Low-Complexity Pupil Tracking for Sunglasses-Wearing Faces for Glasses-Free 3D HUDs
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a pupil center localization system applicable to both bare faces and sunglasses-wearing faces. We classified facial images into these two categories and performed pupil tracking accordingly.
- For sunglasses-wearing faces, we inferred the eye position behind the sunglasses by applying a supervised regression method to the non-occluded areas.
2. Methods
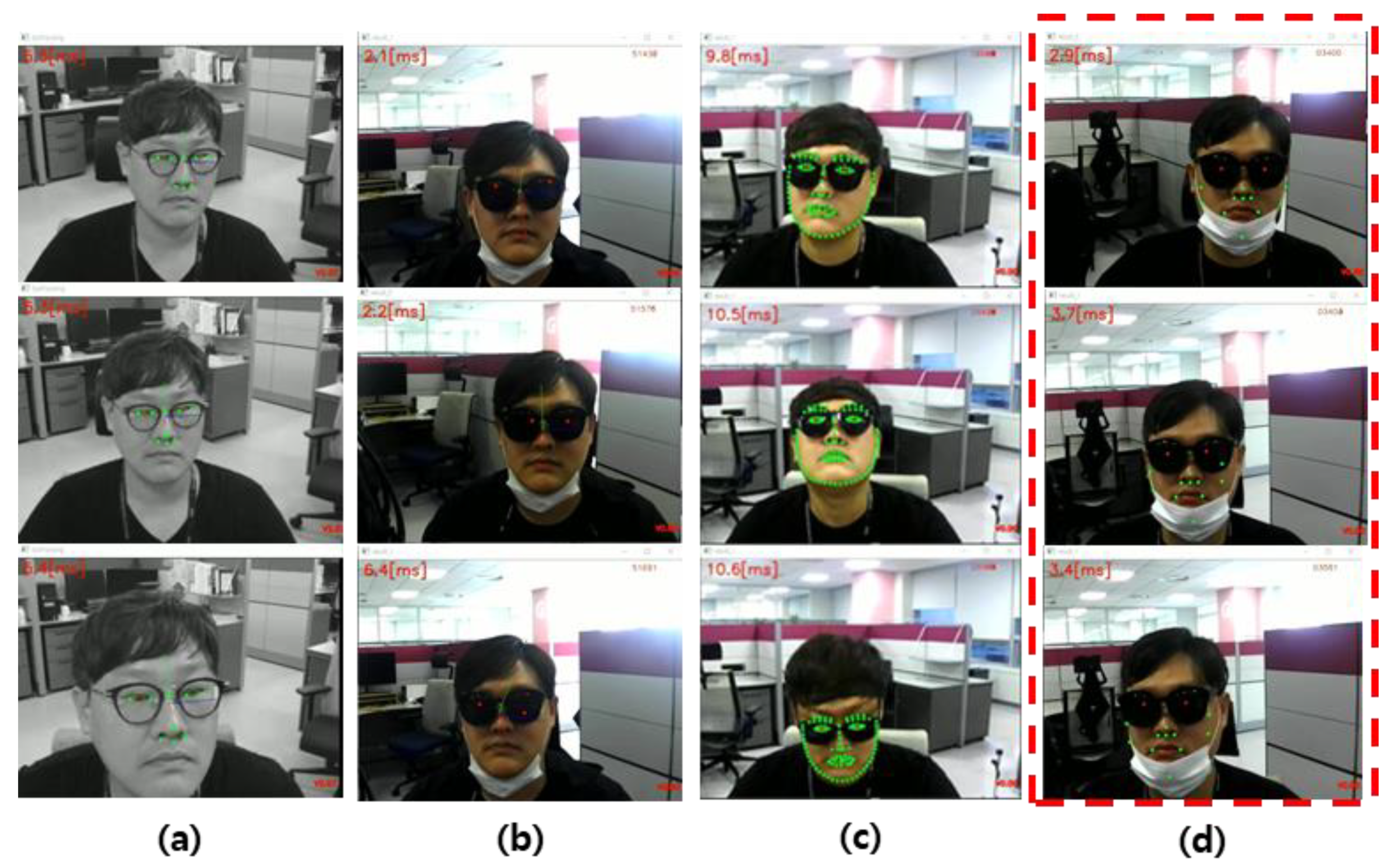
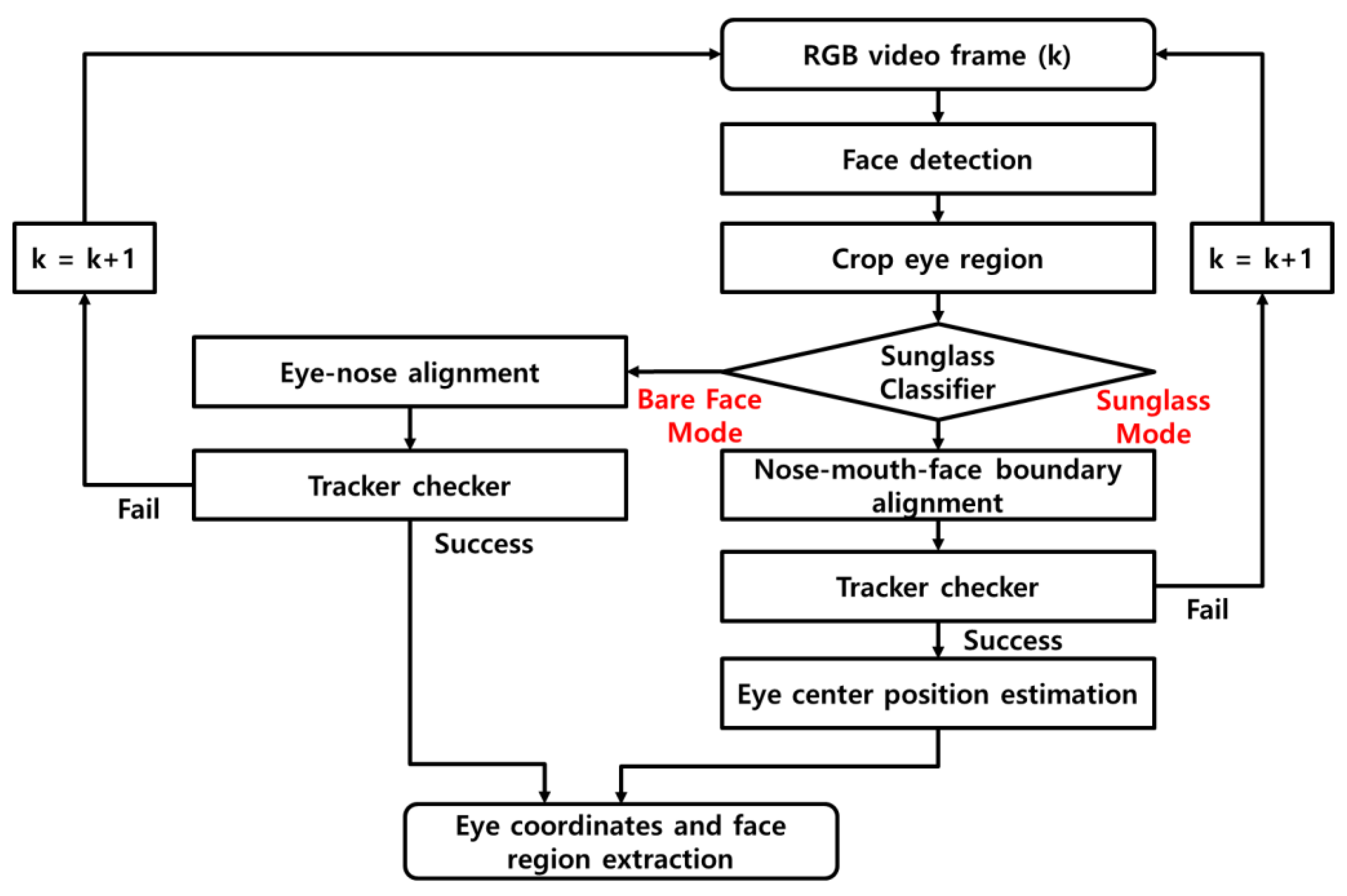
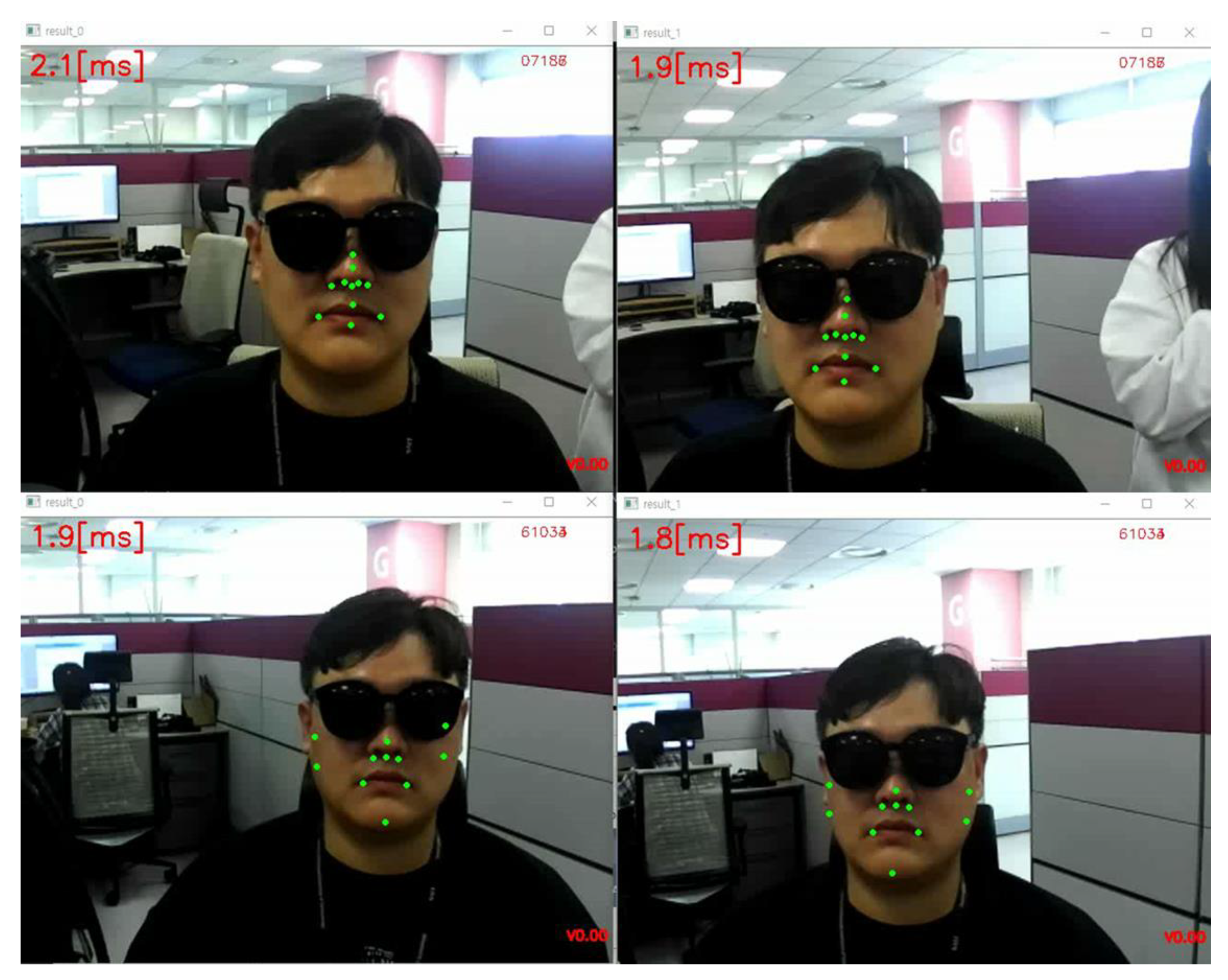
2.1. Whole-Face Detection and Classification of Faces with Sunglasses
2.2. Nose–Mouth–Face Boundary Tracking: Alignment and Tracker Checker
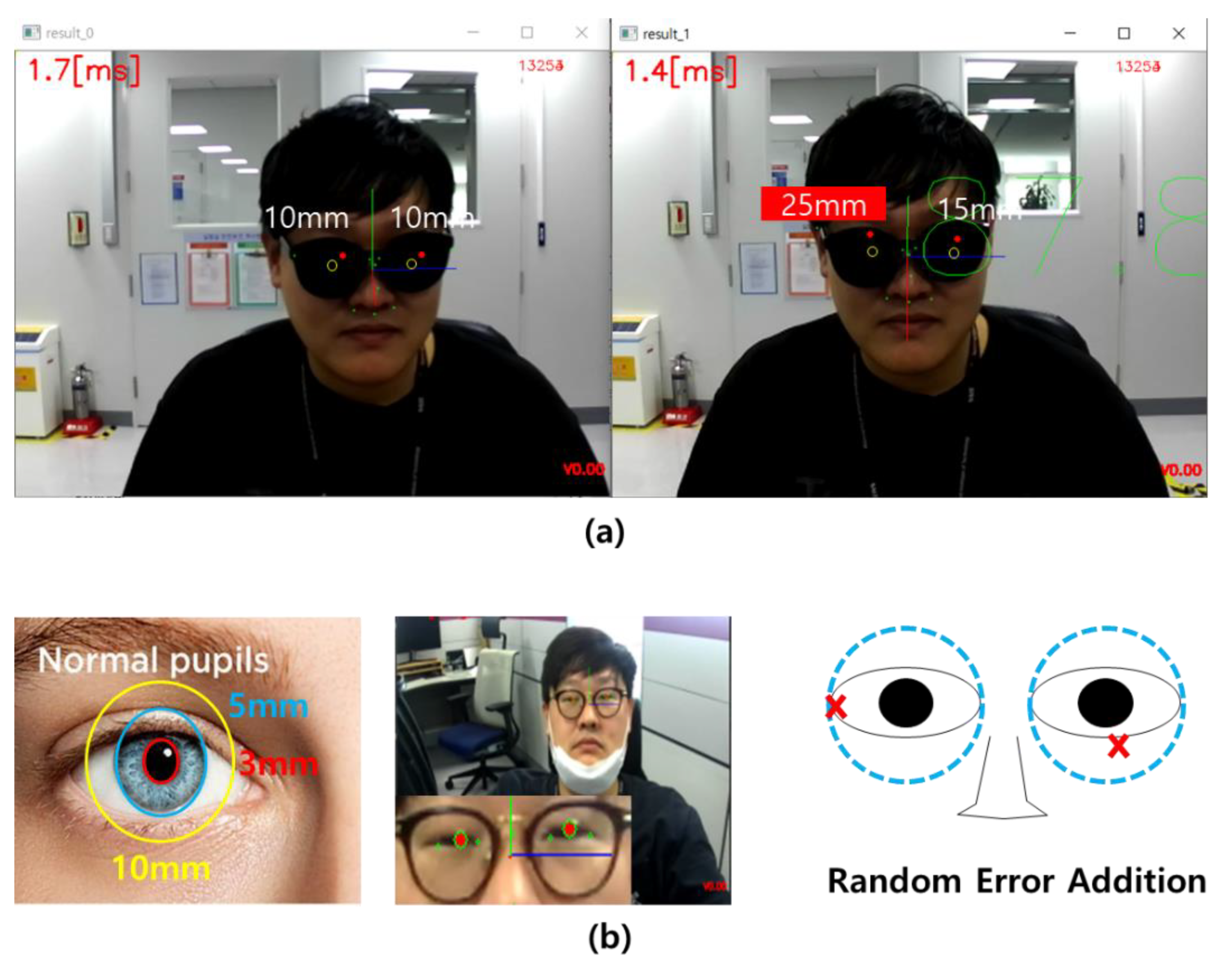
2.3. Eye Center Position Estimation from Nose–Mouth–Face Boundary Points Using a Supervised Linear Regression Algorithm
- ✓
- 1-sample
- : eye position from 11 NMB points
- :
- :
- :
- :
- ✓
- n-samples
- : n-samples’ eye positions from n-samples’ 11 NMB points by linear regres-sion
- :
- :
- ➔
- ➔
- ➔
- ➔
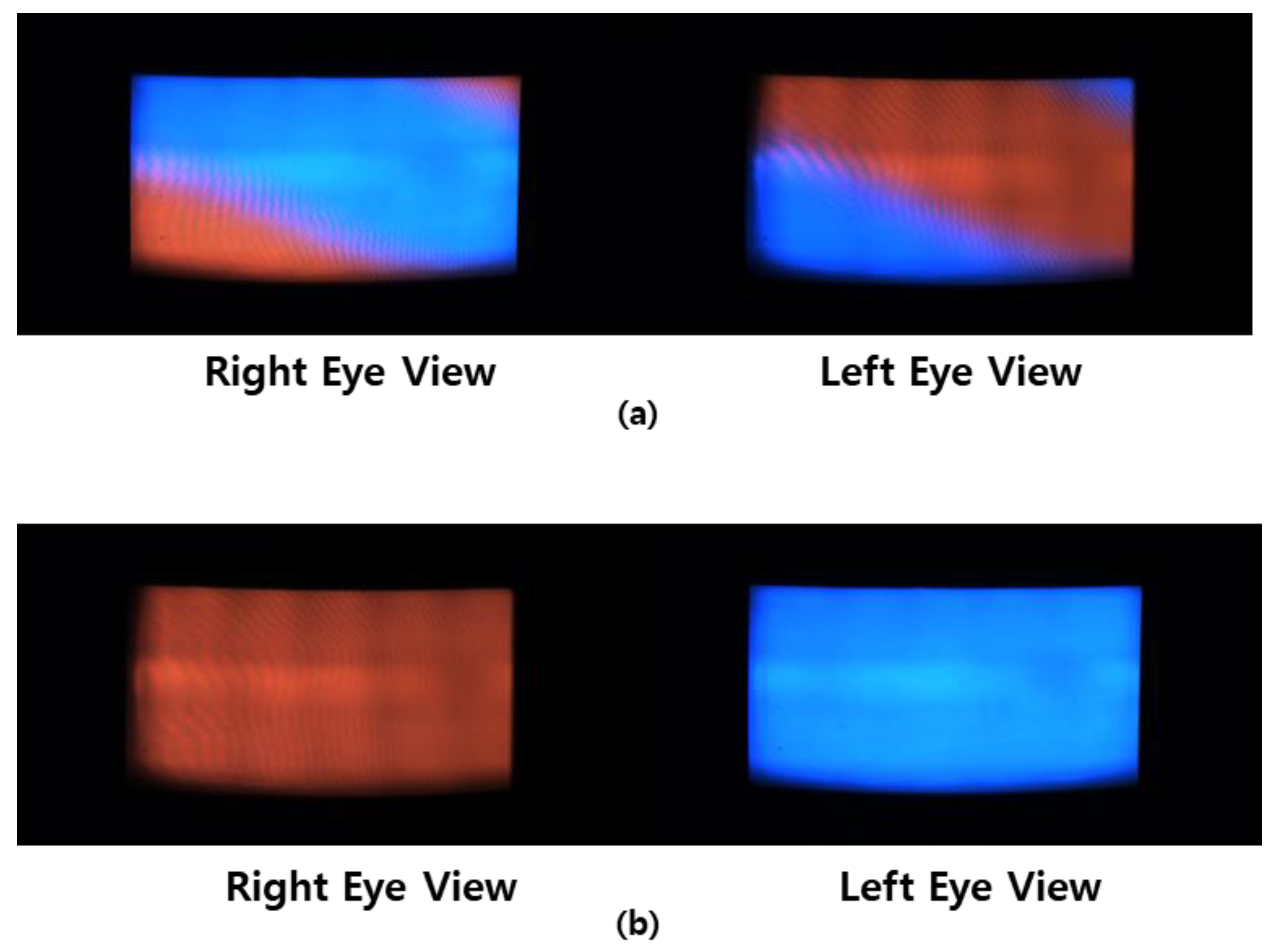
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nam, D.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Hwang, H.; Park, D.S. Flat Panel Light-Field 3-D Display: Concept, Design, Rendering, and Calibration. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 876–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, J.; Heo, J.; Kang, B.; Kang, D.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; Choi, K.; Nam, D. Autostereoscopic 3D display using directional subpixel rendering. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 20233–20247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Yin, K.; Li, K.; Wu, S.-T. Holographic Optical Elements for Augmented Reality: Principles, Present Status, and Future Perspectives. Adv. Photonics Res. 2021, 2, 2000049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Nam, D.K. Content Visualizing Device and Method. U.S. Patent 20190139298, 9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, L.A.V.; Orozoco, L.F.E. Head-Up Display System Using Auto-Stereoscopy 3D Transparent Electronic Display. U.S. Patent 20160073098, 10 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Yanusik, I.; Choi, Y.; Kang, B.; Hwang, C.; Park, J.; Hong, S. Automotive augmented reality 3D head-up display based on light-field rendering with eye-tracking. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 29788–29804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Wu, S.-T. Aberration-free pupil steerable Maxwellian display for augmented reality with cholesteric liquid crystal holographic lenses. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1760–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killioğlu, M.; Taşkiran, M.; Kahraman, N. Anti-spoofing in face recognition with liveness detection using pupil tracking. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), Herl’any, Slovakia, 26–28 January 2017; pp. 000087–000092. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, C.; Khwaounjoo, P.; Cakmak, Y.O. Human and Human-Interfaced AI Interactions: Modulation of Human Male Autonomic Nervous System via Pupil Mimicry. Sensors 2021, 21, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, T.; Fuhl, W.; Kasneci, E. PuRe: Robust pupil detection for real-time pervasive eye tracking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 170, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mompeán, J.; Aragón, J.L.; Prieto, P.M.; Artal, P. Design of an accurate and high-speed binocular pupil tracking system based on GPGPUs. J. Supercomput. 2018, 74, 1836–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.-L.; Kuo, T.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Fan, C.-P. Deep-Learning-Based Pupil Center Detection and Tracking Technology for Visible-Light Wearable Gaze Tracking Devices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozomitu, R.G.; Păsărică, A.; Tărniceriu, D.; Rotariu, C. Development