Abstract
Aiming at the problem that mining conveyor belts are easily damaged under severe working conditions, the paper proposed a deep learning-based conveyor belt damage detection method. To further explore the possibility of the application of lightweight CNNs in the detection of conveyor belt damage, the paper deeply integrates the MobileNet and Yolov4 network to achieve the lightweight of Yolov4, and performs a test on the exiting conveyor belt damage dataset containing 3000 images. The test results show that the lightweight network can effectively detect the damage of the conveyor belt, with the fastest test speed 70.26 FPS, and the highest test accuracy 93.22%. Compared with the original Yolov4, the accuracy increased by 3.5% with the speed increased by 188%. By comparing other existing detection methods, the strong generalization ability of the model is verified, which provides technical support and empirical reference for the visual monitoring and intelligent development of belt conveyors.
1. Introduction
Belt conveyor is one of the most important transportation equipment in the field of bulk material transportation, widely used in coal mines, docks, ports, chemical industries, and other fields. At present, it is developing towards long-distance, high-speed, small-radius space turning, and intelligence [1]. The intelligentization of belt conveyors refers to the realization of self-perception and status adjustment of its operating status through modern sensing technology and artificial intelligence, while the realization of autonomous operation and unattended operation of the equipment [2,3].
The intelligent transportation system is a safe, efficient, intelligent, and unmanned transportation system that integrates advanced technologies such as intelligent driving, intelligent control, intelligent operation and maintenance, and unmanned driving. Its core lies in intelligent mining transportation equipments [4]. The current research work on the intelligent development of belt conveyors is focused on: energy-efficient equipment or energy-saving technology for belt conveyors, especially load-based energy-saving speed regulation systems for belt conveyors [5,6,7,8,9,10,11]; expert-based fault diagnosis systems based on noise and vibration monitoring [12,13]; running state detection technology based on vision and image processing: including deviation monitoring [14], belt speed monitoring [15], material flow detection [16], foreign body identification [17], tear detection, roller temperature monitoring [18], etc. This article focuses on the visual monitoring of mining conveyor belt damage.
Conveyor belt, as an important component of belt conveyor, plays an important role in carrying materials and traction, with its cost accounts for 30–50% of the total price of belt conveyor [19]. The health of the conveyor belt seriously affects the normal operation of the belt conveyor, which in turn affects the safe and efficient production of the entire enterprise. In the actual production process, conveyor belts often suffer problems such as the falling material impact, chute jamming, piercing by a foreign body, etc., which can easily cause abnormal damage to the conveyor belt, thereby shortening the service life of the conveyor belt and increasing production costs. Further, if the damage of the conveyor belt cannot be detected and treated in time, it may eventually cause the occurrence of the conveyor belt tearing accident, which will cause greater harm. The current detection methods for conveyor belt tearing include: weak magnetic test [20], built-in sensor chip method [21], machine vision method [22,23,24,25], line laser-assisted method [26], infrared camera assisted method [27,28,29,30], audio-visual fusion method [31].Among them, most of the research work only focuses on the detection of tearing of conveyor belt, without the detection of other types of damage, which has a certain limitation.
As for the detection of multiple forms of conveyor belt damage, relatively little research work has been done on the subject. A conveyor belt damage detection method based on ADCN (Adaptive Deep Convolutional Network), which is essentially a variant of SPP-Yolov3, was mentioned in Ref. [32], enabling the detection of both Scratch and Tearing damage states. Then a deep learning-based detection method was mentioned in Ref. [3]: by constructing a conveyor belt damage dataset and classifying the belt damage types into four categories, namely surface wear, surface damage, breakdown, and tear, an Efficientnet-Yolov3-based target detection network was proposed to classify and locate the damage, achieved the highest prediction accuracy of 97.26% and the fastest prediction speed effect of 42 FPS on the dataset.
The work of this paper mainly focuses on improving the detection speed of conveyor belt damage based on deep learning method, which is to be realized through the lightweight of target detection network. As the conveyor belt moves faster, cameras with a higher frame rate are needed to capture clear and stable images of the conveyor belt surface. Otherwise, missing detection or moving shadows may occur. At the same time, if the processing speed or prediction speed is not accelerated, the image input and signal output will be out of sync, which is easy to cause delay and lag, also affect the detection results. Therefore, this paper mainly discusses the application and performance of lightweight convolutional neural network in conveyor belt damage detection, which is suitable for scene resources with limited storage space and computing capacity, and also meets the needs of the development of high speed belt conveyor.
