Abstract
This paper presents a Scott transformer model to be applied in electromagnetic transients (EMT) programs, particularly in the absence of a detailed Scott transformer model for performing real-time simulations (RTS). Regarding a Scott transformer, a common topology for converting a three-phase network into two single-phase networks, the transformer model in EMT programs is essential to simulate large-scale electric railway systems. A code-based model has been developed to simulate the transformer in RTS directly and contain the transformer’s actual impedance characteristics. By establishing a mathematical foundation with the current injection method, we presented a matrix representation in conjunction with a network solution of EMT programs. The proposed model can handle more practical parameters of Scott transformers with a relatively low computational load. Thus, it supports the flexible computation of real-time simulators with a finite number of processor units. The accuracy of the model is verified by simulating it and comparing the simulation results with an industrial transformer’s certified performance. Furthermore, a case study involving a comparison of the results with the field measurement data of an actual Korean railway system demonstrated the efficacy of the model.
1. Introduction
As electric railway systems have been widely employed around the world, various concerns regarding electric power systems have emerged. Since electric railway systems intermittently consume huge amounts of active and reactive power, they hinder load forecasting for power system operators and raise power quality problems such as harmonics, flickers, and negative-sequence currents in the three-phase balanced systems [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In severe cases, this might threaten the stability of the whole electric power system. Thus, it is essential to develop a model of an electric railway system, calculate the power flows, and analyze the effect on the transmission network [7,8,9,10,11,12]. The electromagnetic transients (EMT) program has been widely used to investigate power quality phenomena in the electric railway system [1,10,13,14]. Furthermore, real-time simulations (RTS) have attracted attention for power system analysis to handle problems closer to the real world [15,16,17,18,19]. In particular, RTS can be utilized to perform a hardware-in-loop (HIL) test for reactive power compensation systems and the coordination of protection systems [19,20,21,22,23]. In South Korea, large-scale real-time simulators are being used to investigate the effect of moving loads and the performance of the protection system.
Among the power quality problems, three-phase unbalance is one of the critical problems that the electric railway system causes on a balanced AC network. Since many electric railway systems act as a strong single-phase load, specially connected transformers such as the Scott, Le Blanc, Woodbridge, and V-connected transformers are required to deliver the power from the transmission network to the railway system [23,24,25,26]. Commonly, the Scott transformer has been employed to convert three-phase to two single-phases and maintain the three-phase balance [27,28,29,30].
Thus, the Scott transformer model is necessary to perform an EMT study for an electric railway system. The problem is that the transformer model is rarely included in the library provided by general EMT programs. Many users combine two transformer models to handle the problem, i.e., a single-phase transformer and a three-winding transformer to implement the Scott connection [10,13,25,26].
In fact, the Scott transformer model has recently been added to the library provided by the EMT program for real-time digital simulators (RSCAD). However, the model cannot set the actual parameters of Scott transformers, such as the leakage reactance of two phases. Accordingly, it cannot accurately involve the Scott transformer’s detailed characteristics, which are essential for simulating the electric railway system. Due to the incomplete model, voltage and current unbalance problems were repeatedly observed in RTS. To address this concern, we formed a Scott transformer by connecting two transformer models in the RSCAD Substep library in the same way as previously mentioned.
When it comes to RTS for electric railway systems, it should be noted that the railway system components, including power electronics-based apparatus and moving loads, require heavier computational resources. However, the Substep library models should completely occupy one of the processor units of real-time simulators. As for the approaches using two transformer models in the Substep library to implement the Scott connections, the limitations of the processor resources become a concern when it comes to executing RTS for electric railway systems.
To overcome the limitations above, we developed a Scott transformer model linked to C source code with a mathematical foundation. It has the following advantages:
- Conveniently embodying the Scott transformer in EMT programs (rather than two transformer models);
- Addressing the detailed impedance characteristics of the Scott transformer, including the leakage reactance of M- and T-phases;
- Facilitating flexible computation in terms of real-time simulation of large-scale systems owing to the lighter computational burden of the proposed model.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the general structure of a Scott connection and the limitations of the conventional Scott model for RTS. Section 3 provides the mathematical foundation and presents a Scott transformer model using the current injection method. In addition, we discuss the computational resources of RTS when using the Scott transformer model in Section 3. In Section 4, the simulation results verify the proposed model’s accuracy by comparing the results with the certified performance of an industrial product. Furthermore, the efficacy of the model is demonstrated by comparing it with field data of an actual Korean railway system.
2. Scott Transformer Model for Real-Time Simulation
2.1. Scott Transformer
Specially connected transformers are essential to delivering power from an AC transmission network to electrical railway system. These apparatuses such as Scott, Le Blanc, and Woodbridge are used to transform the three-phase transmission structure of the grid into two single-phases. As a common connection, two single-phases (M-phase and T-phase) are connected to the three-phase network using a Scott transformer as shown in Figure 1.
