Frictional Behavior of Cochlear Electrode Array Is Dictated by Insertion Speed and Impacts Insertion Force
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
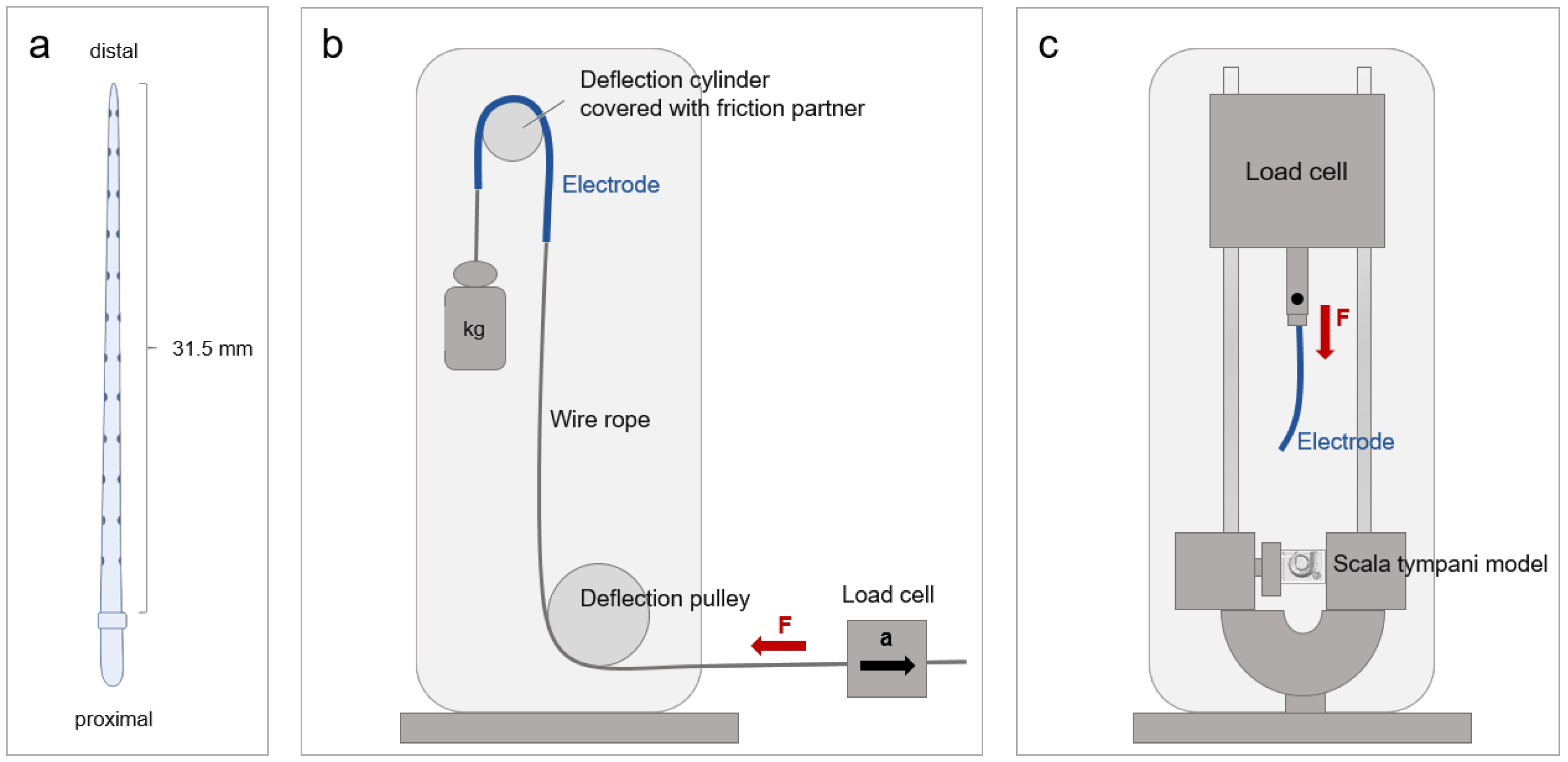
2.1. Electrode Array
2.2. Friction Measurements and Friction Coefficient Calculation
2.2.1. Friction Partner and Lubricant
2.2.2. Friction Test Bench
2.2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.2.4. Frictional Coefficient Calculation
2.3. Insertion Force Measurements
2.3.1. Artificial Scala Tympani Model
2.3.2. Insertion Force Test Bench
2.3.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Pulling Speed to Electrode Friction Forces
3.2. Calculation and Comparison of Friction Coefficient
3.3. Impact of Insertion Speed to Electrode Insertion Forces
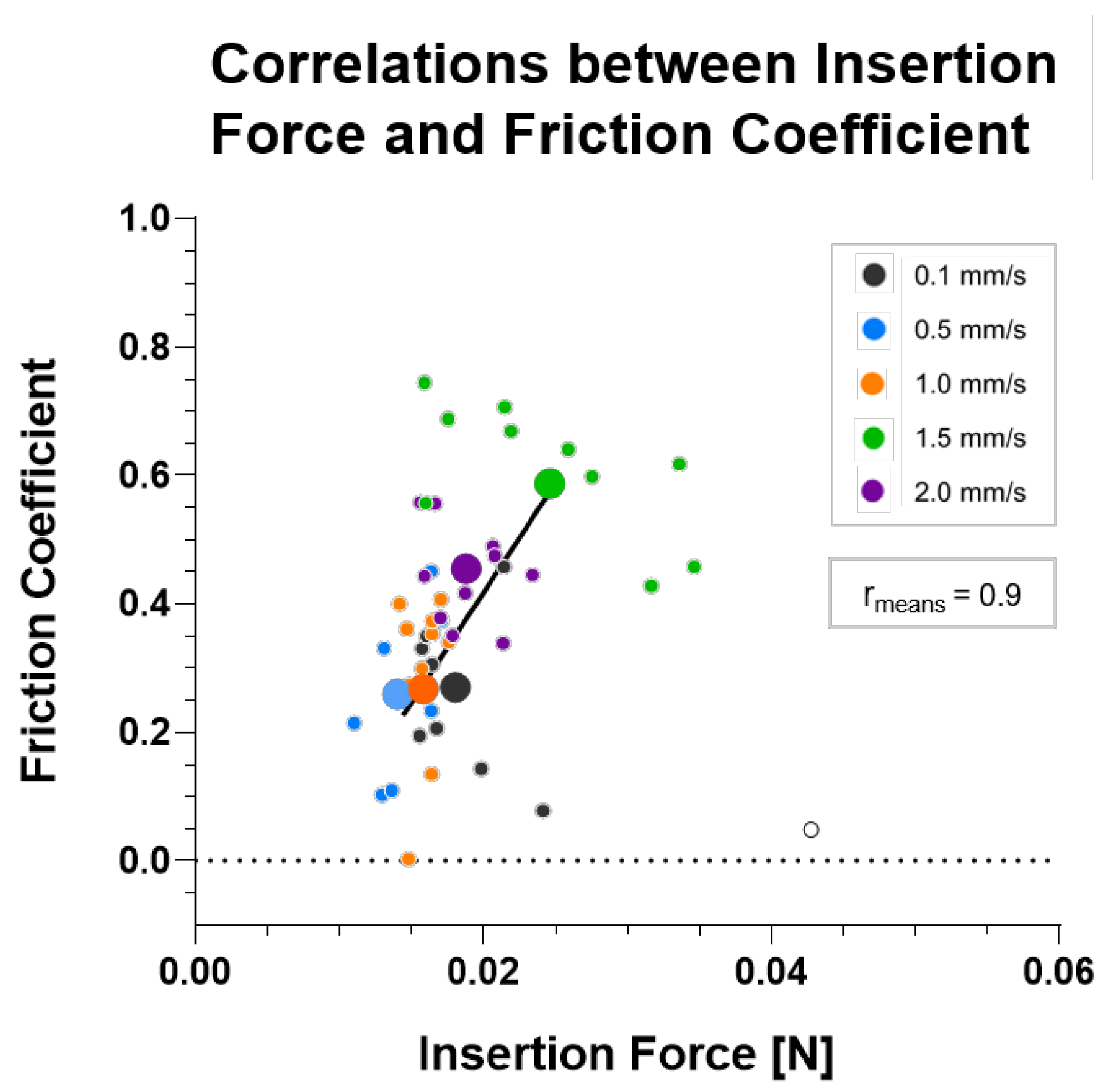
3.4. Correlation between Insertion Force and Friction Coefficient
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Image Manipulation
Abbreviations
| CI | Cochlear Implant |
| µ | friction coefficient |
| F | friction force |
| FG | weight force |
References
- D’Haese, P.S.; Van Rompaey, V.; De Bodt, M.; Van de Heyning, P. Severe Hearing Loss in the Ageing Population poses a Global Public Health Challenge. How can we better realise the Benefits of Cochlea Implantation to Mitigate this Crisis? Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, R.K.; Pyman, B.C.; Clark, G.M.; Webb, R.L. Banded intracochlear electrode array: Evaluation of insertion trauma in human temporal bones. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1985, 94, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykocinski, M.; Saunders, E.; Cohen, L.T.; Treaba, C.; Briggs, R.J.; Gibson, P.; Clark, G.M.; Cowan, R.S. The contour electrode array: Safety study and initial patient trials of a new perimodiolar design. Otol. Neurotol. 2001, 22, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.; Risi, F.; Escudé, B.; Durmo, I.; James, C.; Lauwers, F.; Deguine, O.; Fraysse, B. Reliability of cone beam computed tomography in scalar localization of the electrode array: A radio histological study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2014, 271, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanna, G.B.; Noble, J.H.; Carlson, M.L.; Gifford, R.H.; Dietrich, M.S.; Haynes, D.S.; Dawant, B.M.; Labadie, R.F. Impact of electrode design and surgical approach on scalar location and cochlear implant outcomes. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Friedmann, D.R.; Treaba, C.; Peng, R.; Roland, J.T., Jr. Does cochleostomy location influence electrode trajectory and intracochlear trauma? Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayad, J.; Linthicum, F.H., Jr.; Galey, F.R.; Otto, S.R.; House, W.F. Cochlear implants: Histopathologic findings related to performance in 16 human temporal bones. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1991, 100, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, A.A.; Yang, N.W.; Balkany, T.J. Comparative study of cochlear damage with three perimodiolar electrode designs. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardrop, P.; Whinney, D.; Rebscher, S.J.; Roland, J.T., Jr.; Luxford, W.; Leake, P.A. A temporal bone study of insertion trauma and intracochlear position of cochlear implant electrodes. I: Comparison of Nucleus banded and Nucleus Contour™ electrodes. Hear. Res. 2005, 203, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adunka, O.; Kiefer, J. Impact of electrode insertion depth on intracochlear trauma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 135, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gstoettner, W.; Plenk, H.; Franz, P.; Hamzavi, J.; Baumgartner, W.; Czerny, C.; Ehrenberger, K. Cochlear implant deep electrode insertion: Extent of insertional trauma. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1997, 117, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Takayama, M.; Takahashi, Y. Mechanical properties of human round window, basilar and Reissner’s membranes. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1995, 115, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Seta, D.; Torres, R.; Russo, F.Y.; Ferrary, E.; Kazmitcheff, G.; Heymann, D.; Amiaud, J.; Sterkers, O.; Bernardeschi, D.; Nguyen, Y. Damage to inner ear structure during cochlear implantation: Correlation between insertion force and radio-histological findings in temporal bone specimens. Hear. Res. 2017, 344, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontorinis, G.; Lenarz, T.; Stöver, T.; Paasche, G. Impact of the insertion speed of cochlear implant electrodes on the insertion forces. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Simaan, N. Model and Parameter Identification of Friction during Robotic Insertion of Cochlear-Implant Electrode Arrays. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 3859–3864. [Google Scholar]