There are various ways to achieve lightweighting of neural networks, in terms of the network structure, a target detection network could be divided into two parts, one is the backbone feature extraction network, and the other is the prediction network. The quality of the features extracted by the feature extraction network directly affects the prediction effect of the prediction network. Similarly, the number of parameters and calculations of the backbone feature extraction network also directly affect the detection speed of the target detection network. Generally, the number of parameters is positively correlated with the detection accuracy while negatively with the detection speed. At present, the tricks to reduce the amount of parameters in CNNs include: using separable convolution [33], depthwise separable convolution [33,34,35], group convolution [36]; using global pooling to replace the fully connected layers(FC) [37], using filter to achieve dimensionality reduction [34], etc., which are more representative by SqueezeNet [38], MobileNet and ShuffleNet [39]. Among them, SqueezeNet adopts a well-designed compression and expansion structure, MobileNet uses a more efficient depthwise separable convolution, and ShuffleNet proposes a channel shuffling operation, which further reduces the computational complexity of the model. The lightweight measures taken in this article are based on MobileNet. By replacing the backbone CSPDarknet53 of Yolov4 with MobileNet, the use of depthwise separable convolution is directly realized, and a lightweight model of Yolov4 network is obtained, and then it is applied to the detection of conveyor belt damage. Theoretically, the detection speed should be faster, and can meet the needs of the development of high-speed conveyor.
2. Principles and Methodology
With the rapid development of computer technology, deep convolutional neural networks have been promoted and are now the mainstream research method in the field of target detection, thanks to their better performance and the complete automation of feature engineering, even replacing the traditional target detection algorithm based on region filtering + feature extraction + feature classification, and eliminating the need to manually design feature extractors, which has been widely used in areas such as handwritten text transcription, image search, autonomous driving, pose estimation and instance segmentation.
Supervised learning-based target detection methods at the current stage can be divided into two categories: The first category is based on the anchor mechanism, and the second is based on the anchor-free or key-point mechanism. While the target detection algorithm based on the anchor mechanism can be roughly divided into two types: one-stage and two-stage. Two-stage target detection algorithms based on candidate regions, which first generate candidate frames through regional proposal networks (RPN), and then use convolutional neural networks for classification and non-maximum suppression (NMS) to remove the duplicated detections for the same instance by computing Intersection over Union (IoU). The process is more accurate but slower and difficult to meet real-time requirements due to more candidate frames, such as the R-CNN series [40,41]; And one-stage target detection algorithms based on regression, represented by SSD (Single Shot MultiBox Detector) and YOLO (You only look once) [42,43], one-stage detectors slide a complex arrangement of possible bounding boxes, called anchors, over the image and classify them directly without specifying the box content. Then the algorithm based on anchor-free or key-point mechanism detects directly by learning the key features of the input image instead of generating a series of anchor box, omitting the process of RPN(Region Proposal Network) and NMS(Non-Maximum Suppression), which makes the prediction process more direct and faster, and the representative algorithms include CornerNet, FCOS, ExtremeNet, CenterNet, etc.
The research of this paper is based on Yolov4 [44], through combining the MobileNet backbone feature extraction network with the Yolov4 network to simplify the Yolov4, thereby reducing the number of parameters and achieving the purpose of improving the detection speed.
2.1. Network Structure and Improvement Methods
MobileNet is an excellent lightweight deep neural network proposed by Google, which includes three versions of V1 [34], V2 [35], and V3 [45]. MobileNet V1 uses depthwise separable convolution instead of standard convolution to achieve feature extraction, which greatly reduces the number of parameters and calculations, making its calculations times that of standard convolutions. When the input is an RGB image, and the size of the convolution kernel is 3 × 3, the calculation amount can be reduced to about 1/9 of the standard convolution. The principle can refer to Figure 1 and Equations (1)–(4). At the same time, the channel number scaling adjustment factor and the input image resolution adjustment factor were introduced to adjust the number of channels in each layer of the network and the input image resolution respectively, to further compress the computational effort, while the parameter amount or calculation amount of the model is positively correlated with and .