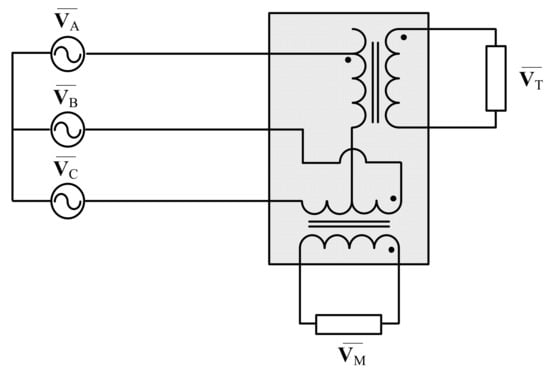
Figure 1.
The basic structure of Scott transformer.
A separate library model is highly required to form a Scott connection in the EMT study for the electric railway system. However, the Scott transformer model is rarely included in the library provided by general EMT programs. Many users combined a single-phase transformer and a three-winding transformer to implement the Scott connection as shown in Figure 2 [10,13,25,26].
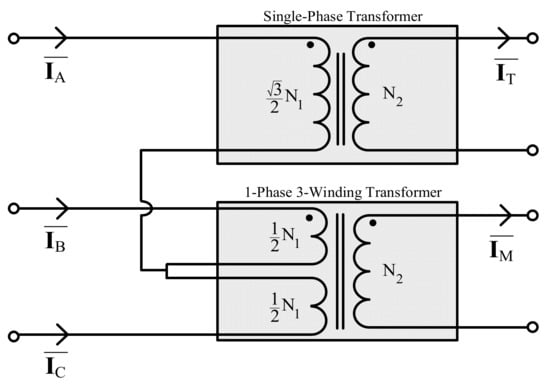
Figure 2.
Scott connection using a single-phase transformer and a single-phase three-winding transformer.
Let the turn ratio of the primary side to the secondary side of the Scott transformer be k = (N1/N2). Then, the relationship between transformer voltage and current can be expressed as follows [3]:
If the magnitude of three-phase current in Equation (1) is denoted as I and identical loads are connected to M- and T-phases, the induced current is derived as
that is, currents of identical magnitude but the phase difference of 90° flow in the secondary side of the Scott transformer. The three-phase current of the primary side achieves the balanced state as follows:
In other words, when an identical load is connected to the M- and T-phases of the Scott transformer, we obtain currents with equal magnitude and a phase difference of 90° flow in these phases. Accordingly, balanced currents with equal magnitude and a phase difference of 120° flow in the three-phase side are obtained.
When it comes to industrial transformer certification, the characteristics of M- and T-phases must be tested separately. In the same manner, while configuring a Scott transformer with two transformers, each transformer’s parameters must be set in detail to contain the characteristics of M- and T-phases, respectively.
2.2. Scott Transformer Model for the Real-Time Simulator
Figure 3 shows the Scott transformer provided in the Library of RSCAD. As shown in Figure 1, a Scott connection converts a three-phase structure into two single phases. However, this model cannot handle the actual parameters of Scott transformers such as the leakage reactance of two phases. Although M- and T-phases have different impedance characteristics, only one reactance element is set into this model. Therefore, it is believed that the Library model cannot fully contain the attributes of the Scott transformer.
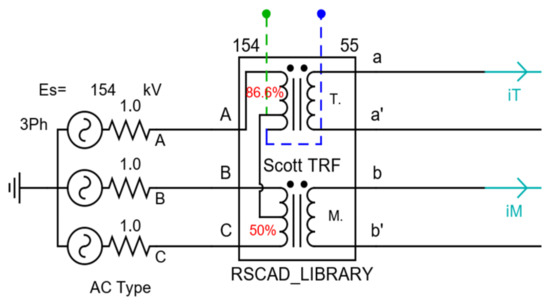
Figure 3.
Scott transformer model in the Library of RSCAD.
To investigate the problem in detail, we performed an impedance voltage test and compared the simulation results with a Scott transformer’s certified performance. The impedance voltage indicates the voltage drop only due to the impedance of the transformer. We can quantify the impedance voltage when one side of the transformer is configured as a short circuit as shown in Figure 4. The voltage when the rated current flows across both sides is called the impedance voltage. Therefore, the impedance voltage (%) is ideally equal to the percentage impedance of a transformer.
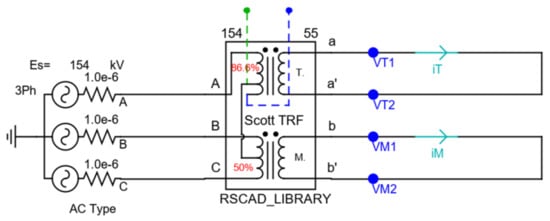
Figure 4.
