Featured Application
Potential use of enzymes in the development of bioprocesses for the degradation and recycling of residual plastic fibers.
Abstract
Terephthalate polyesters such as poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) have been massively produced over the last few decades due to their attractive properties in multiple applications. However, due to their limited biodegradability, they have accumulated in landfills and oceans, posing an environmental threat. Enzymatic recycling technologies are predicted to generate long-term socioeconomic benefits. In the present work, we compared the IsPETase (from Ideonella sakaiensis 201-F6) activity on a series of polyesters, including poly(butylene) terephthalate (PBT), poly(hexamethylene) terephthalate (PHT) and Akestra™, with PET. The IsPETase showed remarkable activity toward PET (39% degradation of the original polyester) that was higher than that toward Akestra™ (0.13%), PBT (0.25%) and PHT (0.13%) after 72 h. Thus, based on experimental data and computational analysis, we report insights into IsPETase activity on a series of terephthalate-based polyesters. Aside from that, the fusion domain (Trx) effect in the production and activity of a recombinant Trx-IsPETase is reported.
1. Introduction
From every piece of plastic ever created, around 80% still exist today [1]. Of the 6.3 billion tons of fossil fuel-derived plastic (FFP) waste produced to date, only 9% has been recycled, 12% has been incinerated, and 79% has been deposited in landfills or the natural environment [2,3]. Global plastics production reached approximately 360 million tons in 2018, with roughly 50% disposed of after a single use [4]. In Europe, 62 million tons of plastics were produced in 2018, where 9.4 million tons of plastic post-consumer waste were collected to be recycled (a 92% increase since 2006) [5]. The poor plastic waste management seen worldwide has provoked extended micro- and nano-plastic pollution in marine environments, mainly caused by the fragmentation of plastics. The ubiquitous presence of microplastics has been reported in freshwater, pristine, remote, and even atmospheric systems. The abundance of nanoplastics reported in the food chain is very concerning for wildlife and human health [6].
Polyesters constitute a major class of plastics, and they are widely used as beverage bottles, packaging, and textiles. Currently, the polyesters on the market are dominated by those containing aromatic units (e.g., terephthalate) in their backbones, which are essential for their superior thermal and mechanical properties [7]. Terephthalic acid (TPA) or its derivative dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) are widely used as precursors for the synthesis of aromatic polyesters. For instance, the most used polyester, poly(ethylene) terephthalate (PET), is synthesized by polymerizing TPA or DMT with ethylene glycol. It is commonly used for synthetic fibers in the textile industry and packaging [8,9,10]. Poly(butylene) terephthalate (PBT) is another aromatic polyester synthesized from TPA (or DMT) and 1,4-butanediol which is widely used in electrical engineering as plug connectors, household devices like irons, and sportswear due to its physical properties. Recently, a more flexible aromatic polyester, poly(hexamethylene) terephthalate (PHT) has attracted growing attention due to its potential in semiconductor materials [11,12,13]. Another recent trend in the development of aromatic polyesters in the industry is toward more durable high-Tg materials, such as AkestraTM (Perstorp AB), PETG (Sumitomo), and TritanTM (Eastman Co.) [14,15,16].
Biodegradation is considered eco-friendly and, in the future, an economically favorable recycling method compared with landfills, chemical recycling, and thermal treatment [17,18]. Enzymatic degradation of plastics could aid in the biological recycling of these waste products [19], reducing energy use, by-product release, and greenhouse gas emissions compared with virgin polyester manufacturing [20]. Enzymatic recycling technologies are predicted to generate long-term socioeconomic benefits, such as added economic value and a number of jobs distributed along the supply chain [20]. As polyesters constitute 60% of the total global synthetic fiber production, there is growing concern for efficient biodegradation of recalcitrant synthetic polymers like PET and other aromatic terephthalate polyesters [18,21].
Enzymes with PET-depolymerizing activity have been found to be mainly from the carboxylic ester hydrolases family (EC 3.1.1.-). The first study in 2005 reported 50% degradation of low-crystallinity (9%) PET after three weeks by using the hydrolase TfH from the actinomycete Thermobifida fusca at 55 °C, adding fresh enzyme every week [22]. Since then, other thermostable esterases have shown effective PET depolymerizing activity in shorter periods [23]. More recently (in 2020), an engineered form of leaf and branch compost cutinase (LCC) has attracted attention for its outstanding PET depolymerizing activity, degrading up to 90% of amorphized and micronized PET in 10 h at 72 °C [24]. At lower temperatures, in 2016, a novel mesophilic bacterium Ideonella sakaiensis 201-F6 was found to use PET as its main carbon and energy source [19]. A key enzyme, IsPETase (EC 3.1.1.101), was identified as being responsible for PET depolymerization, which showed more activity than others when compared at mild temperatures (27–40 °C) [19,25,26]. Several IsPETase structural studies were published [17,27,28,29], which set the basis for mechanistic studies [30,31] as well as for the development of a series of mutants with increased activity [32] or thermostability [33,34,35,36,37]. Both thermostable and mesostable PET-active enzymes constitute a valuable toolbox for diverse applications. Mesostable PETases could be used in processes where high temperatures are not convenient. However, practical applications will most likely need the integration of waste plastic pretreatment processes (for example, micronization, amorphization, or others) and the use of engineered enzymes or whole cells.