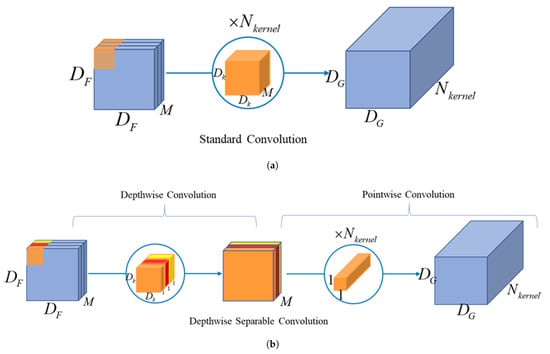
Figure 1.
The structure comparison of depthwise separable convolution and standard convolution: (a) structure of standard convolution (b) structure of depthwise separable convolution( It is assumed that the output feature map has the same spatial dimensions as the input and both feature maps are square).
The parameter calculation method of depthwise separable convolution and standard convolution can be based on Equations (1)–(4), and at the same time, according to Equation (5), the comparison of the parameters of the two can be obtained.
In the formula, , , means the number of parameters and calculation of standard convolution, , , means the number of parameters and calculation of depthwise separable convolution. is the kernel size, is the number of the kernel, is the input size.
MobilenetV2 continues to use depthwise separable convolution based on MobilenetV1, and uses an inverted residual connection similar to the residual network, as shown in Figure 2. Considering that a large amount of feature information cannot be extracted by applying a convolutional layer to filter low-dimensional tensors, MobilenetV2 uses an expansion convolution layer to obtain a large tensor, uses depthwise convolution to filter the data, and then uses a projection layer to reduce the tensor [35]. By adjusting the low-dimensional tensor, the parameter amount of MobilenetV2 is reduced to about 80% of V1, and the speed is increased by about 33%.
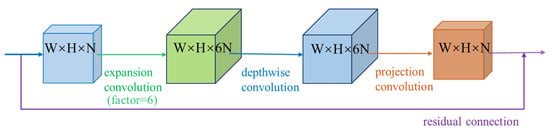
Figure 2.
The structure of the inverted residual connection in MobilenetV2.
MobilenetV3 was designed mainly based on a combination of complementary search techniques, through a combination of hardware-aware network architecture search (NAS) complemented by the NetAdapt algorithm [45]. The former(NAS) is used to search the various modules of the network under the premise of limited calculation and parameter quantity, also called Block-wise Search, and the latter(NetAdapt) is used to fine-tune the network layer after each module is determined; At the same time, it continues the depthwise separable convolution of MobilenetV1 and the bottleneck with the residual structure of MobilenetV2. On this basis, a lightweight attention model based on the squeeze and excitation structure in SENet was also added to adjust the number of channels, as shown in Figure 3; Besides, h-swish was used as the activation instead of the swish to reduce the amount of calculation and improve the performance.
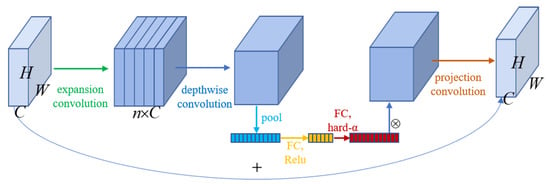
Figure 3.
The structure of the bneck in MobilenetV3.
As an improved version of Yolov3, Yolov4 has made many improvements on the basis of Yolov3. The network structure is shown in Figure 4. CSPDarknet53 is used instead of Darknet53 as the backbone feature extraction network. The use of CSPnet enables the fusion of high-level and low-level semantic information and reduces the loss. SPPnet and PAnet are used to expand the receptive field and repeatedly extract image features, which greatly improves the feature extraction capability. Same as Yolov3, Yolov4 also uses the extracted feature information to make predictions through YoloHead.
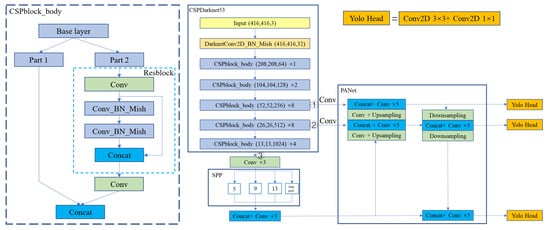
Figure 4.
