Influence on Bone-to-Implant Contact of Non-Thermal Low-Pressure Argon Plasma: An Experimental Study in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Description
2.2. Animals Keeping
2.3. Implant Features
- -
- Group I (M): (n = 36) Mechanized implants.
- -
- Group II (M-P): (n = 36) Mechanized implants treated with non-thermal low-pressure argon plasma.
- -
- Group III (RBM): (n = 36) RBM implants.
- -
- Group IV (RBM-P): (n = 36) RBM implants treated with non-thermal low-pressure argon plasma.
2.4. Randomization
2.5. Surgery Protocol
2.6. Euthanasia
2.7. Sample Processing
2.7.1. Sample Preparation
2.7.2. Microtomography
2.7.3. Histological Preparation
- -
- Block preparation
- -
- Sheet preparation and evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
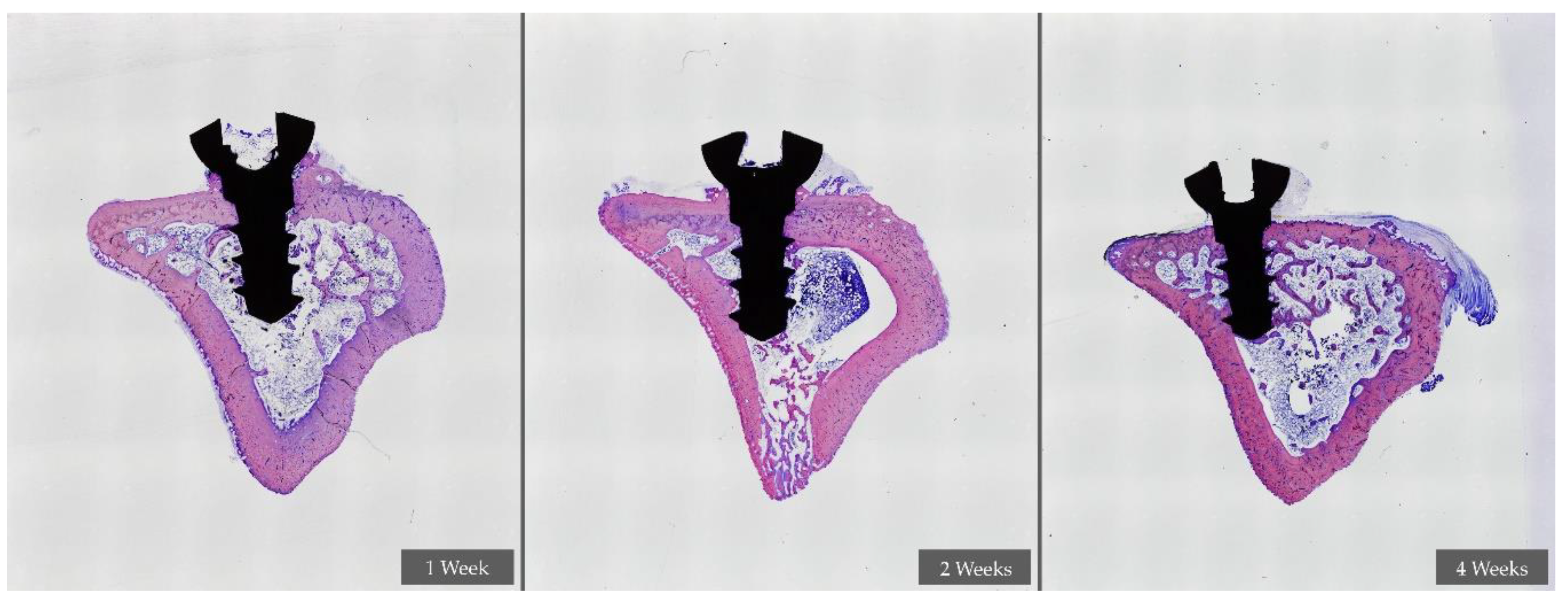
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- In the first week of healing, the application of NTLP-ArP over the implant surface does not represent any improvement among the experimental groups.
- -
- At two weeks of healing, the groups treated with NTLP-ArP obtained higher BIC values.
- -
- At two weeks of healing, the mechanized surface treated with NTLP-ArP obtained similar BIC values as the RBM surface.
