Effects of Amending Phosphatic Fertilizers with Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Phosphorus Availability and Its Fractionation in an Acid Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Physical and Chemical Analysis of Soil, Clinoptilolite Zeolite, and Phosphorus Fertilizers
2.3. Phosphorus Fractionation Study
2.4. Laboratory Incubation Study
2.5. Pot Study
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Phosphorus Fertilizers, and Soil
3.2. Soil Total Phosphorus, Available Phosphorus, and Selected Soil Chemical Properties
3.3. Soil Inorganic Phosphorus Speciation
3.4. Plant Dry Matter Production, Phosphorus Concentration, Phosphorus Uptake, and Phosphorus Use Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gikonyo, E.W.; Zaharah, A.R.; Hanafi, M.M.; Anuar, A.R. Evaluation of Phosphorus Pools and Fractions in an Acid Tropical Soil Recapitalized with Different Phosphorus Sources. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 1385–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Ranjbar, F. Aging effects on phosphorus transformation rate and fractionation in some calcareous soils. Geoderma 2010, 155, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondre, N. Phosphorus: How much is enough? Glob. Chang. 2011, 76, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Filippelli, G.M. Phosphate rock formation and marine phosphorus geochemistry: The deep time perspective. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, N. Environment: The disappearing nutrient. Nature 2009, 461, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajirloo, G.S.; Jadid, A.P.; Nasirtabrizi, M.H. Effect of zeolite application on soil purification and some chemical properties of soil (case study). Tech. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2013, 3, 970–974. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, K.; Reddy, D.D. Zeolites and Their Potential Uses in Agriculture. In Advances in Agronomy; Donald, L.S., Ed.; University of Delaware: Newark, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 113, pp. 219–241. [Google Scholar]
- Daković, A.; Tomašević-Čanović, M.; Rottinghaus, E.G.; Matijašević, S.; Sekulić, Ž. Fumonisin B1 adsorption to octadecyldimetylbenzyl ammonium modified clinoptilolite rich zeolitic tuff. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 105, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.W.; Allen, E.R. Use of natural zeolites in agronomy, horticulture, and environmental soil remediation. In Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry; Ribbe, P.H., Ed.; Blacksburg Press: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2001; Volume 5, pp. 619–653. