Fibril Growth Behavior of Amyloid β on Polymer-Based Planar Membranes: Implications for the Entanglement and Hydration of Polymers
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
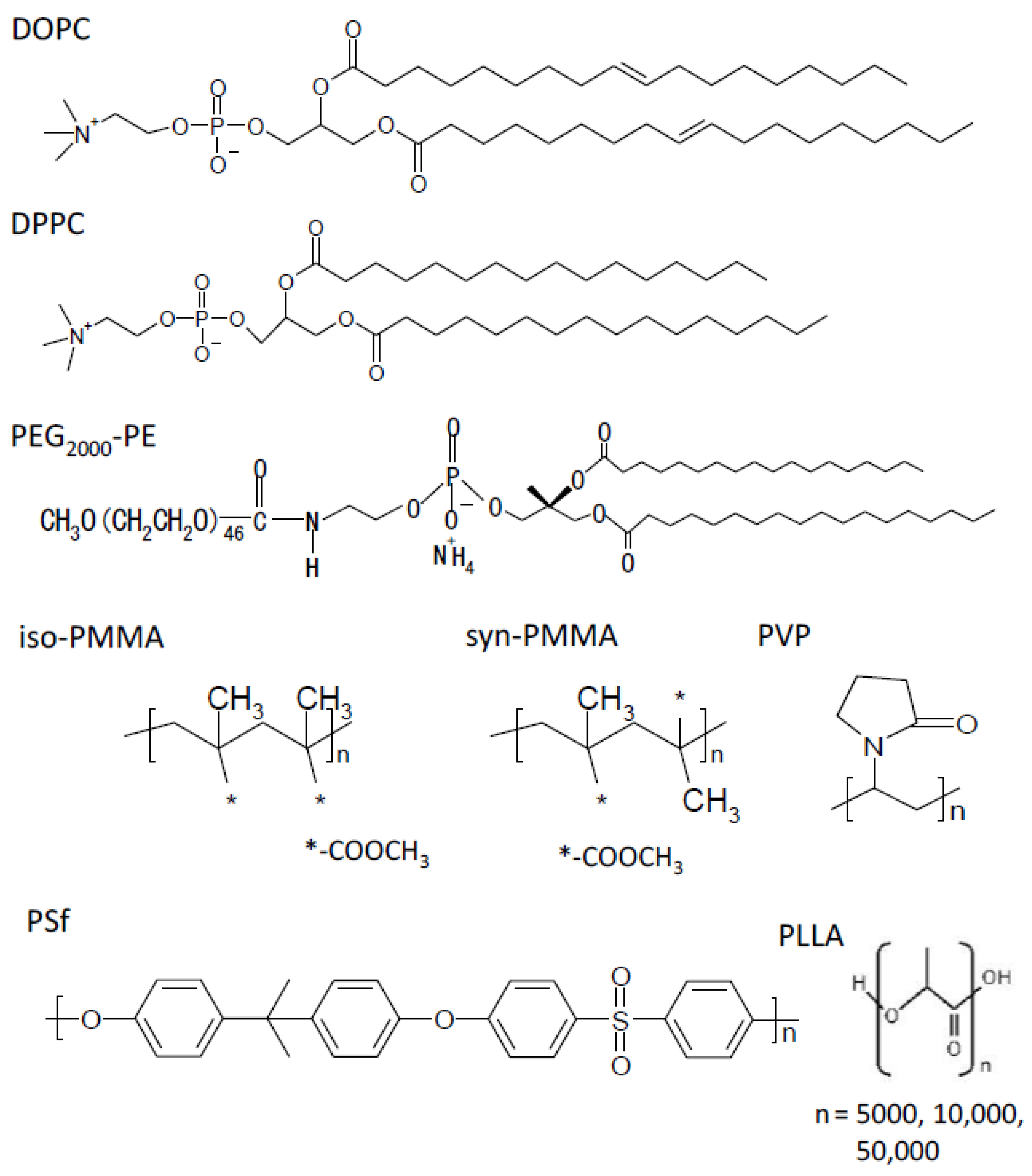
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Planar Membranes Using Phospholipid and Polymers
2.3. Aβ Fibril Formation and Its Observation
2.4. QCM Method
2.5. Entanglement Molecular Weight (Me)
3. Results
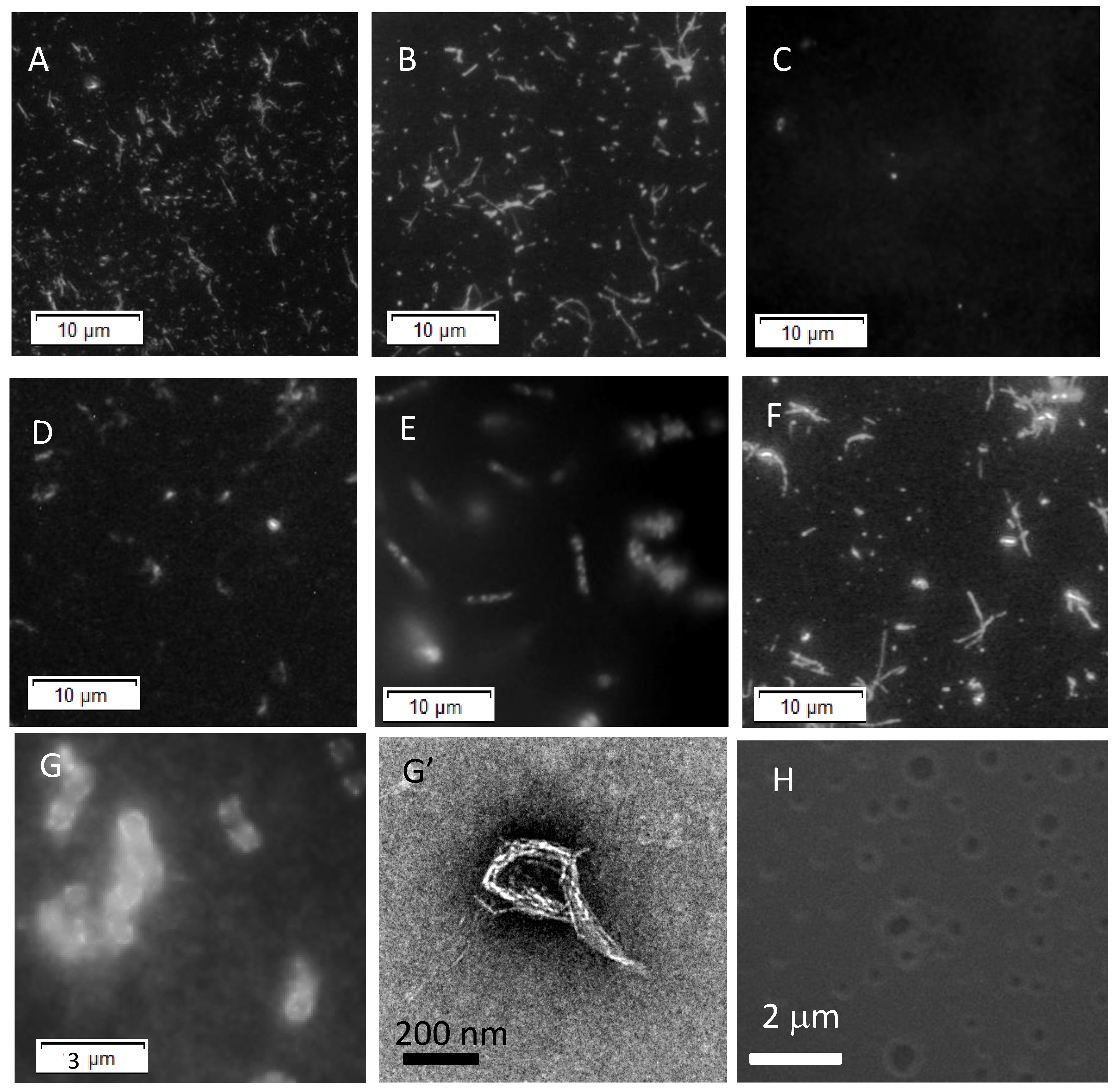
3.1. Fibrillogenesis of Aβ on Each Planar Membrane
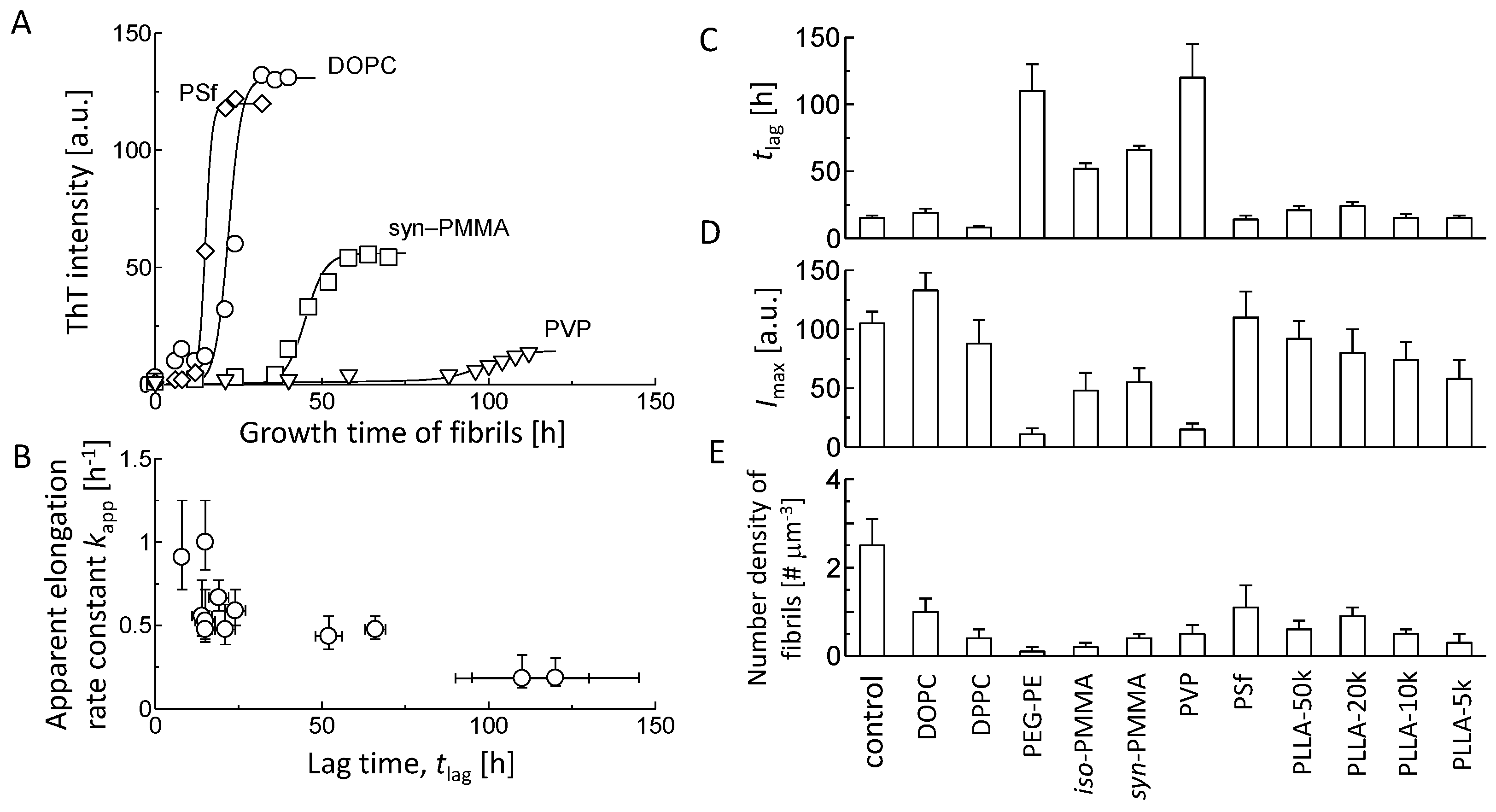
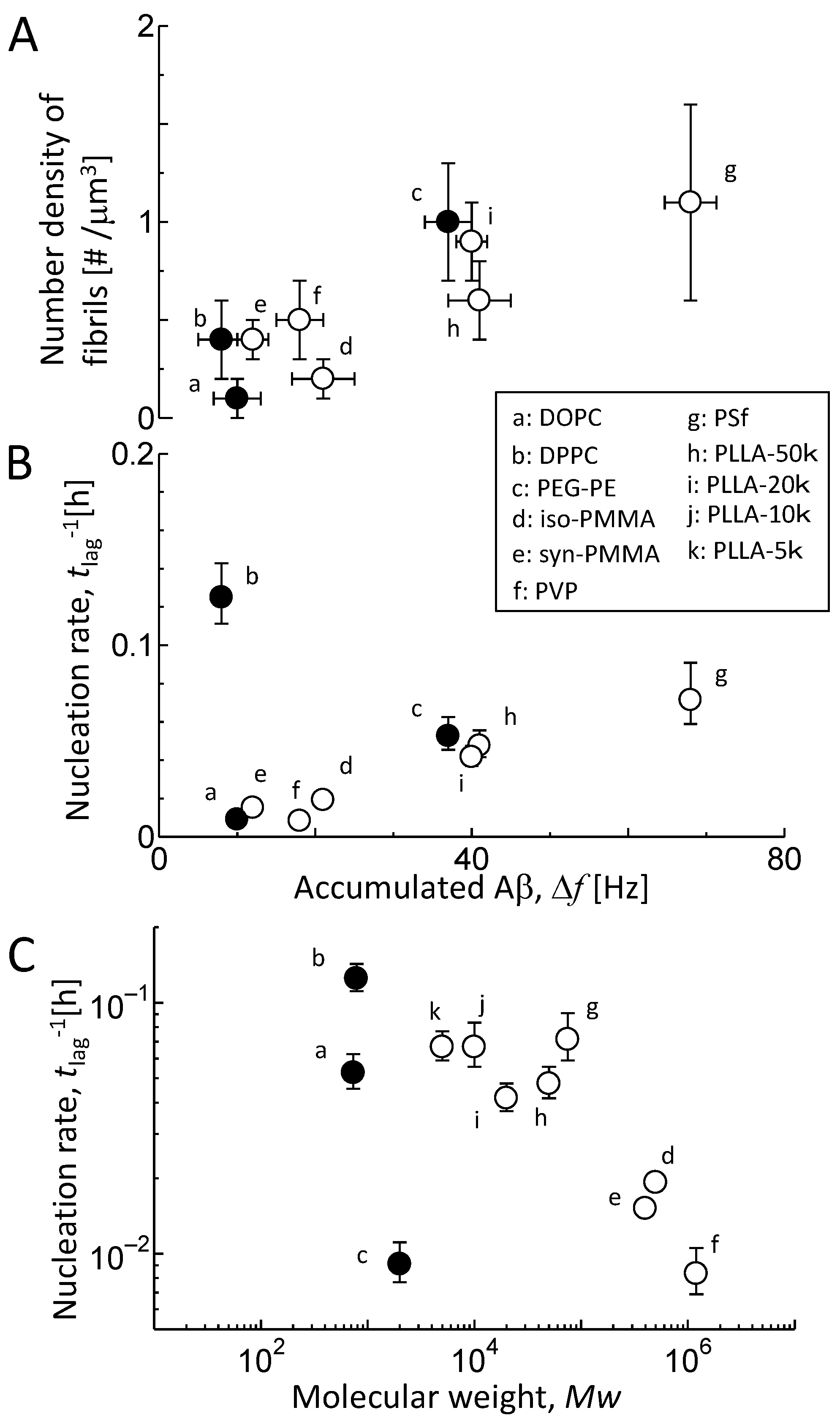
3.2. Kinetic Analysis of Aβ Fibril Growth on Various Membranes
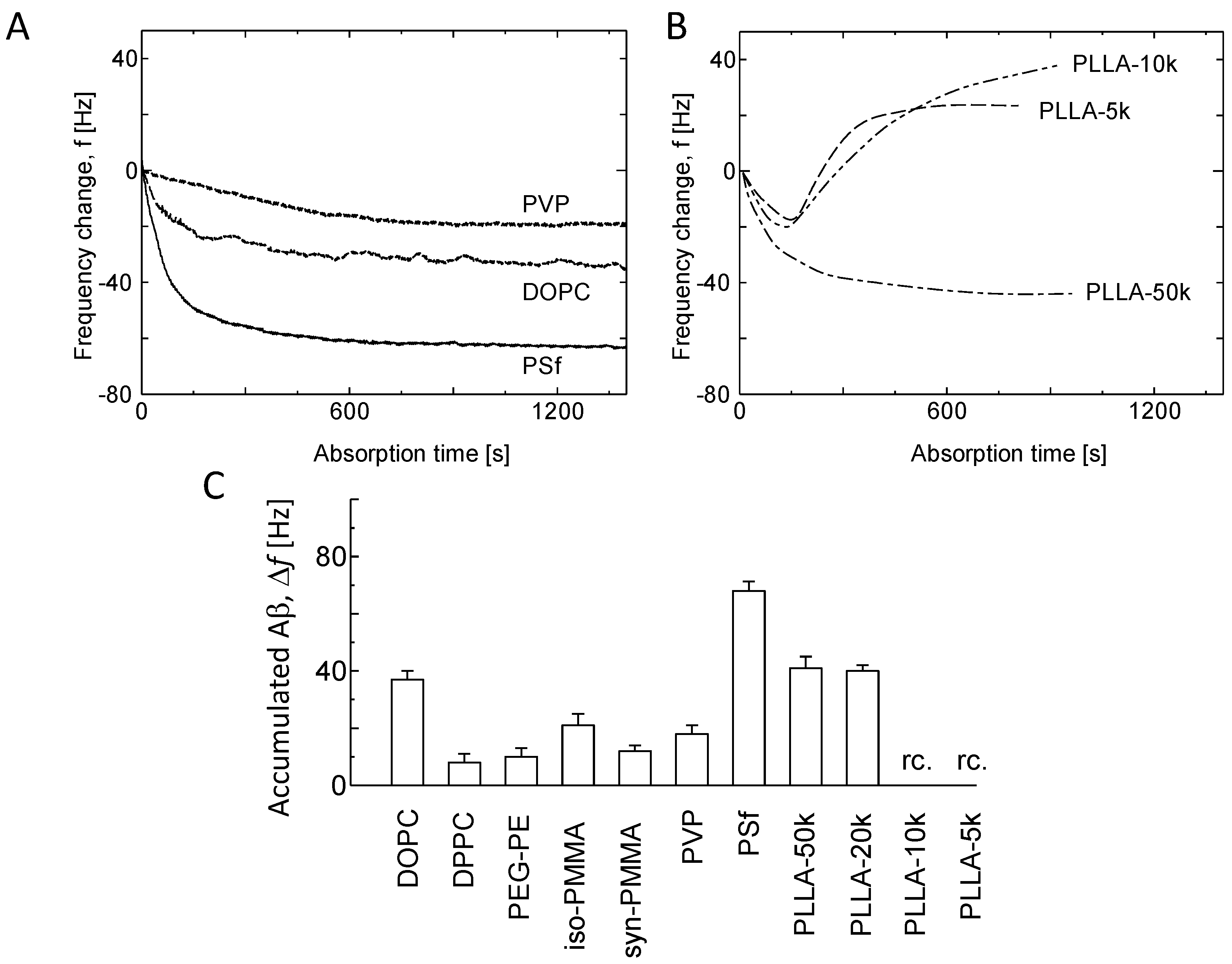
3.3. Aβ Accumulation on Membranes
3.4. Comparison of Aβ Accumulation with Its Fibril Formation
4. Discussion
4.1. Interaction of Aβ with Planar Membranes
4.2. Contribution of Polymer Entanglement to Aβ Accumulation
4.3. Contribution of the Hydrated Structure of Polymer Membranes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mizuno, H.; Hoshino, J.; So, M.; Kogure, Y.; Fujii, T.; Ubara, Y.; Takaichi, K.; Nakaniwa, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kurisu, G.; et al. Dialysis-related amyloidosis associated with a novel β2-microglobulin variant. Amyloid 2021, 28, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiki, H.; Okoshi, T.; Ozawa, D.; Hamaguchi, I.; Hasegawa, K. Molecular pathogenesis of human amyloidosis: Lessons from β2-microglobulin-related amyloidosis. Pathol. Int. 2016, 66, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaguchi, N.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Kawachi, H.; Sakata, M.; Kaneko, M.; Kato, M.; Sakai, K.; Ohashi, N.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Adsorptive filtration systems for effective removal of blood amyloid β: A potential therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 21, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M. Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)—A versatile polymer for biomedical and beyond medical applications. