Active and Quantum Integrated Photonic Elements by Ion Exchange in Glass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
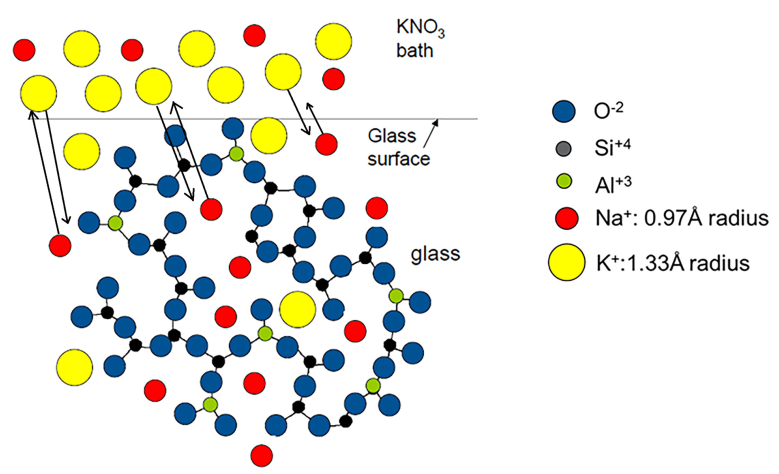
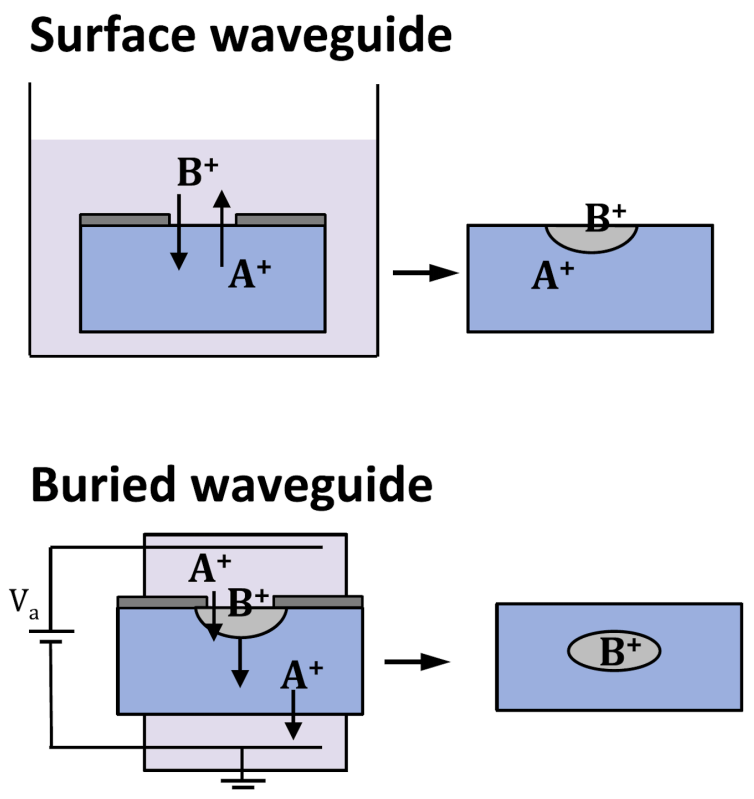
2. Fundamentals of Ion-Exchanged Glass Waveguide Circuits
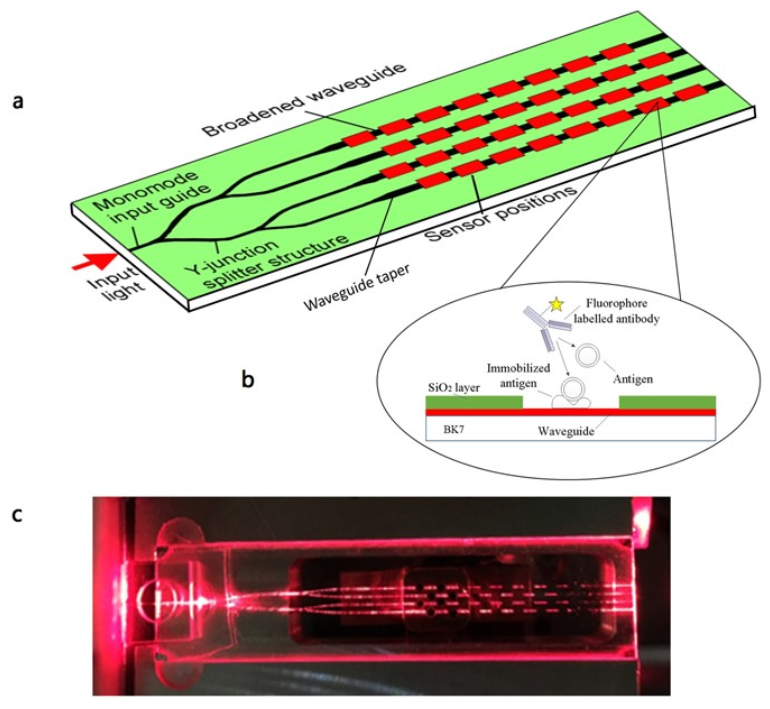
3. Ion-Exchanged Active Integrated Photonic Devices
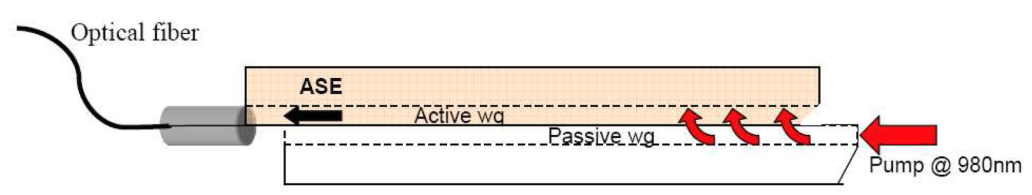
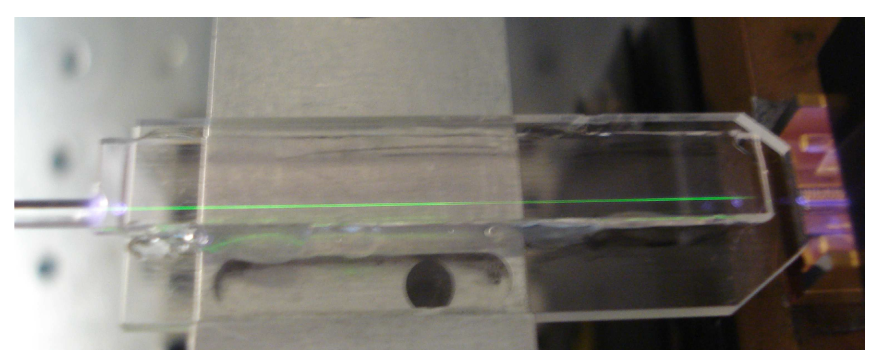
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
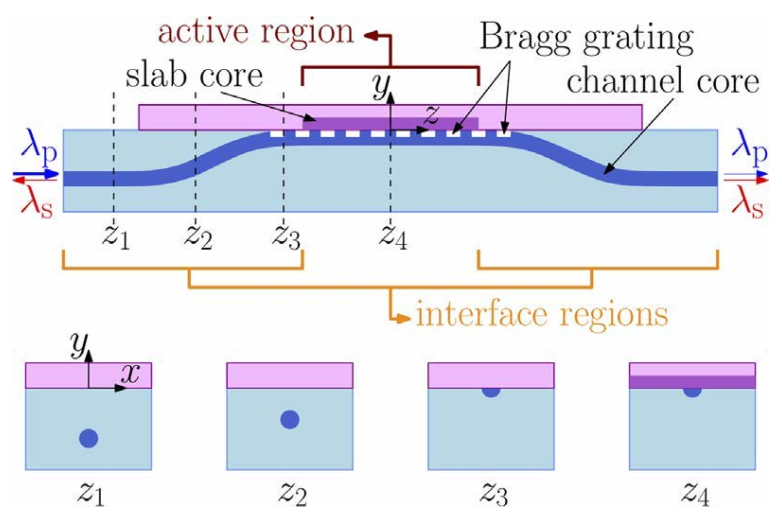
4. Quantum Integrated Photonic Devices
4.1. Fundamental Aspects of Quantum Integrated Optical Components
4.2. Integrated Quantum Circuits for Quantum Cryptography
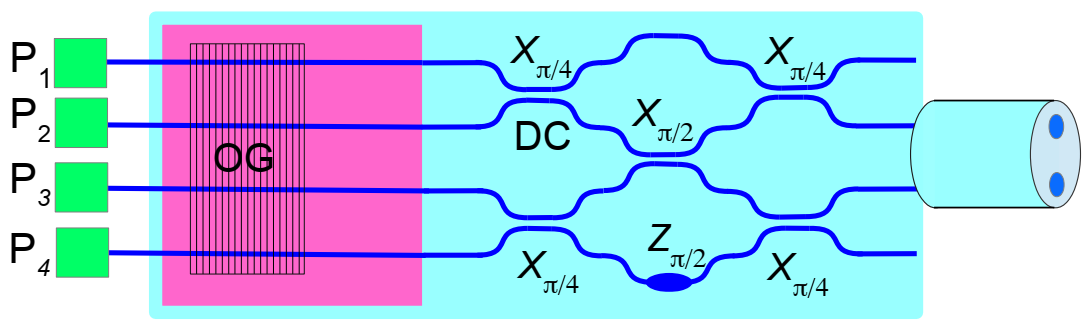
4.2.1. Quantum States Generator and Quantum Projectors On-Chip for BB84
4.2.2. Bell States Measurement Integrated Device for MDI
4.3. Fabrication and Characterization of a Quantum Projector
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Aluminosilicate |
| ASE | Amplified Spontaneous Emission |
| BB84 | Bennett and Brassard 1984 |
| CMOS | Complementary Meta Oxide Semiconductor |
| DC | Directional Coupler |
| EDFA | Er-Doped Fiber Amplifier |
| EDWA | Erbium-Doped Waveguide Amplifier |
| EYDWA | Erbium-Ytterbium-Doped Waveguide Amplifier |
| EOCB | Electro-Optical Circuit Board |
| FMF | Few-Mode Optical Fiber |
| IExG | Ion-Exchanged Glass |
| IQP | Integrated Quantum Photonics |
| MC | Minford et al. Curve |
| MCF | Multicore Optical Fiber |
| MDI | Measurement Device Independent |
| MMI | Multi-Mode Interference |
| MUBs | Mutually Unbiased Bases |
| NLO | Nonlinear optics |
| OG | Optical Grating |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| PECVD | Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition |
| RED | Rare-Earth Doped |
| SPDC | Spontaneous Parametric Down-Conversion) |
| SL | Soda–Lima–silicate |
| WDM | Wavelength Division Multiplexing |
References
- Pezzella, S. Il Trattato di Antonio da Pisa Sulla Fabbricazione Delle Vetrate Artistiche; Umbria Edizioni: Perugia, Italy, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, G. Versuche über die diffusion von silber in glas. Angew. Physik 1913, 40, 335–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.C.; Pelli, S. 1969–2019: 50 Years of Integrated Optics; Integrated Optics; Righini, G.C., Ferrari, M., Eds.; The IET: London, UK, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Izawa, T.; Nakagome, H. Optical waveguide formed by electrically induced migration of ions in glass plates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1972, 21, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallorenzi, T.G.; West, E.J.; Kirk, R.; Ginther, R.; Andrews, R.A. Optical waveguides formed by thermal migration of ions in glass. Appl. Opt. 1973, 12, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, K.; Sumimoto, T.; Matsushita, S.; Furukawa, M. Ion Exchange Process for Manufacturing Integrated Optical Circuits. U.S. Patent N. 3,857,689, 31 December 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Sumimoto, T.; Matsushita, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Koizumi, K. Method for Manufacturing Optical Integrated Circuits Utilizing an External Electric Field. U.S. Patent N. 3,836,348A, 17 September 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Najafi, S.I. (Ed.) Glass Integrated Optics and Optical Fiber Devices; Number CR53 in Critical Reviews of Optical Science and Technology; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kita, H.; Kitano, I.; Uchida, T.; Furukawa, M. Light-Focusing Glass Fiber and Rods. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1971, 54, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmi, S.; Sakai, H.; Asahara, Y.; Nakayama, S.; Yoneda, Y.; Izumitani, T. Gradient-index rod lens made by a double ion-exchange process. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Montero, C.; Prieto, X. Graded-index bifocal spectacle lenses produced by ion-exchange in glass: Paraxial designing. Pure Appl. Opt. 1995, 4, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Reino, C.; Perez, M.; Bao, C.; Flores-Arias, M. Design of GRIN optical components for coupling and interconnects. Laser Photonics Rev. 2008, 2, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graydon, O. Graded lens surprise. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findakly, T. Glass waveguides by ion-exchange: A review. Opt. Engin. 1985, 24, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, R.V.; Srivastava, R. Ion-exchanged glass waveguides: A review. J. Light. Technol. 1988, 6, 984–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.I. Introduction to Glass Integrated Optics; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Righini, G.C.; Pelli, S. Ion exchange in glass: A mature technology for photonic devices. In Materials and Devices for Photonic Circuits II; Armenise, M.N., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4453, pp. 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkanen, S.; West, B.R.; Yliniemi, S.; Madasamy, P.; Morrell, M.; Auxier, J.; Schulzgen, A.; Peyghambarian, N.; Carriere, J.; Frantz, J.; et al. Recent advances in ion exchanged glass waveguides and devices. Phys. Chem. Glas. 2006, 47, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Tervonen, A.; Honkanen, S.K.; West, B.R. Ion-exchanged glass waveguide technology: A review. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Righini, G.C.; Chiappini, A. Glass optical waveguides: A review of fabrication techniques. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 071819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, T.; Sakakura, M.; Eaton, S.; Sotillo, B.; Siegel, J.; Solis, J.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Miura, K. Bespoke photonic devices using ultrafast laser driven ion migration in glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 94, 68–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelin, J.; Ghibaudo, E.; Broquin, J.E. Study of deeply buried waveguides: A way towards 3D integration. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2008, 149, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.; Wang, G.; Yang, B.; Yang, L.; Hao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J. Study of selectively buried ion-exchange glass waveguides using backside masking. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2015, 13, 021301. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, X. Thermal history and its implications: A case study for ion exchange. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 3971–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, E.; Geoffray, F.; Bouchard, A.; Ghibaudo, E.; Broquin, J.E. Development of Tl+/Na+ ion-exchanged single-mode waveguides on silicate glass for visible-blue wavelengths applications. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 7996–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Montero, C.; Sotelo, D. Theory and design of an integrated optical sensor based on planar waveguiding lenses. Opt. Commun. 2000, 180, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, D.; Liñares-Beiras, J.; Montero-Orille, C.; Moreno, V.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Grazu, V.; Sánchez, C.; Seara, R. Integrated Ion-Exchanged Glass Bimodal Optical Biosensor based on Modal Interference Imaging. In Proceedings of the IX Optoelectronics Spanish Meeting OPTOEL 2015, Salamanca, Spain, 13–15 July 2015; p. PO–SII–35, ISBN 978-84-606-9716-9. [Google Scholar]