Several commercial polyesters underwent biodegradation studies [38,39,40]. However, to our knowledge, apart from PET, little is known about the biodegradation of aromatic polyesters. IsPETase has also shown some activity against a novel synthetic AB-type indole-base polyester [16]. In this work, IsPETase activity against various aromatic polyesters with terephthalate bound to diols of different lengths and rigidity is assessed. Semicrystalline forms of PET, PBT, PHT, and Akestra™, which is amorphous, are used as potential substrates for IsPETase, and molecular docking is performed to explore the structural implications.
On the other hand, the production of recombinant PETases is an efficient type of technology that can be scalable to industrial levels. However, one of the main drawbacks is the production of a soluble enzyme, and a significant fraction of IsPETase produced in Escherichia coli can precipitate as inclusion bodies, losing their activity and negatively affecting the yield. A common strategy to enhance the solubility of recombinant proteins is the use of fusion partners, such as thioredoxin (Trx) [41]. Therefore, the Trx domain effect both in production and IsPETase (Trx-IsPETase) activity is also evaluated in this work.
This article focuses on understanding the fundamental aspects of IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase activities; more practical aspects will be addressed in the future. The dissolution–precipitation of the polymers used here is not related to their recycling but with their preparation in a similar physical form, such as powders, for enzymatic studies. The pretreatment to reduce the degree of crystallinity, as mentioned before, of PET and other polyesters facilitate the enzyme activity, even for thermostable enzymes, which have the advantage of working closer to the PET glass transition point [23].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production and Purification of Enzymes
IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase were produced in Escherichia coli Rosetta-gamiTM2 (DE3) according to standard protocols [15,16]. The gene encoding the IsPETase from I. sakaiensis (GenBank accession code GAP38373.1) without a signal peptide (first 29 amino acids from the N-terminal) was chemically synthesized (GenScript USA Inc., Piscataway, NJ, USA) with codons optimized for E. coli and cloned into the expression vectors pET28b(+) and pET32b(+). The latter added a thioredoxin fusion domain (Trx) in the N-terminal of the IsPETase. The obtained plasmids, pET28b(+)::IsPETase and pET32b(+)::Trx-IsPETase, were introduced into E. coli Rosetta-gamiTM2 (DE3) (Novagen, U.S) by heat shock transformation. The recombinant strains were grown at 37 °C in an LB medium supplemented with 35 μg/mL kanamycin or 100 μg/mL ampicillin as selection factors for the cells harboring pET28b(+)::IsPETase or pET32b(+)::Trx-IsPETase plasmids, respectively. The recombinant strains were cultivated in 300 mL of the LB medium at 37 °C until OD600nm = 0.6–1.0 was reached. Then, the production of IsPETase or Trx-IsPETase was induced by adding 1 mM isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and overnight incubation at 20 °C. IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase were purified from cell extracts by Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC). A HisTrap™ Fast Flow column installed in an ÄKTA start protein purification system (GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB, Uppsala, Sweden) was equilibrated with a binding buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, pH 7.4). Then, the cell extract was loaded. After a washing step, the bound proteins were eluted with an elution gradient using a buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, 500 mM imidazole, pH 7.4). The protein purity was analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), while the concentration was determined spectrophotometrically at 280 nm.
IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase were produced in Escherichia coli Rosetta-gamiTM2 (DE3) according to standard protocols [15,16]. The gene encoding the IsPETase from I. sakaiensis (GenBank accession code GAP38373.1) without a signal peptide (first 29 amino acids from the N-terminal) was chemically synthesized (GenScript USA Inc., Piscataway, NJ, USA) with codons optimized for E. coli and cloned into the expression vectors pET28b(+) and pET32b(+). The latter added a thioredoxin fusion domain (Trx) in the N-terminal of the IsPETase. The obtained plasmids, pET28b(+)::IsPETase and pET32b(+)::Trx-IsPETase, were introduced into E. coli Rosetta-gamiTM2 (DE3) (Novagen, U.S) by heat shock transformation. The recombinant strains were grown at 37 °C in an LB medium supplemented with 35 μg/mL kanamycin or 100 μg/mL ampicillin as selection factors for the cells harboring pET28b(+)::IsPETase or pET32b(+)::Trx-IsPETase plasmids, respectively. The recombinant strains were cultivated in 300 mL of the LB medium at 37 °C until OD600nm = 0.6–1.0 was reached. Then, the production of IsPETase or Trx-IsPETase was induced by adding 1 mM isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and overnight incubation at 20 °C. IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase were purified from cell extracts by Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC). A HisTrap™ Fast Flow column installed in an ÄKTA start protein purification system (GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB Uppsala, Sweden) was equilibrated with a binding buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, pH 7.4). Then, the cell extract was loaded. After a washing step, the bound proteins were eluted with an elution gradient using a buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, 500 mM imidazole, pH 7.4). The protein purity was analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), while the concentration was determined spectrophotometrically at 280 nm.
2.2. Polymer Preparation
The AkestraTM was a courtesy from Perstorp (intrinsic viscosity (IV)~0.64 dL/g, Tg~95 °C). The PET (Ramapet N180) was purchased from Indorama (IV~0.8 dL/g, Tg~78 °C, Tm~245 °C), and the PBT was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Mn~38,000 g/mol, Tm~203 °C). The PHT (Mn~26,000 g/mol, Mw~43,000 g/mol, IV~1.26, Tg~17 °C, Tm~140 °C) was synthesized according to a previously published protocol [11,12]. The PHT and Akestra™ were dissolved in chloroform and precipitated into methanol, and the resulting fine powders were dried in a vacuum oven for 12 h before use. The PET and PBT were dissolved in hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) and precipitated into methanol, and the resulting fine powders were dried in a vacuum oven for 12 h before use. Changes in crystallinity were assessed by differential scanning calorimetry.
