More Than 50-Fold Enhanced Nonlinear Optical Response of Porphyrin Molecules in Aqueous Solution Induced by Mixing Base and Organic Solvent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
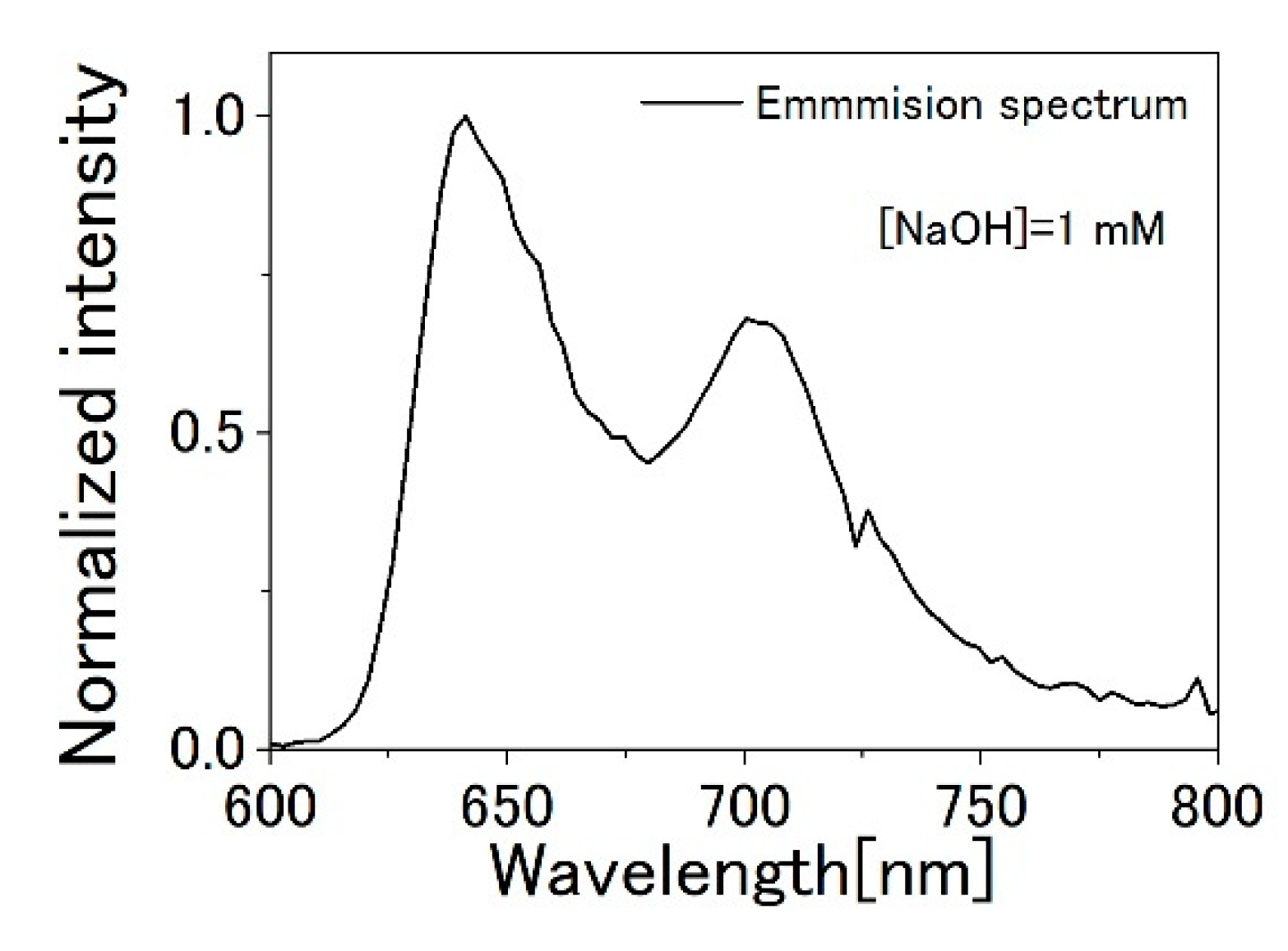
3.1. TPPS Aqueous Solution
3.2. PVA Sample
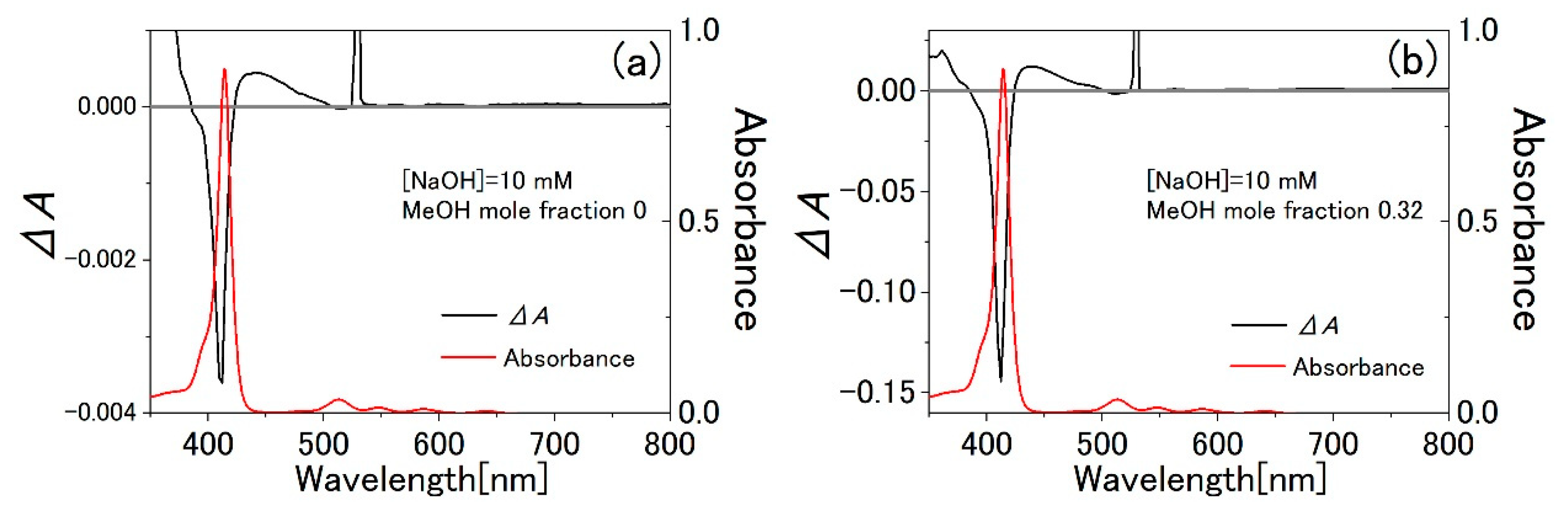
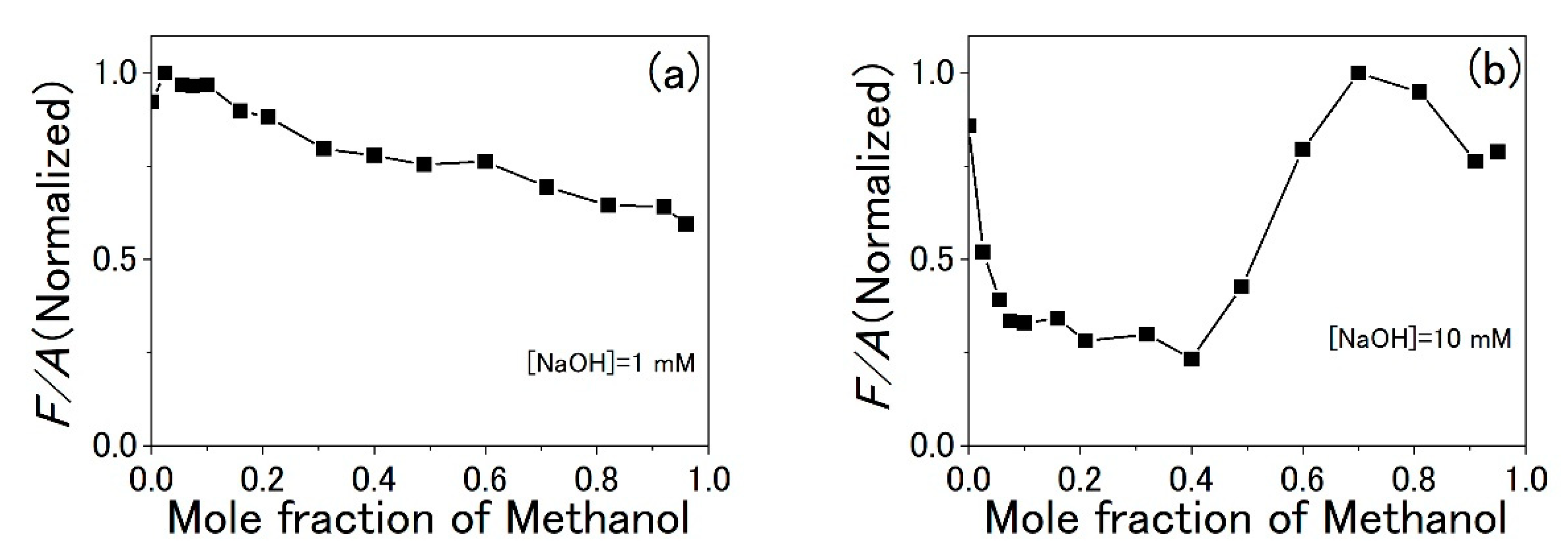
3.3. Water-Methanol Mixed Solution of TPPS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirakawa, M.; Nakata, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tokunaga, E. Nonlinear absorption spectroscopy of porphyrin j-aggregates in aqueous solution: Evidence for control of degree of association by light-induced force. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 86, 044703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tokunaga, E. Solvent effects in highly efficient light-induced molecular aggregation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, S.; Watarai, H. Kinetics for acid-dissociation of tetraphenylporphinetetrasulfonate in the ground state measured by laser photolysis relaxation method. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, R.; Ridge, R.J. Pulsed irradiation of water-soluble porphyrins. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1982, 78, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, K.; Neumann-Spallart, M. Photophysical and redox properties of water-soluble porphyrins in aqueous media. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 86, 5163–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, S.; Illyaskutty, N.; Sreedhanya, S.; Philip, R.; Muneera, C.I. An organic dye-polymer (phenol red-poly (vinyl alcohol)) composite architecture towards tunable-optical and -saturable absorption characteristics. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 193106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Long, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Shehzad, F.K.; Asif, H.M. Notable third-order optical nonlinearities realized in layer-by-layer assembled composite films by intercalation of porphyrin/polyoxometalate into layered double hydroxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 22549–22557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, P.J.; Sciuti, L.F.; Neto, N.M.B.; Silva, R.C.E.; Silveira-Alves, E., Jr.; Mendonça, C.R.; Zílio, S.C.; Borissevitch, I.E.; Boni, L.D. Effects of pH on the ultrafast transient absorption of iron (III) meso-tetrakis (4-N-methyl-pyridiniumyl) porphyrin (Fe3 + TMPyP) molecular complexes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2021, 408, 113082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijisha, M.V.; Ramesh, J.; Arunkumar, C.; Chandrasekharan, K. Impressive nonlinear optical responses of a cationic porphyrin derivative in a flexible all-polymer Bragg stack on optical Tamm mode coupling. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 12689–12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, H.A.; Abul-Hail, R.C.; Shaker, H.S.; Musa, A.I.; Hassan, Q.M.A. An all-optical switch and third-order optical nonlinearity of 3,4-pyridinediamine. Appl. Phys. B 2017, 123, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mu, C.; Ren, H.; Hassan, D.; Yanga, D.; Asifa, H.M. New supramolecular compounds based on porphyrin and polyoxometalate: Synthesis, characterization and nonlinear optical and optical limiting properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50277–50284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, G.; Frobel, P.G.L.; Muneera, C.I.; Sathiyamoorthy, K.; Vijayan, C.; Mukherjee, C. Saturable