- Asquini, R.; Buzzin, A.; Caputo, D.; de Cesare, G. Integrated Evanescent Waveguide Detector for Optical Sensing. IEEE Trans. CPMT 2018, 8, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Tong, Z.; Mu, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Cao, W.; Qi, Z.M. A Potassium Ion-Exchanged Glass Optical Waveguide Sensor Locally Coated with a Crystal Violet-SiO2 Gel Film for Real-Time Detection of Organophosphorus Pesticides Simulant. Sensors 2019, 19, 4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mamtmin, G.; Abdurahman, R.; Yan, Y.; Nizamidin, P.; Yimit, A. A highly sensitive and selective optical waveguide sensor based on a porphyrin-coated ZnO film. Sen. Actuators A 2020, 309, 111918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Hua, P.; Song, B.; Shi, H. Integrated optical waveguide-based fluorescent immunosensor for fast and sensitive detection of microcystin-LR in lakes: Optimization and Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikonorov, N.V.; Petrovskii, G.T. Ion-exchanged glasses in integrated optics: The current state of research and prospects (a review). Glass Phys. Chem. 1999, 25, 16–55. [Google Scholar]
- Opilski, A.; Rogozinski, R.; Gut, K.; Blahut, M. Aspects of application of ion exchange in glass. In Lightguides and Their Applications; Wojcik, J., Wojcik, W., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 4239, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackel, J.L.; Vogel, E.M.; Aitchison, J.S. Ion-exchanged optical waveguides for all-optical switching. Appl. Opt. 1990, 29, 3126–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussignol, P.; Ricard, D.; Flytzanis, C. Nonlinear optical properties of commercial semiconductor doped glasses. Appl. Phys. A 1987, 44, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawandy, N.M.; MacDonald, R.L. Optically encoded phase-matched second-harmonic generation in semiconductor-microcrystallite-doped glasses. JOSA B 1991, 8, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.; Pelli, S.; Blasi, C.D.; Fagherazzi, G.; Manno, D. Ion-exchanged waveguides in semiconductor-doped glasses. In Glasses for Optoelectronics II; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1991; Volume 1513, pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, B.; Bastard, L.; Broquin, J.E. 1 kW peak power passively Q-switched Nd3+-doped glass integrated waveguide laser. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 1987–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffray, F.; Bastard, L.; Broquin, J.E. High confinement ion-exchanged waveguides for nonlinear applications. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 8034–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, L.; Bouchard, A.; Grosa, G.; Broquin, J.E. Hybrid integration of 300 nm-thick LiNbO3 films on ion-exchanged glass waveguides for efficient nonlinear integrated devices. In Integrated Optics: Devices, Materials, and Technologies XXII; García-Blanco, S.M., Cheben, P., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10535, pp. 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial. The rise of integrated quantum photonics. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politi, A.; Crya, M.J.; Rarity, J.G.; Yu, S.; O’Brien, J.L. Silica-on-silicon waveguide quantum circuits. Science 2008, 320, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Politi, A.; Matthews, J.C.F.; Thompson, M.G.; O’Brien, J.L. Integrated Quantum Photonics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2009, 15, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogdanov, S.; Shalaginov, M.Y.; Boltasseva, A.; Shalaev, V.M. Material platforms for integrated quantum photonics. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sciarrino, F.; Laing, A.; Thompson, M. Integrated photonic quantum technologies. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.H.; Mennea, P.L.; Gates, J.C. Integrated quantum photonics. In Integrated Optics; Righini, G.C., Ferrari, M., Eds.; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 337–359. [Google Scholar]
- Elshaari, A.W.; Pernice, W.; Srinivasan, K.; Benson, O.; Zwiller, V. Hybrid integrated quantum photonic circuits. Nat. Photonics 2015, 14, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meany, T.; Gräfe, M.; Heilmann, R.; Perez-Leija, A.; Gross, S.; Steel, M.J.; Withford, M.J.; Szameit, A. Laser written circuits for quantum photonics. Laser Photonics Rev. 2015, 9, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liñares, J.; Nistal, M.C.; Barral, D.; Moreno, V.; Montero, C.; Prieto, X. Quantum Integrated Optics: Theory and Applications. Opt. Pura Apl. 2011, 44, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Amezcua-Correa, R.; Bai, N.; Antonio-Lopez, E.; May-Arrioja, D.; Schulzgen, A.; Richardson, M.; Liñares, J.; Montero, C.; Mateo, E.; et al. Hole-Assisted Few-Mode Multicore Fiber for High-Density Space-Division Multiplexing. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2012, 24, 1914–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balado, D.; Liñares, J.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Barral, D. Phase and polarization autocompensating N-dimensional quantum cryptography in multicore optical fibers. JOSA B 2019, 36, 2793–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Ip, E.; Huang, Y.K.; Mateo, E.; Yaman, F.; Li, M.J.; Bickham, S.; Ten, S.; Liñares, J.; Montero, C.; et al. Mode-division multiplexed transmission with inline few-mode fiber amplifier. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 2668–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Winick, K.A.; Griffin, H.C.; Hayden, J.S. Systematic modeling study of channel waveguide fabrication by thermal silver ion exchange. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Blanco, X.; Liñares, J. Two-Mode Waveguide Characterization by Intensity Measurements from Exit Face Images. IEEE Photonics J. 2012, 4, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.C.; Pelli, S.; Ferrari, M.; Armellini, C.; Zampedri, L.; Tosello, C.; Ronchin, S.; Rolli, R.; Moser, E.; Montagna, M.; et al. Er-doped silica-based waveguides prepared by different techniques: RF-sputtering, sol-gel and ion-exchange. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2002, 34, 1151–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luff, B.J.; Harris, R.D.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Wilson, R.; Schiffrin, D.J. Integrated-optical directional coupler biosensor. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tepper, J.; Labadie, L.; Diener, R.; Minardi, S.; Pott4, J.U.; Thomson, R.; Nolte, S. Integrated optics prototype beam combiner for long baseline interferometry in the L and M bands. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 602, A66-1–A66-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conzone, S.D.; Hayden, J.S.; Funk, D.S.; Roshko, A.; Veasey, D.L. Hybrid glass substrates for waveguide device manufacture. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, J.S.; Simpson, R.D.; Conzone, S.D.; Hickernell, R.K.; Callicoatt, B.; Roshko, A.; Sanford, N.A. Passive and active characterization of hybrid glass substrates for telecommunication applications. In Rare-Earth-Doped Materials and Devices VI; Jiang, S., Keys, R.W., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002; Volume 4645, pp. 