Investigation of the Impact of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Chemical Composition and Wettability of Medical Grade Polyvinylchloride
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
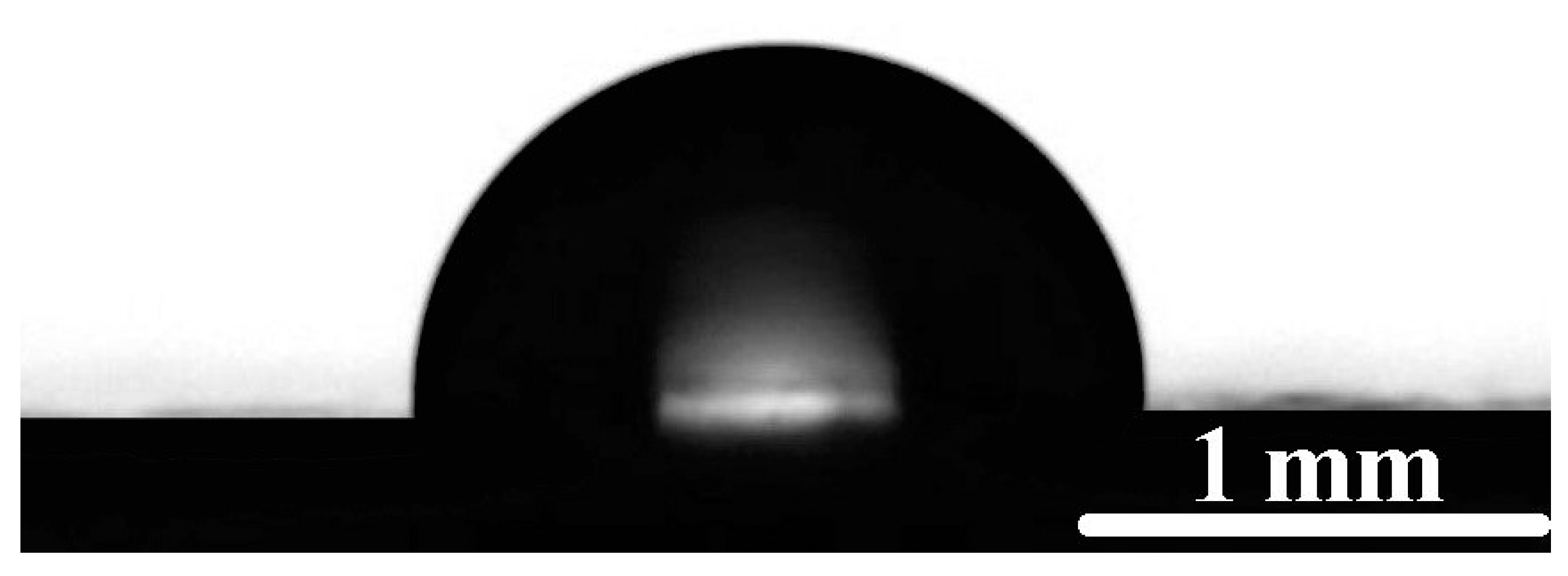
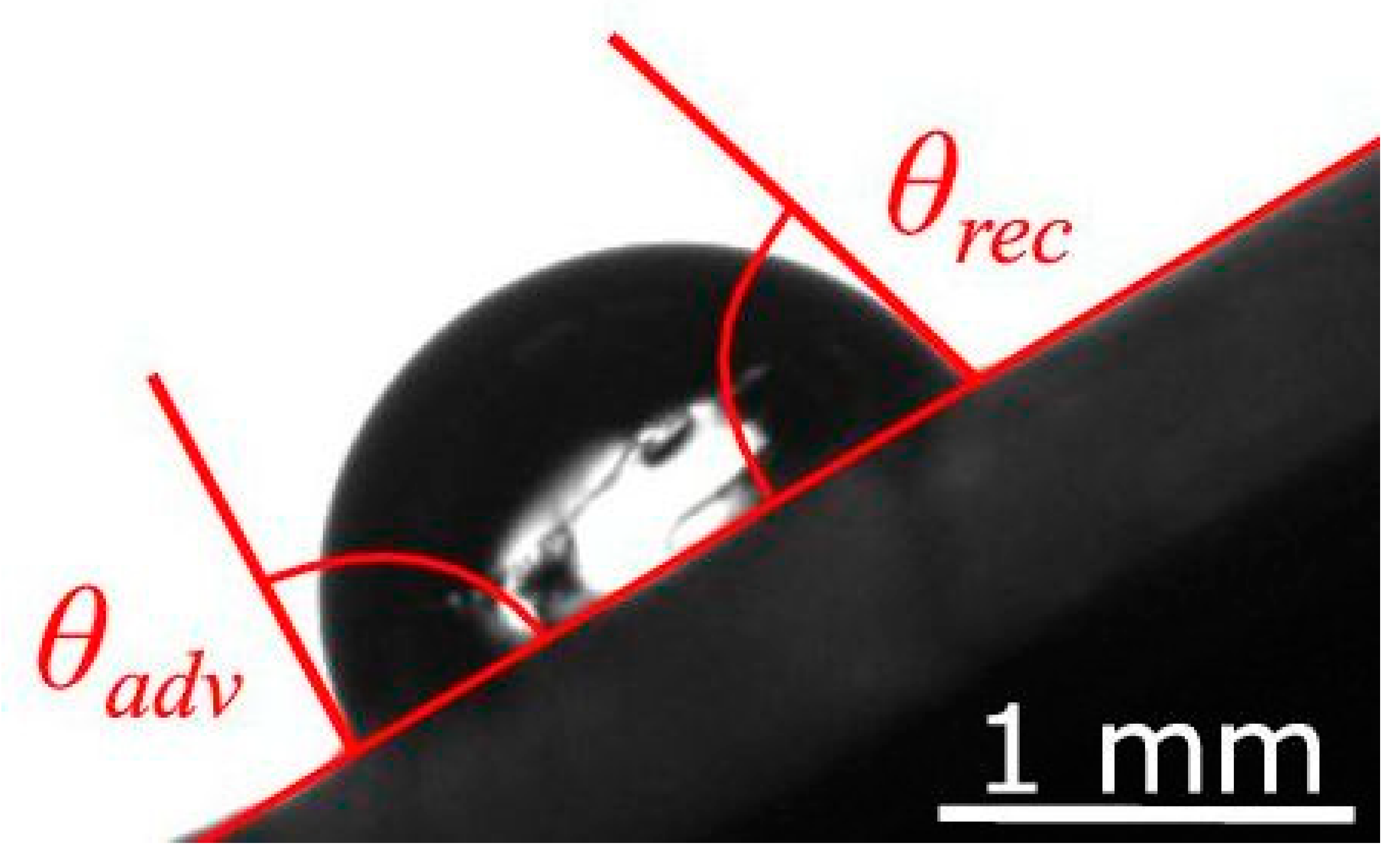
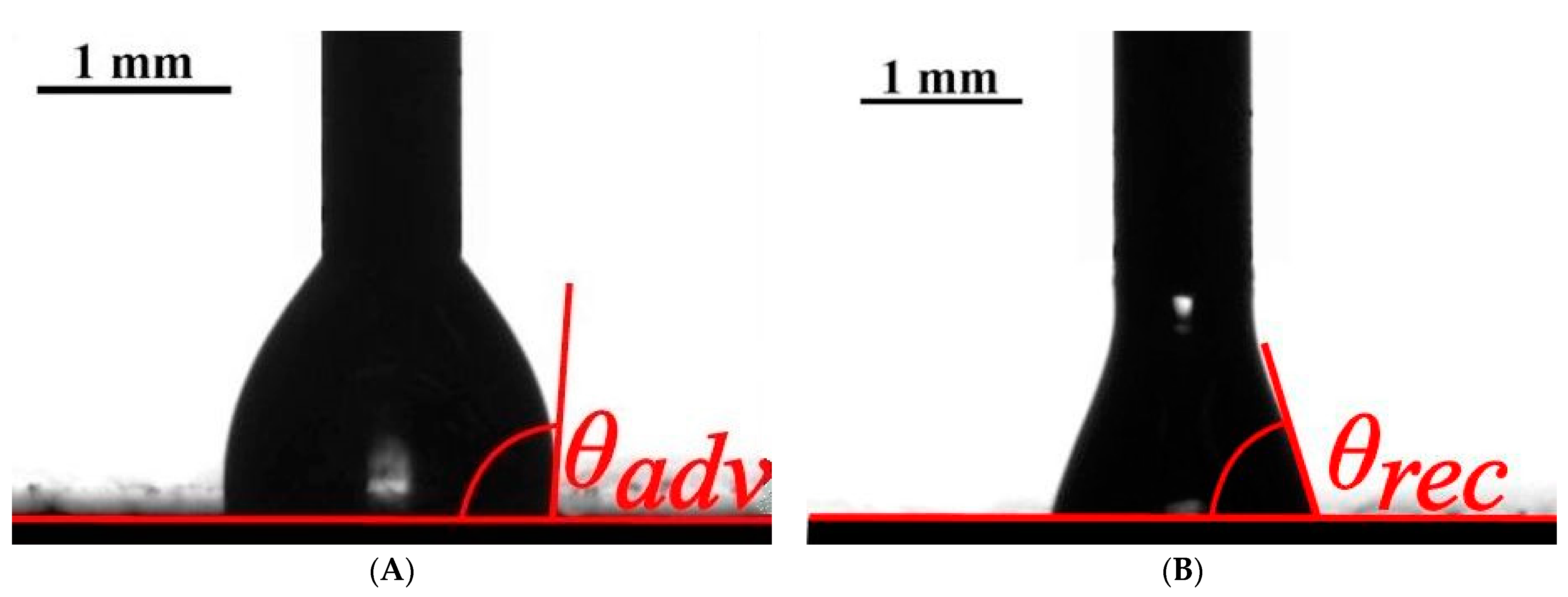
3.1. Experimental Study of Wetting of the Pristine PVC Tubing
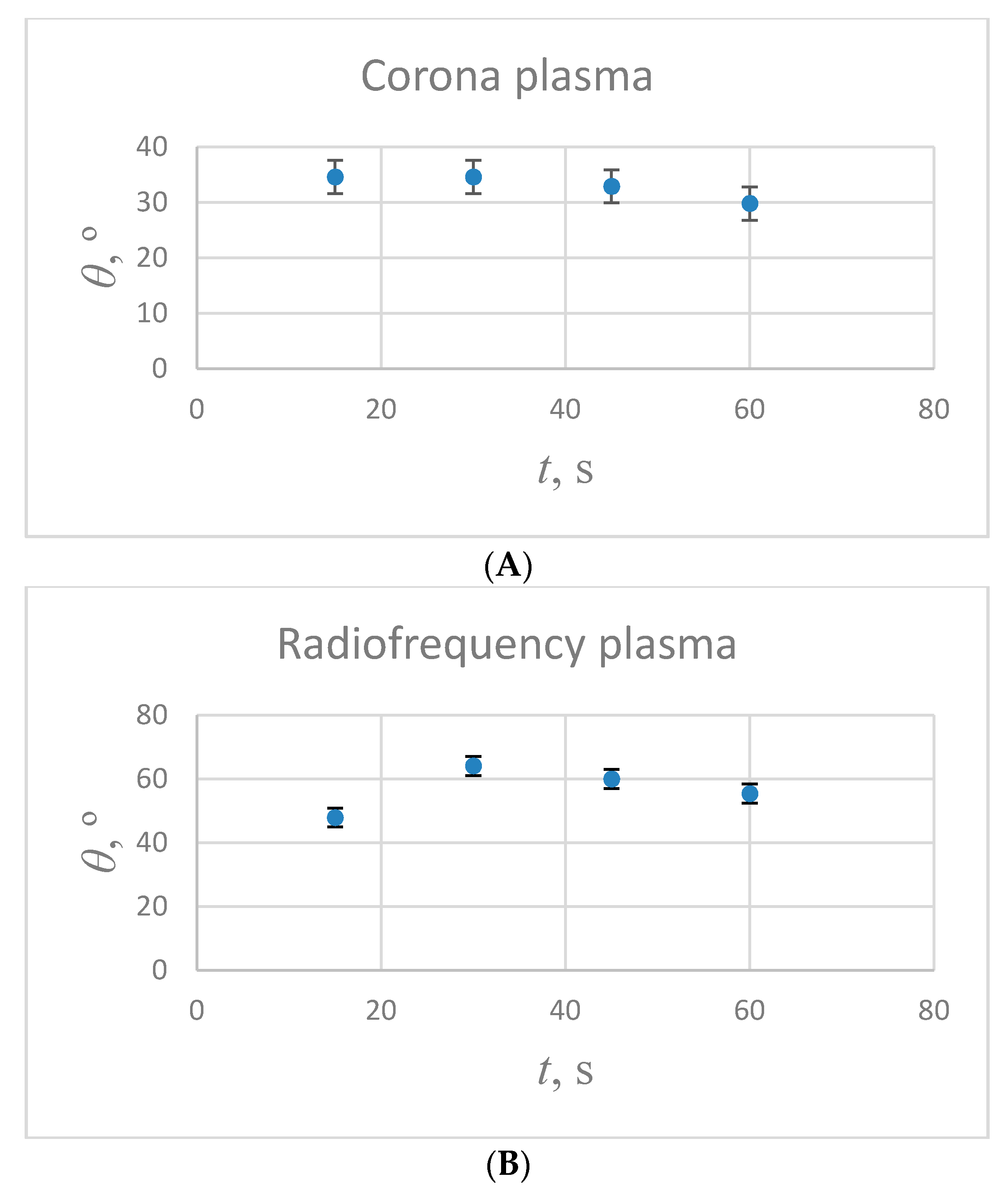
3.2. Influence of the Plasma Treatment on the Wetting of PVC Tubing
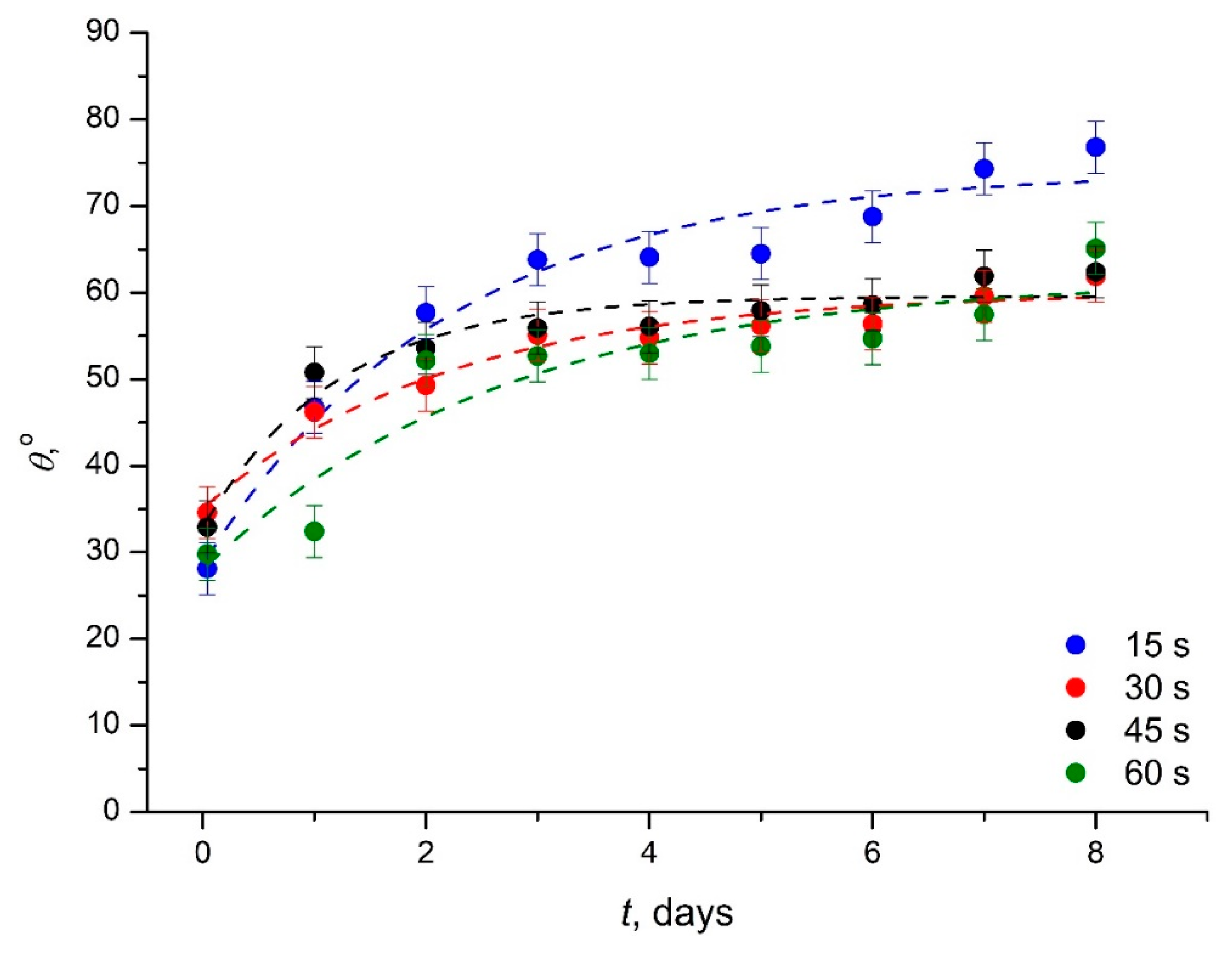
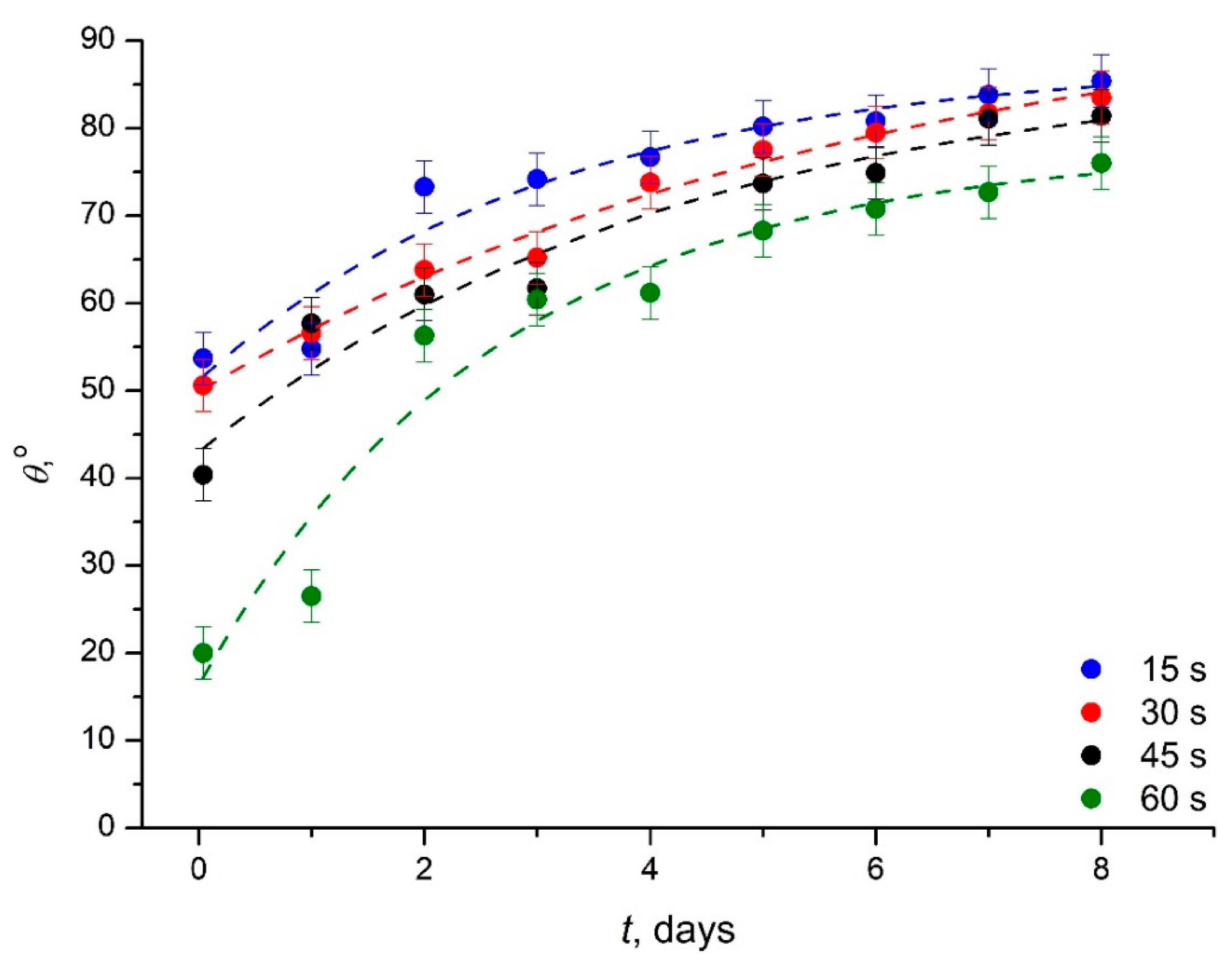
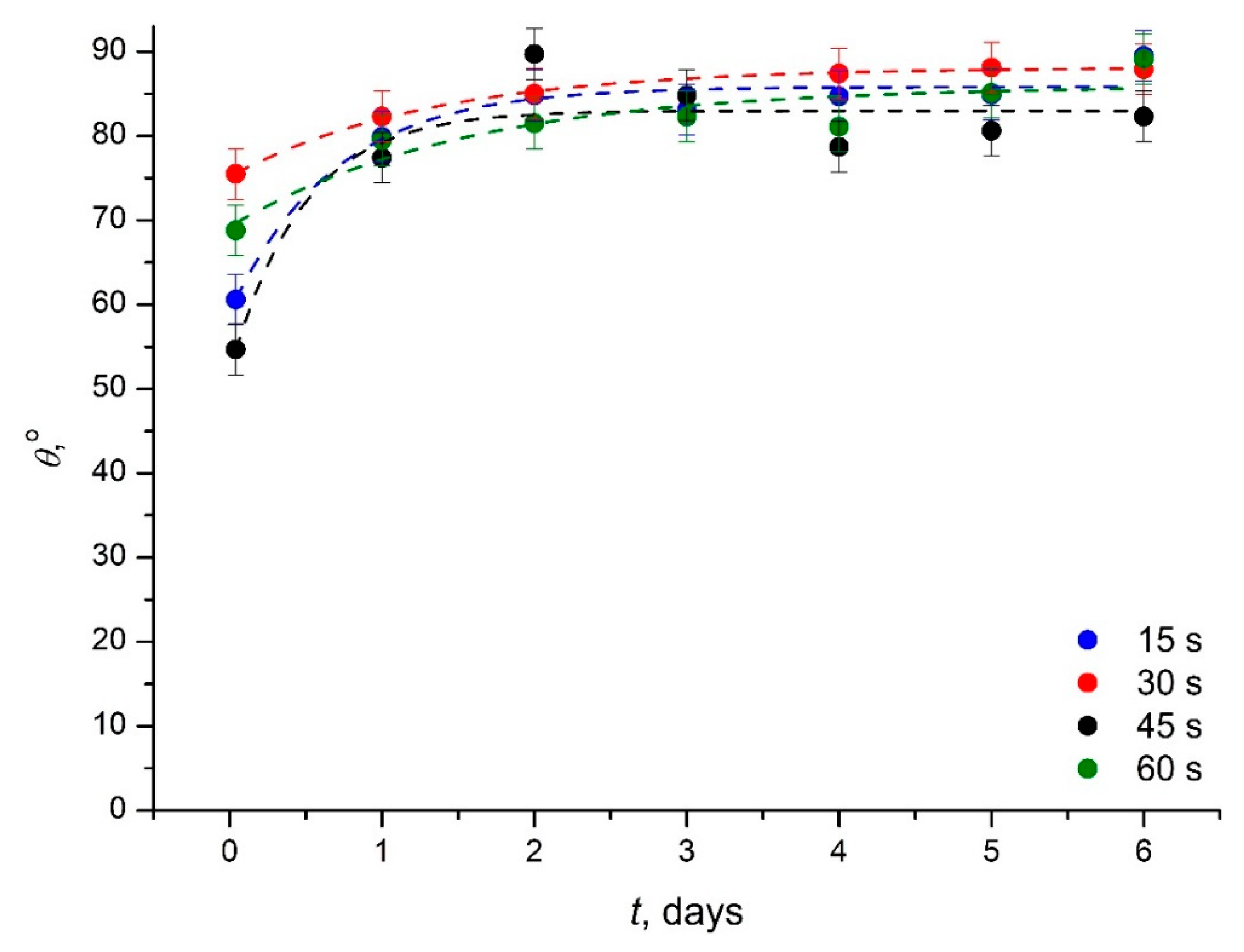
3.3. Study of the Hydrophobic Recovery Following the Plasma Treatment of the Medical Grade PVC
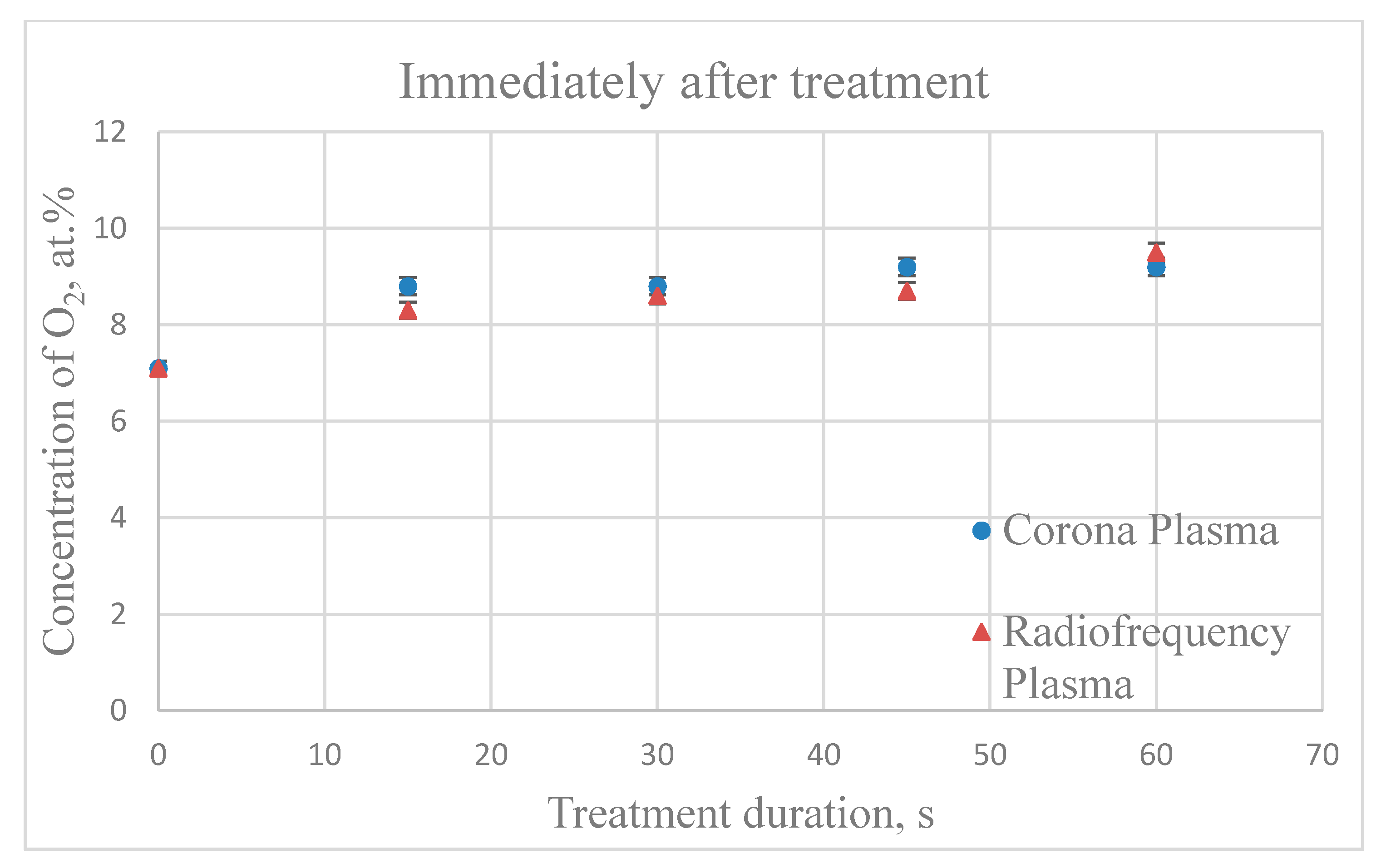
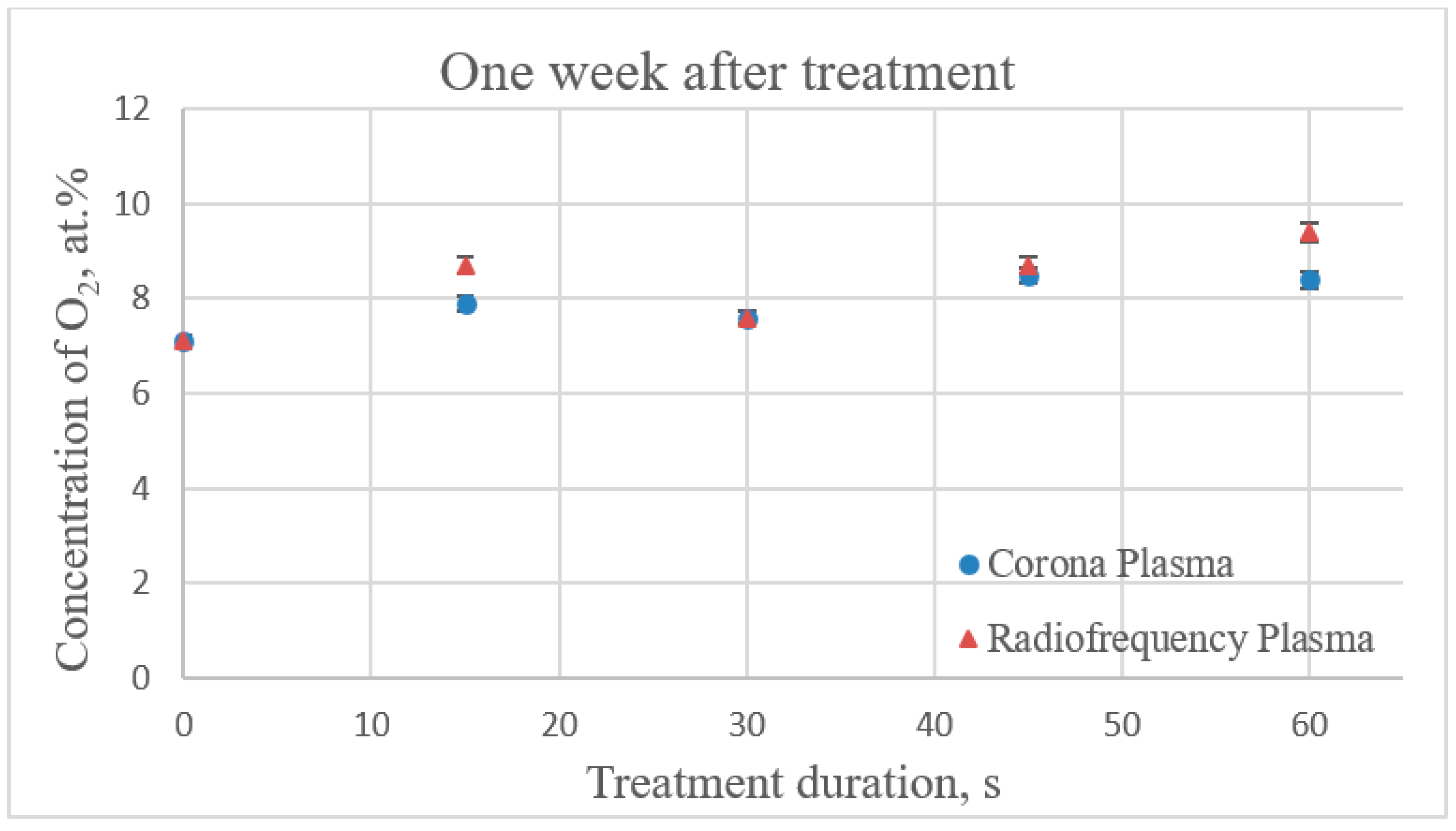
3.4. EDS Analysis of the Chemical Composition of the Plasma Treated PVC Catheters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasuda, H.; Gazicki, M. Biomedical applications of plasma polymerization and plasma treatment of polymer surfaces. Biomaterials 1982, 3, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehr, C. Plasma surface modification of polymers for biomedical use. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. B 2003, 208, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, N.; Sureshkumar, A.; Neogi, S. RF plasma-treated polymers for biomedical applications, Current Science. Curr. Sci. 2008, 94, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Cheruthazhekatt, S.; Černák, M.; Slavíček, P.; Havel, J. Gas plasmas and plasma modified materials in medicine. J. Appl. Biomed. 2010, 8, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshy, K.S.; Snigdha, S.; Thomas, S. Plasma Modified Polymeric Materials for Scaffolding of Bone Tissue Engineering. In Non-Thermal Plasma Technology for Polymeric Materials; Thomas, S., Mozetič, M., Cvelbar, U., Špatenka, P., Praveen, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 439–458. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, J.M.; Gerenser, L.J. Plasma treatment of polymers. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2003, 24, 305–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, M.; Lyons, C.S.; Mittal, K.L. (Eds.) Plasma Surface Modification of Polymers: Relevance to Adhesion; VSP: Zeist, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Mittal, K.L. (Eds.) Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment of Polymers, Plasma Surface Modification of Polymers: Relevance to Adhesion; Scrivener Publishing: Beverly, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, H.K. (Ed.) Plasma Polymerization and Plasma Treatment; J. Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- France, R.M.; Short, R.D. Plasma treatment of polymers: The Effects of energy transfer from an Argon plasma on the surface chemistry of polystyrene, and polypropylene. A High-Energy resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4827–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, R.M.; Short, R.D. Plasma treatment of polymers: Effects of energy transfer from an argon plasma on the surface chemistry of poly(styrene), low density poly(ethylene), poly(propylene) and poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1997, 93, 3173–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.; Kesmodel, L.L. High resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy investigation of plasma-modified polystyrene surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2001, 19, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiser, S.; Schütz, U.; Hegemann, D. Top-down approach to attach liquid polyethylene glycol to solid surfaces by plasma interaction. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 7, 1900211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Whyman, G.; Multanen, V.; Shulzinger, E.; Chaniel, G. Physical mechanisms of interaction of cold plasma with polymer surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, Y.; Chaniel, G.; Bormashenko, E. Surface charging by the cold plasma discharge of lentil and pepper seeds in comparison with polymers. Colloids Surf. B. 2018, 172, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehocky, M.; Drnovska, H.; Lapcikova, B.; Barros-Timmons, A.M.; Trindade, T.; Zembala, M.; Lapcik, L., Jr. Plasma surface modification of polyethylene. Colloids Surf. A 2003, 222, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preedy, E.C.; Brousseau, E.; Evans, S.L.; Perni, S.; Prokopovich, P. Adhesive forces and surface properties of cold gas plasma treated UHMWPE. Colloids Surf. A. 2014, 460, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegemann, D.; Brunner, H.; Oehr, C. Plasma treatment of polymers for surface and adhesion improvement. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2003, 208, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Alikind, D.; Kholkin, A.L.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Rebouta, L.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Vaz, F.; Costa, C.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Surface wettability modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and copolymer films and membranes by plasma treatment. Polymer 2019, 169, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, B.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Fabrication of “roll-off” and “sticky” superhydrophobic cellulose surfaces via plasma processing. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4785–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Eldar, B.; Chaniel, G.; Multanen, V.; Whyman, G. Influence of cold radiofrequency air and nitrogen plasmas treatment on wetting of polypropylene by the liquid epoxy resin. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 506, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, A.; Kaczmarek, H.; Kowalonek, J. The influence of side groups and polarity of polymers on the kind and effectiveness of their surface modification by air plasma action. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Chua, Y.C.; Kang, T.G. Oxygen plasma treatment for reducing hydrophobicity of a sealed polydimethylsiloxane microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 032204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerch, R.; McIntyre, N.S.; Hunter, D.H. Oxidation of polyethylene surfaces by remote plasma discharge: A comparison study with alternative oxidation methods. J. Polym. Sci. A 1990, 28, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, Y.; D’Orlye, F.; Perreard, C.; Da Silva, B.; Guyon, C.; Tatoulian, M.; Griveau, S.; Bedioui, F.; Varenne, A. Surface functionalization by plasma treatment and click chemistry of a new family of fluorinated polymeric materials for microfluidic chips. Plasma Process. Polym. 2014, 11, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhiello, E.; Morra, M.; Garbassi, F.; Johnson, D.; Humphrey, P. SSIMS studies of hydrophobic recovery: Oxygen plasma treated PS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1991, 47, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.; Kerdraon, M.; Rezard, Q.; Jullien, M.-C.; Champougny, L. Wettability patterning in microfluidic devices using thermally-enhanced hydrophobic recovery of PDMS. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 9253–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Chaniel, G.; Grynyov, R. Towards understanding hydrophobic recovery of plasma treated polymers: Storing in high polarity liquids suppresses hydrophobic recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegemann, D.; Lorusso, E.; Butron-Garcia, M.-I.; Blanchard, N.E.; Rupper, P.; Favia, P.; Heuberger, M.; Vandenbossche, M. Suppression of Hydrophobic Recovery by Plasma Polymer Films with Vertical Chemical Gradients. Langmuir 2016, 32, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, M.; Nosonovsky, M. A model for diffusion-driven hydrophobic recovery in plasma treated polymers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6876–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, L.; Jie-rong, C. Studies on wettability of medical poly(vinyl chloride) by remote argon plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 5076–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chu, P.K.; Jia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Fu, R.K.Y.; Ha, P.C.T.; Yan, Q. Plasma surface modification of poly vinyl chloride for improvement of antibacterial properties. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoranneviss, M.; Shahidi, S.; Wiener, J. Surface Modification of Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC) Using Low Pressure Argon and Oxygen Plasma. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2010, 12, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, P.; Keszler, A.M.; Bódis, E.; Drotár, E.; Klébert, S.; Károly, Z.; Szépvölgy, J. Optical emission spectra analysis of thermal plasma treatment of poly(vinyl chloride). Open Chem. 2015, 13, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, R. Line Energy and the Relation between Advancing, Receding, and Young Contact Angles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7659–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadmor, R.; Yadav, P.S. As-placed contact angles for sessile drops. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gennes, P.G.; Brochard-Wyart, F.; Quéré, D. Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Erbil, H.Y. Surface Chemistry of Solid and Liquid Interfaces; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bormashenko, E. Wetting of Real Surfaces; de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Extrand, C.W.; Kumagai, Y. An Experimental Study of Contact Angle Hysteresis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 191, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Krevelen, D.W. Properties of Polymers, Their Correlation with Chemical Structure. In Their Numerical Estimation and Prediction from Additive Group Contributions, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jierong, C.; Jing-Lian, Y.; Yun-Ze, Z. Surface modification of medical PVC by remote oxygen plasma. Compos. Interfaces 2004, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Perea-Carpio, R. Problems of contact angle and solid surface free energy determination. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Bormashenko, Y.; Whyman, G.; Pogreb, R.; Musin, A.; Jager, R.; Barkay, Z. Contact angle hysteresis on polymer substrates established with various experimental techniques, its interpretation, and quantitative characterization. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4020–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E. Surface free energy of a solid from contact angle hysteresis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 103, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, T. Surface free energy of extruded polymer compositions. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, T.T.; Kelen, T.; Turcsányi, B.; Tüdös, F. Initiated oxidation of polyenes formed in the thermal degradation of PVC. J. Polym. Sci. 1977, 15, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, H.; Kowalonek, J.; Szalla, A.; Sionkowska, A. Surface modification of thin polymeric films by air-plasma or UV-irradiation. Surf. Sci. 2002, 507–510, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewoud, L.M.H.; Terlingen, J.G.A.; Engbers, G.H.M.; Feijen, J. Removal of Pendant Groups of Vinyl Polymers by Argon Plasma Treatment. Langmuir 1999, 15, 5396–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogreb, R.; Loew, R.; Bormashenko, E.; Whyman, G.; Multanen, V.; Shulzinger, E.; Abramovich, A.; Rozban, D.; Shulzinger, A.; Zussman, E.; et al. Relaxation Spectra of Polymers and Phenomena of Electrical and Hydrophobic Recovery: Interplay between Bulk and Surface Properties of Polymers. J. Polym. Sci. B 2017, 55, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gong, L.; Qu, Z.; Hao, P.; Liu, J.; Fu, L. Wettability enhancement of hydrophobic artificial sandstones by using the pulsed microwave plasma jet. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2020, 36, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PVC Tubing | Specific Energy of Adhesion, |
|---|---|
| Pristine | |
| Corona discharge treated | |
| Radiofrequency plasma discharge treated | |
| DBD plasma discharge treated |
| Exposure Time, s | θSat, ° | , ° | τ, Days |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 73 ± 2.8 | 45 ± 3.7 | 2.2 ± 0.5 |
| 30 | 60 ± 1.6 | 25 ± 2.1 | 2.2 ± 0.5 |
| 45 | 60 ± 1.2 | 27 ± 2.6 | 1.2 ± 0.3 |
| 60 | 62 ± 5.3 | 34 ± 5.7 | 2.7 ± 1.3 |
| Exposure Time, s | θSat, ° | , ° | τ, Days |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 87 ± 5.0 | 36 ± 4.8 | 3.1 ± 1.2 |