and reverse saturable absorption and nonlinear refraction in nanoclustered Amido Black dye–polymer films under low power continuous wave He–Ne laser light excitation. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2009, 11, 125204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.K.M.N.; Rao, S.V.; Rao, D.N. Saturable and reverse saturable absorption of Rhodamine B in methanol and water. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2003, 20, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, S.; Vacha, M. Large reverse saturable absorption at the sunlight power level using the ultralong lifetime of triplet excitons. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3683–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lystrom, L.; Yin, H.; Hetu, M.; Kilina, S.; McFarland, S.A.; Sun, W. Increasing the triplet lifetime and extending the ground-state absorption of biscyclometalated Ir(III) complexes for reverse saturable absorption and photodynamic therapy applications. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 16366–16378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, W.; Byrne, H.; Dennis, W.M. Reverse saturable absorption in tetraphenylporphyrins. Opt. Commun. 1985, 56, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrthner, F.; Kaiser, T.E.; Saha-Mller, C.R. J-Aggregates: From serendipitous discovery to supramolecular engineering of functional dye materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3376–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Misawa, K. Hierarchical structure of one-dimensional J-aggregates. J. Lumin. 1997, 72, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biroli, A.O.; Tessore, F.; Righetto, S.; Forni, A.; Macchioni, A.; Rocchigiani, L.; Pizzotti, M.; Carlo, G.D. Intriguing influence of −cooh-driven intermolecular aggregation and acid−base interactions with n,n-dimethylformamide on the second-order nonlinear-optical response of 5,15 push−pull diarylzinc(ii) porphyrinates. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6438–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ray, P.C.; Leszczynski, J. Nonlinear optical properties of highly conjugated push–pull porphyrin aggregates: Role of intermolecular interaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 419, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergendahl, L.T.; Paterson, M.J. Excited states of porphyrin and porphycene aggregates: Computation insights. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2014, 1040, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Tokunaga, E.; Kobayashi, T. Giant electrooptic response of excitons in porphyrin J-aggregates. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 408, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapes, M.; Petera, J.; Jirsa, M. Photodynamic therapy of cutaneous metastases of breast cancer after local application of meso-tetra-(para-sulphophenyl)-porphin (TPPS4). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 1996, 36, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Bhupathiraju, N.V.S.; Dinesh, K.; Arianna, G.; Tiwari, K.; Drain, C.M. Glycosylated porphyrins, phthalocyanines, and other porphyrinoids for diagnostics and therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10261–10306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethirajan, M.; Chen, Y.; Joshi, P.; Pandey, R.K. The