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, M.; Bucci, D.; Bastard, L.; Broquin, J.E. Hybrid erbium-doped DFB waveguide laser made by wafer bonding of two ion-exchanged glasses. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 7466–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaize, S.; Bastard, L.; Cassagnetes, C.; Broquin, J.E. Multiwavelengths DFB waveguide laser arrays in Yb-Er codoped phosphate glass substrate. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2003, 15, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minford, W.J.; Korotky, S.K.; Alferness, R.C. Low-Loss Ti:LiNbO3 Waveguide Bends at λo = 1.3 μm. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1982, QE-18, 1802–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelli, S.; Righini, G.C.; Scaglione, A.; Yip, G.L.; Noutsios, P.C.; Braeuer, A.H.; Dannberg, P.; Linares, J.; Reino, C.R.; Mazzi, G.; et al. Testing of optical waveguides (TOW) cooperative project: Preliminary results of the characterization of k-exchanged waveguides. In Linear and Nonlinear Integrated Optics; Righini, G.C., Yevick, D., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1994; Volume 2212, pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Prieto, X.; Montero, C. A Novel Refractive Index Profile for Optical Characterization of Nonlinear Diffusion Processes and Planar Waveguides in Glass. Opt. Mater. 1994, 3, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, S.; Berneschi, S.; Brenci, M.; Nunzi-Conti, G.; Pelli, S.; Righini, G.C. Simple approach to calculate the refractive index profile of ion-exchanged waveguides. Opt. Eng. 2005, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Moreno, V.; Nistal, M.C.; Salgueiro, J.R. Modelling of ion-exchanged monomode channel guides with quasi-exact modal solutions by the effective index method. J. Mod. Opt. 2001, 48, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R. Interdiffusion in a one-dimensional interacting system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1993, 152, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervonen, A. A general model for fabrication processes of channel waveguides by ion exchange. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 2746–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmio, R.; Saarinen, J.; Turunen, J.; Tervonen, A. Graded-index diffractive elements by thermal ion exchange in glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, X.; Liñares, J. Increasing resistivity effects in field-assisted ion exchange for planar optical waveguide fabrication. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1363–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Blanco, X. Electro-diffusion equations of monovalent cations in glass under charge neutrality approximation for optical waveguide fabrication. Opt. Mater. 2008, 31, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Carral, G.M.; Nistal, M.C. Quantum Photonic Simulation of Spin-Magnetic Field Coupling and Atom-Optical Field Interaction. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzawa, N.; Saitoh, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Matsui, T.; Tomita, S.; Koshiba, M. Demonstration of mode-division multiplexing transmission over 10 km two-mode fiber with mode coupler. In Proceedings of the 2011 Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–10 March 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Snitzer, E. Optical maser action of Nd3+ in a barium crown glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1961, 7, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koester, C.J.; Snitzer, E. Amplification in a fiber laser. Appl. Opt. 1964, 3, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, H.; Kawase, S.; Sekimoto, Y. Amplification at 1.06 μm using a Nd: Glass thin-film waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1972, 21, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saruwatari, M.; Izawa, T. Nd-glass laser with three-dimensional optical waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1974, 24, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.I.; Wang, W.; Currie, J.F.; Leonelli, R.; Brebner, J.L. Fabrication and characterization of neodymium-doped glass waveguides. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1989, 1, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, H.; Maruyama, O.; Asahara, Y. Glass waveguide laser. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1990, 2, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, H.; Ishikawa, E.; Asahara, Y. Nd3+-doped glass waveguide amplifier at 1.054 μm. Electron. Lett. 1991, 27, 2351–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwarania, E.; Reekie, L.; Wang, J.; Wilkinson, J. Low-threshold monomode ion-exchanged waveguide lasers in neodymium-doped BK-7 glass. Electron. Lett. 1990, 26, 1317–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanford, N.A.; Malone, K.J.; Larson, D.R.; Hickernell, R.K. Y-branch waveguide glass laser and amplifier. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, J.E.; Winick, K.A. Neodymium-doped glass channel waveguide laser containing an integrated distributed Bragg reflector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1992, 61, 2744–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miliou, A.N.; Cao, X.F.; Srivastava, R.; Ramaswamy, R.V. 15-dB amplification at 1.06 μm in ion-exchanged silicate glass waveguides. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1993, 5, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, J.A.; Malone, K.J.; Veasey, D.L.; Sanford, N.A.; Roshko, A. Passively Q-switched Nd-doped waveguide laser. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, R.; Reekie, L.; Jauncey, I.; Payne, D. Low-noise erbium-doped fibre amplifier operating at 1.54 μm. Electron. Lett. 1987, 23, 1026–1028(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desurvire, E.; Simpson, J.R.; Becker, P.C. High-gain erbium-doped traveling-wave fiber amplifier. Opt. Lett. 1987, 12, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniscalco, W.J. Erbium-doped glasses for fiber amplifiers at 1500 nm. J. Light. Technol. 1991, 9, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feuchter, T.; Mwarania, E.K.; Wang, J.; Reekie, L.; Wilkinson, J.S. Erbium-doped ion-exchanged waveguide lasers in BK-7 glass. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1992, 4, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitagawa, T.; Hattori, K.; Shuto, K.; Yasu, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Horiguchi, M. Amplification in Erbium-doped silica-based planar lightwave circuits. Optical Amplifiers and Their Applications. Optical Society of America. Electron. Lett. 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.C.; Faber, A.J.; de Waal, H.; Kik, P.G.; Polman, A. Erbium-doped phosphate glass waveguide on silicon with 4.1 dB/cm gain at 1.535 μm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 2922–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polman, A. Erbium implanted thin film photonic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 82, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.; LaBorde, P.; Lerminiaux, C.; Benveniste, C.; Hall, D. Integrated Optical Signal Amplifier. U.S. Patent N. 5,128,801, 7 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- LaBorde, P. Optical Signal Amplifier Glasses. U.S. Patent N. 5,475,528, 6 March 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuki, T.; Honkanen, S.; Ingenhoff, J.; Heyden, J.; Fabricius, N.; Najafi, S.I.; Peyghambarian, N. Polarization-insensitive planar glass waveguide amplifiers by silver ion exchange. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Optical Society of America, Anaheim, CA, USA, 2–7 June 1996; p. CThQ6. [Google Scholar]