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, E.R.; Hossner, L.R.; Ming, D.W.; Henninger, D.L. Solubility and Cation Exchange in Phosphate Rock and Saturated Clinoptilolite Mixtures. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, H.P.; Menzies, N.W.; Hunter, M.N.C. Zeolite/rock phosphate—A novel slow release phosphorus fertilizer for potted plant production. Sci. Hortic. 2002, 94, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.; Ming, D.; Hossner, L.; Henninger, D.; Galindo, C. Growth and nutrient uptake of wheat in a clinoptilolite-phosphate rock substrate. Agron. J. 1995, 87, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.-M.; Eberl, D.D. Controlled and renewable release of phosphorous in soils from mixtures of phosphate rock and NH4-exchanged clinoptilolite. Zeolites 1986, 6, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Biswas, A.K.; Somasundaram, J.; Rao, A.S. Nanoporous zeolites in farming: Current status and issues ahead. Curr. Sci. 2010, 99, 760–764. [Google Scholar]
- Eberl, D.D. Controlled-Release Fertilizers Using Zeolites, U.S. Department of the Interior U.S Geological Survey. 1993. Available online: http://www.usgs.gov/tech-transfer/factsheets/94-066b.html (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Dixon, J.B.; Weed, S.B.; Parpitt, R.L. Minerals in Soil Environments. Soil Sci. 1990, 150, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Survey of Larimer County, CO, U.S. USDA-NRCS Soil Survey; U.S. Gov. Print. Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Peech, M. Hydrogen-ion Activity. In Methods of Soil Analysis Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Black, C.A., Evans, D.D., White, J.L., Ensminger, L.E., Clark, F.E., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 914–925. [Google Scholar]
- Piccolo, A. Humus and soil conservation. In Humic Substances in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Piccolo, A., Ed.; Elseiver: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 225–264. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.H. Soil Sampling, Preparation, and Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottenie, A. Soil testing and plant testing as a basis of fertilizer recommendation. Fao Soils Bull. 1980, 38, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlich, A. Determination of P, K, Na, Ca, Mg and NH4; Soil Test Division Mimeo, North Carolina Department of Agriculture: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Rimmer, D.L.; Rodwell, D.L. Soil Science: Methods and Application. J. Ecol. 1995, 83, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Agronomy 9. The American Society of Anesthesiologists, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 869–920. [Google Scholar]