Circuit configuration for impedance voltage test of the Library Scott transformer model.
In the simulation experiment using RSCAD, the percentage of impedance of the Library Scott transformer model was set to 12.5%, and the short circuit was configured as shown in Figure 4. We then generated the input voltage and changed its magnitude to quantify the impedance voltage (i.e., the voltage when the rated current flows between both ends).
The measured impedance voltages are presented in Table 1. As the transformer’s percentage impedance was set to 12.5%, the measured impedance voltage should be 12.5% in the normal condition. However, the Library Scott transformer’s impedance voltages (8.49% and 11.36%) differed significantly compared to the theoretical value as represented in Table 1. Furthermore, when the library model is used, both sides of the transformer are expected to maintain the balanced condition following Equations (2) and (3). However, Figure 5a shows that an unbalanced current flowed in the three phases. Although the currents flowing in M- and T-phases had a normal phase difference (90°), the two currents differed in magnitude, as shown in Figure 5b. To sum up, impedance voltage tests show that the Library model cannot accurately simulate the Scott transformer.

Table 1.
Impedance voltage test results of the Library Scott transformer model when the input parameter (percent impedance, %Z) is set as 12.5%.
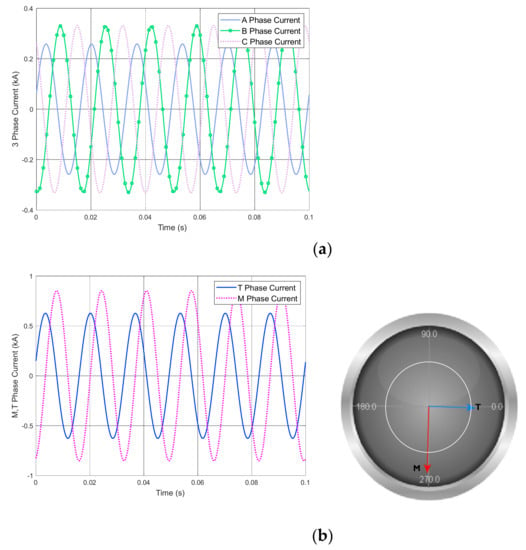
Figure 5.
Impedance voltage test result for the Library Scott transformer model: (a) unbalanced three-phase current waveform; (b) unbalanced M- and T-phase current waveforms and vector representation.
3. Development of Scott Transformer with Electromagnetic Transients Program
3.1. Electromagnetic Transients Modeling
To address the limitation of the Library model illustrated in Section 2.2, we developed a Scott transformer model that can be seamlessly integrated into various EMT programs. In other words, the proposed model is based on the current injection method so that it can be easily solved in general EMT programs [14,31].
3.1.1. Matrix Representation for EMT Programs
The generalized equivalent circuit of a single-phase transformer is represented in Figure 6. Based on the circuit above, the terminal voltages can be expressed as follows:
To explain the n-winding transformer, it can be reorganized as follows, including the resistance matrix R and the inductance matrix L [14].
Consequently, the matrix representation for the n-winding transformer is presented as (5). Then, the voltage and current values are calculated and updated in each solution time step for the EMT program of the corresponding network.
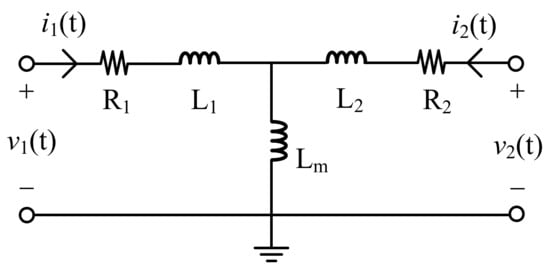
Figure 6.
Configuration of an equivalent circuit for a single-phase transformer.
3.1.2. Current Injection Model for Scott Transformer
Considering the n-winding transformer in (5), the voltage and current input matrices are defined as follows:
Subsequently, to include the matrices R and L, the voltage and current are defined as Equation (7) based on Equation (5).
Adjusting these equations to EMT programs, the matrix representation of the transformer can be represented by being numerically integrated over a time step using trapezoidal integration.
Then, the voltage and current in Equation (7) can be reorganized as:
It can be represented in the form of the current injection model as follows [14]:
Equation (9) can be rearranged to express it as a conductance matrix G:
Consequently, it can be formed as follows:
where , G is composed of R and L matrices, and ih(t) indicates the current of the previous time step.
Meanwhile, the current injection method including the Dommel algorithm is used in the EMT program to adjust the formula for each solution time step [14]. Unlike the typical Norton equivalent circuit in which one end is connected to the ground, the current injection model handles the voltage of each terminal rather than measuring the voltage across the terminals of each winding [31]. Based on the numerical trapezoidal method including Equations (8)–(11), the current injection model can be formed using the voltage and current at both ends as follows:
where i1+(t), i1-(t),v1+(t), and v1-(t) are for the primary-side terminal, i2+(t), i2-(t),v2+(t), and v2-(t) are for the secondary-side terminal, and ih1(t) and ih2(t) are the current elements from the previous solution time step. GTR is the conductance matrix based on G in Equation (11) for the Dommel algorithm [14].