- Delavaux, J.P.; Granlund, S.; Mizuhara, O.; Tzeng, L.D.; Barbier, D.; Rattay, M.; Andre, F.S.; Kevorkian, A. Integrated optics erbium ytterbium amplifier system in 10 Gb/s fiber transmission experiment. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Optical Communication, Oslo, Norway, 19 September 1996; Volume 1, pp. 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Honkanen, S.; Laine, J.P.; Ohtsuki, T.; Tervonen, A.; Peyghambarian, N. Modeling of Er-doped ion-exchanged glass waveguide amplifiers. In Rare-Earth-Doped Devices; Honkanen, S., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1997; Volume 2996, pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, D.; Rattay, M.; Saint Andre, F.; Clauss, G.; Trouillon, M.; Kevorkian, A.; Delavaux, J.P.; Murphy, E. Amplifying four-wavelength combiner, based on erbium/ytterbium-doped waveguide amplifiers and integrated splitters. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1997, 9, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempstead, M. Ion-exchanged glass waveguide lasers and amplifiers. In Rare-Earth-Doped Devices; Honkanen, S., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1997; Volume 2996, pp. 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shooshtari, A.; Meshkinfam, P.; Touam, T.; Andrews, M.P.; Najafi, S.I. Ion-exchanged Er/Yb phosphate glass waveguide amplifiers and lasers. Opt. Eng. 1998, 37, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.Q.; Wong, R.S.F.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Chung, P.S. Frequency upconversion in Er3+-doped alkali bismuth gallate glasses. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE LEOS Annual Meeting Conference, (Cat. No.99CH37009). San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–11 November 1999; Volume 2, pp. 812–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, P.M.; Funk, D.S.; Peskin, A.P.; Veasey, D.L.; Sanford, N.A.; Houde-Walter, S.N.; Hayden, J.S. Ion-exchanged waveguide lasers in Er3+-Yb3+ codoped silicate glass. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 6879–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, K.; Hongo, K.; Demura, F.; Takamiya, S. Erbium/ytterbium co-doped optical waveguide amplifier in soda-lime glass by silver ion exchange. In Proceedings of the Technical Digest, CLEO/Pacific Rim ’99, (Cat. No.99TH8464). Seoul, Korea, 30 August–3 September 1999; Volume 4, pp. 1087–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, G.N.; Ayras, P.; Cavaliere, C.; Hwang, B.C.; Luo, T.; Rantala, J.T.; Jiang, S.; Honkanen, S.; Peyghambarian, N. Strip-loaded structure for ion-exchanged Er3+-doped glass waveguide amplifiers. In Rare-Earth-Doped Materials and Devices III; Jiang, S., Honkanen, S., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; Volume 3622, pp. 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araci, I.E.; Mendes, S.B.; Yurt, N.; Honkanen, S.; Peyghambarian, N. Highly sensitive spectroscopic detection of heme-protein submonolayer films by channel integrated optical waveguide. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 5595–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veasey, D.L.; Funk, D.S.; Sanford, N.A.; Hayden, J.S. Arrays of distributed-Bragg-reflector waveguide lasers at 1536 nm in Yb/Er codoped phosphate glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmulovich, J.; Muehlner, D.; Bruce, A.; Delavaux, J.M.; McIntosh, C.; Lenz, G.; Gomez, L.; Laskowski, E.; Paunescu, A.; Pafchek, R.; et al. Erbium-doped planar waveguide amplifiers integrated with silica waveguide technology. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 7 March 2000; p. WA1. [Google Scholar]
- Hehlen, M.P.; Cockroft, N.J.; Gosnell, T.R.; Bruce, A.J. Spectroscopic properties of Er3+- and Yb3+-doped soda-lime silicate and aluminosilicate glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, 9302–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossler, G.L.; Brooks, C.J.; Winik, K.A. Planar Er:Yb glass ion exchanged waveguide laser. Electron. Lett. 1995, 31, 1162–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, P.; Meshkinfam, P.; Fardad, M.A.; Andrews, M.P.; Najafi, S.I. Potassium ion-exchanged Er-Yb doped phosphate glass amplifier. Electron. Lett. 1997, 33, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camy, P.; Roman, J.E.; Willems, F.W.; Hempstead, M.; Van Der Plaats, J.C.; Prel, C.; Beguin, A.; Koonen, A.M.J.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Lerminiaux, C. Ion-exchanged planar lossless splitter at 1.5 μm. Electron. Lett. 1996, 32, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, D.; Delavaux, J.M.; Kevorkian, A.; Gastaldo, P.; Jouanno, J.M. Yb/Er Integrated optics amplifiers on phosphate glass in single and double pass configurations. In Optical Fiber Communications Conference; Optical Society of America: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1995; p. PD3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, D.; Bruno, P.; Cassagnettes, C.; Trouillon, M.; Hyde, R.L.; Kevorkian, A.; Delavaux, J.M.P. Net gain of 27 dB with a 8.6-cm-long Er/Yb-doped glass-planar-amplifier. In Proceedings of the OFC ’98, Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibit, OSA Technical Digest Series Volume2 (IEEE Cat. No.98CH36177). San Jose, CA, USA, 22–27 February 1998; pp. 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipsen, J.L.; Barbier, D.; Kévorkian, A.; Cassagnettes, C.; Krebs, N.; Bruno, P. Compact gain-block consisting of an Er3+-doped waveguide amplifier (EDWA) and a pump/signal multiplexer, realized by ion exchange. In Optical Amplifiers and Their Applications; OSA: Québec, QC, Canada, 2000; p. OTuD2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, A.; Guglielmi, M.; Fick, J.; Pelli, S.; Forastiere, M.A.; Righini, G.C.; Battaglin, C. Germania sol-gel waveguides for optical amplifiers. In Sol-Gel Optics V; Dunn, B.S., Pope, E.J.A., Schmidt, H.K., Yamane, M., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 3943, pp. 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelli, S.; Brenci, M.; Fossi, M.; Righini, G.C.; Duverger, C.; Montagna, M.; Rolli, R.; Ferrari, M. Optical and spectroscopic characterization of Er/Yb-activated planar waveguides. In Rare-Earth-Doped Materials and Devices IV; Jiang, S., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 3942, pp. 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.C.; Pelli, S.; Fossi, M.; Brenci, M.; Lipovskii, A.A.; Kolobkova, E.V.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M. Characterization of Er-doped sodium-niobium phosphate glasses. In Rare-Earth-Doped Materials and Devices V; Jiang, S., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4282, pp. 