- Rofiee, M.S. Involvement of CYP450 system in hepatoprotective activity of Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute (MARDI)-produced virgin coconut oils. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Aainaa, H.N.; Majid, N.M.A. Zeolites to Unlock Phosphorus Fixation in Agriculture; Universiti Putra Malaysia: Serdang, Malaysia, 2017; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Kasim, S.; Haruna, A.O.; Majid, N.M.A.; Yusop, M.K.; Jalloh, M.B. Effect of Organic Based N Fertilizer on Dry Matter (Zea mays L.), Ammonium and Nitrate Recovery in an Acid Soil of Sarawak, Malaysia. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A. Nitrogen use efficiency: State of the art. In Proceedings of the IFA International Workshop on Enhanced-Efficiency Fertilizers, Frankfurt, Germany, 28–30 June 2005; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Latifah, O.; Haruna, A.O.; Majid, N.M.A. Enhancing nitrogen availability from urea using clinoptilolite zeolite. Geoderma 2017, 306, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramananthan, S. Soils of Malaysia: Their Characteristics and Identification; Academy of Sciences Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 11–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gichangi, E.M.; Mnkeni, P.N.S.; Brookes, P.C. Effects of goat manure and inorganic phosphate addition on soil inorganic and microbial biomass phosphorus fractions under laboratory incubation conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2009, 55, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Syersy, J.K.; Tillman, R.W.; Kirkman, J.H. Effect of liming on phosphate sorption by acid soils. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 41, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstic, D.; Djalovic, I.; Nikezic, D.; Bjelic, D. Aluminium in Acid Soils: Chemistry, Toxicity and Impact on Maize Plants. In Food Production—Approaches, Challenges and Tasks; Aladjadjiyan, A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 231–242. ISBN 978-953-307-887-8. [Google Scholar]
- Azura, A.E.; Shamshuddin, J.; Fauziah, C.I. Root Elongation, Root Surface Area and Organic Acid by Rice Seedling under Al3+ and/or H+ Stress. Am. J. Agric. Boil. Sci. 2011, 6, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, R.; Sims, J.; Coale, F.J. Phosphorus Solubility in Biosolids-Amended Farm Soils in the Mid-Atlantic Region of the USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-T.; Traina, S.J.; Logan, T.J. Chemical Properties of Municipal Solid Waste Composts. J. Environ. Qual. 1992, 21, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anetor, M.O.; Akinrinde, E.A. Lime effectiveness of some fertilizers in a tropical acid Alfisol. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2007, 8, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C.; Jones, C.A. Growth and Mineral Nutrition of Field Crops, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aainaa, H.N.; Ahmed, O.H.; Ab Majid, N.M. Effects of clinoptilolite zeolite on phosphorus dynamics and yield of Zea mays L. cultivated on an acid soil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulos, D. Availability of phosphorus in the coffee soil of Southwest Ethiopia. In Soil the Resource Base for Survival, Proceedings of the 2nd Conference of Ethiopian Society of Soil Science (ESSS’93), 23–24 September 1993; Tekalign, M., Mitiku, H., Eds.; Ethiopian Society of Soil Science: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1996; pp. 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Vaananen, R.; Hristov, J.; Tanskanen, N.; Hartikainen, H.; Nieminen, M.; Ilvesniemi, H. Phosphorus sorption properties in podzolic forest soils and soil solution phosphorus concentration in undisturbed and disturbed soil profiles. Boreal Environ. Res. 2008, 13, 553–567. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparatos, D.; Haidouti, C.; Haroulis, A.; Tsaousidou, P. Estimation of Phosphorus Status of Soil Fe-Enriched Concretions with the Acid Ammonium Oxalate Method. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 2375–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, R.E.; McLaughlin, M.J. Interferences in the determination of isotopically exchangeable P in soils and a method to minimise them. Soil Res. 2002, 40, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, J.S.; Grewal, J. Phosphorus Fixation in Indian Soils, New Delhi, India, 2nd ed.; Indian Council of Agricultural Research: New Delhi, India, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Nr, A.; Čakmak, D.; Saljnikov, E.; Roglic, G.; Koković, N.; Manojlović, D. Effect of waste Al-phosphate on soil and plant. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongqing, H.; Chunying, T.; Chongfa, C.; He, J.-Z.; Xueyuan, L. Availability and residual effects of phosphate rocks and inorganic P fractionation in a red soil of Central China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 59, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresh, R.J.; Smithson, P.C.; Hellums, D.T.; Sanchez, P.A.; Calhoun, F. Building Soil Phosphorus Capital in Africa. In Soil Testing: Prospects for Improving Nutrient Recommendations; SSSA Special Publication No. 51; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; pp. 111–149. [Google Scholar]
- Basri, M.H.; Junejo, N.; Abdu, A.; Hamid, H.A.; Kusno, M.A. Elevation and variability of acidic sandy soil pH: Amended with conditioner, activator, organic and inorganic fertilizers. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 4020–4024. [Google Scholar]