Based on the representation above, we obtain the current injection model for the n-winding transformer as follows:
where in+(t),in-(t), vn+(t), and vn-(t) are components for the nth terminal, ihn(t) is the current in the previous solution time step, and Gn,TR is the conductance matrix for the n-winding transformer defined by [14].
Then, Equation (13) is rearranged based on the Dommel representation for Scott transformer to yield as follows:
where GScott,TR is the conductance matrix for Scott transformer derived through the Dommel representation.
Consequently, we develop the matrix representation in Equation (14) as a C source format to insert it into a network solution in EMT programs. The proposed Scott transformer based on the C source is shown in Figure 7.
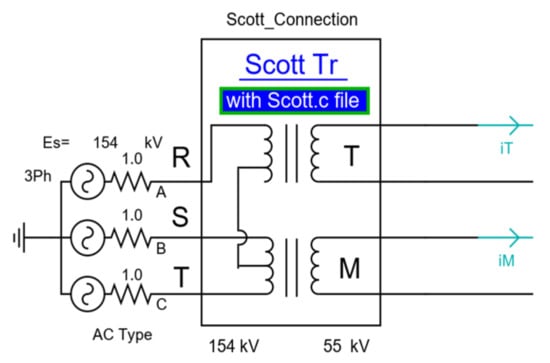
Figure 7.
The proposed Scott transformer model linked to C source code in RSCAD.
3.2. Computational Load for Simulations of Electric Railway System
As an EMT program does not provide a Scott transformer model, many users combine a single-phase transformer and a three-winding transformer to form the Scott connection as shown in Figure 2. In RSCAD, the Scott transformer can also be configured using two transformers as shown in Figure 8.
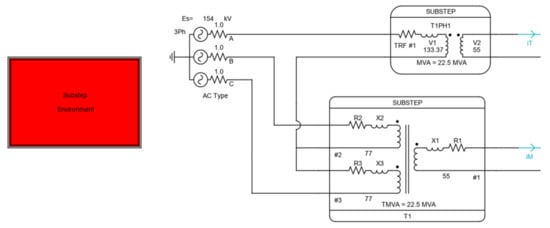
Figure 8.
Scott connection using a single-phase transformer and a single-phase three-winding transformer in the Substep library.
Note that the network solution must be computed with the Substep, which performs as many operations as an integer multiplied by the main time step. This is because the model in Figure 8 uses a transformer in the Substep Library. For instance, if the main time step is 50 µs, the time step of Substep can be 25 µs or smaller. This increases the total computational load of real-time simulators. Moreover, it should be noted that the Substep model entirely occupies one of the processor units as shown in Figure 9a. This implies that a processor unit would be occupied entirely even when only one Scott transformer is to be utilized. This increases the total computational load and lowers the computation efficiency.
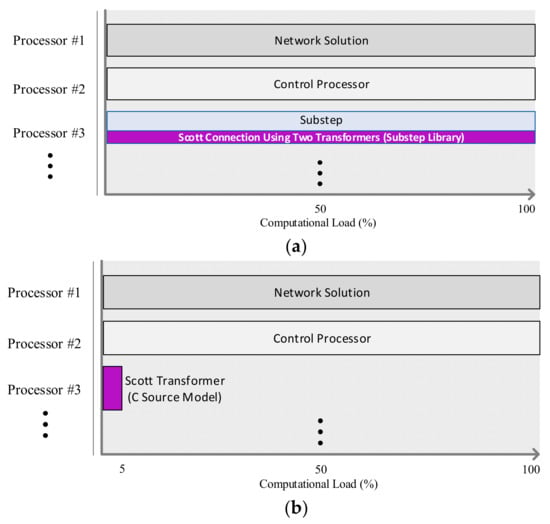
Figure 9.
Comparison between computational loads of (a) Scott connection using the Substep library models (processor assignment for Scott connection using a single-phase transformer and 3-winding transformer from the Substep library) and (b) the proposed Scott transformer (processor assignment for Scott connection based on the proposed model).
In contrast, since the proposed model was formed as a C source, it can be easily utilized at any time step. Furthermore, the computational load can be decreased and the computation efficiency increased. Figure 9b shows that approximately 5% of the total computational load is utilized by this model.
It is necessary to compare the computational load utilized by the Substep model and the proposed model since the simulation of a large-scale electric railway system requires a large number of computations, such as those for accurately finding the state of each facility and for simulating moving vehicles. Suppose the elements incur a large computational load in scenarios where the number of processor units in a real-time digital simulator is limited. In that case, these can pose a problem for the RTS study for the electric railway system.
