Simulated Annealing for Resource Allocation in Downlink NOMA Systems in 5G Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Preliminaries
1.2. Related Work
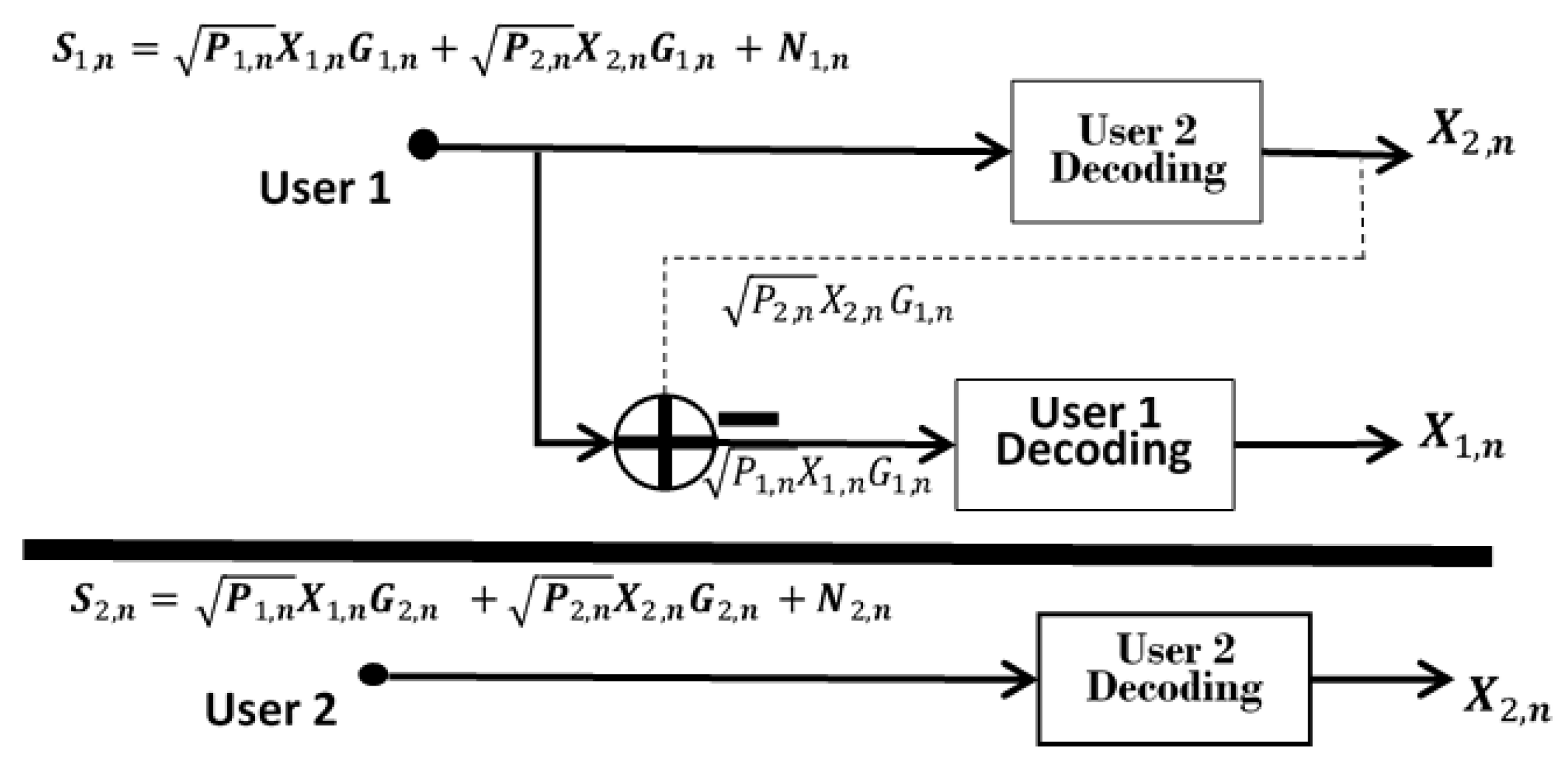
2. NOMA System Model
Problem Formulation
3. Simulated Annealing Based Resource Allocation
3.1. SA for User Pairing
| Algorithm 1: Proposed SA Subchannel and User Matching Scheme. |
|
3.2. SA for Subchannel Power Allocation
3.3. SA for Proportional Power Allocation
| Algorithm 2: Proposed SA-based Subchannel Power Scheme. |
|
| Algorithm 3: Proposed SA-based proportional Power Scheme. |
|
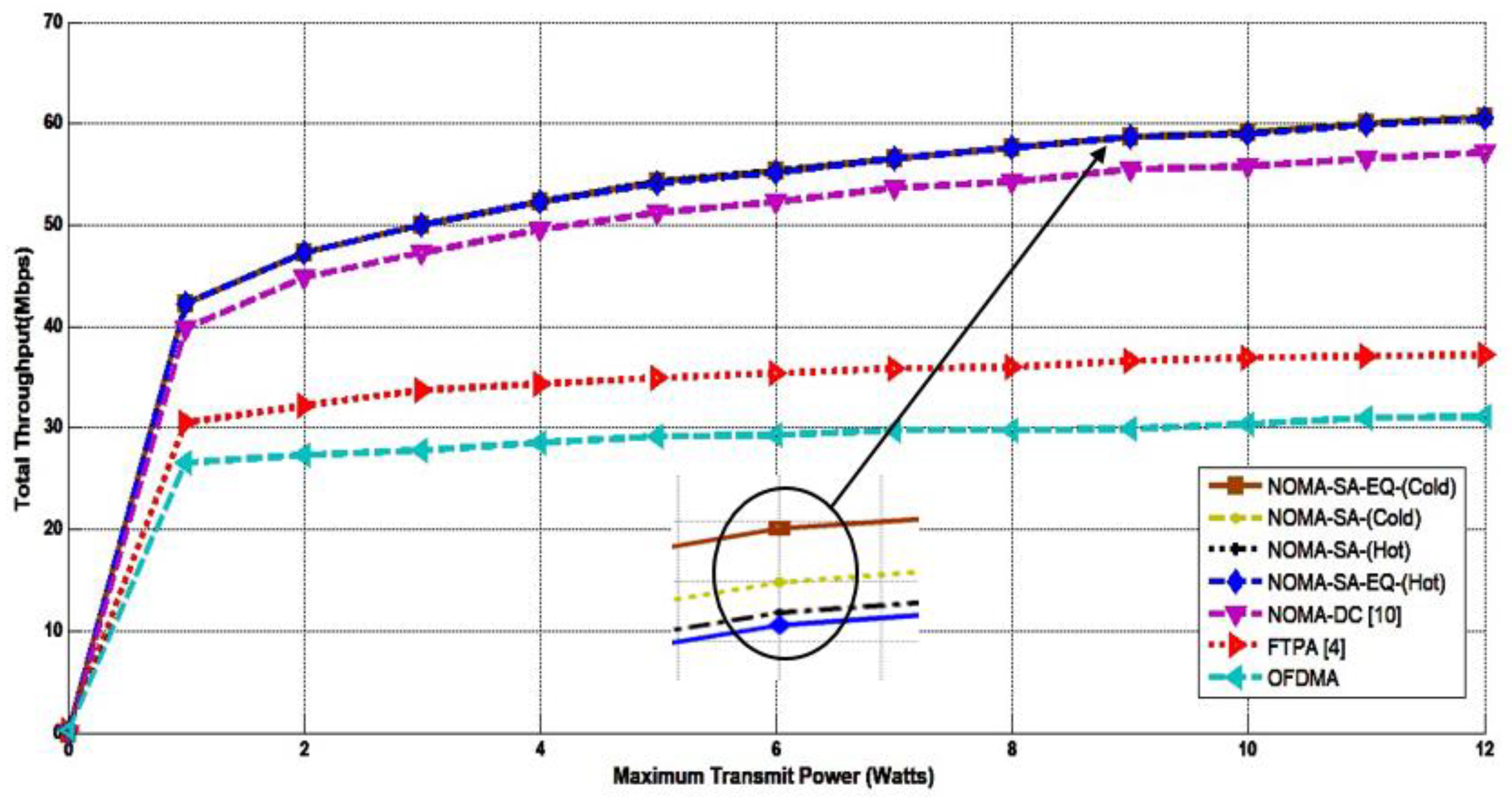
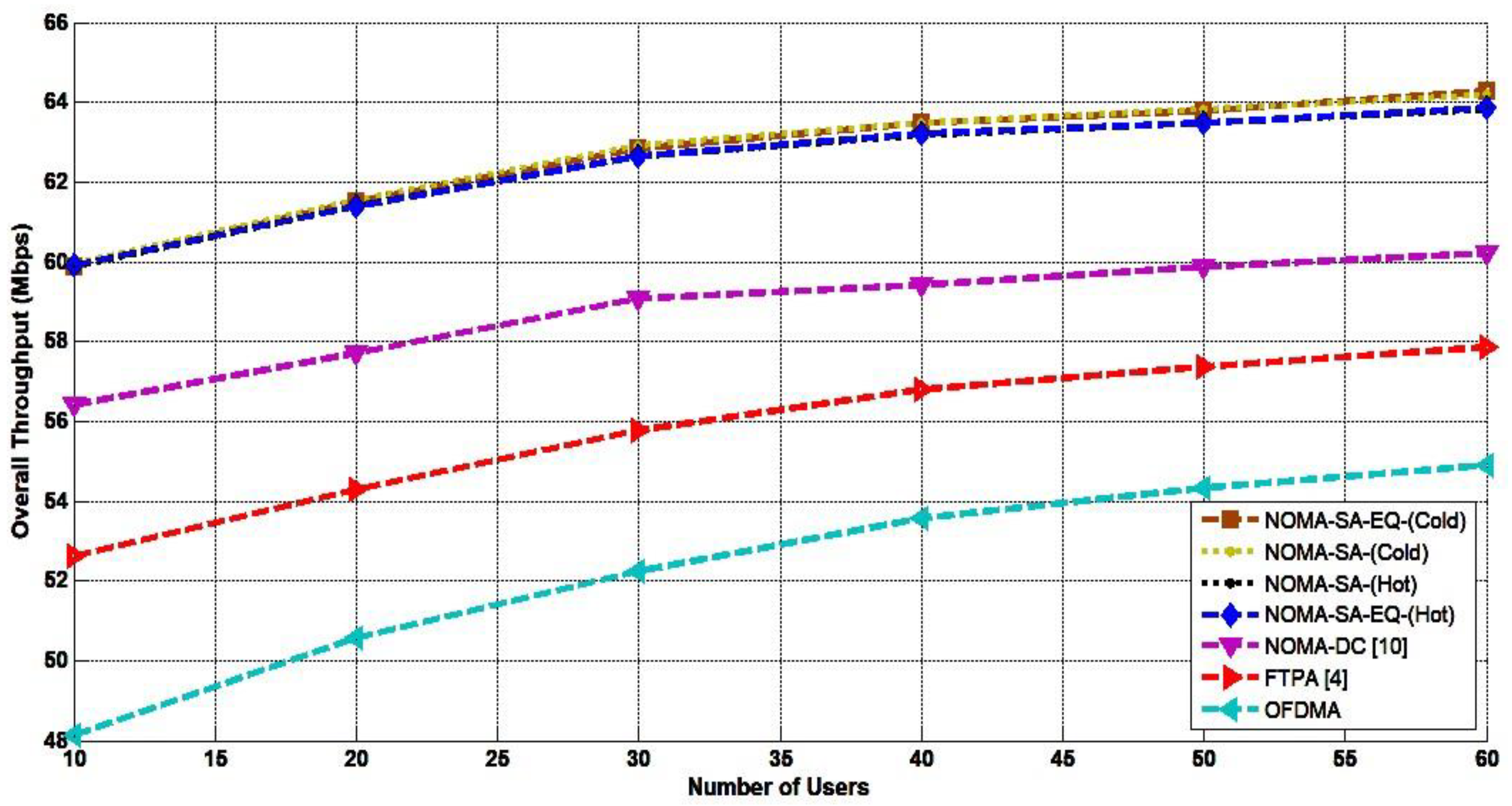
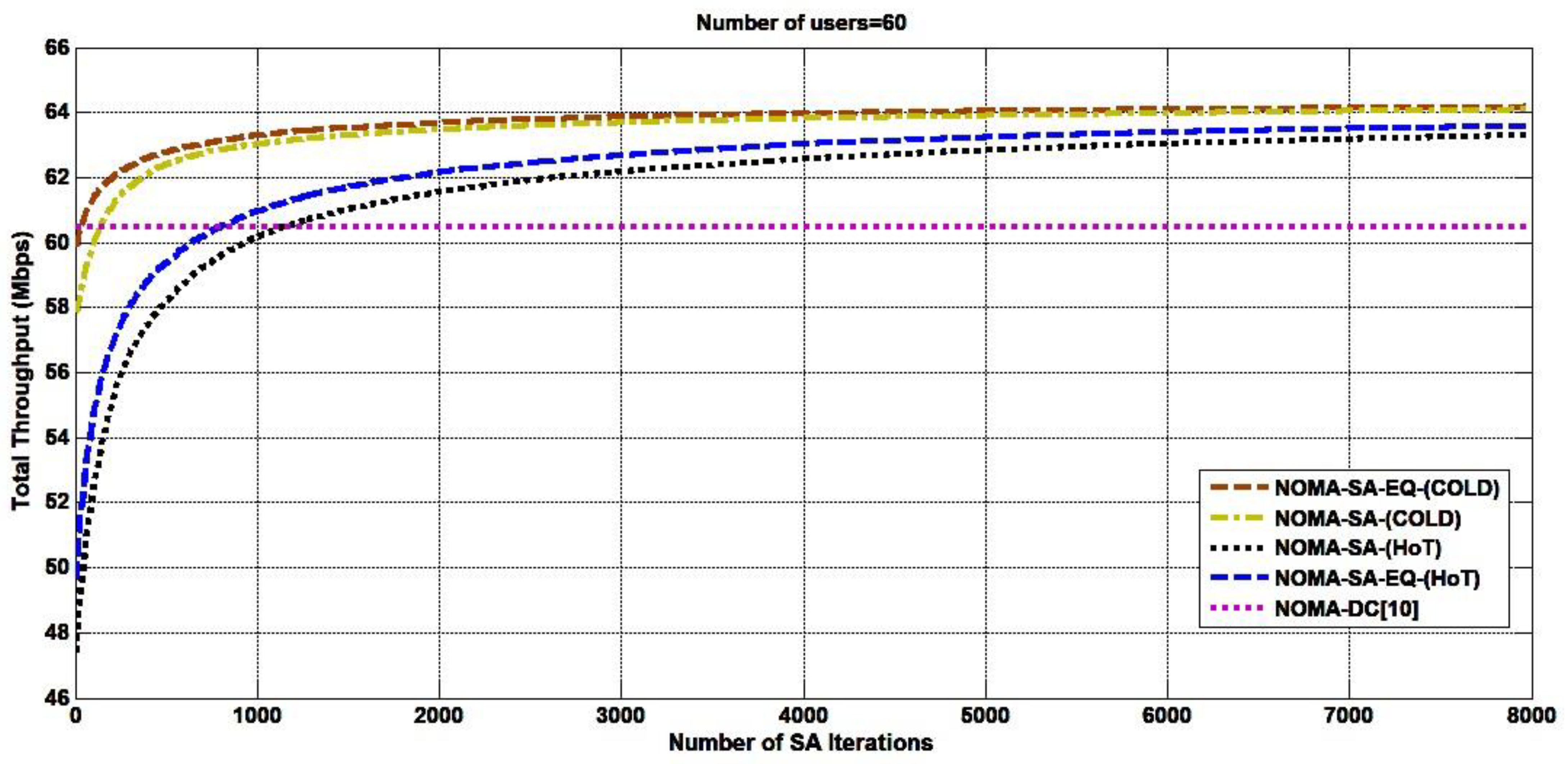
4. Result and Performance Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Han, S.; Chih-Lin, I.; Wang, Z. Non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G: Solutions, challenges, opportunities, and future research trends. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahy, N.; Alani, O.Y. Technologies for 5G networks: Challenges and opportunities. IT Prof. 2017, 19, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, G.Y.; Chen, W.; Ng, D.W.K.; Schober, R. An overview of sustainable green 5G networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, R.; Dianati, M.; Imran, M.A. Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) for future radio access. 5G Mob. Commun. 2016, 135–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J. Power allocation for a downlink non-orthogonal multiple access system. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2016, 5, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.R.; Eslami, M.; Khorramizadeh, M. Optimal sum-rate maximization in a NOMA system with channel estimation error. In Proceedings of the 26th Iranian Conference Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Mashhad, Iran, 8–10 May 2018; pp. 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Han, S.; Chin-Lin, I.; Pan, Z. On the ergodic capacity of MIMO NOMA systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2015, 4, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.C.; Lanjie, L.B. Pairing and power allocation for downlink nonorthogonal multiple access systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 10084–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, P.; Das, S.S. Power Allocation in OFDM Based NOMA Systems: A DC Programming Approach. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Globecom Work, GC Workshops, Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014; pp. 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Leung, V.C.M. Energy-efficient resource allocation for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access network. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 64, 3722–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, F. Joint spectrum and power allocation for noma enhanced relaying networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 27008–27016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abbasi, Z.Q.; So, D.K.C. Power Allocation for Sum Rate Maximisation in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access System. In Proceedings of the PIMRC IEEE International Symposium on Personal Indoor Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 7–10 September 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 1649–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J. Power allocation for max-sum rate and max-min rate proportional fairness in NOMA. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Xu, Y.; Meng, Q. Low-complexity power allocation in NOMA systems with imperfect SIC for maximizing weighted sum-rate. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 94238–94253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Yasmin, R.; Homyara, H.; Hasan, M.A.F.R. Generalized power allocation (GPA) Scheme for non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) Based wireless communication system. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Fan, P.; Poor, H.V. Impact of user pairing on 5G non-orthogonal multiple-access downlink transmissions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 6010–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Vucetic, B. Joint rate control and power allocation for non-orthogonal multiple access systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2798–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; He, S.; You, X.; Yang, L. On optimal power allocation for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2744–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abbasi, Z.Q.; So, D.K.C. Resource allocation in non-orthogonal and hybrid multiple access system with proportional rate constraint. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 6309–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Salaun, L.; Sung, C.W.; Chen, C.S. Subcarrier and power allocation for the downlink of multicarrier NOMA systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 11833–11847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuajwa, O.; Tan, C.K.; Ng, Y.H.; Lee, C.K. ACO-based power allocation for throughput maximization in the downlink 5G NOMA systems. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2020, 13, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, C.; Capozzi, V. A simulated annealing algorithm for scheduling problems. J. Appl. Math. Phys. 2019, 7, 2579–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjebbour, A.; Li, A.; Kishiyama, Y.; Jiang, H.; Nakamura, T. System-Level Performance of Downlink NOMA Combined with SU-MIMO for Future LTE Enhancements. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Globecom Work, GC Workshops, Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014; pp. 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjebbour, A.; Saito, K.; Li, A.; Kishiyama, Y.; Nakamura, T. Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA): Concept, Performance Evaluation and Experimental Trials. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Networks Mobile Communication (WINCOM), Marrakech, Morocco, 20–23 October 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Objective | Proposed Algorithm |
|---|---|---|
| [5] | To maximize the sum rate for SISO and MIMO NOMA system. | Closed-form solution for power allocation with KKT condition. |
| [6] | Maximize the sum rate for the NOMA system with imperfect channel state information (CSI). | Optimal power using KKT condition. |
| [7] | Maximization of the ergodic capacity. | Bisection search-based power allocation. |