| 30 | 97 ± 6.8 | 47 ± 6.2 | 6 ± 1.6 |
| 45 | 88 ± 8.7 | 45 ± 7.7 | 4.3 ± 1.9 |
| 60 | 78 ± 5.7 | 62 ± 6.2 | 2.7 ± 0.8 |
| Exposure Time, s | θSat | Τ, Days | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 86 ± 1.2 | 27 ± 2.7 | 0.7 ± 0.2 |
| 30 | 88 ± 0.2 | 13 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| 45 | 83 ± 2.2 | 31 ± 5.6 | 0.5 ± 0.3 |
| 60 | 85 ± 2.5 | 17 ± 3.4 | 1.5 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bormashenko, E.; Legchenkova, I.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Frenkel, M.; Bormashenko, Y. Investigation of the Impact of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Chemical Composition and Wettability of Medical Grade Polyvinylchloride. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010300
Bormashenko E, Legchenkova I, Navon-Venezia S, Frenkel M, Bormashenko Y. Investigation of the Impact of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Chemical Composition and Wettability of Medical Grade Polyvinylchloride. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(1):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010300
Chicago/Turabian StyleBormashenko, Edward, Irina Legchenkova, Shiri Navon-Venezia, Mark Frenkel, and Yelena Bormashenko. 2021. "Investigation of the Impact of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Chemical Composition and Wettability of Medical Grade Polyvinylchloride" Applied Sciences 11, no. 1: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010300
APA StyleBormashenko, E., Legchenkova, I., Navon-Venezia, S., Frenkel, M., & Bormashenko, Y. (2021). Investigation of the Impact of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Chemical Composition and Wettability of Medical Grade Polyvinylchloride. Applied Sciences, 11(1), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010300