- Zoysa, A.; Loganathan, P.; Hedley, M.J. A technique for studying rhizosphere processes in tree crops: Soil phosphorus depletion around camellia (Camellia japonica L.) roots. Plant Soil 1997, 190, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lookman, R.; Jansen, K.; Merckx, R.; Vlassak, K. Relationship between soil properties and phosphate saturation parameters a transect study in northern Belgium. Geoderma 1996, 69, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Gilkes, R.; Armitage, T.M.; Bolland, M.D.A. Identification of residual P compounds in fertilized soils using density fractionation, X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1994, 37, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsinger, P.; Gilkes, R. Dissolution of phosphate rock in the rhizosphere of five plant species grown in an acid, P-fixing mineral substrate. Geoderma 1997, 75, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.H.; Marschner, H. The Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. J. Ecol. 1988, 76, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aainaa, H.N.; Haruna, A.O.; Kasim, S.; Majid, N.M.A. Reducing Egypt Rock Phosphate Use in Zea mays Cultivation on an Acid Soil Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Sustain. Agric. Res. 2014, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabai, K.A.; Kasim, S.; Ahmed, O.H. Use of formulated nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium compound fertilizer using clinoptilolite zeolite in maize (Zea mays L.) cultivation. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2013, 25, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Sumalatha, G.; Majid, N.M.A. Use of zeolite in maize (Zea mays) cultivation on nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus uptake and use efficiency. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2010, 5, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, C.; Bittman, S.; Montreal, M.; Plenchette, C.; Morel, C. Soil and fertilizer phosphorus: Effects on plant P supply and mycorrhizal development. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2005, 85, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beqiraj, E.; Gjoka, F.; Muller, F.; Baillif, P. Use of zeolitic material from Munella region (Albania) as fertilizer in the sandy soils of Divjaka region (Albania). Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2008, 3, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
| Pi Fraction | Extractant | Extraction Time | Other Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| A: Sol-P (Loosely soluble-P) | 50 mL 1 M NH4Cl | Shake (30 minutes), centrifuge, save supernatant as A | |
| B: Al–P (Aluminum bound P) | 50 mL 0.5 M NH4F (adjusted to pH 8.2) | Shake (1 hour), centrifuge, save supernatant as B | Wash soil residue twice with 25 ml saturated NaCl and combine the washings with B |