Regarding this, the proposed Scott transformer model can enhance the flexibility of computational resources while simulating a large-scale electric railway system (see Figure 9).
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Impedance Voltage Tests
In this section, we present the simulation results using a real-time digital simulator (RTDS) to verify the effectiveness of the proposed model. To begin with, we tried to verify the model’s accuracy through an impedance voltage test. The equivalent circuit for the impedance voltage test of the proposed transformer was organized as shown in Figure 10. The parameters in Table 2 are identical to those of the transformer certified by the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI). After we set the input parameter as Table 2, the impedance voltage test was performed.
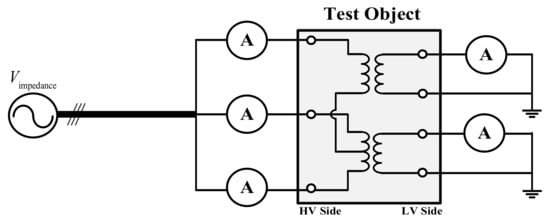
Figure 10.
An equivalent circuit diagram for impedance voltage test.

Table 2.
Detailed parameters of Scott transformer (identical to those of the transformer certified by KERI).
Note that the currents in M- and T-phases became unbalanced in the impedance voltage test of the RSCAD Library model as shown in Figure 5. By comparison, in the results shown in Figure 11, both sides of the proposed model are in a balanced state. As a transformer parameter, the measured impedance voltage in Table 3 is identical to the leakage value (12.5%) input. Thus, the effectiveness of the model is demonstrated by the fact that the three-phase structure was accurately converted to two single phases (i.e., M- and T-phases), and the balance of each phase was maintained.
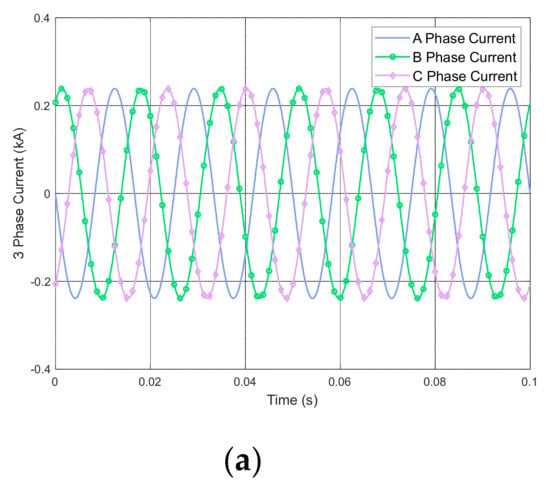
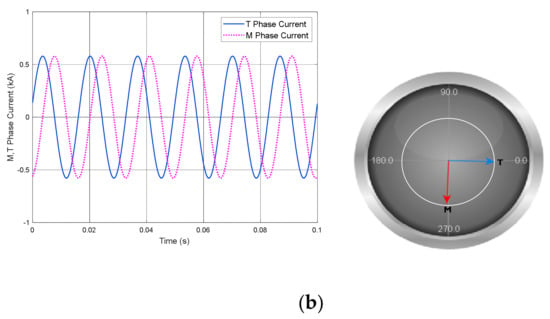
Figure 11.
Result of impedance voltage test for the proposed Scott transformer: (a) three-phase current waveforms; (b) M- and T-phase current waveforms and vector representation.

Table 3.
Result of impedance voltage test (a comparison of the result with the certified test report of an actual Scott transformer by KERI).
4.2. Short-Circuit Tests
The short-circuit test is a representative procedure that is performed for assessing a transformer’s characteristics. Note that owing to the limitation of the system configuration for the generation of a rated voltage (154 kV) on the high-voltage (HV) side, a rated voltage (55 kV) was formed on the low-voltage (LV) side, whereas the HV side was configured as a short circuit as shown in Figure 12. We measured the short-circuit current when the switching operation occurs, while the rated voltage is formed on the LV side shown in Figure 12.
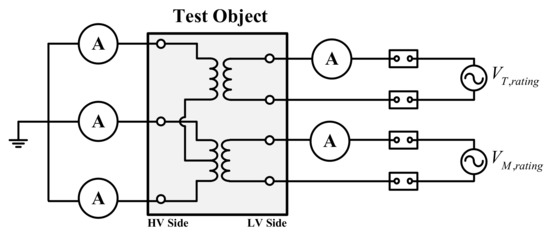
Figure 12.
Circuit diagram for short-circuit test of the Scott transformer.
Figure 13a shows the short-circuit current waveform when the T side is configured as an open circuit and voltage is generated on the M side. The actual waveform of the short-circuit current of the transformer certified by KERI is shown in Figure 13b. As illustrated, the waveform of the short-circuit current for the proposed model is similar to that of the actual short-circuit current. In addition, the peak and RMS current values are almost equal to those shown in Table 4.