role of porphyrin chemistry in tumor imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 340–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman, E.S.; Hynninen, P.H. Research advances in the use of tetrapyrrolic photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2004, 73, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, J.; Mittal, A.K.; Banerjee, A.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Applications of phototheranostic nanoagents in photodynamic therapy. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1373–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhang, X.; Pijper, T.C.; Browne, W.R.; Feringa, B. Reversible photochemical control of singlet oxygen generation using diarylethene photochromic switches. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Ding, L.; Xu, H.; Shen, Z.; Ju, H.; Jia, L.; Bao, L.; Yu, J. Cell-specific and pH-activatable rubyrin-loaded nanoparticles for highly selective near-infrared photodynamic therapy against cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18850–18858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Niu, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochsner, M. Photophysical and photobiological processes in the photodynamic therapy of tumours. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 1997, 39, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, K.; Gratzel, M. Light induced redox reactions of water soluble porphyrins, sensitization of hydrogen generation from water by zincporphyrin derivatives. Helv. Chim. Acta 1980, 63, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLendon, G.; Miller, D.S. Metalloporphyrins catalyse the photo-reduction of water to H2. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1980, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriman, A.; Richoux, M. Photoproduction of hydrogen from reductive quenching of a water-soluble zinc porphyrin. J. Photochem. 1981, 15, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriman, A.; Porter, G.; Richoux, M. Photosensitised reduction of water to hydrogen using water-soluble zinc porphyrins. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1981, 77, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, I.; Kim-Thuan, N. Hydrogen generation by visible light with tris-(2,2′-bipyridine) ruthenium dication. J. Mol. Catal. 1979, 5, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Pollard, J.A.; Webb, M.A.; McHale, J.L. Counterion-dependent excitonic spectra of tetra(p-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin aggregates in acidic aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, N.; Tokunaga, E.; Adachi, S.; Kimura, T.; Matsuda, H.; Kobayashi, T. Optical frequency- and vibrational time-resolved two-dimensional spectroscopy by real-time impulsive resonant coherent Raman scattering in polydiacetylene. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 023811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akins, D.L.; Özçelik, S.; Zhu, H.; Guo, C. Fluorescence decay kinetics and structure of aggregated tetrakis(p-sulfonatophenyl)porphyrin. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 14390–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, D.F. Reference materials for fluorescence measurement. Pure Appl. Chem. 1988, 60, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T. J-Aggregates, 1st ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 1996; pp. 