The structure of YoloV4.
It can be seen from Figure 4 that three feature layers from the backbone feature extraction network were extracted for feature enhancement of SPPnet and PAnet in YoloV4, and then were passed to YoloHead for prediction. In order to realize the lightweight Yolov4 network structure, the paper proposed to replace the backbone feature extraction network CSPDarknet53 of YoloV4 with MobileNet, continue to use the feature fusion and feature enhancement strategy in the original YoloV4, and make predictions through YoloHead. In this paper, the structure of MobilenetV1-YoloV4 is used to explain the replacement operation, and the structure or replacement principle of MobilenetV2-YoloV4 and MobilenetV3-YoloV4 is the same. In YoloV4, the feature layers input to the SPPnet or PAnet are the original images compressed 3, 4, and 5 times. Similarly, in the MobilenetV1 network, we pass the feature layers which compressed 3, 4, and 5 times into the subsequent feature enhancement, as shown in Figure 5; At the same time, we also change the number of channels of the layers by adjusting the value of to achieve different degrees of lightness. In addition, we have taken a small trick, that is replacing the convolution in PAnet with a depthwise separable convolution, to better reduce the number of parameters.
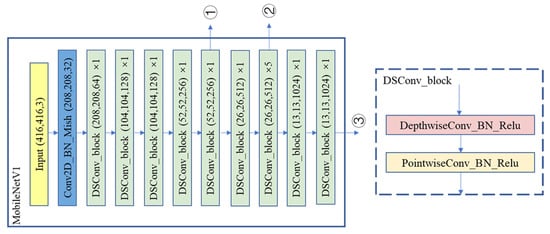
Figure 5.
The backbone feature extraction network of MobilenetV1.
2.2. Calculation of Loss-Function
The loss function during network training consists of three parts: regression loss , classification loss , and confidence loss . Among them, the regression loss refers to the error between the position and width of the prediction box and the true label; the classification loss refers to the error between the prediction classification and the real classification, and the confidence loss is relevant to the confidence score of the predicted value of each bounding box. The calculation method of the loss function is shown in Equations (6)–(11). The regression loss of the prediction frame is calculated by function, and the scale information of the overlap, center distance, and aspect ratio of the frame is considered based on , which can better ensure the stability of the training process; the calculation of confidence loss and classification loss uses cross-entropy function.
In the equation, — the intersection ratio between the predicted box and the real labeled box; — the Euclidean distance between the predicted box and the line point in the real labeled box; m — the diagonal distance of the smallest enclosed area that contains both the predicted box and the real labeled box; — weight function; —length-to-width ratio similarity measurement coefficient; —width and height of the real label box; — width and height of the prediction box; — number of grids; B — prediction box on each grid; — the target is included in the prediction frame; — the target is not included in the prediction frame; —prediction confidence; — true confidence; — calculation coefficient set by yourself; c — target classification number; — the true probability that the target in the frame belongs to a certain category; — the predicted probability that the target in the frame belongs to a certain category.
2.3. Operating Environment and Parameter Settings:
The rapid development of neural networks is based on the development of computers and mathematics. The powerful computing power of computers makes it possible to detect objects based on deep learning. With limited computing resources, the width, depth, and resolution of the input image will all affect the parameters of the network, thereby affecting the calculation and prediction speed [46]. This is also the purpose of this paper to explore the application possibilities of lightweight neural networks in conveyor belt damage detection. It aims to improve the speed of the algorithm while ensuring the accuracy of the model as much as possible through the lightweight of the model under limited computing resources, in order to meet the needs of belt conveyors with high belt speed.
The running and testing environment of the algorithm in this paper is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Algorithm running environment.
2.4. Data Preparation
The conveyor belt damage dataset used in this paper is provided in Ref. [3], which contains 3000 images. The damage types are divided into four categories: surface wear, surface damage, tear and breakdown, and each type of damage occupies 1/4. The establishment of the dataset was completed through manual labeling, and finally stored in the format of VOC2007.