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljevic, V.; Jelinkova, P.; Jimenez, A.M.J.; Moulick, A.; Haddad, Y.; Buchtelova, H.; Krizkova, S.; Heger, Z.; Kalina, L.; Richtera, L.; et al. Alternative synthesis route of biocompatible polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles and their effect on pathogenic microorganisms. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmowafy, E.M.; Tiboni, M.; Soliman, M.E. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and biomedical applications of poly(lactic acid)/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) micro and nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 347–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-C.; Lee, I.; Wang, J.-H.; Yang, S.-H.; Young, T.-H. Preparation of PLLA membranes with different morphologies for culture of MG-63 Cells. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4047–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punet, X.; Mauchauffe, R.; Rodriguez-Cabello, J.C.; Alonso, M.; Engle, E.; Mateos-Timoneda, M.A. Biomolecular functionalization for enhanced cell–material interactions of poly(methyl methacrylate) surfaces. Regener. Biomater. 2015, 2, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witvrouw, M.; Fikkert, V.; Pluymers, W.; Matthews, B.; Mardel, K.; Schols, D.; Raff, J.; Debyser, Z.; de Clercq, E.; Holan, G.; et al. Polyanionic (i.e., polysulfonate) dendrimers can inhibit the replication of human immunodeficiency virus by interfering with both virus adsorption and later steps (reverse transcriptase/integrase) in the virus replicative cycle. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millon, L.E.; Wan, W.K. The polyvinyl alcohol–bacterial cellulose system as a new nanocomposite for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2006, 79B, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ube, T.; Aoki, H.; Ito, S.; Horinaka, J.; Takigawa, T. Relaxation of single polymer chain in binary molecular weight blends observed by scanning near-field optical microscopy. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5603–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Adachi, T.; Bout, D.V.; Zhu, X.Y. A mobile precursor determines amyloid-β peptide fibril formation at interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14172–14178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.K.; Wong, A.S.W.; de Hong, H.-P.M.; Rangamani, P.; Parikh, A.N.; Nallani, M.; Sandin, S.; Liedberg, B. Spontaneous formation of nanometer scale tubular vesicles in aqueous mixtures of lipid and block copolymer amphiphiles. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjabian, M.; Abetz, V. Tailored pore sizes in integral asymmetric membranes formed by blends of block copolymers. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Kohori, F.; Uesaka, T.; Ueno, Y.; Sugaya, H.; Itagaki, I.; Sakai, K. Nanoscopic behavior of polyvinylpyrrolidone particles on polysulfone/polyvinylpyrrolidone film. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, D.; Azuma, T.; Noguchi, H.; Uosaki, K.; Takai, M. Role of interfacial water in protein adsorption onto polymer brushes as studied by SFG spectroscopy and QCM. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 17193–17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2004, 430, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problem on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease linked to pathological α-synuclein: New targets for drug discovery. Neuron 2006, 52, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hane, F.; Leonenko, Z. Effect of metals on kinetic pathways of amyloid-β aggregation. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabate, R.; Estelrich, J. Evidence of the existence of micelles in the fibrillogenesis of beta-amyloid peptide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 11027–11032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimanouchi, T.; Nishiyama, K.; Hiroiwa, A.; Vu, H.T.; Kitaura, N.; Umakoshi, H.; Kuboi, R. Growth behavior of Aβ protofibrils on liposome membranes and their membrane perturbation effect. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 71, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Ban, T.; Morigaki, K.; Naiki, H.; Goto, Y. Visualization and classification of amyloid β supramolecular assemblies. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 15009–15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.R.H.; MacPhee, C.E.; Miller, A.F.; Dunlop, I.E.; Dobson, C.M.; Donald, A.M. The formation of spherulites by amyloid fibrils of bovine insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14420–14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.R.H.; Bromley, E.H.C.; Rogers, S.S.; Donald, A.M. The mechanism of amyloid spherulite formation by bovine insulin. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimanouchi, T.; Shimauchi, N.; Onishi, R.; Kitaura, N.; Yagi, H.; Goto, Y.; Umakoshi, H.; Kuboi, R. Formation of spherulitic amyloid β aggregate by anionic liposomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2012, 426, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimanouchi, T.; Kitaura, N.; Onishi, R.; Umakoshi, H.; Kuboi, R. Secondary nucleation of Aβ fibrils on liposome membrane. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 3625–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Morigaki, M.K.; Yagi, H.; Kawasaki, T.; Kobayashi, A.; Yuba, S.; Naiki, H.; Goto, Y. Real-time and single fibril observation of the formation of amyloid β spherulitic structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33677–33683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Matsuzaki, K. Driving force of binding of amyloid β-protein to lipid bilayers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2008, 370, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K. Physicochemical interactions of amyloid β-peptide with lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuboi, R.; Shimanouchi, T.; Yoshimoto, M.; Umakoshi, H. Detection of conformational change of protein under stress conditions. Sens. Mater. 2004, 16, 241–254. [Google Scholar]
