Numerical Study of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics Comparison between a Ducted Propeller and a Rim-Driven Thruster
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CFD Model Setup and Validation
2.1. Numerical Model
2.2. Grid Generation and Validation Study
3. Results and Discussion
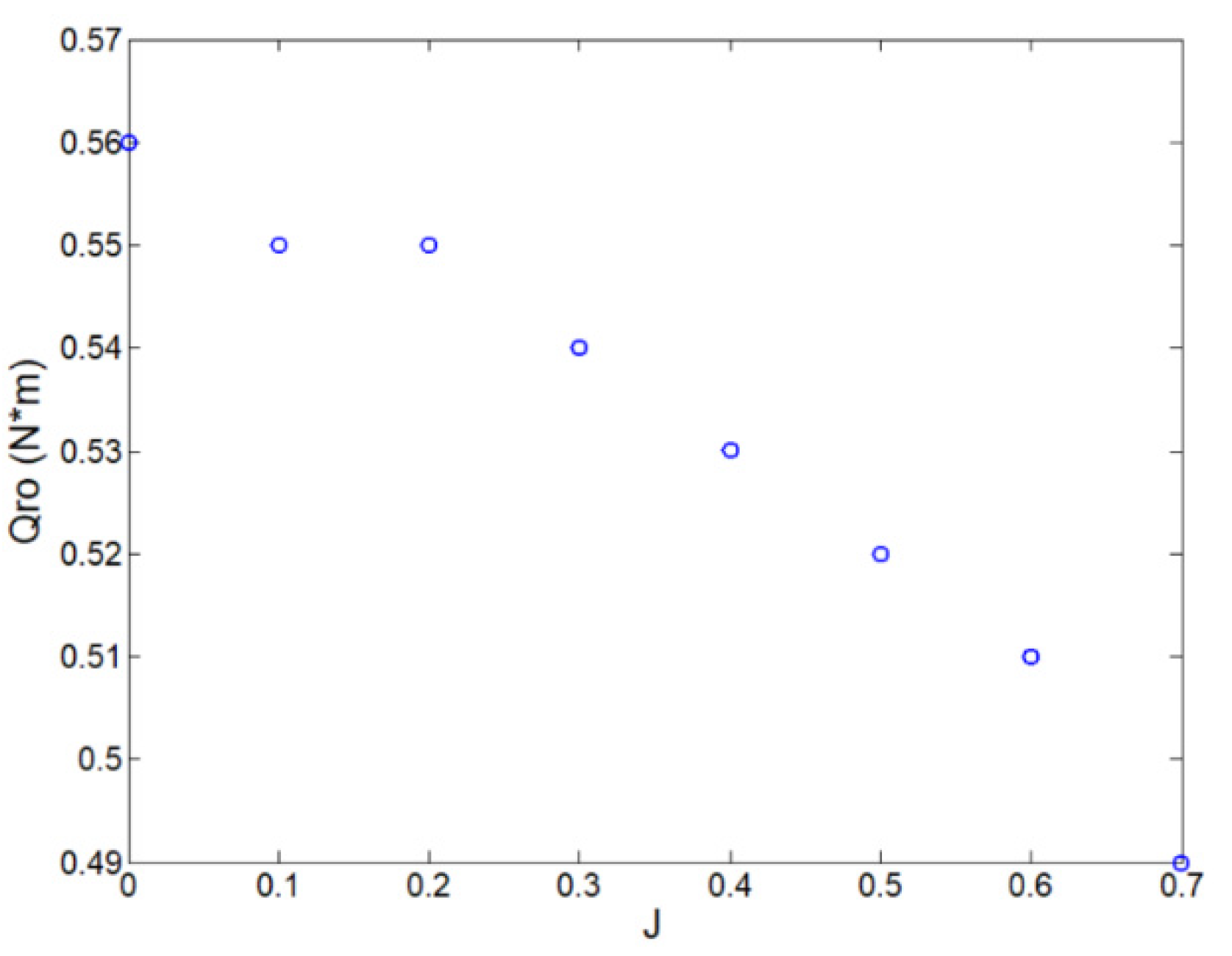
3.1. Open Water Performance
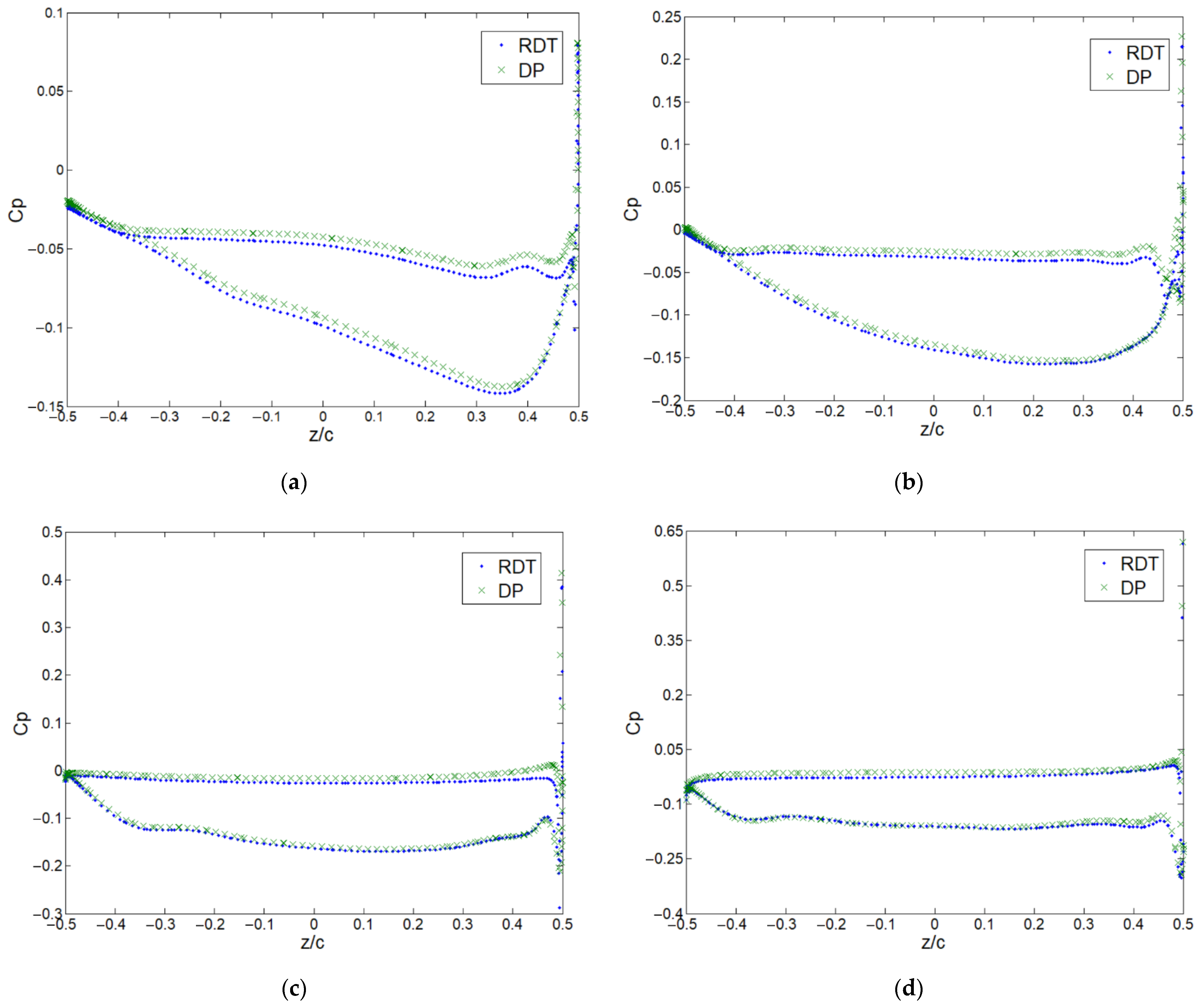
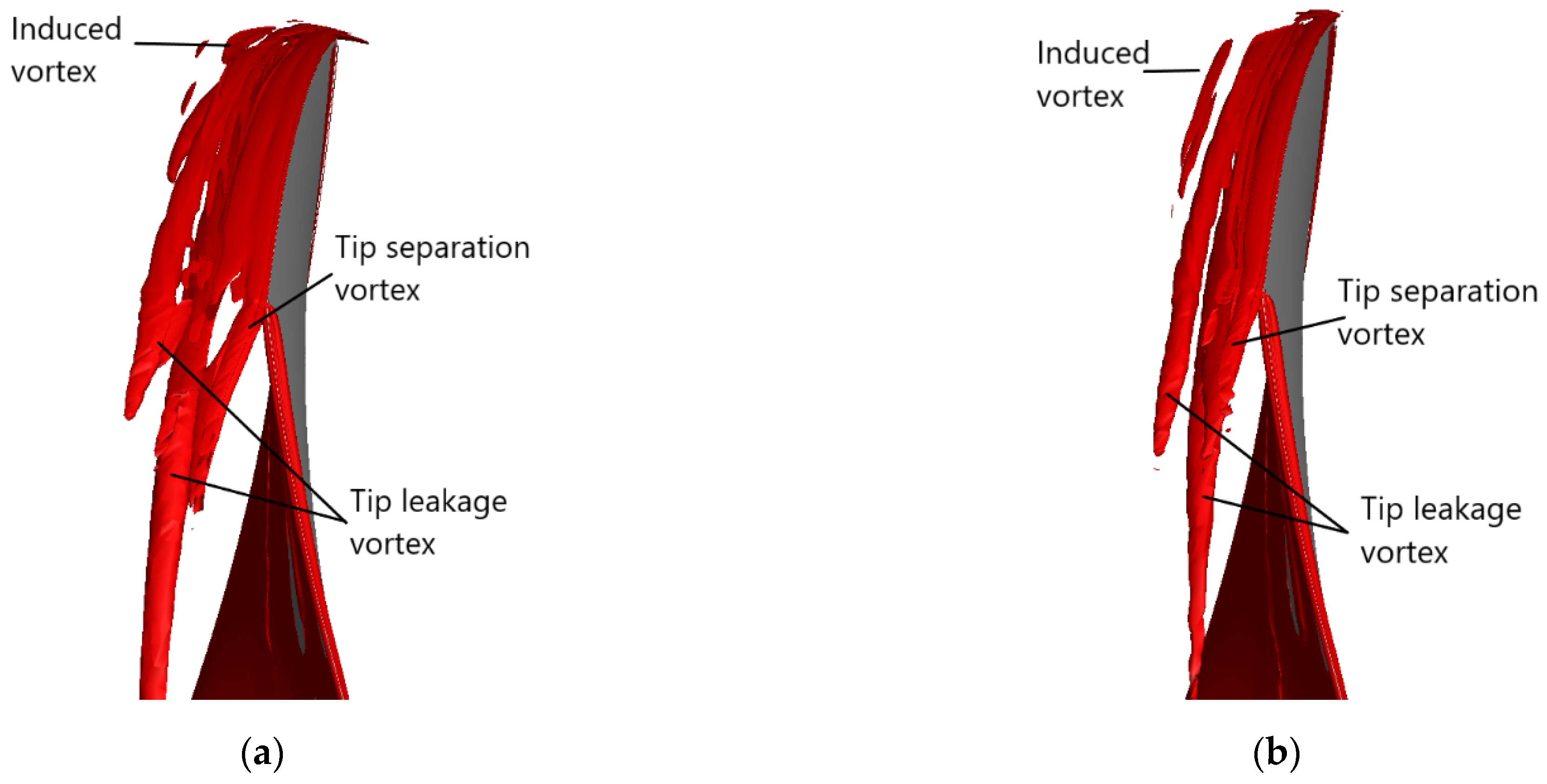
3.2. Tip Leakage Flow in the Ducted Propeller
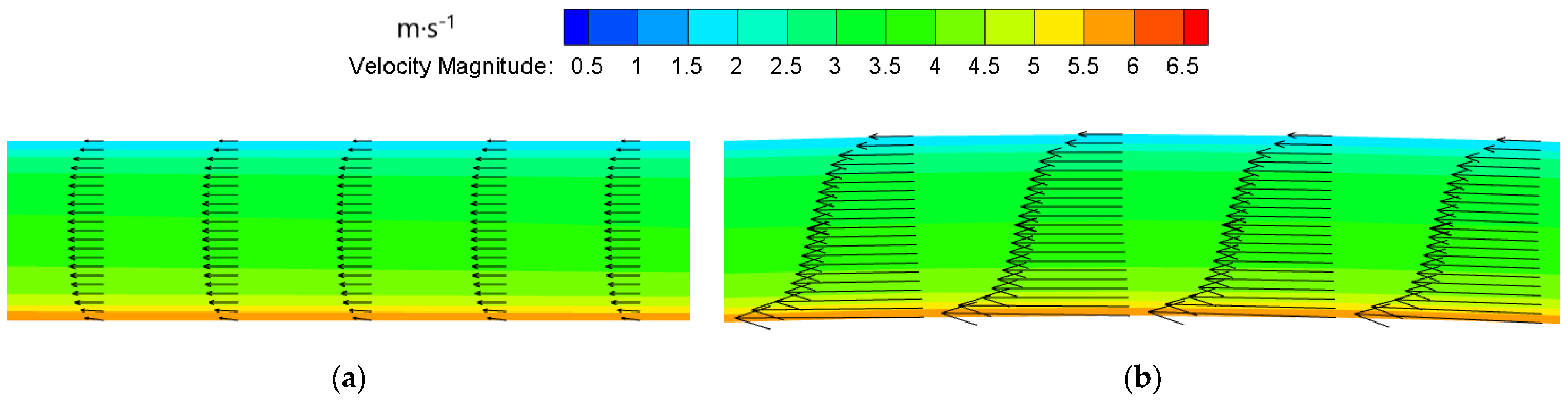
3.3. Gap Flow in the RDT
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, W.Z.; Yan, X.P.; Liu, Z.L. Technology development and prospect of shaftless rim-driven propulsion system. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Transp. Sci. Eng. 2015, 39, 601–605. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.P.; Liang, X.X.