During the training process, the Mosaic and CutMix data enhancement strategies were used to increase the variability of the input image, enrich the image background information, and improve the robustness and generalization ability of the model. At the same time, the gradually decreasing learning rate was used to train 100 Epoch, the initial learning rate was , and dropped to 1/10 of the previous value at 50 Epoch and 80 Epoch, and the Batch size was set to 16.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Detection Results of Unscaled Networks
In actual engineering practice, the superiority of an algorithm is usually measured by the mean Average Precision (mAP) and the test speed FPS. mAP, the average value of AP of each class of objects, is the average value of AP obtained by multiple verification set individuals, which measures the overall detection accuracy of the algorithm. FPS, which is the frame rate that can be processed per second, is used to measure the processing speed of the algorithm.
Figure 6 shows the detection results of MobilenetV3-YoloV4-1.0 (1.0 means = 1.0, that is, the channel number scaling factor is 1.0) on the dataset of this article. Figure 6a–d corresponds to the damage types in order of tear, breakdown, damage, and surface wear; it can be seen that this algorithm can better realize the detection of multiple damage types.
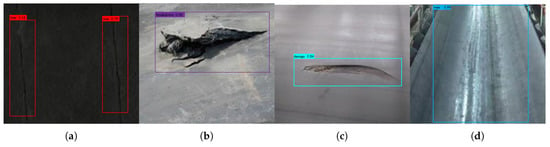
Figure 6.
The detection results of the target detection algorithm on the dataset: (a) tear, (b) breakdown, (c) damage, (d) surface wear.
Table 2 shows the results achieved by multiple models quantitatively, including the prediction accuracy (AP), mean Average Precision(mAP) and prediction speed (FPS) of the various algorithms for the various damage types. The data in Table 2 can be divided into three parts: The first part is the result using 7 current mainstream target detection algorithms, including Two-stage target detection algorithm: Faster R-CNN, One-stage detection algorithms: SSD and YOLO, then a key point based prediction algorithm: Centernet. It can be seen that the Resnet50 based Centernet algorithm has reached the highest average prediction accuracy of 95.05% with a fastest detection speed of 32.4 FPS; The second part is the detection results obtained in Ref. [3]. Among them, the EfficientNetB0 based EfficientNet-B0-Yolov3 has achieved the fastest detection speed of 41.91 FPS, and the EfficientNet-B4-Yolov3 has achieved the highest detection accuracy with 97.26%. Compared with the original Yolov3 algorithm, the accuracy is increased by 10.4%, with the speed 45.9%. The third part is the detection result of 3 lightweight neural networks that combines Mobilenet and Yolov4 network proposed in this paper. Among them, the MobilenetV1-YoloV4-1.0 has achieved the fastest prediction speed of 51.12 FPS, MobilenetV3-YoloV4-1.0 achieved the highest prediction accuracy of 93.08%, compared with the detection speed of 24.39 FPS with an accuracy of 90% obtained by the Yolov4 network, it can be seen that the lightweight algorithms shown in Table 2 has achieved an improvement on the highest prediction accuracy by increasing 3.4% and 109% in prediction speed compared to the original Yolov4, but it should be noted that the fastest prediction speed and the highest prediction accuracy are not achieved by the same lightweight network.

Table 2.
The performance of various algorithms on the dataset. (*: Channel number scaling factor = 1.0).
3.2. Detection Results of Scaled Networks
As mentioned in the previous, in MobileNet, the number of channels in each layer of the backbone feature extraction network is adjusted through the channel number adjustment coefficient to achieve the purpose of adjusting the amount of parameters. The paper selects different scaling factors for different backbone feature extraction networks: when the backbone feature extraction network is MobilenetV1, = 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0; when the backbone feature extraction network is MobilenetV2, = 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.3; when the backbone feature extraction network is MobilenetV3, = 0.75, 1.0; the model test results with the scaling factor = 1 are only shown in Table 2, and the remaining results are shown in Figure 7.
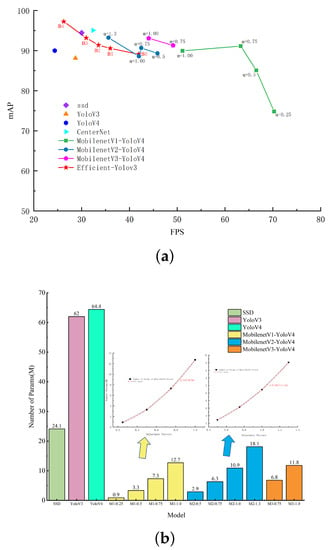
Figure 7.
