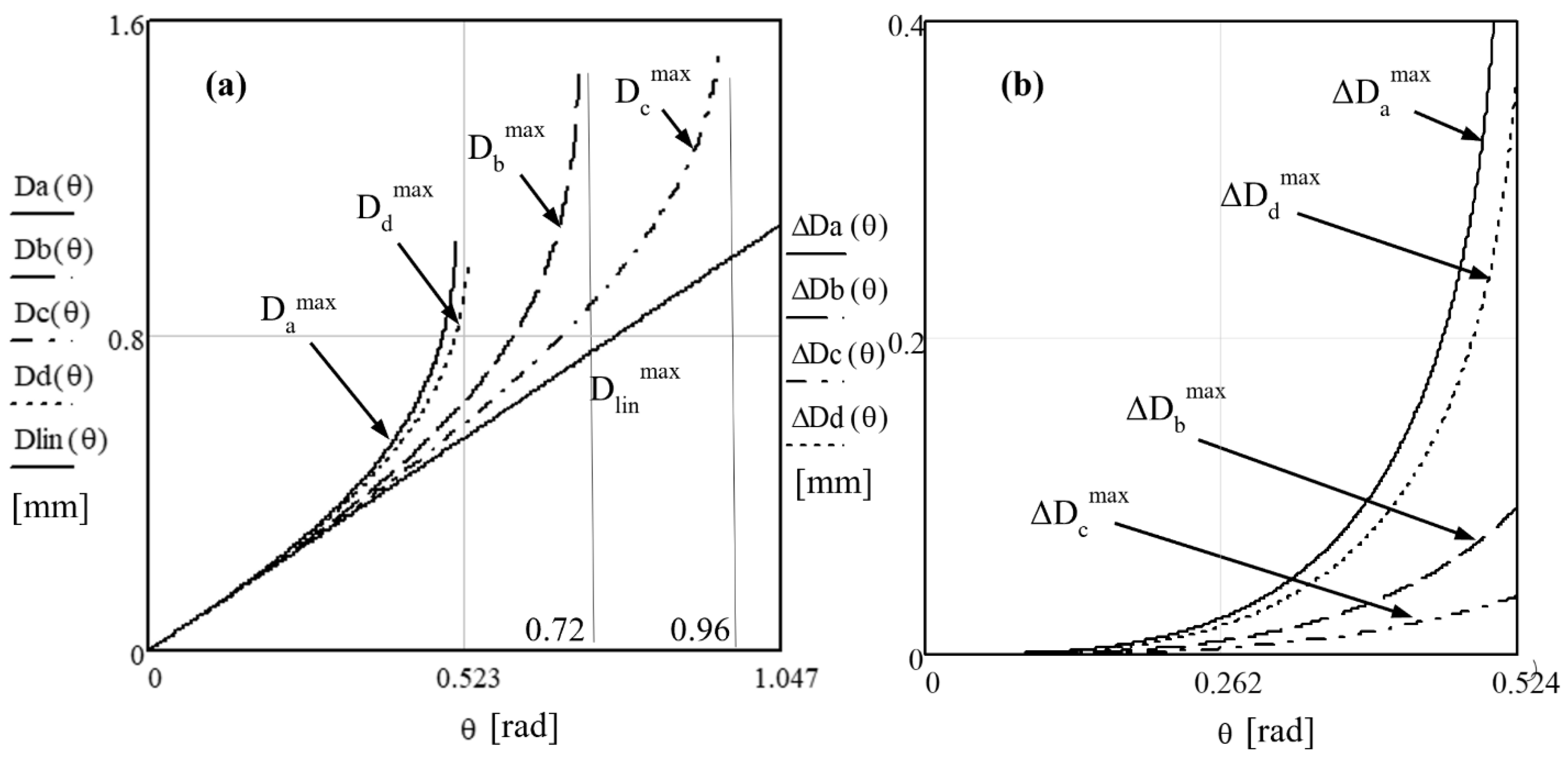
5.1. Multi-Parameter Analysis of Angular Deviations
- -
- From Figure 2a, for scanner (a) ab-ab, the conditions to have a beam emerging from the scanner arefrom which, for identical prisms and for small angles,
- -
- From Figure 2b, for scanner (b) ab-ba, the conditions to have a beam emerging from the scanner arefrom which, for identical prisms and for small angles,
- -
- From Figure 2c, for scanner (c) ba-ba, the conditions to have a beam emerging from the scanner arefrom which, for identical prisms and for small angles, the condition (44) is valid in this case, as well, therefore . However, this is clearly not true for the exact limit angles that refer to the non-linear curves of the maximum angular deviations in Figure 9a.
- -
- From Figure 2d, for scanner (d) ba-ab, the conditions to have a beam emerging from the scanner arefrom which, for identical prisms and for small angles,
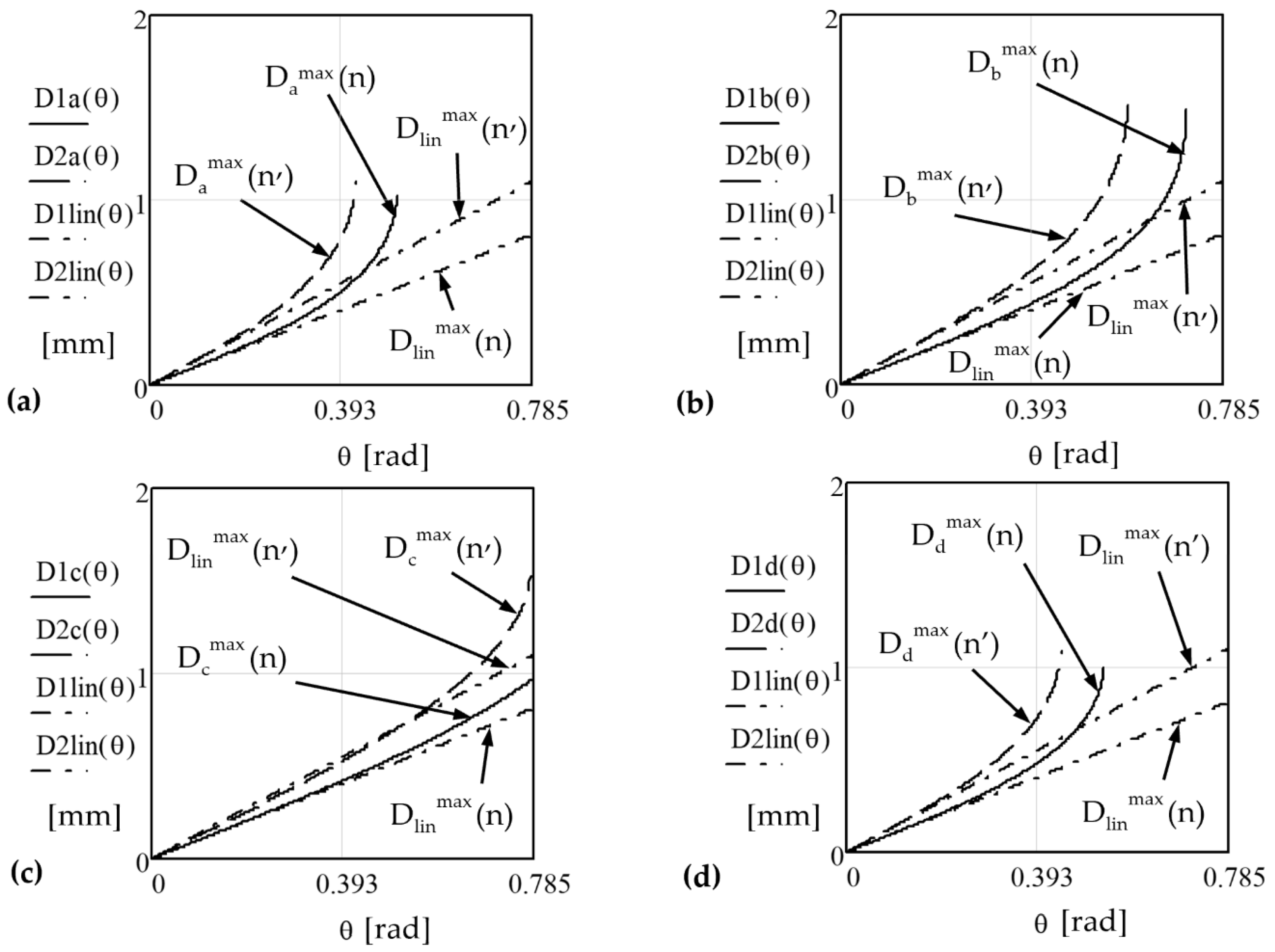
5.2. Multi-Parameter Analysis of Linear Deviations
6. Analysis of Scan Patterns Dimensions: Rules-of-Thumb for Scanner Designs
6.1. FOV of Scanners with a Pair of Rotational Risley Prisms
6.1.1. Study with Regard to the Prisms Angles
6.1.2. Study with Regard to the Refractive Index n of the Prisms
6.1.3. Study with Regard to the Distance e between the Two Prisms
6.1.4. Study with Regard to the Distance L from the Scanner to the Target
6.1.5. Study with Regard to the Scanner Configuration
6.2. Blind (Inner) Zone of the Scan Patterns
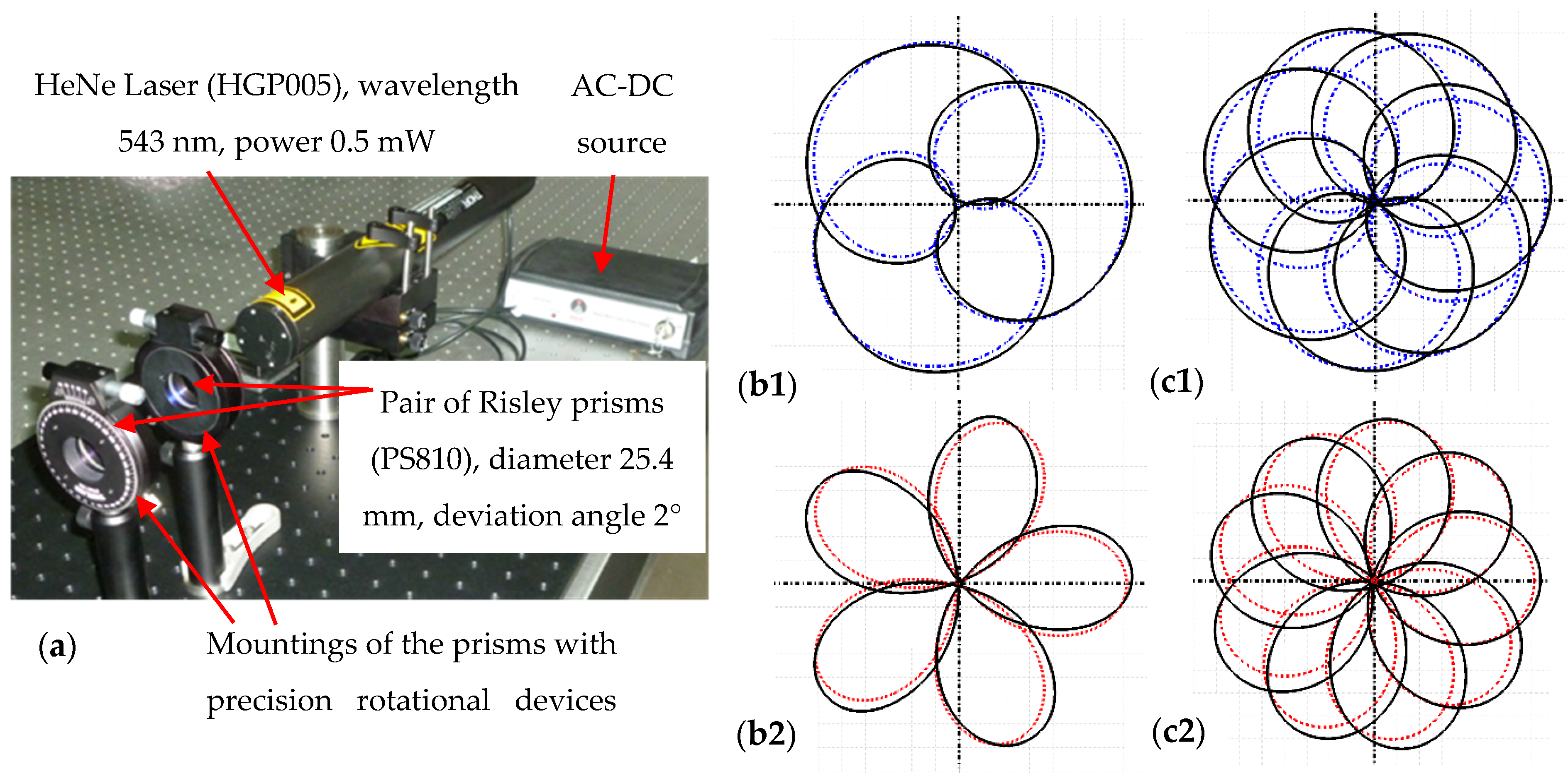
7. Experimental
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Maximum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (a) ab-ab (for )
Appendix A.2. Minimum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (a) ab-ab (for )
Appendix B
Appendix B.1. Maximum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (b) ab-ba (for )
Appendix B.2. Minimum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (b) ab-ba (for )
Appendix C
Appendix C.1. Maximum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (c) ba-ba (for )
Appendix C.2. Minimum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (c) ba-ba (for )
Appendix D