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurements were performed using a TA Instruments DSC Q2000. The samples of PET, PBT, and PHT were studied with a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 under nitrogen with a purge rate of 50 mL min−1. The heating ramp was from 25 °C to 200 °C or 300 °C. It was observed that the crystallinity of the PET decreased from ~24% to ~11.3% after dissolution–precipitation, according to DSC analysis and calculated with the following equation:
where and are the heats of melting and cold crystallization, respectively, and is the heat of melting for a 100% crystalline polymer estimated to be 140 J/g [26]. No such change was observed for the PBT and PHT after precipitation, indicating that the original crystallinity degree was not affected by dissolution–precipitation (data not shown). Considering the theoretical = 140 J/g [42], the calculated degree of crystallinity of the PBT used was 38.6%. As PHT analysis did not show a cold crystallization temperature after precipitation, it was assumed that it was as a semicrystalline form.
2.4. Enzymatic Reactions
The reactions were prepared by soaking ~20 mg of Akestra, which is an amorphous polymer, semicrystalline PET, PBT, or PHT in 2 mL of a 50-mM phosphate buffer with a pH of 7.2, 10% (v/v) dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and 0.09–0.3 mg of freshly prepared enzyme [19,27,28,43]. All reactions were prepared in triplicate, including a negative control (reaction mixture without enzyme). The reactions, including the negative controls, were incubated at 37 °C with shaking at 200 rpm for a variable time from 7 to 240 h [16,17,19,27,28,32,43] for determining the apparent saturation curve for Txr-IsPETase and for 72 h for assessing the depolymerization activity against a series of polymers.
2.5. HPLC Analysis
Samples (0.5 mL of each reaction and the controls) were retrieved and diluted at a 1:1 ratio with DMSO, filtered (200-nm PTFE membrane), and transferred to HPLC vials for further analysis. An Ultimate 3000 RS (Dionex) equipped with a UV/Vis detector (SPD-20A) and a hydrophobic C18 column (Kinetex® 1.7 µm XB-C18 100 Å, LC Column 50 × 2.1 mm) was used to analyze the components of each sample. Mobile phases A (20%) and B (80%) consisted of acetonitrile and an aqueous solution containing 0.1% formic acid, respectively. The flow rate was fixed at 0.4 mL/min for 3 min of analysis per sample. Analytes containing TPA were detected at 260 nm. The HPLC method and data were processed with Chromeleon v. 6.8 software. The TPA and equivalents in the TPA were quantified using a standard curve of TPA and dissolved in DMSO in a range from 830 µg/L to 2 g/L.
2.6. LCMS Analysis
The separation was performed as described in Section 2.4 using a similar Ultimate 3000 RS HPLC-system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) coupled with an LTQ Velos Pro Ion trap mass spectrom (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using a heated electrospray ionization source (HESI-II). The samples were analyzed in full scan mode between m/z 100 and 400 in negative mode while employing a spray voltage of −3 kV.
2.7. Effec of the Enzymatic Activity on PET Crystalinity
The residual PET samples from enzymatic reactions and controls, after 9 days of incubation, were washed with detergent vortexing, rinsed with copious amounts of ultrapure water, and dried under airflow for 48 h. The final dry weights were measured and compared to the initial weights (~20 mg). The dried samples were subjected to DSC analysis (Section 2.3) to determine the thermal parameters.
2.8. Molecular Modeling of Trx-IsPETase
The structure of the Trx-IsPETase fusion protein was modeled using the atomic coordinates of the crystallized IsPETase (PDB: 5XJH) and thioredoxin domain (Trx) (PDB: 5E4W). All water molecules and ligands were removed from the crystallized structures. The interdomain linker structure was predicted by ab initio protein assembly using the QUARK [44,45] program. These three modules were manually assembled in YASARA [46], with the Trx domain in the N-terminal and the catalytic IsPET domain in the C-terminal, both connected by the interdomain linker. The resulting fusion protein was energetically optimized.
2.9. Molecular Dynamic Simulations
The modeled Trx-IsPETase and IsPET (PDB: 5XJH) were subjected to molecular dynamics simulations using GROMACS [47,48]. Each system included one protein solvated in TIP3P water molecules containing 0.15% CaCl2 ions into a box of a 10-Å extension from the protein. The calculations were performed by applying the OPLS-AA/L force field [49], periodic boundaries, 8-Å cut-off of short-range electrostatic and van der Waals forces, and long-range forces calculated by the particle mesh Ewald method. The simulations consisted of three steps: energy minimization, equilibrations, and production, as described in a previous publication [50]. After 500 ns of production, the root-mean-square deviations (RMSDs) of the alpha carbons and root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF) were calculated. The graphical analysis and molecular pictures were performed using UCSF Chimera software v. 1.15 [51].
2.10. Molecular Docking
The receptor was prepared from the IsPETase crystallographic structure (PDB: 6EQE). The ligands studied were PET monomer (bis-(hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET)), PBT monomer (bis-(hydroxybuthyl) terephthalate (BHBT)), PHT monomer (bis-(hydroxyhexyl) terephthalate (BHHT)), and an AkestraTM fragment (Figure 1). All ligands were modeled using the Avogadro program [52]. The molecular geometries were optimized through molecular mechanics using the MMFF94 force field, with 5000 steps, a steepest descent algorithm, and a convergence of 10e−7. All ligands were docked using Autodock Vina [53] implemented in YASARA [46]. Visual analysis was performed with USCF Chimera v. 1.15 [51].