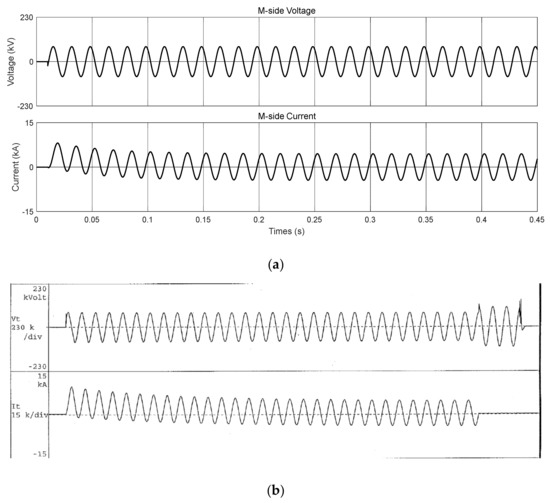
Figure 13.
M-phase short-circuit test results of Scott transformer (comparison between short-circuit test results obtained by RTDS and those in the certified test report by KERI): (a) waveform of short-circuit test result of the proposed Scott transformer, obtained by RTDS simulation (M-phase); (b) waveform in the certified test report (M-phase).

Table 4.
M-phase short-circuit test result of Scott transformer (comparison between short-circuit test results obtained by RTDS and those in the certified test report).
Similarly, Figure 14 shows the short-circuit current waveform when the M side was configured as an open circuit and voltage was generated on the T side. Figure 14 and Table 5 show that the test result for the proposed transformer model is identical to that presented in the certified test report of KERI.
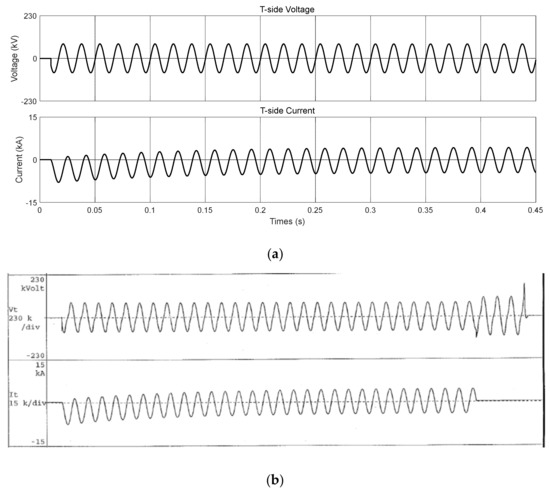
Figure 14.
T-phase short-circuit test result of Scott transformer (comparison between short-circuit test results obtained by RTDS and those in the certified test report by KERI): (a) waveform of the short-circuit test result of the proposed Scott transformer (T-phase); (b) waveform in the certified test report (T-phase).

Table 5.
T-phase short-circuit test result of Scott transformer (comparison between short-circuit test results obtained by RTDS and those in the certified test report).
4.3. Case Study
This section presents a case study performed on an existing electric railway system in South Korea. Figure 15 shows a substation in the Jeolla province in South Korea and a feeding system. The parameters of this system are listed in Table 6. We investigated the section from the supply substation (S/S) to the parallel post (PP) as represented in Table 6 and Figure 15. This case study examined the efficacy of the models by comparing the result when the Library model is used (Figure 3), the Substep library model is used (Figure 8), and the proposed model is used (Figure 7).
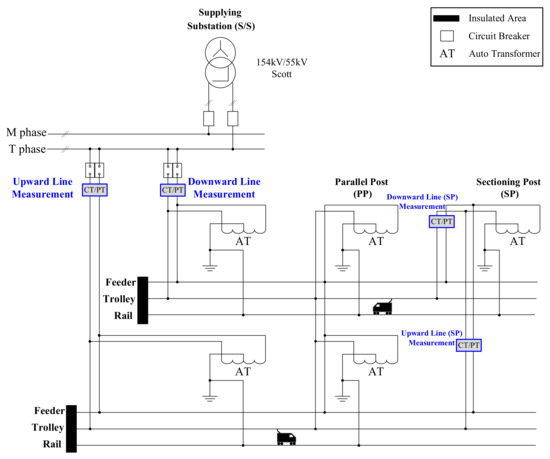
Figure 15.
Part of the electric railway system in Jeolla province in South Korea.

Table 6.
Specifications of a railway power supply system in Jeolla province in South Korea used in the case study.
The case study system was set in RTDS to evaluate a system condition at a specific time. We measured each feeder’s voltage, current, and active power using the CT and PT at 6:14:03 AM in an existing system. Then, we compared the measurement values with evaluated values by the simulations. The comparison results are summarized in Table 7.