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, Z.L.; Liu, B.; Lan, J.F. A review of progress and applications of ship shaft-less rim-driven thrusters. Ocean Eng. 2017, 144, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkh, S.M.; Lai, S.H. Slotless PM brushless motor with helical edge-wound laminations. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, P.F.; Jin, S.B.; Wei, Y.S.; Lan, R.S.; Zhuang, S.J.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, S.W.; Chen, J.Q.; Wang, D.; et al. Design of novel shaftless pump-jet propulsor for multi-purpose long-range and high-speed autonomous underwater vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Sharkh, S.M.; Turnock, S.R.; Draper, G. Performance of a tip-driven electric thruster for unmanned underwater vehicles. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Stavanger, Norway, 17–22 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.J.; Yang, C.J.; Wu, S.J.; Zhu, Y.S.; Xie, Y. Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Rim-Driven Thruster Based on RANS Method. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2015—MTS/IEEE Washington, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Z.L. Hydrodynamic performance analysis of hubless rim-driven propulsors. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 256, 2565–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.M.; Zhao, W.F.; Tang, D.H.; Hong, F.W. Effect of gap flow on the torque for blades in a rim driven thruster without axial pressure gradient. ICFM7. Procedia Eng. 2015, 126, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Q.M.; Hong, F.W.; Tang, D.H.; Hu, F.L.; Lu, L.Z. Prediction of loading distribution and hydrodynamic measurements for propeller blades in a rim driven thruster. J. Hydrodynam. 