| C: Fe–P (iron bound P) | 50 mL 0.1 M NaOH | Shake (17 hours), centrifuge, save supernatant as C | Wash soil residue twice with 25 ml saturated NaCl and combine the washings with C |
| D: Red-P (Reductant soluble P) | 40 mL 0.3 M Na3C6H5O7, 5 mL 1 M NaHCO3, (add while heating) | Shake (15 minutes), heat in water bath (85 °C, 15 minutes) Add 1 g NaS2O4, stir rapidly, and continue heating (15 minutes). Centrifuge and save supernatant as D | Wash soil residue twice with 25 ml saturated NaCl and combine the washings with D |
| E: Ca–P (Calcium bound P) | 50 mL 0.25 M H2SO4 | Shake (1 hour), centrifuge, save supernatant as E | Wash soil residue twice with 25 ml saturated NaCl and combine the washings with E |
| F: Occl-P (Occluded P) | 50 mL 0.1 M NaOH | Shake (1 hour), centrifuge, save supernatant as F | Wash soil residue twice with 25 ml saturated NaCl and combine the washings with F |
| Treatments | P Fertilizer | Urea | MOP | Clinoptilolite Zeolite | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ------------------------- (g pot−1)------------------------ | ||||||
| T0 | 250 g soil | |||||
| TSP | T1 | 250 g soil | +4.85 | +4.85 | +2.47 | |
| T2 | 250 g soil | +3.64 | +3.64 | +1.85 | +10.34 | |
| T0 | 250 g soil | |||||
| ERP | E1 | 250 g soil | +7.95 | +4.85 | +2.47 | |
| E2 | 250 g soil | +5.96 | +3.64 | +1.85 | +13.00 | |
| T0 | 250 g soil | |||||
| CIRP | C1 | 250 g soil | +7.42 | +4.85 | +2.47 | |
| C2 | 250 g soil | +5.57 | +3.64 | +1.85 | +12.50 | |
| Property | TSP | ERP | CIRP | CZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (water) | 2.46 | 7.42 | 7.93 | 8.54 |
| CEC (cmol(+)kg−1) | ND | ND | ND | 75.4 |
| Total P (%) | 18.09 | 11.96 | 10.62 | 0.01 |
| Total P2O5 (%) | 41.12 | 27.19 | 24.15 | ND |
| Total K (%) | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.37 |
| Total Ca (%) | 4.88 | 47.55 | 51.73 | 0.67 |
| Total Mg (%) | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.10 |
| Total Fe (%) | 0.38 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.11 |
| Soil Properties | Value Obtained | Standard Range | Soil Properties | Value Obtained | Standard Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (water) | 4.32 | 4.6–4.9 | CEC (cmol(+)kg−1) | 5.33 | 3.86–8.46 |
| Bulk density (g·cm−3) | 1.01 | NA | Total Fe (cmol(+)kg−1) | 7.51 | NA |
| Total P (mg·kg−1) | 49.96 | NA | Tot. acidity (cmol(+)kg−1) | 1.38 | NA |
| Available P (mg·kg−1) | 2.48 | NA | Exch. Al (cmol(+)kg−1) | 0.9 | NA |
| Organic matter (%) | 5.60 | Nd | Exch. H (cmol(+)kg−1) | 0.48 | NA |
| Total carbon (%) | 3.25 | 0.57–2.51 | Exch. K (cmol(+)kg−1) | 0.24 | 0.05–0.19 |
| Texture | SL | SL | Exch. Ca (cmol(+)kg−1) | 0.76 | 0.01 |