Appendix D.1. Maximum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (d) ba-ab (for )
Appendix D.2. Minimum Linear Deviation of the Scanner (d) ba-ab (for )
References
- Marshall, G.F.; Stutz, G.E. (Eds.) Handbook of Optical and Laser Scanning, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, M. Handbook of Optics, 3rd ed.; Mc. Graw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 30.1–30.68. [Google Scholar]
- Rosell, F.A. Prism scanner. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1960, 50, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.F. Risley Prism Scan Patterns. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3787, 74–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Analytic solution of free space optical beam steering using Risley prisms. J. Lightwave Technol. 2008, 26, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Third-order theory of the Risley-prism-based beam steering system. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Closed form analytical inverse solutions for Risley-prism-based beam steering systems in different configurations. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 4302–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Kong, X. Superresolution imaging and field of view extension using a single camera with Risley prisms. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 33701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Liu, X.; Gong, W.; Sun, W.; Sun, J. Prelocation image stitching method based on flexible and precise boresight adjustment using Risley prisms. JOSA A 2019, 36, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yi, W.; Zuo, Q.; Sun, W. Performance characterization of scanning beam steered by tilting double prisms. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 23543–23556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ding, Y.; Bian, Y.; Liu, L. Inverse solutions for tilting orthogonal double prisms. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 3712–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Jiang, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, L. Laser coarse-fine coupling scanning method by steering double prisms. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Torales, G.; Strojnik, M.; Paez, G. Risley prisms to control wave-front tilt and displacement in a vectorial shearing interferometer. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, V.-F.; Nicolov, M. Neutral density filters with Risley prisms: Analysis and design. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florea, C.; Sanghera, J.; Aggarwal, I. Broadband beam steering using chalcogenide-based Risley prisms. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 033001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, D.; Fan, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G. Laser scanning by rotating polarization gratings. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 5149–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, G.; Cao, X.; Bernier, R.; Roy, S. Enhanced scanning agility using a double pair of Risley prisms. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 10213–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Investigation of scan errors in the three-element Risley prism pair. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 25322–25335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-S.; Chang, R.-C. Characteristics of a prism-pair anamorphotic optical system for multiple holography. Opt. Eng. 1998, 37, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyokura, T.; Ito, T.; Sawada, R. Small Fourier transform spectroscope using an integrated prism-scanning interferometer. Appl. Spectrosc. 2001, 55, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, K.; Kaneko, T. Compact complete imaging polarimeter using birefringent wedge prisms. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Cho, H.; Janabi-Sharifi, F. Optical design of a variable view imaging system with the combination of a telecentric scanner and double wedge prisms. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warger, W.C.; DiMarzio, C.A. Dual-wedge scanning confocal reflectance microscope. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 2140–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, X.; Luan, Z.; Liu, D.; Yan, A.; Xu, N. An Integrated Test-Bed for PAT Testing and Verification of Inter-Satellite Lasercom Terminals. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6709, 670904. [Google Scholar]