- Damm, P.; Bender, A.; Duda, G.; Bergmann, G. In vivo measured joint friction in hip implants during walking after a short rest. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, A.W. The Friction Coefficient of Soft Contact Lens Surfaces in Relation to Comfort and Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, City University London, London, UK, March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kha, H.N.; Chen, B.K. Determination of frictional conditions between electrode array and endosteum lining for use in cochlear implant models. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontorinis, G.; Paasche, G.; Lenarz, T.; Stöver, T. The effect of different lubricants on cochlear implant electrode insertion forces. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, W.; Grabow, N.; Behrens, P.; Schmitz, K.P. Trackability, crossability, and pushability of coronary stent systems-an experimental approach. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 47, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriam, J.L.; Kraige, L.G. Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York City, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 389–390. [Google Scholar]
- Rau, T.S.; Hussong, A.; Leinung, M.; Lenarz, T.; Majdani, O. Automated insertion of preformed cochlear implant electrodes: Evaluation of curling behaviour and insertion forces on an artificial cochlear model. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2010, 5, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, E.; Nauwelaers, T.; Hamacher, V.; Kral, A. Three-dimensional force profile during cochlear implantation depends on individual geometry and insertion trauma. Ear Hear. 2017, 38, e168–e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, F.H. Visceral Fascia. Fascia: The Tensional Network of the Human Body-E-Book: The Science and Clinical Applications in Manual and Movement Therapy; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, J.T., Jr. A model for cochlear implant electrode insertion and force evaluation: Results with a new electrode design and insertion technique. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, C.A.; Naghdy, F.; Svehla, M.J. Force application during cochlear implant insertion: An analysis for improvement of surgeon technique. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radeloff, A.; Unkelbach, M.H.; Mack, M.G.; Settevendemie, C.; Helbig, S.; Mueller, J.; Hagen, R.; Mlynski, R. A coated electrode carrier for cochlear implantation reduces insertion forces. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.D.; Scoffings, D.; Chung, M.; Baguley, D.; Donnelly, N.P.; Axon, P.R.; Gray, R.F.; Tysome, J.R. Computed tomography estimation of cochlear duct length can predict full insertion in cochlear implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
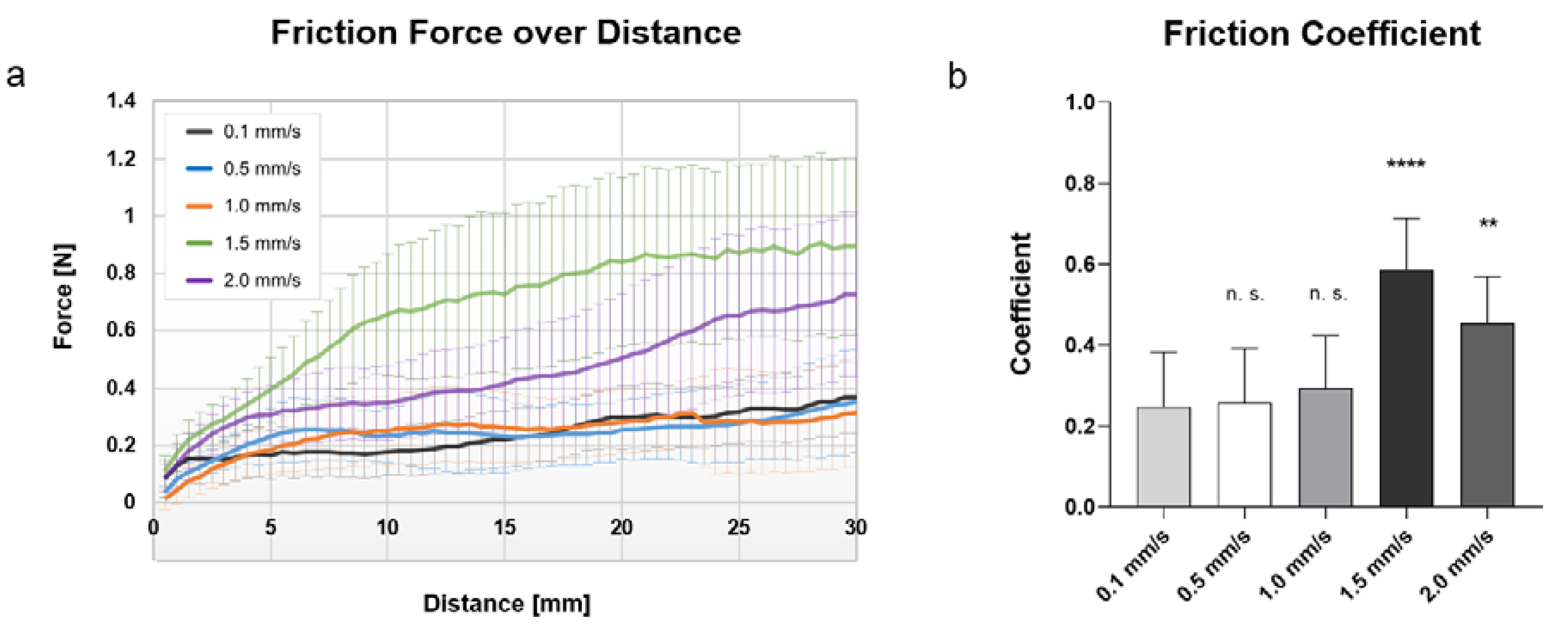

| Speed [mm/s] | Insertion Force [N] | Friction Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.020 ± 0.008 | 0.24 ± 0.13 |
| 0.5 | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 0.26 ± 0.12 |
| 1.0 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.27 ± 0.14 |
| 1.5 | 0.025 ± 0.007 | 0.59 ± 0.12 |
| 2.0 | 0.019 ± 0.003 | 0.45 ± 0.11 |
| Correlation coefficient (rmeans) | 0.9129 | |
| p-value (insertion force vs. friction coefficient) | 0.03 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dohr, D.; Fiedler, N.; Schmidt, W.; Grabow, N.; Mlynski, R.; Schraven, S.P. Frictional Behavior of Cochlear Electrode Array Is Dictated by Insertion Speed and Impacts Insertion Force. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115162
Dohr D, Fiedler N, Schmidt W, Grabow N, Mlynski R, Schraven SP. Frictional Behavior of Cochlear Electrode Array Is Dictated by Insertion Speed and Impacts Insertion Force. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115162
Chicago/Turabian StyleDohr, Dana, Nicklas Fiedler, Wolfram Schmidt, Niels Grabow, Robert Mlynski, and Sebastian P. Schraven. 2021. "Frictional Behavior of Cochlear Electrode Array Is Dictated by Insertion Speed and Impacts Insertion Force" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115162
APA StyleDohr, D., Fiedler, N., Schmidt, W., Grabow, N., Mlynski, R., & Schraven, S. P. (2021). Frictional Behavior of Cochlear Electrode Array Is Dictated by Insertion Speed and Impacts Insertion Force. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115162