Table 7.
Case study result (comparison of actual measurement data with the RTDS simulation results obtained using each model (the Substep model, the proposed model, and the Library model)).
The measurement points (Upward Line and Downward Line in S/S and SP) are marked in blue in Figure 15. It is observed that the results of using the Substep model and the proposed model are similar to the actual measurement data. On the other hand, the results of the Library model differ significantly from the actual measurement data. In addition, Figure 16 compares the accuracy of the results obtained using each model with the actual measurements (Table 7). The accuracy is remarkably low when the Library model was utilized as shown in Figure 16.
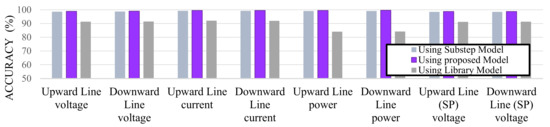
Figure 16.
Comparison of accuracy between the simulation results of each model and the actual measurement data.
As mentioned in Section 3.2, it should be emphasized that RTS for electric railway systems requires heavy computational resources. The problem is that the Substep library models should completely occupy one of the processor units of real-time simulators (see Figure 9a and Figure 17a). This hinders the flexible calculation of processor units of real-time simulations. In contrast, the proposed model occupied only 5% of a processor unit as shown in Figure 17b. With the Substep model, the overall RTS should occupy four cores of an RTDS as shown in Figure 17a. In contrast, the RTS with the proposed model holds fewer cores as shown in Figure 17b. Consequently, the proposed model achieved lower absolute computational load and higher flexibility in the use of the processor unit while configuring a large-scale electric railway system.
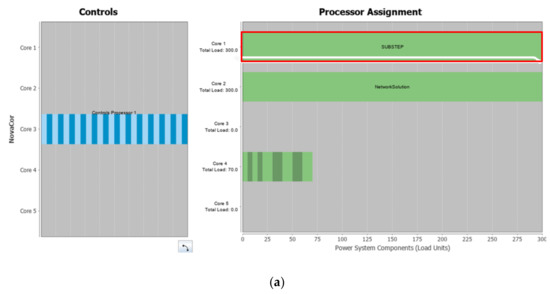
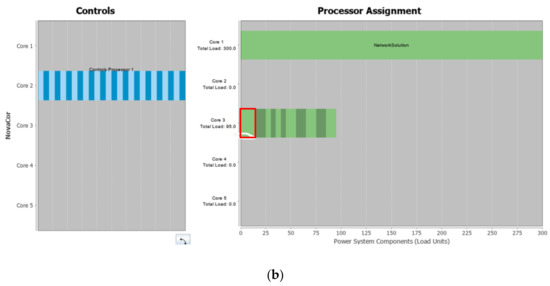
Figure 17.
Processor assignment of the RTDS for the case study: (a) processor assignment when the Scott Connection is configured using the Substep model; (b) processor assignment using the proposed model.
5. Conclusions
A precise Scott transformer model with a lighter computational burden is presented in this paper. The limitation of the existing Library model in RSCAD was revealed and proved experimentally. To overcome it and facilitate a system modeling procedure, the authors developed the Scott transformer model based on C source for EMT programs including RTS. The proposed model can be seamlessly integrated with the network solution programs since it is based on the current injection model, which is the most common method for EMT study. Furthermore, a code-based model can directly form the Scott connection in RTS and handle the impedance characteristics closer to the real world. The accuracy and efficacy of the proposed model are thoroughly demonstrated by following the same test procedure as a certified transformer test. In addition, it is confirmed that the computational burden becomes lighter, and the flexibility of the overall RTS computation has been notably improved. Therefore, it is believed that the proposed Scott transformer model will be of immediate help in modeling and studying the electric railway system.