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorbello, G.; Taccheo, S.; Marano, M.; Marangoni, M.; Osellame, R.; Ramponi, R.; Laporta, P. Comparative study of Ag–Na thermal and field-assisted ion exchange on Er-doped phosphate glass. Opt. Mater. 2001, 17, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobkobal, E.V.; Lipovskii, A.A.; Montero, C.; Liñares, J. Formation and modelling of optically waveguiding structures in a high-concentration Er-doped phosphate glass. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Jiang, S.; Wu, J.; Song, F.; Peyghambarian, N.; Pun, E.Y.B. Er3+-doped Na2O–Nb2O5–TeO2 glasses for optical waveguide laser and amplifier. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, G.N.; Tikhomirov, V.K.; Bettinelli, M.; Berneschi, S.; Brenci, M.; Chen, B.; Pelli, S.; Speghini, A.; Seddon, A.B.; Righini, G.C. Characterization of ion-exchanged waveguides in tungsten tellurite and zinc tellurite Er3+-doped glasses. Opt. Eng. 2003, 42, 2805–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelli, S.; Bettinelli, M.; Brenci, M.; Calzolai, R.; Chiasera, A.; Ferrari, M.; Nunzi Conti, G.; Speghini, A.; Zampedri, L.; Zheng, J.; et al. Erbium-doped silicate glasses for integrated optical amplifiers and lasers. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 345–346, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Pun, E.Y.B. K+-Na+ ion-exchanged waveguides in Er3+ -Yb3+ codoped phosphate glasses using field-assisted annealing. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pissadakis, S.; Ikiades, A.; Hua, P.; Sheridan, A.K.; Wilkinson, J.S. Photosensitivity of ion-exchanged Er-doped phosphate glass using 248 nm excimer laser radiation. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 3131–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capek, P.; Mika, M.; Oswald, J.; Tresnakova, P.; Salavcova, L.; Kolek, O.; Schrofel, J.; Spirkova, J. Effect of divalent cations on properties of Er3+-doped silicate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2004, 27, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, M.; Kolek, O.; Spirkova, J.; Capek, P.; Berneschi, S.; Brenci, M.; Conti, G.N.; Pelli, S.; Sebastiani, S.; Righini, G.C. The effect of Ca2+, Mg2+, and Zn2+ on optical properties of Er3+-doped silicate glass. In Optical Components and Materials II; Jiang, S., Digonnet, M.J., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5723, pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrac, F.; Ek; Salavcova, L.; Míka, M.; Špirková, J. Characterization of Erbium Doped Glass Optical Waveguides by a Fine Tunable Semiconductor Laser. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2005, 5, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bucci, D.; Grelin, J.; Ghibaudo, E.; Broquin, J.E. Study of a pump/signal multiplexer based on a segmented asymmetric Y junction by silver/sodium ion exchange on glass. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6123, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berneschi, S.; Bettinelli, M.; Brenci, M.; Dall’Igna, R.; Nunzi Conti, G.; Pelli, S.; Profilo, B.; Sebastiani, S.; Speghini, A.; Righini, G.C. Optical and spectroscopic properties of soda-lime alumino silicate glasses doped with Er3+ +and/or Yb3+. Opt. Mater. 2006, 28, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliniemi, S.; Albert, J.; Laronche, A.; Castro, J.M.; Geraghty, D.; Honkanen, S. Negligible birefringence in dual-mode ion-exchanged glass waveguide gratings. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 6602–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, P.; Jose, G. Erbium doped phospho-tellurite glasses for 1.5 μm optical amplifiers. Opt. Commun. 2006, 265, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, V.; Chillcce, E.; Rodriguez, E.; Cesar, C.; Barbosa, L. Planar waveguides by ion exchange in Er3+-doped tellurite glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakida, S.; Nanba, T.; Miura, Y. Refractive-index profiles and propagation losses of Tb3+-doped tungsten tellurite glass waveguide by Ag+–Na+ ion-exchange. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 3413–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, D.; Grelin, J.; Ghibaudo, E.; Broquin, J. Realization of a 980-nm/1550-nm Pump-Signal (De)multiplexer Made by Ion-Exchange on Glass Using a Segmented Asymmetric Y-Junction. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2007, 19, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondráček, F.; Salavcová, L.; Míka, M.; Lahodný, F.; Slavík, R.; Špirková, J.; Čtyroký, J. Fabrication and characterization of channel optical waveguides in Er-Yb-doped silicate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2007, 30, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakida, S.; Nanba, T.; Miura, Y. Optical properties of Er3+-doped tungsten tellurite glass waveguides by Ag-Na ion-exchange. Opt. Mater. 2007, 30, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svecova, B.; Spirkova, J.; Janakova, S.; Mika, M. Ion-exchanged optical waveguides fabricated in novel Er3+ and Er3+. Yb3+-doped silicate glasses: Relations between glass composition, basicity and waveguide properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2008, 149, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.; Maia, L.; Nascimento, A.; Gonçalves, R.; Poirier, G.; Messaddeq, Y.; Ribeiro, S. Er3+-doped germanate glasses for active waveguides prepared by Ag or K - Na ion-exchange. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 4743–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svecova, B.; Spirkova, J.; Janakova, S.; Mika, M.; Oswald, J.; Mackova, A. Diffusion process applied in fabrication of ion-exchanged optical waveguides in novel Er3+ and Er3+ - Yb3+-doped silicate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2009, 20, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.L.; Pun, E.Y.; Lin, H. Tm3+-doped ion-exchanged aluminum germanate glass waveguide for S-band amplification. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 151106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozelli, J.C.; Nunes, L.A.d.O.; Sigoli, F.A.; Mazali, I.O. Erbium and Ytterbium Codoped Titanoniobophosphate Glasses for Ion-Exchange-Based Planar Waveguides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 2689–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Sakida, S.; Benino, Y.; Nanba, T. Fabrication and characterization of Er3+-doped tellurite glass waveguide by Ag-Na ion-exchange method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 18, 112018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Doualan, J.L.; Camy, P.; Lhermite, H.; Adam, J.L.; Nazabal, V. Development of Praseodymium doped fluoride waveguide. In Optical Components and Materials IX; Jiang, S., Digonnet, M.J.F., Dries, J.C., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8257, pp. 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Chen, B.; Lin, H.; Pun, E. Praseodymium ion doped phosphate glasses for integrated broadband ion-exchanged waveguide amplifier. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.F.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Chung, P.S. Er3+-Yb3+ codoped phosphate glass waveguide amplifier using Ag-Li ion exchange. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2002, 14, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Dai, J.Z.; Yang, Y.P.; Guan, Z.G.; Huang, X.L. Er3+/Yb3+ codoped phosphate glass waveguide amplifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2002 International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems, Chengdu, China, 29 June–1 July 2002; Volume 1, pp. 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, G.; Sorbello, G.; Taccheo, S.; Cianci, E.; Foglietti, V.; Laporta, P. Active waveguide devices by Ag–Na ion exchange on erbium–ytterbium doped phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 322, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardillou, F.; Bastard, L.; Broquin, J.E. 4.25 dB gain in a hybrid silicate/phosphate glasses optical amplifier made by wafer bonding and ion-exchange techniques. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 5176–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardillou, F.; Broquin, J.E. Optical amplifier made by reporting an Er3+- Yb3+-codoped glass layer on an ion-exchanged passive glass substrate by wafer bonding. In Integrated Optics: Devices, Materials, and Technologies IX; Sidorin, Y., Waechter, C.A., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5728, pp. 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo-Liang, J.; Gong-Wang, S.; Huan, M.; Li-Li, H.; Qu, L. Gain and Noise Figure of a Double-Pass Waveguide Amplifier Based on Er/Yb-Doped Phosphate Glass. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2005, 22, 2862–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardillou, F.; Broquin, J.E. Net gain demonstration with glass hybrid optical amplifiers made by ion-exchange and wafer bonding. Integr. Opt. Devices Mater. Technol. X 2006, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Valle, G.; Taccheo, S.; Laporta, P.; Sorbello, G.; Cianci, E.; Foglietti, V. Compact high gain erbium-ytterbium doped waveguide amplifier fabricated by Ag-Na ion exchange. Electron. Lett. 2006, 42, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zian, H.; Yigang, L.; Yanwu, Z.; Dongxiao, L.; Liying, L.; Lei, X. Er3+-Yb3+ co-doped waveguide amplifier and lossless power splitter fabricated by a two-step ion exchange on a commercial phosphate glass. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2006, 49, 2159–2163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Mu, S.; Tan, C.; Zhang, D.; Pun, E.; Zhang, D. Er3+–Yb3+ co-doped glass waveguide amplifiers using ion exchange and field-assisted annealing. Opt. Commun. 2006, 268, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Pun, E.Y. Modeling and experiments of packaged Er3+–Yb3+ co-doped glass waveguide amplifiers. Opt. Commun. 2007, 273, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondracek, F.; Jagerska, J.; Salavcova, L.; Mika, M.; Spirkova, J.; Ctyroky, J. Er–Yb Waveguide Amplifiers in Novel Silicate Glasses. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2008, 44, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, G.; Jin, G.; Li, Q. Gain and noise figure characteristics of an Er3+–Yb3+ doped phosphate glass waveguide amplifier with a bidirectional pump scheme and double-pass configuration. Opt. Eng. 2008, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onestas, L.; Nappez, T.; Ghibaudo, E.; Vitrant, G.; Broquin, J.E. 980 nm–1550 nm vertically integrated duplexer for hybrid erbium-doped waveguide amplifiers on glass. In Integrated Optics: Devices, Materials, and Technologies XIII; Broquin, J.E., Greiner, C.M., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7218, pp. 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Jin, G.; Zhan, L.; Li, Q. Influence of multimode-pump propagation on the gain characteristics of erbium-ytterbium doped waveguide amplifier. Appl. Phys. B 2009, 97, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzella, V.; Toccafondo, V.; Faralli, S.; Pasquale, F.D.; Cassagnettes, C.; Barbier, D.; Figueroa, H.H. Ion-exchanged Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped waveguide amplifiers longitudinally pumped by broad area lasers. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 12690–12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Lin, L.; Zhao, X.; Pun, E.; Yang, D.; Lin, H. Mixing up-conversion excitation behaviors in Tb3+–Tb3+ codoped aluminum germanate glasses for visible waveguide devices. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 503, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onestas, L.; Bucci, D.; Ghibaudo, E.; Broquin, J. Vertically Integrated Broadband Duplexer for Erbium-Doped Waveguide Amplifiers Made by Ion Exchange on Glass. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2011, 23, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, L. Ion-exchanged silica-on-silicon structured channel erbium-doped waveguide amplifiers. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 2964–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmejcký, J.; Jeřábek, V.; Nekvindová, P. Gain determination of optical active doped planar waveguides. In Photonics, Devices, and Systems VII; Fliegel, K., Páta, P., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10603, pp. 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmejckỳ, J.; Jeřábek, V. Differential Gain Comparison of Optical Planar Amplifier on Silica Glasses Doped with Bi-Ge and Er, Yb Ions. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 7, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yliniemi, S.; Honkanen, S.; Ianoul, A.; Laronche, A.; Albert, J. Photosensitivity and volume gratings in phosphate glasses for rare-earth-doped ion-exchanged optical waveguide lasers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2006, 23, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Montiel, R.; Bastard, L.; Grosa, G.; Broquin, J.E. Hybrid Neodymium-doped passively Q-switched waveguide laser. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2008, 149, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, M.; Bucci, D.; Bastard, L.; Broquin, J.E. 1.55 μm hybrid waveguide laser made by ion-exchange and wafer bonding. In Integrated Optics: Devices, Materials, and Technologies XVI; Broquin, J.E., Conti, G.N., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8264, pp. 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Dhingra, S.; D’Urso, B.; Kannan, P.; Shepherd, D.P. Graphene Q-Switched Mode-Locked and Q-Switched Ion-Exchanged Waveguide Lasers. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Jiang, S.; Luo, T.; Hu, Y.; Peyghambarian, N. Optical waveguides prepared in Er3+-doped tellurite glass by Ag+-Na+ ion exchange. In Rare-Earth-Doped Materials and Devices V; Jiang, S., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4282, pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, G.N.; Berneschi, S.; Bettinelli, M.; Brenci, M.; Chen, B.; Pelli, S.; Speghini, A.; Righini, G. Rare-earth doped tungsten tellurite glasses and waveguides: Fabrication and characterization. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 345–346, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Fang, D.; Xu, S.; Hu, L. Spectroscopic properties and thermal stability of Er3+-doped tungsten tellurite glass for waveguide amplifier application. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 424, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.C.; Forastiere, M.A.; Guglielmi, M.; Martucci, A. Rare-earth-doped sol-gel waveguides: A review. In Rare-Earth-Doped Devices II; Honkanen, S., Jiang, S., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Volume 3280, pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Syms, R.R.A.; Yeatman, E.M.; Ahmad, M.M.; Clapp, T.V.; Ojha, S.M. Fiber-device-fiber gain from a sol-gel erbium-doped waveguide amplifier. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2002, 14, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peled, A.; Chiasera, A.; Nathan, M.; Ferrari, M.; Ruschin, S. Monolithic rare-earth doped sol-gel tapered rib waveguide laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 221104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, F.T.; Ferrari, J.L.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Ferrier, A.; Goldner, P.; Gonçalves, R.R. Broadband NIR emission in novel sol–gel Er3+-doped SiO2–Nb2O5 glass ceramic planar waveguides for photonic applications. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.M.; Marques, A.C. The potential of ion exchange in sol–gel derived photonic materials and structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2008, 149, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaouen, Y.; du Mouza, L.; Barbier, D.; Delavaux, J.; Bruno, P. Eight-wavelength Er-Yb doped amplifier: Combiner/splitter planar integrated module. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1999, 11, 1105–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Milanese, D.; Chen, Q.; Ferraris, M.; Righini, G.C. Fabrication and direct bonding of photosensitive multicomponent silicate glasses for lossless planar waveguide splitters. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.; Pollnau, M. Erbium-doped integrated waveguide amplifiers and lasers. Laser Photonics Rev. 2011, 5, 368–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrichi, F.; Cattaruzza, E.; Ferrari, M.; Gonella, F.; Martucci, A.; Ottini, R.; Riello, P.; Righini, G.C.; Trave, E.; Vomiero, A.; et al. Role of Ag multimers as broadband sensitizers in Tb3+/Yb3+ co-doped glass-ceramics. In Fiber Lasers and Glass Photonics; Taccheo, S., Mackenzie, J.I., Ferrari, M., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10683, pp. 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vařák, P.; Vytykáčová, S.; Nekvindová, P.; Michalcová, A.; Malinský, P. The influence of copper and silver in various oxidation states on the photoluminescence of Ho3+/Yb3+ doped zinc-silicate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2019, 91, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrichi, F.; Belmokhtar, S.; Benedetti, A.; Bouajaj, A.; Cattaruzza, E.; Coccetti, F.; Colusso, E.; Ferrari, M.; Ghamgosar, P.; Gonella, F.; et al. Ag nanoaggregates as efficient broadband sensitizers for Tb3+ ions in silica-zirconia ion-exchanged sol-gel glasses and glass-ceramics. Opt. Mater. 2018, 84, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vařák, P.; Nekvindová, P.; Vytykáčová, S.; Michalcová, A.; Malinský, P.; Oswald, J. Near-infrared photoluminescence enhancement and radiative energy transfer in RE-doped zinc-silicate glass (RE = Ho, Er, Tm) after silver ion exchange. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 557, 120580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N. Rare-Earth-Doped Lasers on Silicon Photonics Platforms. Ph.D. Thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Demirtaş, M.; Ay, F. High-Gain Er3+:Al2O3 On-Chip Waveguide Amplifiers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2020, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, W.A.P.M.; Chang, L.; van Emmerik, C.I.; Mu, J.; de Goede, M.; Dijkstra, M.; Garcia-Blanco, S.M. Rare-earth ion doped Al2O3 for active integrated photonics. Adv. Phys. X 2021, 6, 1833753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipovskii, A.; Zhurikhina, V.; Tagantsev, D. 2D-structuring of glasses via thermal poling: A short review. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2018, 9, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateo, E.F.; Linares, J. A phase insensitive all-optical router based on nonlinear lenslike planar waveguides. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 3355–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimenko, V.S.; Gerasimenko, N.D.; Kiselev, F.D. Numerical modelling of an error of manufacturing of ion- exchange waveguide for the tasks of quantum computations. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1410, 012136-1-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimenko, V.S.; Gerasimenko, N.D.; Kiselev, F.D.; Samsonov, E.; Kozlov, S. Numerical modeling of ion exchange waveguide for the tasks of quantum computations. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math 2019, 10, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nahra, S.P.M.; Joos, M.; Muhammad, M.H.; Agafonov, V.; Lhuillier, E.; Geoffra, F.; Davydov, V.; Glorieu, Q.; Giacobin, E.; Blaiz, S.; et al. Nanophotonic approaches for integrated quantum photonics. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.10343. [Google Scholar]
- Couteau, C.; Nahra, M.; Muhammad, M.H.; Pierini, S.; Xu, X.; Broussier, A.; Bachelot, R.; Blaize, S. Towards a new platform for quantum photonics applications. In Advances in Photonics of Quantum Computing, Memory, and Communication XII; Hemmer, P.R., Migdall, A.L., Hasan, Z.U., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 10933, pp. 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Blanco, X.; Montero-Orille, C.; Liñares, J.; González-Núñez, H.; Balado, D. Quantum projectors implemented with optical directional couplers fabricated by Na/K ion-exchange in soda-lime glass. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.01169. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, H.; Neitz, M.; Schneider-Ramelow, M. Demonstration of glass-based photonic interposer for mid-board-optical engines and electrical-optical circuit board (EOCB) integration strategy. In Optical Interconnects XVIII; Schröder, H., Chen, R.T., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10538, pp. 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, J.; Metcalf, B.; Humphreys, P.; Kolthammer, W.; Jin, X.; Barbieri, M.; Datta, A.; Thomas-Peter, N.; Langford, N.K.; Kundys, D.; et al. Boson sampling on photonic chip. Science 2013, 239, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perets, H.B.; Lahini, Y.; Pozzi, F.; Sorel, M.; Morandotti, R.; Silberberg, Y. Realization of Quantum Walks with Negligible Decoherence in Waveguide Lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett 2008, 100, 170506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balado, D.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Barral, D.; Liñares, J. Autocompensating high-dimensional quantum cryptography by using integrated photonic devices in multicore optical fiber spatial multiplexing systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Integrated Quantum Photonics (ICIQP), Paris, France, 15–17 October 2018; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, G.L.; Finak, J. Directional-coupler power divider by two-step K+-ion exchange. Opt. Lett. 1984, 9, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkanen, S.; Pöyhönen, P.; Tervonen, A.; Najafi, S.I. Waveguide coupler for potassium- and silver-ion-exchanged waveguides in glass. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 2109–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.C.; Conti, G.N.; Forastiere, M.A. Integrated optical directional couplers: How effective are design and modeling for device production? In Integrated Optics Devices: Potential for Commercialization; Najafi, S.I., Armenise, M.N., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1997; Volume 2997, pp. 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Bai, N.; Zhao, N.; Xia, C. Space-division multiplexing: The next frontier in optical communication. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2014, 6, 413–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauwels, J.; Van der Sande, G.; Verschaffelt, G. Space division multiplexing in standard multi-mode optical fibers based on speckle pattern classification. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montero-Orille, C.; Moreno, V.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Mateo, E.F.; Ip, E.; Crespo, J.; Liñares, J. Ion-exchanged glass binary phase plates for mode-division multiplexing. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Blanco, X.; Montero-Orille, C.; Moreno, V.; Mateo, E.F.; Liñares, J. Chromatic characterization of ion-exchanged glass binary phase plates for mode-division multiplexing. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3308–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, E.; Milione, G.; Li, M.J.; Cvijetic, N.; Kanonakis, K.; Stone, J.; Peng, G.; Prieto, X.; Montero, C.; Moreno, V.; et al. SDM transmission of real-time 10GbE traffic using commercial SFP+ transceivers over 0.5km elliptical-core few-mode fiber. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 17120–17126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Montero-Orille, C.; Moreno, V.; Mouriz, D.; Nistal, M.C.; Prieto-Blanco, X. Ion-exchanged glass binary phase plates for mode multiplexing in graded-index optical fibers. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 7099–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Moreno, V.; Montero-Orille, C.; Mouriz, D.; Nistal, M.C.; Barral, D. Interferometric space-mode multiplexing based on binary phase plates and refractive phase shifters. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 10925–10938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Montero-Orille, C.; Moreno, V. Spatial mode multiplexing/demultiplexing by Gouy phase interferometry. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel1, M.F.; Binosi, D.; Thew, R.; Calarco1, T. The European quantum technologies flagship programme. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2017, 2, 030501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, E. Chinese satellite is one giant step for the quantum internet. Nature 2016, 535, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavaliere, F.; Prati, E.; Poti, L.; Muhammad, I.; Catuogno, T. Secure Quantum Communication Technologies and Systems: From Labs to Markets. Quantum Rep. 2020, 2, 80–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Integrated Quantum Optical Circuits Market by Material Type and Application: Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2018–2025. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/integrated-quantum-optical-circuits-market (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, 10–12 December 1984; pp. 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Liñares-Beiras, J.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Balado, D.; Carral, G.M. Autocompensating high-dimensional quantum cryptography by phase conjugation in optical fibers. EPJ Web Conf. 2020, 238, 11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Prieto-Blanco, X.; Balado, D.; Carral, G.M. Fully autocompensating high-dimensional quantum cryptography by quantum degenerate four-wave mixing. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 043710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.K.; Curty, M.; Qi, B. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xavier, J.; Yu, D.; Jones, C.; Zossimova, E.; Vollmer, F. Quantum nanophotonic and nanoplasmonic sensing: Towards quantum optical bioscience laboratories on chip. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 1387–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janszky, J.; Sibilia, C.; Bertolotti, M.; Yushin, Y. Non-classical Light in a Linear Coupler. J. Mod. Opt. 1988, 35, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perina, J., Jr.; Perina, J. Quantum statistics of nonlinear optical couplers (Chapter 5). In Progress in Optics; Wolf, E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 41, pp. 362–419. [Google Scholar]
- Liñares, J.; Nistal, M.C. Quantization of coupled modes propagation in integrated optical waveguides. J. Mod. Opt. 2003, 50, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Nistal, M.C.; Barral, D. Quantization of Coupled 1D Vector Modes in Integrated Photonics Waveguides. New J. Phys 2008, 10, 063023.1–063023.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Luo, F.; Cao, M.; Chen, W. MMI splitter by ion exchange on K9. In Passive Components and Fiber-based Devices II; Sun, Y., Chen, J., Lee, S.B., White, I.H., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 6019, pp. 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkman, O.; JeYábek, V.; Prajzler, V. Optical Splitters Based on Self-Imaging Effect in Multi-Mode Waveguide Made by Ion Exchange in Glass. Radioengineering 2013, 22, 352–356. [Google Scholar]
- Gnewuch, H.; Román, J.E.; Hempstead, M.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Ulrich, R. Beat-length measurement in directional couplers by thermo-optic modulation. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stosch, J.H.; Kühler, T.; Griese, E. Optical directional coupler for graded index waveguides in thin glass sheets for PCB integration. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 20th Workshop on Signal and Power Integrity (SPI), Turin, Italy, 8–11 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, J.; Montero, C.; Moreno, V.; Nistal, M.C.; Prieto, X.; Salgueiro, J.R.; Sotelo, D. Glass processing by ion exchange to fabricate integrated optical planar components: Applications. Proc. SPIE 2000, 3936, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







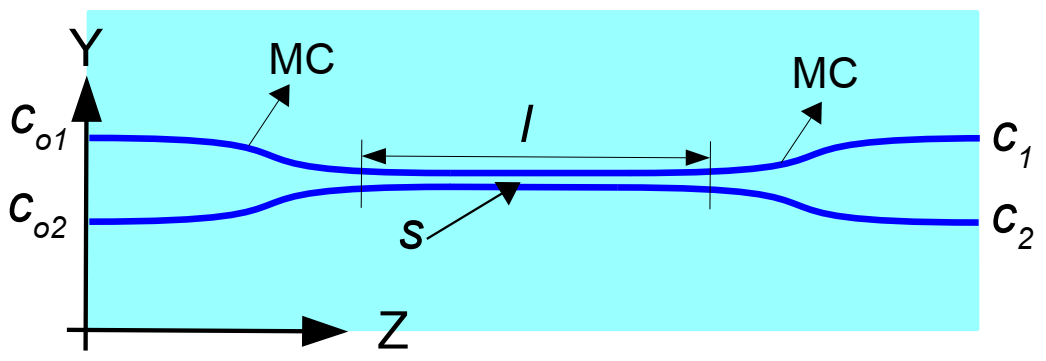
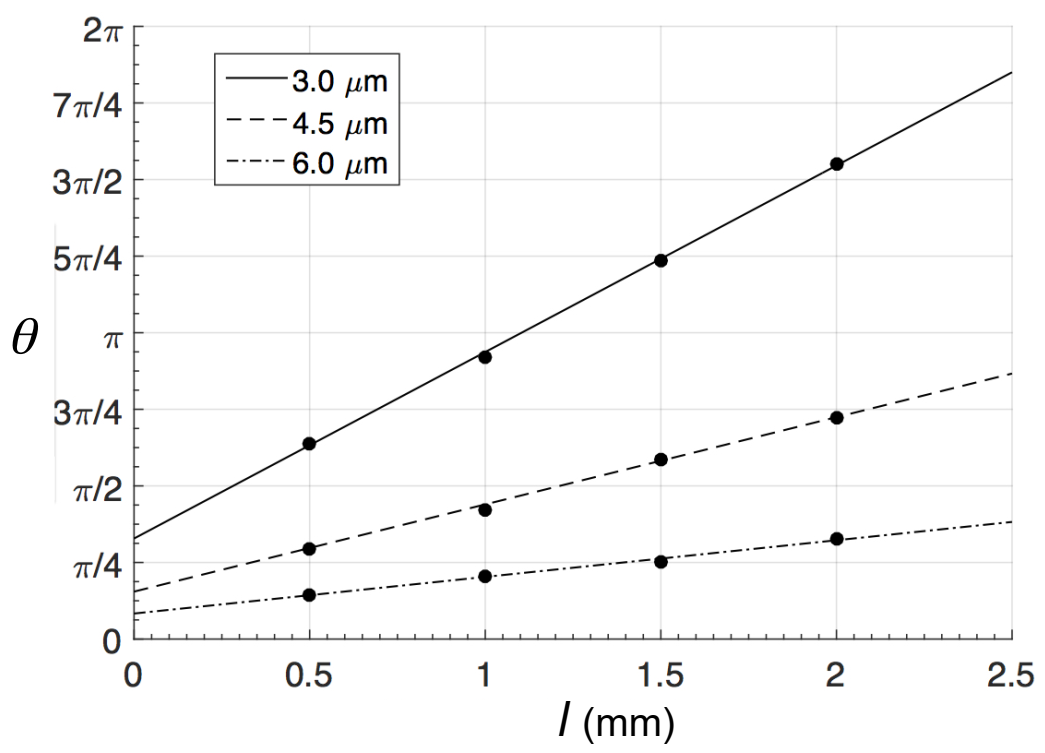
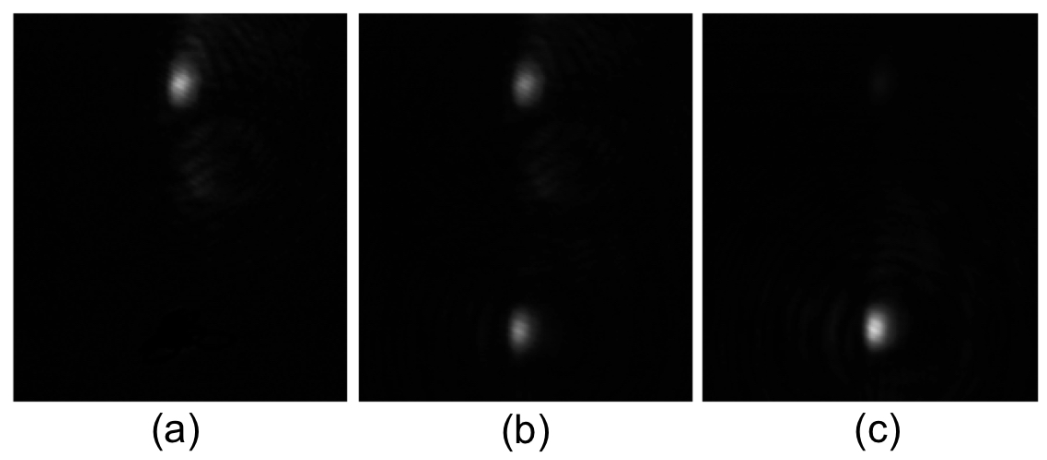
| Series of Couplers | l (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | ||
| s (μm) | 3.0 | (17.8|82.2) | (93.6|06.4) | (54.9|45.1) | (02.5|97.5) |
| 4.5 | (35.9|64.1) | (05.9|94.1) | (07.4|92.6) | (40.9|59.1) | |
| 6.0 | (80.7|19.3) | (63.8|36.2) | (49.3|50.7) | (26.8|73.2) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Righini, G.C.; Liñares, J. Active and Quantum Integrated Photonic Elements by Ion Exchange in Glass. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115222
Righini GC, Liñares J. Active and Quantum Integrated Photonic Elements by Ion Exchange in Glass. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115222
Chicago/Turabian StyleRighini, Giancarlo C., and Jesús Liñares. 2021. "Active and Quantum Integrated Photonic Elements by Ion Exchange in Glass" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115222
APA StyleRighini, G. C., & Liñares, J. (2021). Active and Quantum Integrated Photonic Elements by Ion Exchange in Glass. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115222