- Shezad, K.; Zhang, K.; Hussain, M.; Dong, H.; He, C.; Gong, X.; Xie, X.; Zhu, J.; Shen, L. Surface roughness modulates diffusion and fibrillation of amyloid-β peptide. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8238–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.L.; Blankschtein, D.; Hatton, T.A. Protein partitioning in two-phase aqueous polymer systems. 4. Protein in solutions of entangled polymers. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 5192–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, Y.; Haratani, T.; Takahashi, T. Miscibility and orientation behavior of poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) blends. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 1990, 28, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Litvinov, V.M.; Ries, M.E.; Baughman, T.W.; Henke, A.; Matloka, P.P. Chain entanglements in polyethylene melts. Why is it studied again? Macromolecules 2013, 46, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama, T.; Tanaka, K.; Takahara, A. Surface thermal molecular motion of chain end-modified polystyrenes. Macromol. Symp. 2003, 192, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, M.C.; Eastman, C.E.; Lodge, T.P. Diffusion in microstructured block copolymers: Chain localization and entanglements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 2591–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Q. Chain dynamics in entangled polymers: Diffusion versus rheology and their comparison. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polm. Phys. 2003, 41, 1589–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.-Y.; Choi, M.-J.; Min, S.-G.; Weiss, J. Formation and stability of multiple-layered liposomes by layer-by-layer electrostatic deposition of biopolymers. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. The origin of chain entanglement: Correlations between entanglement and chain structure. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1993, 33, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Gu, F.; Watanabe, K.; Okada, K.; Toda, A.; Hikosaka, M. Two-step formation of entanglement from disentangled polymer melt detected by using nucleation rate. Polymer 2006, 47, 6422–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinyashiki, N.; Matsumura, Y.; Miura, N.; Yagihara, S.; Mashimo, S. Dielectric study of water structure in polymer solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 13612–13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, D.; Miller, I.R. Hydration of phospholipid bilayers in the presence and absence of cholesterol. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2005, 136, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Furukawa, H. Prediction of mechanical properties of glassy polymers by group contribution method. Kobunnshi Ronbunnsyu 1995, 52, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Chain structure and entanglement. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1989, 27, 723–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgan, J.R.; Williams, J.S. Melt rheology of poly(lactic acid): Entanglement and chain architecture effects. J. Rheol. 1999, 43, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, P.S.; Boxer, S.G. Formation and spreading of lipid bilayers on planar glass supports. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 2554–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhamad, Y.; Mokarian-Tabari, P.; Clarke, N.; Jones, R.A.L.; Geoghegan, M. Dynamics of polymer film formation during spin coating. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 123513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E. Entropy-driven tension in vesicle membranes and unbinding of adherent vesicles. Langmuir 1991, 7, 1900–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lee, J.P. Selectively 2H-labeled Glu/Asp: Application to pKa measurement in Aβ amyloid peptide. J. Pept. Res. 2000, 55, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Clancy, E.L.; Zhang, Y.; Ray, D.G.; Wollenberg, K.; Zagorski, M.G.J. Residue-specific pKa measurements