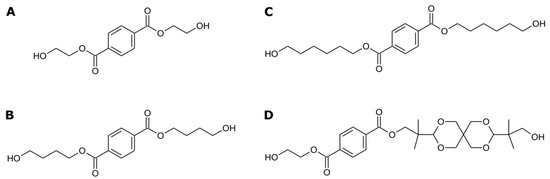
Figure 1.
Modeled ligands. (A) Bis-(hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET). (B) Bis-(hydroxybuthyl) terephthalate (BHBT). (C) Bis-(hydroxyhexyl) terephthalate (BHHT). (D) AkestraTM fragment.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Enzyme Production
Recombinant IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase were successfully produced as soluble enzymes in E. coli Rosetta-gamiTM2 (DE3). The SDS-PAGE analysis showed proteins of 31.5 and 43.5 kDa, which is consistent with the theoretically calculated molecular weights of IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase, respectively (Figure 2A). IsPETase had a production yield of 79 mg/L of culture, with an estimated purity higher than 90%, while Trx-IsPETase had a yield of 93 mg/L and purity of ~80%. A larger elution gradient was needed to achieve an acceptable purity compared with the Trx-IsPETase (Figure 2B). Furthermore, the purified Trx-IsPETase eluted in more concentrated fractions than the IsPETase, as shown by the shape of the peak in the purification chromatograms (Figure 2B). It is worth mentioning that IsPETase is sensitive to precipitation, which limits its production. To overcome this drawback, several strategies were evaluated, such as secretion systems, expression hosts, and the Trx fusion domain. The Trx domain together with the host strain E. coli Rosetta-gamiTM2, conferred the highest production level compared with other cytoplasmic and even some extracellular systems (Table 1).
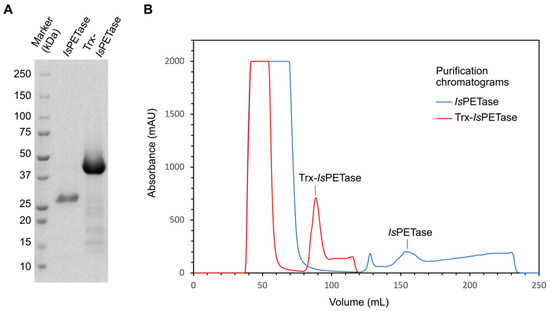
Figure 2.
Purification analysis of IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase. (A) SDS-PAGE. (B) IMAC purification chromatograms. The sharp peak at 130 mL of elution in the IsPETase purification chromatogram corresponds to impurities.

Table 1.
Production of recombinant IsPETase in different systems.
3.2. Product Profile and Activity of IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase
The products of both enzymes against PET were evaluated by HPLC. DMSO was used as a co-solvent for the depolymerization products. TPA, MHET, and BHET have low solubility in water. All controls containing the polymers, buffer, and DMSO did not show any detectable degrading effect of the DMSO under the same experimental conditions as the enzymatic reactions. Furthermore, dissolved products are required for analysis by HPLC.
The chromatograms showed the same product profiles (Figure 3A). With terephthalic acid (TPA) eluted at ~0.61 min, other peaks at ~0.76 and ~0.96 min were identified by HPLC-MS (Figure 3B) as mono-(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (MHET) and bis-(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET), respectively. According to the relative area of the peaks, MHET was the main product, followed by TPA, while BHET was present in a significantly smaller fraction.
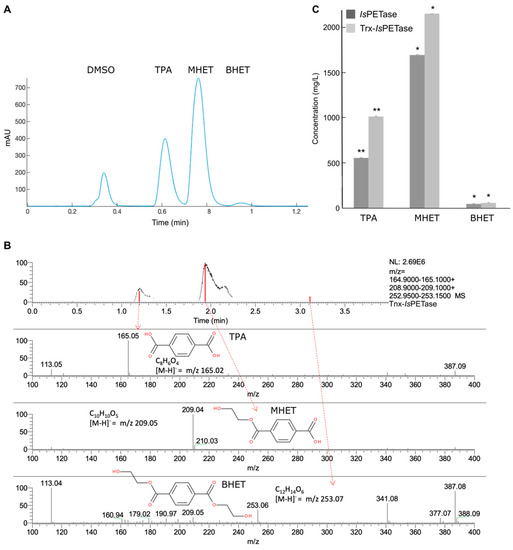
Figure 3.
Analysis of the products of the IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase activity on PET. (A) Both enzymes have the same product profile, where the main product is MHET, followed by TPA and a small fraction of BHET. (B) LC-MS analysis confirming the identity of TPA, MHET, and BHET. (C) Production of degradation products after 72 h. Trx-IsPETase showed higher activity than IsPETase for an independent samples student’s t-test where (*) p < 0.05 and (**) p < 0.01 (also see Table 2).
Trx-IsPETase showed slightly higher activity than IsPETase (Figure 3C). All resulting peaks from HPLC analysis mentioned in this section were regarded as terephthalic acid equivalents (TPAeq), assuming the same molar extinction coefficient ε = 17,000 M−1cm−1 conferred by the aromatic ring. Thus, the calculated TPAeq produced could be determined. The total amount of degraded polymer could be calculated using the TPAeq and the repeating molecular weight (192 g/mol). The results of the depolymerization are shown in Table 1. The degree of depolymerization after 72 h by IsPETase was 23%, and for Trx-IsPETase, it was 32%. The enzyme/PET ratio was slightly higher for Trx-IsPETase (0.005) than IsPETase (0.004). However, the specific activity, defined here as the mg of product per mg of enzyme and time (mg degradation products/mg enzyme h−1 or h−1), gave a higher value for Trx-IsPETase (0.7 h−1) than IsPETase (0.9 h−1) (Table 2). Although the differences were not remarkable, the student’s t-test gave a statistically significant higher product formation for Trx-IsPETase than IsPETase (Figure 3C).