of an Eye Tracking-Based Human-Computer Interface for Real-Time Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fu, H.; Wen, D.; Lo, W. Etracker: A Mobile Gaze-Tracking System with Near-Eye Display Based on a Combined Gaze-Tracking Algorithm. Sensors 2018, 18, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J. Pupil and Glint Detection Using Wearable Camera Sensor and Near-Infrared LED Array. Sensors 2015, 15, 30126–30141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Heo, H.; Park, K.R. A Novel Gaze Tracking Method Based on the Generation of Virtual Calibration Points. Sensors 2013, 13, 10802–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, M.; Ko, B.C. Energy Efficient Pupil Tracking Based on Rule Distillation of Cascade Regression Forest. Sensors 2020, 20, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.-C.; U, T.-M.; Hsieh, Y.-Z.; Yeh, Z.-F.; Lee, S.-F.; Lin, S.-S. An Eye-Tracking System based on Inner Corner-Pupil Center Vector and Deep Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Basterretxea, A.; Mendez-Zorrilla, A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Eye/Head Tracking Technology to Improve HCI with iPad Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 2244–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousseau, B.; Rose, J.; Eizenman, M. Hybrid Eye-Tracking on a Smartphone with CNN Feature Extraction and an Infrared 3D Model. Sensors 2020, 20, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.E.; Yoon, H.S.; Hong, H.G.; Park, K.R. Fuzzy-System-Based Detection of Pupil Center and Corneal Specular Reflection for a Driver-Gaze Tracking System Based on the Symmetrical Characteristics of Face and Facial Feature Points. Symmetry 2017, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, S.Y.; Cho, C.W.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, W.O.; Park, K.R. Gaze Tracking System for User Wearing Glasses. Sensors 2014, 14, 2110–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Heo, J. Content-Aware Eye Tracking for Autostereoscopic 3D Display. Sensors 2020, 20, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Heo, J.; Kang, B.; Nam, D. Pupil detection and tracking for AR 3D under various circumstances. In Proceedings of the Electronic Imaging, Autonomous Vehicles and Machines Conference; Society for Imaging Science and Technology, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 January 2019; pp. 55-1–55-5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3730–3738. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Iandola, F.; Jin, P.H.