of the β-peptide and mechanism of pH-induced amyloid formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8698–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Buck, S.M.; Chen, Z. Molecular chemical structure on poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) surface studies by sum frequency generation (SFG) vibrational spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 12118–12125.(54). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.; Oradd, G.; Lindblom, G. Influence of cholesterol and water content on phospholipid lateral diffusion in bilayers. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6397–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizaki, K.; Taguchi, H.; Itoh, C.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Saito, Y.; Ogawa, N. Effects of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chain length of PEG-lipid on the permeability of liposomal bilayer membranes. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimanouchi, T.; Iwamura, M.; Deguchi, S.; Kimura, Y. Fibril Growth Behavior of Amyloid β on Polymer-Based Planar Membranes: Implications for the Entanglement and Hydration of Polymers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104408
Shimanouchi T, Iwamura M, Deguchi S, Kimura Y. Fibril Growth Behavior of Amyloid β on Polymer-Based Planar Membranes: Implications for the Entanglement and Hydration of Polymers. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104408
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimanouchi, Toshinori, Miki Iwamura, Shintaro Deguchi, and Yukitaka Kimura. 2021. "Fibril Growth Behavior of Amyloid β on Polymer-Based Planar Membranes: Implications for the Entanglement and Hydration of Polymers" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104408
APA StyleShimanouchi, T., Iwamura, M., Deguchi, S., & Kimura, Y. (2021). Fibril Growth Behavior of Amyloid β on Polymer-Based Planar Membranes: Implications for the Entanglement and Hydration of Polymers. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104408