- -
- At four weeks of healing, the RBM-P group obtained the highest BIC values compared to the other experimental groups
- -
- These results should be implemented and verified with human clinical trials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buser, D.; Sennerby, L.; De Bruyn, H. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, C.; Rodriguez, D.; Gil, F.J. Variation of roughness and adhesion strength of deposited apatite layers on titanium dental implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizzari, V.L.; Marconi, G.D.; De Colli, M.; Zara, S.; Zavan, B.; Salini, V.; Fontana, A.; Cataldi, A.; Piatelli, A. In vitro behavior of primary human osteoblast onto microrough titanium surface. Impl. Dent. 2015, 24, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, F.; D’Aurora, M.; Gugliandolo, A.; Merciaro, I.; Ettore, V.; Bramanti, A.; Piatelli, A.; Gatta, V.; Mazzon, E.; Fontana, A.; et al. A novel role in skeletal segment regeneration of extracellular vesicles released from periodontal-ligament stem cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3805–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, F.; D’Aurora, M.; Gugliandolo, A.; Merciaro, I.; Orsini, T.; Gatta, V.; Piatelli, A.; Trubiani, O.; Mazzon, E. Biofunctionalized scaffold in bone tissue repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. On implant surfaces: A review of current knowledge and opinions. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2010, 25, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shibli, J.A.; Grassi, S.; de Figueiredo, L.C. Influence of implant surface topography on early osseointegration: A histological study in human jaws. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 80, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.F. A role for surface topography in creating and maintaining bone at titanium endosseous implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2000, 84, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. Off. Publ. Acad. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosyn, J.; Sabzevar, M.M.; De Wilde, P.; De Rouck, T. Two-piece implants with turned versus microtextured collars. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronsson, B.O.; Lausmaa, J.; Kasemo, B. Glow discharge plasma treatment for surface cleaning and modification of metallic biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 35, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Genova, T.; Tallarico, M.; Gautier, G.; Mussano, F.; Botticelli, D. Plasma of argon affects the earliest biological response of different implant surfaces: An in vitro comparative study. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanish Royal Decree 53/2013 of February 1st; no.34; Official State Bulletin (BOE): Madrid, Spain, 8 February 2013; pp. 11370–11421.
- Randomness and Integrity Systems. 2020. Available online: www.random.org (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1-review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Von Wilmowsky, C.; Moest, T.; Nkenke, E.; Stelzle, F.; Schlegel, K.A. Implants in bone: Part I. A current overview about tissue response, surface modifications and future perspectives. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 18, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Alfonso-Rodríguez, C.A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; España-López, A.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Garzón, I.; Alaminos, M.; Gil, F.J. Relevant aspects in the surface properties in titanium dental implants for the cellular viability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2016, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Silvente, A.I.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Ortiz-Garcia, I.; Monsalve Guil, L.; Gil, J.; Jimenez-Guerra, A. Influence of the titanium implant Surface treatment on the surface roughness and chemical composition. Materials 2020, 13, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppe, H.; Wolff, C.; Bauer, F.; Ruthenberg, R.; Sculean, A.; Mücke, T. Dental implant surfaces after insertion in bone: An in vitro study in four commercial implant systems. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 22, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, C.; Rotolo, P.; de Ricardis, F.; Milella, E.; Napoli, A.; Wieland, M. Comparative investigation of the surface properties of commercial titanium dental implants. Part I: Chemical composition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, F.; Romanos, G.E. The role of primary stability for successful immediate loading of dental implants. A literature review. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, A.; Suarez, F.; Garaicoa, C.A.; Monje, F.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Garcia-Nogales, A.; Wang, H.L. Effect of location on primary stability and healing of dental implants. Implant Dent. 2014, 23, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, G.E.; Ciornei, G.; Jucan, A.; Malmstrom, H.; Gupta, B. In vitro assessment of primary stability of Straumann Implant designs. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Abrahamsson, I.; Lang, N.P.; Lindhe, J. De Novo Alveolar Bone Formation Adjacent to Endosseous Implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 14, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Perrotti, V.; Artese, L.; Degidi, M.; Degidi, D.; Piatelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Blood vessels are concentarted within the implant surface concavities: A histologic study in rabbit tibia. Odontology 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardaropoli, G.; Araújo, M.; Lindhe, J. Dynamics of Bone Tissue Formation in Tooth Extraction Sites. An Experimental Study in Dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2003, 30, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J.; Cheong, S.Y.; Han, J.H.; Heo, S.J.; Chung, J.P.; Rhyu, I.C.; Choi, Y.C.; Baik, H.K.; Ku, Y.; Kim, M.H. Evaluation of design parameters of osseointegrated dental implants using finite element analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhussein, H.; Pagni, G.; Rebaudi, A.; Wang, H.L. The effect of thread pattern upon implant osseointegration: Review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2010, 21, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Linder, E.; Lang, N.P.; Lindhe, J. Early bone formation adjacent to rough and turned endosseous implant surfaces. An experimental study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.K.; Denzer, A.J.; Cochran, D.L.; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S.G. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Alcoforado, G.; Nelson, K.; Schaer, A.; Taylor, T.; Beuer, F.; Strietzel, F.P. Impact of implant-abutment connection, positioning of the machined collar/microgap, and platform switching on crestal bone level changes. Camlog foundation consensus report. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 25, 1301–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmagnola, D.; Abati, S.; Addis, A.; Ferrieri, G.; Chiapasco, M.; Romeo, E.; Vogel, G. Time sequence of bone healing around two implant systems in minipigs: Preliminary histologic results. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2009, 29, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Haq, J.; Karabuda, C.Z.; Arisan, V.; Mutlu, Z.; Kürkçü, M. Osseointegration and stability of a modified sand-blasted acid-etched implant: An experimental pilot study in sheep. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.P.; Salvi, G.E.; Huynh-Ba, G.; Ivanovski, S.; Donos, N.; Bosshardt, D.D. Early osseointegration to hydrophilic and hydrophobic implant surfaces in humans. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosshardt, D.D.; Salvi, G.E.; Huynh-Ba, G.; Ivanovski, S.; Donos, N.; Lang, N.P. The role of bone debris in early healing adjacent to hydrophilic and hydrophobic implant surfaces in man. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpler, M.; Woesz, A.; Dunlop, J.W.; van Dongen, J.T.; Fratzl, P. The effect of geometry on three-dimensional tissue growth. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnaudeix, A.; Usseglio, J.; Lasgorceix, M.; Lalloue, F.; Damia, C.; Brie, J.; Pascaud-Mathieu, P.; Champion, E. Quantitative analysis of vascular colonization and angio-conduction in porous silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite with various pore shapes in a chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) model. Acta Biomater. 2016, 38, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juignet, L.; Charbonnier, B.; Dumas, V.; Bouleftour, W.; Thomas, M.; Laurent, C.; Vico, L.; Douard, N.; Marchat, D.; Malaval, L. Macrotopographic closure promotes tissue growth and osteogenesis in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatewood, R.R.; Cobb, C.M.; Killoy, W.J. Microbial colonization on natural tooth structure compared with smooth and plasma-sprayed dental implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1993, 4, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.G.; Giro, G.; Teixeira, H.S. Argon-based atmospheric pressure plasma enhances early bone response to rough titanium surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2012, 100, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duske, K.; Koban, I.; Kindel, E. Atmospheric plasma enhances wettability and cell spreading on dental implant metals. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Crocetta, E.; Quaranta, A.; Lorusso, F. Influence of the thermal treatment to address a better osseointegration of Ti6Al4V dental implants: Histological and histomorphometrical study in a rabbit model. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Group | n | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 4 Weeks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIC (%) | C.I. 95% | BIC (%) | C.I. 95% | BIC (%) | C.I. 95% | ||
| I (M) | 12 | 70.67 | 61.09–80.25 | 76.97 | 73.42–80.52 | 76.16 | 71.05–81.27 |
| II (M-P) | 12 | 75.52 | 71.73–79.31 | 73.48 | 70.09–76.87 | 77.92 | 73.34–82.50 |
| III (RBM) | 12 | 77.85 | 74.38–81.38 | 75.60 | 72.11–79.09 | 75.81 | 71.48–80.14 |
| IV (RBM-P) | 12 | 73.78 | 68.13–79.43 | 74.83 | 69.61–80.05 | 78.80 | 72.95–84.65 |
| Experimental Group | n | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 4 Weeks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIC (%) | C.I. 95% | BIC (%) | C.I. 95% | BIC (%) | C.I. 95% | ||
| I (M) | 12 | 66.20 | 51.89–80.51 | 69.06 α β | 62.93–77.19 | 78.56 Φ | 70.10–87.02 |
| II (M-P) | 12 | 69.27 | 62.20–76.34 | 79.66 α | 74.75–84.57 | 79.92 γ | 71.46–88.38 |
| III (RBM) | 12 | 73.90 | 65.27–82.53 | 73.97 Ω | 68.34–79.60 | 83.91 | 78.20–89.62 |
| IV (RBM-P) | 12 | 71.92 | 62.55–81.29 | 83.35 β Ω | 80.47–90.23 | 89.49 Φ γ | 86.82–92.16 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez-Perez, A.; Nicolas-Silvente, A.I.; Sanchez-Matas, C.; Muñoz-Guzon, F.; Navarro-Cuellar, C.; Romanos, G.E. Influence on Bone-to-Implant Contact of Non-Thermal Low-Pressure Argon Plasma: An Experimental Study in Rats. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093069
Sanchez-Perez A, Nicolas-Silvente AI, Sanchez-Matas C, Muñoz-Guzon F, Navarro-Cuellar C, Romanos GE. Influence on Bone-to-Implant Contact of Non-Thermal Low-Pressure Argon Plasma: An Experimental Study in Rats. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(9):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093069
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez-Perez, Arturo, Ana I. Nicolas-Silvente, Carmen Sanchez-Matas, Fernando Muñoz-Guzon, Carlos Navarro-Cuellar, and Georgios E. Romanos. 2020. "Influence on Bone-to-Implant Contact of Non-Thermal Low-Pressure Argon Plasma: An Experimental Study in Rats" Applied Sciences 10, no. 9: 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093069
APA StyleSanchez-Perez, A., Nicolas-Silvente, A. I., Sanchez-Matas, C., Muñoz-Guzon, F., Navarro-Cuellar, C., & Romanos, G. E. (2020). Influence on Bone-to-Implant Contact of Non-Thermal Low-Pressure Argon Plasma: An Experimental Study in Rats. Applied Sciences, 10(9), 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093069