Table 2.
PET depolymerization activity of IsPETase and Trx-IsPETase. Degradation products consist of the sum of the TPA, MHET, and BHET quantified.
The dynamic stability of Trx-IsPETase was determined by monitoring the formation of the product for 240 h. The degradation products increased in concentration during the first 72 h until reaching saturation (Figure 4). The saturation was attributed to the inactivation of the enzyme and not to the completion of the reaction, since the substrate conversion reached ~35%. The apparent inactivation rate constant () was determined according to first-order kinetics with the coexistence of a sufficient substrate (20 mg PET per 2 mL) [56]:
where is the degradation products concentration, is the enzyme concentration, and and are the initial enzyme activity in a given time (). The integrate form describes the apparent saturation curve (Figure 4). Thus, yielded 0.09 h−1, and yielded .
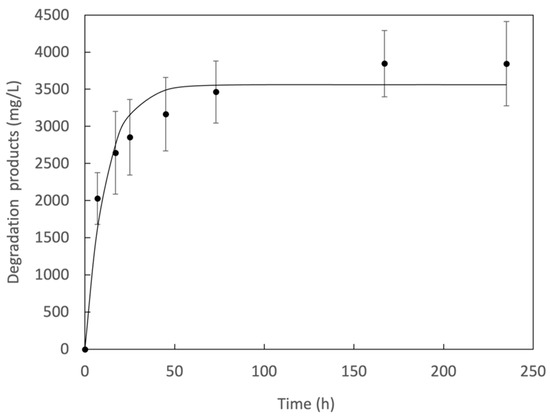
Figure 4.
Apparent saturation curve of the PET depolymerization activity of Trx-IsPETase.
We noticed that the enzymatic reactions apparently showed an impact on the crystallinity (or re-crystallization rate) of the residual PET, as indicated by the DSC results (Figure 5). The DSC analysis showed a cold crystallization peak at 122 °C in all three enzymatically treated PET samples, while the control did not (Figure 5). The measured crystallinity of the residual PET after enzymatic reaction (~22%) or the control (30.5%) was higher than that of the initial PET powder sample (~11%). This suggests that PET, prepared by precipitation, could re-crystallize under the reaction conditions. Thus, assuming that the Trx-IsPETase primarily attacks amorphous regions, it may retard the re-crystallization rate. We should emphasize that the observed change of crystallinity of the PET was likely a complex consequence including the cold re-crystallization process under the reaction conditions, selectivity of the enzymatic degradation of the crystalline and amorphous regions, and the possible influence of the enzyme on the rate of re-crystallization. More thorough investigations on the crystallization processes will be needed to allow for deeper insight into the impact of enzymes on the crystallization rate and crystallinity of PET.
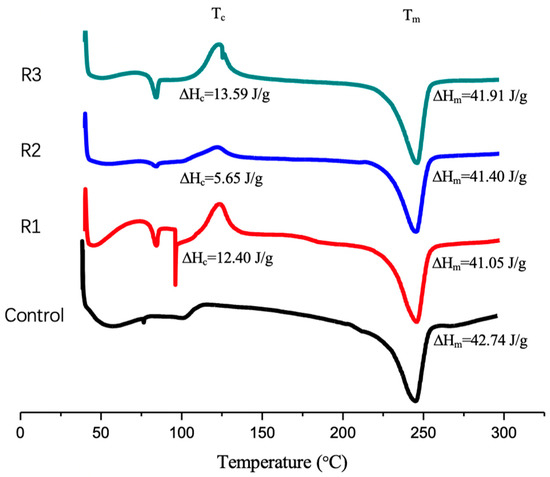
Figure 5.
DSC diagrams of PET samples treated with Trx-IsPETase (R1, R2, and R3 denote three independent reactions) and the control without the enzyme. Notice that all enzymatic reactions produced a cold crystallization peak (Tc) at 122 °C, while the control did not.
On the other hand, the residual weight of the enzymatically treated PET corresponded to 34 ± 5% degradation at 235 h, consistent with the percentage of degradation calculated by the HPLC method at 72 h (Table 2), considering that the reactions reached saturation at the maximum product formation at 72 h.
3.3. Structural Studies
The obtained molecular structure of Trx-IsPETase included a Trx domain in the N-terminal, followed by an interdomain linker module and the catalytic domain in the C-terminal (Figure 6A). Two amino acids, Met1 and Ser2, were added in the N-terminal of the Trx domain, which extends until Ser111. The interdomain linker starts in Gly112 and ends in Ala169. The catalytic domain encompasses Arg170, which corresponds to the Arg34 in the IsPETase, to Ser426, which corresponds to Ser290 in IsPETase. While the Trx and catalytic domains were obtained from crystallographic structures, the interdomain linker structure was predicted using an ab initio approach. It was modeled as a structure composed of three α-helices, with the third one containing six histidines used in the purification by affinity chromatography (IMAC) (Figure 6A).