| [8] | Maximize the weighted sum rate of a downlink NOMA system. | Minimum mean square error (MMSE). |
| [9] | Maximize the total sum rate for orthogonal frequency-division multiple-access (OFDM) based NOMA. | User, channel matching, and iterative power allocation scheme based on the difference of convex (DC) programming. |
| [10] | Improve Throughput and energy efficiency for the NOMA system. | Subchannel matching for user and subchannel assignment and DC. |
| [11] | Maximize the Throughput for the NOMA-enhanced relay network. | Simulated annealing (SA) for subcarrier and user assignment and DC for power allocation |
| [12] | Maximize the NOMA’s system total sum rate. | Two closed-form suboptimal solutions using the Lagrange multiplier. |
| [13] | Maximize the sum rate with minimum rate constraint for downlink NOMA with two users. | The proportional fairness scheduling (PFS). |
| [14] | Maximize the weighted sum rate (WSR). | Iterative fractional quadratic transformation algorithm. |
| [15] | Maximize the sum rate and investigate the BER performance in the NOMA system. | Generalized power allocation (GPA). |
| [16] | Maximize the sum rate by evaluating the impact of user pairing. | Channel gain difference with fixed power allocation. |
| [17] | Maximize the Throughput in the NOMA system. | Lyapunov optimization framework. |
| [18] | Improve the Throughput for the NOMA system. | Two-sided matching scheme combining the power allocation and maximum fairness (MMF). |
| [19] | Sum-rate maximization under constraints of total power and proportional rate. | Hierarchical pairing power allocation (HPPA). |