2012, 24, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterveld, M.W.C. Wake Adapted Ducted Propellers; H. Veenman & Zonen: Wagensingen, Holland, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.C.; Liu, H.Y.; Tsao, M.L.; Chu, H.H. Ducted Propellers with Simplified Duct Profile. J. Shipbuild. China 1978, 9, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Moukalled, F.; Mangani, L.; Darwish, M. The Finite Volume Method in Computational Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 113. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celik, I.B.; Ghia, U.; Roache, P.J.; Freitas, C.J. Procedure for estimation and reporting of uncertainty due to discretization in CFD applications. J. Fluids Eng. 2008, 130, 078001. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, S.; Brizzolara, S. Relevance of transition turbulent model for hydrodynamic characteristics of low Reynolds number propeller. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 87, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubas, A.J.; Bressloff, N.W.; Sharkh, S.M. Numerical modelling of rotor–stator interaction in rim driven thrusters. Ocean Eng. 2015, 106, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, D.; Wang, M.; Moin, P.; Mittal, R. Large-eddy simulation analysis of mechanisms for viscous losses in a turbomachinery tip-clearance flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 586, 177–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.; Hussain, F. On the identification of a vortex. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 285, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgen, E.; Boulos, R. Functional dependence of torque coefficient of coaxial cylinders on gap width and Reynolds numbers. J. Fluids Eng. 1973, 95, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.M.; Wei, X.Z.; Tang, D.H.; Hong, F.W. Study of gap flow effects on hydrodynamic performance of rim driver thrusters with/without pressure difference. Chin. J. Hydrodynam. 