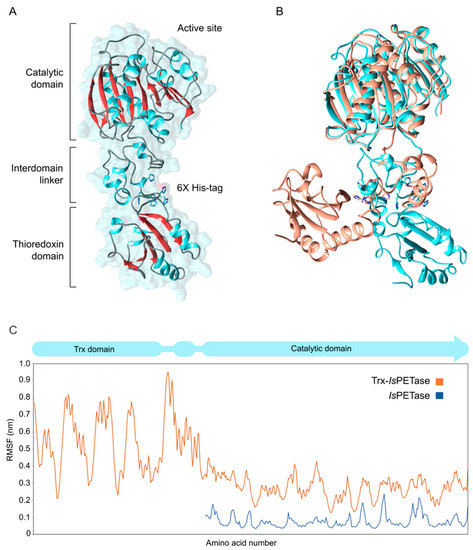
Figure 6.
Molecular structure and dynamics of Trx-IsPETase. (A) Average molecular model of Trx-IsPETase after 500 ns of molecular dynamic simulations. (B) Overlapped structures of Trx-IsPETase before MD simulations (in orange) in closed form and average structure (in cyan) in open form. (C) RSMF analysis of Trx-IsPETase and IsPETase.
The initial structure of Trx-IsPETase was obtained in a closed-form conformation, with the Trx domain oriented toward the catalytic domain (Figure 6B). Although this structure was energetically minimized, molecular dynamics simulations showed a significant conformational change, giving an open-shaped conformation (Figure 6B,C). which resulted in a more energetically favorable structure.
3.4. IsPETase Activity on Terephthalate Aromatic Polyesters
PET, PBT, PHT, and AkestraTM were used as substrates for IsPETase. In all cases, the main product was TPA (Figure 7), unlike previous reactions where MHET was the predominant product of PET depolymerization (Figure 3A). This could be due to the substantially higher amount of enzyme used for these substrates (0.01 mg IsPETase per mg of the substrate). The enzymatic products were quantified as TPAeq, and the percentage of depolymerization was calculated as described in Section 3.2. Thus, PET showed remarkable enzymatic depolymerization (39%) compared with the other polymers (<0.25%) (Table 3). Interestingly, although by far, the second-best substrate was PBT, followed by PHT and Akestra™, suggesting a correlation of IsPETase activity with the length and size of the TPA linker group present on the polymer.
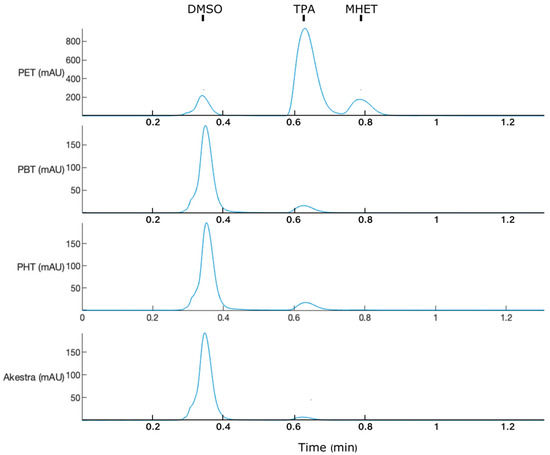
Figure 7.
HPLC analysis of IsPETase depolymerization of terephthalate polyesters after 72 h: poly(ethylene) terephthalate (PET), poly(butylene) terephthalate (PBT), poly(hexamethylene) terephthalate PHT), and Akestra™.

Table 3.
Depolymerization of different terephthalate polyesters after 72 h with an IsPETase/substrate ratio of 0.01 (mg/mg).
The ligand binding modes were studied by coupling monomers BHET, BHBT, BHHT, and an AkestraTM fragment at subsite I of IsPETase (Figure 8). The complexes obtained were compared with the co-crystallized structure of the hydroxyethyl methyl terephthalate (HEMT)/IsPETase double mutant (PDB: 5XH3). This mutant has glycine instead of arginine 132 and alanine instead of nucleophilic serine 160 (corresponding to R103G/S131A in 5XH3) [23]. The coupled BHET, corresponding to a PET monomer, had the same pose as the co-crystallized HEMT analog (Figure 8A), indicating a reliable coupling prediction, and no further refinements were needed. Indeed, the aromatic and carbonyl groups of all the ligands overlapped very well with the corresponding groups of HEMT (Figure 8B–D). Therefore, the main interactions between the studied ligands and the subsite I were conserved. It was suggested that Trp 185 and Trp 159 form p-p interactions with the aromatic groups of the ligands at subsites I and II, respectively [17]. In the complexes obtained here, Trp 185 forms p-p interactions with all ligands. However, the length of the diol linkers in BHBT and BHHT seems unfavorable for an interaction of a second aromatic ring with Trp 159. Interestingly, one of the m-dioxane rings of the AkestraTM fragment formed a hydrophobic interaction with Trp 159 (Figure 8D), but the complexity of its polymeric form could significantly reduce the enzyme’s access to ester linkages. Therefore, the low IsPETase activity in PBT, PHT, and AkestraTM could be attributed to limited access or unfavorable interactions at subsite II.
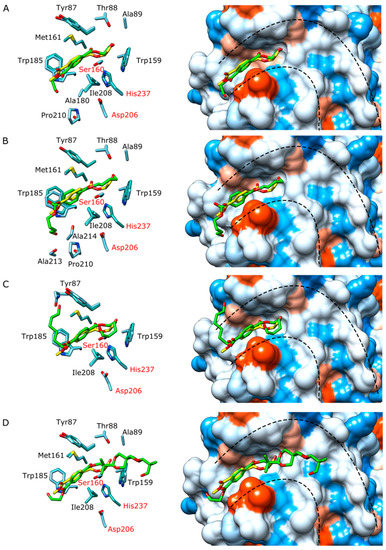
Figure 8.