| [20] | Maximize the sum rate for MC-NOMA. | Projected gradient descent algorithm and greedy heuristic search. |
| [21] | Maximize the sum rate for NOMA. | Ant colony optimization (ACO) and LTE bandwidth division. |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth BW | 5 MHz |
| Subcarrier BW | 2 kHz |
| Cell Radius | 500 m |
| Min distance between UE-BS | 50 m |
| Min distance between UE-UE | 40 m |
| Number of Subchannels () | 128 |
| Maximum Transmit Power () | 12 Watt |
| Maximum multiplexed users on the same subchannel | 2 users |
| Total Number of users | 60 users |
| Noise Power Spectral Density (No) | −174 dBm/Hz |
| User Minimum Data Rate | 500 b/s |
| Number of Transmit Antenna | 1 |
| Noise Figure | 9 dBm |
| Shadow Standard Deviation | 8 dB |
| Throughput calculation | Shannon’s capacity |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abuajwa, O.; Roslee, M.B.; Yusoff, Z.B. Simulated Annealing for Resource Allocation in Downlink NOMA Systems in 5G Networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104592
Abuajwa O, Roslee MB, Yusoff ZB. Simulated Annealing for Resource Allocation in Downlink NOMA Systems in 5G Networks. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104592
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbuajwa, Osama, Mardeni Bin Roslee, and Zubaida Binti Yusoff. 2021. "Simulated Annealing for Resource Allocation in Downlink NOMA Systems in 5G Networks" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104592
APA StyleAbuajwa, O., Roslee, M. B., & Yusoff, Z. B. (2021). Simulated Annealing for Resource Allocation in Downlink NOMA Systems in 5G Networks. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104592