| Sand (%) | 74.84 | 72–76 | Exch. Mg (cmol(+)kg−1) | 0.45 | 0.07–0.21 |
| Silt (%) | 12.67 | 8–9 | Exch. Na (cmol(+)kg−1) | 3.60 | 0.01 |
| Clay (%) | 12.49 | 16–19 |
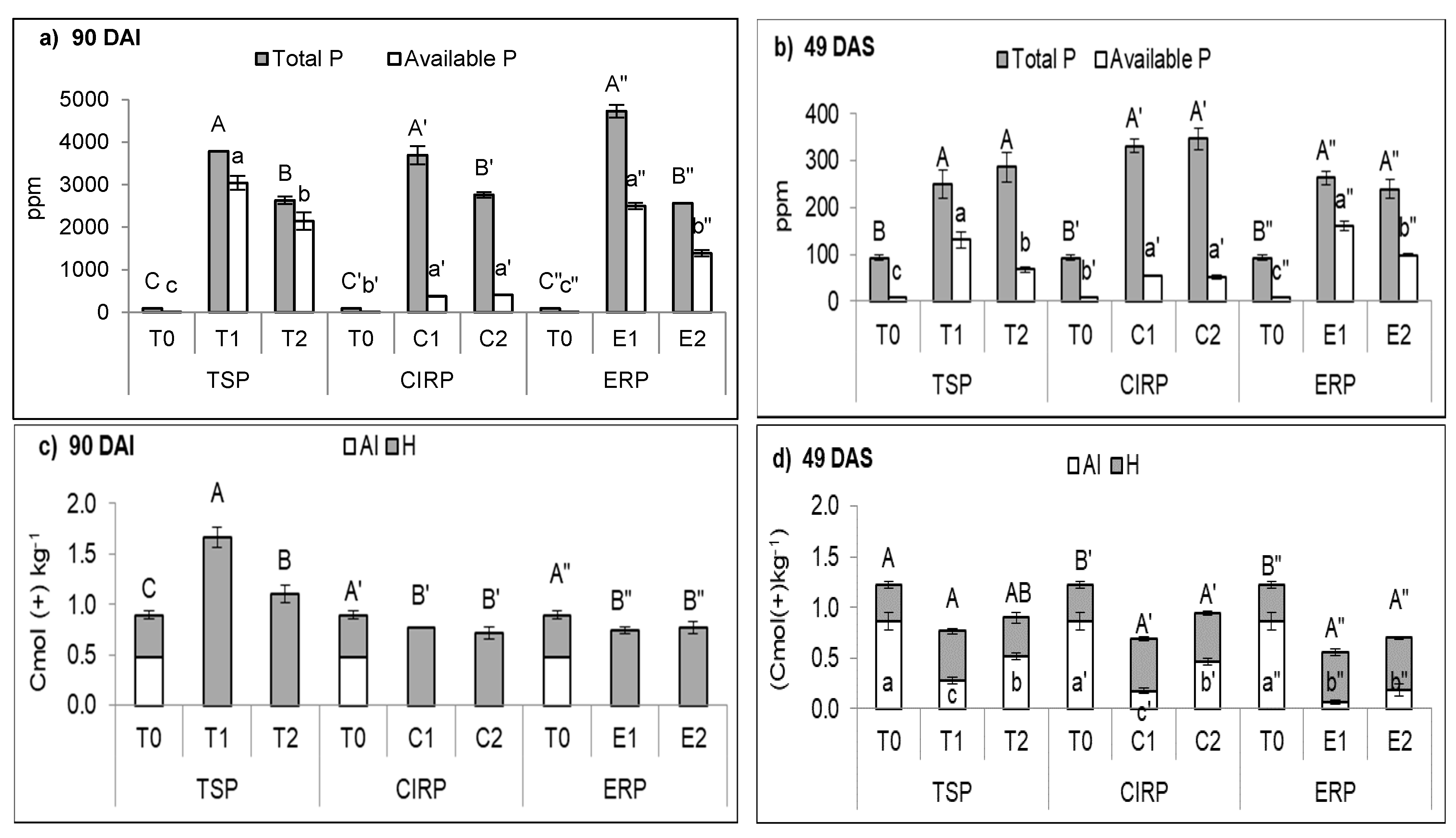
| Chemical Properties | TSP | ERP | CIRP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | E1 | E2 | T0 | C1 | C2 | |
| 90 DAI | |||||||||
| pH | 5.40b | 7.36a | 7.44a | 5.40c’ | 7.36b’ | 7.53a’ | 5.40b” | 7.37a” | 7.47a” |
| Exch. Cation (cmol (+) kg−1) | |||||||||
| K | 0.19c | 14.64a | 9.51b | 0.19c’ | 15.16a’ | 8.79b’ | 0.19c” | 17.13a” | 9.26b” |
| Ca | 0.23b | 8.23a | 7.76a | 0.23b’ | 18.50a’ | 17.22a’ | 0.23b” | 9.33a” | 9.55a” |
| Mg | 0.45c | 1.57a | 1.39b | 0.45c’ | 0.66b’ | 0.75a’ | 0.45b” | 1.01a” | 0.93a” |
| Fe | 2.21a | 0.72b | 0.63b | 2.21a’ | 0.20c’ | 0.22b’ | 2.21a” | 0.30c” | 0.31b” |
| 49 DAS | |||||||||
| pH | 5.31a | 5.11b | 4.98b | 5.31ab’ | 5.46a’ | 5.14b’ | 5.31a” | 5.49a” | 5.56a” |
| Exch. Cation (cmol (+) kg-1) | |||||||||
| K | 0.10c | 0.47a | 0.33b | 0.10c’ | 0.55a’ | 0.34b’ | 0.10b” | 0.52a” | 0.54a” |
| Ca | 0.04c | 0.32a | 0.19b | 0.04c’ | 0.45a’ | 0.37b’ | 0.04c” | 2.08a” | 1.01b” |
| Mg | 0.41a | 0.44a | 0.47a | 0.41b’ | 0.53a’ | 0.49a’ | 0.41b” | 0.50a” | 0.47ab” |
| Fe | 1.05a | 0.79b | 0.83b | 1.05a’ | 0.85b’ | 0.88b’ | 1.05a” | 0.73b” | 0.81b” |
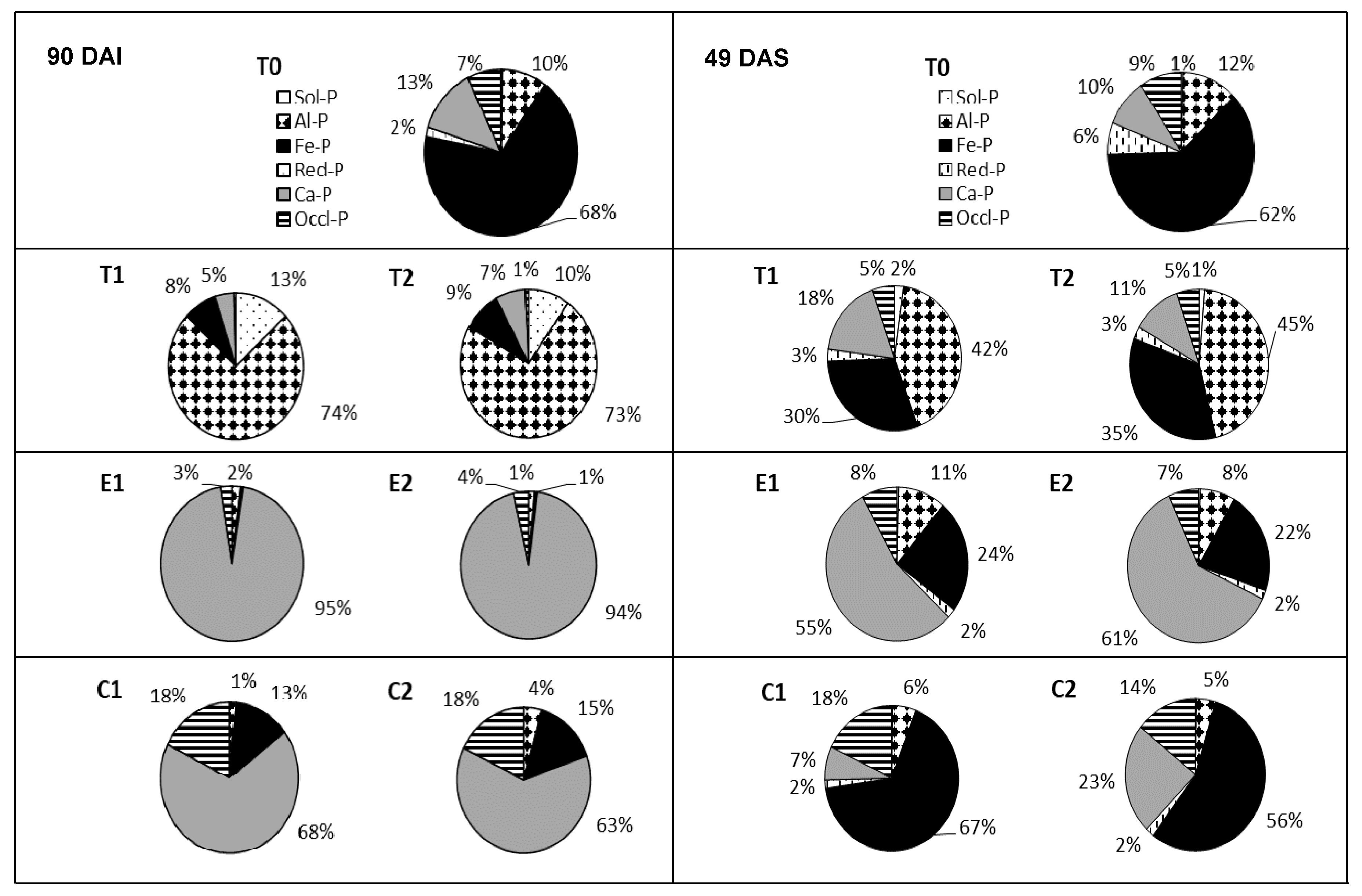
| Pi | TSP | ERP | CIRP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | E1 | E2 | T0 | C1 | C2 | |
| Sol-P | 0.1c | 309.5a | 146.6b | 0.1a’ | 0.1a’ | 0.1a’ | 0.1b” | 0.3a” | 0.1b” |
| (ppm) | ±0.01 | ±12.38 | ±9.07 | ±0.01 | ±0.01 | ±0.01 | ±0.01 | ±0.03 | ±0.01 |
| Al–P | 3.6c | 1750.0a | 1103.3b | 3.6c’ | 42.6a’ | 30.2b’ | 3.4c” | 26.0b” | 41.9a” |
| (ppm) | ±0.03 | ±42.02 | ±56.36 | ±0.03 | ±2.04 | ±2.60 | ±0.03 | ±0.27 | ±1.58 |
| Fe–P | 25.9c | 188.0a | 133b | 25.9a’ | 11.0b’ | 12.3b’ | 25.87c” | 234.1a” | 143.6b” |
| (ppm) | ±0.9 | ±2.1 | ±12.5 | ±0.89 | ±0.75 | ±0.13 | ±0.89 | ±10.66 | ±4.79 |
| Ca–P | 4.91b | 108.1a | 105.3a | 4.91b’ | 2122.5a’ | 2090.8a’ | 4.91c” | 1217.0a” | 595.7b” |
| (ppm) | ±0.1 | ±1.3 | ±6.6 | ±0.1 | ±90.6 | ±102.6 | ±0.08 | ±40.08 | ±31.38 |
| Red-P | 0.7ab | 0.8ab | 0.9a | 0.7c’ | 3.2a’ | 2.9b’ | 0.7c” | 2.3a” | 1.6b” |
| (ppm) | ±0.04 | ±0.07 | ±0.07 | ±0.04 | ±0.10 | ±0.02 | ±0.04 | ±0.08 | ±0.05 |
| Occl-P | 2.7c | 10.7b | 12.5a | 2.7c’ | 56.7b’ | 79.1a’ | 2.71c” | 317.0a” | 169.6b” |
| (ppm) | ±0.16 | ±0.34 | ±0.08 | ±0.16 | ±3.70 | ±3.90 | ±0.16 | ±5.25 | ±4.92 |
| Pi Fraction | TSP | ERP | CIRP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | E1 | E2 | T0 | C1 | C2 | |
| Sol-P | 0.23c | 3.46a | 1.71b | 0.23b’ | 0.96a’ | 0.86a’ | 0.23c” | 0.69b” | 0.98a” |
| (ppm) | ±0.02 | ±0.33 | ±0.11 | ±0.02 | ±0.11 | ±0.08 | ±0.02 | ±0.02 | ±0.11 |