The effect of adjusting the model scaling factor on the test results: (a) the performance comparison between different models, (b) comparison of model parameters.
In general, the number of channels is positively correlated with the feature extraction capability of the backbone and inversely correlated with the amount of computation or number of parameters. The higher the number of channels, the more feature information the network extracts, which in turn increases the detection accuracy, but the increase in the number of parameters results in a certain loss of speed. The effect of different channel number scaling on detection accuracy and speed was shown in Figure 7 and Table 3.

Table 3.
The influence of different adjustment factors on the test results.
As can be seen from Table 3, the improved algorithm using network scaling achieved faster detection accuracy compared to the unscaled ones, with MobilenetV1-Yolov4-0.25 achieving the fastest detection speed of 70.26 FPS among all algorithms, and MobilenetV2-Yolov4-1.3 achieving the highest detection accuracy of 93.22%.
The effect of different channel number adjustment factors on the test results can be found in Figure 7a. When adjusting the number of channels for MobilenetV1, the average prediction accuracy of the algorithm generally shows an increase trend as increases, but the detection speed continues to decrease as shown in Figure 7a. when adjusting for MobilenetV2, the prediction accuracy shows an increasing-decreasing-increasing trend as increases, which may be due to the small capacity of the dataset or the inappropriate batch size setting; When adjusting for MobilenetV3, the pattern of the change is basically the same as that for MobilenetV1, i.e., as increases, the number of channels increases, the detection accuracy increases, but there is a small loss in detection speed. When compared with the results obtained by Efficientnet-Yolov3 in Ref. [3], the lightweight network proposed in this paper has a great advantage in detection speed, except for MobilenetV2-Yolov4-1.3, and the fastest detection speed achieved in this paper is approximately 1.7 times faster than the fastest detection speed achiveved by Efficientnet-Yolov3, reaching 70 FPS. However, due to the compression and adjustment of channel number, the improved algorithm proposed in this paper is relatively deficient in image information feature extraction ability, and does not achieve a higher detection accuracy as mentioned in Ref. [3].
The parameters of the target detection model under various zoom ratios are compared in Figure 7b. By comparing the increasing trend of the parameter amount of various improved algorithms under different ratios, it can be confirmed that the size of the parameter amount is proportional to . Also can be clearly seen that the combination of Mobilenet and Yolov4 could reduce the amount of parameters of Yolov4 effectively, then combined with the detection speed, it can be proved that reducing the amount of parameters by compressing the channels of networks is an effective measure to improve the target detection speed, but not conducive to ensuring the detection accuracy.
3.3. Verification of Generalization Proficiency
In addition to testing the algorithm on the dataset, we chose conveyor belt damage data from the Refs. [25,26,29,30,32] for validation of the model’s generalization ability, and the results are shown in Figure 8. Generalization ability refers to the ability of the neural network model to adapt to fresh samples, and we expect that the model we obtain through training on the dataset will still give reasonable output when faced with data outside the dataset, i.e. fresh samples. The generalization ability of a model is the third common measure of the superiority of a neural network model, besides the mean Average Precision (mAP), and the prediction speed (FPS).
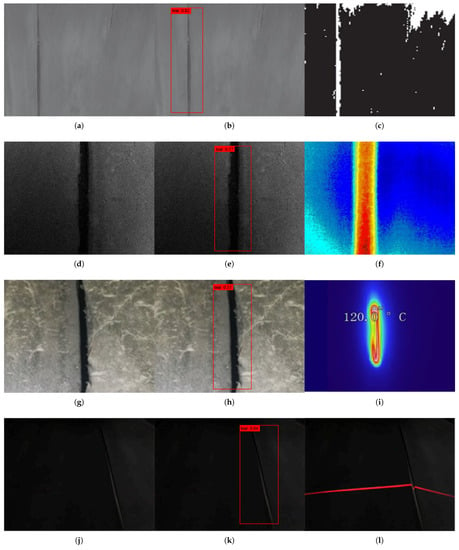
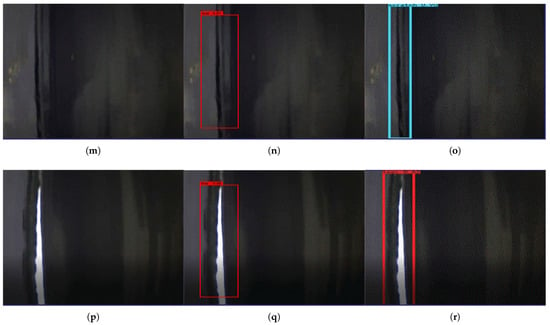
Figure 8.