2015, 30, 485–494. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, Y. Torque resistance of a flow between rotating co-axial cylinders having axial flow. Bull. JSME 1962, 5, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
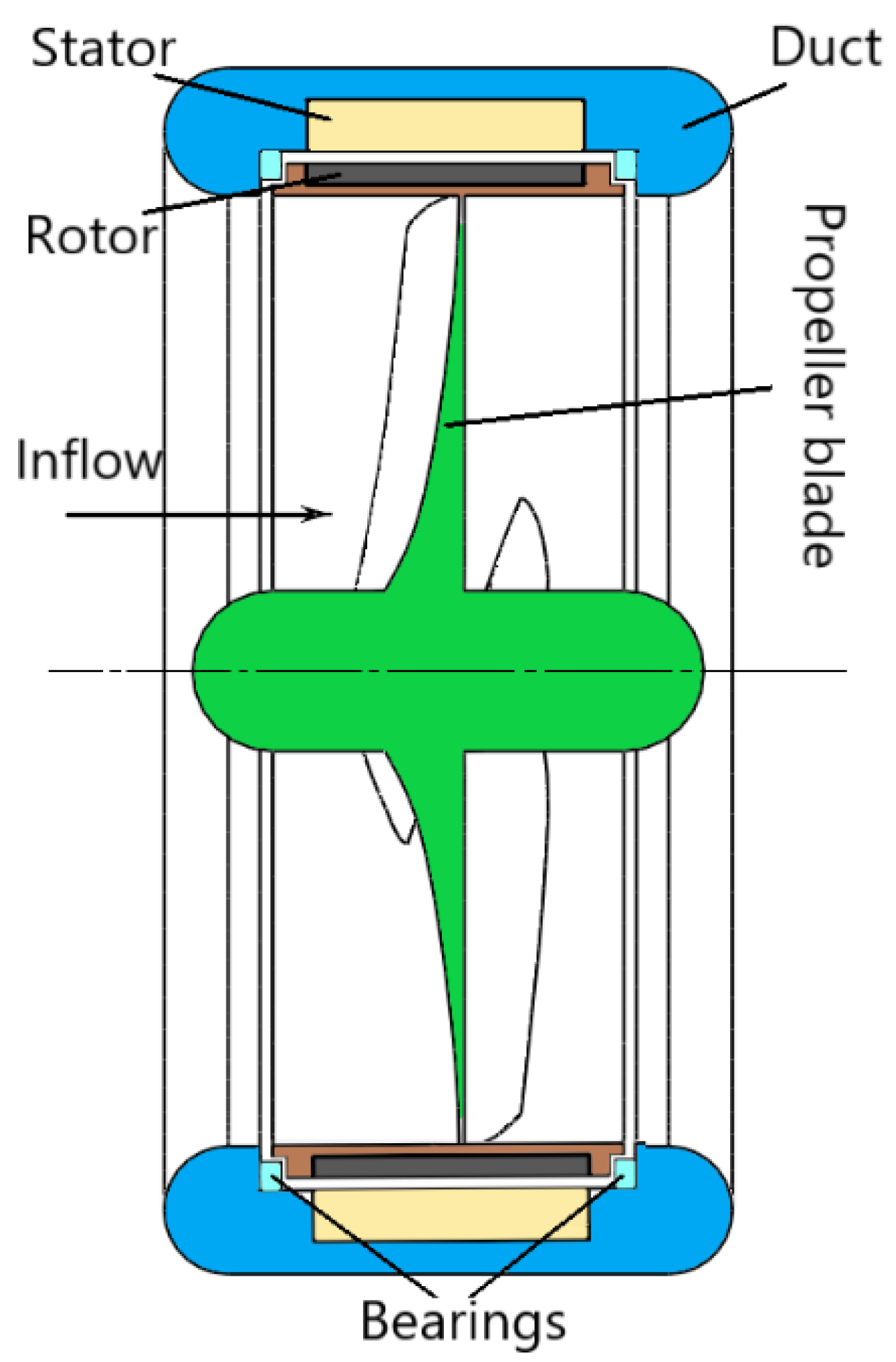
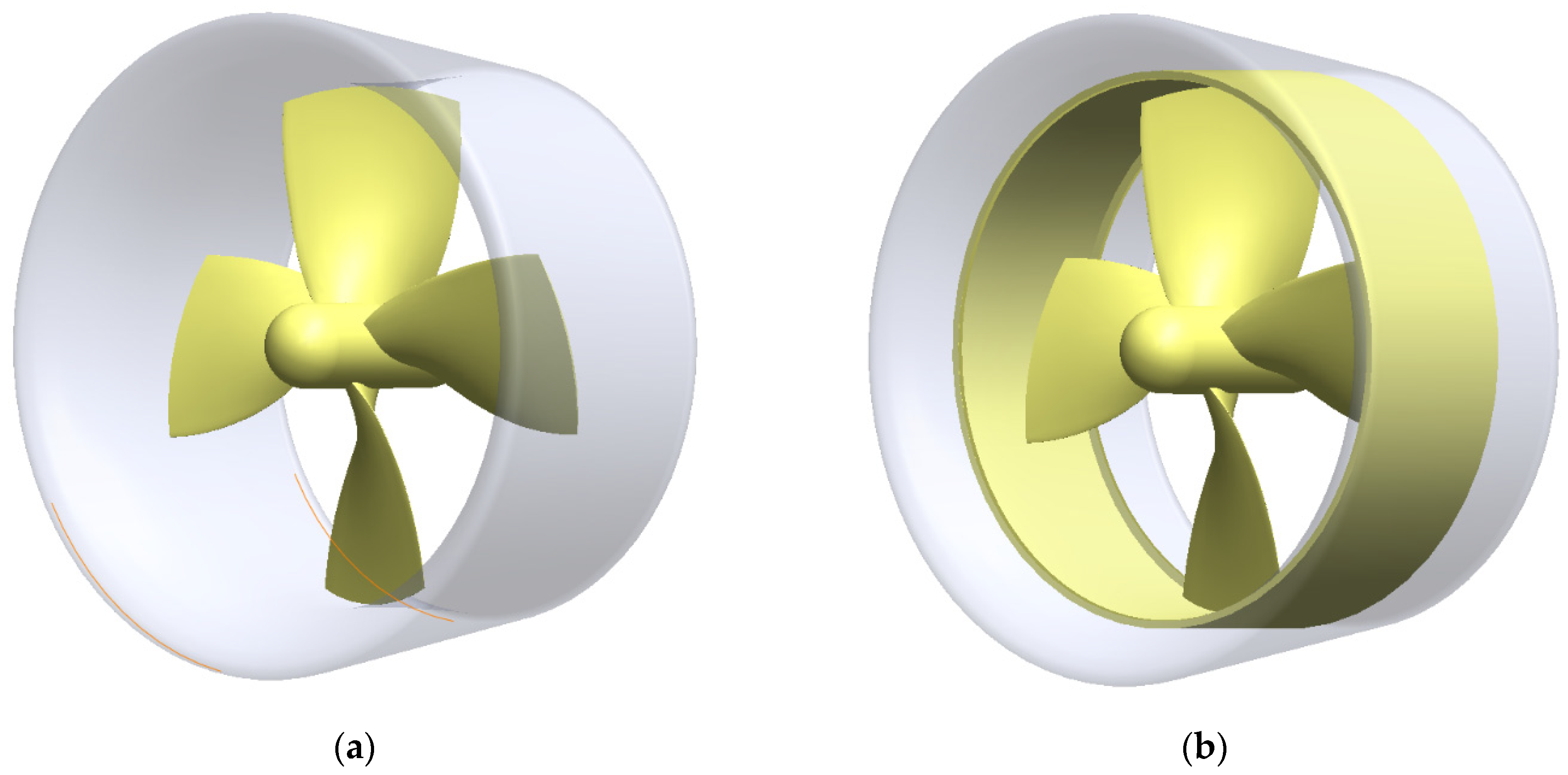

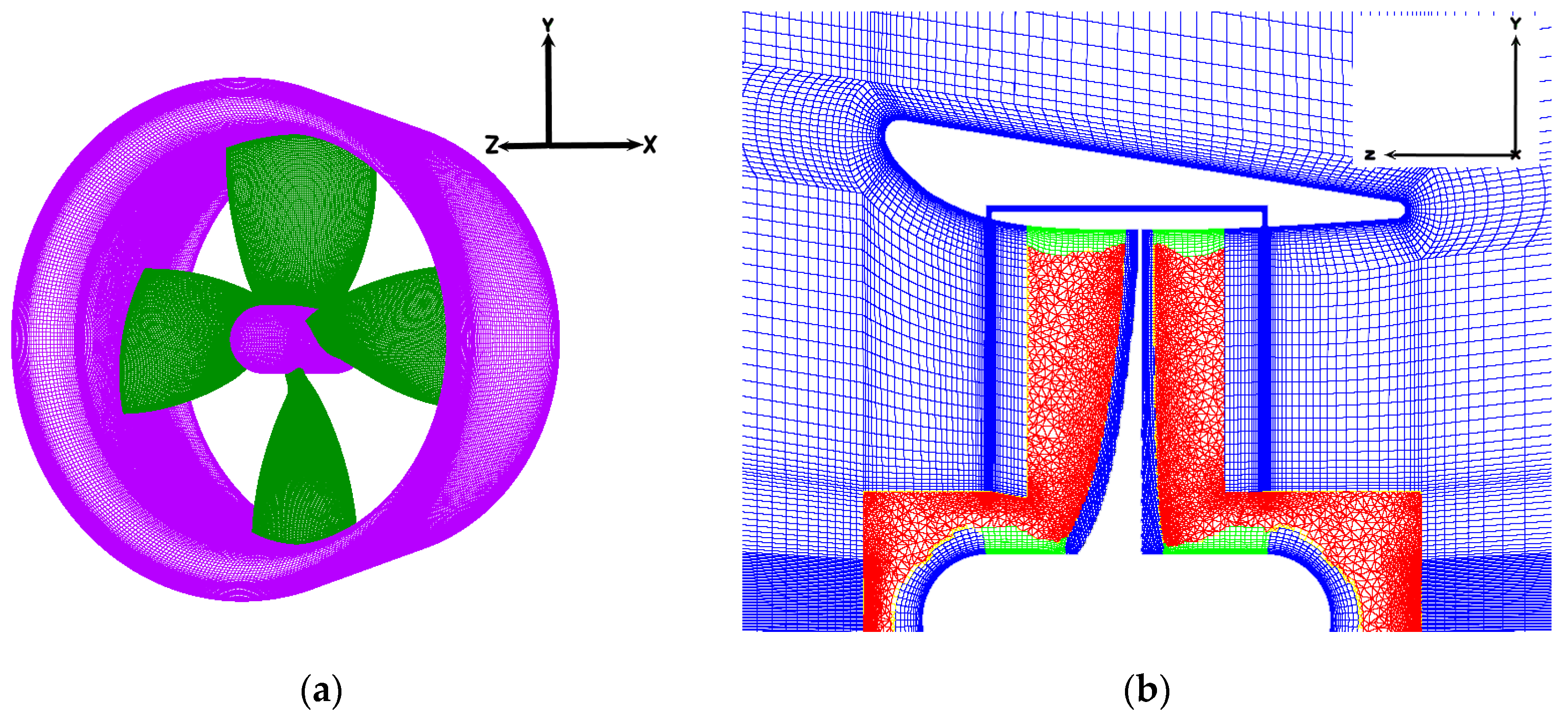


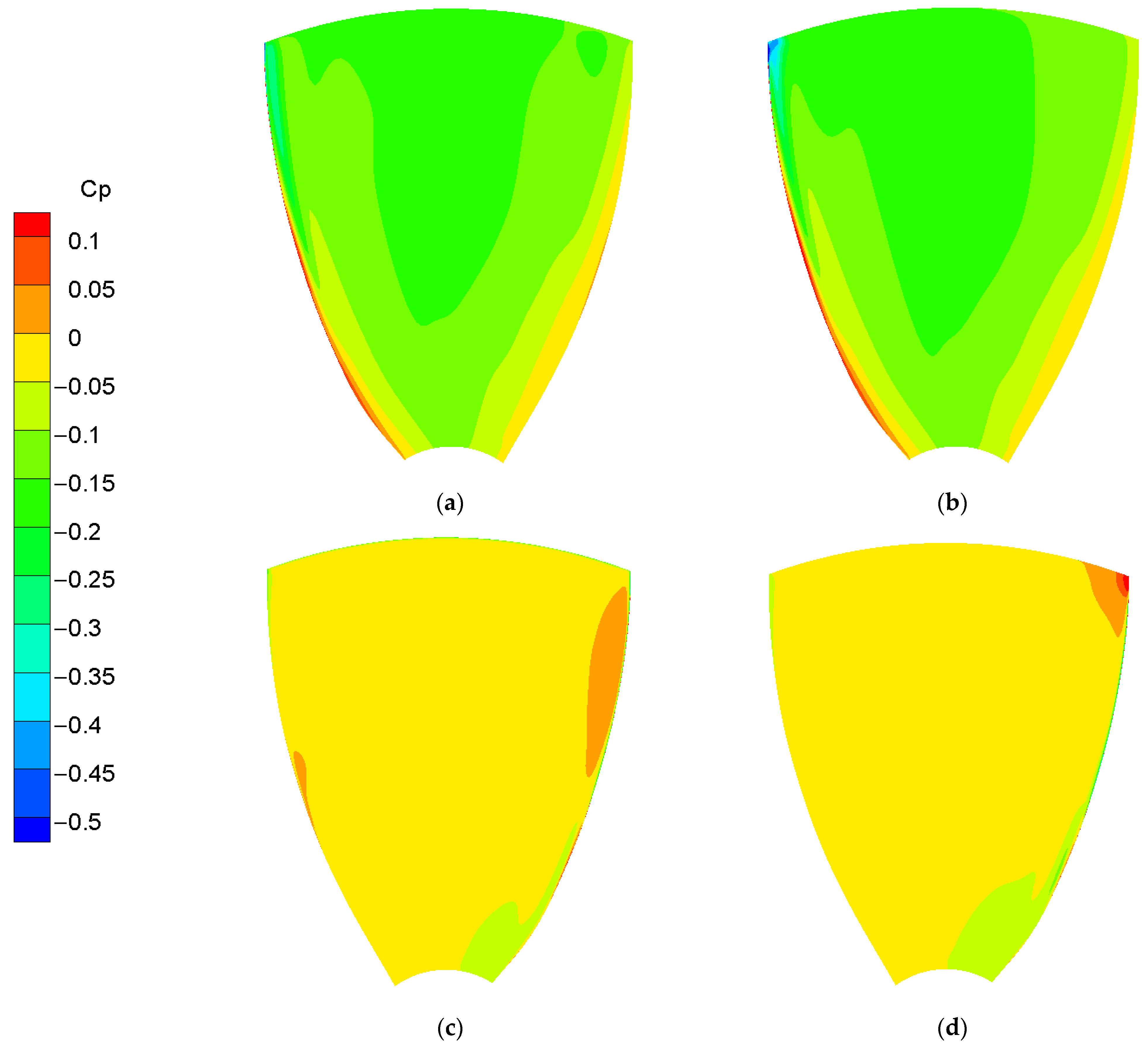


| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Number of blades | - | 4 |
| Blade diameter | m | 0.25 |
| Blade area ratio | - | 0.7 |
| Blade pitch ratio | - | 1.0 |
| Duct type | - | 19A |
| Propeller type | - | Ka |
| Mesh Density | Total Cells (Million) | Refinement Ratio r | J = 0.1 | J = 0.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ktp/Kq | GCI (%) Ktp/Kq | Ktp/Kq | GCI (%) Ktp/Kq | |||