| Al–P | 6.42b | 66.43a | 62.10a | 6.42c’ | 24.54a’ | 19.14b’ | 6.42c” | 18.65a” | 15.42b” |
| (ppm) | ±0.58 | ±6.76 | ±2.51 | ±0.58 | ±1.40 | ±1.73 | ±0.58 | ±0.65 | ±0.60 |
| Fe–P | 33.42a | 47.27a | 47.27a | 33.42b’ | 54.14a’ | 54.68a’ | 33.42b” | 219.87a” | 204.40a” |
| (ppm) | ±1.49 | ±5.37 | ±4.43 | ±1.49 | ±0.91 | ±1.85 | ±1.49 | ±6.37 | ±11.78 |
| Ca–P | 3.15a | 4.16a | 3.35a | 3.15b’ | 4.37ab’ | 4.91a’ | 3.15b” | 6.22a” | 7.39a” |
| (ppm) | ±0.12 | ±0.46 | ±0.25 | ±0.12 | ±0.55 | ±0.36 | ±0.12 | ±0.33 | ±0.66 |
| Red-P | 5.60c | 27.67a | 16.90b | 5.60b’ | 124.27a’ | 146.85a’ | 5.60c” | 24.45b” | 89.35a” |
| (ppm) | ±0.32 | ±3.87 | ±1.13 | ±0.32 | ±9.12 | ±12.41 | ±0.32 | ±2.57 | ±9.35 |
| Occl-P | 5.43b | 8.48a | 7.80a | 5.43b’ | 18.31a’ | 18.02a’ | 5.43b” | 59.06a” | 56.26a” |
| (ppm) | ±0.09 | ±0.82 | ±0.91 | ±0.09 | ±1.21 | ±0.53 | ±0.09 | ±4.55 | ±0.81 |
| Treatment | Total Dry Matter (g plant−1) | Total P Concentration (%) | Total P Uptake (g plant−1) | Total P Use Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSP | ||||
| T0 | 2.29b | 0.61a | 0.005b | - |
| T1 | 49.58a | 0.54ab | 0.093a | 8.93a |
| T2 | 47.57a | 0.41b | 0.081a | 10.42a |
| CIRP | ||||
| T0 | 2.29b’ | 0.61a’ | 0.005b’ | - |
| C1 | 32.93a’ | 0.44b’ | 0.049a’ | 4.51a’ |
| C2 | 37.48a’ | 0.40b’ | 0.050a’ | 6.09a’ |
| ERP | ||||
| T0 | 2.29b” | 0.61a” | 0.005b” | - |
| E1 | 34.99a” | 0.39b” | 0.036a” | 4.20a” |
| E2 | 31.49a” | 0.41b” | 0.038a” | 5.22a” |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasbullah, N.A.; Ahmed, O.H.; Ab Majid, N.M. Effects of Amending Phosphatic Fertilizers with Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Phosphorus Availability and Its Fractionation in an Acid Soil. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093162
Hasbullah NA, Ahmed OH, Ab Majid NM. Effects of Amending Phosphatic Fertilizers with Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Phosphorus Availability and Its Fractionation in an Acid Soil. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(9):3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093162
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasbullah, Nur Aainaa, Osumanu Haruna Ahmed, and Nik Muhamad Ab Majid. 2020. "Effects of Amending Phosphatic Fertilizers with Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Phosphorus Availability and Its Fractionation in an Acid Soil" Applied Sciences 10, no. 9: 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093162
APA StyleHasbullah, N. A., Ahmed, O. H., & Ab Majid, N. M. (2020). Effects of Amending Phosphatic Fertilizers with Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Phosphorus Availability and Its Fractionation in an Acid Soil. Applied Sciences, 10(9), 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093162