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Tokunaga, E. Electric field-controlled dissociation and association of porphyrin J-aggregates in aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 17756–17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, T.; Ishihara, H. Proposed nonlinear resonance laser technique for manipulating nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 087402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Masuhara, H. Laser-induced self-assembly of pseudoisocyanine j-aggregates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 18457–18460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, M.A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Furey, W.S.; Klenerman, D. Optically biased diffusion of single molecules studied by confocal fluorescence microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3160–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mototsuji, A.; Shoji, T.; Wakisaka, Y.; Murakoshi, K.; Yao, H.; Tsuboi, Y. Plasmonic optical trapping of nanometer-sized J-/H-dye aggregates as explored by fluorescence microspectroscopy. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 13617–13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollie, M.E.; Patonay, G.; Warner, I.M. Deoxygenation of solutions and its analytical applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1987, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalyar, S.R.; Bradley, M.P.T.; Honganen, R. The role of dissolved gases in high -performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1978, 158, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, L.; Benson, G.C. A deuterium isotope effect on the excess enthalpy of methanol-water solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakisaka, A.; Abdoul-Carime, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kiyozumi, Y. Non-ideality of binary mixtures Water–methanol and water–acetonitrile from the viewpoint of clustering structure. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nose, A.; Hojo, M.; Ueda, T. Effects of salts, acids, and phenols on the hydrogen-bonding structure of water−ethanol mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

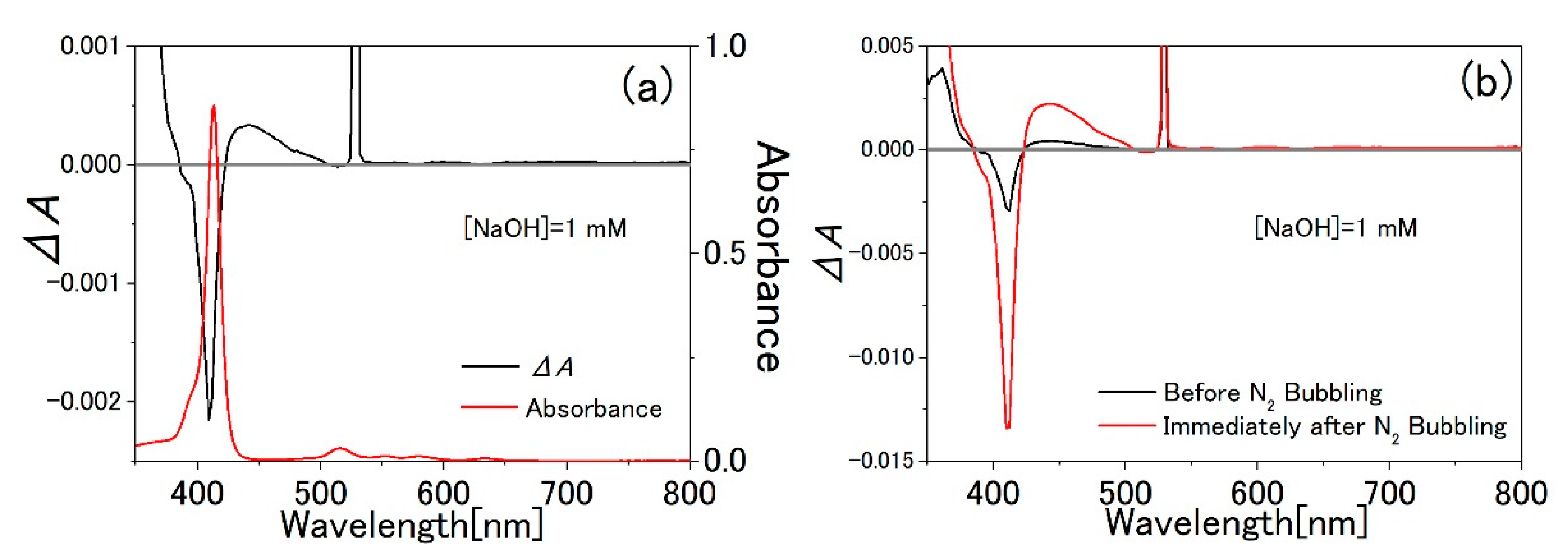
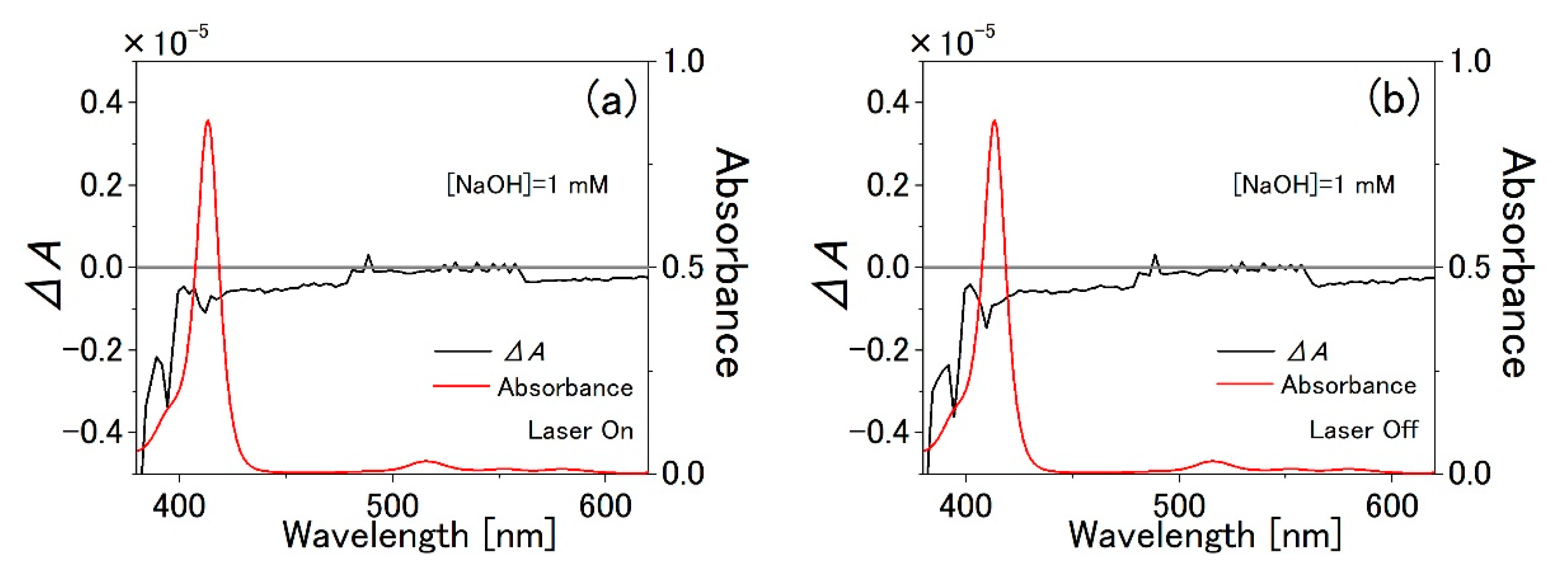
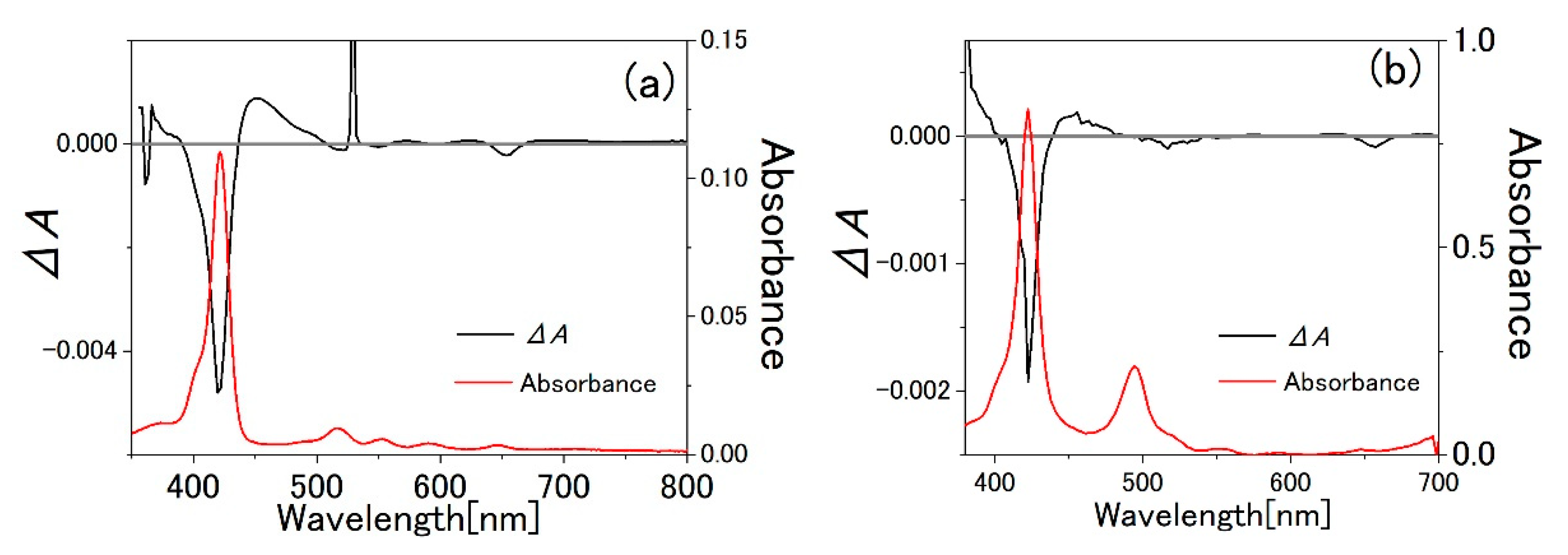
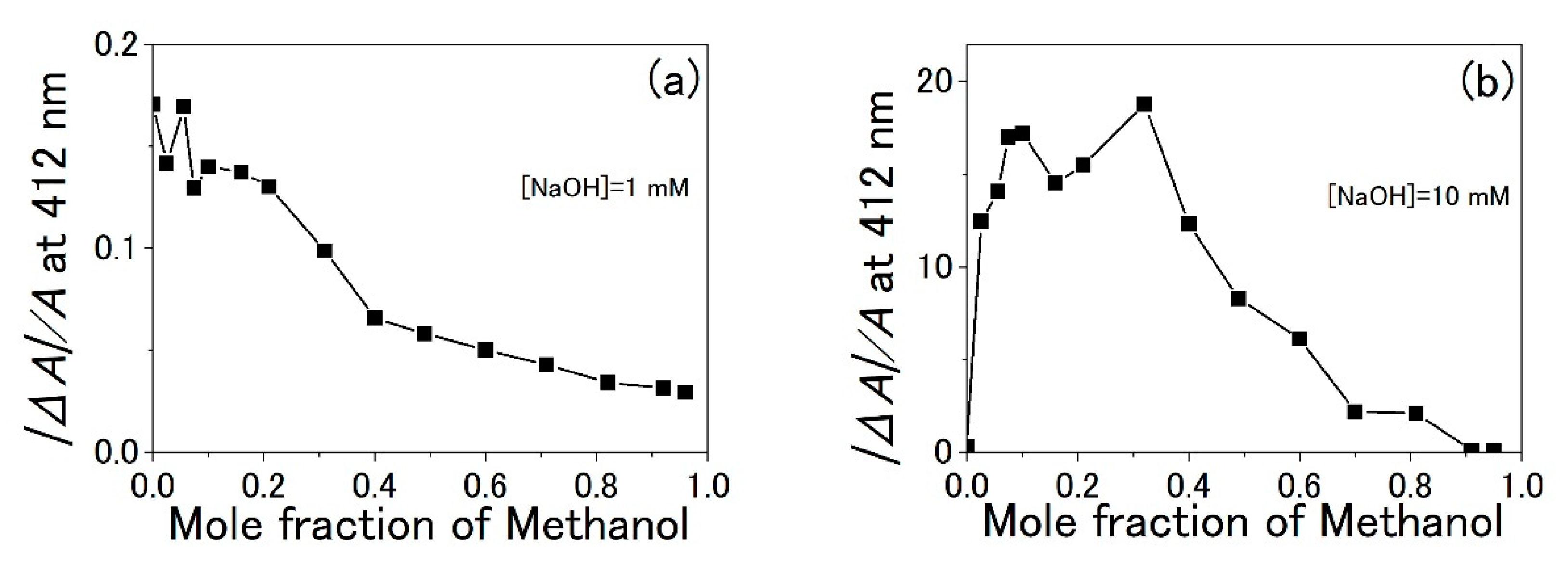
| [TPPS] | [NaOH] | Mole Fraction of MeOH |
|---|---|---|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imura, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Tokunaga, E. More Than 50-Fold Enhanced Nonlinear Optical Response of Porphyrin Molecules in Aqueous Solution Induced by Mixing Base and Organic Solvent. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114892
Imura S, Kobayashi T, Tokunaga E. More Than 50-Fold Enhanced Nonlinear Optical Response of Porphyrin Molecules in Aqueous Solution Induced by Mixing Base and Organic Solvent. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114892
Chicago/Turabian StyleImura, Satoshi, Takayoshi Kobayashi, and Eiji Tokunaga. 2021. "More Than 50-Fold Enhanced Nonlinear Optical Response of Porphyrin Molecules in Aqueous Solution Induced by Mixing Base and Organic Solvent" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114892
APA StyleImura, S., Kobayashi, T., & Tokunaga, E. (2021). More Than 50-Fold Enhanced Nonlinear Optical Response of Porphyrin Molecules in Aqueous Solution Induced by Mixing Base and Organic Solvent. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11114892