| Coarse | 5.02 | - | 0.257/0.0456 | - | 0.170/0.0334 | - |
| Medium | 9.79 | 1.25 | 0.262/0.0465 | 4.32/4.39 | 0.174/0.0340 | 5.23/3.19 |
| Fine | 19.6 | 1.26 | 0.263/0.0461 | 0.86/1.95 | 0.175/0.0337 | 1.22/1.88 |
| Advance Coefficient | Contributor | DP | RDT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thrust (N) | Torque (N·m) | Thrust (N) | Torque (N∙m) | ||
| J = 0.1 | Pressure | 97.41 | 3.87 | 90.5 | 3.56 |
| Viscous | −2.05 | 0.43 | −1.99 | 0.4 | |
| J = 0.7 | Pressure | 46.57 | 2.01 | 41.45 | 1.83 |
| Viscous | −2.16 | 0.44 | −2.11 | 0.41 | |
| Methods | Ktr × 102 |
|---|---|
| Numerical | 0.57 |
| Empirical | 0.37 |
| J = 0 | Propeller (N∙m) | Rim (N∙m) |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | 3.6 | ≈0 |
| Viscosity | 0.4 | 1.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Vanierschot, M. Numerical Study of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics Comparison between a Ducted Propeller and a Rim-Driven Thruster. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114919
Liu B, Vanierschot M. Numerical Study of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics Comparison between a Ducted Propeller and a Rim-Driven Thruster. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114919
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bao, and Maarten Vanierschot. 2021. "Numerical Study of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics Comparison between a Ducted Propeller and a Rim-Driven Thruster" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114919
APA StyleLiu, B., & Vanierschot, M. (2021). Numerical Study of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics Comparison between a Ducted Propeller and a Rim-Driven Thruster. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114919