Generalization proficiency verification: (a,d,g,j,m,p) are the original images, (b,e,h,k,n,q) belong to the detection results using method in this paper, (c,f,i,l,o,r) are the detection results given in Refs. [25,26,29,30,32].
In Figure 8, the first row show the original image of the conveyor belt damage, figures shown in the second row are the detection results using the method in this paper, and the third row are the detection results given in Refs. [25,26,29,30,32] respectively. Among them, (c) shows the tear detection method based on image processing, (f) shows the detection method based on infrared, (i) shows the method based on infrared spectral analysis, which integrates the problem of local temperature increase due to sliding friction during the tearing process of the conveyor belt, and (l) shows the method assisted by a line laser, which transforms the detection problem of tears into the detection of corner points in a continuous smooth curve with the help of a line laser generator, (m,n) are the damage form of the conveyor belt proposed in Ref. [32], (m) shows scratch, and (n) shows tear, but the recognition results in this paper are all tears, because the annotations in our dataset are different from that. As shown in Figure 8, the algorithm in this paper achieves good detection results in these fresh samples, proving the strong model generalization capability of the algorithmic model in this paper.
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Aiming at the problem of conveyor belt damage detection, the paper proposed a detection method based on a lightweight neural network, which aims to increase the detection speed to meet the development needs of high-speed belt conveyors, also to match the cameras with high frame rate, making the signal processing speed more real-time.
In this paper, the Mobilenet network and the Yolov4 target detection network are effectively combined to achieve the simplification of the Yolov4 network. Meanwhile, a series of different lightweight models are achieved by adjusting the number of channels, also achieved a good detection effect on the conveyor belt damage dataset, with a highest detection accuracy of 93.22% and a fastest detection speed of 70.26 FPS. Compared with Yolov4, the accuracy is increased by 3.5%, and the speed is increased by 188%.
The contributions of this paper can be summaried as follows:
- (1)
- A lightweight Yolov4 network is realized through the effective combination of MobileNet and Yolov4 network.
- (2)
- A series of lightweight networks with different degrees of lightness are obtained by adjusting the number of channels, and their influence on detection speed and detection accuracy is explored.
- (3)
- The application of lightweight neural networks in conveyor belt damage detection is further explored. The results show that lightweight neural networks can bring significant improvement in detection speed with certain loss of accuracy compared to the original neural networks, but when the number of channels of lightweight neural networks is further expanded, their backbone feature extraction capability is further enhanced and their prediction accuracy even catches up with the original Yolov4.
- (4)
- The generalization capability of the target detection model is further validated by comparing the conveyor belt damage data in the existing literature.
In the following research, in addition to further expanding the dataset and improving the detection accuracy, we will also attach importance to the potential effects of image collection conditions carefully, such as dust, light, etc.
Author Contributions
M.Z. (Mengchao Zhang): Methodology, Writing—original draft, Software; Y.Z.: Supervision; M.Z. (Manshan Zhou): Conceptualization; K.J.: Network structure drawing and improvement; H.S.: Data curation; Y.Y.: Investigation, Supervision; N.H.: Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports by State Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control (MDPC2016ZR05).
Data Availability Statement
The data in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Yibing Shang at University of Exeter, United Kingdom and Zhengxu Zhang, postgraduate of Shandong University of Science and Technology, China, for their help in collecting the original data and labeling.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Lodewijks, P.D.I.G.; Ottjes, D.I.J.A.; Pang, D.I.Y. Intelligent belt conveyor monitoring and control. Des. Eng. 2010. Available online: http://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:585579aa-7406-4e57-af8e-66c7df9b83bd (accessed on 24 July 2021).