Docking of different ligands (represented in green) into IsPETase (in cyan) subsite I. The whole active site is indicated with segmented lines. The hydrophobicity surfaces of the active sites are represented according to the Kyte-Doolittle scale, ranging from dodger blue for the most hydrophilic to white and to orange-red for the most hydrophobic [57]. Every obtained enzyme/ligand complex is overlapped with the co-crystallized structure HEMT/double mutant IsPETase (5XH3), where the HEMT is represented in yellow and the mutant IsPETase is in light sea green. The catalytic amino acids are labeled in red. (A) BHET/IsPETase. (B) BHBT/IsPETase. (C) BHHT/IsPETase. (D) AkestraTM fragment/IsPETase.
4. Conclusions
The thioredoxin fusion domain confers a positive effect both in production as well as in PET depolymerization activity. Aside from that, the structural molecular modeling and dynamics showed that the Trx domain neither interfered with the active site nor induced significant conformational changes in the catalytic domain.
On the other hand, IsPETase showed remarkable PET-depolymerizing activity compared with PBT, PHT, and AkestraTM. These results suggest that larger or bulkier TPA linkers negatively affect the interaction of polyesters with the enzyme.
The enzymatic depolymerization of terephthalate aromatic polyesters other than PET is an open field to be explored, both by discovering novel enzymes or engineering polyethylene terephthalate hydrolases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.A.L.-P. and B.Z.; methodology, P.W.-E., V.T., P.W. and C.G.; software, P.W.-E. and J.A.L.-P.; validation, P.W.-E., V.T., P.W. and C.G.; formal analysis, J.A.L.-P., P.W.-E., V.T., P.W., C.G. and B.Z.; investigation, J.A.L.-P., P.W.-E., V.T., P.W., C.G. and B.Z.; resources, J.A.L.-P. and B.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, P.W.-E. and J.A.L.-P.; writing—review and editing, J.A.L.-P., P.W.-E., V.T., P.W., C.G. and B.Z.; supervision, J.A.L.-P. and B.Z.; project administration, J.A.L.-P.; funding acquisition, J.A.L.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Crafoord Foundation, grant number 2020-0774.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The files of the models presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. Other data are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
The molecular dynamic simulations were enabled by resources provided by the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing (SNIC) at Lunarc at Lund University and Uppmax at Uppsala University, partially founded by the Swedish Research Council through a grant agreement (No. 2018-05973).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Mendenhall, E. Oceans of plastic: A research agenda to propel policy development. Mar. Policy 2018, 96, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forrest, A.; Giacovazzi, L.; Dunlop, S.; Reisser, J.; Tickler, D.; Jamieson, A.; Meeuwig, J.J. Eliminating Plastic Pollution: How a Voluntary Contribution From Industry Will Drive the Circular Plastics Economy. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthos, D.; Walker, T.R. International policies to reduce plastic marine pollution from single-use plastics (plastic bags and microbeads): A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association of Plastic Manufacturers; BPE. Plastics—The Facts 2019—An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data; BPE: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lionetto, F.; Esposito Corcione, C. An Overview of the Sorption Studies of Contaminants on Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) Microplastics in the Marine Environment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönmayr, D. Automotive Recycling, Plastics, and Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Welle, F. Twenty years of PET bottle to bottle recycling—An overview. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic degradation and its environmental implications with special reference to poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2013, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, N.; Kumar, P.; Shrivastava, S.; Ghosh, S.B. An overview on PET waste recycling for application in packaging. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2017, 21, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankar, S.V.; Garcia Gonzalez, M.N.; Warlin, N.; Valsange, N.G.; Rehnberg, N.; Lundmark, S.; Jannasch, P.; Zhang, B. Synthesis, Life Cycle Assessment, and Polymerization of a Vanillin-Based Spirocyclic Diol toward Polyesters with Increased Glass-Transition Temperature. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19090–19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warlin, N.; Gonzalez, M.N.G.; Mankar, S.; Valsange, N.G.; Sayed, M.; Pyo, S.-H.; Rehnberg, N.; Lundmark, S.; Hatti-Kaul, R.; Jannasch, P. A rigid spirocyclic diol from fructose-based 5-hydroxymethylfurfural: Synthesis, life-cycle assessment, and polymerization for renewable polyesters and poly(urethane-urea)s. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 6667–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, K.; Qiao, R.; Chen, S.; Luo, H.; Zhang, D. Enhanced permittivity in polymer blends via tailoring the orderliness of semiconductive liquid crystalline polymers and intermolecular interactions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 8440–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qu, Y. Biodegradation and biotransformation of indole: Advances and perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arza, C.R.; Wang, P.; Linares-Pastén, J.; Zhang, B. Synthesis, thermal, rheological characteristics, and enzymatic degradation of aliphatic polyesters with lignin-based aromatic pendant groups. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Linares-Pastén, J.; Zhang, B. Synthesis, molecular docking simulation and enzymatic degradation of AB-type indole-based polyesters with improved thermal properties. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.; Cho, I.J.; Seo, H.; Son, H.F.; Sagong, H.-Y.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-J. Structural insight into molecular mechanism of poly(ethylene terephthalate) degradation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshti, R.; Mehta, L.; Samarth, N. Biological Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate: A Mini-Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3520–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Rorrer, N.A.; Nicholson, S.R.; Erickson, E.; DesVeaux, J.S.; Avelino, A.F.; Lamers, P.; Bhatt, A.; Zhang, Y.; Avery, G. Techno-economic, life-cycle, and socioeconomic impact analysis of enzymatic recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Joule 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Fontana, G.; Mossotti, R.; Montarsolo, A. Assessment of microplastics release from polyester fabrics: The impact of different washing conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 113960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.J.; Schrader, H.; Profe, J.; Dresler, K.; Deckwer, W.D. Enzymatic degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate): Rapid hydrolyse using a hydrolase from T. fusca. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F. The current state of research on PET hydrolyzing enzymes available for biorecycling. Catalysts 2021, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, V.; Topham, C.; Gilles, A.; David, B.; Folgoas, C.; Moya-Leclair, E.; Kamionka, E.; Desrousseaux, M.-L.; Texier, H.; Gavalda, S. An engineered PET depolymerase to break down and recycle plastic bottles. Nature 2020, 580, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Y.; He, L.; Luo, Y.; Bao, R. IsPETase Is a Novel Biocatalyst for Poly(ethylene terephthalate)(PET) Hydrolysis. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Ni, K.; Hao, H.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Qian, Z. Secretory expression in Bacillus subtilis and biochemical characterization of a highly thermostable polyethylene terephthalate hydrolase from bacterium HR29. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 143, 109715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecker, T.; Galaz-Davison, P.; Engelberger, F.; Narui, Y.; Sotomayor, M.; Parra, L.P.; Ramírez-Sarmiento, C.A. Active site flexibility as a hallmark for efficient PET degradation by I. sakaiensis PETase. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.-W.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ko, T.-P.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Guo, R.-T. Structural insight into catalytic mechanism of PET hydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; He, L.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y.; Bao, R. Protein crystallography and site-direct mutagenesis analysis of the poly(ethylene terephthalate) hydrolase PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boneta, S.; Arafet, K.; Moliner, V. QM/MM Study of the Enzymatic Biodegradation Mechanism of Polyethylene Terephthalate. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2021, 61, 3041–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, C.H.S.; Dos Santos, A.M.; Alves, C.N.; Martí, S.; Moliner, V.; Santana, K.; Lameira, J. Assessment of the PETase Conformational Changes Induced by Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Binding. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, H.P.; Allen, M.D.; Donohoe, B.S.; Rorrer, N.A.; Kearns, F.L.; Silveira, R.L.; Pollard, B.C.; Dominick, G.; Duman, R.; El Omari, K. Characterization and engineering of a plastic-degrading aromatic polyesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4350–E4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, S.; Tian, Y.e.; Qiao, Y.; Mitra, R.; Han, J.; Li, C.; Han, X. Computational redesign of a PETase for plastic biodegradation under ambient condition by the GRAPE strategy. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.F.; Cho, I.J.; Joo, S.; Seo, H.; Sagong, H.-Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-J. Rational protein engineering of thermo-stable PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis for highly efficient PET degradation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3519–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.F.; Joo, S.; Seo, H.; Sagong, H.-Y.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, H.; Kim, K.-J. Structural bioinformatics-based protein engineering of thermo-stable PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 141, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, N. Protein engineering of stable IsPETase for PET plastic degradation by Premuse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Pan, H.; Lian, J. Recent Advances in the Discovery, Characterization, and Engineering of Poly(ethylene terephthalate)(PET) Hydrolases. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 150, 109868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šerá, J.; Serbruyns, L.; De Wilde, B.; Koutný, M. Accelerated biodegradation testing of slowly degradable polyesters in soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 171, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhang, K.; Kai, D.; Li, Z.; Loh, X.J. Polyester elastomers for soft tissue engineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4545–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellis, A.; Acero, E.H.; Ferrario, V.; Ribitsch, D.; Guebitz, G.M.; Gardossi, L. The closure of the cycle: Enzymatic synthesis and functionalization of bio-based polyesters. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woźniak-Braszak, A.; Jurga, J.; Jurga, K.; Brycki, B.; Hołderna-Natkaniec, K. Investigation of molecular reorientation in poly(butylene terephthalate)/decylamine/fullerene nanocomposites. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Kim, S.; Son, H.F.; Sagong, H.-Y.; Joo, S.; Kim, K.-J. Production of extracellular PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis using sec-dependent signal peptides in E. coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Ab initio protein structure assembly using continuous structure fragments and optimized knowledge-based force field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Toward optimal fragment generations for ab initio protein structure assembly. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2013, 81, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krieger, E.; Koraimann, G.; Vriend, G. Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA—A self-parameterizing force field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2002, 47, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.; van der Spoel, D.; van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaminski, G.A.; Friesner, R.A.; Tirado-Rives, J.; Jorgensen, W.L. Evaluation and reparametrization of the OPLS-AA force field for proteins via comparison with accurate quantum chemical calculations on peptides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 6474–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Pastén, J.A.; Jonsdottir, L.B.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Fridjonsson, O.H.; Watzlawick, H.; Karlsson, E.N. Modeled 3D-Structures of Proteobacterial Transglycosylases from Glycoside Hydrolase Family 17 Give Insight in Ligand Interactions Explaining Differences in Transglycosylation Products. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woestenburg, B.; Meijnster, L. Production of IsPETase in an engineered E. coli BL21. Avans J. Biotechnol. 2021, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Qiu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Du, C.; Dong, W.; Cheng, C.; He, B. Excretory expression of IsPETase in E. coli by an enhancer of signal peptides and enhanced PET hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyawaki, O.; Kanazawa, T.; Maruyama, C.; Dozen, M. Static and dynamic half-life and lifetime molecular turnover of enzymes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).