- Piyawattanametha, W.; Ra, H.; Qiu, Z.; Friedland, S.; Liu, J.T.C.; Loewke, K.; Kino, G.S.; Solgaard, O.; Wang, T.D.; Mandella, M.J.; et al. In vivo near-infrared dual-axis confocal microendoscopy in the human lower gastrointestinal tract. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagu, J. Scanners-galvanometric and resonant. In Encyclopedia of Optical and Photonic Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 2465–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Benner, W.R. Laser Scanners: Technologies and Applications; Pangolin Laser Systems Inc.: Lexington, KY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Duma, V.-F.; Tankam, P.; Huang, J.; Won, J.J.; Rolland, J.P. Optimization of galvanometer scanning for Optical Coherence Tomography. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 5495–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Beam deflection and scanning by two-mirror and two-axis systems of different architectures: A unified approach. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 5976–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duma, V.-F. Polygonal mirror laser scanning heads: Characteristic functions. Proc. Rom. Acad. Ser. A 2017, 18, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Duma, V.-F. Laser scanners with oscillatory elements: Design and optimization of 1D and 2D scanning functions. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 67, 456–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathman, M.; Liu, Y.; Keeler, E.G.; Song, M.; Baran, U.; Xi, J.; Sun, M.-T.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Lin, L.Y. MEMS scanning micromirror for optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gora, M.J.; Suter, M.J.; Tearney, G.J.; Li, X. Endoscopic optical coherence tomography: Technologies and clinical applications. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2405–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cogliati, A.; Canavesi, C.; Hayes, A.; Tankam, P.; Duma, V.-F.; Santhanam, A.; Thompson, K.P.; Rolland, J.P. MEMS-based handheld scanning probe with pre-shaped input signals for distortion-free images in Gabor-Domain Optical Coherence Microscopy. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 13365–13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podoleanu, A.G.; Rosen, R.B. Combinations of techniques in imaging the retina with high resolution. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 464–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grulkowski, I.; Gorczynska, I.; Szkulmowski, M.; Szlag, D.; Szkulmowska, A.; Leitgeb, R.A.; Kowalczyk, A.; Wojtkowski, M. Scanning protocols dedicated to smart velocity ranging in Spectral OCT. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 23736–23754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.J.; Heisler, M.; Athwal, A.; Sarunic, M.V.; Jian, Y. Effective bidirectional scanning pattern for optical coherence tomography angiography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A.; et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drexler, W.; Liu, M.; Kumar, A.; Kamali, T.; Unterhuber, A.; Leitgeb, R.A. Optical coherence tomography today: Speed, contrast, and multimodality. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 071412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-S.; Ho, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chuang, C.-C.; Tsai, J.-C.; Lin, K.-F.; Sun, C.-W. Dental Optical Coherence Tomography. Sensors 2013, 13, 8928–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, H.; Park, K.-J.; Häfer, M.; Rüger, C.; Schmalz, G.; Krause, F.; Schmidt, J.; Ziebolz, D.; Haak, R. Dental Applications of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Cariology. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdelyi, R.-A.; Duma, V.-F.; Sinescu, C.; Dobre, G.M.; Bradu, A.; Podoleanu, A. Dental Diagnosis and Treatment Assessments: Between X-rays Radiography and Optical Coherence Tomography. Materials 2020, 13, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meemon, P.; Yao, J.; Lee, K.-S.; Thompson, K.P.; Ponting, M.; Baer, E.; Rolland, J.P. Optical Coherence Tomography Enabling Non Destructive Metrology of Layered Polymeric GRIN Material. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van’t Oever, J.J.F.; Thompson, D.; Gaastra, F.; Groendijk, H.A.; Offerhaus, H.L. Early interferometric detection of rolling contact fatigue induced micro-cracking in railheads. NDT E Int. 2017, 86, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutiu, G.; Duma, V.-F.; Demian, D.; Bradu, A.; Podoleanu, A.G. Assessment of ductile, brittle, and fatigue fractures of metals using optical coherence tomography. Metals 2018, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duma, V.-F.; Sinescu, C.; Bradu, A.; Podoleanu, A. Optical Coherence Tomography Investigations and Modeling of the Sintering of Ceramic Crowns. Materials 2019, 12, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; You, X.; Wang, Y.; Gu, K.; Liu, C.; Tan, J. The alpha-beta circular scanning with large range and low noise. J. Microsc. 2017, 266, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Zevallos, O.M.; Viehland, C.; Keller, B.; McNabb, R.P.; Kuo, A.N.; Izatt, J.A. Constant linear velocity spiral scanning for near video rate 4D OCT ophthalmic and surgical imaging with isotropic transverse sampling. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duma, V.-F.; Schitea, A. Laser scanners with rotational Risley prisms: Exact scan patterns. Proc. Rom. Acad. Ser. A 2018, 19, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, K.; Seo, Y.-H.; Ahn, J.; Kim, P.; Jeong, K.-H. Frequency selection rule for high definition and high frame rate Lissajous scanning. Sc. Rep. 2017, 7, 14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanguy, Q.A.A.; Gaiffe, O.; Passilly, N.; Cote, J.-M.; Cabodevila, G.; Bargiel, S.; Lutz, P.; Xie, H.; Gorecki, C. Real-time Lissajous imaging with a low-voltage 2-axis MEMS scanner based on electrothermal actuation. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, L.; Yun, M.; Wan, L.; Zhang, M. Distortion of beam shape by a rotating double prism wide-angle laser beam scanner. Opt. Eng. 2006, 45, 043004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, V.; Ricard, B. Fast Risley prisms camera steering system: Calibration and image distortions correction through the use of a three-dimensional refraction model. Opt. Eng. 2007, 46, 43201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, G. Beam steering limitation of a Risley prism system due to total internal reflection. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 6079–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Medina, B.; Strojnik, M.; Garcia-Torales, G.; Torres-Ortega, H.; Estrada-Marmolejo, R.; Beltrán-González, A.; Flores, J.L. Error compensation in a pointing system based on Risley prisms. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yi, W.; Sun, W.; Liu, L. Tilting double-prism scanner driven by cam-based mechanism. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 5788–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hei, M.; Liu, G.; Fan, D. Motion control of the wedge prisms in Risley-prism-based beam steering system for precise target tracking. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-F.; Lee, C.-C. Analytic inverse solutions for Risley prisms in four different configurations for positing and tracking systems. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 10172–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Gong, W. Laser coarse-fine coupling tracking by cascaded rotation Risley-prism pairs. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 3873–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schitea, A.; Tuef, M.; Duma, V.-F. Modeling of Risley prisms devices for exact scan patterns. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8789, 878912. [Google Scholar]
- Dimb, A.-L.; Duma, V.-F. Experimental validations of simulated exact scan patterns of rotational Risley prisms scanners. Proc. SPIE 2020, 11354, 113541U. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, W. Rhodonea Curves as Sampling Trajectories for Spectral Interpolation on the Unit Disk. Constr. Approx. 2020, 53, 281–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=147 (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Duma, M.-A.; Duma, V.-F. Theoretical approach on the linearity increase of scanning functions using supplemental mirrors. Proc. SPIE 2019, 11028, 1102817. [Google Scholar]
- Duma, V.-F. A novel, graphical method to analyze optical scanners with Risley prisms. Proc. SPIE 2021, 11830, 118300F. [Google Scholar]
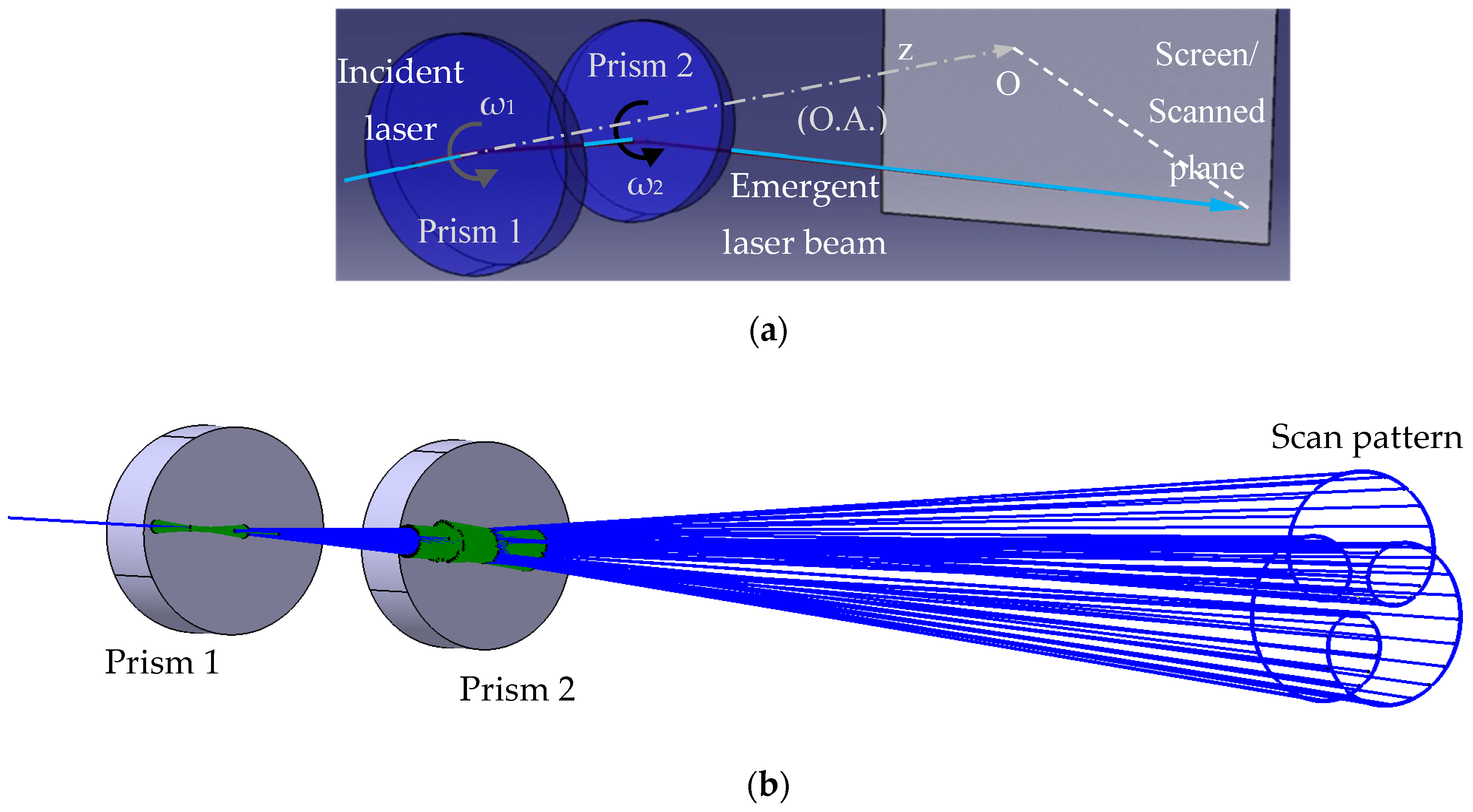
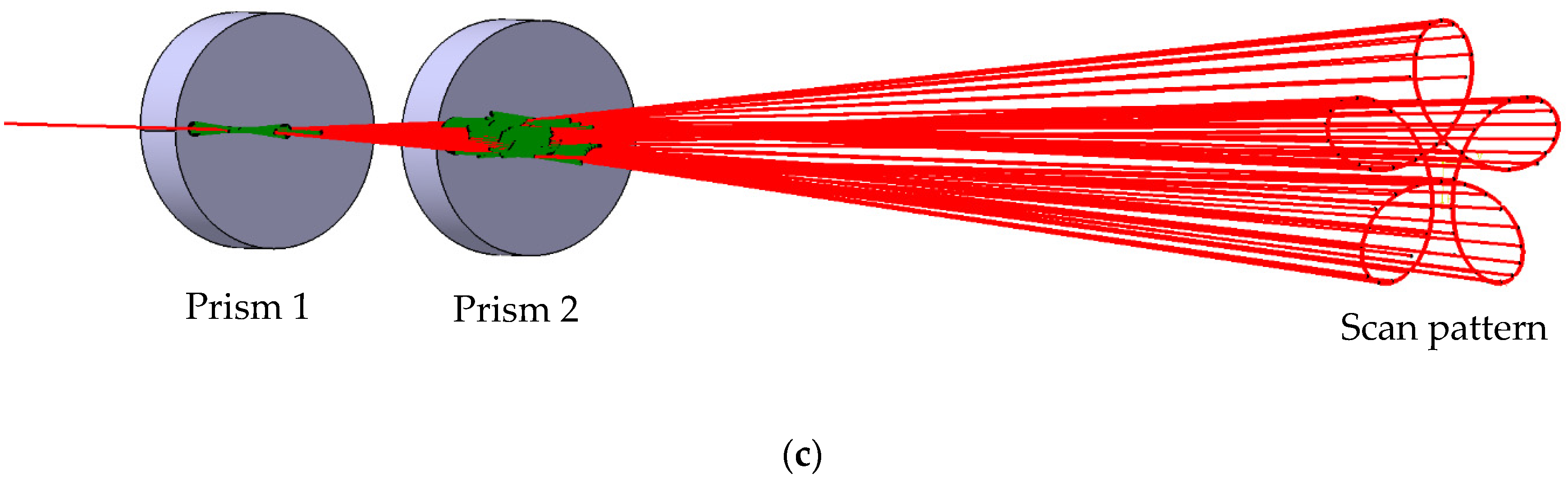
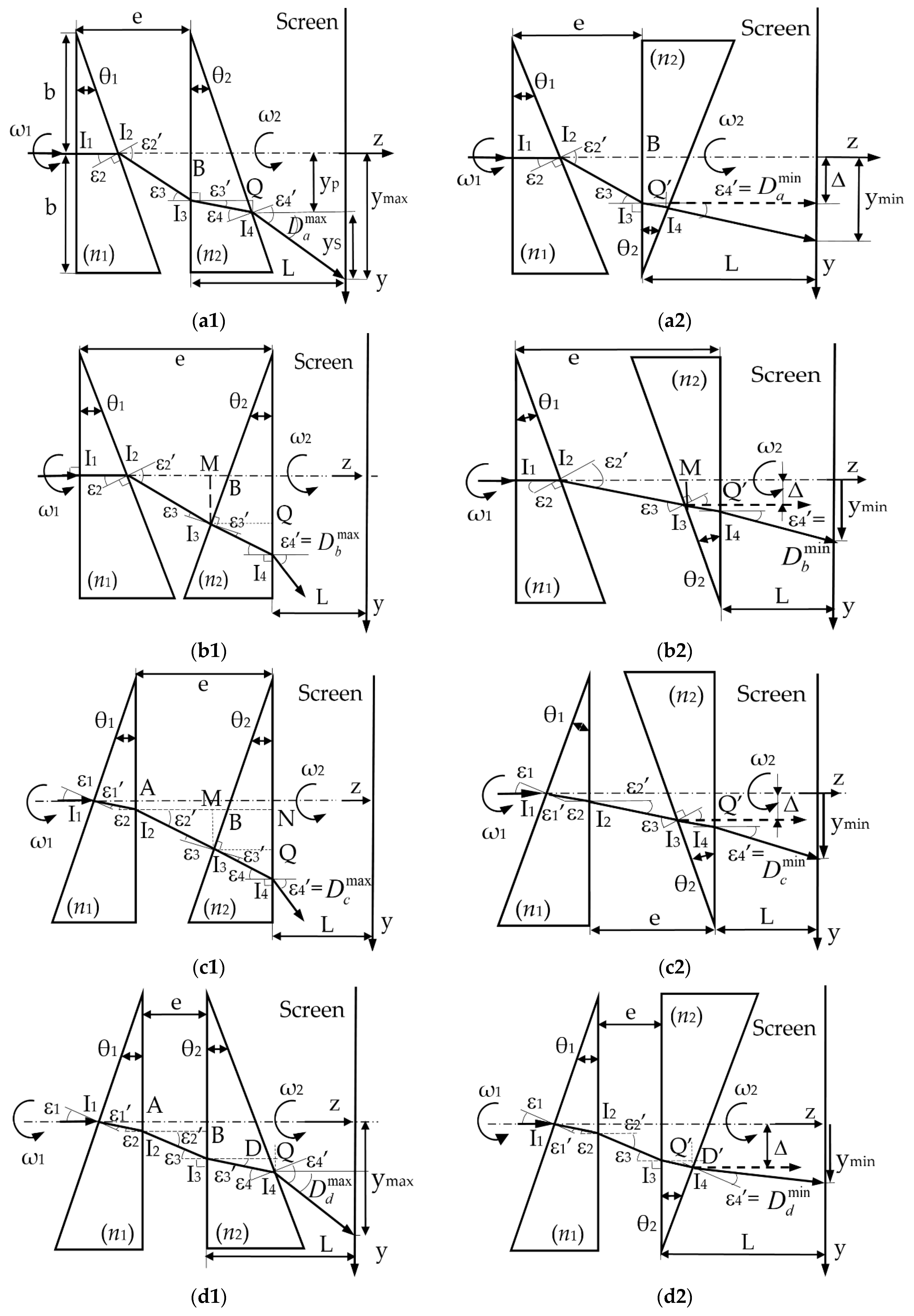