Author Contributions
C.L. has developed the model and conducted simulation studies and written the paper with support of G.-J.C. under supervision of the corresponding author, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport’s Railway Technology Research Project, “Development of Real Time Simulator and Analysis Model for Railway Power System”: 21RTRP-B146034-04.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, H.; Lee, C.; Jang, G.; Kwon, S. Harmonic Analysis of the Korean High-Speed Railway Using the Eight-Port Representation Model. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneschke, T.A. Control of Utility System Unbalance Caused by Single-phase Electric Traction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1985, 21, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-P.; Wu, C.-J.; Chuang, Y.-S.; Peng, S.-K.; Yen, J.-L.; Han, M.-H. Loading Characteristics Analysis of Specially Connected Transformers Using Various Power Factor Definitions. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanta, M.; Pinto, J.G.; Monteiro, V.; Martins, A.P.; Carvalho, A.S.; Afonso, J.L. Topologies and Operation Modes of Rail Power Conditioners in AC Traction Grids: Review and Comprehensive Comparison. Energies 2020, 13, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi Gazafrudi, S.M.; Tabakhpour Langerudy, A.; Fuchs, E.F.; Al-Haddad, K. Power Quality Issues in Railway Electrification: A Comprehensive Perspective. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Li, R.-J.; Hsi, P.-H. Traction System Unbalance Problem-Analysis Methodologies. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, M.; Foiadelli, F.; Zaninelli, D. Electromagnetic Model of High Speed Railway Lines for Power Quality Studies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chymera, M.Z.; Renfrew, A.C.; Barnes, M.; Holden, J. Modeling Electrified Transit Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 2748–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, L.; Monjo, L.; Riera, S.; Pedra, J. Study of the Steinmetz Circuit Influence on ac Traction System Resonance. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 27, 2295–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guihua, H.; Weirong, C.; Yankun, L.; Yang, Z. Simulation of Traction Transformer Based on PSCAD/EMTDC. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Engineering and Automation Conference, Wuhan, China, 8–9 September 2011; pp. 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.H. Simplified Models of Electric Substations for Three-Phase Power-Flow Studies. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 2–6 October 1994; Volume 3, pp. 2245–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Langerudy, A.T.; Mariscotti, A.; Abolhassani, M.A. Power Quality Conditioning in Railway Electrification: A Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 6653–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, J.; Le, Y.; Bo, Z.Q.; Klimek, A. Developments in Digital Simulation of Traction Transformer. In Proceedings of the 43rd International Universities Power Engineering Conference, Padua, Italy, 1–4 September 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dommel, E.W. Electromagnetic Transients Program (EMTP) Theory Book; Bonneville Power Administration: Portland, OH, USA, 1987.
- Shu, Z.; Xie, S.; Lu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Nan, X.; Qiu, D.; Zhou, F.; Gao, S.; Li, Q. Digital Detection, Control, and Distribution System for Co-Phase Traction Power Supply Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busco, B.; Marino, P.; Porzio, M.; Schiavo, R.; Vasca, F. Digital Control and Simulation for Power Electronic Apparatus in Dual Voltage Railway Locomotive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2003, 18, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, P.G.; Kuél, R.; Wierckx, R.; Giesbrecht, J.; Arendt, L. A Real Time Digital Simulator for Testing Relays. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1992, 7, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos, A.; Zamora, A.; Escamilla, O.; Paternina, M.R.A. Real-Time Hardware-In-the-Loop Implementation for Power Systems Protection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE PES Transmission & Distribution Conference and Exhibition—Latin America (T&D-LA), Lima, Peru, 18–21 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.-M.; Tsou, T.-L. The Effect Analysis and Simulation Test of Harmonics on Differential Protection of Scott Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Porto Power Tech. Proceedings (Cat No. 01EX502), Porto, Portugal, 10–13 September 2001; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sadek, M.Z. Static VAR Compensation for Phase Balancing and Power Factor Improvement of Single Phase Train Loads. Electr. Mach. Power Syst. 1998, 26, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen-Shyan, C.; Jyh-Cherng, G. A New Hybrid SVC Scheme with Scott Transformer for Balance Improvement. In Proceedings of the Rail Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–6 April 2006; pp. 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.K.; Dai, N.Y.; Wong, M.C.; Lao, K.W. Hybrid Power Quality Conditioner for Co-Phase Power Supply System in Electrified Railway. IET Power Electron. 2012, 5, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.K.; Guo, B.S. Three Phase Models of Specially Connected Transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1996, 11, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukala, B.; Paleček, J. Comparison of Schemes of Traction Transformer Stations in Terms of Their Impact on the Asymmetry in the Power Supply System. In Proceedings of the 2014 15th International Scientific Conference on Electric Power Engineering (EPE), Brno-Bystrc, Czech Republic, 12–14 May 2014; pp. 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Firat, G.; Yang, G.; Al-Ali, H.A.H. Comparative Study of Different Transformer Connections for Railway Power Supply Mitigation of Voltage Unbalance. In Proceedings of the IET Conference, Hong Kong, China, 8–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Santiyanon, D.; Hongesombut, K.; Srisonphan, S. Simulation on Voltage Unbalance Reduction in Railway Electrification System by Different Special Transformers. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 86, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, D.V. Rotating Electric Machinery and Transformer Technology; Reston Publishing Company: Reston, VA, USA, 1978; pp. 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Kosow, I.L. Electric Machinery and Transformer; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 559–562. [Google Scholar]
- Brittain, J.C.; Scott, C.F. A Pioneer in Electrical Power Engineering. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2002, 8, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, Y.; Miyazawa, R.; Koizumi, H. A Study on the Effect of the Scott Transformer on the Three-Phase Unbalance in Distribution Network with Single-Phase Generators. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Aalborg, Denmark, 25–28 June 2012; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, N.; Arrillaga, J. Power Systems Electromagnetic Transients Simulation; IET: Stevenage, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).