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeDet: Unified, small, low power fully convolutional neural networks for real-time object detection for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q. Look at boundary: A boundary-aware face alignment algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2129–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Yan, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Yang, Y. Style aggregated network for facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Xuehan, X.; De la Torre, F. Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M.J. Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 57, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M.J. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; pp. 511–518. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. Experiments with a new boosting algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Bari, Italy, 28 June–1 July 1996; pp. 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, R.; Patel, V.M.; Chellappa, R. Hyperface: A deep multi-task learning framework for face detection, landmark localization, pose estimation, and gender recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Ling, H. PFLD: A practical facial landmark detector. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.10859. [Google Scholar]




| Bare-Face Eye Tracker | Sunglasses-Wearing Face Eye Tracker | |
|---|---|---|
| Precision (mean error) | 2 mm | 10 mm |
| Distance between camera and user | ~50–200 cm | ~50–200 cm |
| Speed (ms/frame) | ~2–5 ms (2.5 GHz CPU) | ~2–5 ms (2.5 GHz CPU) |
| CPU consumption | 10% | 10% |
| Bare-Face Eye Tracker | Sunglasses-Wearing Eye Tracker | |
|---|---|---|
| 3D crosstalk experimental system | AR 3D HUD prototype (3D margin 12 mm) | |
| 3D content | 3D arrows with glow effects | |
| Number of participants reporting 3D crosstalk (static) | 0/20 | 0/20 |
| Number of participants reporting 3D crosstalk (dynamic) | 2/20 | 11/20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.; Chang, H.S. Low-Complexity Pupil Tracking for Sunglasses-Wearing Faces for Glasses-Free 3D HUDs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104366
Kang D, Chang HS. Low-Complexity Pupil Tracking for Sunglasses-Wearing Faces for Glasses-Free 3D HUDs. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104366
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Dongwoo, and Hyun Sung Chang. 2021. "Low-Complexity Pupil Tracking for Sunglasses-Wearing Faces for Glasses-Free 3D HUDs" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104366
APA StyleKang, D., & Chang, H. S. (2021). Low-Complexity Pupil Tracking for Sunglasses-Wearing Faces for Glasses-Free 3D HUDs. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104366