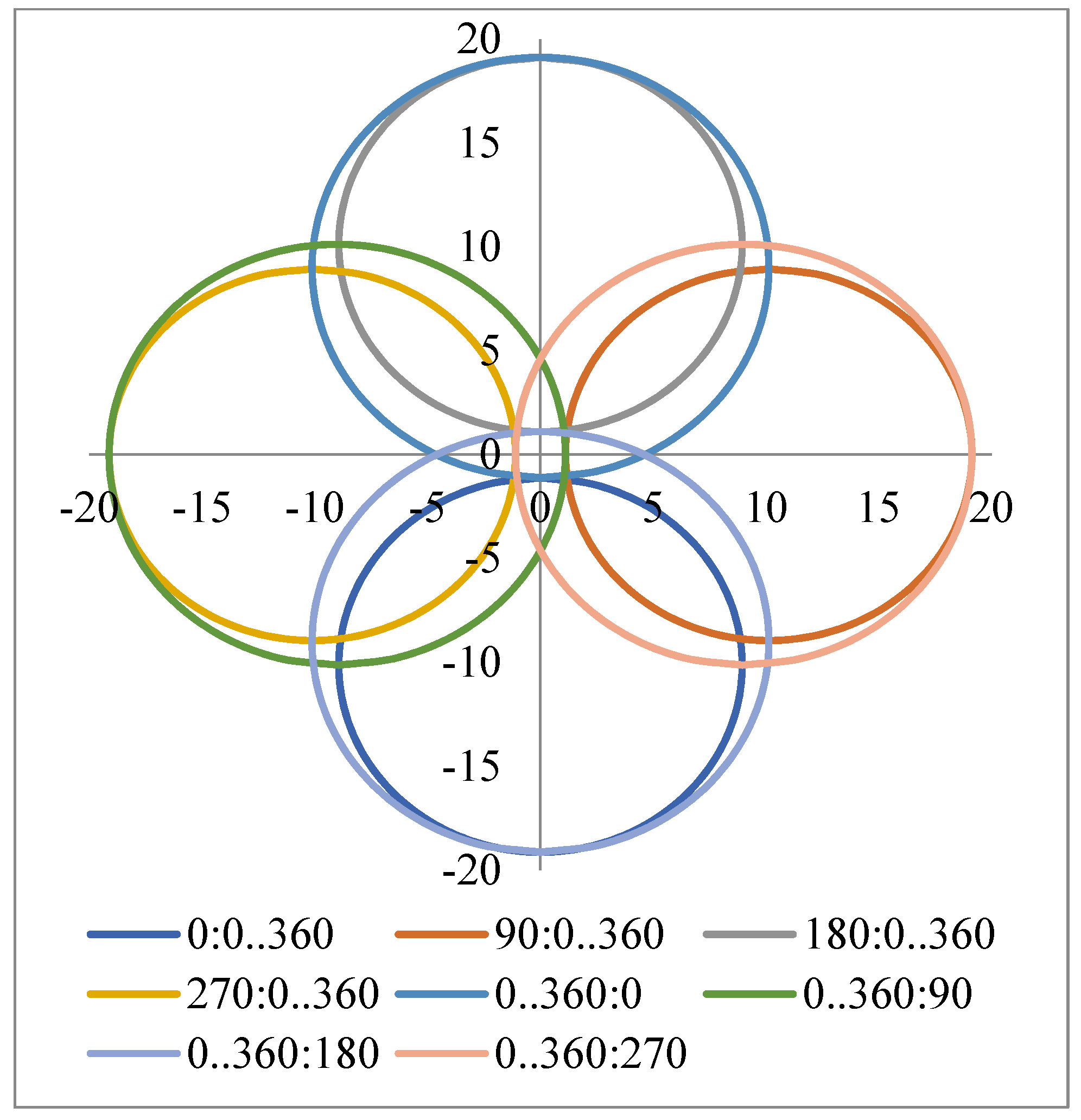
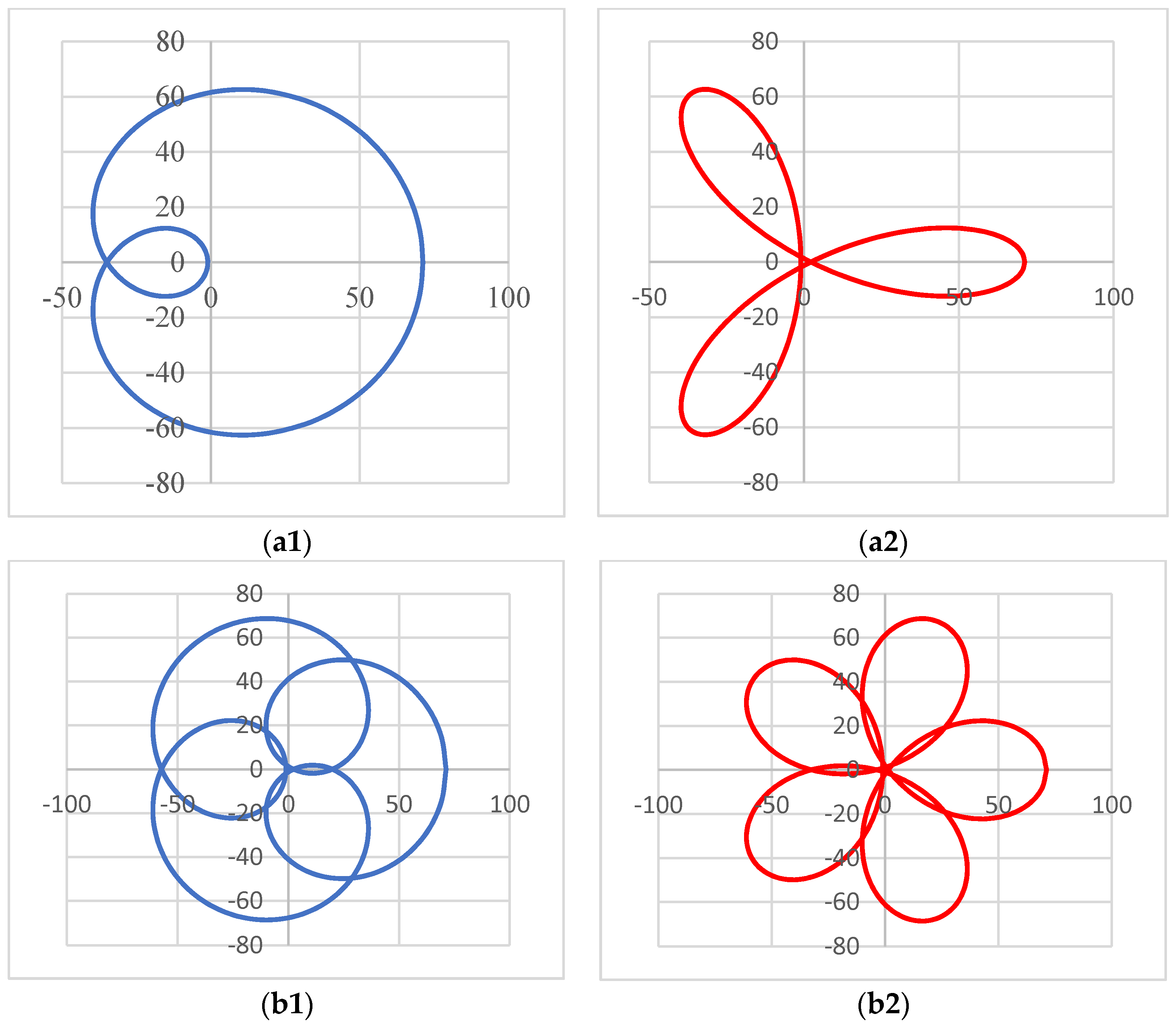
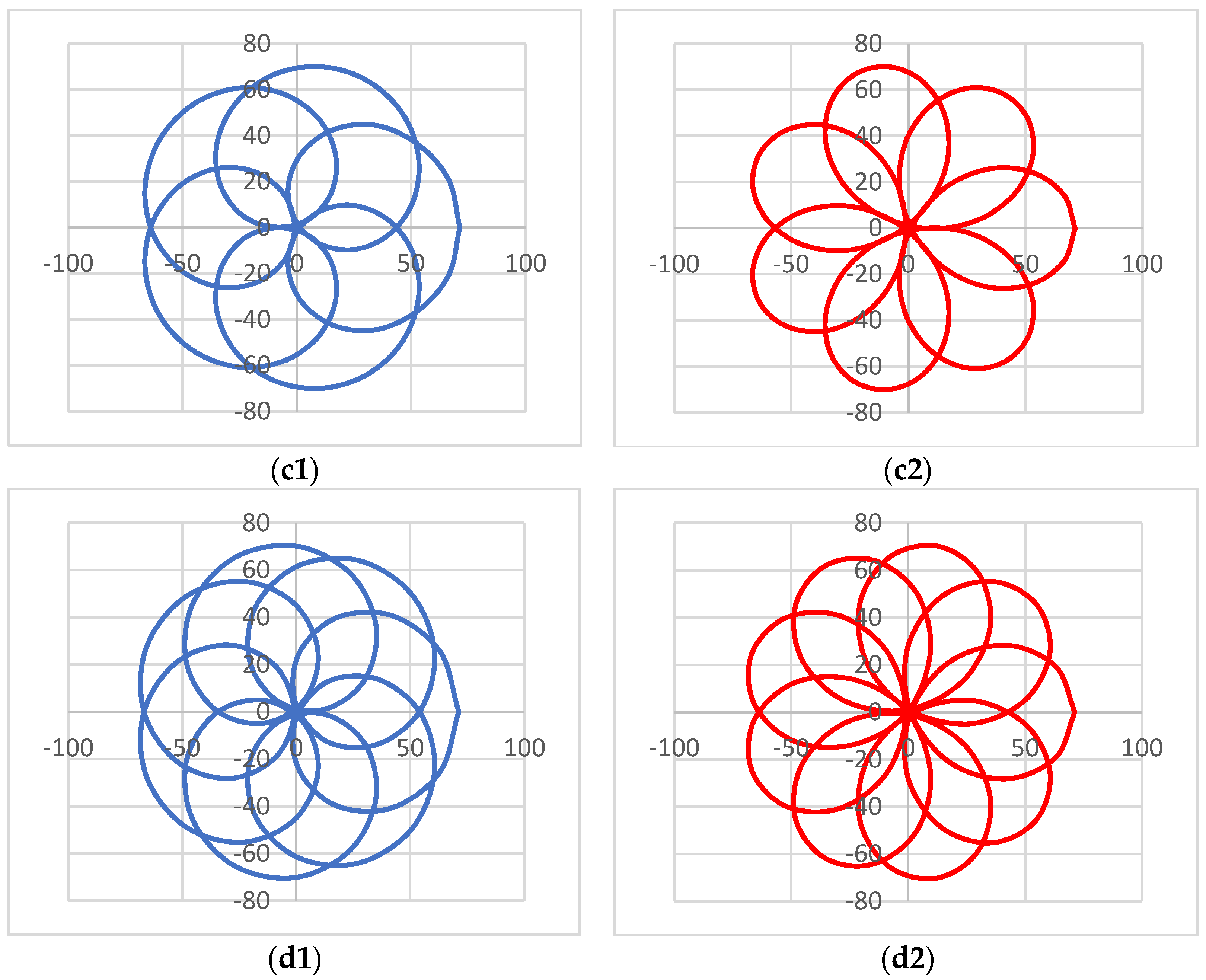
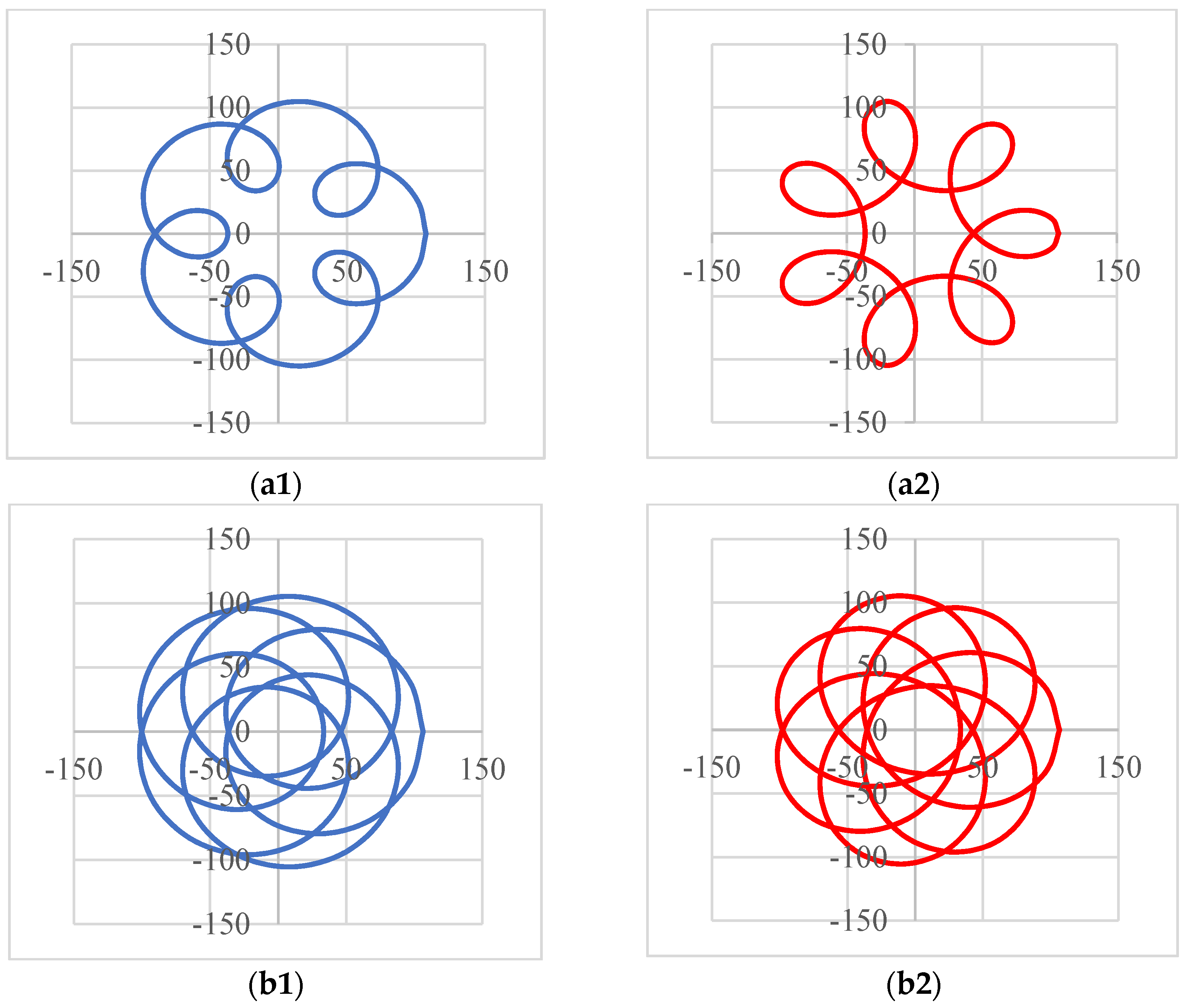
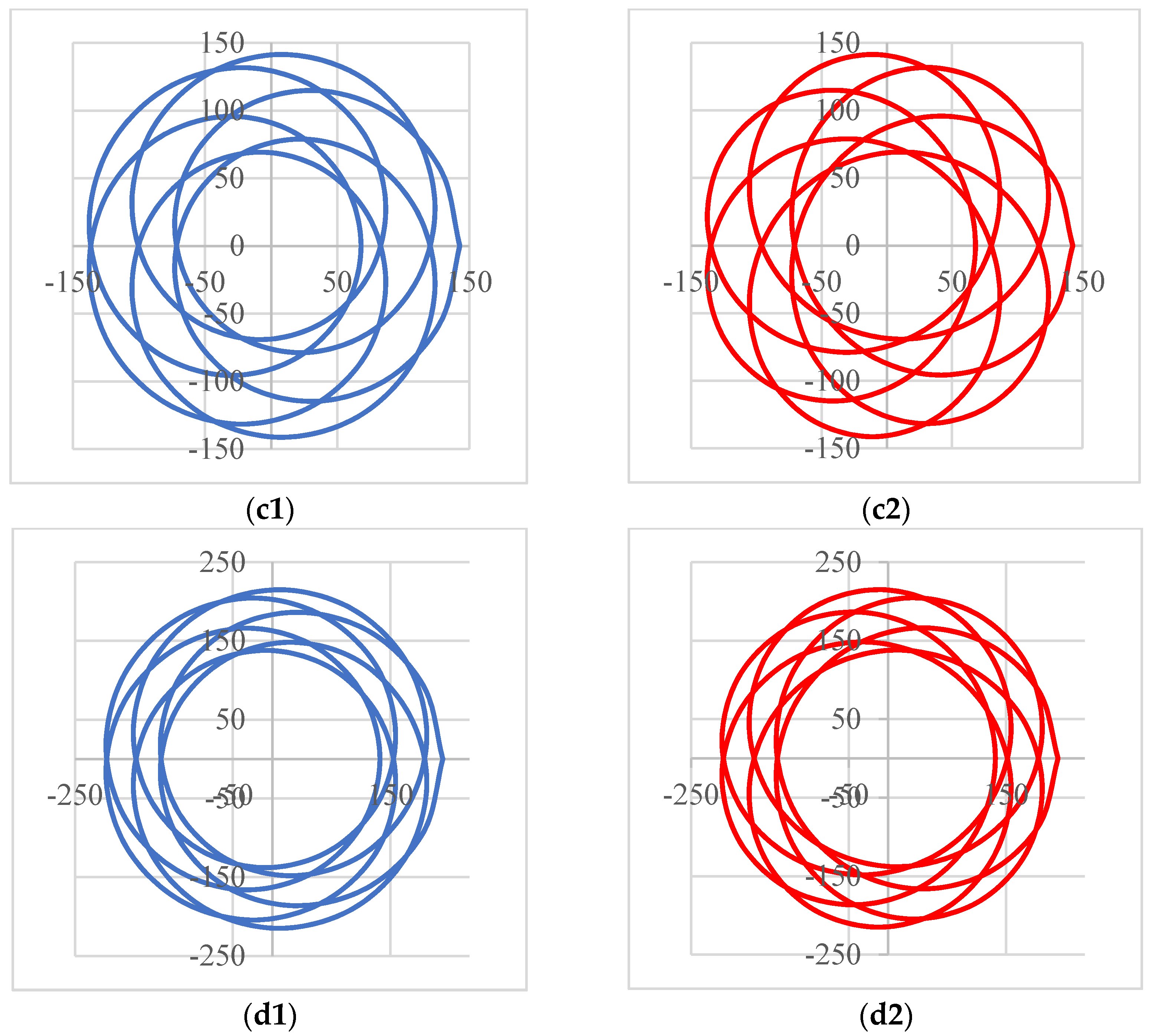
| Configuration (Figure 2) | (a) Scanner ab-ab | (b) Scanner ab-ba | (c) Scanner ba-ba | (d) Scanner ba-ab |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence angle | ||||
| Point I1 | ||||
| Prism 1 | ||||
| Point I2 | ||||
| Inter-prisms | ||||
| Point I3 | ||||
| Prism 2 | ||||
| Point I4 | ||||
| Deviation angles , j = a, b, c, d | ||||
| Scanner Configurations | Refractive Index | |
|---|---|---|
| n = 1.517 | n’ = 1.7 | |
| Figure 2a | ||
| Figure 2b | ||
| Figure 2c | ||
| Figure 2d | ||
| Ratio of the Rotational Speeds, Equation (1) | M = 4 | M = −4 | M = 8 | M = −8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value of the FOV radius: | 72.709 | 72.827 | 72,961 | 73.794 |
| Standard deviation of the FOV radius: | 0.591 | 0.645 | 1.336 | 1.708 |
| Relative error: | 2.027 | 2.192 | 2.207 | 3.548 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duma, V.-F.; Dimb, A.-L. Exact Scan Patterns of Rotational Risley Prisms Obtained with a Graphical Method: Multi-Parameter Analysis and Design. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8451. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188451
Duma V-F, Dimb A-L. Exact Scan Patterns of Rotational Risley Prisms Obtained with a Graphical Method: Multi-Parameter Analysis and Design. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8451. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188451
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuma, Virgil-Florin, and Alexandru-Lucian Dimb. 2021. "Exact Scan Patterns of Rotational Risley Prisms Obtained with a Graphical Method: Multi-Parameter Analysis and Design" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8451. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188451
APA StyleDuma, V.-F., & Dimb, A.-L. (2021). Exact Scan Patterns of Rotational Risley Prisms Obtained with a Graphical Method: Multi-Parameter Analysis and Design. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8451. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188451