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, W. Research on Intelligent Monitoring and Warning Method of Belt Conveyor. J. Graph. 2017, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, M. Deep learning-based damage detection of mining conveyor belt. Measurement 2021, 175, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Research status and development trend ofintelligenttechnologies for mine transportation equipment. J. Intell. 2020, 1, 78–88.
- Zhang, S.; Xia, X. Modeling and energy efficiency optimization of belt conveyors. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, X. Optimal control of operation efficiency of belt conveyor systems. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chauhan, V.; Zhou, M. A machine vision based smart conveyor system. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Machine Vision. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Rome, Italy, 2–6 November 2021; p. 11605. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Miao, C.; Li, X. Research on the energy-saving control strategy of a belt conveyor with variable belt speed based on the material flow rate. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Pang, Y.; Lodewijks, G. Green operations of belt conveyors by means of speed control. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Liu, X.; Zhong, B. Sustainable belt conveyor operation by active speed control. Measurement 2020, 154, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Pang, Y.; Lodewijks, G. Speed control of belt conveyors during transient operation. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhou, W.; Song, T. Audio-based fault diagnosis for belt conveyor rollers. Neurocomputing 2020, 397, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczylas, A.; Stefaniak, P.; Anufriiev, S.; Jachnik, B. Belt Conveyors Rollers Diagnostics Based on Acoustic Signal Collected Using Autonomous Legged Inspection Robot. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, M. A computer vision based conveyor deviation detection system. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wei, H. A contactless measuring speed system of belt conveyor based on machine vision and machine learning. Measurement 2019, 139, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, M.; Shi, H. A Computer Vision-Based Real-Time Load Perception Method for Belt Conveyors. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dang, L. Video detection of foreign objects on the surface of belt conveyor underground coal mine based on improved SSD. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pang, Y.; Lodewijks, G.; He, D. Experimental research on condition monitoring of belt conveyor idlers. Measurement 2018, 127, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharwade, S.G.; Nagpal, S. Analysis of transient belt stretch for horizontal and inclined belt conveyor system. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2019, 4, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Lu, X.; Yan, L. Research on the Signal Feature Extraction Method in Steel-Cord Conveyor Belt with Metal Magnetic Memory Testing. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 11, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Lodewijks, G. A novel embedded conductive detection system for intelligent conveyor belt monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 21–23 June 2006; pp. 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, H.; Pang, Y.; Xiong, X. Multispectral visual detection method for conveyor belt longitudinal tear. Measurement 2019, 143, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Liu, W.; Pang, Y.; Yan, G. Research on visible light and infrared vision real-time detection system for conveyor belt longitudinal tear. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2016, 10, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Miao, C.; Li, X. Adaptive Multi-View Image Mosaic Method for Conveyor Belt Surface Fault Online Detection. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Liang, H. A multi-class support vector machine real-time detection system for surface damage of conveyor belts based on visual saliency. Measurement 2019, 146, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianguo, L.; Lifang, S.; Zixu, M.; Can, Z.; Hangqi, J. Laser-based on-line machine vision detection for longitudinal rip of conveyor belt. Optik 2018, 168, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hou, C.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L. Longitudinal tear early-warning method for conveyor belt based on infrared vision. Measurement 2019, 147, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Chen, L.; Pang, Y.; Yan, G.; Miao, C. Integrative binocular vision detection method based on infrared and visible light fusion for conveyor belts longitudinal tear. Measurement 2017, 110, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Qiao, T.; Pang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, G. Infrared spectrum analysis method for detection and early warning of longitudinal tear of mine conveyor belt. Measurement 2020, 165, 107856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, H.; Yan, G. Dual band infrared detection method based on mid-infrared and long infrared vision for conveyor belts longitudinal tear. Measurement 2018, 120, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Qiao, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pang, Y. Longitudinal Tear Detection Method of Conveyor Belt Based on Audio-visual Fusion. Measurement 2021, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Qiao, T.; Pang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Research On ADCN Method for Damage Detection of Mining Conveyor Belt. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 8662–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network In Network. Comput. Sci. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.4400. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.01083. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Sheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L.; Ling, H. M2det: A single-shot object detector based on multi-level feature pyramid network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–February 2019; pp. 9259–9266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Krähenbühl, P. Objects as points. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07850. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).